Specific and Simultaneous Detection of E. coli O157:H7 and Shiga-like Toxins Using a Label-Free Photonic Immunosensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
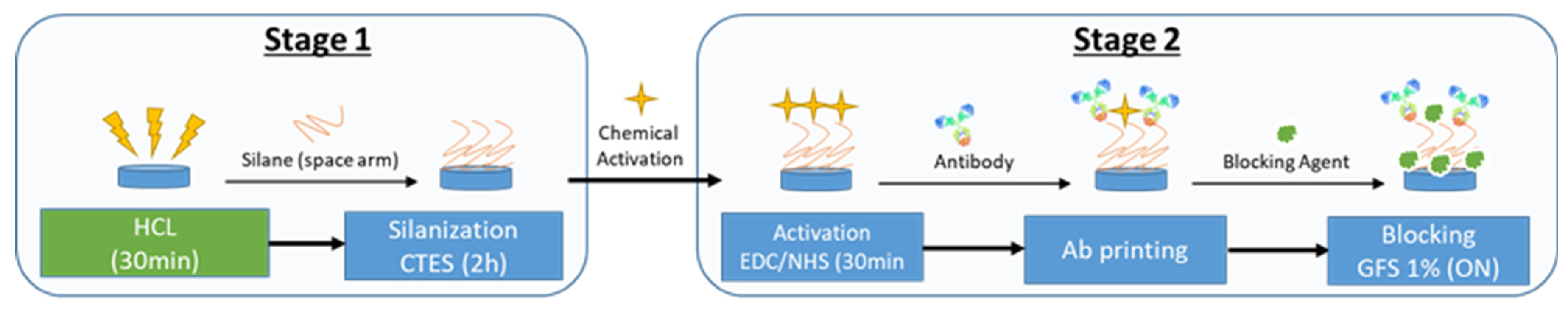
2.1.1. Functionalization
2.1.2. Indirect ELISA
2.1.3. Immunosensor Validation
2.2. Indirect ELISA
2.3. PIC Fabrication and Functionalization Process
2.4. Photon Transduction Setup Reader
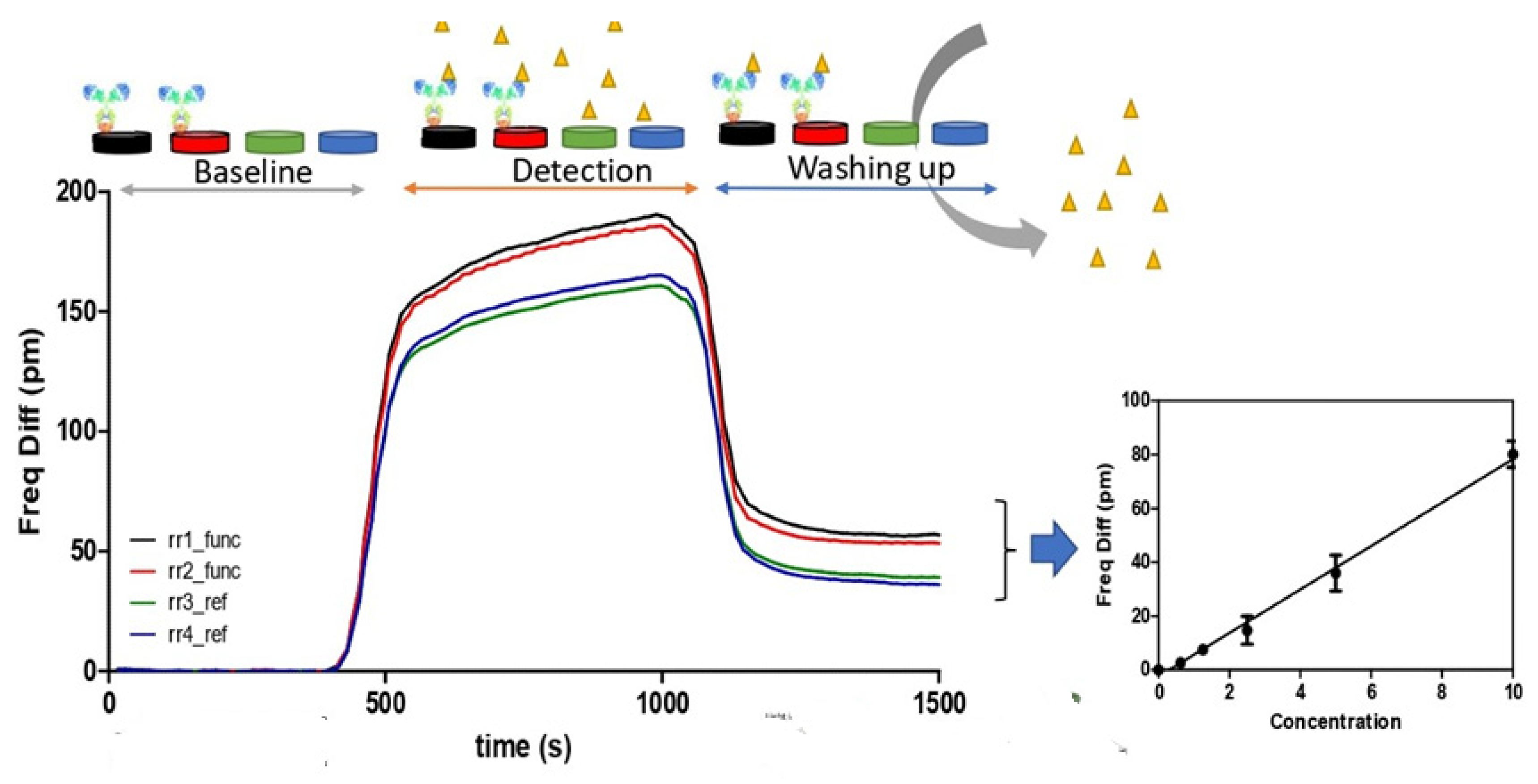
2.5. Immunosensor Validation for E. coli O157:H7 and Shiga-like Toxins
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. iELISA and Sensitivity Studies
3.2. Immunosensor Specificity and Sensitivity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Zhu, P.; Shelton, D.R.; Li, S.; Adams, D.L.; Karns, J.S.; Amstutz, P.; Tang, C.M. Detection of E. coli O157:H7 by immunomagnetic separation coupled with fluorescence immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 30, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laster, B.A.; Harris, K.B.; Lucia, L.M.; Castillo, A.; Savell, J.W. Efficacy of trimming chilled beef during fabrication to control Escherichia coli O157:H7 surrogates on subsequent subprimals. Meat Sci. 2012, 90, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.-R.H.A.-A.; de la Escosura-Muñiz, A.; Merkoçi, A. Highly sensitive and rapid determination of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in minced beef and water using electrocatalytic gold nanoparticle tags. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.Y.; Ye, W.W.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, L.D.; Leung, P.H.; Li, Y.; Yang, M. Ultrasensitive detection of E. coli O157:H7 with biofunctional magnetic bead concentration via nanoporous membrane based electrochemical immunosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of United Nations (FAO); World Health Organization (WHO). Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli (STEC) and Food: Attribution, Characterization, and Monitoring; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018; ISBN 978-92-5-130682-6 (FAO). ISBN 978-92-4-151427-9 (WHO). [Google Scholar]
- Scientific Committee of the Spanish Agency for Food Safety and Nutrition (AESAN). Preventative Measures and Applicable Recommendations for Avoiding Possible Food-Borne Infections Caused by Strains of Verotoxigenic/Shiga Toxin-Producing/Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (VTEC/STEC/EHEC); AESAN-2012-007; AESAN: Majadahonda, Spain, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Zhao, S.; Mao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, X.; Zeng, L. A sensitive lateral flow biosensor for Escherichia coli O157:H7 detection based on aptamer mediated strand displacement amplification. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 861, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commission Regulation (EC). No 2073/2005 of 15 November 2005 on microbiological criteria for foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2005, L338, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, F.J.G.; Mohammed Ahmed Sheikh, H.; Selvin, R. Advances in screening, detection and enumeration of Escherichia coli using nanotechnology-based methods: A review. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2018, 14, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umesha, S.; Manukumar, Y.H. Advanced molecular diagnostic techniques for detection of food-borne pathogens: Current applications and future challenges. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 84–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Tang, H.; Cheng, W.; Yan, L.; Zhang, D.; Ju, H.; Ding, S. A sensitive electrochemical DNA biosensor for specific detection of Enterobacteriaceae bacteria by exonuclease III-assisted signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 48, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huertas-Caro, C.; Urbano-Cáceres, E.; Torres-Caycedo, Y.M. Diagnóstico molecular una alternativa para la detección de patógenos en alimentos. Rev. Habanera Cienc. Médicas 2019, 18, 513–528. [Google Scholar]
- Fratamico, P.M.; Bhunia, A.K.; Smith, J.A. Foodborne Pathogens: Microbiology and Molecular Biology; CRC Press LLC eBooks: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Mustapha, A. Simultaneous Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella, and Shigella in Apple Cider and Produce by a Multiplex PCR. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, P.; Collier, T.; Doyle, S. PCR-ELISA detection of Escherichia coli in milk. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 34, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, R.T.; Weisberg, S.B. A review of technologies for rapid detection of bacteria in recreational waters. J. Water Health 2005, 3, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pebdeni, A.B.; Mousavizadegan, M.; Hosseini, M. Sensitive detection of S. aureus using aptamer-and vancomycin-copper nanoclusters as dual recognition strategy. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, G.; Chang, L.C.; Savran, C. An optical biosensor for rapid and labelfree detection of cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 3862–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornbeck, P. Double-Immunodiffusion Assay for Detecting Specific Antibodies. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2017, 116, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, T.T. Immunoassay. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1991, 2, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plested, J.S.; Coull, P.A.; Gidney, M.A.J. ELISA. Methods Mol. Med. 2003, 71, 243–261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, B.; Chen, K.; He, K. Development of a Sandwich ELISA for EHEC O157:H7 Intimin γ1. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Kawde, A.; Daud, M. Designs, formats and applications of lateral flow assay: A literature review. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2015, 19, 689–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posthuma-Trumpie, G.A.; Korf, J.; Van Amerongen, A. Lateral flow (immuno)assay: Its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. A literature survey. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.P.; Sharma, S.; Nara, S. Evaluation of gold nanoparticle based lateral flow assays for diagnosis of enterobacteriaceae members in food and water. Food Chem. 2015, 170, 470–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, H.J.; Lowe, R.C.; Pollard-Knight, D.V. Optical biosensor for monitoring microbial cells. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 2465–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riu, J.; Giussani, B. Electrochemical biosensors for the detection of pathogenic bacteria in food. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 126, 115863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Guo, H.; Sun, X. Recent progress on cell-based biosensors for analysis of food safety and quality control. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velusamy, V.; Arshak, K.; Korostynska, O.; Oliwa, K.; Adley, C.C. An overview of foodborne pathogen detection: In the perspective of biosensors. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 232–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Guerrero, A.B.; Dante, S.; Duval, D.; Osmond, J.; Lechuga, L.M. Advanced photonic biosensors for point-of-care diagnostics. Procedia Eng. 2011, 25, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shrivastava, A.; Gupta, V.B. Methods for the determination of limit of detection and limit of quantitation of the analytical methods. Chron. Young Sci. 2011, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; White, I.M.; Shopova, S.I.; Zhu, H.; Suter, J.D.; Sun, Y. Sensitive optical biosensors for unlabeled targets: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 620, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, K.; Bartolozzi, I.; Schacht, E.; Bienstman, P.; Baets, R. Silicon-on-Insulator microring resonator for sensitive and label-free biosensing. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 7610–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narsaiah, K.; Jha, S.N.; Bhardwaj, R.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, R. Optical biosensors for food quality and safety assurance—A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 383–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donagh, C.M.; Burke, C.S.; Crai BD, M. Optical biosensors. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 422–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pebdeni, A.B.; Hosseini, M.; Ganjali, M.R. Fluorescent turn-on aptasensor of Staphylococcus aureus based on the FRET between green carbon quantum dot and gold nanoparticle. Food Anal. Methods 2020, 13, 2070–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcka, O.; Del Campo, F.J.; Munoz, F.X. Pathogen detection: A perspective of traditional methods and biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurliyana, M.R.; Wibowo, K.M.; Muslihati, A.; Saim, H.; Ahmad, S.A.; Sari, Y.; Mansor, Z. The detection method of Escherichia coli in water resources: A review. IOP Conf. Ser. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 995, 012065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, R.E. Biosensor platforms for rapid detection of E. coli bacteria. In Escherichia coli–Recent Advances on Physiology, Pathogenesis and Biotechnological Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bange, A.; Halsall, H.B.; Heineman, W.R. Microfluidic immunosensor systems. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 2488–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luka, G.; Ahmadi, A.; Najjaran, H.; Alocilja, E.; DeRosa, M.; Wolthers, K.; Malki, A.; Aziz, H.; Althani, A.; Hoorfar, M. Microfluidics integrated biosensors: A leading technology towards lab-on-a-chip and sensing applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 30011–30031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, K.; Shahbazi, M.A.; Dave, V.P.; Ngo, T.A.; Chidambara, V.A.; Than, L.Q.; Bang, D.D.; Wolff, A. Microfluidic devices for sample preparation and rapid detection of foodborne pathogens. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1003–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 16654:2001/Amd 1:2017; Microbiology of food and animal feeding stuffs. Horizontal method for the detection of Escherichia coli O157. Amendment 1: Annex B: Result of interlaboratory studies. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Fernández Blanco, A.; Hernández Pérez, M.; Moreno Trigos, Y.; García-Hernández, J. Development of Optical Label-Free Biosensor Method in Detection of Listeria monocytogenes from Food. Sensors 2023, 23, 5570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkenazi, S.; Cleary, T.G. Rapid method to detect Shiga toxin and Shiga-like toxin I based on binding to globotriosyl ceramide (Gb3), their natural receptor. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, N.V.; Hulet, R.; Jayarao, B.M.; Muldoon, M.; Lindpaintner, K.; Kapur, V.; DebRoy, C. Detection of the top six non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O groups by ELISA. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttikonda, S.; Wang, W.W.; Suresh, M.R. Molecular zipper assays: A simple homosandwich with the sensitivity of pcr. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 7, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vytrasova, J.; Zachová, I.; Cervenka, L.; Štepanková, J.; Pejchalová, M. Non-specific reactions during immunomagnetic sepa-ration of Listeria. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 43, 397–401. [Google Scholar]
- Kehl, K.S.; Havens, P.; Behnke, C.E.; Acheson, D.W. Evaluation of the premier EHEC assay for detection of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 2051–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teel, L.D.; Daly, J.A.; Jerris, R.C.; Maul, D.; Svanas, G.; O’Brien, A.D.; Park, C.H. Rapid detection of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli by optical immunoassay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3377–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Skinner, C.; Patfield, S.; Stanker, L.H.; Fratamico, P.; He, X. New high-affinity 4 monoclonal antibodies against Shiga toxin 1 facilitate the detection of hybrid Stx1/Stx2 in vivo. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; McMahon, S.; Skinner, C.; Merrill, P.; Scotcher, M.C.; Stanker, L.H. Development and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Shiga toxin 2 and their application for toxin detection in milk. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 389, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ching, K.H. Lateral Flow Immunoassay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1318, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Yu, Z.; Liu, D.; Peng, T.; Liu, K.; Wang, S.; Xiong, Y.; Wei, H.; Xu, H.; Lai, W. Dual gold nanoparticle late flow immunoassay for sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 876, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, K.H.; He, X.; Stanker, L.H.; Lin, A.V.; McGarvey, J.A.; Hnasko, R. Detection of shiga toxins by lateral flow assay. Toxins 2015, 7, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, S.M.; Alocilja, E.C. A high density microelectrode array biosensor for detection of E. coli O157:H7. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 1662–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.Y.; Xing, F.F.; Deng, S.P. A disposable amperometric enzyme immunosensor for rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in food based on agarose/nano–Au membrane and screen-printed electrode. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.L.; Li, Y.B. A self-assembled monolayer-based piezoelectric immunosensor for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 19, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waswaa, J.; Irudayarajb, J.; DebRoy, C. Direct detection of E. coli O157:H7 in selected food systems by a surface plasmon resonance biosensor. LWT 2007, 40, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.J.; Feng, Y.Y.; Zhou, L.; Ye, Z.Z.; Wang, J.P.; Ying, Y.B.; Ruan, C.M.; Wang, R.H.; Li, Y.B. Label-free capacitive immunosensor based on quartz crystal Au electrode for rapid and sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 687, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Chen, J.-Q. Real-Time PCR Methodology for Selective Detection of Viable Escherichia coli O157:H7 Cells by Targeting Z3276 as a Genetic Marker. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 5297–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, X.H.; He, K.W.; Jiang, P.; Zhao, P.; Ye, Q.; Luan, X.; Wen, L.; Ni, Y.; Zhou, J.; et al. Duplex PCR Procedure for the Detection of EHEC O157:H7. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin. 2011, 26, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibekwe, A.M.; Grieve, C.M. Detection and quantification of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in environmental samples by real-time PCR. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.Y.; Wu, Y.H.; Xiong, Q.R.; Xu, H.Y.; Xiong, Y.H.; Liu, K.; Jin, Y.; Lai, W.H. Advantages of fluorescent microspheres compared with colloidal gold as a label in immunochromatographic lateral flow assays. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Lai, W.; Xiong, Y.; Wei, H.; Xu, H. Novel strategies to enhance lateral flow immunoassay sensitivity for detecting foodborne pathogens. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, J.G. Application of DNA aptamers and quantum dots to lateral flow test strips for detection of foodborne pathogens with improved sensitivity versus colloidal gold. Pathogens 2014, 3, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Xing, K.; Zhang, G.; Yuan, M.; Xu, S.; Liu, D.; Chen, W.; Peng, J.; Hu, S.; Lai, W.-H. Novel ELISA based on fluorescent quenching of DNA-stabilized silver nanoclusters for detecting E. coli O157:H7. Food Chem. 2019, 281, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, B.; Zhao, C.; Li, L.; Song, X.; Xu, K.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Fu, K.; Bao, H.; Song, D.; et al. Development of a low-cost paper-based ELISA method for rapid Escherichia coli O157:H7 detection. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 542, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perumal, V.; Hashim, U. Advances in biosensors: Principle, architecture and applications. J. Appl. Biomed. 2014, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kane, M.D.; Kim, S.; Dominguez, W.; Applegate, B.M.; Savikhin, S. A molecular beacon DNA microarray system for rapid detection of E. coli O157:H7 that eliminates the risk of a false negative signal. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalhai, M.H.; Fernandes, A.M.; Xia, X.; Musa, A.; Ji, J.; Sun, X. Electrochemical genosensor to detect pathogenic bacteria (Escherichia coli O157:H7) as applied in real food samples (fresh beef) to improve food safety and quality control. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 5017–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Si, C.; Ying, Y. Monitoring of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in food samples using lectin based surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisocherova-Lisalova, H.; Visova, I.; Ermini, M.L.; Springer, T.; Song, X.C.; Mrazek, J.; Lamacova, J.; Scott Lynn, N., Jr.; Sedivak, P.; Homola, J. Low-fouling surface plasmon resonance biosensor for multi-step detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens in complex food samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shi, X.; Gehring, A.G.; Paoli, G.C. Automated immunomagnetic separation for the detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from spinach. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 179, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.; Ravindran, V.B.; Surapaneni, A.; Shahsavari, E.; Haleyur, N.; Mantri, N.; Ball, A.S. Evaluation and comparison of recombinase polymerase amplification coupled with lateral-flow bioassay for Escherichia coli O157:H7 detection using different genes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Su, H.; Ding, H.; Sun, X.; Gao, H.; Geng, Y.; Wang, Z. Rapid analysis of Escherichia coli O157:H7 using isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification combined with triple-labeled nucleotide probes. Mol. Cell. Probes 2020, 50, 101501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Detection Technology | Working Interval (CFU/mL) | Limit of Detection (CFU/mL) | Storage Life | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface plasmon resonance | 102–103 | 6 × 102 | - | [59] |
| Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy | 104–107 | 104 | - | [56] |
| Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy | 103–105 | 103 | 1 week | [60] |
| Cyclic voltammetry | 105–109 | 7.374 × 104 | 1 week | [57] |
| Quartz crystal microbalance | 103–108 | 103 | 1 week | [58] |
| Photonic immunosensor | 101–106 | 101 | 6 months | This work |
| Detection Technology | Speed in Testing | Cost | Applicability | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plate culture | 24 h | Low | Wide | Low | Low |
| Lateral flow immunoassay | 30–45 min | Moderate | Limited | Low | Low |
| Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) | 3–5 h | High | Wide | Low | Low |
| qPCR | 6 h | High | Wide | Moderate | Moderate |
| Multiplex PCR | 6 h | High | Wide | Moderate | Moderate |
| Hybridization | 18–24 h | Moderate | Limited | Moderate | Moderate |
| Microarrays | 48–72 h | High | Wide | High | High |
| Optical biosensors | 45 min–3 h | High | Limited | High | Moderate |
| Electrochemical biosensors | 18–24 h | Moderate | Limited | High | Moderate |
| Photonic immunosensor | 30–45 min | Low | Wide | High | High |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández, A.; Hernández, M.; Moreno, Y.; García-Hernández, J. Specific and Simultaneous Detection of E. coli O157:H7 and Shiga-like Toxins Using a Label-Free Photonic Immunosensor. Photonics 2024, 11, 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11040374
Fernández A, Hernández M, Moreno Y, García-Hernández J. Specific and Simultaneous Detection of E. coli O157:H7 and Shiga-like Toxins Using a Label-Free Photonic Immunosensor. Photonics. 2024; 11(4):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11040374
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández, Ana, Manuel Hernández, Yolanda Moreno, and Jorge García-Hernández. 2024. "Specific and Simultaneous Detection of E. coli O157:H7 and Shiga-like Toxins Using a Label-Free Photonic Immunosensor" Photonics 11, no. 4: 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11040374
APA StyleFernández, A., Hernández, M., Moreno, Y., & García-Hernández, J. (2024). Specific and Simultaneous Detection of E. coli O157:H7 and Shiga-like Toxins Using a Label-Free Photonic Immunosensor. Photonics, 11(4), 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11040374





