Abstract
Optical frequency rulers (OFRs) can be used as optical wavelengths or frequency references for spectra modulation or to determine unknown wavelengths. In the past, difficult-to-perform and complicated mechanisms were used to make OFRs, such as double slits with a high-speed fluid or an external circuit to control the liquid crystal birefringence. Since then, a later research study introduced a simple structure for producing OFRs by utilizing the optical activity block and two polarizers. This achieved a movable OFR that was controllable by simply rotating one of the polarizers. However, this mechanical rotation hindered its high-speed applicability. In this article, a more advanced, scalable OFR scheme using the Faraday effect is proposed. It is controlled by varying the magnetic field intensity, which is not a mechanical method, and it can be changed at high speeds. The numerical results demonstrate that those OFR spectral ticks can be scaled to reach a higher or lower tick density, greatly benefiting the wavelength decision jobs.
1. Introduction
Polychromatic wave diffractions have been investigated since the mid-1980s [1] when the scaling law was proposed. This states that spectral variations occur unless the degree of spectral coherence of the sources meets that law [2]. There were many valuable results, such as singular optics in polychromatic light [3,4] and spatial and spectral correspondence relationships [5]. Some applications were proposed, such as spectra manipulation [6], spectral switches [7,8], and Talbot spectra [9]. It was also noted that when a polychromatic light passes through a double slit, the interfered or diffracted spectrum detected in the far field changes substantially. There are many peaks and valleys (dark lines), and they follow the interference law [10]. Those lines are wavelengths satisfying destructive interference and vanishing in the output spectrum. One of the authors, Han, suggested that those disappearing wavelengths could be used as optical wavelength (or frequency) references as long as their frequencies are known. This was named an “optical frequency ruler (OFR)” because the dark lines work like a ruler’s ticks. Some similar reference lines are usually produced by the Fabry–Perot etalon or optical comb techniques with a resonant cavity [11,12]. Following this, two more OFR schemes were proposed without cavities, utilizing a moving fluid [13] and liquid crystal birefringence [14,15]. However, in the former, the required high fluid speed is too difficult to reach; in the latter, an external circuit is needed to control the liquid crystal orientation. The latest scheme was a movable OFR with optical activity [16], which has the benefits of easy OFR realization and control by rotating one of the polarizers. In this article, we progress one step further. An OFR configuration can also be easily attained, and the control method is even simpler. It utilizes the Faraday effect to achieve a scalable OFR and varies the ruler’s tick spacing by manipulating the magnetic field intensity. Therefore, no movable mechanical parts are needed, such as the polarizer rotation, which is required for the previous work. Thus, the control or modulation speed can increase substantially, for example, by simply changing the current in a multiple-turn coil wire. The Faraday effect is also widely utilized in fiber optics, especially for current or magnetic field sensing [17,18]. Thus, the results of this work may also be suitable for applications in that field.
2. Theory and Numerical Results
In the presence of a static magnetic field, many materials act as polarization rotators, called the Faraday effect, and they are termed magneto-optical (MO) materials. The two normal modes are right- and left-circularly polarized waves. Usually, the refraction index of an optically active medium is described as and for the right and left circular polarization waves, respectively. The rotatory power (rotation angle per unit length) is [19]
where is the wavelength in vacuum, B is the magnetic field, and V is the Verdet constant. It can be seen from Equation (1) that both and V are strongly wavelength-dependent. Thus, a linearly polarized wave travels in the material with thickness d, and the angle of polarization rotation is
If , is positive, such materials are said to be dextrorotary, whereas those for which are termed levorotary. For example, a terbium gallium garnet (TGG) is a levorotary material with V = −237.1 [rad/™] at = 500 nm, where T is the unit tesla for measuring the strength of a magnetic field.
As we show below, this Faraday effect-induced polarization rotating ability can be used as a dynamical intensity modulator for a monochromatic wave and a scalable optical frequency ruler for a polychromatic wave.
2.1. Monochromatic Wave Situation
Consider the configuration shown in Figure 1. There is a magneto-optical material placed between the two polarizers, P1 and P2, with polarization angles and (with respect to the x-axis), respectively. As indicated below the figure, the polarization states can be described as Jones vectors and Jones matrices [20]. The three Jones matrices are named J1, JMO, and J2, respectively, for P1, magneto-optical material, and P2. For an incident wave field with the Jones vector , the output field
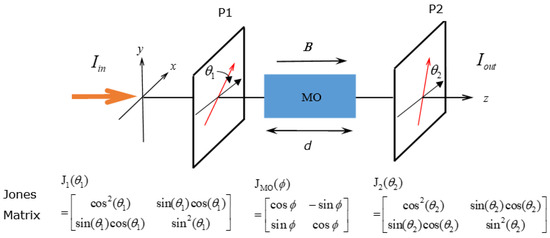
Figure 1.
Configuration for illustrating using a magnetic–optical material as an intensity modulator. The Jones matrix of each component is presented below.
Without losing generality and for simplicity, we set to be linearly polarized along the x-axis, with the components and being 0. Substituting these two conditions into Equation (3), is
Thus, the final output intensity is
where is the incident intensity. Here, we intentionally include three letters in the parenthesis of in this order and explain it as follows: The first letter is a variable that can be varied by changing the value of B, while the other two letters and indicate the polarization angle of P2 and the operating wavelength selected. Note that the rotatory power and are wavelength-dependent. TGG operating at 500 nm is used as an example with and d = 20 mm. Figure 2 shows the normalized output intensity vs. B at that wavelength. Here, we neglect the material absorption and Fresnel loss because the former is very small (the absorption coefficient is about cm−1 [21] in the visible and NIR region), and the latter can be fairly accounted for by applying a suitable anti-reflection coating both sides of the TGG block.
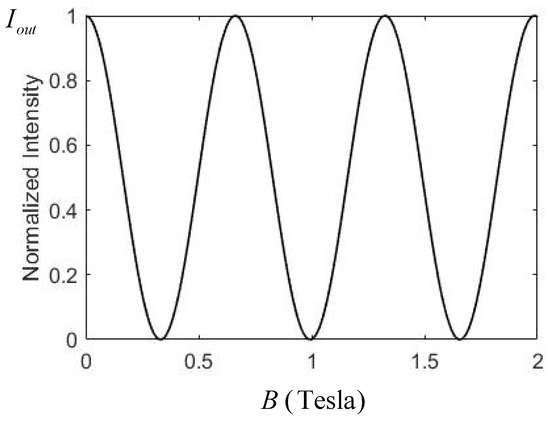
Figure 2.
The normalized output intensity versus the magnetic field strength B.
It can be seen in Figure 2 that the output intensity can be controlled by changing the value of the external magnetic field strength B. Of course, a similar intensity control can be achieved by simply rotating the polarization angle of P2 without using the MO material. Here, a solid TGG block is used for intensity control illustration, and some useful equations in monochromatic form, such as Equation (5), are acquired and will be modified to be reused later. This will become obvious when we consider polychromatic spectrum controls, as discussed in the next section.
2.2. Polychromatic Wave Situation
After studying the intensity modulation for a monochromatic wave case, we turn our attention to a polychromatic one. We already know that the refraction index depends on the wavelength (so-called dispersion), but when it comes to the MO effect, the strong rotary power wavelength dependence = V•B is dominant because the Verdet constant itself is strongly wavelength-dependent, as [19], where γ is the magneto gyration coefficient. In order to give a full description and correct numerical calculations, the following two formulas are used for and , which are verified empirically and adapted from the literature [22,23]. Figure 3 depicts the behavior of the absolute value of and for TGG in the wavelength range from 0.5 to 1.0 um. The much larger extent of value change for than that of is obvious.
The parameters used in Equation (6) are as follows: F = 820.3 rad/Tm, G = −6.2 rad/Tm, = 0.2392 um, E0 = 9.223 eV, and Ed = 25.208 eV.
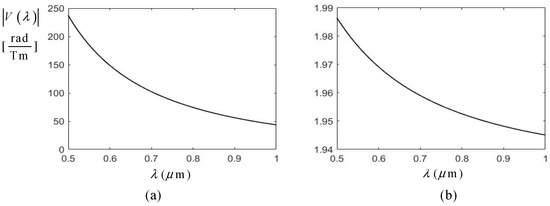
Figure 3.
(a) The behavior of for TGG. (b) The behavior of for TGG. Note that the extent of variation in is much larger than in .
Now, we consider an incident polychromatic spectrum with a flat-top distribution ranging from to , as shown in Figure 4. Because each wavelength component experiences various rotatory powers , even at a fixed value of B, the final rotation angle is also different after traversing the MO material, as illustrated in the lower section of the figure. Thus, the final output spectrum is modulated after passing the polarizer 2, as shown schematically on the right in Figure 5. Using the superposition principle and with the help of Equation (5), the output spectrum at each wavelength is
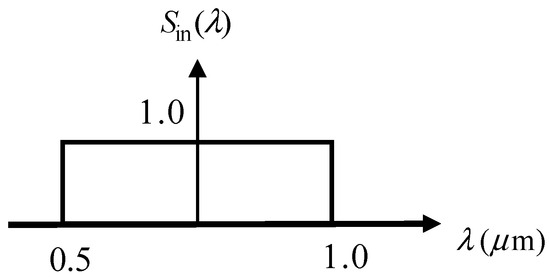
Figure 4.
The incident flat-top polychromatic spectrum .
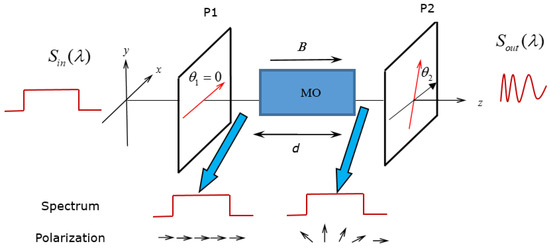
Figure 5.
The configuration illustrates the principle of an optical frequency ruler using MO material. The output spectrum is modulated by polarization changes.
Comparing this with Equation (5), note that now the first letter in the parenthesis of is a variable, while the other two letters and are parameters, which are set by the material (), B and d), and the polarization angle of P2. Using the same configuration as in Figure 1, Figure 6a–c show with for three values of magnetic field strength with B = 3, 5, 7 Tesla, respectively, in the wavelength interval of .
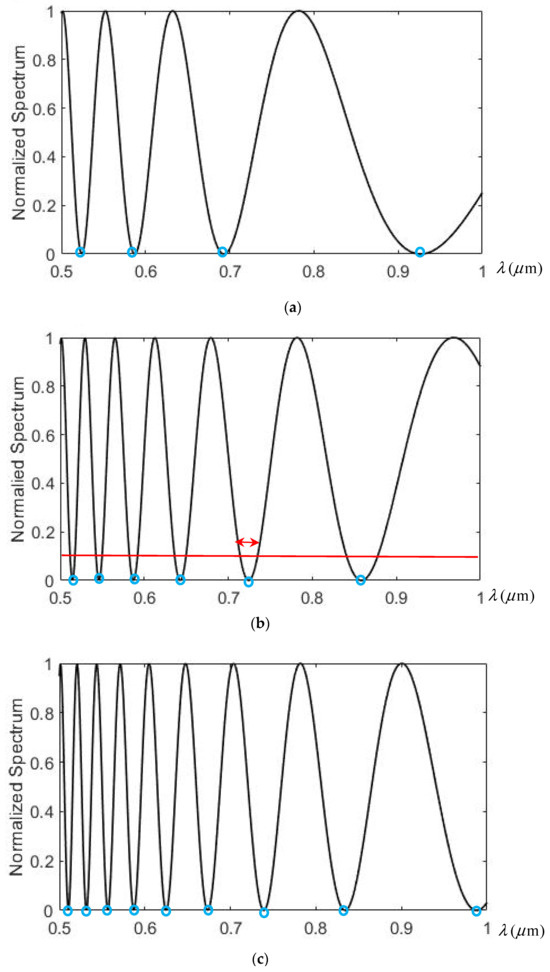
Figure 6.
The output spectrum for three values of magnetic field strength. (a) B = 3.0 Tesla. (b) B = 5.0 Tesla. (c) B = 7.0 Tesla. In (b), the red horizontal line shows the level at 10% intensity, and the red arrow shows the wavelength width at that level of one of the selected frequency ticks. Blue circles are the vanishing wavelengths (OFR ticks) in the output modulated spectrum.
The above figures demonstrate that there are many peaks and valleys and that some wavelengths indicated by blue circles can disappear. As explained in Figure 5, these wavelength components are those with polarization direction vertical to the P2 polarizer, and they are filtered out. These vanishing wavelengths (or dark lines) in the continuous spectrum can be used as wavelength references because their positions can be found numerically. As mentioned in the introduction, one of the authors, Han, named this effect an optical frequency ruler (OFR) since those lines are like the ticks of a ruler, which can help determine an unknown optical frequency or wavelength. However, as can be seen in Figure 6, the spacing between the ticks is not regular due to the nonlinear wavelength dependence of the rotary power. The spacing becomes bigger for larger wavelengths. Additionally, note that the modulated spectrum and the frequency ruler can be controlled by varying the magnitude of the magnetic field strength B. When B increases, the number of dark lines increases, and the spacing between adjacent ticks decreases; thus, we have a scalable OFR, as suggested in the title of this work. Certainly, spectrum manipulation can also be achieved by rotating the polarization angle of P2, i.e., , and this method has been studied in a previous article [16]. In that polarizer rotation case, a movable OFR was achieved. The scalable property of an OFR facilitates the determination of an unknown wavelength, as explained in the following section.
3. Results
In the last section, a scalable OFR using the MO effect is suggested, and it can be used to determine an unknown wavelength. Here, we present a possible measurement configuration. As shown in Figure 7, a Y-coupler is used to couple an unknown wavelength source and the optical frequency ruler (OFR) source, say, with the spectral distribution, as in Figure 6a. After coming out of the fiber end, a lens is used to collimate the light beam, and a dispersive element (prism or grating) is used to disperse the spectrum. A piece of white paper or board can be placed on the observation plane, and on the paper, the dispersed spectrum’s blow-up is plotted schematically below. For simplicity, we only plot the visible light band, approximately from 0.5 to 0.8 um, that is, from purple/blue to red colors. Now, we turn our attention to that blow-up. We plot the colored continuous spectrum in the middle, and the unknown source is shown as a long, bright green line. The upper part reveals a similar spectrum to Figure 6a, with black-white grey tones indicating spectral density variations (i.e., those peaks and valleys in the spectrum). We also use some black lines to locate valleys’ minimums to indicate the OFR ticks. As seen in Figure 6a, there are a total of three blue circles in the range of 0.5 to 0.8 um, and thus, three black ticks are plotted in the upper part. Since the unknown wavelength position falls between the second and third ticks (counting from the left), it is not easy to determine it precisely. Therefore, we can vary the magnetic field and rescale the OFR ticks until one of the ticks coincides with the unknown wavelength, like the situation in Figure 6b, which is shown in the lower part of the blow-up figure. Thus, the unknown wavelength can be determined more accurately.
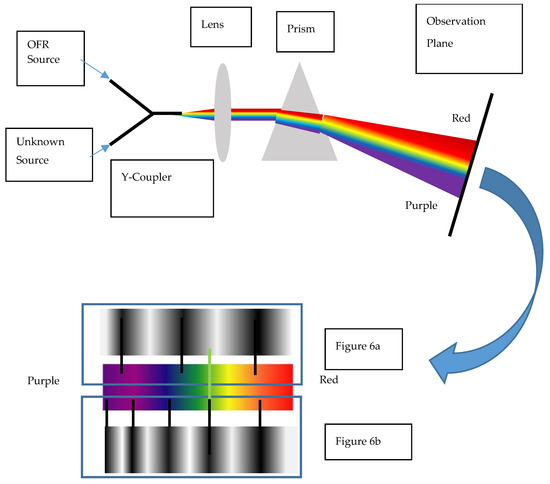
Figure 7.
Scheme for determining an unknown wavelength using scalable OFRs. The lower part is the blow-up plot of the observation plane, showing the dispersed spectrum and the unknown wavelength. The dark lines in the blow-up are the OFR ticks.
Regarding the wavelength measurement accuracy, it is determined by the way in which the dark line is placed in the wavelength. It is reasonable to assume that it can be placed in the wavelength interval for the dark line level between 0 and 10% of the peak, as the red line interval in Figure 6b shows. In this case, the accuracy is approximately ±8 nm. Note that this interval width varies with the dark line’s wavelength due to the nonlinearity of the spectrum distribution. It increases as the wavelength increases; therefore, the accuracy is higher when shorter wavelengths are used. The advantage of this scheme is that a spectrometer is not necessary to determine a wavelength when high precision is not required. Note that the ideal incident flat-top polychromatic spectrum in Figure 4 can be replaced by a real broad-band source spectrum, such as the supercontinuum white light laser. Using this ideal model is only for the convenience of the illustration. A real source will only affect the maximum of the peaks in the output spectrum and have no effect on the ticks of OFR. Thus, the performance of this scheme will not be affected too much. Neither the backreflections of polarizers (if any) will affect this OFR scheme for the same reason.
4. Discussion
In this work, we present a scheme using the magneto-optical effect to control an incident spectrum and achieve a scalable OFR. The configuration consists of two polarizers, one MO material, TGG, and a variable magnetic field, B. We studied the monochromatic case first. By selecting a specific wavelength and a fixed block thickness, the relation between the rotatory power at that wavelength (thus the rotation angle of the polarization) and the magnetic field intensity can be derived using the Jones matrix. The output intensity showed a cosine square function of B. In order to provide more information about the materials used in this work (such as the Faraday Effect, Jones formalism, and magneto-optical effect), some more references were included [24,25,26,27].
The polychromatic situation can be obtained by superposing various wavelength components. However, the strong Verdet constant (thus rotary power) wavelength dependence and the material dispersion should be carefully considered; therefore, verified empirical relations for these two factors are used in this work. The results show that for a flat-top incident spectrum, the output spectrum form is directly related to the modulated monochromatic intensity. However, the modulated spectral behavior is not in cosine square form anymore, mainly due to the strong nonlinear wavelength dependence of the polarization rotation angles. Finally, with the formula and numerical examples, we successfully illustrated the scalable optical frequency ruler phenomenon. Those vanishing wavelengths act as the ruler’s ticks, which can be used as references for measuring an unknown wavelength. Moreover, we showed that those ticks can be rescaled by varying the strength of the magnetic field. The advantage of this scheme lies in its flexible scale and its compact configuration, compared with those using resonant cavities or those needing external circuits to control the liquid crystal’s birefringence.
In conclusion, this work contributes another straightforward method to provide an optical frequency ruler effect, which may be suitable for applications in spectroscopy or for spectra manipulation. Since this optical frequency ruler method has many potential applications, feature research directions include finding faster, easier, and/or reliable mechanisms, such as the acousto-optics effect or the material’s nonlinearities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.-P.C. and P.H.; methodology, P.D.; validation, J.P.; data curation, C.-M.T.; writing—original draft preparation, J.-P.C.; writing—review and editing, P.H.; and funding acquisition P.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) of Taiwan under contract number MOST 111-2221-E-005-033-MY2.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their thanks for the support from National Chung Hsing University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wolf, E. Invariance of the spectrum of light on propagation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 56, 1370–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, E. Red shifts and blue shifts of spectral lines emitted by two correlated sources. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 58, 2646–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, T.D.; Wolf, E. Spectral anomalies near phase singularities in partially coherent focused wavefields. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2003, 5, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soskin, M.S.; Vasnetov, M.V. Singular optics. In Progress in Optics; Wolf, E., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 42, pp. 219–276. [Google Scholar]
- Han, P. Spatial–Spectral Correspondence Relationship for Mono—Poly chromatic Light Diffraction. In Progress in Optics; Visser, T.D., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 63, pp. 33–87. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.P.; Weng, J.H.; Hsu, H.C.; Lee, P.Y.; Han, P. A Data Transmission Method with Spectral Switches via Electroabsorption. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Pu, J.; Weng, J.; Han, P. Spectral anomalies by superposition of polychromatic Gaussian beam and Gaussian vortex beam. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 213037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, J.T.; Wolf, E. Phenomenon of spectral switches as a new effect in singular optics with polychromatic light. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2002, 19, 2510–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasouli, S.; Khazaei, A.M.; Hebri, D. Talbot carpet at the transverseplane produced in the diffraction of plane wave from amplituderadial gratings. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2018, 35, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Born, M.; Wolf, E. Principles of Optics, 7th ed.; Cambridge University: Cambridge, UK, 1999; p. 587. [Google Scholar]
- Bartels, A.; Heinecke, D.; Diddams, S.A. 10-GHz self-referenced optical frequency comb. Science 2009, 326, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, K.J. Laser Engineering; Prentice-Hall Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; Chapter 3. [Google Scholar]
- Han, P. Optical frequency ruler with moving fluid. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2013, 11, 122601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanseri, B.; Rathi, A.K. Broadband spectral shaping using nematic liquid crystal. Results Phys. 2019, 12, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.F.; Hsu, H.C.; Han, P. Spectral manipulation and tunable optical frequency ruler using liquid crystal’s birefringence. OPTIK 2019, 179, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.M.; Weng, J.H.; Lin, K.W.; Han, P. Movable optical frequency ruler with optical activity. Appl. Sci. 2023, 10, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailovic, P.; Petricevic, S. Fiber Optic Sensors Based on the Faraday Effect. Sensors 2021, 21, 6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, T. Theory for the Faraday effect in optical fiber. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2005, 22, 1856–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teich, M.; Saleh, B. Fundamentals of Photonics, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 228–230. [Google Scholar]
- Iizuka, K. Elements of Photonics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; Volume 1, p. 421. [Google Scholar]
- Slezak, O.; Yasuhara, R.; Lucianetti, A.; Mocek, T. Wavelength dependence of magneto-optic properties of terbium gallium garnet ceramics. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 013641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vojna, D.; Slezak, O.; Lucianetti, A.; Mocek, T. Verdet constant of magneto-active materials developed for high-power Faraday devices. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlarb, U.; Sugg, B. Refractive index of Terbium Gallium Garnet. Phys. Stat. Sol. 1994, 182, K91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.C. New calcules for the treatment of optical systems. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1947, 37, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, J.J. Characteristic properties of Mueller matrices. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2000, 17, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, J.J.; Ossikovski, R. Polarized Light and the Mueller Matrix Approach; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Glushkov, A.V. Optical Communication Systems: Signal Processing and Cybersecurity; Astroprint: San Diego, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).