A Novel Two-Stage Approach for Nonlinearity Correction of Frequency-Modulated Continuous-Wave Laser Ranging Combining Data-Driven and Principle-Based Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
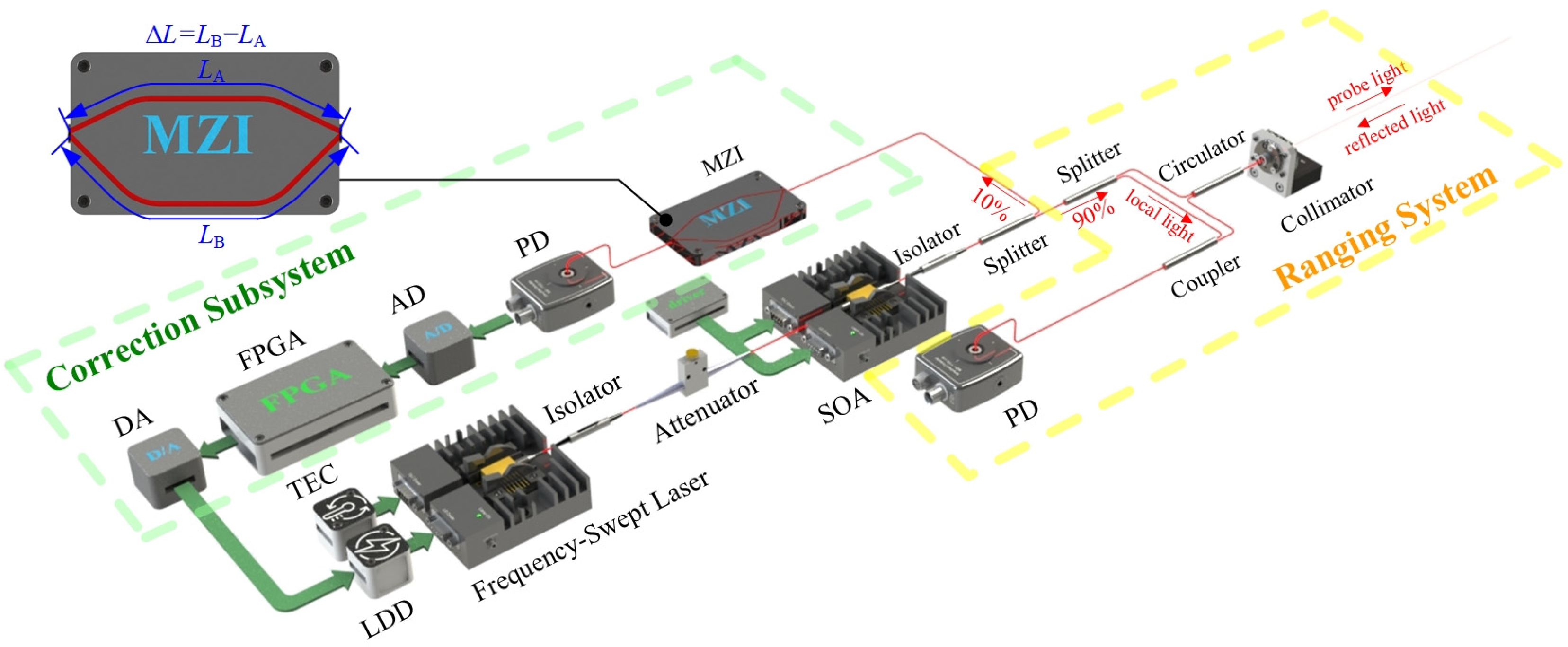
2. Materials and Methods
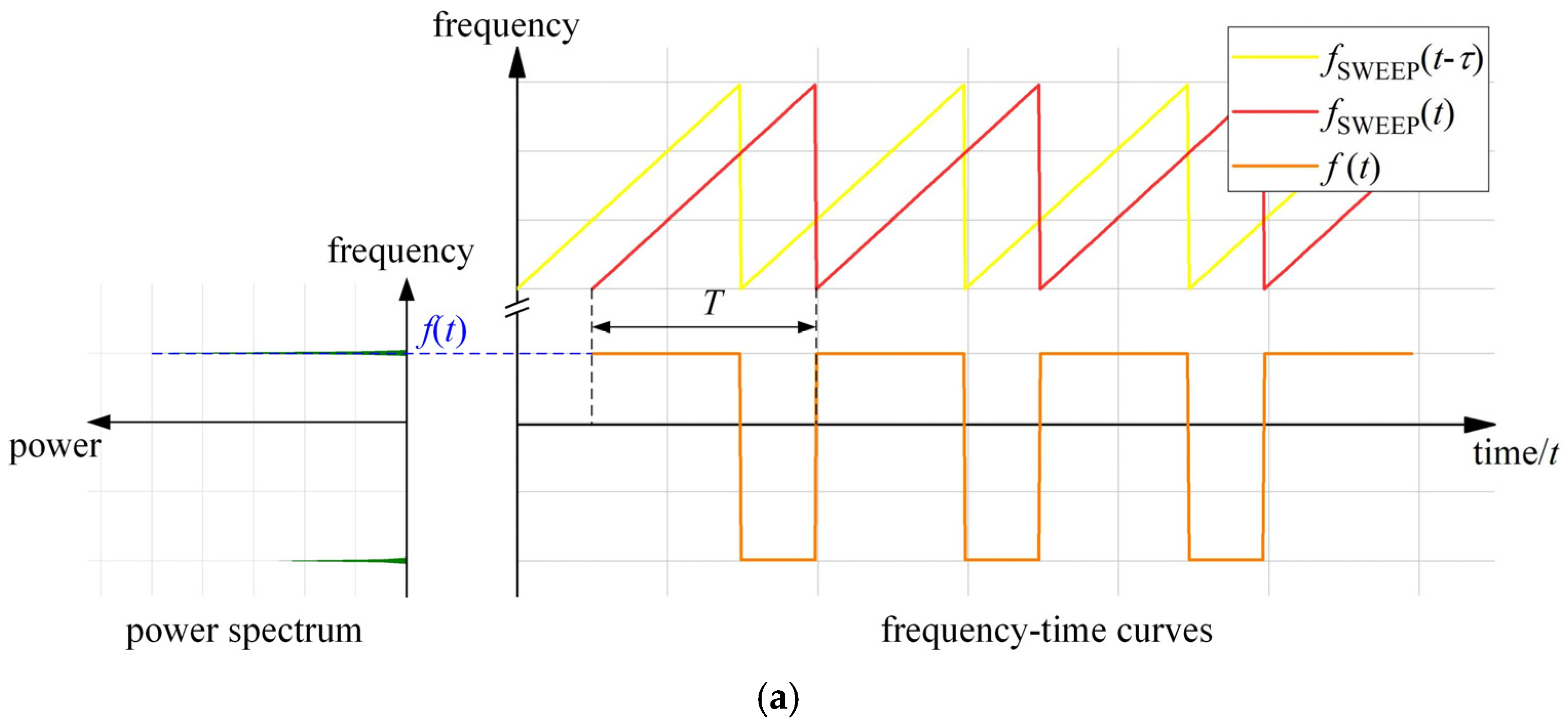
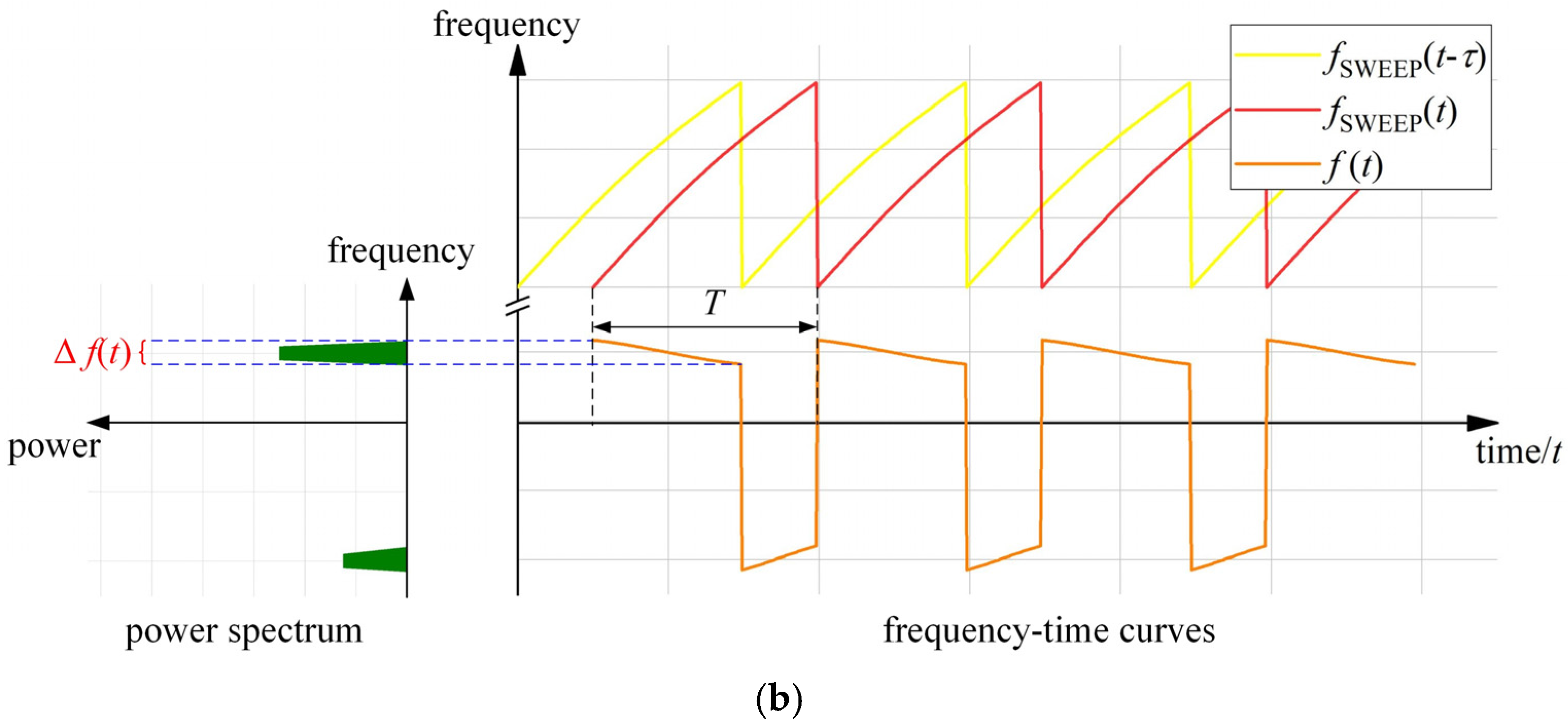
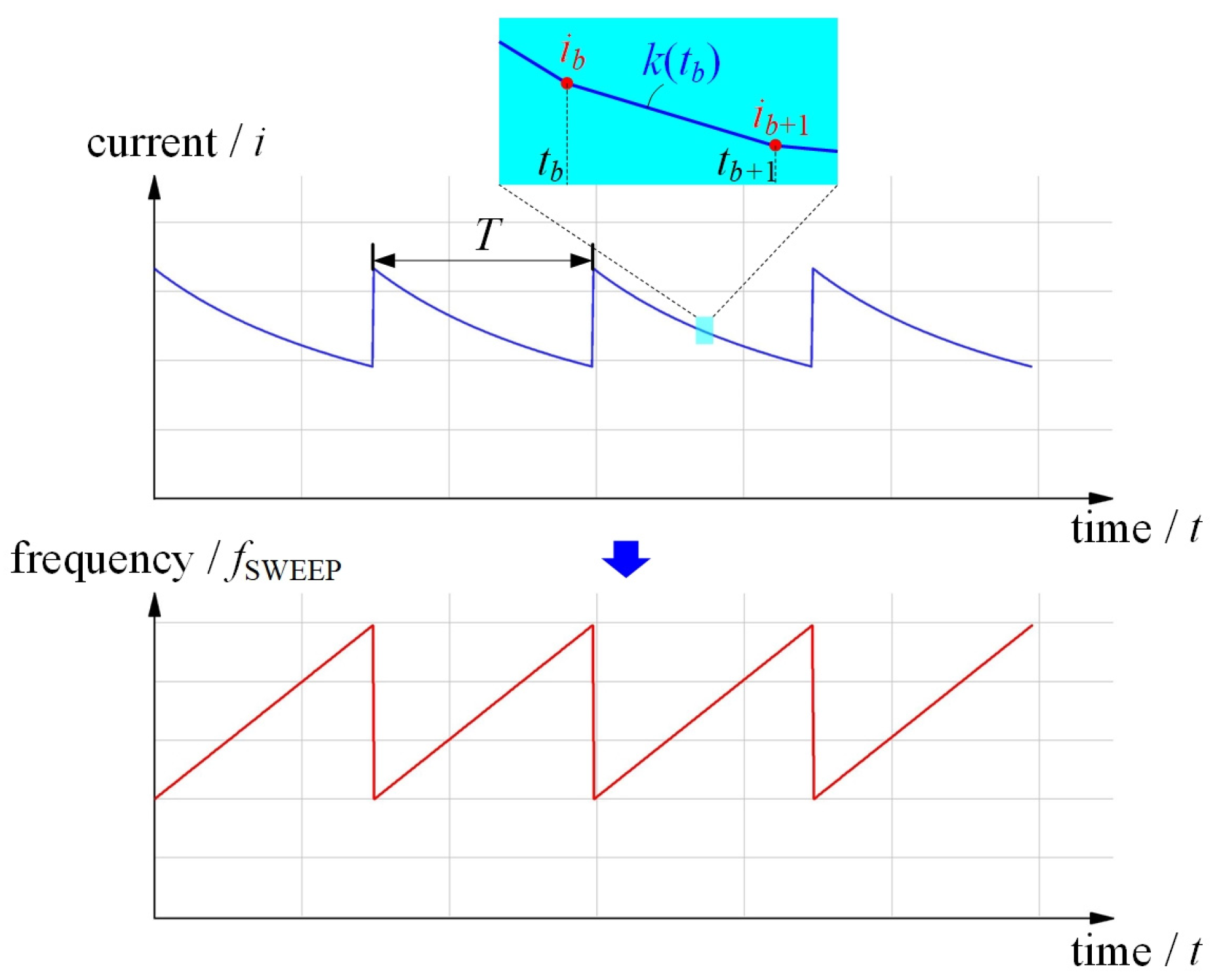
2.1. FMCW Ranging Principle
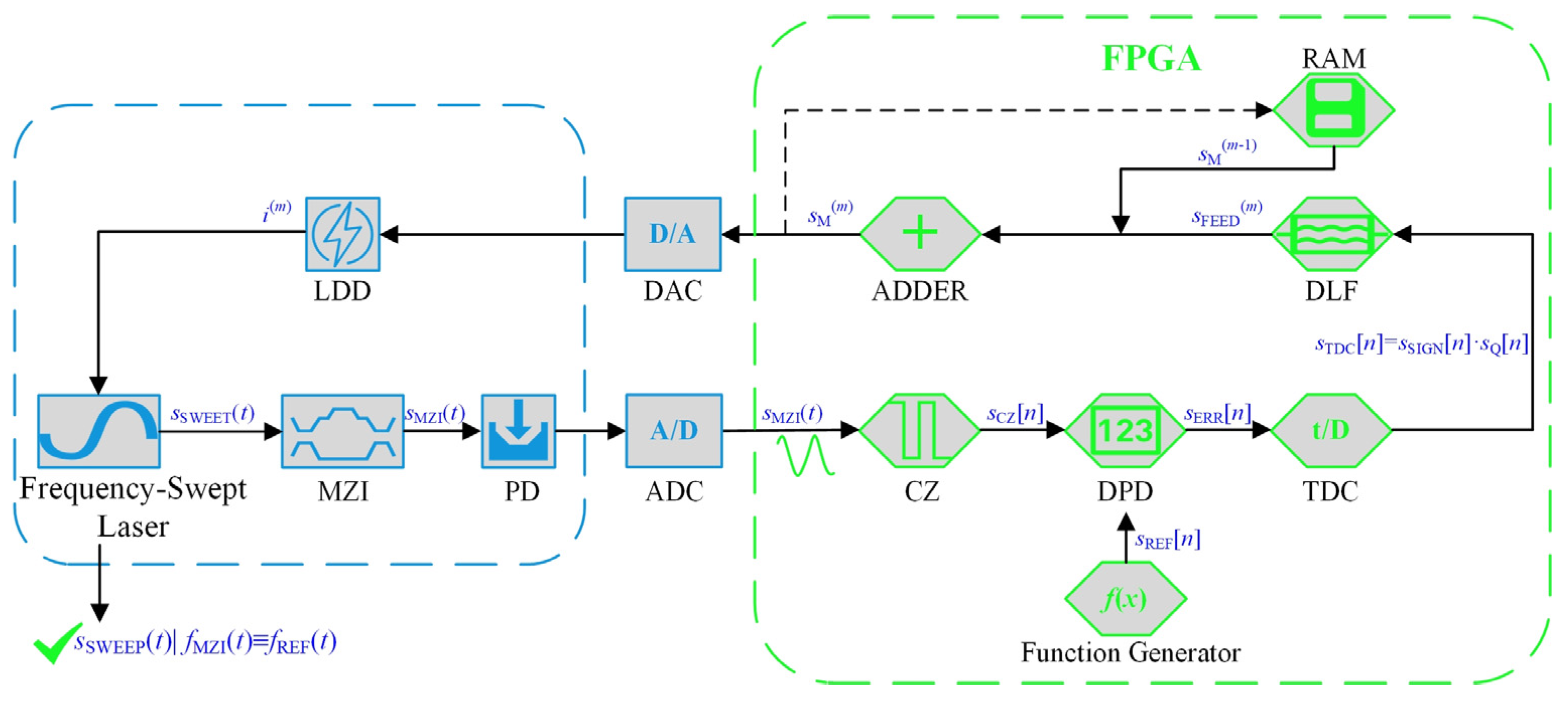
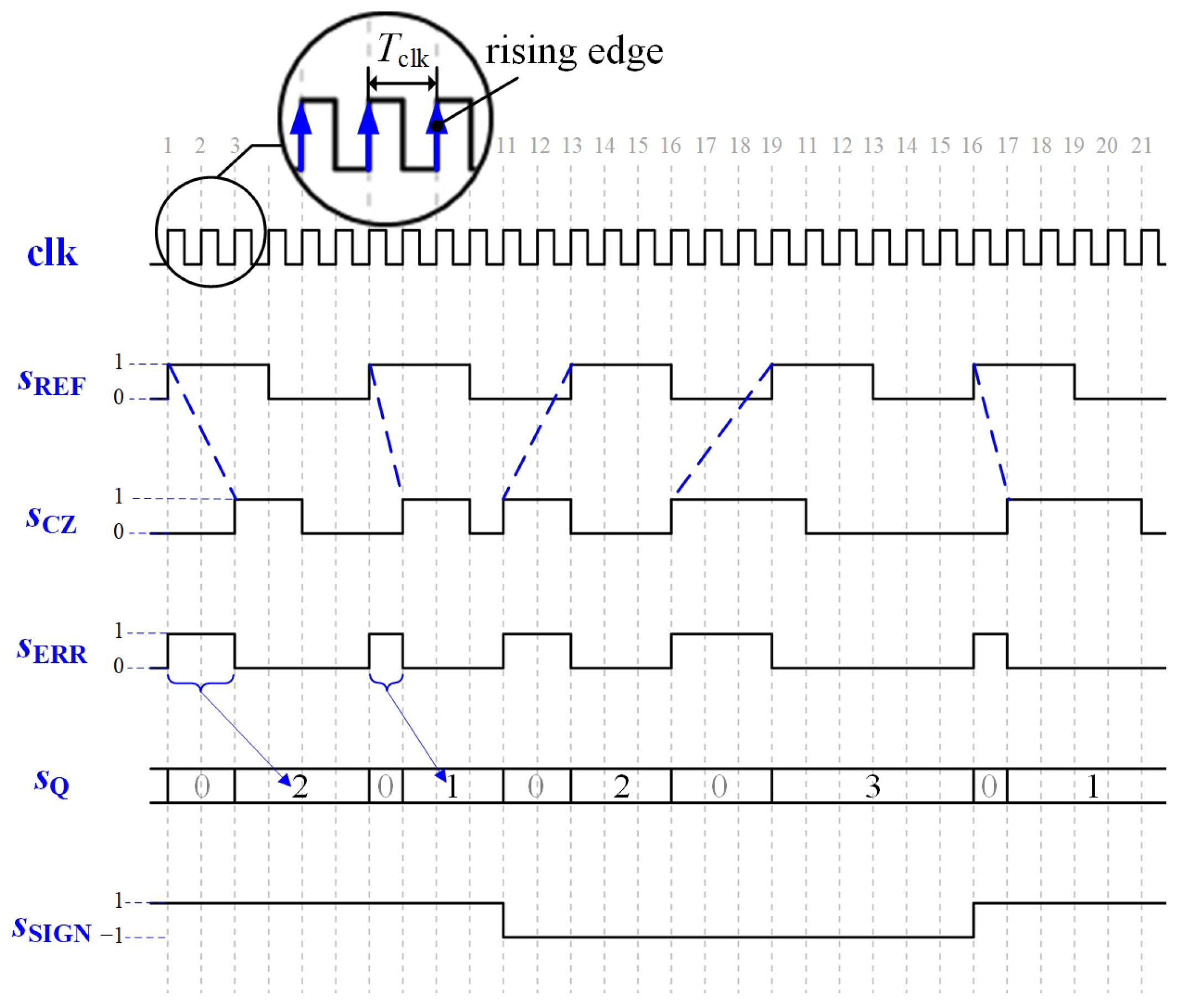
2.2. The Main Correction Based on EO-PLL
2.3. The Pre-Correction Based on NN-SAC
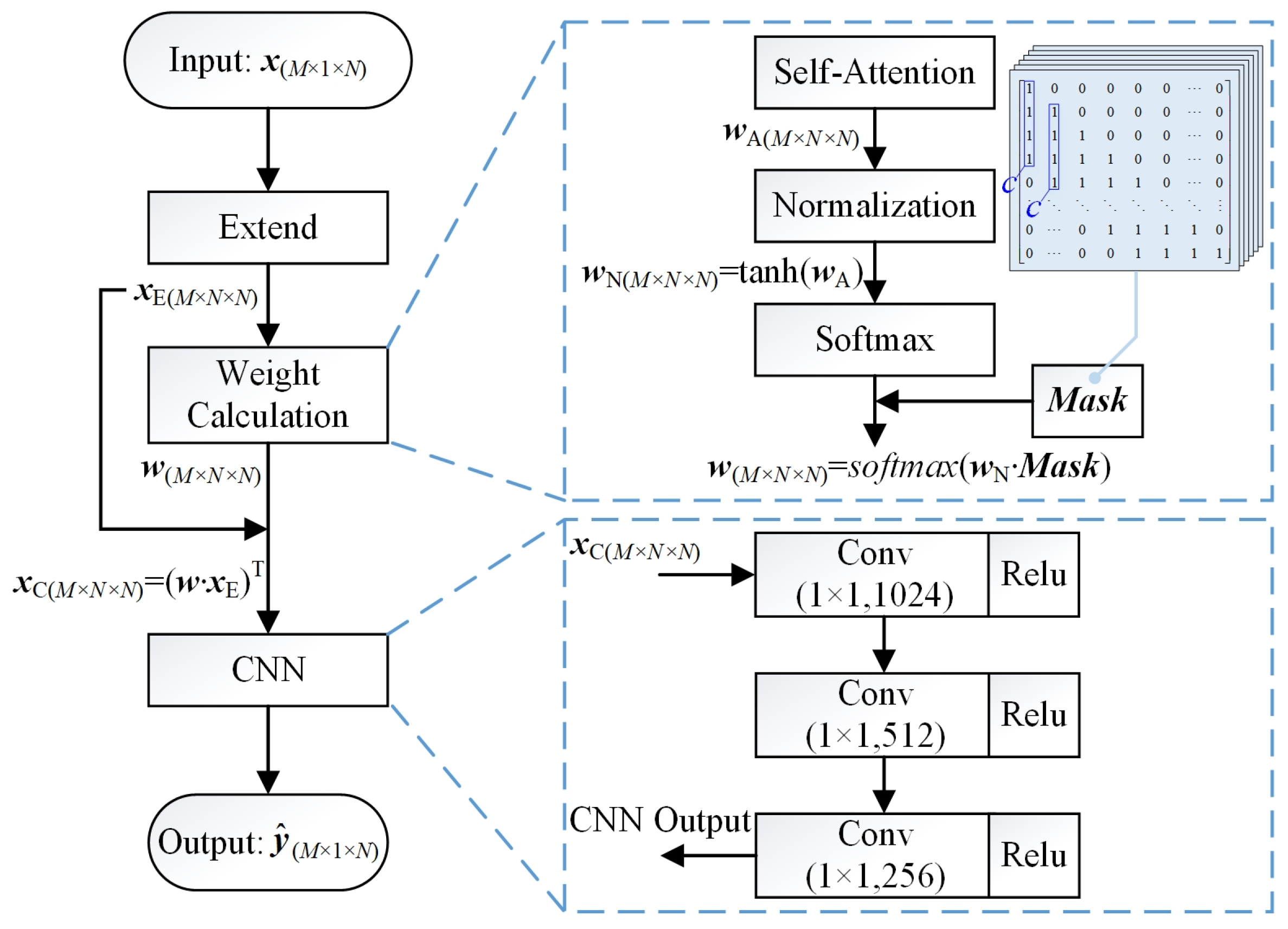
2.3.1. NN Model
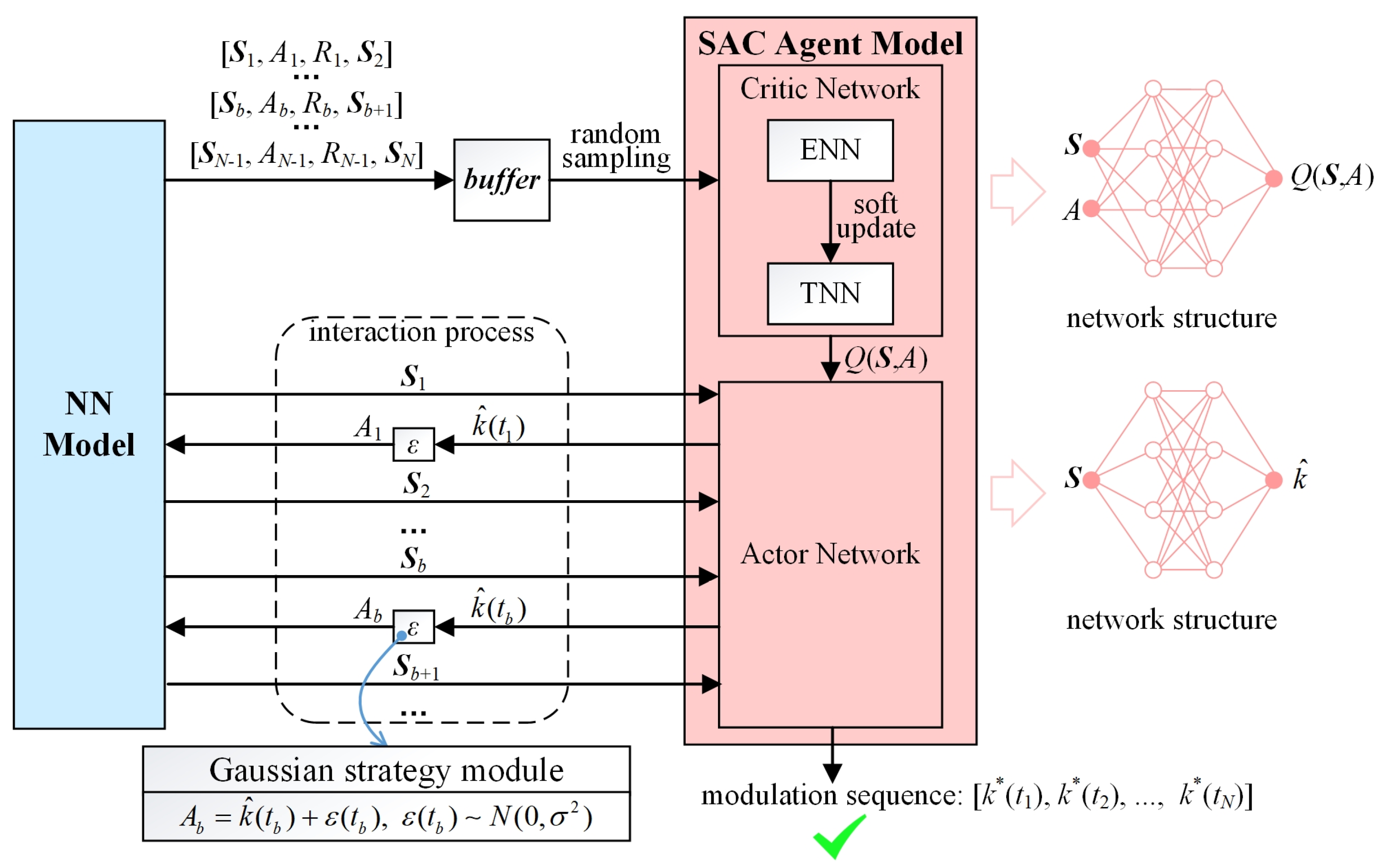
2.3.2. SAC Agent Model
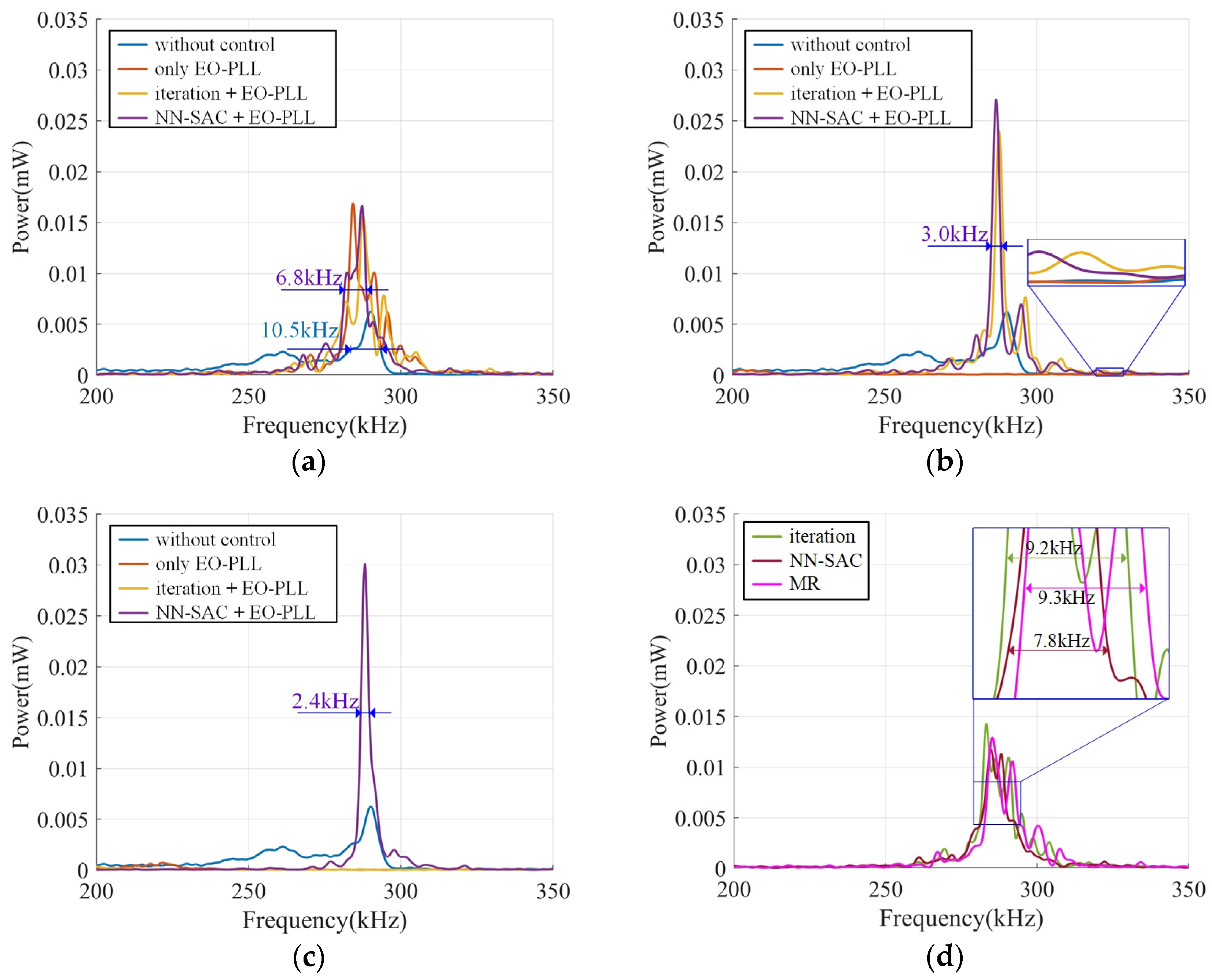
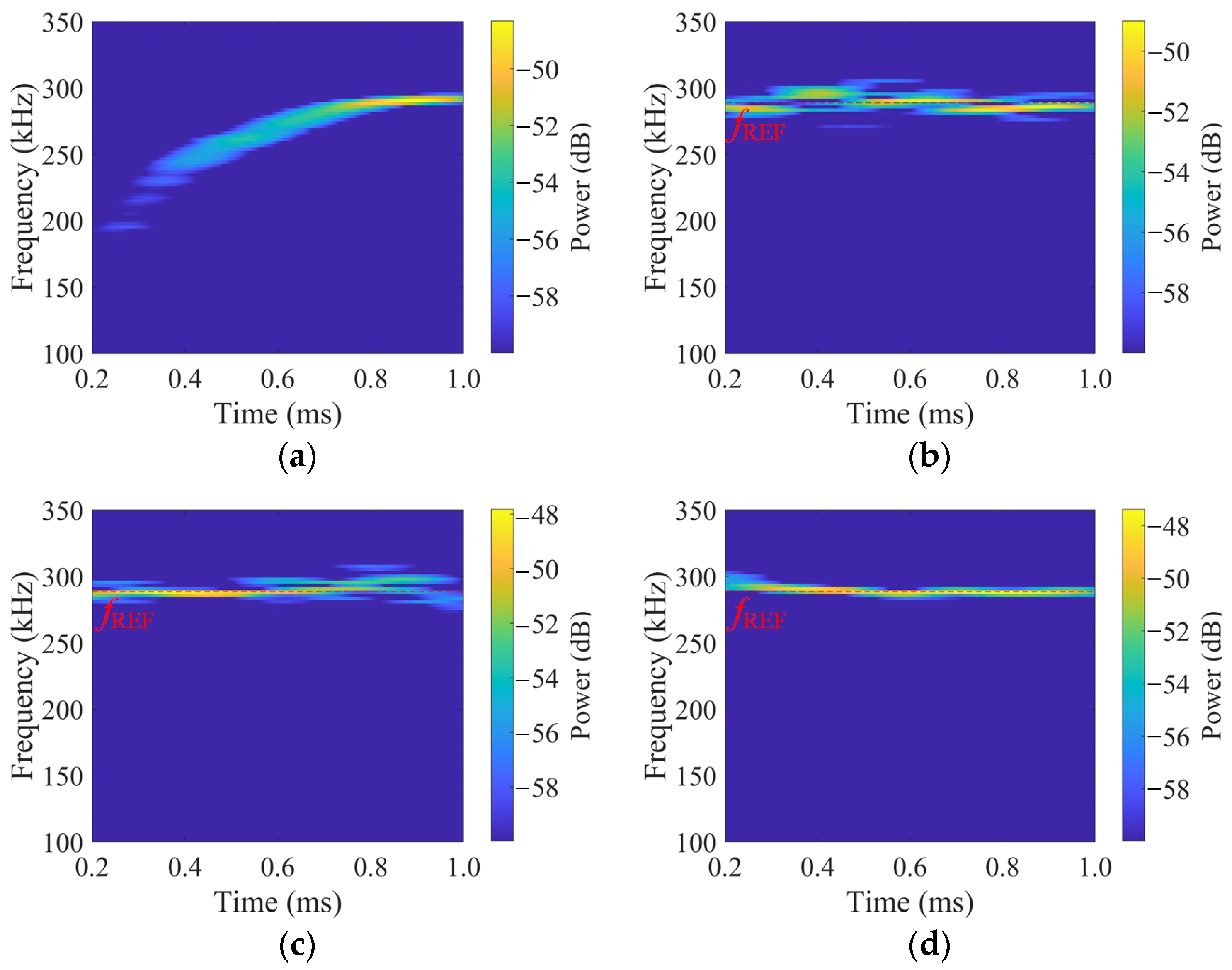
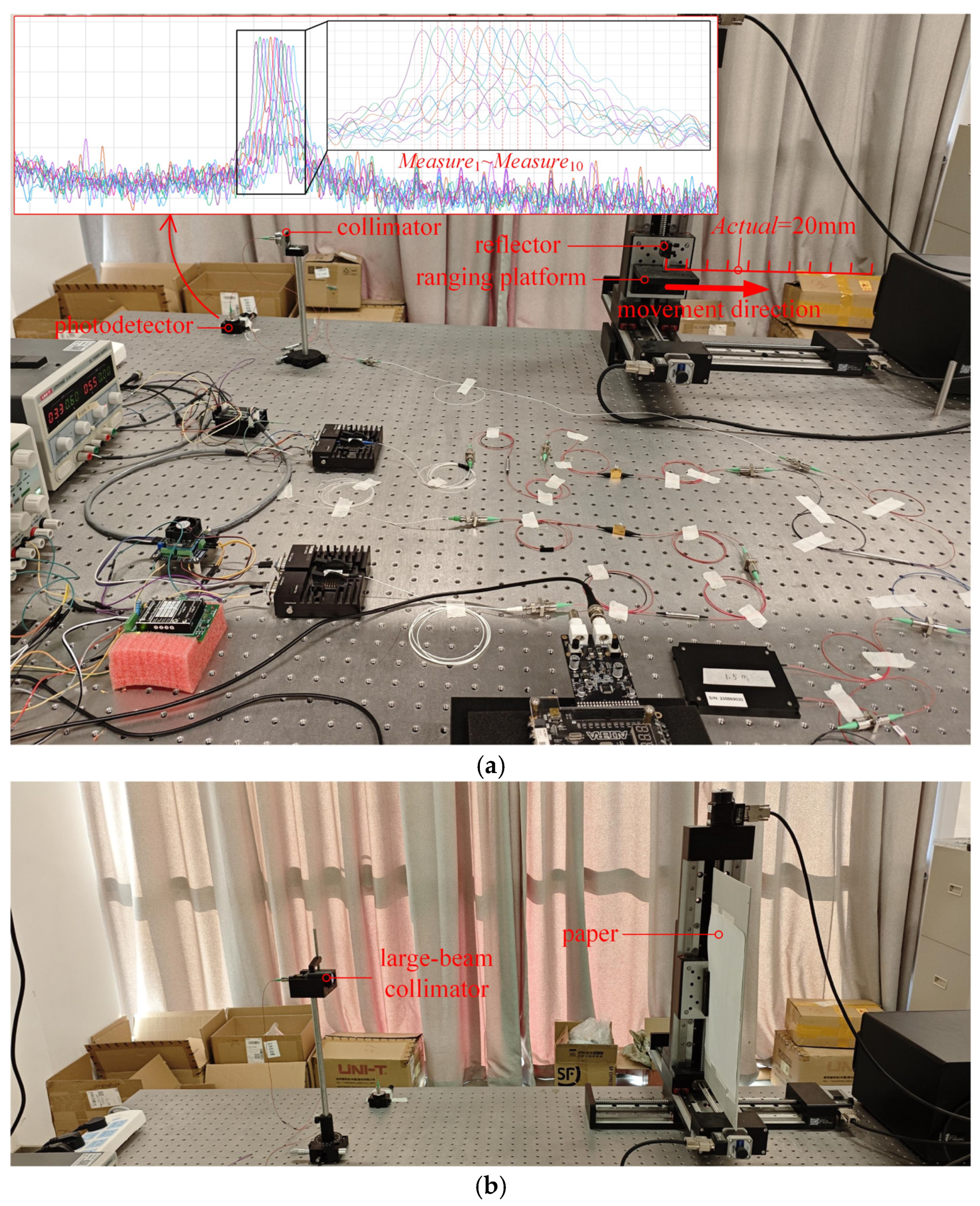
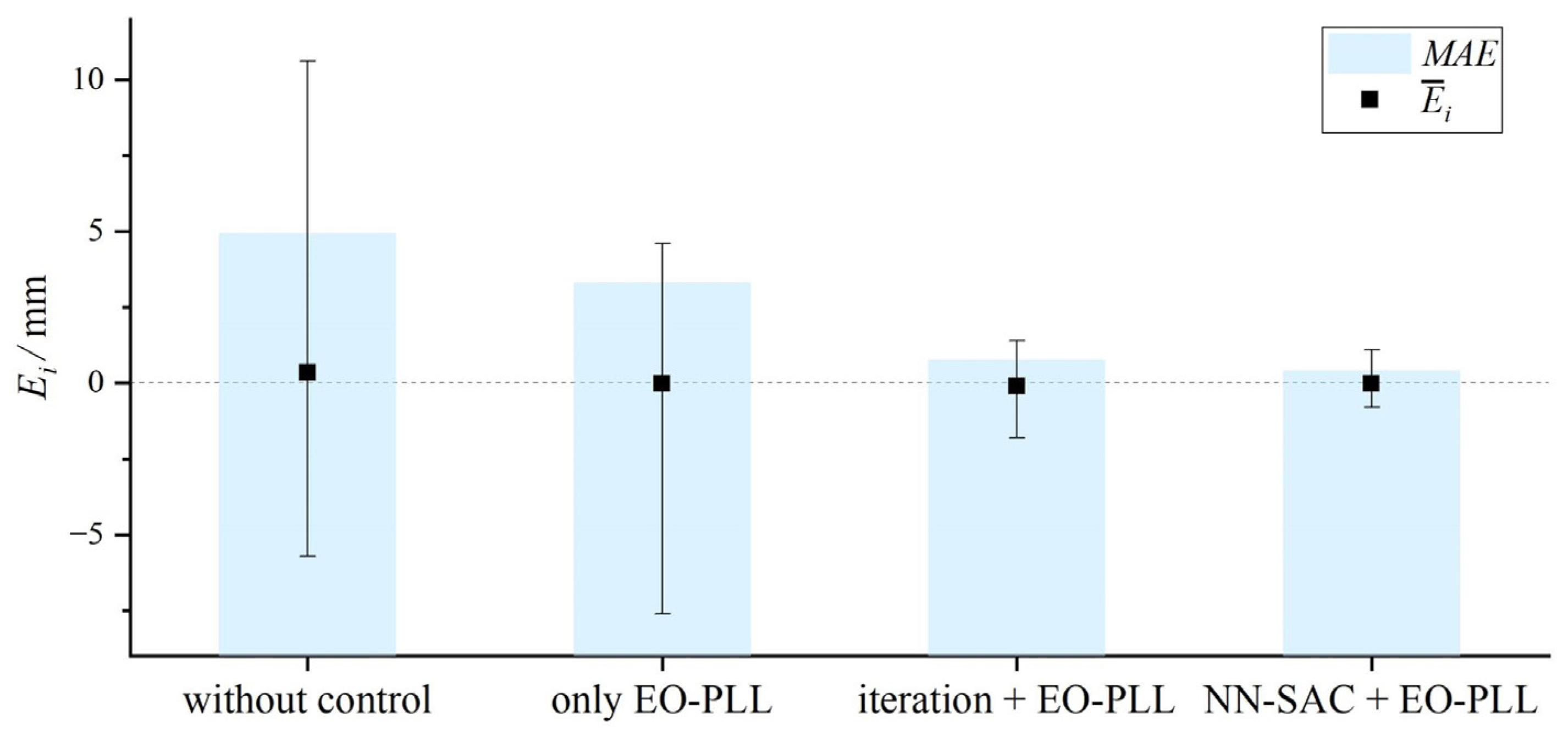
3. Results
3.1. Frequency-Swept Characteristic Analysis Experiment
3.2. Ranging Experiment
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FMCW | Frequency-Modulated Continuous-Wave |
| EO-PLL | Electro-Optic Phase-Locked Loop |
| DLF | Digital Loop Filter |
| NN | Neural Network |
| SAC | Soft Actor-Critic |
| LiDAR | Light Detection and Ranging |
| NN-SAC | Neural Network-Soft Actor-Critic |
| RL | Reinforcement Learning |
| SOA | Semiconductor Optical Amplifier |
| MZI | Mach-Zehnder Interferometer |
| PD | Photodetector |
| FPGA | Field Programmable Gate Array |
| ADC | Analog-to-Digital Converter |
| CZ | Cross-Zero Circuit |
| DPD | Digital Phase Detector |
| TDC | Time-to-Digital Converter |
| RAM | Random Access Memory |
| DAC | Digital-to-Analog Converter |
| LDD | Laser Diode Driver |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| ENN | Evaluate Neural Network |
| TNN | Target Neural Network |
| FWHM | Full Width at Half Maxima |
| MR | Mapping Relationship |
| STFT | Short Time Fourier Transform |
References
- Okano, M.; Chong, C.H. Swept source lidar simultaneous FMCW ranging and nonmechanical beam steering with a wideband swept source. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 23898–23915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.W.; Chen, S.T.; Wang, T.Y.; Liu, J.S.; Wang, K.J.; Yang, Z.G. Nonlinear error correction for Terahertz FMCW System by a new beat frequency estimation method. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 34510–34521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.H.; Hung, Y.H.; Hwang, S.K. Frequency-modulated continuous-wave microwave generation using stabilized period-one nonlinear dynamics of semiconductor lasers. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 3334–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerald, H.; Chen, Z.; Wei, T. Extended-bandwidth frequency sweeps of a distributed feedback laser using combined injection current and temperature modulation. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 075104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, D.; Hyyppä, K. Advantages of a new modulation scheme in an optical self-mixing frequency-modulated continuous-wave system. Opt. Eng. 2002, 41, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vasilyev, A.; Satyan, N.; Rakuljic, G.; Yariv, A. Terahertz chirp generation using frequency stitched VCSELs for increased LIDAR resolution. In Proceedings of the 2012 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO), San Jose, CA, USA, 6–11 May 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Qu, X.H.; Zhang, F.M. Nonlinear error correction for FMCW ladar by the amplitude modulation method. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 11519–11528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.Y.; Wu, K.; Li, C.; Zhang, G.J.; Chen, J.P. Highly efficient iteration algorithm for a linear frequency-sweep distributed feedback laser in frequency-modulated continuous wave lidar applications. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B-Opt. Phys. 2021, 38, D8–D14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ula, R.K.; Noguchi, Y.; Iiyama, K. Three-dimensional object profiling using highly accurate FMCW optical ranging system. J. Light. Technol. 2019, 37, 3826–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.Q.; Cui, J.W.; Wang, Z.Y.; Tan, J.B. Nonlinear correction of a laser scanning interference system based on a fiber ring resonator. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiev, R.R.; Kondratiev, N.M.; Lobanov, V.E.; Bilenko, I.A. Optimization of a frequency comb-based calibration of a tunable laser. In Proceedings of the Conference on Optical Metrology and Inspection for Industrial Applications VII, Online, 11–16 October 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, E.; Giorgetta, F.R.; Coddington, I.; Sinclair, L.C.; Knabe, K.; Swann, W.C.; Newbury, N.R. Comb-calibrated frequency-modulated continuous-wave ladar for absolute distance measurements. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 2026–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, H. Regression analysis of FMCW-LiDAR beat signals for non-linear chirp mitigation. Electron. Lett. 2019, 55, 914–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binaie, A.; Ahasan, S.; Krishnaswamy, H. A Spurless and wideband continuous-time electro-optical phase locked loop (CT-EOPLL) for high performance LiDAR. IEEE Open J. Solid-State Circuits Soc. 2021, 1, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.X.; Xie, W.L.; Meng, Y.X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.W.Y.; Wei, W.; Dong, Y. High-performance optical frequency-domain reflectometry based on high-order optical phase-locking-assisted chirp optimization. J. Light. Technol. 2020, 38, 6227–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, M.; Hofbauer, M. FPGA-based EO-PLL with repetitive control for highly linear laser frequency tuning in FMCW LIDAR applications. IEEE Photonics J. 2022, 14, 6808608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Gerald, H.; Wei, T. Digitally controlled chirped pulse laser for sub-terahertz-range fiber structure interrogation. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Chen, Z.P.; Jia, H.K.; Yan, A.X.; Sun, S.Y.; Chen, G.P.; Wang, Z.H.; Chi, B.Y. A self-adapted two-point modulation type-II digital PLL for fast chirp rate and wide chirp-bandwidth FMCW signal generation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2022, 57, 1162–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.T.; Liu, C.; Su, L.W.; Fu, X.H.; Jin, W.; Bi, W.H.; Fu, G.W. Wide range linearization calibration method for DFB Laser in FMCW LiDAR. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2024, 174, 107961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, F. The perceptron a probabilistic model for information storage and organization in the brain. Psychol. Rev. 1958, 65, 386–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselt, H.V.; Wiering, M.A. Reinforcement learning in continuous action spaces. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Approximate Dynamic Programming and Reinforcement Learning, Honolulu, HI, USA, 1–5 April 2007; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulkumaran, K.; Deisenroth, M.P.; Brundage, M.; Bharath, A.A. Deep reinforcement learning a brief survey. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2017, 6, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.D.; Wei, Z.B.; Li, W.H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.W.; Sauer, D.U. Battery thermal- and health-constrained energy management for hybrid electric bus based on soft actor-critic DRL algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 3751–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.H.; Yuan, G.H.; Xiao, J.; Li, J.F.; Zhang, H.; Fang, K.; Wang, Z.R. Linearization of nonlinear frequency modulated continuous wave generation using model-based reinforcement learning. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 20647–20658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durak, L.; Arikan, O. Short-time Fourier transform two fundamental properties and an optimal implementation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2003, 51, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of control points/N | 1700 |
| Dataset size in NN training | 800 |
| Test set ratio | 20% |
| Batch size in NN training/M | 4 |
| Number of NN training iterations | 20,000 |
| Learning rate of NN | 0.0025 |
| Coefficient of Smooth L1 loss function/α | 4 |
| Number of SAC training epochs | 2000 |
| Size of replay buffer | 7 × 107 |
| Standard deviation of Gaussian strategy module/σ | 5 |
| Exploration coefficient/β | 0 |
| Discount factor/γ | 0.4 |
| Learning rate of actor network | 0.003 |
| Learning rate of critic network | 0.003 |
| Soft update step size of TNN/Γ | 10 |
| Scenario | 1: NN-SAC (Original) | 2: Without Control (Substitute) | 3: NN-SAC (Substitute, Not Retrained) | 4. NN-SAC (Substitute, Retrained) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| fRMSE (MHz) | 108.1 | 1404.3 | 194.5 | 110.3 |
| f1−r2 | 4.5036 × 10−5 | 7.6003 × 10−3 | 1.458 × 10−4 | 4.6888 × 10−5 |
| Correction Mechanism | Without Control | Only EO-PLL ΔWDLF = 30 kHz | Iteration + EO-PLL ΔWDLF = 25 kHz | NN-SAC + EO-PLL ΔWDLF = 20 kHz |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emax/mm | 10.6 | 7.6 | 1.8 | 1.1 |
| MAE/mm | 5.0 | 3.3 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| RMSE/mm | 5.4 | 3.7 | 1.0 | 0.5 |
| Ranging Method | NN-SAC + EO-PLL | Resampling Method | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specular reflection | Emax/mm | 1.1 | 2.3 |
| MAE/mm | 0.4 | 1.5 | |
| RMSE/mm | 0.5 | 1.8 | |
| Diffuse reflection | Emax/mm | 1.8 | 2.7 |
| MAE/mm | 0.8 | 1.8 | |
| RMSE/mm | 0.9 | 2.2 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Yuan, G.; Zhang, H.; Hou, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, P.; Xu, W.; Wang, Z. A Novel Two-Stage Approach for Nonlinearity Correction of Frequency-Modulated Continuous-Wave Laser Ranging Combining Data-Driven and Principle-Based Strategies. Photonics 2025, 12, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040356
Xu S, Yuan G, Zhang H, Hou C, Li Z, Zhang P, Xu W, Wang Z. A Novel Two-Stage Approach for Nonlinearity Correction of Frequency-Modulated Continuous-Wave Laser Ranging Combining Data-Driven and Principle-Based Strategies. Photonics. 2025; 12(4):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040356
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Shichang, Guohui Yuan, Hongwei Zhang, Chunyu Hou, Zhirong Li, Pansong Zhang, Wenhao Xu, and Zhuoran Wang. 2025. "A Novel Two-Stage Approach for Nonlinearity Correction of Frequency-Modulated Continuous-Wave Laser Ranging Combining Data-Driven and Principle-Based Strategies" Photonics 12, no. 4: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040356
APA StyleXu, S., Yuan, G., Zhang, H., Hou, C., Li, Z., Zhang, P., Xu, W., & Wang, Z. (2025). A Novel Two-Stage Approach for Nonlinearity Correction of Frequency-Modulated Continuous-Wave Laser Ranging Combining Data-Driven and Principle-Based Strategies. Photonics, 12(4), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040356







