Probing nS/nD Rydberg States via 6P3/2 Intermediate Level Using Electromagnetically Induced Transparency in 87Rb
Abstract
1. Introduction
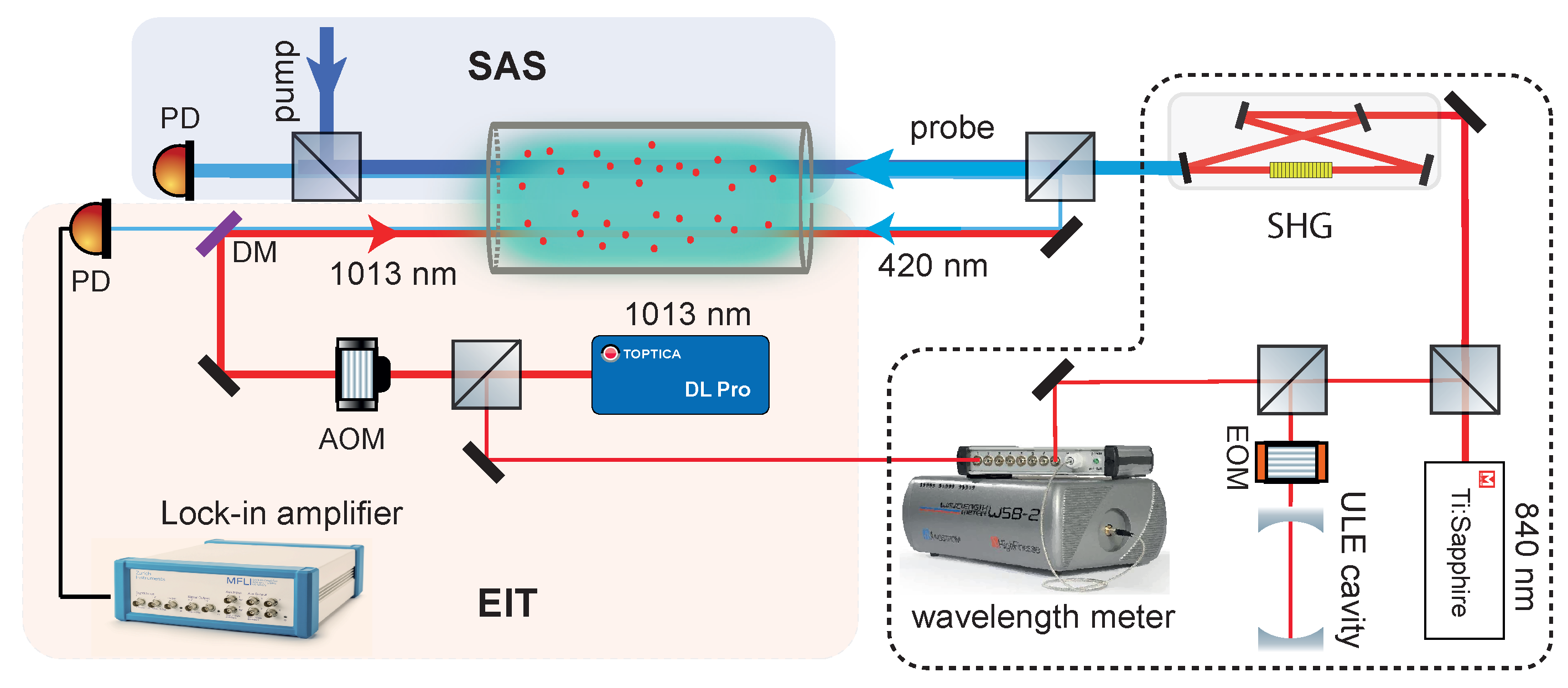
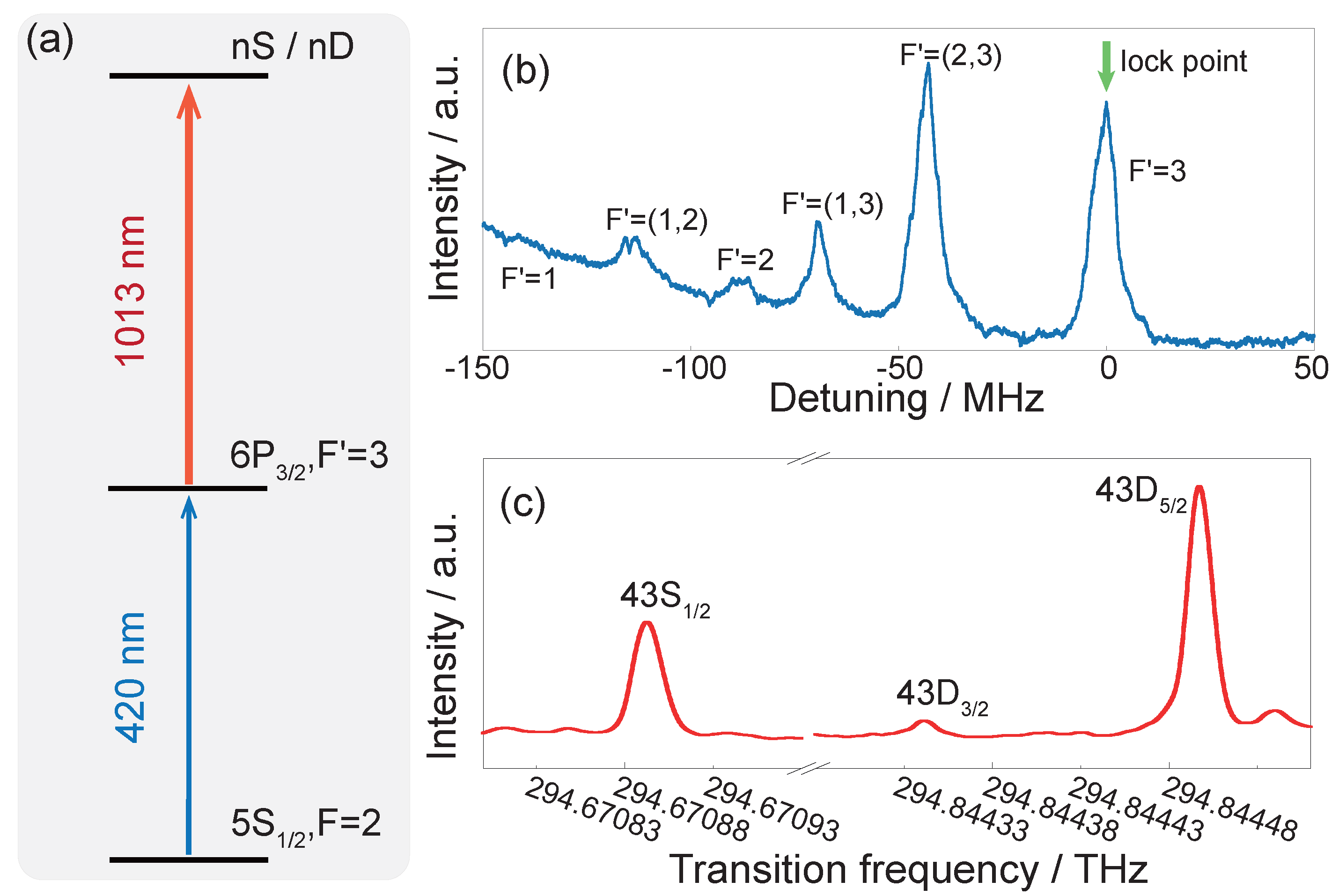
2. Experimental Setup
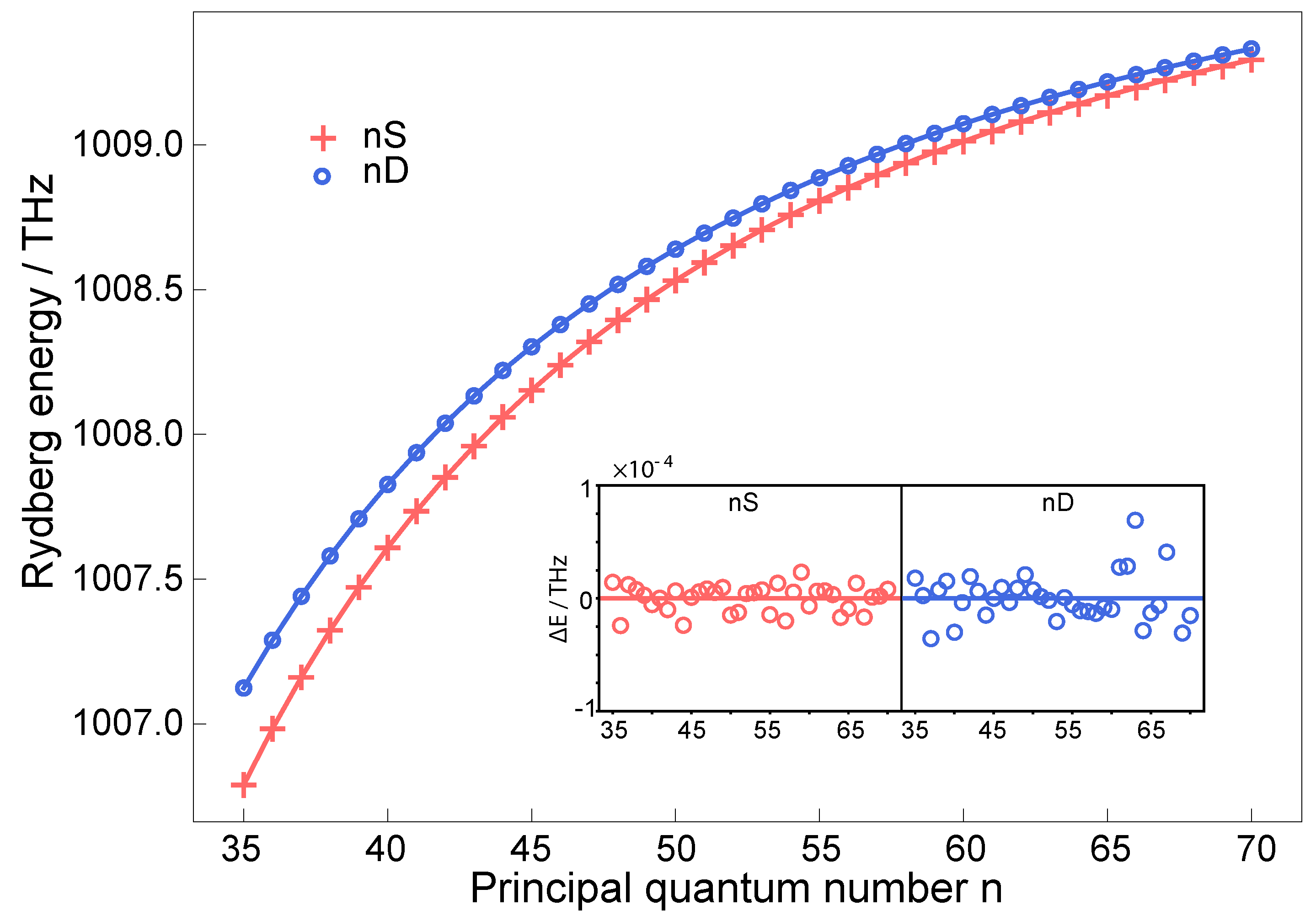
3. Results
| n | nS1/2 (THz) | nD3/2 (THz) | nD5/2 (THz) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theory | Exp | Theory | Exp | Theory | Exp | |
| 35 | 293.501710 | 293.501345(10) | 293.836011 | 293.835671(10) | 293.836291 | 293.835947(10) |
| 36 | 293.695816 | 293.695414(10) | 294.001250 | 294.000881(10) | 294.001506 | 294.001141(10) |
| 37 | 293.872984 | 293.872618(10) | 294.152780 | 294.152374(10) | 294.153016 | 294.152608(10) |
| 38 | 294.035129 | 294.034759(10) | 294.292079 | 294.291713(10) | 294.292296 | 294.291928(10) |
| 39 | 294.183901 | 294.183527(10) | 294.420428 | 294.420057(10) | 294.420627 | 294.420266(10) |
| 40 | 294.320733 | 294.320351(10) | 294.538944 | 294.538536(10) | 294.539129 | 294.538721(10) |
| 41 | 294.446868 | 294.446492(10) | 294.648608 | 294.648222(10) | 294.648779 | 294.648397(10) |
| 42 | 294.563394 | 294.563008(10) | 294.750279 | 294.749911(10) | 294.750438 | 294.750079(10) |
| 43 | 294.671262 | 294.670892(10) | 294.844716 | 294.844341(10) | 294.844864 | 294.844492(10) |
| 44 | 294.771309 | 294.770909(10) | 294.932589 | 294.932204(10) | 294.932727 | 294.932334(10) |
| 45 | 294.864273 | 294.863898(10) | 295.014493 | 295.014115(10) | 295.014621 | 295.014244(10) |
| 46 | 294.950807 | 294.950437(10) | 295.090955 | 295.090595(10) | 295.091075 | 295.090708(10) |
| 47 | 295.031492 | 295.031124(10) | 295.162449 | 295.162065(10) | 295.162561 | 295.162182(10) |
| 48 | 295.106842 | 295.106471(10) | 295.229394 | 295.229027(10) | 295.229500 | 295.229134(10) |
| 49 | 295.177317 | 295.176951(10) | 295.292170 | 295.291818(10) | 295.292269 | 295.291916(10) |
| 50 | 295.243330 | 295.242940(10) | 295.351114 | 295.350753(10) | 295.351207 | 295.350842(10) |
| 51 | 295.305249 | 295.304861(10) | 295.406534 | 295.406158(10) | 295.406621 | 295.406251(10) |
| 52 | 295.363406 | 295.363035(10) | 295.458703 | 295.458331(10) | 295.458785 | 295.458413(10) |
| 53 | 295.418100 | 295.417729(10) | 295.507872 | 295.507479(10) | 295.507949 | 295.507560(10) |
| 54 | 295.469600 | 295.469232(10) | 295.554266 | 295.553897(10) | 295.554339 | 295.553972(10) |
| 55 | 295.518150 | 295.517760(10) | 295.598090 | 295.597706(10) | 295.598159 | 295.597787(10) |
| 56 | 295.563971 | 295.563609(10) | 295.639531 | 295.639158(10) | 295.639596 | 295.639219(10) |
| 57 | 295.607264 | 295.606868(10) | 295.678758 | 295.678381(10) | 295.678820 | 295.678443(10) |
| 58 | 295.648212 | 295.647842(10) | 295.715926 | 295.715547(10) | 295.715985 | 295.715607(10) |
| 59 | 295.686980 | 295.686628(10) | 295.751177 | 295.750806(10) | 295.751232 | 295.750861(10) |
| 60 | 295.723722 | 295.723339(10) | 295.784640 | 295.784269(10) | 295.784693 | 295.784321(10) |
| 61 | 295.758575 | 295.758206(10) | 295.816434 | 295.816095(10) | 295.816485 | 295.816151(10) |
| 62 | 295.791667 | 295.791298(10) | 295.846669 | 295.846337(10) | 295.846717 | 295.846385(10) |
| 63 | 295.823115 | 295.822743(10) | 295.875445 | 295.875142(10) | 295.875490 | 295.875200(10) |
| 64 | 295.853025 | 295.852633(10) | 295.902854 | 295.902471(10) | 295.902897 | 295.902509(10) |
| 65 | 295.881497 | 295.881113(10) | 295.928981 | 295.928611(10) | 295.929022 | 295.928651(10) |
| 66 | 295.908622 | 295.908259(10) | 295.953905 | 295.953542(10) | 295.953944 | 295.953581(10) |
| 67 | 295.934482 | 295.934090(10) | 295.977699 | 295.977379(10) | 295.977737 | 295.977421(10) |
| 68 | 295.959155 | 295.958781(10) | 296.000430 | 296.000057(10) | 296.000466 | 296.000089(10) |
| 69 | 295.982713 | 295.982340(10) | 296.022161 | 296.021778(10) | 296.022195 | 296.021809(10) |
| 70 | 296.005225 | 296.004855(10) | 296.042948 | 296.042575(10) | 296.042982 | 296.042611(10) |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bluvstein, D.; Evered, S.J.; Geim, A.A. Logical quantum processor based on reconfigurable atom arrays. Nature 2024, 626, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriet, L.; Beguin, L.; Signoles, A. Quantum computing with neutral atoms. Quantum 2020, 4, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunami, S.; Tamiya, S.; Inoue, R. Scalable Networking of Neutral-Atom Qubits: Nanofiber-Based Approach for Multiprocessor Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computer. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.11111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornet, G.; Emperauger, G.; Chen, C. Scalable spin squeezing in a dipolar Rydberg atom array. Nature 2023, 621, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholl, P.; Schuler, M.; Williams, H.J. Quantum simulation of 2D antiferromagnets with hundreds of Rydberg atoms. Nature 2021, 595, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barredo, D.; Lienhard, V.; De Leseleuc, S.; Lahaye, T.; Browaeys, A. Synthetic three-dimensional atomic structures assembled atom by atom. Nature 2018, 561, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskara, N.; Ostermann, S.; Shee, J. Programmable Simulations of Molecules and Materials with Reconfigurable Quantum Processors. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.02265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endres, M.; Bernien, H.; Keesling, A. Atom-by-atom assembly of defect-free one-dimensional cold atom arrays. Science 2016, 354, 1024–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.; Jin-Guo, L.; Wurtz, J. Quantum Optimization with Arbitrary Connectivity Using Rydberg Atom Arrays. PRX Quantum 2023, 4, 010316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffman, M. Quantum computing with atomic qubits and Rydberg interactions: Progress and challenges. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2016, 49, 2020001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evered, S.J.; Bluvstein, D.; Kalinowski, M. High-fidelity parallel entangling gates on a neutral-atom quantum compute. Nature 2023, 622, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, T.M.; Song, Y.; Scott, J. Multi-qubit entanglement and algorithms on a neutral-atom quantum computer. Nature 2022, 604, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crescimanna, V.; Taylor, J.; Goldberg, A.Z. Quantum Control of Rydberg Atoms for Mesoscopic Quantum State and Circuit Preparation. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2023, 20, 034019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbyn, S.; Abanin, D.A.; Papić, Z. Quantum many-body scars and weak breaking of ergodicity. Nat. Phys. 2021, 17, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Ramette, J.; Metlitski, M.A. Landau-Forbidden Quantum Criticality in Rydberg Quantum Simulators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2023, 131, 083601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browaeys, A.; Thierry, L. Many-body physics with individually controlled Rydberg atoms. Nat. Phys. 2020, 16, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadi, S.; Wang, T.T.; Ha Levine, A. Quantum phases of matter on a 256-atom programmable quantum simulator. Nature 2021, 595, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernien, H.; Schwartz, S.; Keesling, A. Probing many-body dynamics on a 51-atom quantum simulator. Nature 2017, 551, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.C.; Khan, S.; Ravi, T.; Pandey, K. Direct spectroscopy of Rubidium using a narrow-line transition at 420 nm. Eur. Phys. J. D 2024, 78, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urvoy, A.; Carr, C.; Ritter, R.; Adams, C.S.; Weatherill, K.J.; Löw, R. Optical coherences and wavelength mismatch in ladder systems. J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2013, 46, 245001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; DeMarco, B. Velocity-selective electromagnetically-induced-transparency measurements of potassium Rydberg states. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 93, 011801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ghosh, S.; Cahn, S.B. Electromagnetically-induced-transparency spectroscopy of high-lying Rydberg states in 39K. Phys. Rev. A 2022, 105, 042808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, C.; Karlewski, F.; Kluge, J. Absolute frequency measurement of rubidium 5S-6P transitions. Phys. Rev. A 2020, 102, 012804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Bao, X.; Yu, S. Electromagnetically Induced Transparency Spectra of 6Li Rydberg Atoms. Photonics 2023, 10, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Bian, G.; Miao, J. Rydberg excitation spectrum of 40K ultracold Fermi gases 5S-6P transitions. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 103, 063305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, M.; Jiang, X.; Qian, J.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y. Optical spectroscopy of nP Rydberg states of 87Rb atoms with a 297-nm ultraviolet laser. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 99, 042502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, M.; Karlewski, F.; Hattermann, H. Measurement of absolute transition frequencies of 87Rb to nS and nD Rydberg states by means of electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 83, 052515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šibalić, N.; Pritchard, J.D.; Adams, C.S. ARC: An open-source library for calculating properties of alkali Rydberg atoms. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2017, 220, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Mourachko, I.; Noel, M.W. Millimeter-wave spectroscopy of cold Rb Rydberg atoms in a magneto-optical trap: Quantum defects of the ns, np, and nd series. Phys. Rev. A 2003, 67, 05250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Jamil, Y.; Noruml, D.V.L. Rb nf quantum defects from millimeter-wave spectroscopy of cold 85Rb Rydberg atoms. Phys. Rev. A 2006, 74, 054502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| This Work | Ref. [27] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.1311650(8) | 3.1311807(8) | ||
| 0.2119(2) | 0.1787(2) | ||
| 1.3493698(11) | 1.3480948(11) | ||
| −1.8656(4) | −0.6054(4) | ||
| 1.3474759(11) | 1.3464622(11) | ||
| −1.5901(4) | −0.5940(4) | ||
| 33,690.94541(6) cm−1 | 33,690.94644(1) cm−1 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Xu, B.; Qin, K.; Jia, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Z. Probing nS/nD Rydberg States via 6P3/2 Intermediate Level Using Electromagnetically Induced Transparency in 87Rb. Photonics 2025, 12, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12030204
Li D, Xu B, Qin K, Jia X, Zhao C, Zhou Y, Xu Z. Probing nS/nD Rydberg States via 6P3/2 Intermediate Level Using Electromagnetically Induced Transparency in 87Rb. Photonics. 2025; 12(3):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12030204
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Donghao, Beining Xu, Keyu Qin, Xin Jia, Changtao Zhao, Yaoting Zhou, and Zhongxiao Xu. 2025. "Probing nS/nD Rydberg States via 6P3/2 Intermediate Level Using Electromagnetically Induced Transparency in 87Rb" Photonics 12, no. 3: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12030204
APA StyleLi, D., Xu, B., Qin, K., Jia, X., Zhao, C., Zhou, Y., & Xu, Z. (2025). Probing nS/nD Rydberg States via 6P3/2 Intermediate Level Using Electromagnetically Induced Transparency in 87Rb. Photonics, 12(3), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12030204





