Research on Diabetes Analysis Based on Deep Learning-Enhanced Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Data
2.2. Model Building and Training
3. Results
3.1. Criteria of Evaluation
3.2. Comparison of Diabetes Classification Between Original Data and Augmented Data
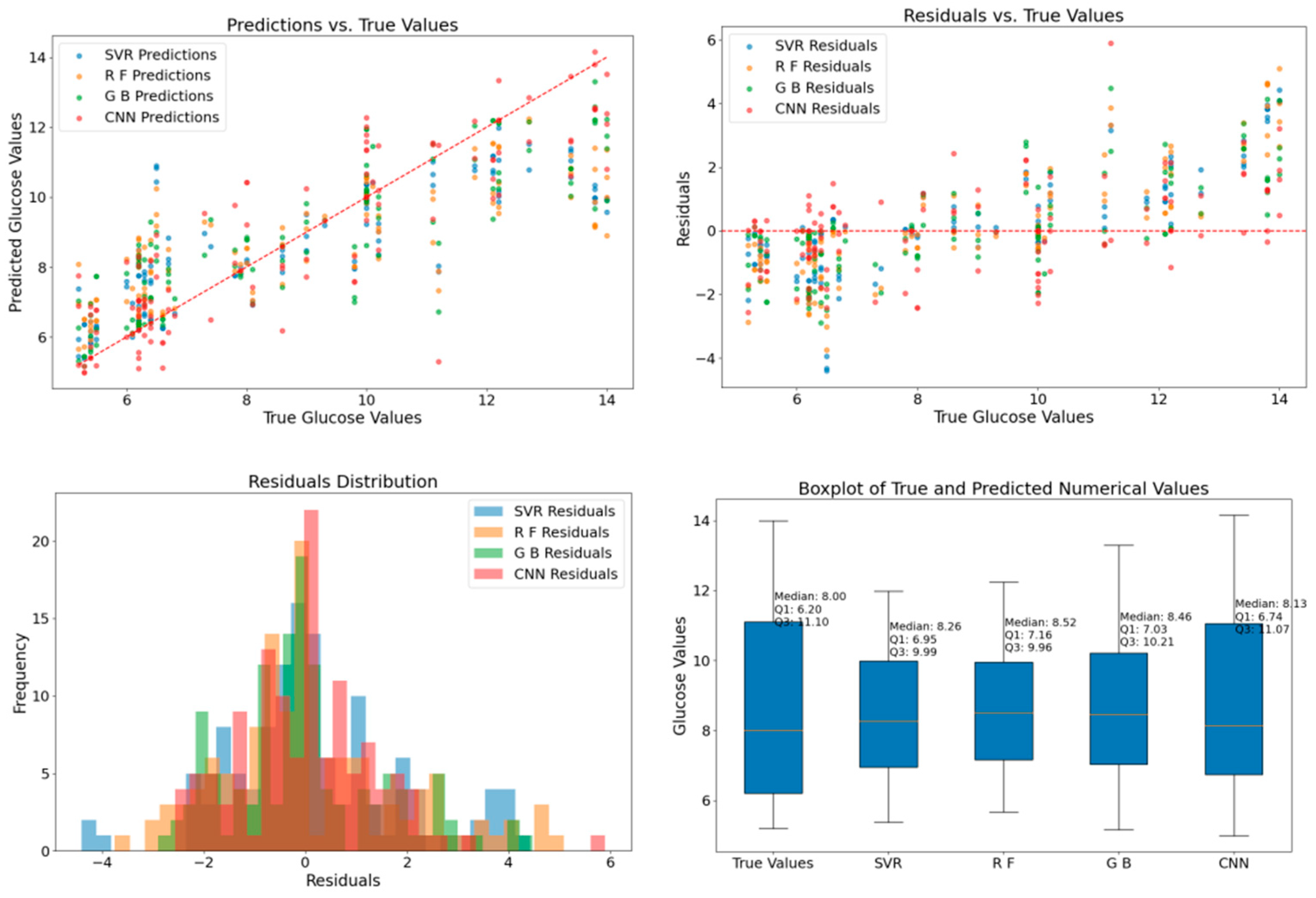
3.3. Comparison of Blood Glucose Prediction Values Between Original Data and Augmented Data
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tomic, D.; Shaw, J.E.; Magliano, D.J. The burden and risks of emerging complications of diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.B.; Florez, J.C. Genetics of diabetes mellitus and diabetes complications. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, E.D.; Gloyn, A.L.; Evans-Molina, C.; Joseph, J.J.; Misra, S.; Pajvani, U.B.; Simcox, J.; Susztak, K.; Drucker, D.J. Diabetes mellitus—Progress and opportunities in the evolving epidemic. Cell 2024, 187, 3789–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hædersdal, S.; Andersen, A.; Knop, F.K.; Vilsbøll, T. Revisiting the role of glucagon in health, diabetes mellitus and other metabolic diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, D.; Immanuel, J.; Hague, W.M.; Teede, H.; Nolan, C.J.; Peek, M.J.; Flack, J.R.; McLean, M.; Wong, V.; Hibbert, E.; et al. Treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus diagnosed early in pregnancy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 2132–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, P.; Magee, L.A.; Banerjee, A.; Coleman, M.A.; Von Dadelszen, P.; Denison, F.; Farmer, A.; Finer, S.; Fox-Rushby, J.; Holt, R.; et al. Gestational diabetes: Opportunities for improving maternal and child health. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Qu, S. The relationship between diabetes mellitus and cancers and its underlying mechanisms. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 800995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorio, A.; Saito, R. Raman spectroscopy for carbon nanotube applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 021102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapliyal, V.; Alabdulkarim, M.E.; Whelan, D.R.; Mainali, B.; Maxwell, J.L. A concise review of the Raman spectra of carbon allotropes. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2022, 127, 109180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Deng, L.; Kinloch, I.A.; Young, R.J. Raman spectroscopy of carbon materials and their composites: Graphene, nanotubes and fibres. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 135, 101089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.; Paidi, S.K.; Valdez, T.A.; Zhang, C.; Spegazzini, N.; Dasari, R.R.; Barman, I. Noninvasive monitoring of blood glucose with Raman spectroscopy. Accounts Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingari, N.C.; Barman, I.; Singh, G.P.; Kang, J.W.; Dasari, R.R.; Feld, M.S. Investigation of the specificity of Raman spectroscopy in non-invasive blood glucose measurements. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 2871–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzstein, G.; Ozcan, A.; Gigan, S.; Fan, S.; Englund, D.; Soljačić, M.; Denz, C.; Miller, D.A.B.; Psaltis, D. Inference in artificial intelligence with deep optics and photonics. Nature 2020, 588, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Sheng, X.; Cao, J.; Jia, H.; Gao, W.; Gu, S.; Wang, X.; Chu, P.K.; Lou, S. Machine-learning-assisted omnidirectional bending sensor based on a cascaded asymmetric dual-core PCF sensor. Opt. Lett. 2023, 48, 4929–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, R.; Feng, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Fu, Z. Fish quality evaluation by sensor and machine learning: A mechanistic review. Food Control 2022, 137, 108902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayassi, R.; Triki, A.; Crespi, N.; Minerva, R.; Laye, M. Survey on the use of machine learning for quality of transmission estimation in optical transport networks. J. Light. Technol. 2022, 40, 5803–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pian, F.; Wang, Q.; Wang, M.; Shan, P.; Li, Z.; Ma, Z. A shallow convolutional neural network with elastic nets for blood glucose quantitative analysis using Raman spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 264, 120229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Pian, F.; Wang, M.; Song, S.; Li, Z.; Shan, P.; Ma, Z. Quantitative analysis of Raman spectra for glucose concentration in human blood using Gramian angular field and convolutional neural network. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 275, 121189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Gou, C.; Duan, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wang, F.-Y. Generative adversarial networks: Introduction and outlook. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2017, 4, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Viveros, N.; Castro-Ramos, J.; Gómez-Gil, P.; Cerecedo-Núñez, H.H.; Gutiérrez-Delgado, F.; Torres-Rasgado, E.; Pérez-Fuentes, R.; Flores-Guerrero, J.L. Quantification of glycated hemoglobin and glucose in vivo using Raman spectroscopy and artificial neural networks. Lasers Med. Sci. 2022, 37, 3537–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, B.; Wang, L.; Zu, C.; Lalush, D.S.; Lin, W.; Wu, X.; Zhou, J.; Shen, D.; Zhou, L. 3D conditional generative adversarial networks for high-quality PET image estimation at low dose. NeuroImage 2018, 174, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Model | Hyperparameter Selection |
|---|---|
| SVR | C = 100, kernel = rbf |
| CNN | Epochs = 100, Batch size = 36 |
| Gradient Boosting | Learning rate = 0.1, max depth = 3, n_estimators = 150 |
| Random Forest | Max depth = 15, n_estimators = 80 |
| Type | Original Datasets | Augmented Datasets |
|---|---|---|
| SVM | 85.48% | 97.67% |
| Random Forest | 87.91% | 99.07% |
| GB | 87.12% | 98.33% |
| CNN | 86.53% | 98.72% |
| Type | Original Dataset (mg/dL) | Augmented Dataset (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|
| SVR | 1.248 | 0.369 |
| Random Forest | 1.068 | 0.308 |
| GBR | 1.081 | 0.421 |
| CNN | 1.179 | 0.283 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Nie, J.; Zhao, H.; Song, J.; Deng, Y. Research on Diabetes Analysis Based on Deep Learning-Enhanced Data. Photonics 2025, 12, 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12111068
Zhang Y, Chen S, Nie J, Zhao H, Song J, Deng Y. Research on Diabetes Analysis Based on Deep Learning-Enhanced Data. Photonics. 2025; 12(11):1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12111068
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yin, Shaolong Chen, Jiawei Nie, Hang Zhao, Jun Song, and Yuanlong Deng. 2025. "Research on Diabetes Analysis Based on Deep Learning-Enhanced Data" Photonics 12, no. 11: 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12111068
APA StyleZhang, Y., Chen, S., Nie, J., Zhao, H., Song, J., & Deng, Y. (2025). Research on Diabetes Analysis Based on Deep Learning-Enhanced Data. Photonics, 12(11), 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12111068





