Fiber Eavesdropping Detection and Location in Optical Communication System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Characteristics of Fiber Eavesdropping
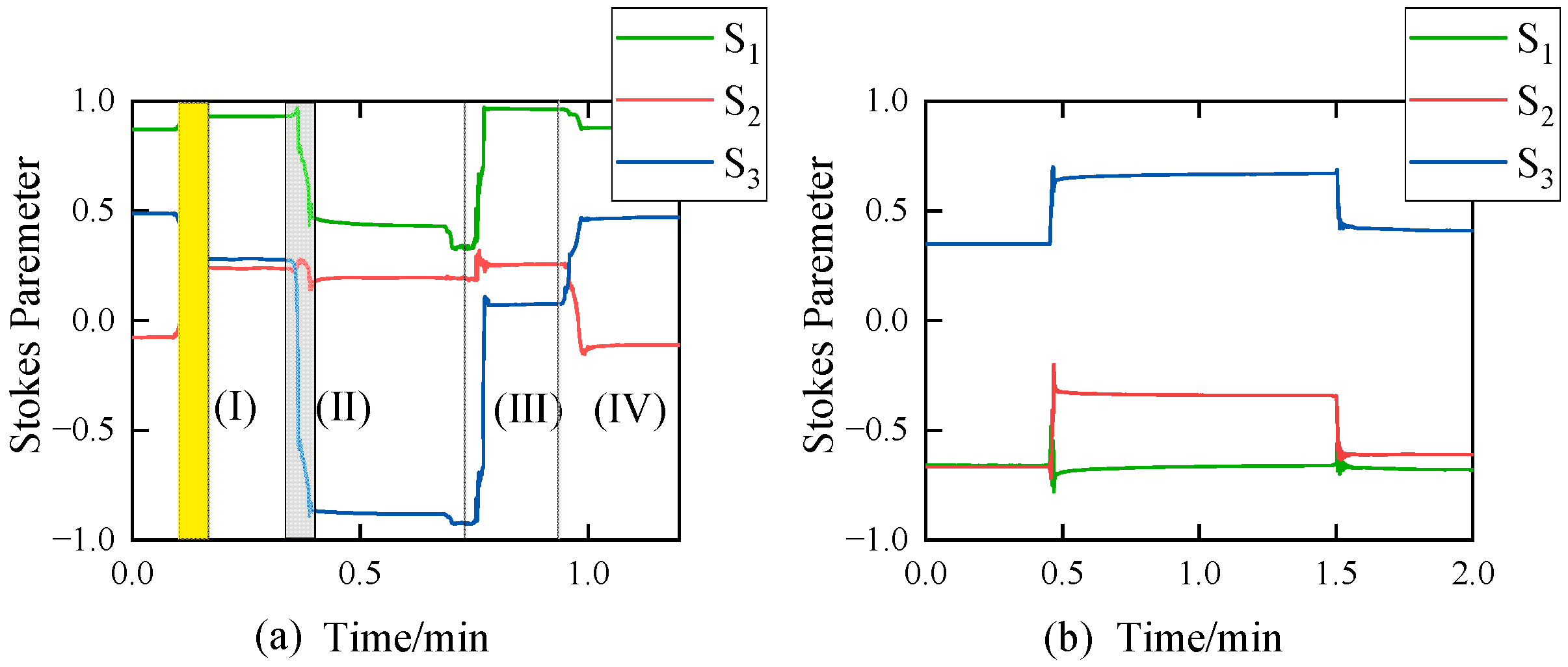
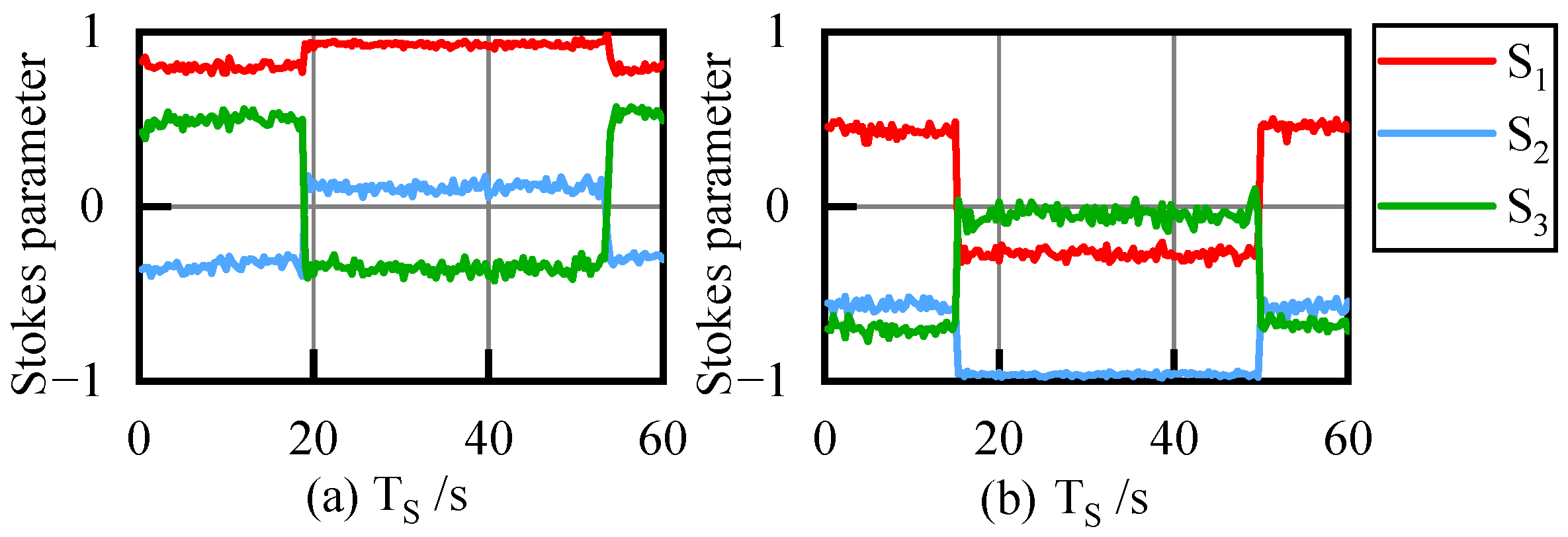
2.1. The Change in SOP
- (I)
- Pull the fiber until it touches the lens groove of the clip-on coupler, as shown in Figure 2c. At this stage, the SOP changes due to the movement of the fiber.
- (II)
- Close the clip-on coupler like Figure 2d. At this stage, there is an instantaneous jump in SOP because the clip-on coupler applies the pressure on the fiber.
- (III)
- Open the clip-on coupler. At this stage, the SOP exhibits an instantaneous jump because the clip-on coupler releases the pressure on the fiber.
- (IV)
- Pull the fiber away from the prism groove of the clip-on coupler. At this stage, the SOP changes again due to the movement of the fiber.
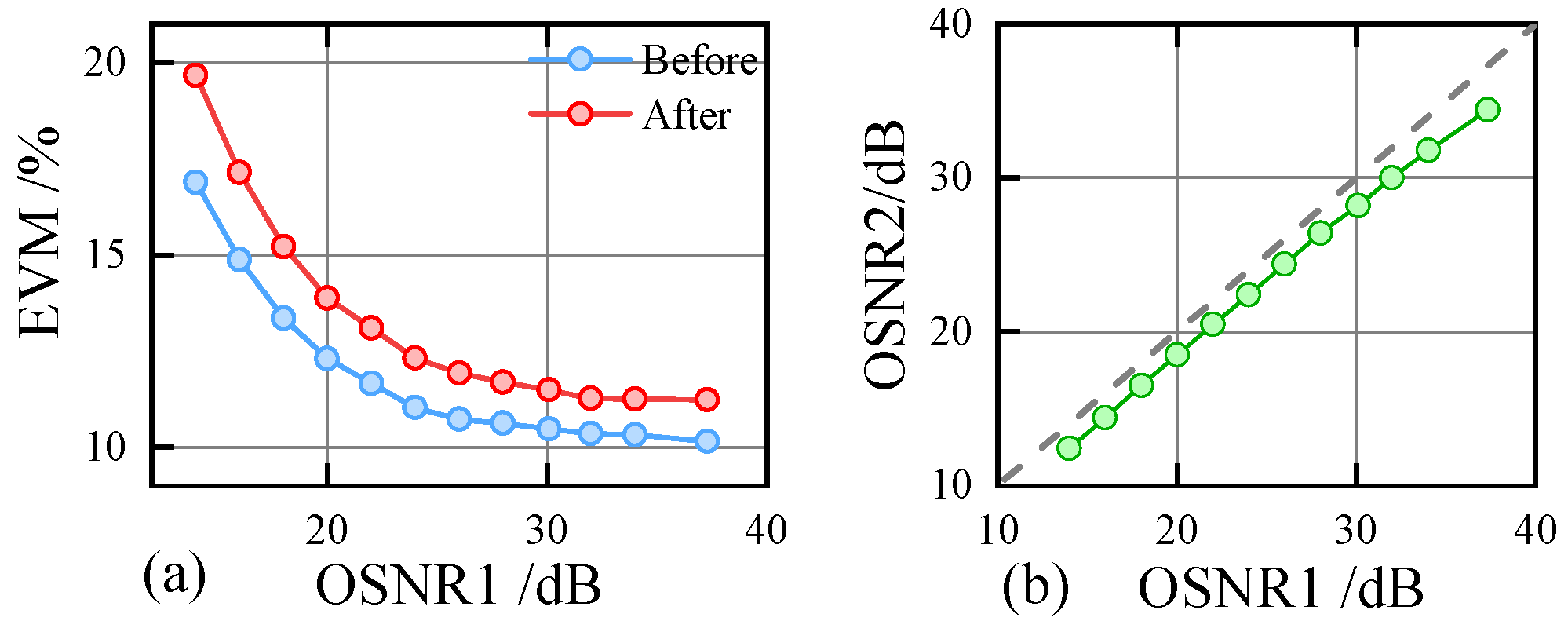
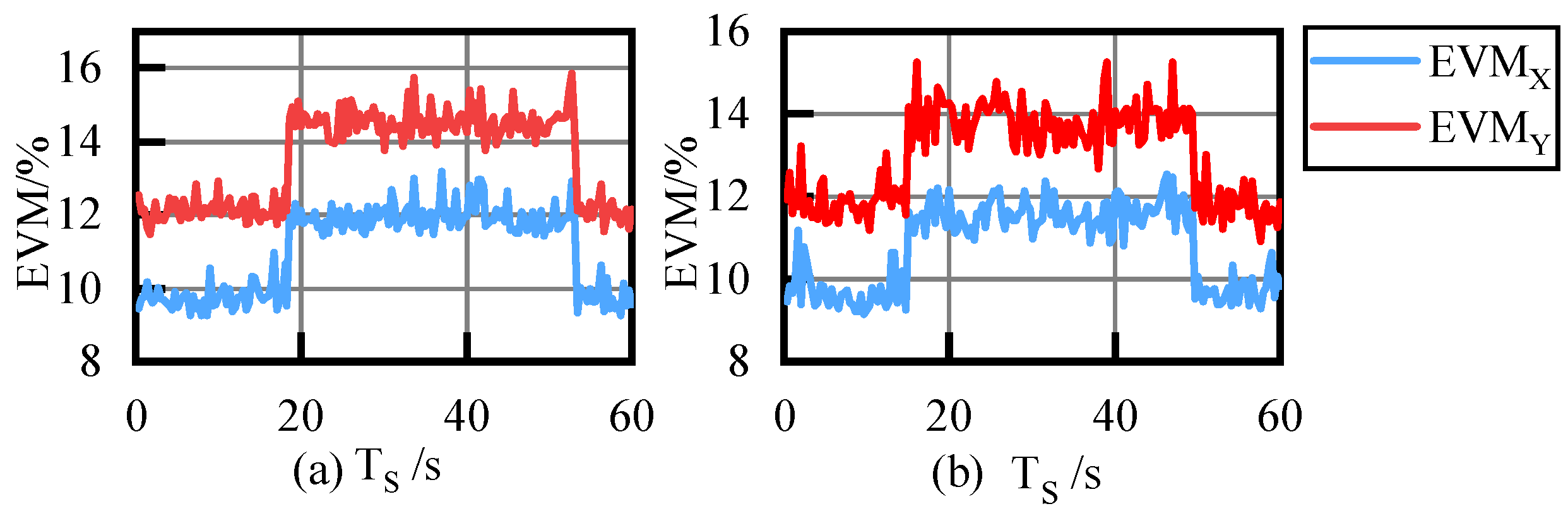
2.2. Optical Power Loss and Degradation of Transmission Performance
3. Scheme Principle
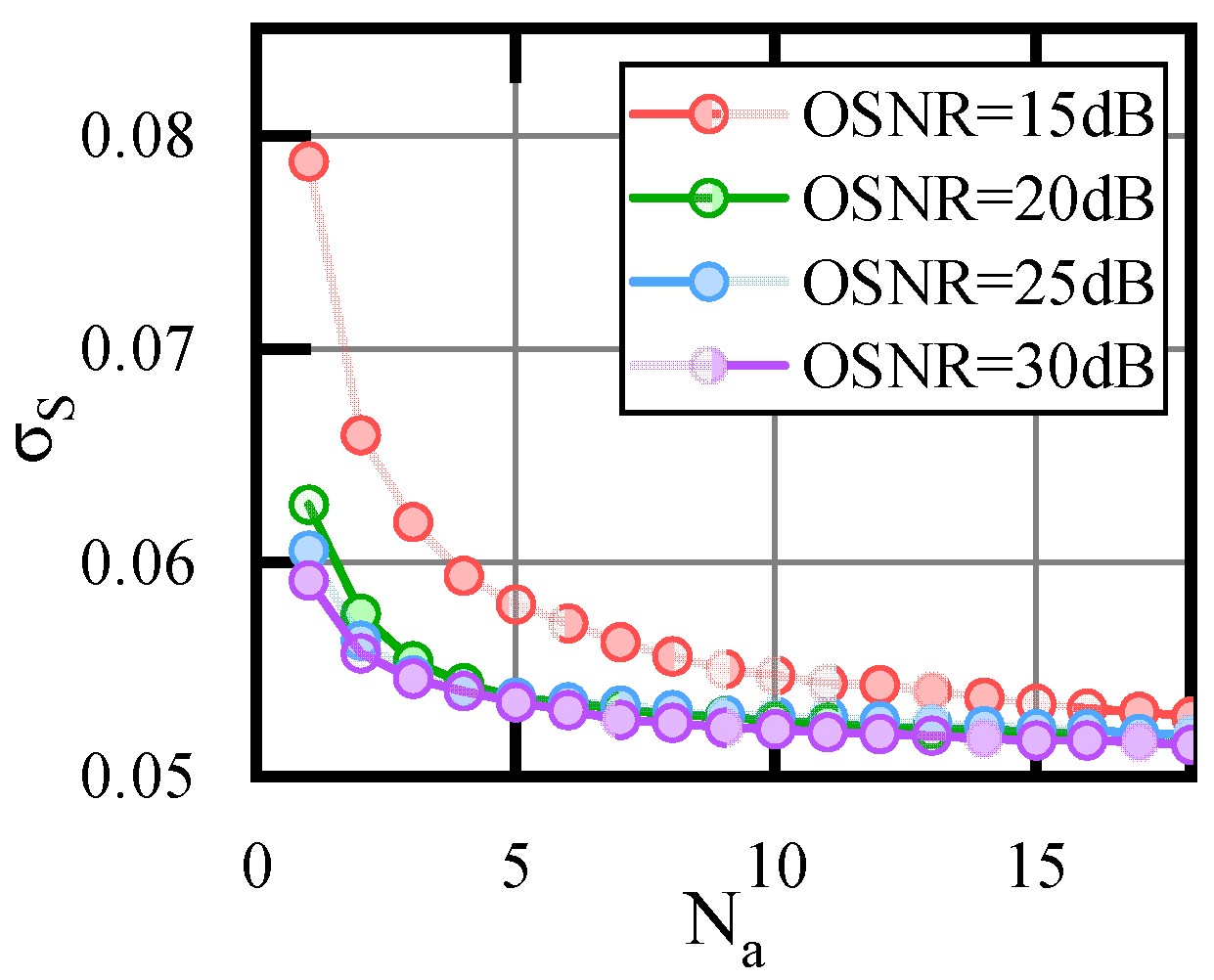
3.1. Multi-Channel Joint SOP Estimation
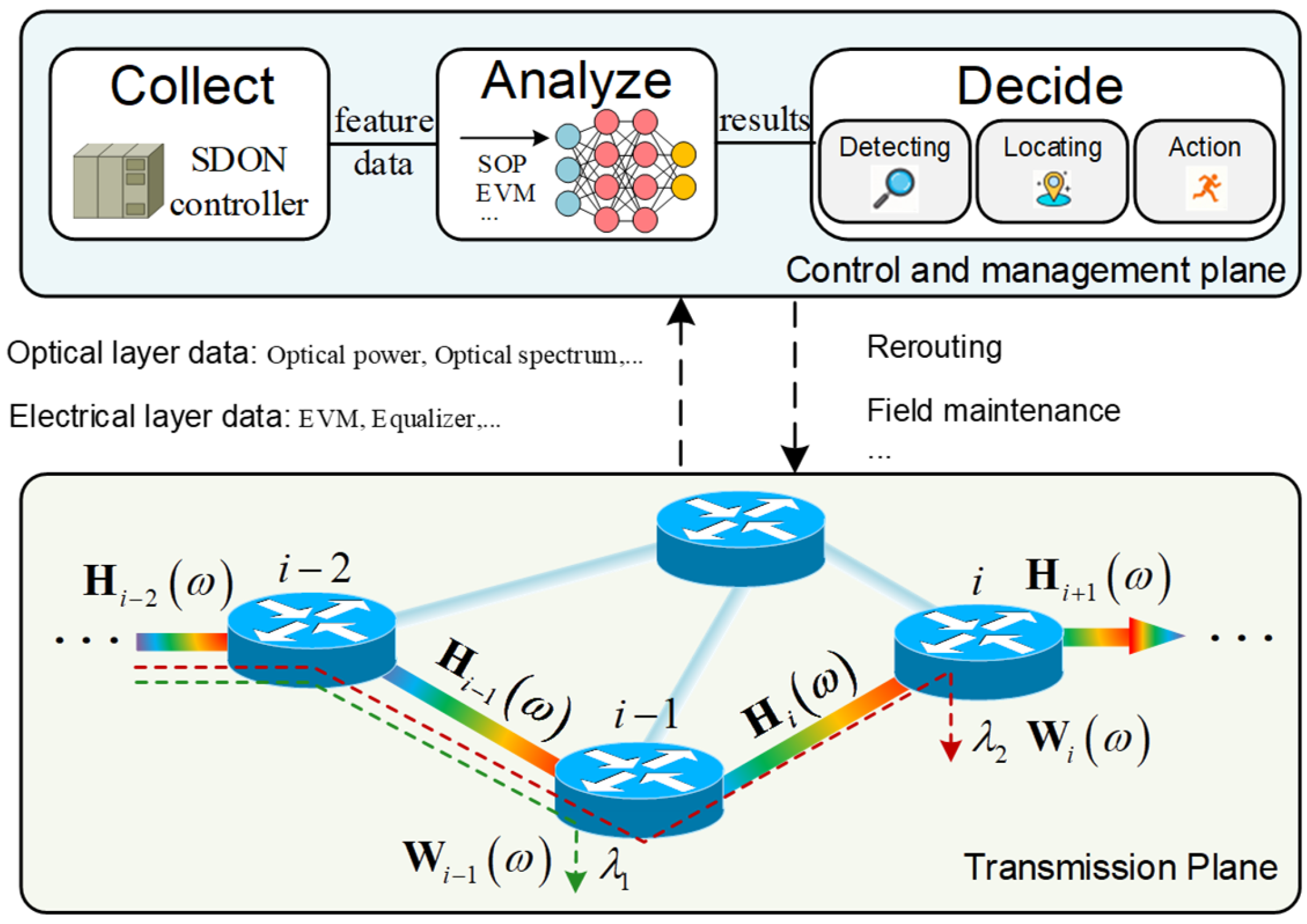
3.2. Comprehensive Solution
- (1)
- Collect: First, the control and management plane collect various parameters from the transmission plane in the optical communication system. These parameters can be obtained from electronical layers, such as an adaptive equalizer, EVM, or BER, or from optical layers, such as an optical power, OSNR, or optical spectrum. The diversity of parameters could help to improve the accuracy of identifications of fiber eavesdropping and other abnormal events.
- (2)
- Analyze: Subsequently, the collected feature data is transmitted to the data center for analysis. The data center could estimate the SOP and OPM data of different based on the proposed multi-channel joint SOP estimation scheme and other techniques [26]. Leveraging powerful computing resources and advanced artificial intelligence models [27], the data center conducts an in-depth analysis of this data. Next, it provides the judgment results for different optical fiber links.
- (3)
- Decide: Finally, the management plane makes decisions based on the judgments provided by the data center. For example, when a certain link is determined to be eavesdropped, network administrators can reroute the transmission path [28], dispatch maintenance personnel to conduct on-site inspections [29], and utilize an OTDR to precisely locate the fiber eavesdropping.
4. Experiment Setup and Results Analysis
4.1. Fiber Eavesdropping Dection in Single-Span System
4.1.1. Experiment Setup
4.1.2. Results Analysis
4.2. Fiber Eavesdropping Coarse Location in Multi-Span System
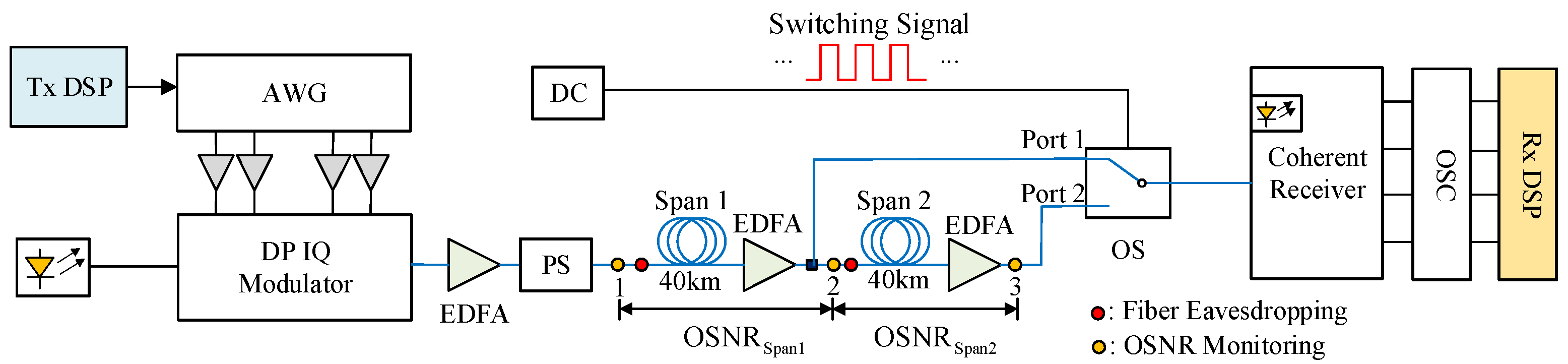
4.2.1. Experiment Setup
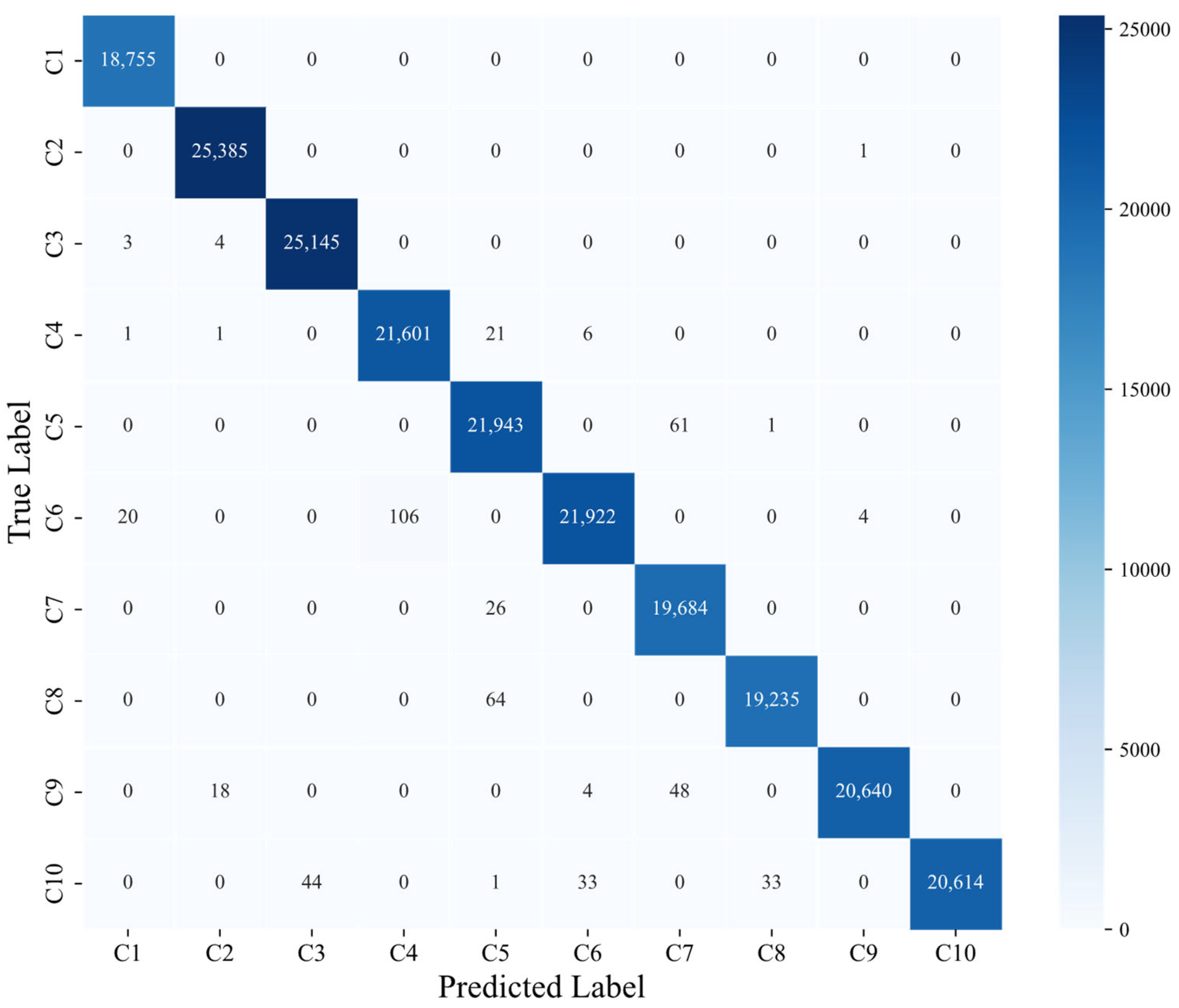
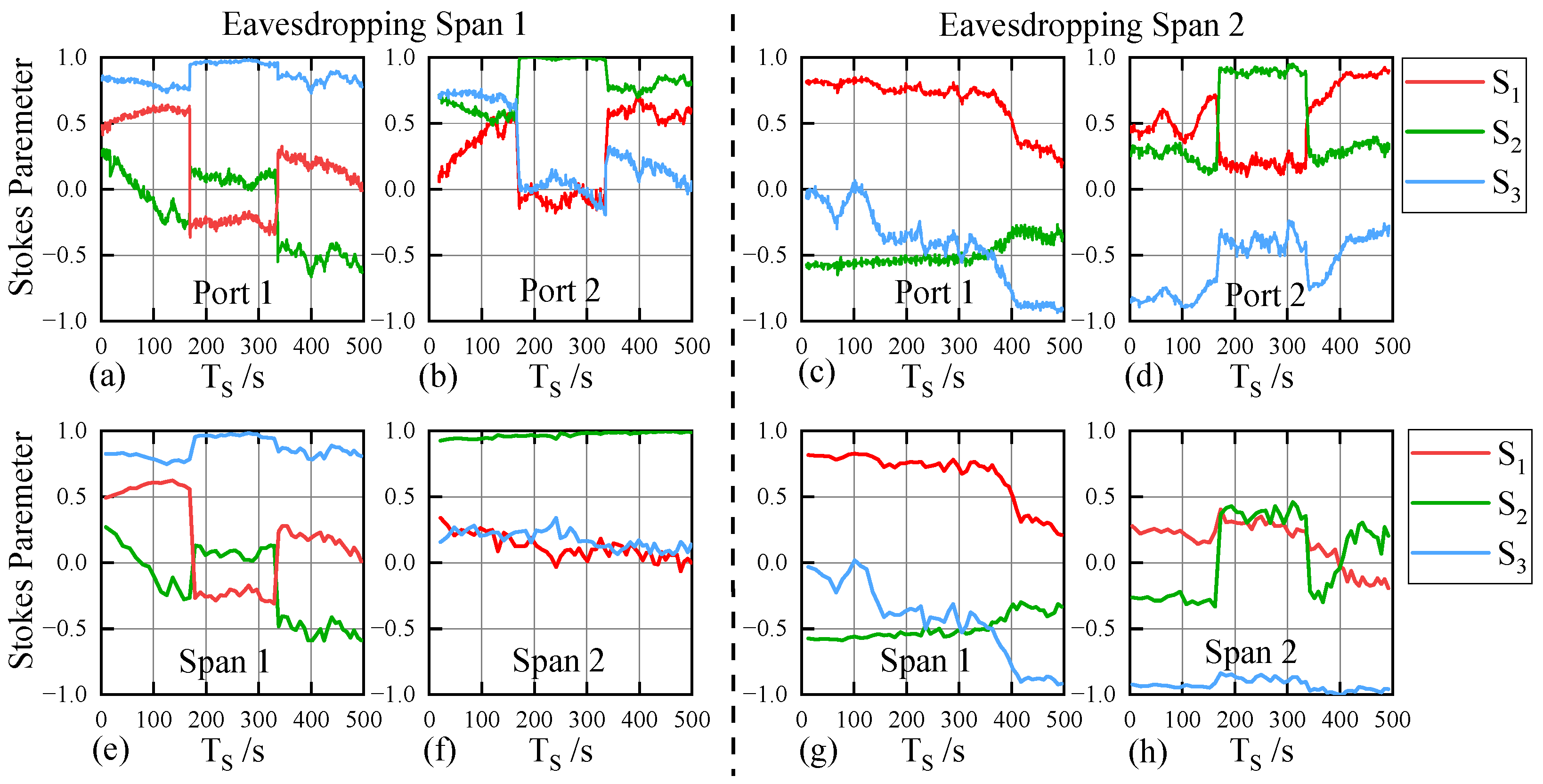
4.2.2. Results Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. The Structure of CNN
Appendix A.2. Data Augmentation
Appendix A.3. Training Setup
References
- Bhatt, V. On Continued Significance of Multimode Links in Data Centers. J. Light. Technol. 2025, 43, 1700–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Zhang, B. Scaling Optical Interconnects for Hyperscale Data Center Networks. Proc. IEEE 2022, 111, 1699–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lam, C.F.; Urata, R.; Liu, H. State-of-the-Art 800G/1.6T Datacom Interconnects and Outlook for 3.2T. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference (OFC) 2023, San Diego, CA, USA, 5–9 March 2023. paper W3D.1. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Dong, B.; Li, Y.; Xiong, B.; Zhang, J.; Sun, C.; Hao, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Han, Y.; et al. Photonics-assisted THz wireless communication enabled by wide-bandwidth packaged back-illuminated modified uni-traveling-carrier photodiode. Opto-Electron. Sci. 2024, 3, 230051-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaneman, K.; Gray, S. Optical network security: Technical analysis of fiber tapping mechanisms and methods for detection & prevention. In Proceedings of the IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM) 2024, Monterey, CA, USA, 31 October–3 November 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sadot, D.; Wohlgemuth, E.; Attia, I.; Balasiano, O.; Jonas, I.; Keller, E.; Shalom, H. Photonic Layer Security in High-Speed Optical Communications. J. Light. Technol. 2025, 43, 1671–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Fan, Y.; Cheng, M.; Gao, X. Secure Spread Spectrum Communication Using Super-Orthogonal Optical Chaos Signals. IEEE Photonics J. 2022, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, K.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Analysis of the encryption penalty in a QAM-based quantum noise stream cipher. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 19006–19020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Probabilistic shaping probability distribution scrambling based on a chaotic system for integrating secure transmission and adaptive key updating. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 42545–42557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekun, N.; Yunhao, X.; Guozhi, X.; Chenhao, D.; Hang, Y.; Chuyan, Z.; Minghui, S.; Lyv, L.; Guoqing, P.; Weisheng, H.; et al. Experimental Demonstration of Integrated Encryption and Communication over Optical Fibre. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2025, nwaf112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michal, R.; Lukas, J.; Petr, D.; Adrian, T.; Vladimir, S.; Petr, M. Classification of Events Violating the Safety of Physical Layers in Fiber-Optic Network Infrastructures. Sensors 2022, 22, 9515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Liu, K.; Jiang, J.; Xu, T.; Wang, S.; Guo, H.; Zhou, Z.; Xue, K.; Huang, Y.; Liu, T. Optical Fiber Distributed Vibration Sensing Using Grayscale Image and Multi-Class Deep Learning Framework for Multi-Event Recognition. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 17, 19112–19120. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelli, K.; Cho, J.Y.; Azendorf, F.; Griesser, H.; Tropschug, C.; Pachnicke, S. Machine-learning-based anomaly detection in optical fiber monitoring. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2022, 14, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, A.; Sedlmeir, F.; Stiller, B.; Marquardt, C. Eavesdropper localization for quantum and classical channels via nonlinear scattering. Opt. Quantum 2024, 2, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Experimental study of machine-learning-based detection and location of eavesdropping in end-to-end optical fiber communications. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2022, 68, 102669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Lin, R.; Wosinska, L.; Monti, P.; Zhang, M.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J. Cluster-based unsupervised method for eavesdropping detection and localization in WDM systems. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2024, 16, F52–F61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadighi, L.; Karlsson, S.; Natalino, C.; Furdek, M. Machine Learning-Based Polarization Signature Analysis for Detection and Categorization of Eavesdropping and Harmful Events. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference (OFC) 2024, San Diego, CA, USA, 24–28 March 2024. paper M1H.1. [Google Scholar]
- Sadighi, L.; Karlsson, S.; Wosinska, L.; Furdek, M. Machine Learning Analysis of Polarization Signatures for Distinguishing Harmful from Non-harmful Fiber Events. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks (ICTON) 2024, Bari, Italy, 14–18 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelli, K.; Lonardi, M.; Gripp, J.; Correa, D.; Olsson, S.; Boitier, F.; Layec, P. Anomaly Detection and Localization in Optical Networks Using Vision Transformer and SOP Monitoring. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference (OFC) 2024, San Diego, CA, USA, 24–28 March 2024. paper Tu2J.4. [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini, S.; Minelli, L.; Andrenacci, L.; Rizzelli, G.; Pilori, D.; Bosco, G.; Della Chiesa, L.; Crognale, C.; Piciaccia, S.; Gaudino, R. Overview on the state of polarization sensing: Application scenarios and anomaly detection algorithms. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2025, 17, A196–A209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, G.; Jesse, E.S.; Fabien, B.; Dan, K.; Jelena, P.; Michael, S. Efficient Classification of Polarization Events Based on Field Measurements. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference (OFC), San Diego, CA, USA, 8–12 March 2020. paper Th3D-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, P.N.; Ye, Z.; Huang, Y.K.; de Lima, T.F.; Aono, Y.; Asahi, K.; Wang, T. Optical Network Anomaly Detection and Localization Based on Forward Transmission Sensing and Route Optimization. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference 2024, San Diego, CA, USA, 24–28 March 2024. paper Tu2J.4. [Google Scholar]
- Yaman, F.; Li, Y.; Han, S.; Inoue, T.; Mateo, E.; Inada, Y. Polarization Sensing Using Polarization Rotation Matrix Eigenvalue Method. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference (OFC) 2023, San Diego, CA, USA, 5–9 March 2023. paper W1J.7. [Google Scholar]
- Stefan, K.; Rui, L.; Lena, W.; Paolo, M.; Eavesdropping, G. 652 vs. G. 657 fibres: A performance comparison. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Optical Network Design and Modeling (ONDM), Warsaw, Poland, 16–19 May 2022; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Thyagaturu, A.S.; Mercian, A.; McGarry, M.P.; Reisslein, M.; Kellerer, W. Software Defined Optical Networks (SDONs): A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 2738–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Yoshikane, N.; Tsuritani, T.; Otani, T. In-band OSNR monitoring technique based on link-by-link estimation for dynamic transparent optical networks. J. Light. Technol. 2008, 26, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, G.; Yang, M.; Yan, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Efficient stochastic parallel gradient descent training for on-chip optical processor. Opto-Electron. Adv. 2024, 7, 230182. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Wang, W.; Ouyang, F.; Hao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Eavesdropping-aware survivable routing in physical-layer secured optical networks. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2025, 17, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantono, M.; Castellanos, J.C.; Batthacharya, S.; Yin, S.; Zhan, Z.; Mecozzi, A.; Kamalov, V. Optical Network Sensing: Opportunities and Challenges. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference (OFC) 2022, San Diego, CA, USA, 6–10 March 2022. paper M2F.1. [Google Scholar]
- Pittala, F.; Slim, I.; Mezghani, A.; Nossek, J.A. Training-aided frequency-domain channel estimation and equalization for single-carrier coherent optical transmission systems. J. Light. Technol. 2014, 32, 4849–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- And, K.Y.; Ahmet, D.; Heha, Y.D. Experimental optical setup to measure power loss versus fiber bent radius for tapping into optical fiber communication links. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Energy Technologies (ICECET), Cape Town, South Africa, 9–10 December 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]






| Entire | OSNR = 15 dB | OSNR = 20 dB | OSNR = 25 dB | OSNR = 30 dB | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 0.9977 | 0.9974 | 0.9977 | 0.9978 | 0.9978 | |||||
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | |
| Precision | 0.9987 | 0.9991 | 0.9983 | 0.9951 | 0.9949 | 0.9980 | 0.9945 | 0.9982 | 0.9998 | 1.0000 |
| Recall | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.9997 | 0.9987 | 0.9972 | 0.9941 | 0.9987 | 0.9967 | 0.9966 | 0.9946 |
| F1-score | 0.9994 | 0.9995 | 0.9990 | 0.9969 | 0.9961 | 0.9961 | 0.9966 | 0.9975 | 0.9982 | 0.9973 |
| OSNR1 | OSNR2 | OSNR3 | OSNRSpan1 | OSNRSpan2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO Eavesdropping | 43.2 | 38.2 | 34.5 | 39.85 | 36.92 |
| Eavesdropping Span1 | 43.2 | 35.2 | 32.9 | 35.83 | 36.91 |
| Eavesdropping Span2 | 43.2 | 35.2 | 31.3 | 39.85 | 33.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wei, S.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Fiber Eavesdropping Detection and Location in Optical Communication System. Photonics 2025, 12, 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050501
Li Y, Liang Y, Zhang M, Wei S, Zhu H, Li Y, Zhao Y, Zhang J. Fiber Eavesdropping Detection and Location in Optical Communication System. Photonics. 2025; 12(5):501. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050501
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuang, Yuyuan Liang, Mingrui Zhang, Shuang Wei, Huatao Zhu, Yajie Li, Yongli Zhao, and Jie Zhang. 2025. "Fiber Eavesdropping Detection and Location in Optical Communication System" Photonics 12, no. 5: 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050501
APA StyleLi, Y., Liang, Y., Zhang, M., Wei, S., Zhu, H., Li, Y., Zhao, Y., & Zhang, J. (2025). Fiber Eavesdropping Detection and Location in Optical Communication System. Photonics, 12(5), 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050501







