Influence of Uncertainties in Optode Positions on Self-Calibrating or Dual-Slope Diffuse Optical Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
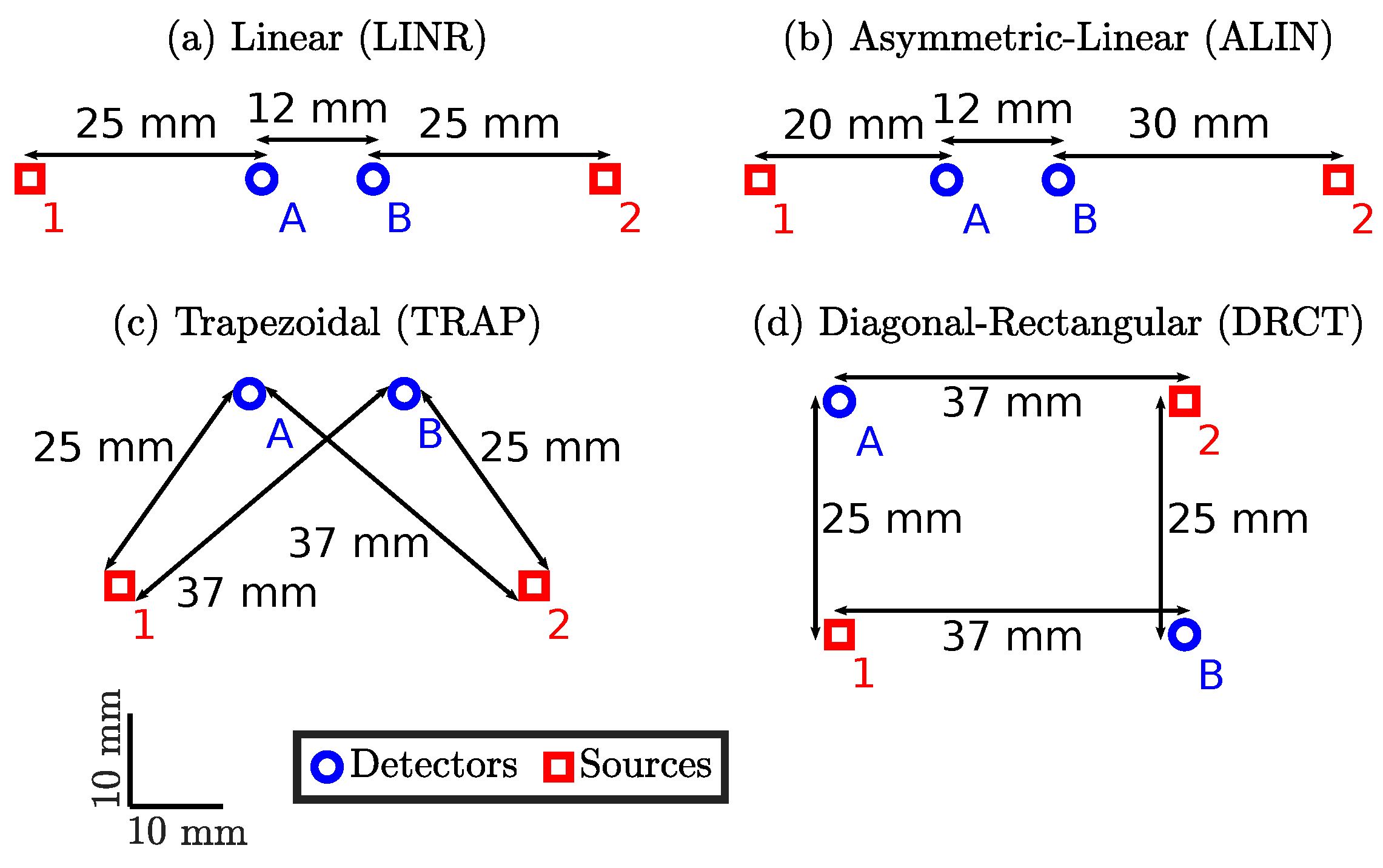
2.1. Dual-Slope Arrangements
2.2. Analytical Forward Model
2.3. Inverse Models
2.3.1. Absolute Optical Properties
2.3.2. Changes in Absorption
2.4. Variable Definitions
3. Results
3.1. Self-Calibrated Recovery of Absolute Optical Properties
3.1.1. Error from the Choice of Optical Property Recovery Method
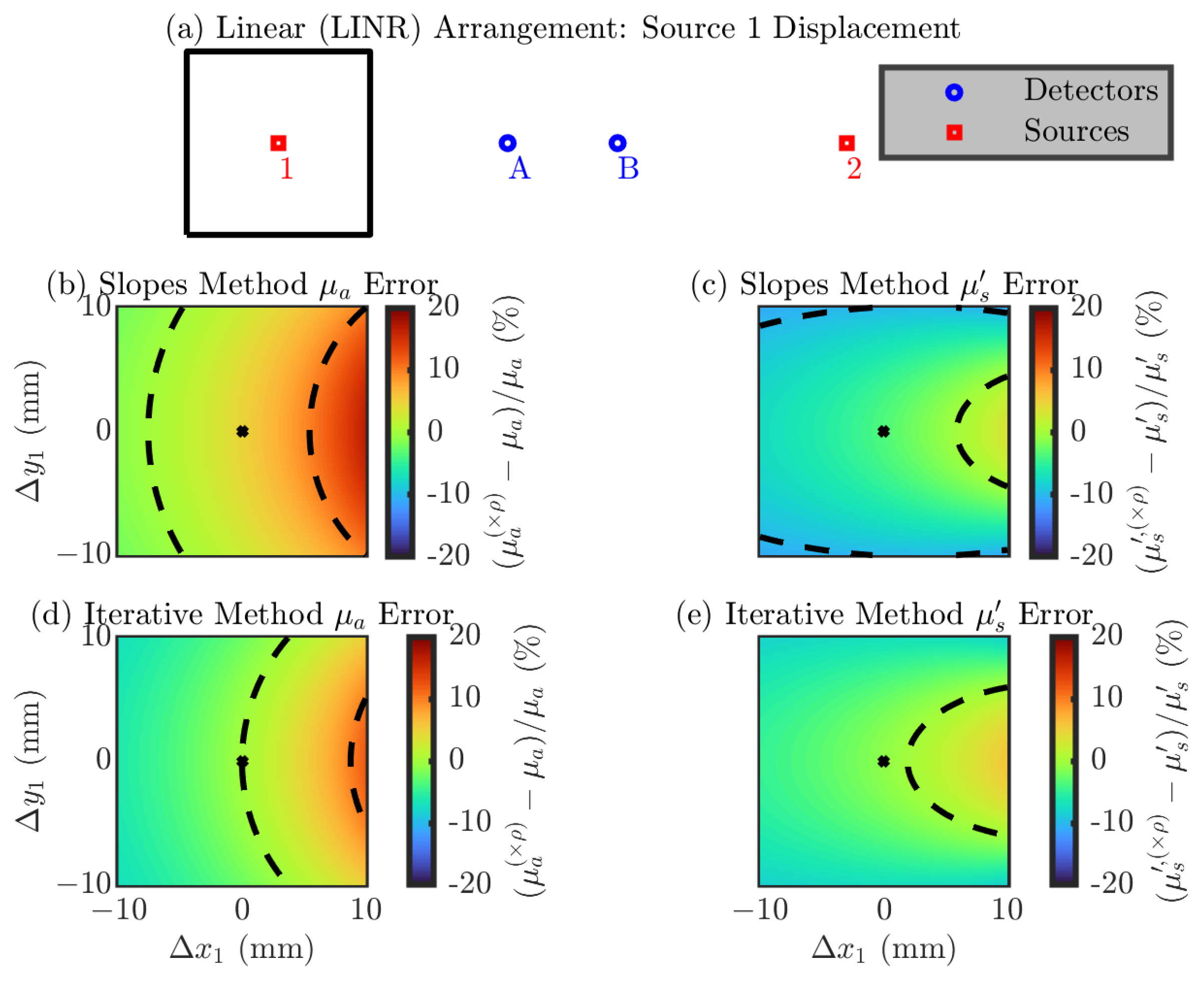
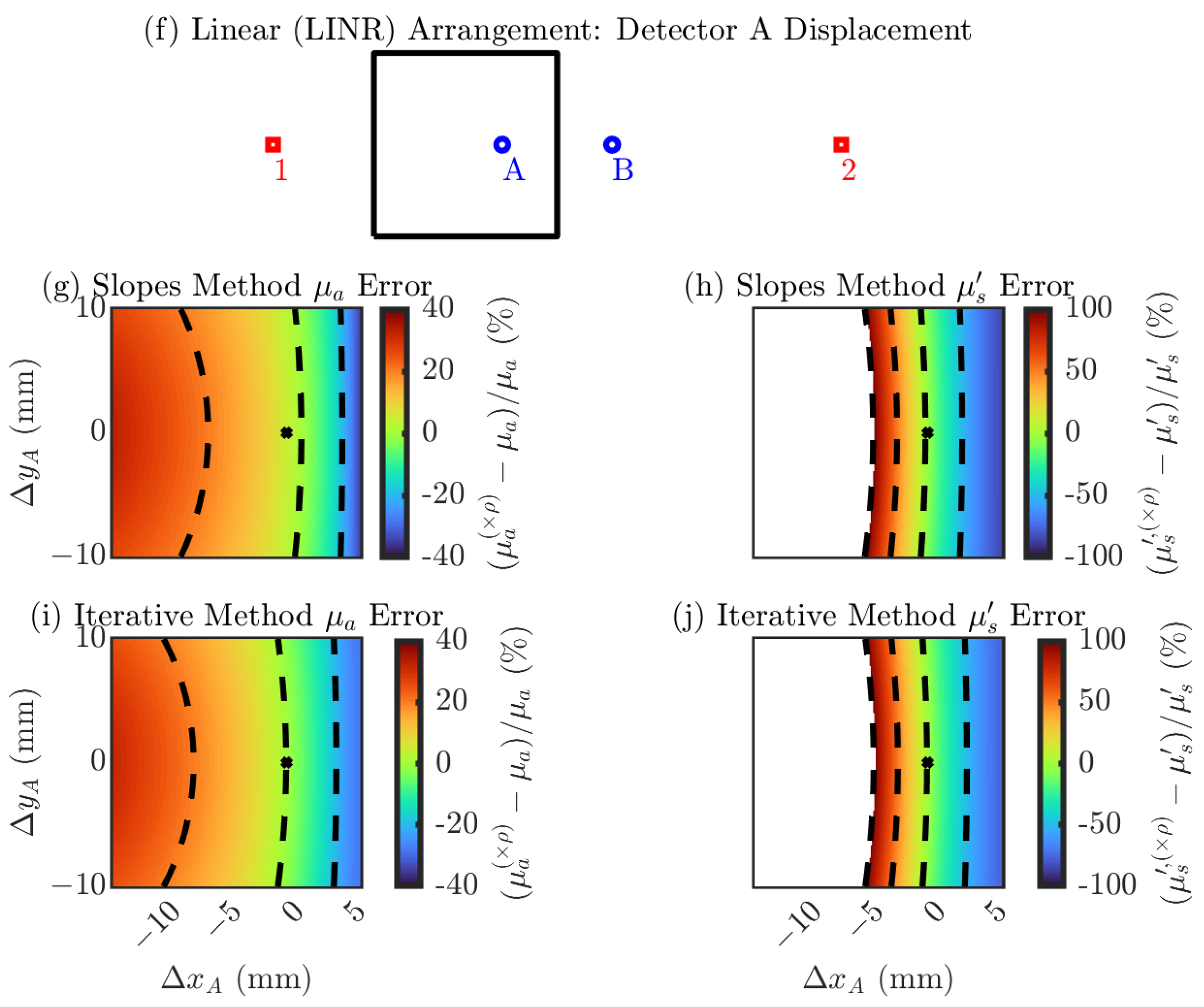
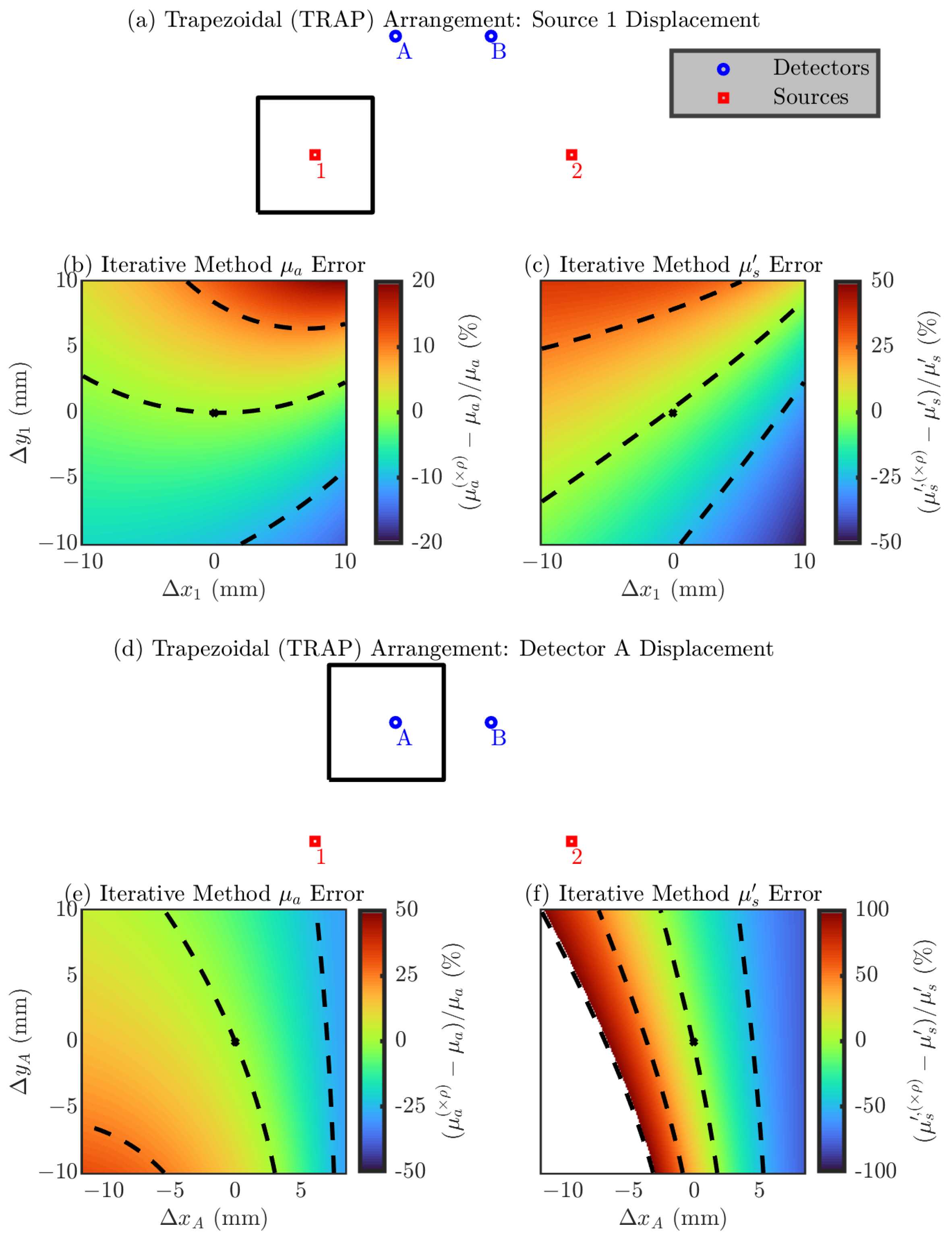
3.1.2. Error from Optode Position Displacement
Single-Optode Displacement
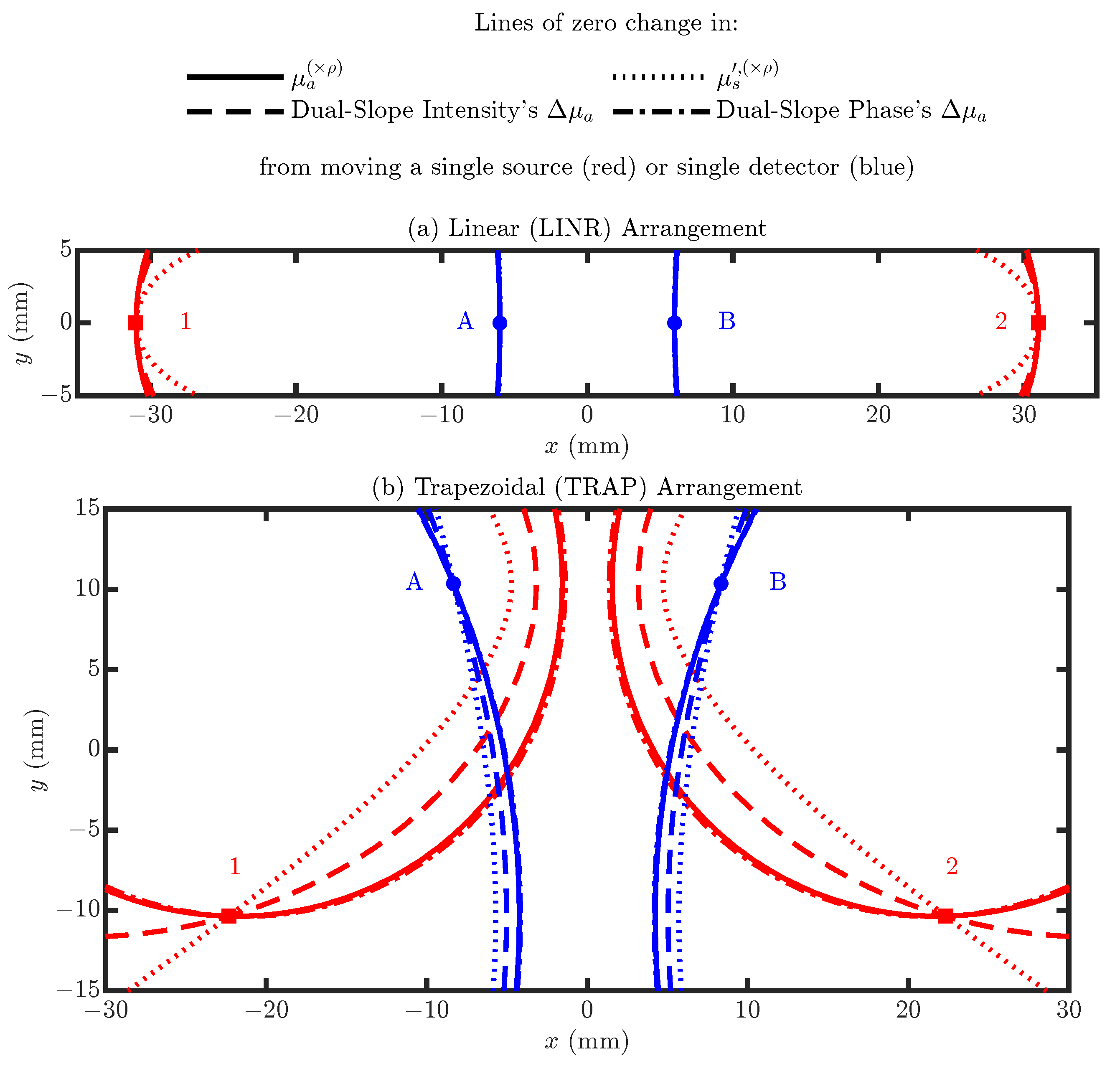
- Linear (LINR) Arrangement
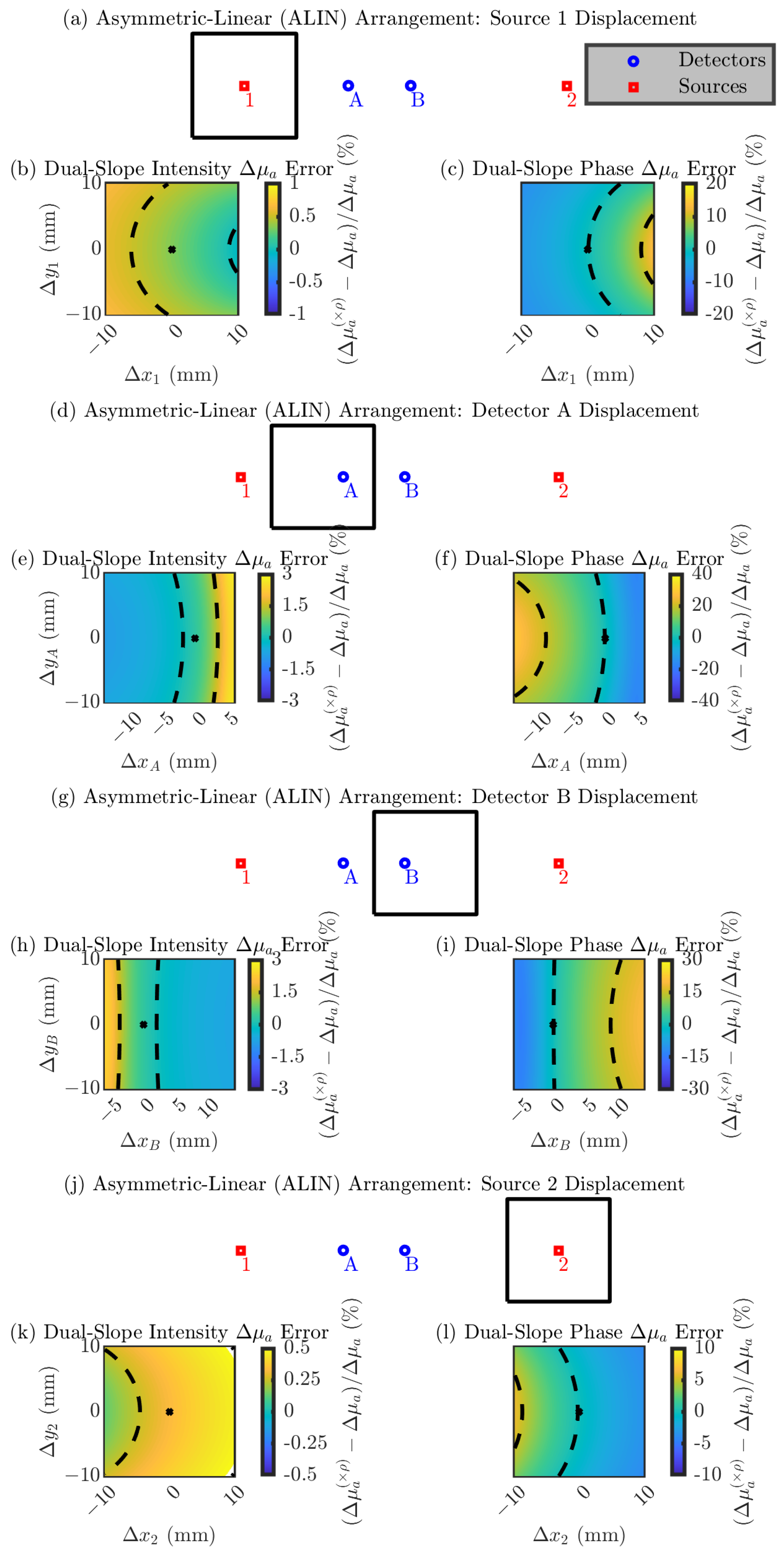
- Asymmetric-Linear (ALIN) Arrangement
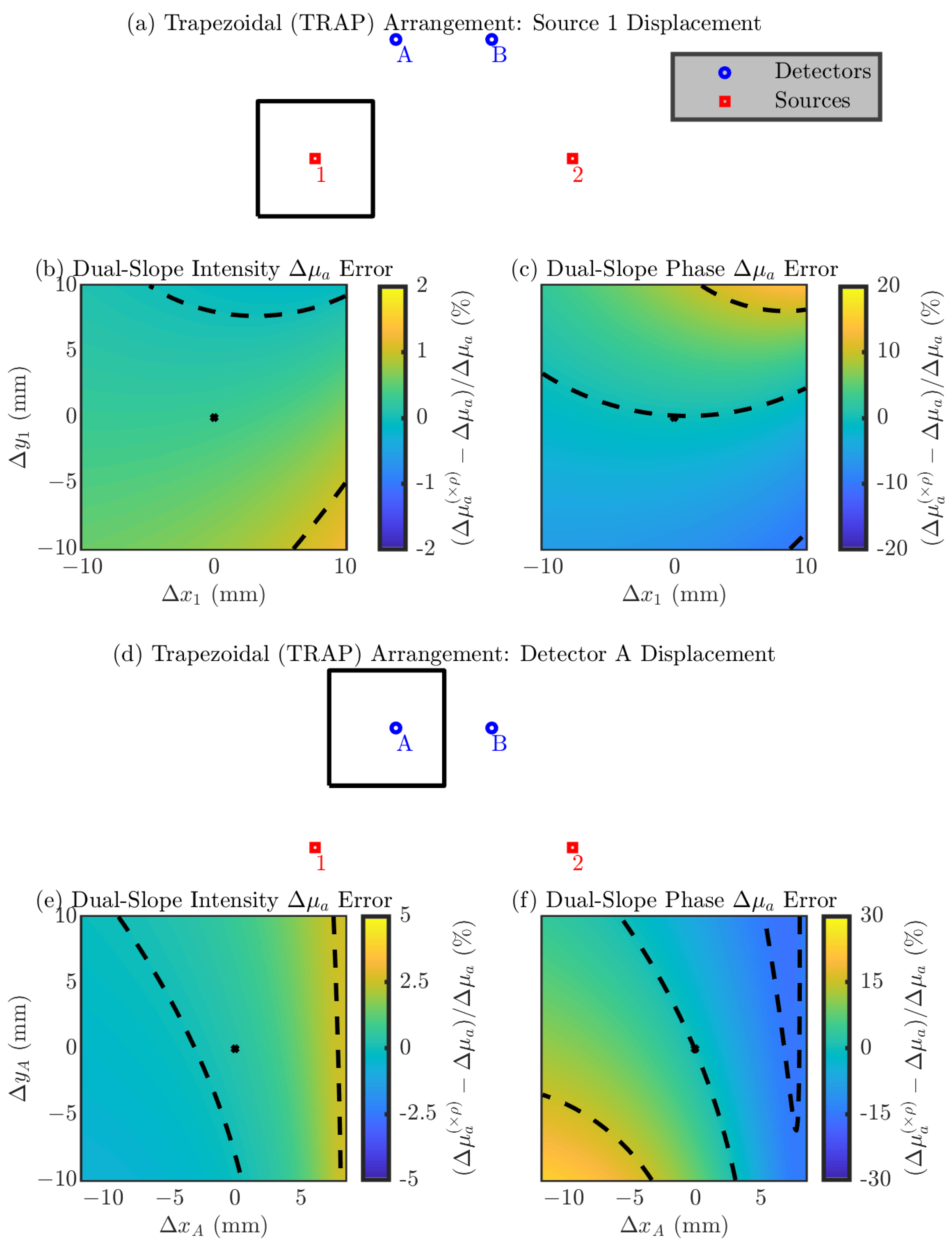
- Trapezoidal (TRAP) Arrangement
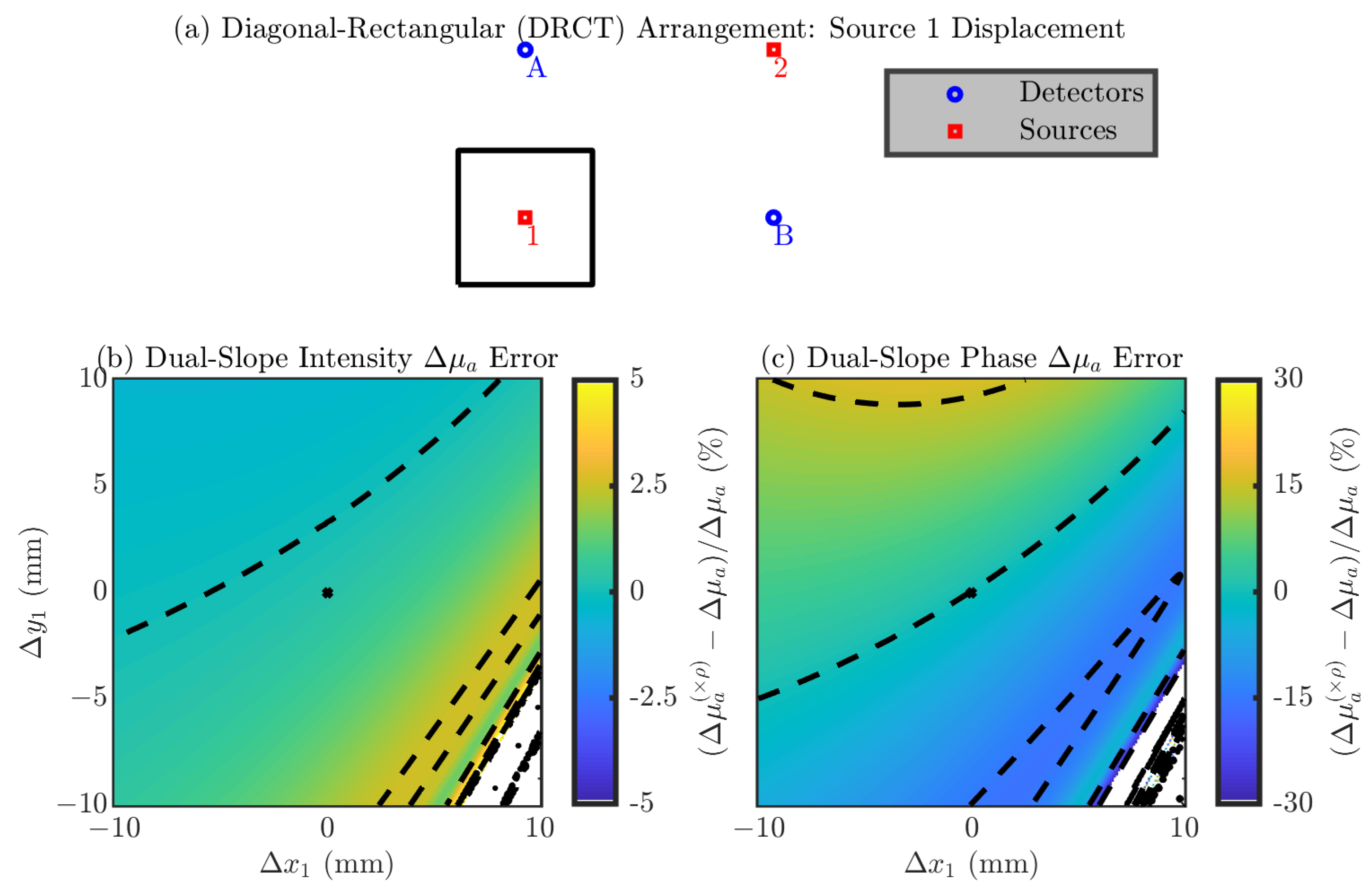
- Diagonal-Rectangular (DRCT) Arrangement
Multi-Optode Displacement
3.2. Dual-Slope Recovery of Relative Changes in the Absorption Coefficient ()
4. Discussion
Design of Optode Support Structure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haskell, R.C.; Svaasand, L.O.; Tsay, T.T.; Feng, T.C.; McAdams, M.S.; Tromberg, B.J. Boundary Conditions for the Diffusion Equation in Radiative Transfer. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1994, 11, 2727–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaney, G.; Sassaroli, A.; Pham., T.; Krishnamurthy, N.; Fantini, S. Multi-Distance Frequency-Domain Optical Measurements of Coherent Cerebral Hemodynamics. Photonics 2019, 6, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pifferi, A.; Torricelli, A.; Bassi, A.; Taroni, P.; Cubeddu, R.; Wabnitz, H.; Grosenick, D.; Möller, M.; Macdonald, R.; Swartling, J.; et al. Performance Assessment of Photon Migration Instruments: The MEDPHOT Protocol. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 2104–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hueber, D.M.; Fantini, S.; Cerussi, A.E.; Barbieri, B.B. New Optical Probe Designs for Absolute (Self-Calibrating) NIR Tissue Hemoglobin Measurements. In Proceedings of the Optical Tomography and Spectroscopy of Tissue III, San Jose, CA, USA, 24 January 1999; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1999; Volume 3597, pp. 618–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, D.B.; Ikeda, K.; Vacchiano, C.; Lobbestael, A.; Wahr, J.A.; Shaw, A.D. Development and Validation of a Cerebral Oximeter Capable of Absolute Accuracy. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2012, 26, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiser, S.; Ostojic, D.; Nasseri, N.; Isler, H.; Bucher, H.U.; Bassler, D.; Wolf, M.; Scholkmann, F.; Tanja Karen, M.D. In Vivo Precision Assessment of a Near-Infrared Spectroscopy-Based Tissue Oximeter (OxyPrem v1.3) in Neonates Considering Systemic Hemodynamic Fluctuations. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 067003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.C.; Tamborini, D.; Renna, M.; Peruch, A.; Huang, Y.; Martin, A.; Kaya, K.; Starkweather, Z.; Zavriyev, A.I.; Carp, S.A.; et al. Open-Source FlexNIRS: A Low-Cost, Wireless and Wearable Cerebral Health Tracker. NeuroImage 2022, 256, 119216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.X.; Qiang, B.; Mao, J.J.; Povoski, S.P. Development of a Handheld Near-Infrared Imager for Dynamic Characterization of in Vivo Biological Tissue Systems. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanka, P.; Lanka, P.; Segala, A.; Segala, A.; Farina, A.; Farina, A.; Sekar, S.K.V.; Nisoli, E.; Valerio, A.; Taroni, P.; et al. Non-Invasive Investigation of Adipose Tissue by Time Domain Diffuse Optical Spectroscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 2779–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.; Wei, L.L.; Roblyer, D. Cross-Wavelength Calibrating Method for Real-Time Imaging of Tissue Optical Properties Using Frequency-Domain Diffuse Optical Spectroscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2024, 15, 4963–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawosz, P.; Liebert, A. Method to Improve the Depth Sensitivity of Diffuse Reflectance Measurements to Absorption Changes in Optically Turbid Medium. Biomed. Opt. Express 2019, 10, 5031–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaney, G.; Sassaroli, A.; Pham, T.; Fernandez, C.; Fantini, S. Phase Dual-Slopes in Frequency-Domain near-Infrared Spectroscopy for Enhanced Sensitivity to Brain Tissue: First Applications to Human Subjects. J. Biophotonics 2020, 13, e201960018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, S.; Blaney, G.; Sassaroli, A. Transformational Change in the Field of Diffuse Optics: From Going Bananas to Going Nuts. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2019, 13, 1930013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davie, S.N.; Grocott, H.P. Impact of Extracranial Contamination on Regional Cerebral Oxygen Saturation: A Comparison of Three Cerebral Oximetry Technologies. Anesthesiology 2012, 116, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholkmann, F.; Metz, A.J.; Wolf, M. Measuring Tissue Hemodynamics and Oxygenation by Continuous-Wave Functional near-Infrared Spectroscopy—How Robust Are the Different Calculation Methods against Movement Artifacts? Physiol. Meas. 2014, 35, 717–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaney, G.; Donaldson, R.; Mushtak, S.; Nguyen, H.; Vignale, L.; Fernandez, C.; Pham, T.; Sassaroli, A.; Fantini, S. Dual-Slope Diffuse Reflectance Instrument for Calibration-Free Broadband Spectroscopy. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perekatova, V.; Kostyuk, A.; Kirillin, M.; Sergeeva, E.; Kurakina, D.; Shemagina, O.; Orlova, A.; Khilov, A.; Turchin, I. VIS-NIR Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy System with Self-Calibrating Fiber-Optic Probe: Study of Perturbation Resistance. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, C.; Biallas, M.; Trajkovic, I.; Fauchère, J.C.; Bucher, H.U.; Wolf, M. Reproducibility of Cerebral Tissue Oxygen Saturation Measurements by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in Newborn Infants. J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 097004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.C.; Martin, A.; Renna, M.; Robinson, M.; Ozana, N.; Carp, S.A.; Franceschini, M.A. Enhancing Diffuse Correlation Spectroscopy Pulsatile Cerebral Blood Flow Signal with Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Photoplethysmography. Neurophotonics 2023, 10, 035008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.; Blaney, G.; Tavakoli, F.; Sassaroli, A.; Fantini, S. Dual-Slope near-Infrared Spectroscopy for Selective Sensitivity to Cerebral Hemodynamics. In Proceedings of the Optical Tomography and Spectroscopy of Tissue XVI, San Francisco, CA, USA, 27 January 2025; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2025; Volume 13314, pp. 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chincarini, M.; Qiu, L.; Spinelli, L.; Torricelli, A.; Minero, M.; Dalla Costa, E.; Mariscoli, M.; Ferri, N.; Giammarco, M.; Vignola, G. Evaluation of Sheep Anticipatory Response to a Food Reward by Means of Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Animals 2019, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiser, S.; Nasseri, N.; Andresen, B.; Greisen, G.; Wolf, M. Comparison of Tissue Oximeters on a Liquid Phantom with Adjustable Optical Properties. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 2973–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoult, C.; Gygax, L. Valence and Intensity of Video Stimuli of Dogs and Conspecifics in Sheep: Approach-Avoidance, Operant Response, and Attention. Animals 2018, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Recovery Method | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s * | Slopes | Iterative | ||||
| (mm) | () | () | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) |
| [25, 25, 37, 37] | 0.005 | 0.5 | 11 | −12 | 0.024 | −0.99 |
| 0.005 | 1.0 | 9.3 | −2.9 | 0.0058 | −0.50 | |
| 0.005 | 1.5 | 7.0 | −1.2 | 0.0013 | −0.33 | |
| 0.010 | 0.5 | 5.0 | −12 | 0.029 | −2.0 | |
| 0.010 | 1.0 | 4.7 | −3.5 | 0.0038 | −0.99 | |
| 0.010 | 1.5 | 3.6 | −1.7 | 0.0046 | −0.67 | |
| 0.015 | 0.5 | 2.9 | −13 | 0.037 | −3.0 | |
| 0.015 | 1.0 | 3.1 | −4.0 | 0.0040 | −1.5 | |
| 0.015 | 1.5 | 2.4 | −2.1 | 0.0025 | −1.00 | |
| [20, 30, 32, 42] | 0.005 | 0.5 | 11 | −13 | 0.025 | −1.00 |
| 0.005 | 1.0 | 9.7 | −3.2 | 0.0070 | −0.50 | |
| 0.005 | 1.5 | 7.4 | −1.3 | 0.0016 | −0.33 | |
| 0.010 | 0.5 | 4.7 | −13 | 0.032 | −2.0 | |
| 0.010 | 1.0 | 4.9 | −3.8 | 0.0046 | −0.99 | |
| 0.010 | 1.5 | 3.8 | −1.8 | 0.0011 | −0.66 | |
| 0.015 | 0.5 | 2.6 | −14 | 0.041 | −3.0 | |
| 0.015 | 1.0 | 3.3 | −4.3 | 0.0048 | −1.5 | |
| 0.015 | 1.5 | 2.6 | −2.2 | 0.0030 | −1.00 | |
| Recovery Method | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optode | Slopes | Iterative | ||||
| () | () | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | |
| 0.005 | 0.5 | 1 or 2 | 1.1 | 0.56 | 1.2 | 0.44 |
| 0.005 | 0.5 | A or B | 5.1 | 16 | 5.0 | 13 |
| 0.005 | 1.0 | 1 or 2 | 0.82 | 0.52 | 0.92 | 0.50 |
| 0.005 | 1.0 | A or B | 3.5 | 15 | 4.6 | 14 |
| 0.005 | 1.5 | 1 or 2 | 0.68 | 0.46 | 0.75 | 0.45 |
| 0.005 | 1.5 | A or B | 2.9 | 14 | 3.8 | 14 |
| 0.010 | 0.5 | 1 or 2 | 0.68 | 0.37 | 0.71 | 0.29 |
| 0.010 | 0.5 | A or B | 3.4 | 15 | 3.0 | 13 |
| 0.010 | 1.0 | 1 or 2 | 0.53 | 0.37 | 0.56 | 0.35 |
| 0.010 | 1.0 | A or B | 2.3 | 14 | 2.8 | 13 |
| 0.010 | 1.5 | 1 or 2 | 0.44 | 0.33 | 0.46 | 0.32 |
| 0.010 | 1.5 | A or B | 1.9 | 14 | 2.3 | 13 |
| 0.015 | 0.5 | 1 or 2 | 0.53 | 0.27 | 0.54 | 0.22 |
| 0.015 | 0.5 | A or B | 2.8 | 15 | 2.3 | 12 |
| 0.015 | 1.0 | 1 or 2 | 0.42 | 0.29 | 0.44 | 0.28 |
| 0.015 | 1.0 | A or B | 1.9 | 14 | 2.2 | 13 |
| 0.015 | 1.5 | 1 or 2 | 0.34 | 0.27 | 0.36 | 0.26 |
| 0.015 | 1.5 | A or B | 1.5 | 13 | 1.8 | 13 |
| () | () | Optode | (%) | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.005 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 0.56 |
| 0.005 | 0.5 | 2 | 0.88 | 0.34 |
| 0.005 | 0.5 | A | 5.3 | 13 |
| 0.005 | 0.5 | B | 4.6 | 13 |
| 0.005 | 1.0 | 1 | 1.3 | 0.69 |
| 0.005 | 1.0 | 2 | 0.67 | 0.37 |
| 0.005 | 1.0 | A | 5.0 | 14 |
| 0.005 | 1.0 | B | 4.3 | 14 |
| 0.005 | 1.5 | 1 | 1.1 | 0.64 |
| 0.005 | 1.5 | 2 | 0.54 | 0.33 |
| 0.005 | 1.5 | A | 4.2 | 14 |
| 0.005 | 1.5 | B | 3.7 | 14 |
| 0.010 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.95 | 0.37 |
| 0.010 | 0.5 | 2 | 0.54 | 0.23 |
| 0.010 | 0.5 | A | 3.2 | 13 |
| 0.010 | 0.5 | B | 2.8 | 12 |
| 0.010 | 1.0 | 1 | 0.81 | 0.48 |
| 0.010 | 1.0 | 2 | 0.41 | 0.26 |
| 0.010 | 1.0 | A | 3.1 | 13 |
| 0.010 | 1.0 | B | 2.7 | 13 |
| 0.010 | 1.5 | 1 | 0.68 | 0.45 |
| 0.010 | 1.5 | 2 | 0.34 | 0.24 |
| 0.010 | 1.5 | A | 2.6 | 14 |
| 0.010 | 1.5 | B | 2.3 | 13 |
| 0.015 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.73 | 0.28 |
| 0.015 | 0.5 | 2 | 0.42 | 0.18 |
| 0.015 | 0.5 | A | 2.4 | 12 |
| 0.015 | 0.5 | B | 2.1 | 12 |
| 0.015 | 1.0 | 1 | 0.63 | 0.38 |
| 0.015 | 1.0 | 2 | 0.32 | 0.21 |
| 0.015 | 1.0 | A | 2.4 | 13 |
| 0.015 | 1.0 | B | 2.1 | 13 |
| 0.015 | 1.5 | 1 | 0.52 | 0.37 |
| 0.015 | 1.5 | 2 | 0.26 | 0.19 |
| 0.015 | 1.5 | A | 2.0 | 13 |
| 0.015 | 1.5 | B | 1.7 | 13 |
| () | () | Optode | (%) | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.005 | 0.5 | 1 or 2 | 1.5 | 2.5 |
| 0.005 | 0.5 | A or B | 3.7 | 9.3 |
| 0.005 | 1.0 | 1 or 2 | 1.2 | 2.7 |
| 0.005 | 1.0 | A or B | 3.3 | 9.9 |
| 0.005 | 1.5 | 1 or 2 | 1.0 | 2.7 |
| 0.005 | 1.5 | A or B | 2.7 | 9.9 |
| 0.010 | 0.5 | 1 or 2 | 0.91 | 2.4 |
| 0.010 | 0.5 | A or B | 2.2 | 8.9 |
| 0.010 | 1.0 | 1 or 2 | 0.77 | 2.6 |
| 0.010 | 1.0 | A or B | 2.0 | 9.5 |
| 0.010 | 1.5 | 1 or 2 | 0.63 | 2.6 |
| 0.010 | 1.5 | A or B | 1.7 | 9.5 |
| 0.015 | 0.5 | 1 or 2 | 0.69 | 2.4 |
| 0.015 | 0.5 | A or B | 1.7 | 8.8 |
| 0.015 | 1.0 | 1 or 2 | 0.59 | 2.5 |
| 0.015 | 1.0 | A or B | 1.6 | 9.3 |
| 0.015 | 1.5 | 1 or 2 | 0.49 | 2.5 |
| 0.015 | 1.5 | A or B | 1.3 | 9.3 |
| () | () | Optode | (%) | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.005 | 0.5 | 1, 2, A, or B | 3.7 | 9.3 |
| 0.005 | 1.0 | 1, 2, A, or B | 3.3 | 9.9 |
| 0.005 | 1.5 | 1, 2, A, or B | 2.7 | 9.9 |
| 0.010 | 0.5 | 1, 2, A, or B | 2.2 | 8.9 |
| 0.010 | 1.0 | 1, 2, A, or B | 2.0 | 9.5 |
| 0.010 | 1.5 | 1, 2, A, or B | 1.7 | 9.5 |
| 0.015 | 0.5 | 1, 2, A, or B | 1.7 | 8.8 |
| 0.015 | 1.0 | 1, 2, A, or B | 1.6 | 9.3 |
| 0.015 | 1.5 | 1, 2, A, or B | 1.3 | 9.3 |
| Arrangement | Optodes | (%) | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LINR | 1 and A | 2.9 | 13 |
| 1 and B | 2.9 | 13 | |
| 1 and 2 | 0.80 | 0.49 | |
| A and B | 4.0 | 19 | |
| 1, A, and B | 4.0 | 19 | |
| 1, 2, and A | 2.9 | 13 | |
| 1, 2, A, and B | 4.1 | 19 | |
| ALIN | 1 and A | 3.2 | 13 |
| 1 and B | 2.8 | 13 | |
| 2 and A | 3.1 | 13 | |
| 2 and B | 2.7 | 13 | |
| 1 and 2 | 0.91 | 0.55 | |
| A and B | 4.1 | 19 | |
| 1, A, and B | 4.2 | 19 | |
| 2, A, and B | 4.1 | 19 | |
| 1, 2, and A | 3.2 | 13 | |
| 1, 2, and B | 2.8 | 13 | |
| 1, 2, A, and B | 4.2 | 19 | |
| TRAP | 1 and A | 2.2 | 9.8 |
| 1 and B | 2.2 | 9.8 | |
| 1 and 2 | 1.1 | 3.6 | |
| A and B | 2.9 | 13 | |
| 1, A, and B | 3.0 | 14 | |
| 1, 2, and A | 2.3 | 10 | |
| 1, 2, A, and B | 3.1 | 14 | |
| DRCT | 1 and A | 2.9 | 13 |
| 1 and B | 2.9 | 13 | |
| 1 and 2 | 2.9 | 13 | |
| 1, A, and B | 3.5 | 16 | |
| 1, 2, A, and B | 4.1 | 19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blaney, G.; Sassaroli, A.; Das, T.; Fantini, S. Influence of Uncertainties in Optode Positions on Self-Calibrating or Dual-Slope Diffuse Optical Measurements. Photonics 2025, 12, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070697
Blaney G, Sassaroli A, Das T, Fantini S. Influence of Uncertainties in Optode Positions on Self-Calibrating or Dual-Slope Diffuse Optical Measurements. Photonics. 2025; 12(7):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070697
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlaney, Giles, Angelo Sassaroli, Tapan Das, and Sergio Fantini. 2025. "Influence of Uncertainties in Optode Positions on Self-Calibrating or Dual-Slope Diffuse Optical Measurements" Photonics 12, no. 7: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070697
APA StyleBlaney, G., Sassaroli, A., Das, T., & Fantini, S. (2025). Influence of Uncertainties in Optode Positions on Self-Calibrating or Dual-Slope Diffuse Optical Measurements. Photonics, 12(7), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070697






