Resolution Enhancement of Geometric Phase Self-Interference Incoherent Digital Holography Using Synthetic Aperture
Abstract
1. Introduction
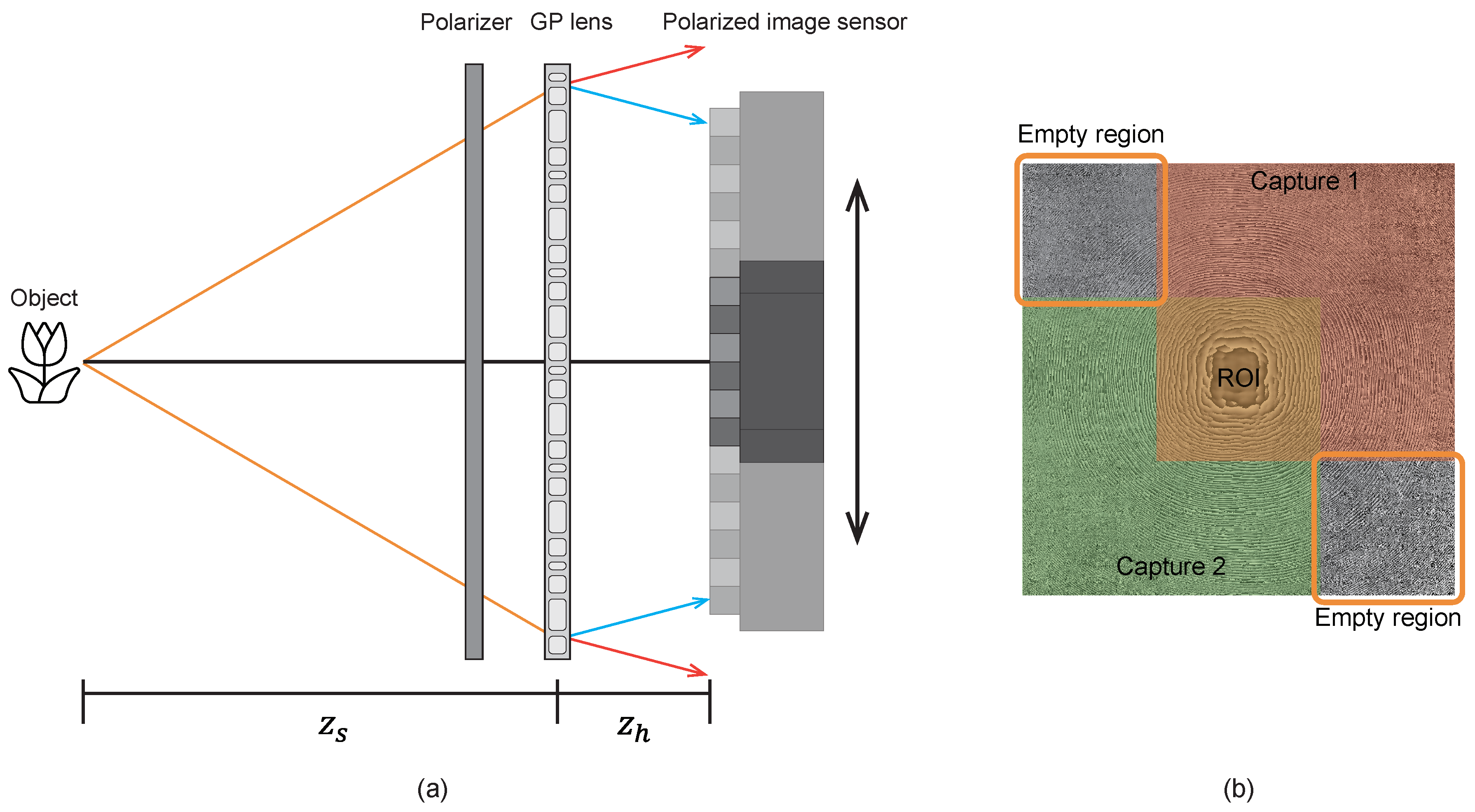
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Resolution Analysis of GP-SIDH
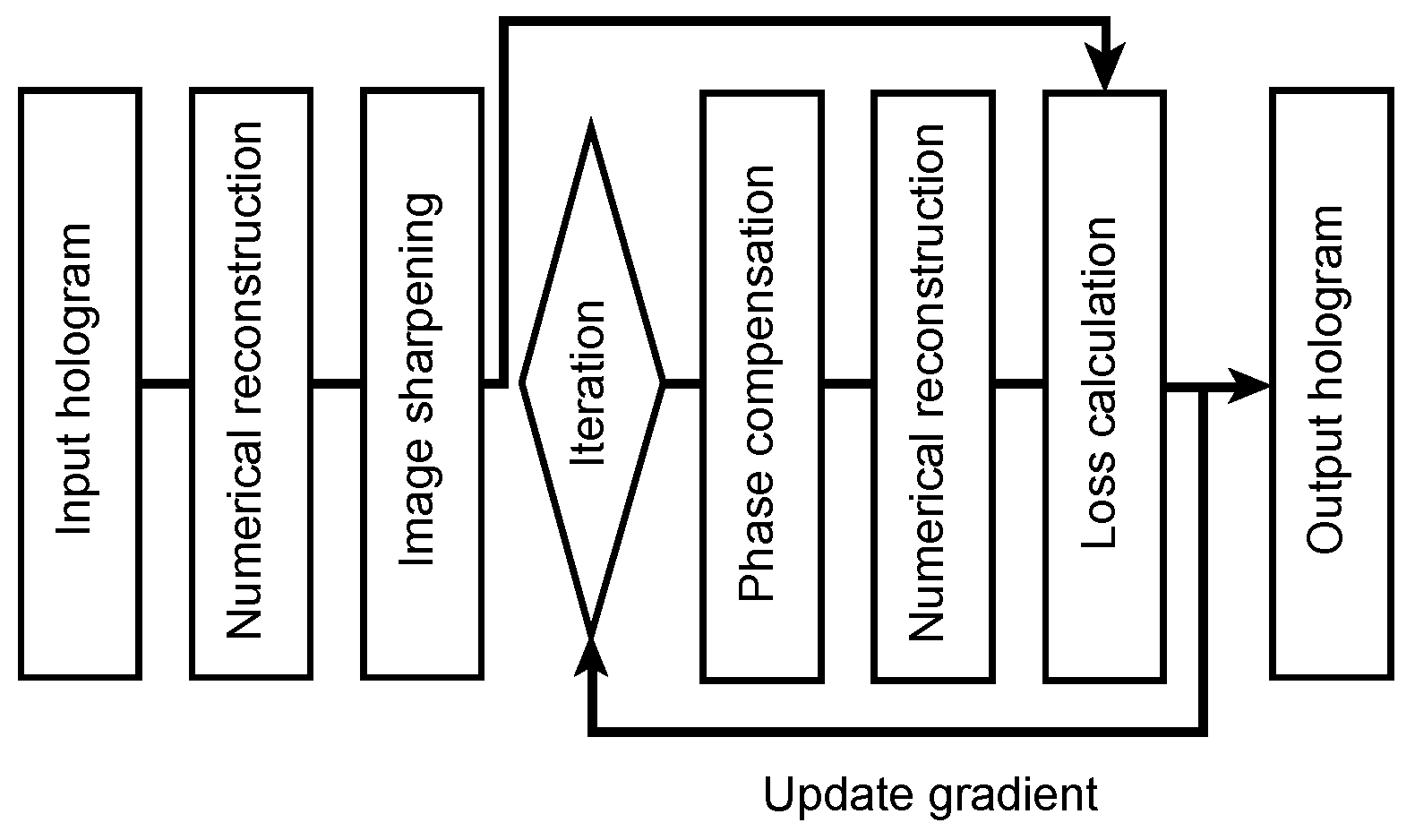
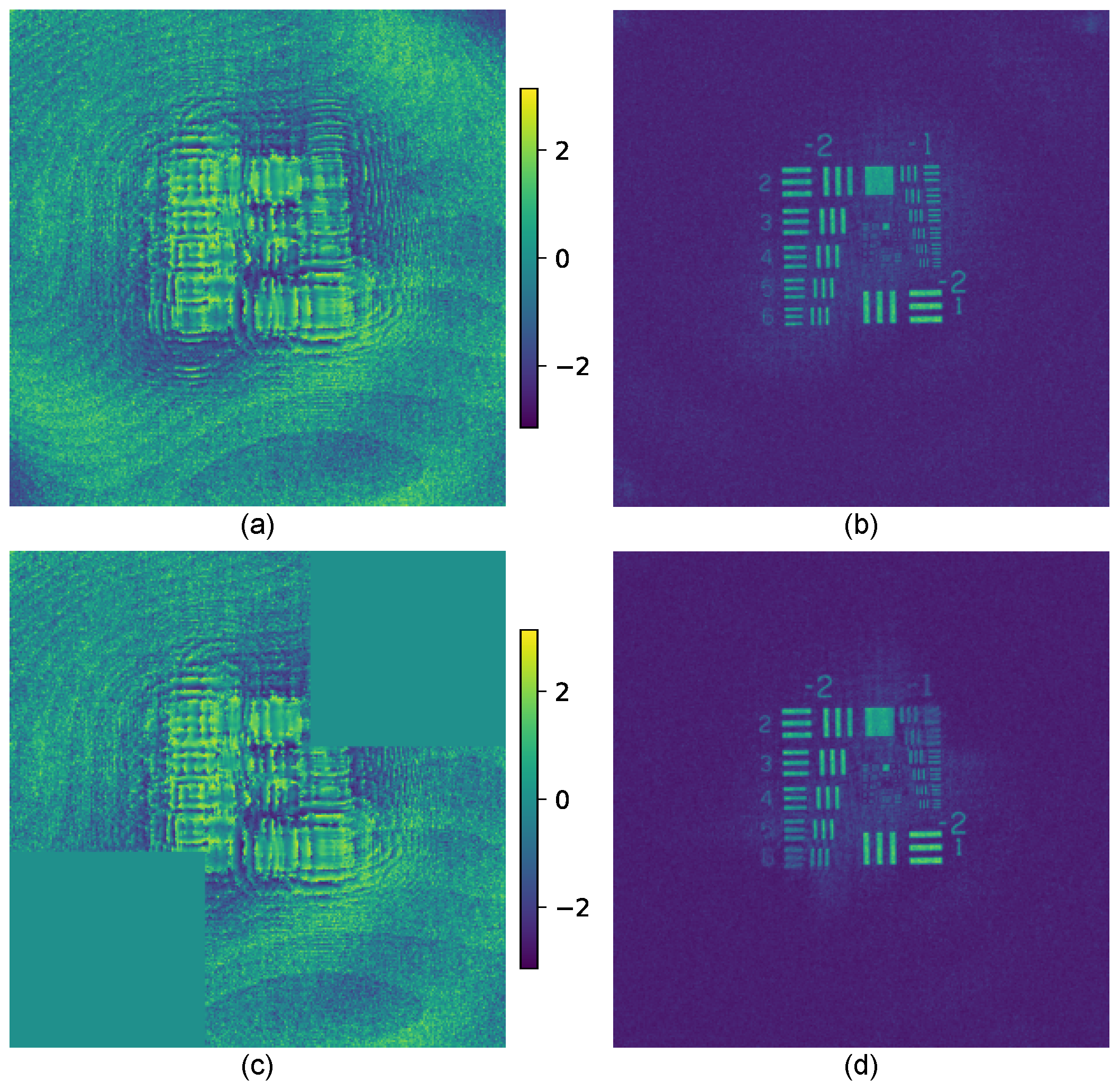
2.2. Sparse Synthetic Aperture with GP-SIDH
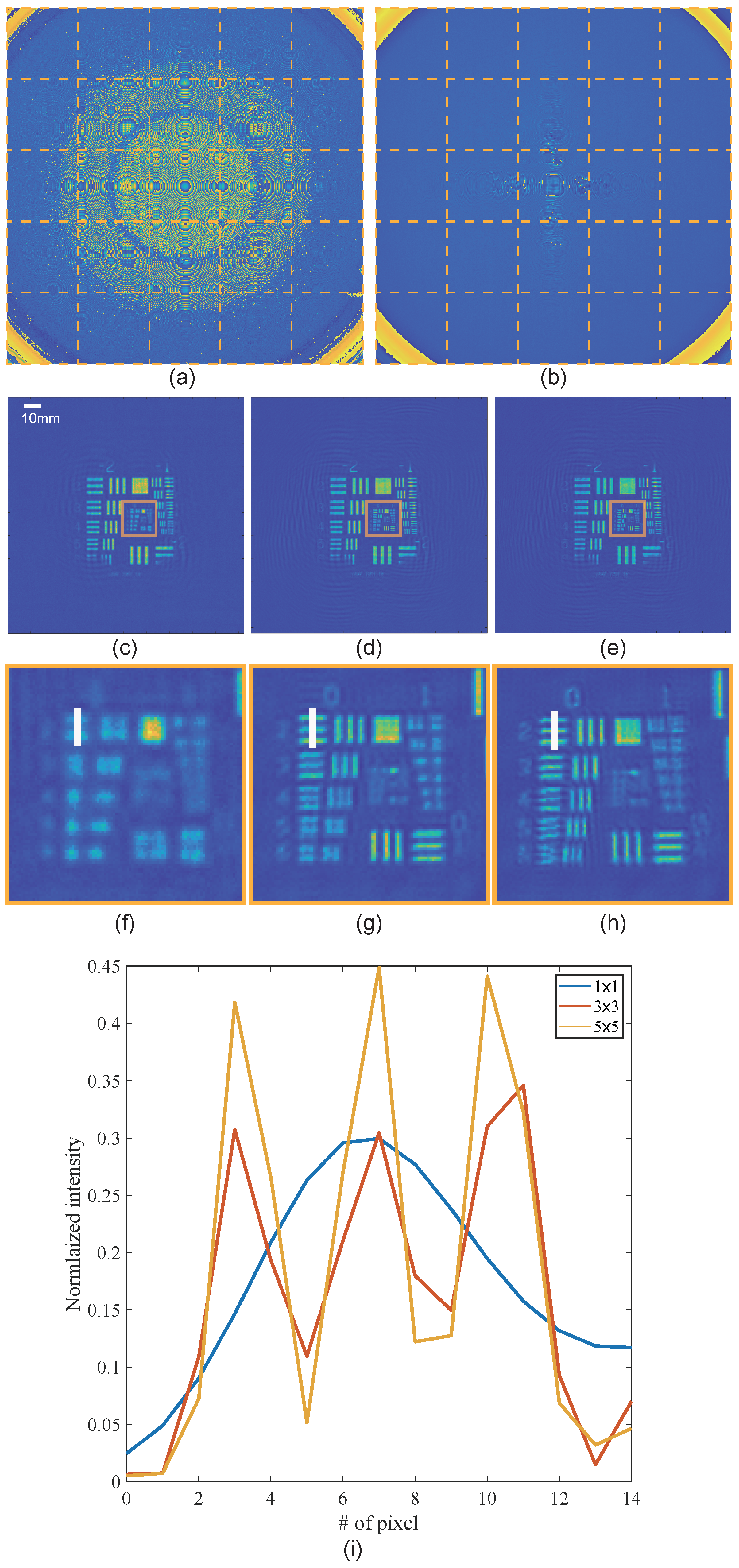
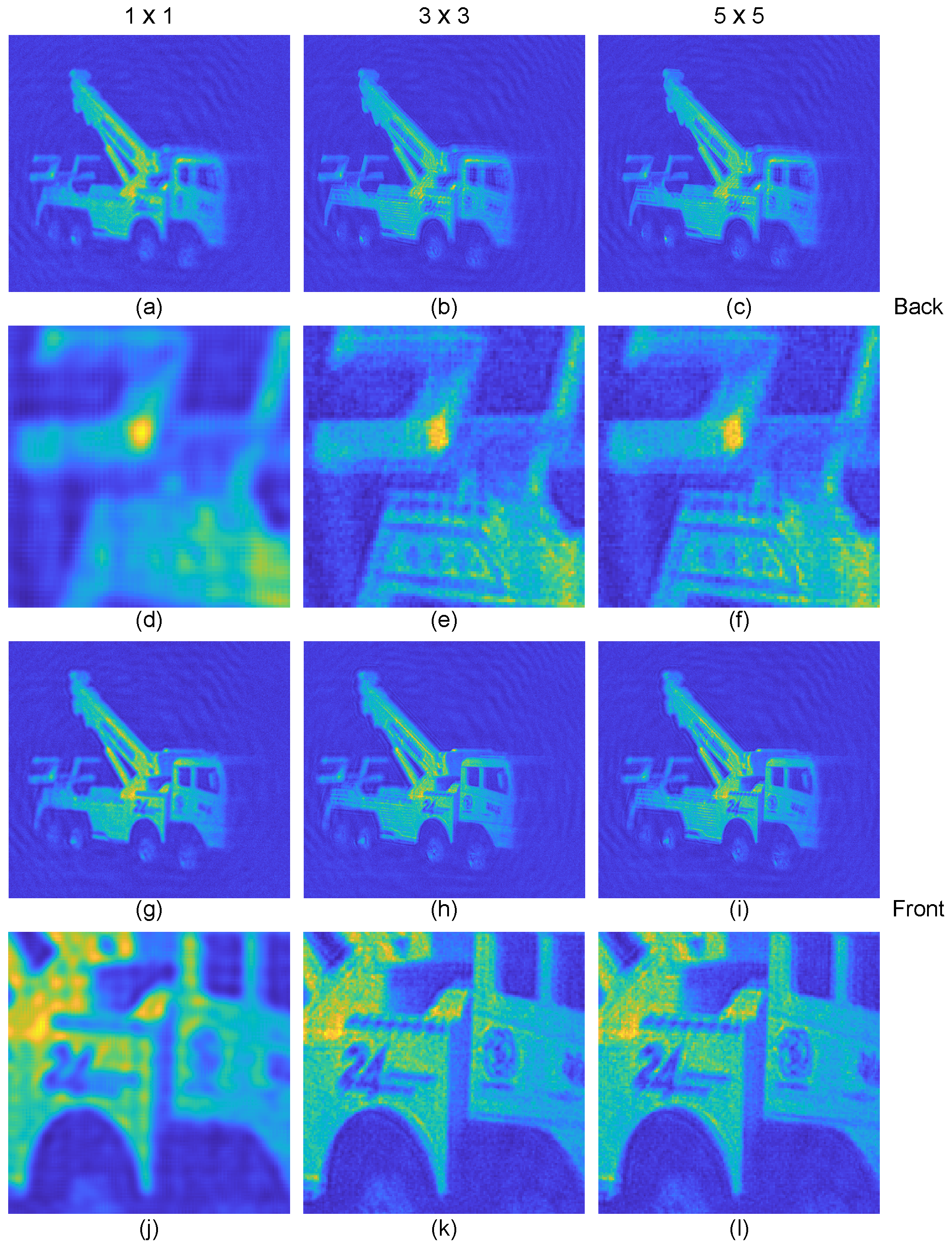
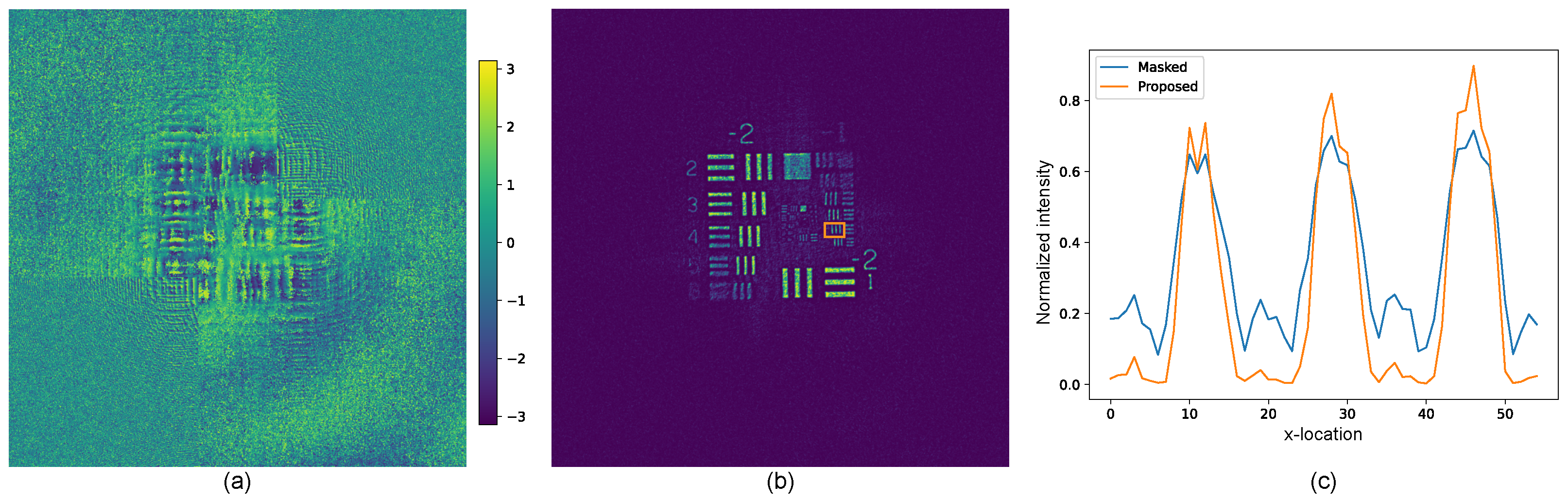
3. Results
- Laplacian operator (Figure 7b):
- Unsharp masking (Figure 7c):
- Roberts operator
- Sobel operator (Figure 7e):
- Prewitt operator (Figure 7f):where represents a Gaussian blur kernel and is the enhancement strength. The Laplace operator takes absolute values to compare with other operations. The Sobel and Prewitt operators demonstrate the best overall performance, offering an optimal balance between edge enhancement and noise suppression. The unsharp mask and Roberts operator also perform well, while the Laplacian filters show more sensitivity to noise.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, B. Three-dimensional displays, past and present. Phys. Today 2013, 66, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, B.C.; Peroz, C. Optical architectures for displays and sensing in augmented, virtual, and mixed reality (AR, VR, MR). In Proc; SPIE: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2020; Volume 11310, p. 1131001. [Google Scholar]
- Benton, S.A.; Bove, V.M., Jr. Holographic Imaging; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Maimone, A.; Georgiou, A.; Kollin, J.S. Holographic near-eye displays for virtual and augmented reality. Acm Trans. Graph. (Tog) 2017, 36, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Bang, K.; Wetzstein, G.; Lee, B.; Gao, L. Toward the next-generation VR/AR optics: A review of holographic near-eye displays from a human-centric perspective. Optica 2020, 7, 1563–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.W. Introduction to Fourier Optics; Roberts and Company Publishers: Greenwood Village, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh, C.K.; Sawchuk, A.A. Computer-generated double-phase holograms. Appl. Opt. 1978, 17, 3874–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerchberg, R.W. A practical algorithm for the determination of plane from image and diffraction pictures. Optik 1972, 35, 237–246. [Google Scholar]
- Poon, T.C.; Liu, J.P. Introduction to Modern Digital Holography: With MATLAB; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Choi, S.; Padmanaban, N.; Wetzstein, G. Neural holography with camera-in-the-loop training. Acm. Trans. Graph. (Tog) 2020, 39, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.; Chen, C.; Lee, B. High-contrast, speckle-free, true 3D holography via binary CGH optimization. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Li, B.; Kim, C.; Kellnhofer, P.; Matusik, W. Towards real-time photorealistic 3D holography with deep neural networks. Nature 2021, 591, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Seo, W.; Yu, H.; Kim, S.I.; Shin, B.; Lee, C.K.; Moon, S.; An, J.; Hong, J.Y.; Sung, G.; et al. Diffraction-engineered holography: Beyond the depth representation limit of holographic displays. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; He, Z.; Chu, D.; Cao, L. Non-convex optimization for inverse problem solving in computer-generated holography. Light. Sci. Appl. 2024, 13, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Kim, M. Overview of techniques applicable to self-interference incoherent digital holography. J. Eur. Opt.-Soc.-Rapid Publ. 2013, 8, 13077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K. Full color natural light holographic camera. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 9636–9642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, J.; Vijayakumar, A.; Kumar, M.; Rai, M.R.; Kelner, R.; Kashter, Y.; Bulbul, A.; Mukherjee, S. Recent advances in self-interference incoherent digital holography. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2019, 11, 1–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, J.; Brooker, G. Digital spatially incoherent Fresnel holography. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 912–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, J.; Brooker, G. Non-scanning motionless fluorescence three-dimensional holographic microscopy. Nat. Photonics 2008, 2, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, T.; Ito, K.; Kakue, T.; Fujii, M.; Shimozato, Y.; Awatsuji, Y.; Nishio, K.; Ura, S.; Kubota, T.; Matoba, O. Parallel phase-shifting digital holographic microscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2010, 1, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, J.; Kelner, R. Modified Lagrange invariants and their role in determining transverse and axial imaging resolutions of self-interference incoherent holographic systems. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 29048–29066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, T.; Kanno, T.; Arai, Y.; Ozawa, T. Single-shot phase-shifting incoherent digital holography. J. Opt. 2017, 19, 065705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, A.; Kashter, Y.; Kelner, R.; Rosen, J. Coded aperture correlation holography–a new type of incoherent digital holograms. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 12430–12441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, S.; Bleahu, A.; Kahro, T.; John Francis Rajeswary, A.S.; Kumar, R.; Kukli, K.; Tamm, A.; Rosen, J.; Anand, V. Enhanced design of multiplexed coded masks for Fresnel incoherent correlation holography. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Anand, V.; Rosen, J. 3D single shot lensless incoherent optical imaging using coded phase aperture system with point response of scattered airy beams. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Yim, J.; Yoo, S.; Min, S.W. Self-interference digital holography with a geometric-phase hologram lens. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 3940–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Lee, J.W.; Shin, J.; Hong, K.; Park, J.; Kim, H.R. Real-time noise-free inline self-interference incoherent digital holography with temporal geometric phase multiplexing. Photonics Res. 2023, 11, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Joo, K.I.; Lee, T.H.; Kim, H.R.; Yim, J.; Do, H.; Min, S.W. Compact self-interference incoherent digital holographic camera system with real-time operation. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 4818–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Hong, K.; Yeom, H.J.; Choi, K.; Park, J.; Min, S.W. Wide-viewing holographic stereogram based on self-interference incoherent digital holography. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 12760–12774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Kim, Y.; Yang, D.; Seo, W.; Kim, Y.; Hong, J.Y.; Song, H.; Sung, G.; Sung, Y.; Min, S.W.; et al. Deep learning-based incoherent holographic camera enabling acquisition of real-world holograms for holographic streaming system. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, B.; Rosen, J. Super-resolution in incoherent optical imaging using synthetic aperture with Fresnel elements. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashter, Y.; Rosen, J. Enhanced-resolution using modified configuration of Fresnel incoherent holographic recorder with synthetic aperture. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 20551–20565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.R.; Rosen, J. Resolution-enhanced imaging using interferenceless coded aperture correlation holography with sparse point response. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, J.P.; Kumar, R.; Rosen, J. Optical incoherent imaging using annular synthetic aperture with the superposition of phase-shifted optical transfer functions. Opt. Lett. 2022, 47, 4012–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Kadis, A.; Mouthaan, R.; Wetherfield, B.; Kaczorowski, A.; Wilkinson, T.D. Perceptually motivated loss functions for computer generated holographic displays. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chi, Y.; Fan, J.; Ma, C. Gradient descent with random initialization: Fast global convergence for nonconvex phase retrieval. Math. Program. 2019, 176, 5–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tian, S.; Zhang, H.; Cao, L.; Jin, G. Phase hologram optimization with bandwidth constraint strategy for speckle-free optical reconstruction. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 11645–11663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Walt, S.; Schönberger, J.L.; Nunez-Iglesias, J.; Boulogne, F.; Warner, J.D.; Yager, N.; Gouillart, E.; Yu, T. scikit-image: Image processing in Python. PeerJ 2014, 2, e453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabov, K.; Foi, A.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 2080–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtinen, J. Noise2Noise: Learning Image Restoration without Clean Data. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.04189. [Google Scholar]

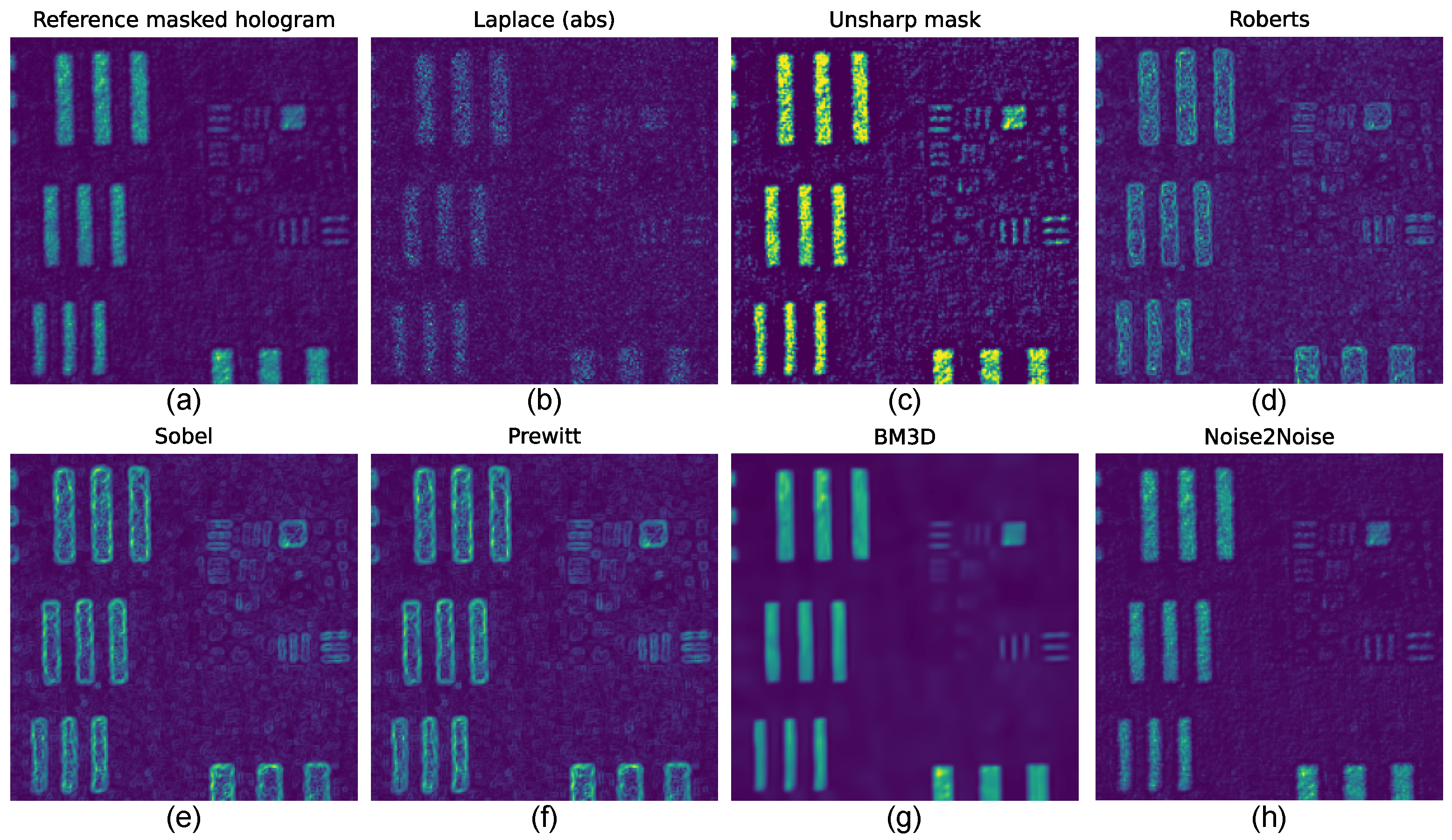
| Method | PSNR (dB) | SSIM |
|---|---|---|
| Reference masked | 18.17 | 0.11 |
| Laplace | 19.02 | 0.25 |
| Unsharp mask | 19.38 | 0.27 |
| Roberts | 20.76 | 0.37 |
| Sobel | 21.64 | 0.42 |
| Prewitt | 21.94 | 0.44 |
| BM3D | 22.29 | 0.46 |
| Noise2Noise | 20.81 | 0.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.; Choi, K.; Hong, K.; Min, S.-W. Resolution Enhancement of Geometric Phase Self-Interference Incoherent Digital Holography Using Synthetic Aperture. Photonics 2024, 11, 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11121170
Kim Y, Choi K, Hong K, Min S-W. Resolution Enhancement of Geometric Phase Self-Interference Incoherent Digital Holography Using Synthetic Aperture. Photonics. 2024; 11(12):1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11121170
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Youngrok, KiHong Choi, Keehoon Hong, and Sung-Wook Min. 2024. "Resolution Enhancement of Geometric Phase Self-Interference Incoherent Digital Holography Using Synthetic Aperture" Photonics 11, no. 12: 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11121170
APA StyleKim, Y., Choi, K., Hong, K., & Min, S.-W. (2024). Resolution Enhancement of Geometric Phase Self-Interference Incoherent Digital Holography Using Synthetic Aperture. Photonics, 11(12), 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11121170





