Characterization of Nanocrystals of Eu-Doped GaN Powders Obtained via Pyrolysis, Followed by Their Nitridation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
+3N2O(g) + 42NO2(g) + 42HNO2(g)
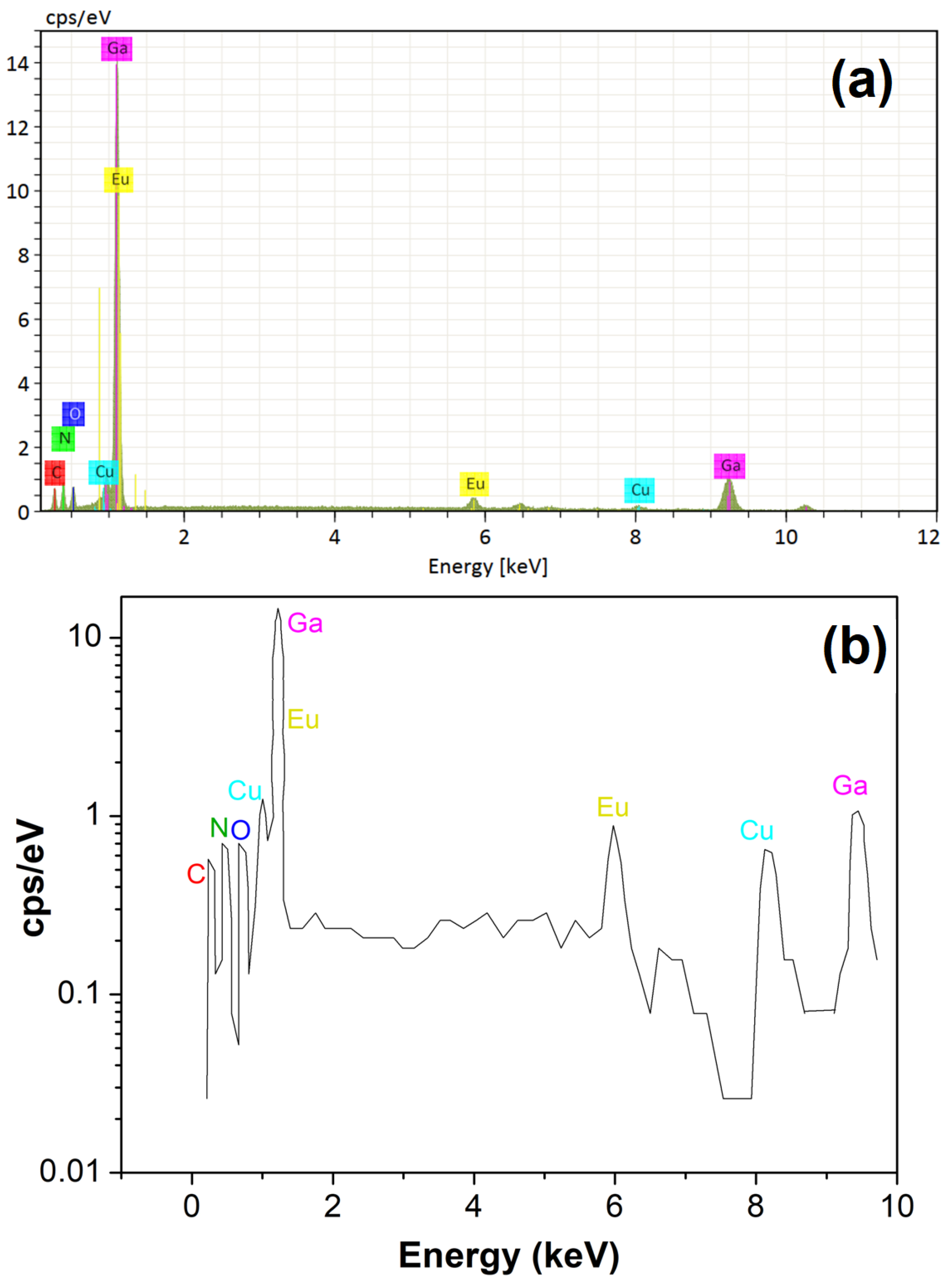
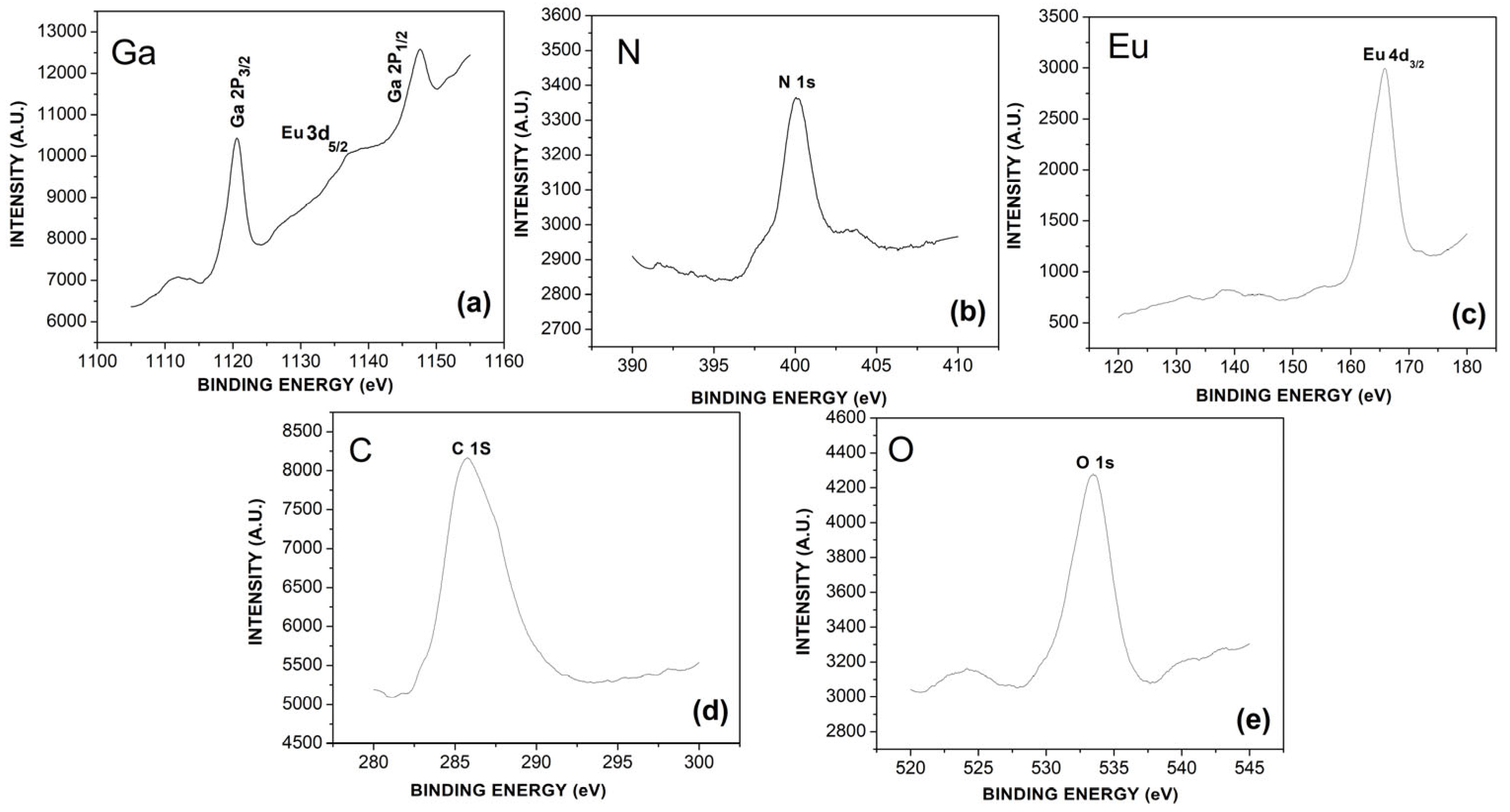
Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Analysis
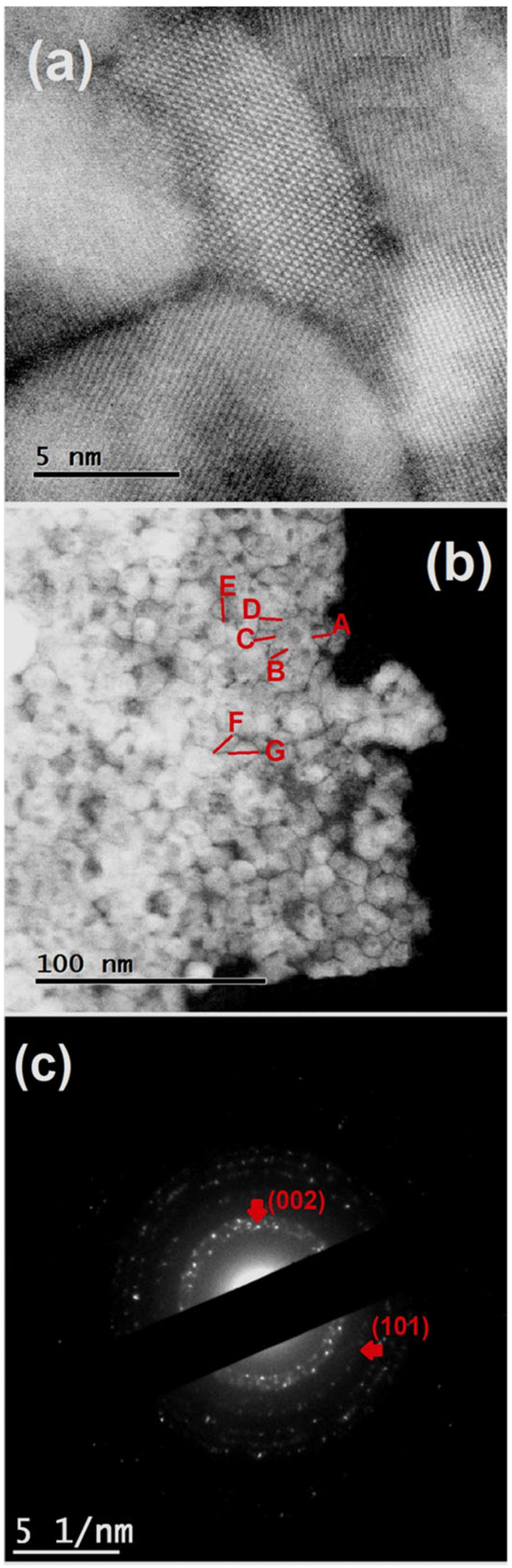
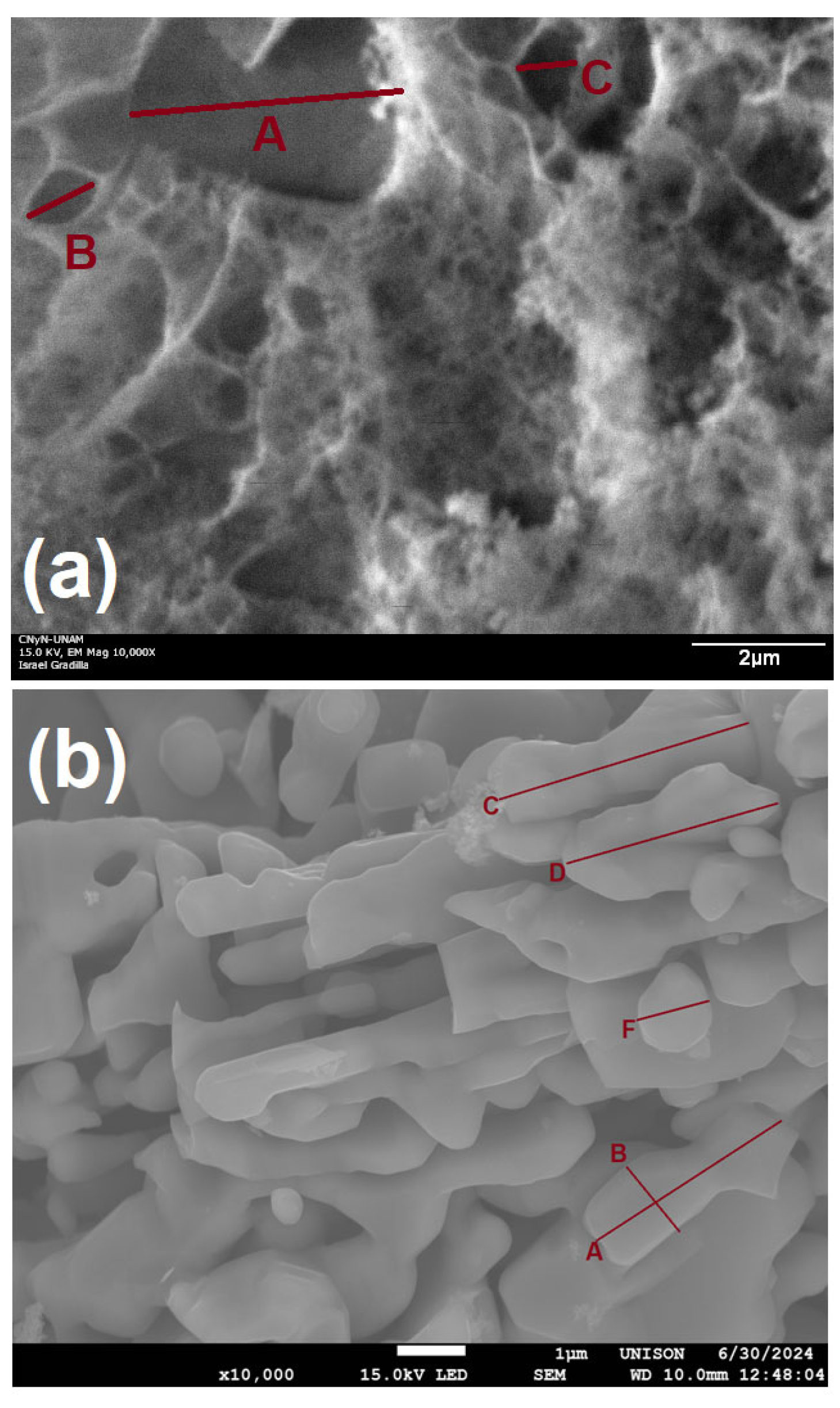
3.2. Electron Microscopy
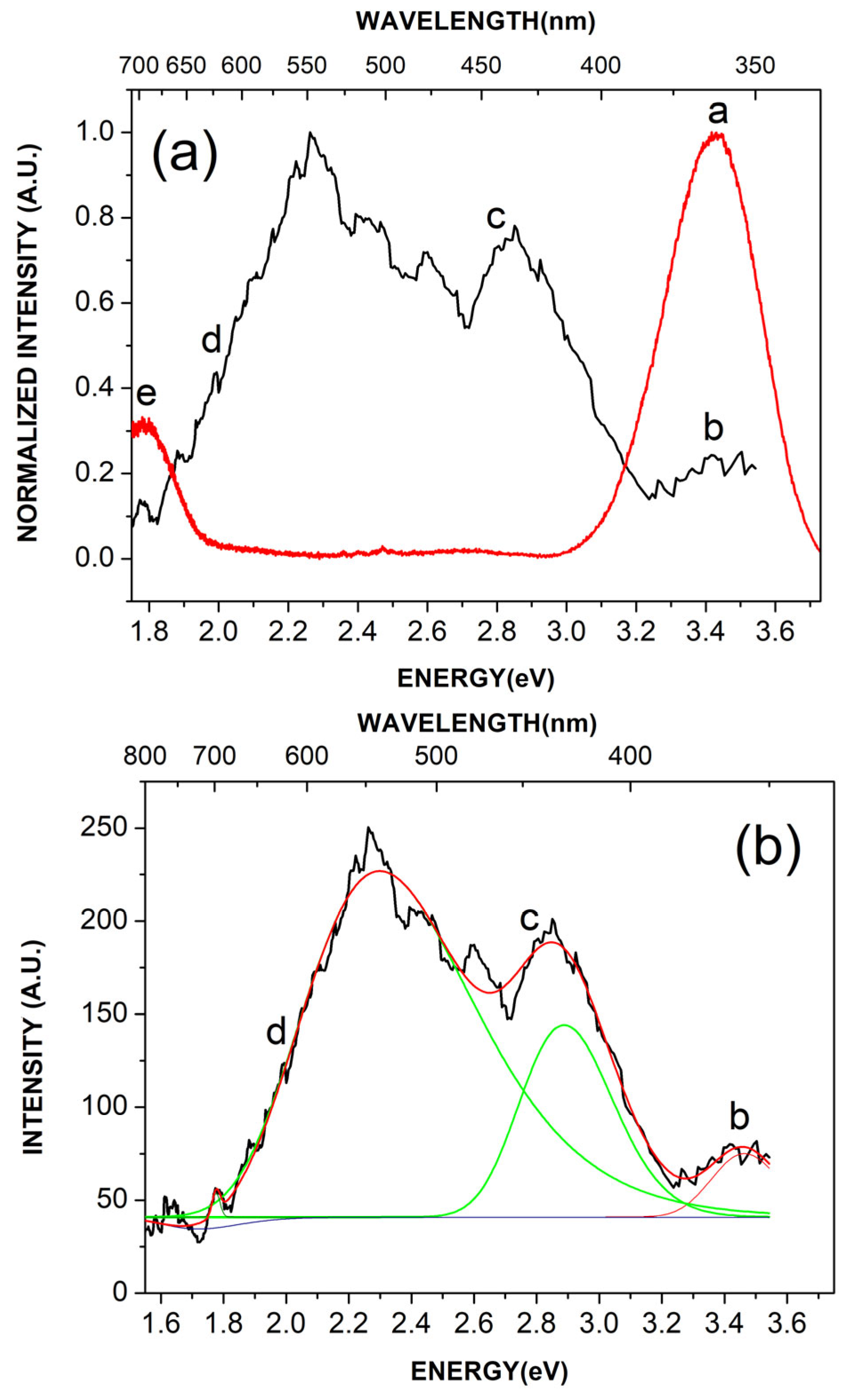
3.3. Photoluminescence
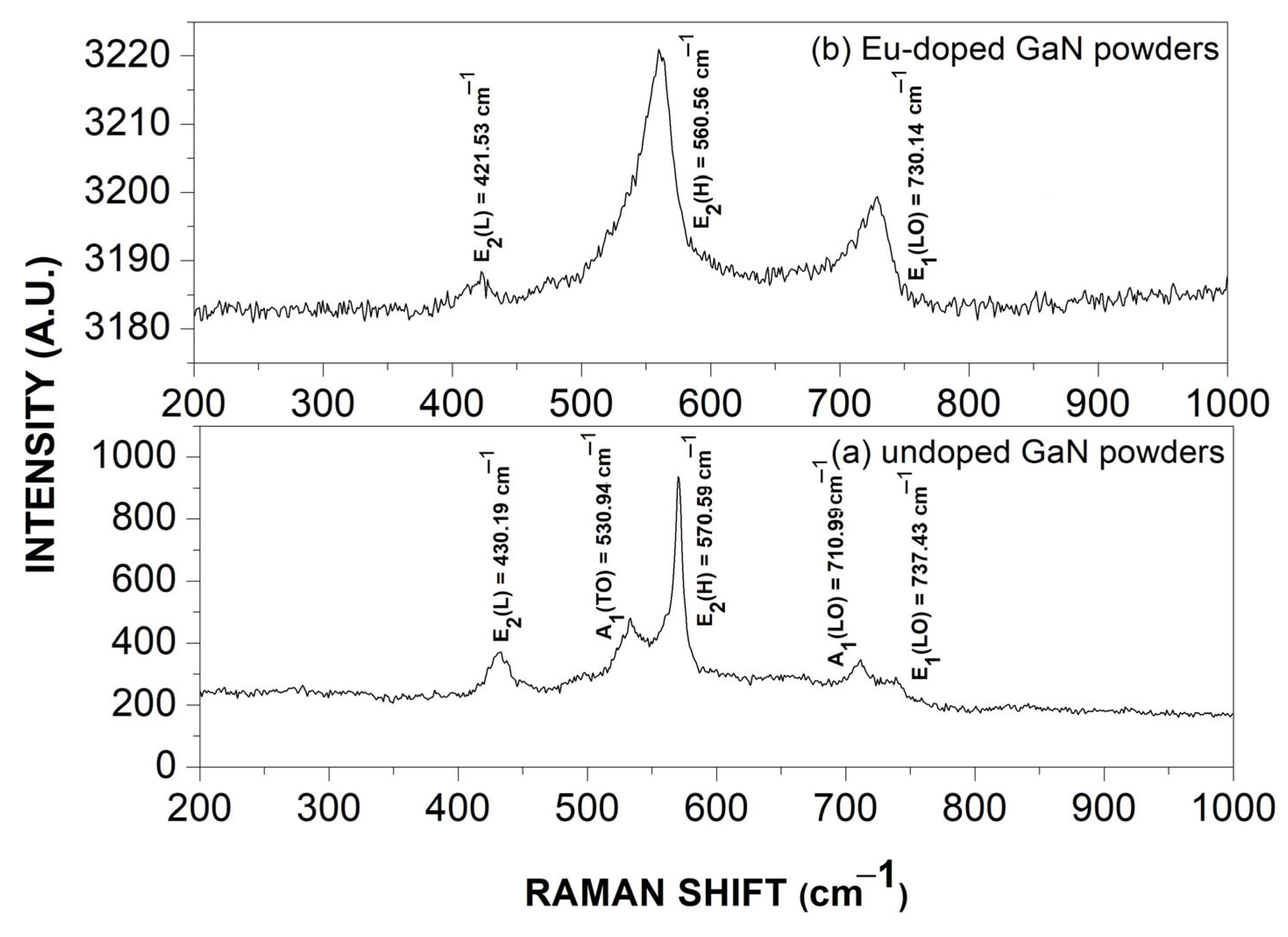
3.4. Raman Scattering
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amir, H.A.A.A.; Fakhri, M.A.; Alwahib, A.A. Review of GaN optical device characteristics, applications, and optical analysis technology. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 42, 2815–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podhorodecki, A.; Kudrawiec, R.; Nyk, M.; Misiewicz, J.; Strek, W. Surface- and volume-related excitation of Eu-doped nanocrystalline GaN powders. Opt. Mater. 2009, 31, 1252–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadwisienczak, W.; Wisniewski, K.; Spencer, M.; Thomas, T.; Ingram, D. Optical properties, luminescence quenching mechanism and radiation hardness of Eu-doped GaN red powder phosphor. Radiat. Meas. 2010, 45, 500–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, F.; Takeo, A.; Mitchell, B.; Dierolf, V.; Fujiwara, Y.; Tonouchi, M. Enhanced luminescence efficiency in Eu-doped GaN superlattice structures revealed by terahertz emission spectroscopy. Commun. Mater. 2023, 4, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaya, T.; Ichikawa, S.; Murakami, M.; Tatebayashi, J.; Fujiwara, Y. Investigation on Suitable Structure for Laser Oscillation in Eu-doped GaN with Two-Dimensional Photonic Crystal Nanocavities. J. Soc. Mater. Sci. Jpn. 2020, 69, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkos, I.E.; Tan, C.K.; Dierolf, V.; Fujiwara, Y.; Tansu, N. Pathway Towards High-Efficiency Eu-doped GaN Light-Emitting Diodes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angadi, V.C.; Benz, F.; Tischer, I.; Thonke, K.; Aoki, T.; Walther, T. Evidence of terbium and oxygen co-segregation in annealed AlN:Tb. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 222102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.; Hömmerich, U.; Yamada, T.; Yamane, H.; Zavada, J. Luminescence spectroscopy of europium doped gallium nitride powder prepared by a Na flux method. Phys. Status Solidi (A) 2011, 208, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Mitchell, B.; Timmerman, D.; Koizumi, A.; Gregorkiewicz, T.; Fujiwara, Y. High-Power Eu-Doped GaN Red LED Based on a Multilayer Structure Grown at Lower Temperatures by Organometallic Vapor Phase Epitaxy. MRS Adv. 2017, 2, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudrawiec, R.; Nyk, M.; Podhorodecki, A.; Misiewicz, J.; Strek, W.; Wołcyrz, M. Change in photoluminescence spectra of Eu-doped GaN powders due to the aggregation of nanosized grains into micrometer-sized conglomerations. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 061916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyk, M.; Podhorodecki, A.; Kudrawiec, R.; Misiewicz, J.; Strek, W. Size Shrinkage of GaN Nanocrystalline Grains Induced by Eu Doping Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2007, 10, H203–H205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, T.; Mitchell, B.; Koizumi, A.; Fujiwara, Y. Emission enhancement and its mechanism of Eu-doped GaN by strain engineering. Opt. Mater. Express 2017, 7, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Himri, A.; Pérez-Coll, D.; Núñez, P.; Martín, I.R.; Lavín, V.; Rodríguez, V.D. Preparation and optical spectroscopy of Eu3+-doped GaN luminescent semiconductor from freeze-dried precursors. J. Solid State Chem. 2004, 177, 4213–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zeng, X.; Xu, K.; Mao, H.; Ma, C. Luminescence mechanism and energy level structure of Eu-doped GaN powders investigated by cathodoluminescence spectroscopy. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2014, 57, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, C.; Mereacre, L.; Chen, Z.; Slabon, A. Closing the yellow gap with Eu- and Tb-doped GaN: One luminescent host resulting in three colours. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Poitras, C.B.; Lipson, M.; Spencer, M.G.; Hunting, J.; DiSalvo, F.J. Photoluminescence and cathodoluminescence analyses of GaN powder doped with Eu. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 011921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pela, R.R.; Hsiao, C.L.; Hultman, L.; Birch, J.; Gueorguiev, G.K. Electronic and optical properties of core–shell InAlN nanorods: A comparative study via LDA, LDA-1/2, mBJ, HSE06, G0W0 and BSE methods. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2024, 26, 7504–7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, M.A.M.; Farmer, W.; Hsiao, C.-L.; dos Santos, R.B.; Hultman, L.; Birch, J.; Ankit, K.; Gueorguiev, G.K. Density Functional Theory-Fed Phase Field Model for Semiconductor Nanostructures: The Case of Self-Induced Core–Shell InAlN Nanorods. Cryst. Growth Des. 2024, 24, 4717–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastellóu, E.; Morales, C.; García, R.; García, G.; Hirata, G.A.; Galeazzi, R.; Herrera, A.M.; Rosendo, E.; Díaz, T.; Ramos, J.R.; et al. Enhanced crystalline size of undoped GaN powders obtained by nitridation of metallic gallium. Opt. Mater. 2018, 83, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, A.M.; Ramos, A.; Gastellóu, E.; García, R.; García, G.; Carrillo, R.C.; Santos, I.; Brown, F.; Mora, R.; Hirata, G.A. Effect of the Pyrolysis Environment in a Complex Compound in the Synthesis of In0.6Ga0.4N Powders and their Characterization. Phys. Status Solidi (A) 2024, 222, 2400593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, A.M.; García, R.; García, G.; Gastellóu, E.; Nieto, F.; Hirata, G.A.; Contreras, O.E.; Morales, C.; Rosendo, E.; Díaz, T. Experimental determination of the pyrolysis temperatures of an organometallic complex to obtain AlxGa1-xN powders. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 775, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, R.; Hirata, G.A.; Thomas, A.C.; Ponce, F.A. Structure and luminescence of nanocrystalline gallium nitride synthesized by a novel polymer pyrolysis route. Opt. Mater. 2006, 29, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Li, T.; Ren, G.; Wang, L.; Lu, W.; Shen, L.; Zhou, H.; Xu, K. Optical characterization of GaN:Eu microcrystals grown by the ammonothermal method. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1008, 176776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshchikov, M.A.; Morkoç, H. Luminescence properties of defects in GaN. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 061301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, G.A.; Ramos, F.; Garcia, R.; Bosze, E.J.; McKittrick, J.; Ponce, F.A. A New Combustion Synthesis Method for GaN:Eu3+ and Ga2O3:Eu3+ Luminescent Powders. Phys. Status Solidi (A) 2001, 188, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Dierolf, V. Present understanding of Eu luminescent centers in Eu-doped GaN grown by organometallic vapor phase epitaxy. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 53, 05FA13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otabara, T.; Tatebayashi, J.; Hasegawa, S.; Timmerman, D.; Ichikawa, S.; Ichimiya, M.; Ashida, M.; Fujiwara, Y. Formation and optical characteristics of GaN:Eu/GaN core–shell nanowires grown by organometallic vapor phase epitaxy. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2022, 61, SD1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, K. Tuning the valence and concentration of europium and luminescence centers in GaN through co-doping and defect association. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2021, 5, 034601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, K. Rare-earth defects in GaN: A systematic investigation of the lanthanide series. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2022, 6, 044601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.E.A.; Hkiri, K.; Khenfouch, M.; Dhlamini, S.; Henini, M.; Maaza, M. Optical properties of biosynthesized nanoscaled Eu2O3 for red luminescence applications. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2020, 37, C73–C79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohata, S.; Kawamura, T.; Akiyama, T.; Usami, S.; Imanishi, M.; Yoshimura, M.; Mori, Y.; Sumi, T.; Takino, J. Influence of oxy-gen-related defects on the electronic structure of GaN. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2022, 61, 061004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, L.; Wang, C.; Dong, K.; Hu, Z.; Ke, W.; Fang, G. Spontaneous crystallization of strongly confined CsSnxPb1-x I3 perovskite colloidal quantum dots at room temperature. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Li, C.; Li, G.; Ren, B.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Ren, F.; et al. Rapid Room Temperature Entropy-Stabilized Synthesis Enabling Super-Stable Metal Halide Perovskite Semiconductor Colloidal Nanocrystals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2423450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivolapchuk, V.V.; Mezdrogina, M.M.; Nasonov, A.V.; Rodin, S.N. Photoluminescence of Bulk Eu-Doped GaN Crystals. Phys. Solid State 2003, 45, 1634–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; An, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Xie, E. Structural and optical properties of GaN:Eu nanoparticles synthesized by simple ammonification method. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 519, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Chandrashekhar, M.V.S.; Reiherzer, J.; Schaff, W.J.; Lu, J.; Disalvo, F.J.; Spencer, M.G. Effect of growth temperature on Eu incorporation in GaN powders. J. Cryst. Growth 2008, 310, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.; Guo, X.; Chandrashekhar, M.; Poitras, C.B.; Shaff, W.; Dreibelbis, M.; Reiherzer, J.; Li, K.; DiSalvo, F.J.; Lipson, M.; et al. Purification and mechanical nanosizing of Eu-doped GaN. J. Cryst. Growth 2009, 311, 4402–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajpeyi, A.P.; Tripathy, S.; Wang, L.S.; Foo, B.C.; Chua, S.J.; Fitzgerald, E.A.; Alves, E. Optical activation of Eu ions in nanoporous GaN films. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 104305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
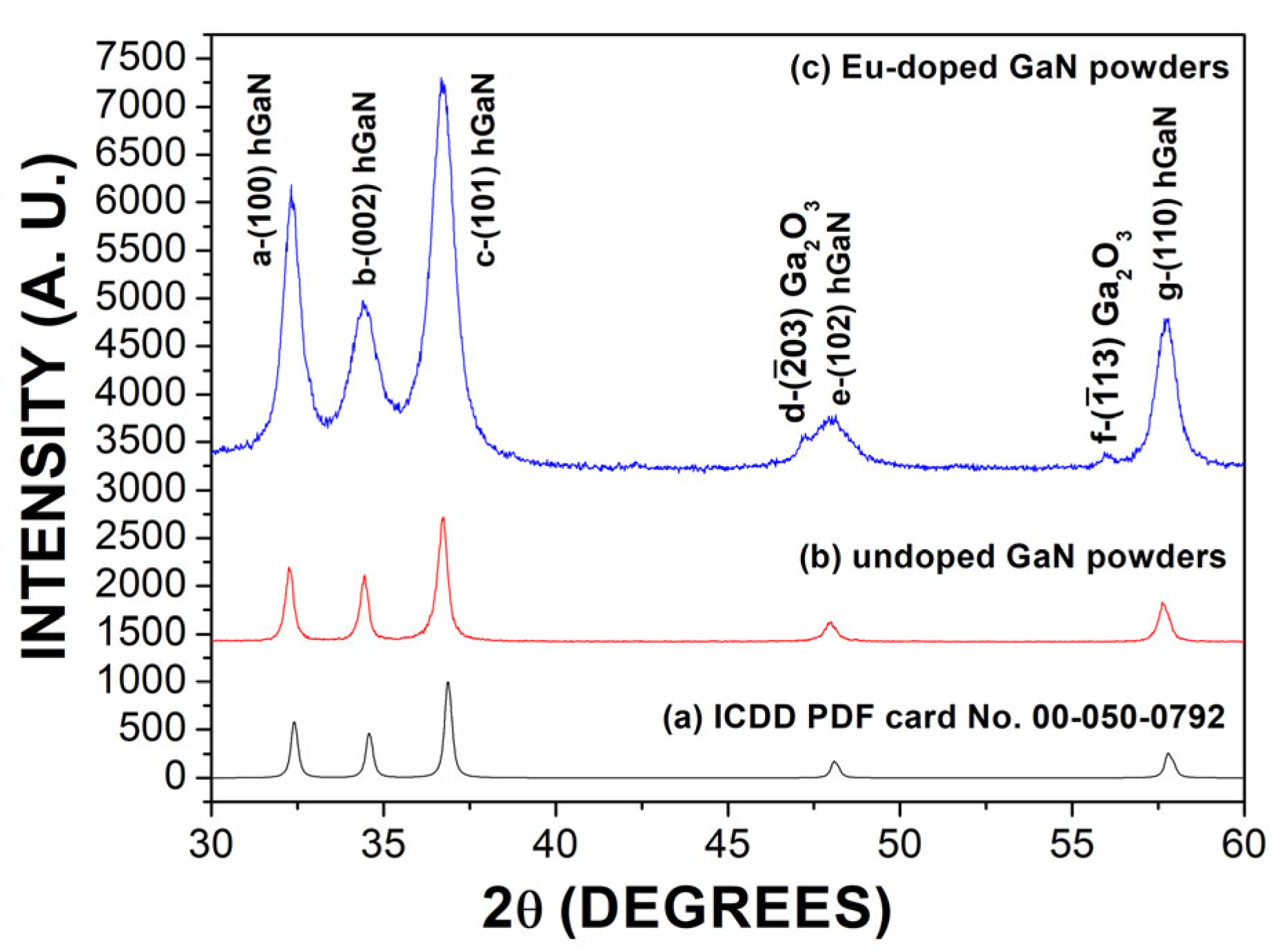

| Undoped GaN Powders | Eu-Doped GaN Powders | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak | Peak Position (Degree) | FWHM (Degree) | Crystal Size (nm) | Interplanar Spacing (Å) | Peak Position (Degree) | FWHM (Degree) | Crystal Size (nm) | Interplanar Spacing (Å) |
| a | 32.27 | 0.32 | 25.20 | 2.77 | 32.34 | 0.74 | 11.10 | 2.76 |
| b | 34.43 | 0.33 | 24.94 | 2.60 | 34.48 | 1.54 | 5.38 | 2.59 |
| c | 36.71 | 0.40 | 20.58 | 2.44 | 36.71 | 0.93 | 8.99 | 2.44 |
| e | 47.97 | 0.43 | 19.92 | 1.89 | 47.94 | 1.21 | 7.17 | 1.89 |
| g | 57.66 | 0.41 | 21.94 | 1.59 | 57.72 | 0.708 | 12.79 | 1.59 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gastellóu, E.; García, R.; Herrera, A.M.; Ramos, A.; García, G.; Hirata, G.A.; Luna, J.A.; Carrillo, R.C.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Romano, R.; et al. Characterization of Nanocrystals of Eu-Doped GaN Powders Obtained via Pyrolysis, Followed by Their Nitridation. Photonics 2025, 12, 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12100982
Gastellóu E, García R, Herrera AM, Ramos A, García G, Hirata GA, Luna JA, Carrillo RC, Rodríguez JA, Romano R, et al. Characterization of Nanocrystals of Eu-Doped GaN Powders Obtained via Pyrolysis, Followed by Their Nitridation. Photonics. 2025; 12(10):982. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12100982
Chicago/Turabian StyleGastellóu, Erick, Rafael García, Ana M. Herrera, Antonio Ramos, Godofredo García, Gustavo A. Hirata, José A. Luna, Roberto C. Carrillo, Jorge A. Rodríguez, Roman Romano, and et al. 2025. "Characterization of Nanocrystals of Eu-Doped GaN Powders Obtained via Pyrolysis, Followed by Their Nitridation" Photonics 12, no. 10: 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12100982
APA StyleGastellóu, E., García, R., Herrera, A. M., Ramos, A., García, G., Hirata, G. A., Luna, J. A., Carrillo, R. C., Rodríguez, J. A., Romano, R., Ramírez, Y. D., Brown, F., & Coyopol, A. (2025). Characterization of Nanocrystals of Eu-Doped GaN Powders Obtained via Pyrolysis, Followed by Their Nitridation. Photonics, 12(10), 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12100982









