Dual-Color and High-Energy X-Ray Kirkpatrick–Baez Microscope for Laser Plasma Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
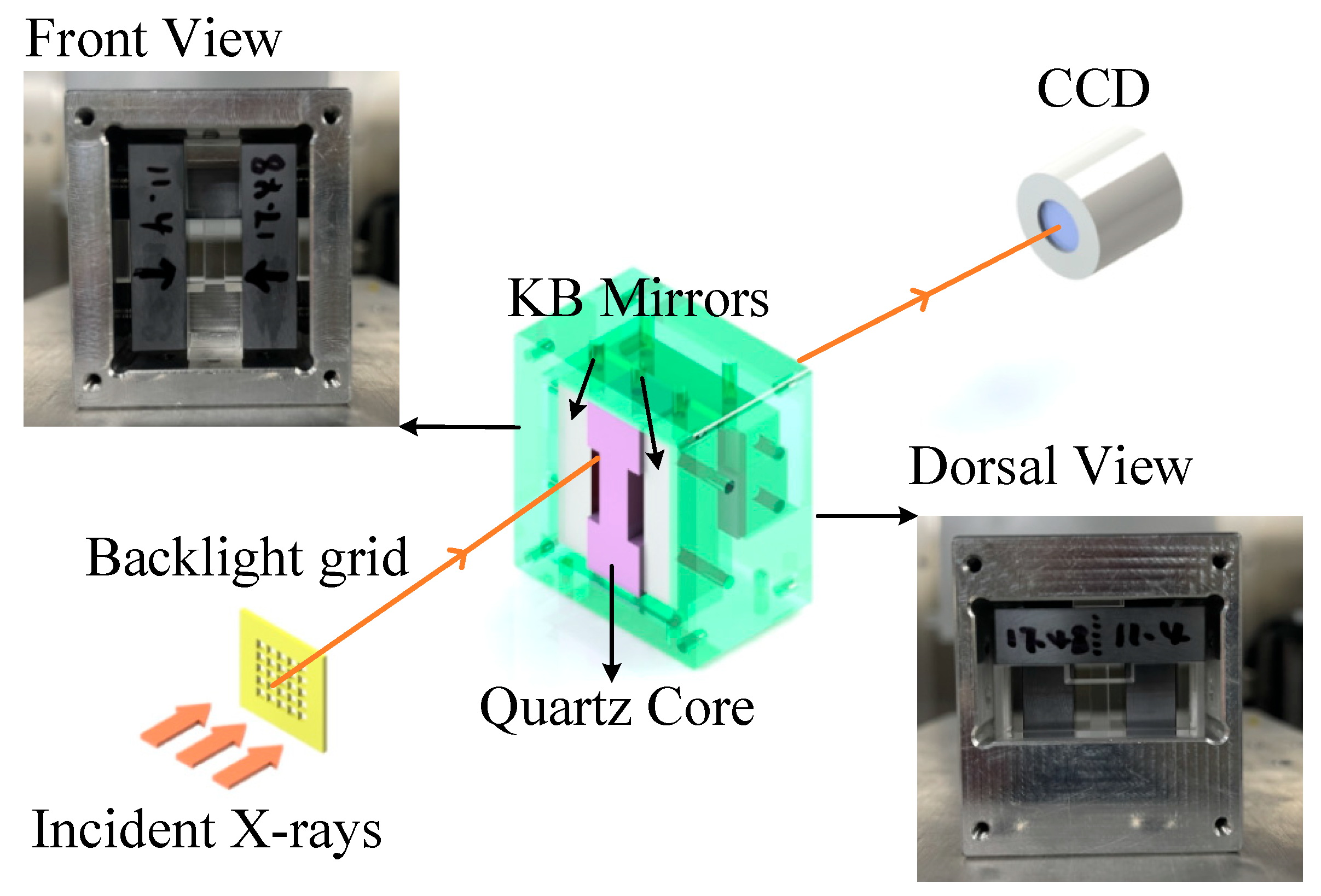
2. Optical Design
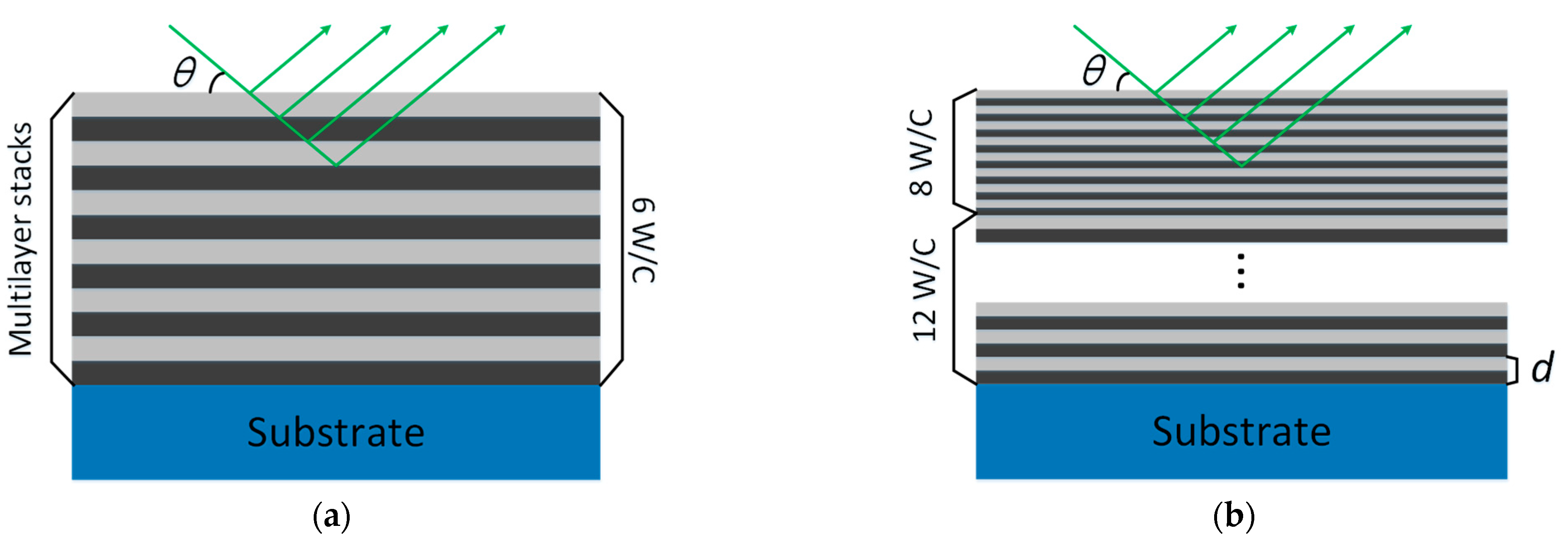
3. Multilayer Design
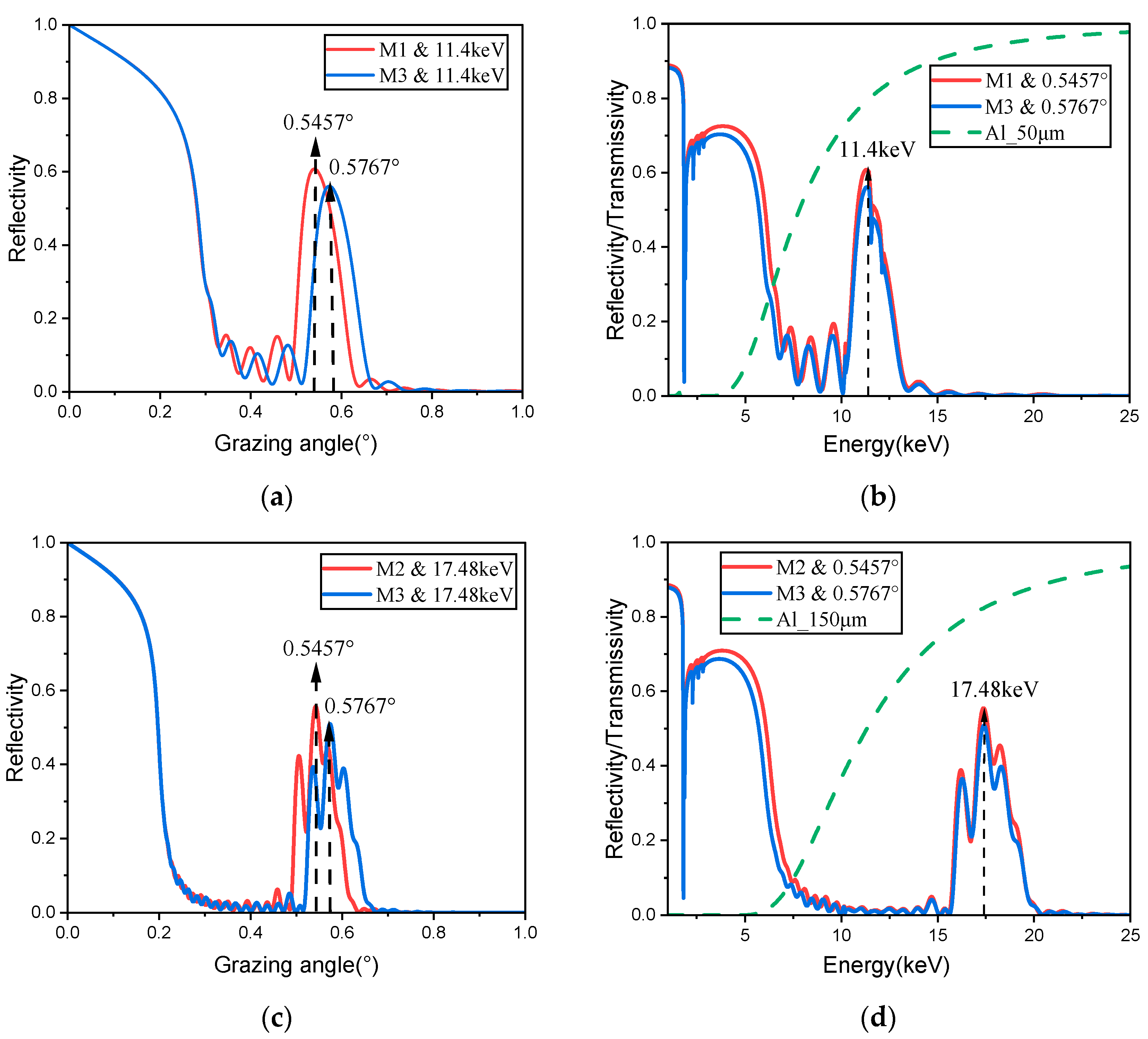
4. Performance Simulation
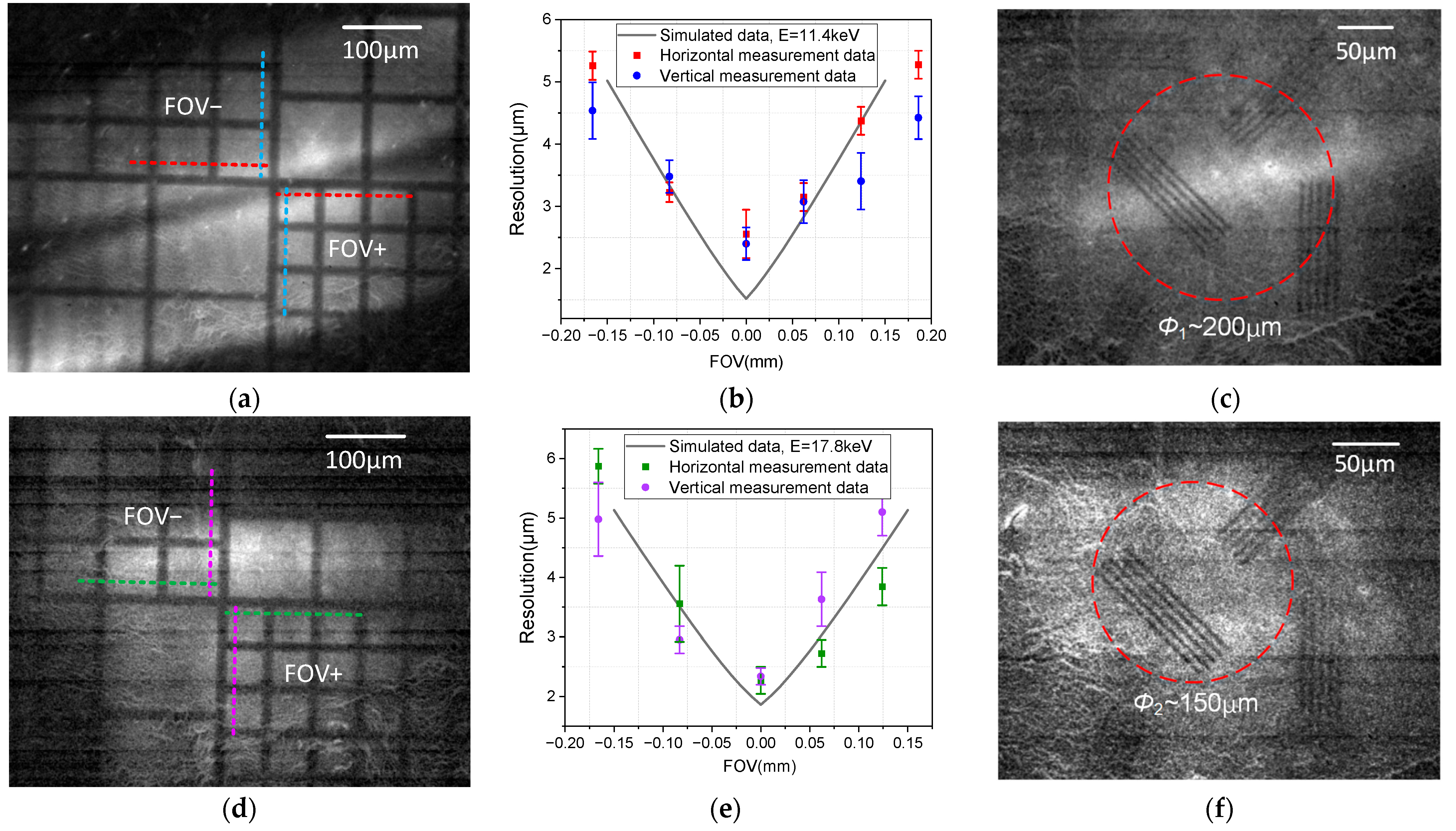
5. Imaging Experiment
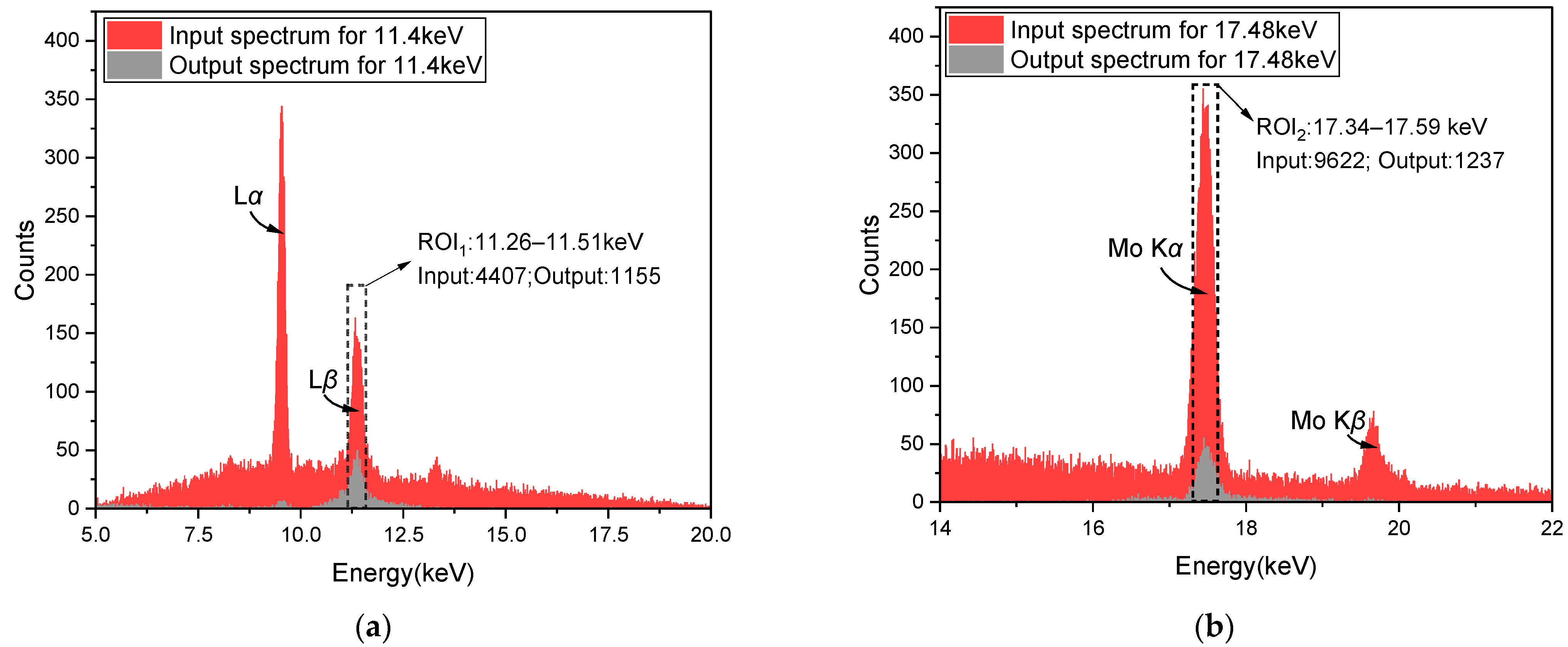
6. Spectral Response Measurements
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Betti, R.; Hurricane, O.A. Inertial-confinement fusion with lasers. Nat. Phys. 2016, 12, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindl, J.D.; Amendt, P.; Berger, R.L.; Glendinning, S.G.; Glenzer, S.H.; Haan, S.W.; Kauffman, R.L.; Landen, O.L.; Suter, L.J. The physics basis for ignition using indirect-drive targets on the National Ignition Facility. Phys. Plasmas 2004, 11, 339–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozioziemski, B.; Bachmann, B.; Do, A.; Tommasini, R. X-ray imaging methods for high-energy density physics applications. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2023, 94, 041102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huntington, C.M.; Park, H.-S.; Maddox, B.R.; Barrios, M.A.; Benedetti, R.; Braun, D.G.; Hohenberger, M.; Landen, O.L.; Regan, S.P.; Wehrenberg, C.E.; et al. Developing a bright 17 keV X-ray source for probing high-energy-density states of matter at high spatial resolution. Phys. Plasmas 2015, 22, 043114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickworth, L.A.; Hammel, B.A.; Smalyuk, V.A.; Robey, H.F.; Tommasini, R.; Benedetti, L.R.; Berzak Hopkins, L.; Bradley, D.K.; Dayton, M.; Felker, S.; et al. Development of new platforms for hydrodynamic instability and asymmetry measurements in deceleration phase of indirectly driven implosions on NIF. Phys. Plasmas 2018, 25, 082705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewald, E.L.; Landen, O.L.; Salmonson, J.; Masse, L.; Tabak, M.; Smalyuk, V.A.; Schiaffino, S.; Heredia, R.; Schneider, M.; Nikroo, A. First study of Hohlraum x-ray preheat asymmetry inside an ICF capsule. Phys. Plasmas 2020, 27, 122703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; Clark, D.; Pak, A.; Alfonso, N.; Bachmann, B.; Berzak Hopkins, L.; Bunn, T.; Crippen, J.; Divol, L.; Dittrich, T. Mixing in ICF implosions on the National Ignition Facility caused by the fill-tube. Phys. Plasmas 2020, 27, 032703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, T.J.; Douglas, M.R.; Fincke, J.R.; Olson, R.E.; Cobble, J.A.; Haines, B.M.; Hamilton, C.E.; Lee, M.N.; Oertel, J.A.; Parra-Vasquez, N.A.G.; et al. Progress in the development of the MARBLE platform for studying thermonuclear burn in the presence of heterogeneous mix on OMEGA and the National Ignition Facility. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 717, 012072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Mu, B.; Jiang, W.; Dong, J.; Yan, J.; Yu, B.; Xu, J.; Wang, X. A four-channels reflective Kirkpatrick-Baez microscope for the hot spot diagnostic in the 100 kJ laser driven inertial confinement fusion in China. J. Instrum. 2019, 14, C11010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Cao, Z.; Dong, J.; Mu, B.; Xie, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, T.; Yang, J.; Wang, F.; et al. Note: New method for high-space-resolving hotspot electron temperature measurements on Shenguang-III prototype. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 096108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badziak, J.; Jabłoński, S.; Wołowski, J. Progress and prospect of fast ignition of ICF targets. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion. 2007, 49, B651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, L.A.; Ampleford, D.J.; Coverdale, C.A.; Argo, J.W.; Owen, A.C.; Jaramillo, D.M. High energy X-ray pinhole imaging at the Z facility. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 063502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laso Garcia, A.; Yang, L.; Bouffetier, V.; Appel, K.; Baehtz, C.; Hagemann, J.; Höppner, H.; Humphries, O.; Kluge, T.; Mishchenko, M.; et al. Cylindrical compression of thin wires by irradiation with a Joule-class short-pulse laser. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, G.N.; Krauland, C.M.; Schollmeier, M.S.; Kemp, G.E.; Buscho, J.G.; Hibbard, R.; Thompson, N.; Casco, E.R.; Ayers, M.J.; Ayers, S.L.; et al. The Crystal Backlighter Imager: A spherically bent crystal imager for radiography on the National Ignition Facility. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 90, 013702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickworth, L.A.; Ayers, J.; Bell, P.; Brejnholt, N.F.; Buscho, J.G.; Bradley, D.; Decker, T.; Hau-Riege, S.; Kilkenny, J.; McCarville, T. The national ignition facility modular kirkpatrick-baez microscope. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 11E316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick, P.; Baez, A.V. Formation of Optical Images by X-Rays. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1948, 38, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotchev, O.V.; Jaanimagi, P.A.; Knauer, J.P.; Marshall, F.J.; Meyerhofer, D.D.; Bassett, N.L.; Oliver, J.B. High-throughput, high-resolution Kirkpatrick–Baez microscope for advanced streaked imaging of ICF experiments on OMEGA. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2003, 74, 2178–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Mu, B.; Ren, K.; Xu, J.; Chen, L.; Li, M.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Yi, R.; et al. Development of a quasi-coaxis dual-energy flat spectral response X-ray imaging instrument for measuring hotspot electron temperature. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 8777–8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, M.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Mu, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, Z. Development of a four-color quasimonochromatic X-ray microscope for laser plasma research. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 22181–22193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troussel, P.; Dennetiere, D.; Maroni, R.; Høghøj, P.; Hedacq, S.; Cibik, L.; Krumrey, M. Multilayer optics for monochromatic high-resolution X-ray imaging diagnostic in a broad photon energy range from 2 keV to 22 keV. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 2014, 767, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Omote, K. Multilayer optics for X-ray analysis. Rigaku J. 2008, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Windt, D.L. IMD—Software for modeling the optical properties of multilayer films. Comput. Phys. 1998, 12, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Li, W.; Xu, X.; Chen, L.; Mu, B. Study on full-aperture intensity response measurement for x-ray Kirkpatrick–Baez microscope. Opt. Eng. 2023, 62, 055103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesen, H.; Tiedje, H.F.; Hey, D.S.; Mo, M.Z.; Beaudry, A.; Fedosejevs, R.; Tsui, Y.Y.; Mackinnon, A.; McLean, H.S.; Patel, P.K. Kirkpatrick-Baez microscope for hard X-ray imaging of fast ignition experiments. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2013, 84, 023704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Mu, B.; Wang, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, Z. Resolution model of kirkpatrick-baez microscope with single-layer films. High Power Laser Part. Beams 2008, 20, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Xu, J.; Mu, B.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Li, W.; Pu, Y.; Ding, Y. Four-channel toroidal crystal x-ray imager for laser-produced plasmas. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 6133–6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, R.; Ikeda, N.; Kato, Y.; Katori, Y.; Iwai, T.; Takeshi, K. Development of an advanced Kirkpatrick–Baez microscope. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 1321–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mirror | Unit | M1/M2 | M3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mirror length | mm | 10 | 10 |
| Radius | m | 40.0 | 40.0 |
| Grazing angle | deg | 0.5457 | 0.5767 |
| Rotation angle | deg | 0.6301 | 0.6549 |
| Object distance | mm | 200 | 212 |
| Image distance | mm | 4000 | 3988 |
| Magnification | 20.0 | 18.8 | |
| Working energy | keV | 11.4/17.48 | 11.4/17.48 |
| Mirror | M1 | M2 | M3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multilayer stacks | 6 W/C | 8 + 12 W/C | 6 W/C | 8 + 12 W/C |
| Energy (keV) | 11.4 | 17.48 | 11.4 | 17.48 |
| Grazing angle (°) | 0.5457 | 0.5457 | 0.5767 | 0.5767 |
| Periodic thickness (nm) | 6.47 | 3.78 + 4.24 | 6.03 | 3.54 + 3.96 |
| Peak reflectivity (%) | 60.74 | 55.69 | 56.08 | 50.96 |
| Angular bandwidth (°) | 0.094 | 0.102 | 0.095 | 0.099 |
| Thickness ratio | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.51 | 0.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Shi, J.; Wang, M.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Mu, B.; Dong, J.; Ren, K.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X.; et al. Dual-Color and High-Energy X-Ray Kirkpatrick–Baez Microscope for Laser Plasma Research. Photonics 2025, 12, 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070630
Li M, Shi J, Wang M, Xu J, Wang X, Mu B, Dong J, Ren K, Liu W, Zhang X, et al. Dual-Color and High-Energy X-Ray Kirkpatrick–Baez Microscope for Laser Plasma Research. Photonics. 2025; 12(7):630. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070630
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Mingtao, Jiapeng Shi, Mingxun Wang, Jie Xu, Xin Wang, Baozhong Mu, Jianjun Dong, Kuan Ren, Wei Liu, Xing Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Dual-Color and High-Energy X-Ray Kirkpatrick–Baez Microscope for Laser Plasma Research" Photonics 12, no. 7: 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070630
APA StyleLi, M., Shi, J., Wang, M., Xu, J., Wang, X., Mu, B., Dong, J., Ren, K., Liu, W., Zhang, X., & Yang, D. (2025). Dual-Color and High-Energy X-Ray Kirkpatrick–Baez Microscope for Laser Plasma Research. Photonics, 12(7), 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070630






