Magneto–Optical Properties and Applications of Magnetic Garnet
Abstract
1. Introduction
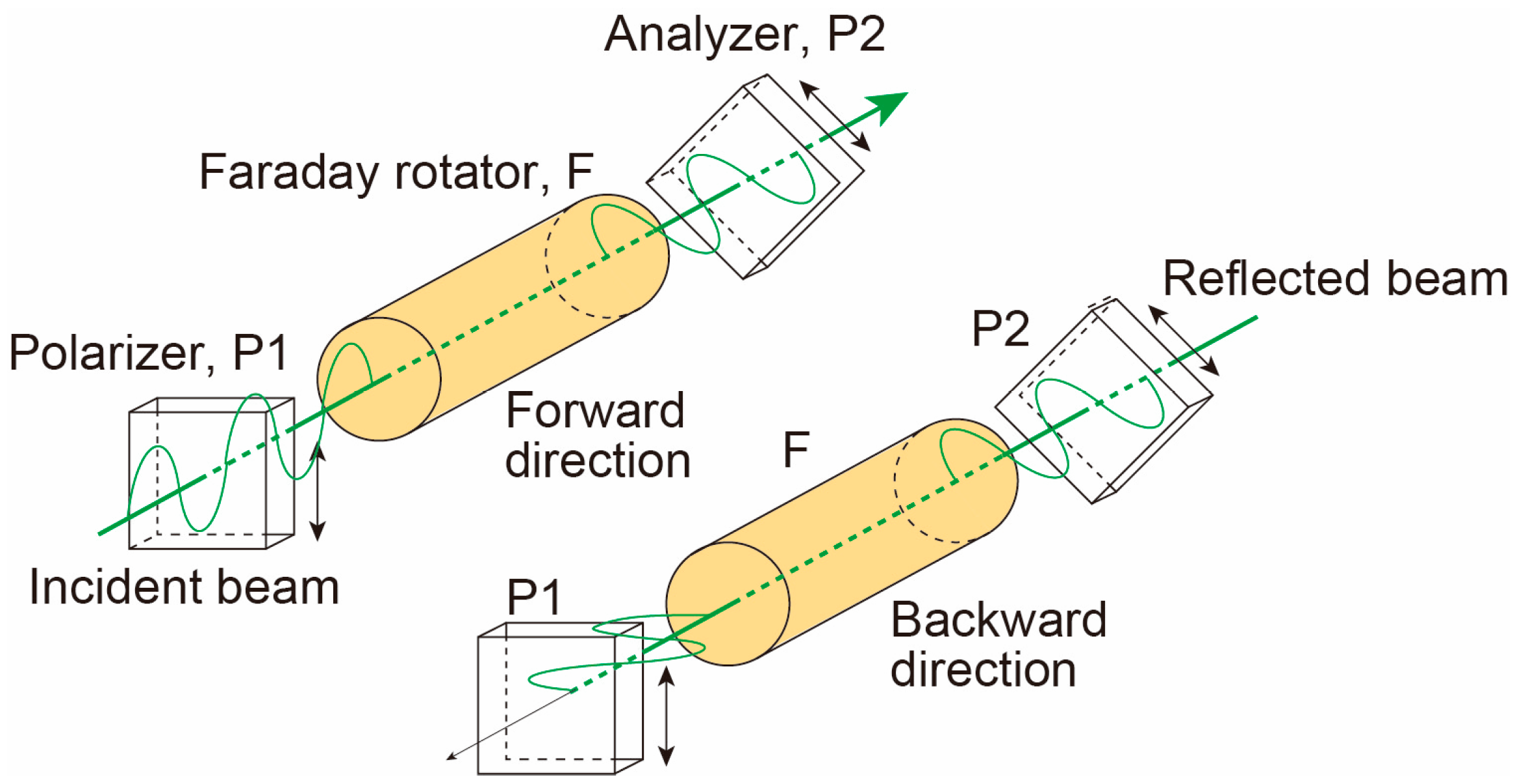
2. Magneto–Optical (Faraday) Effects
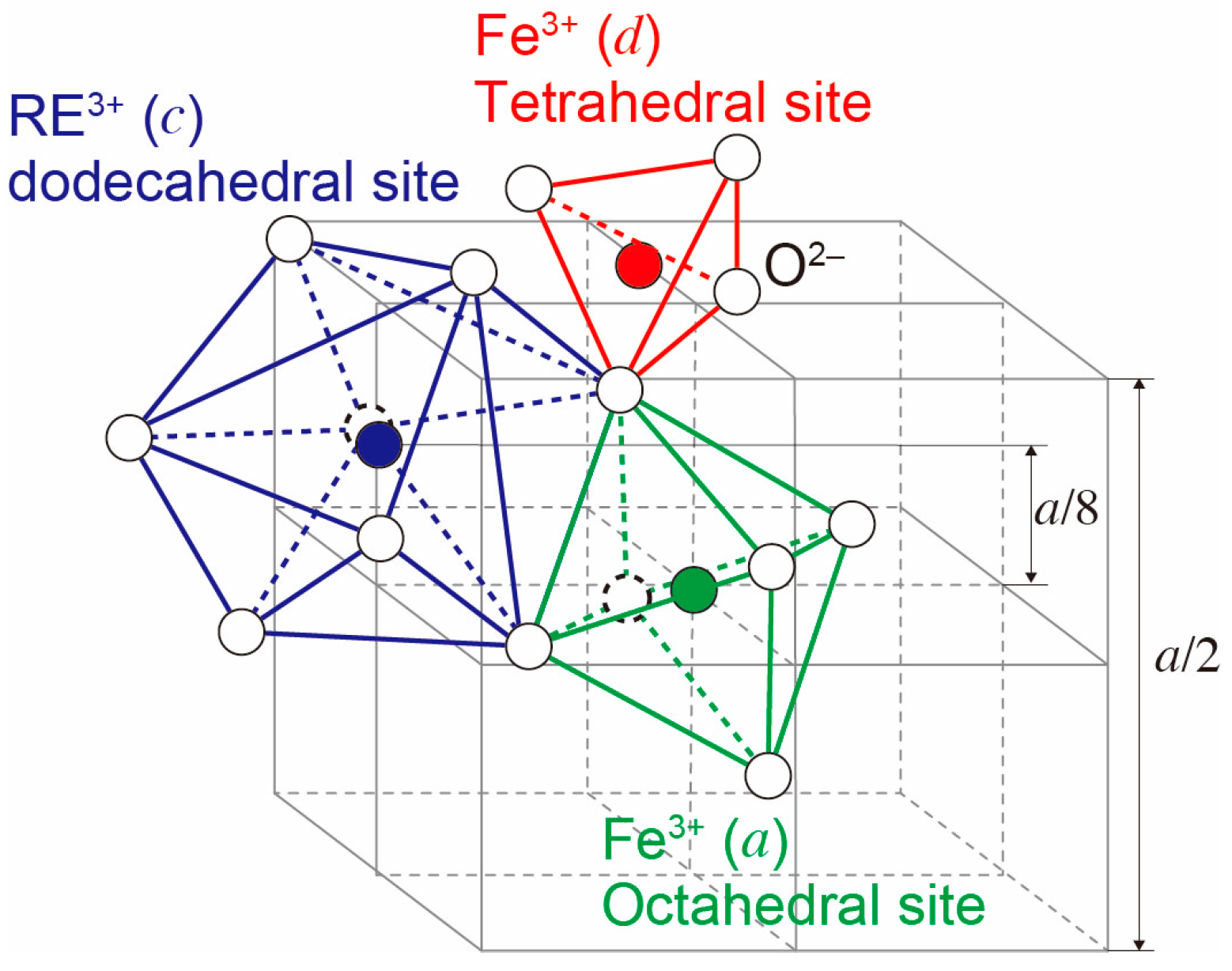
3. Rare-Earth Iron Garnets
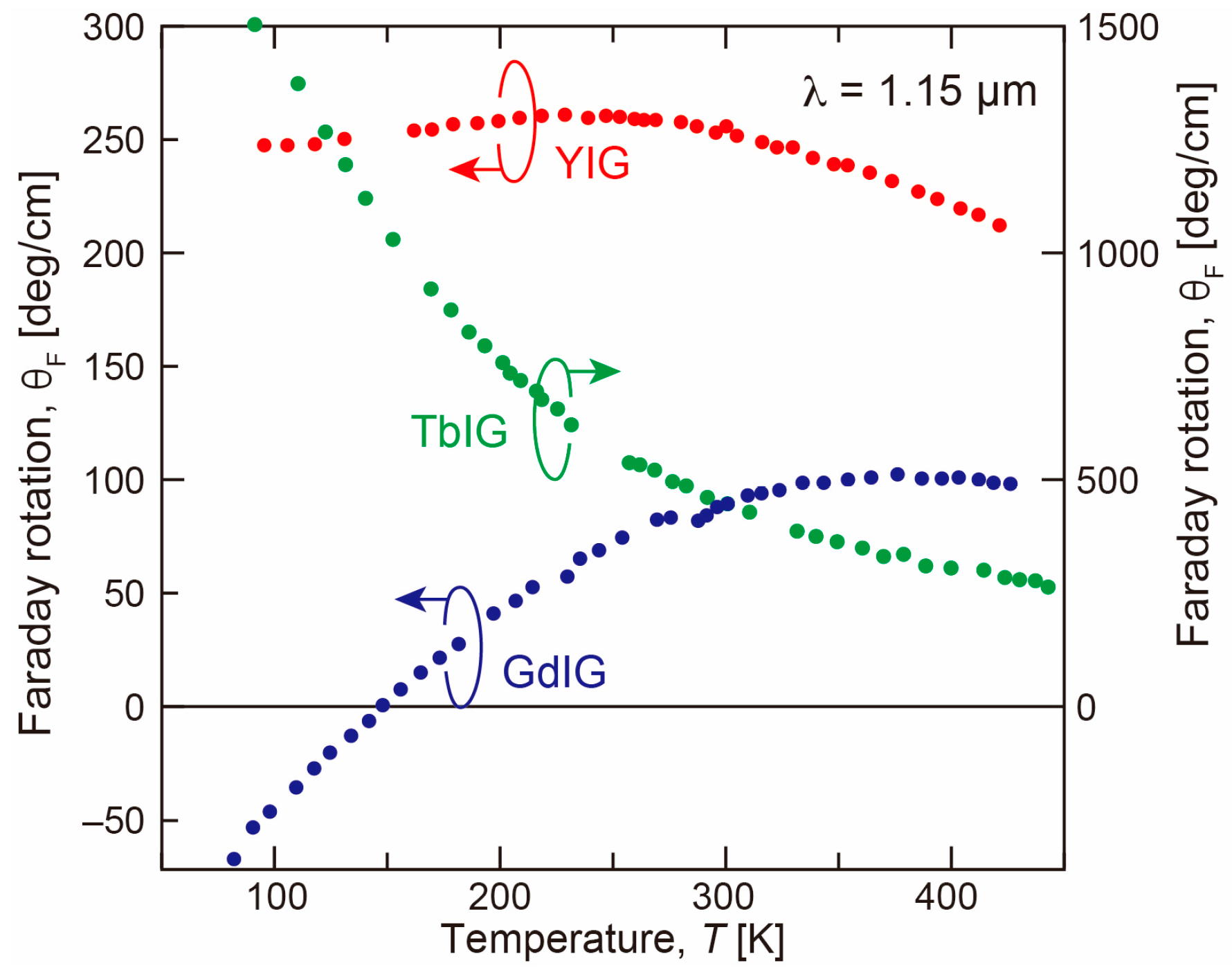
3.1. Effect of Rare-Earth Site Substitution
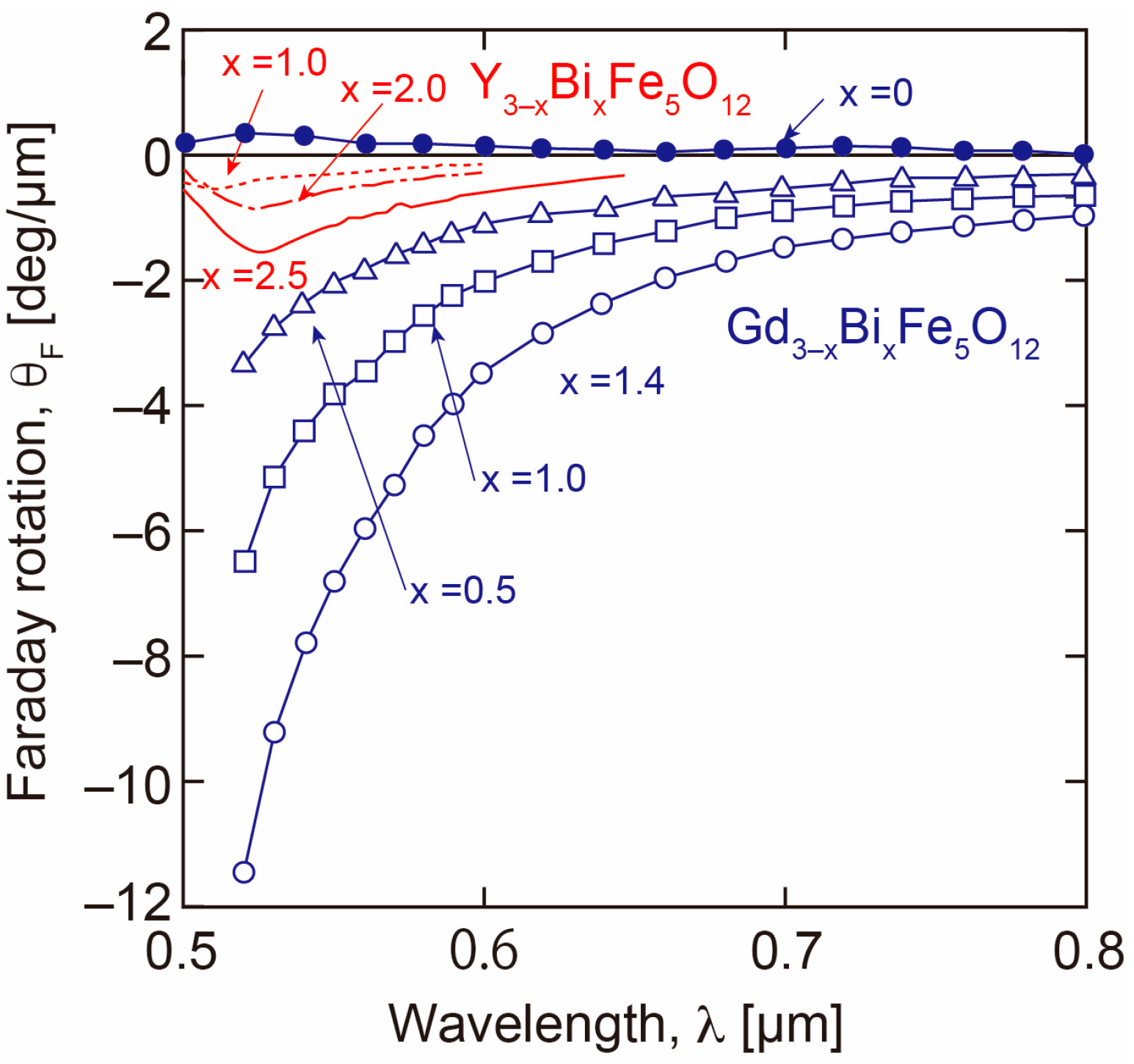
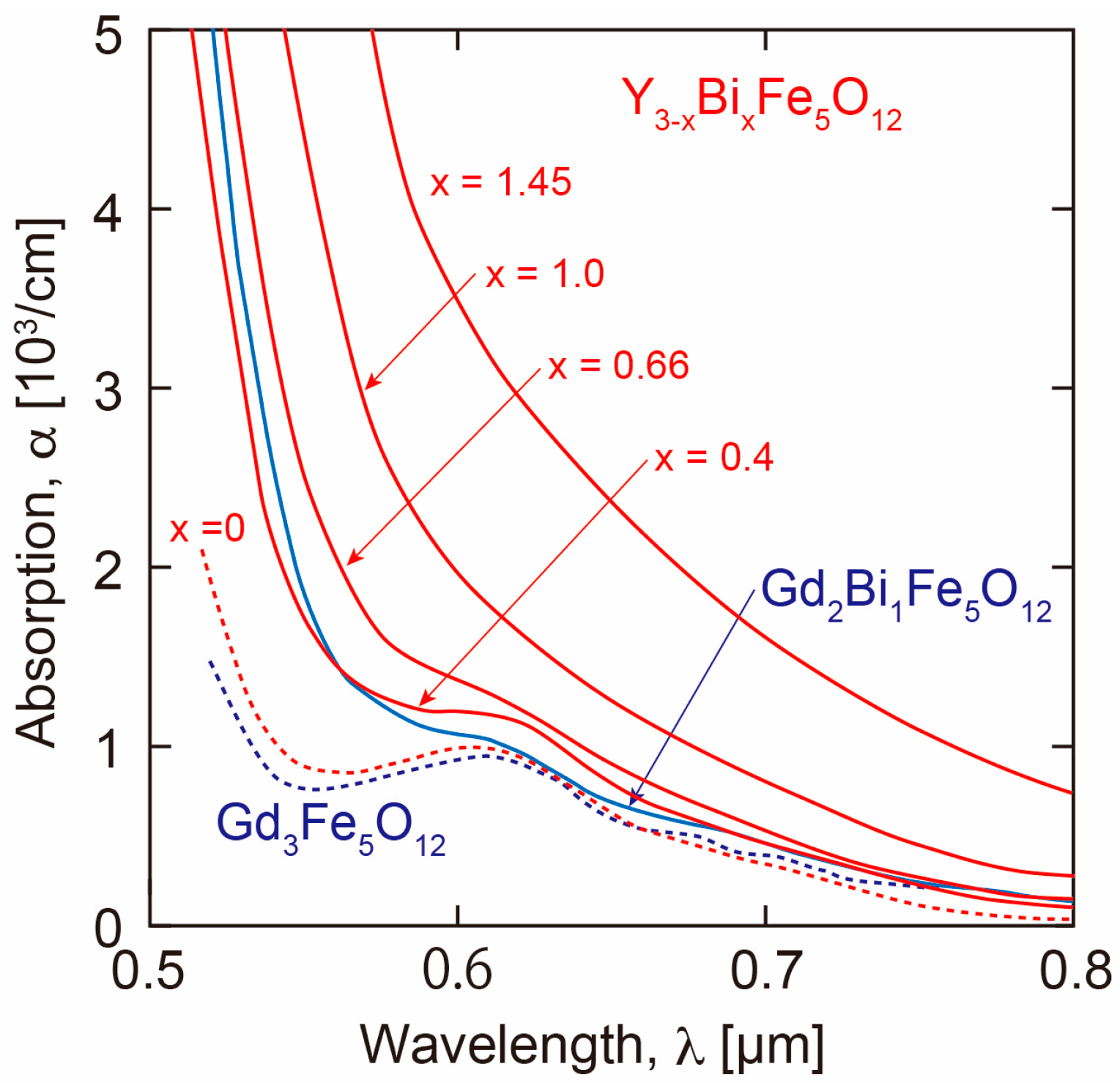
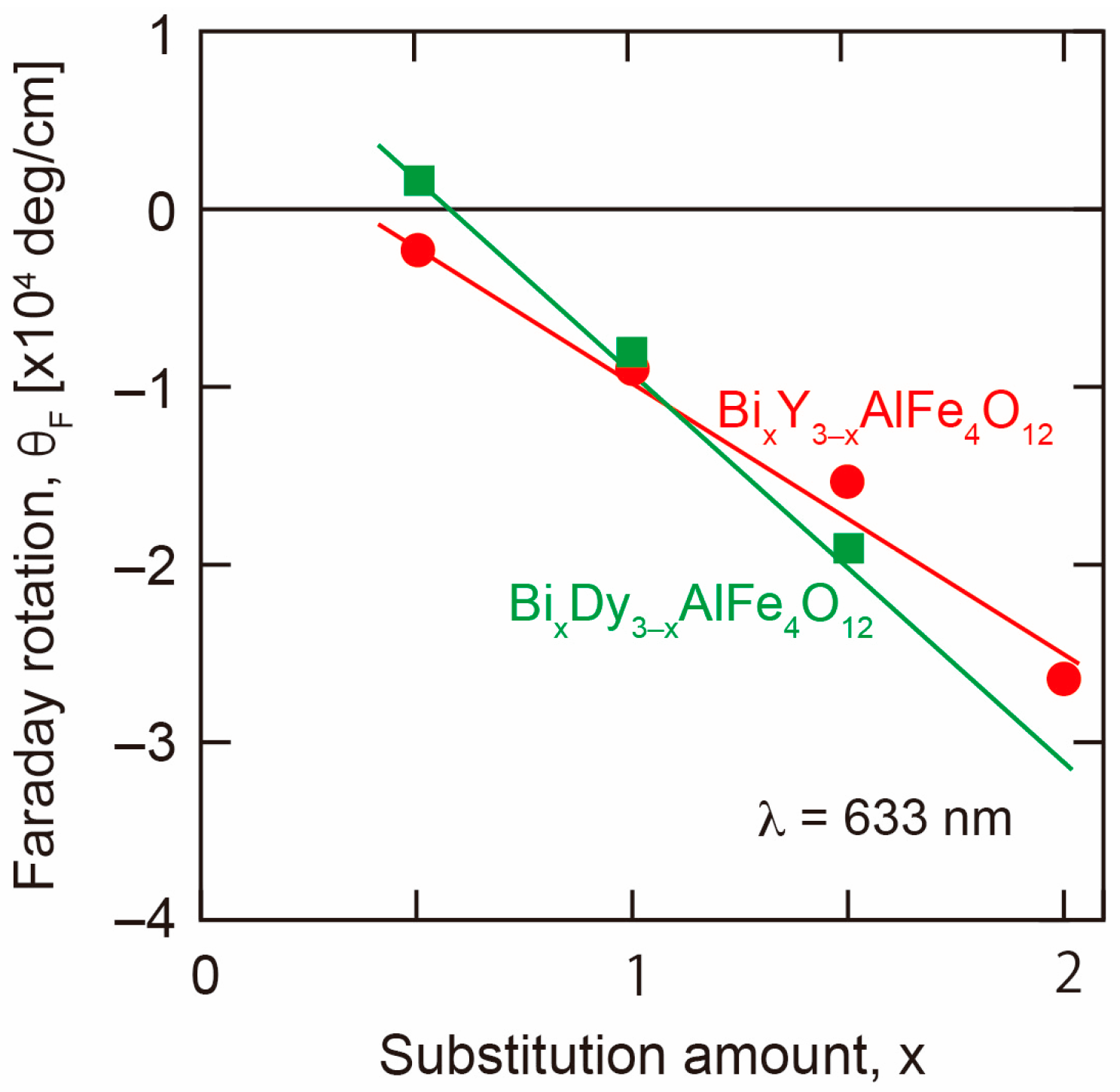
3.1.1. Bi and RE Substitution
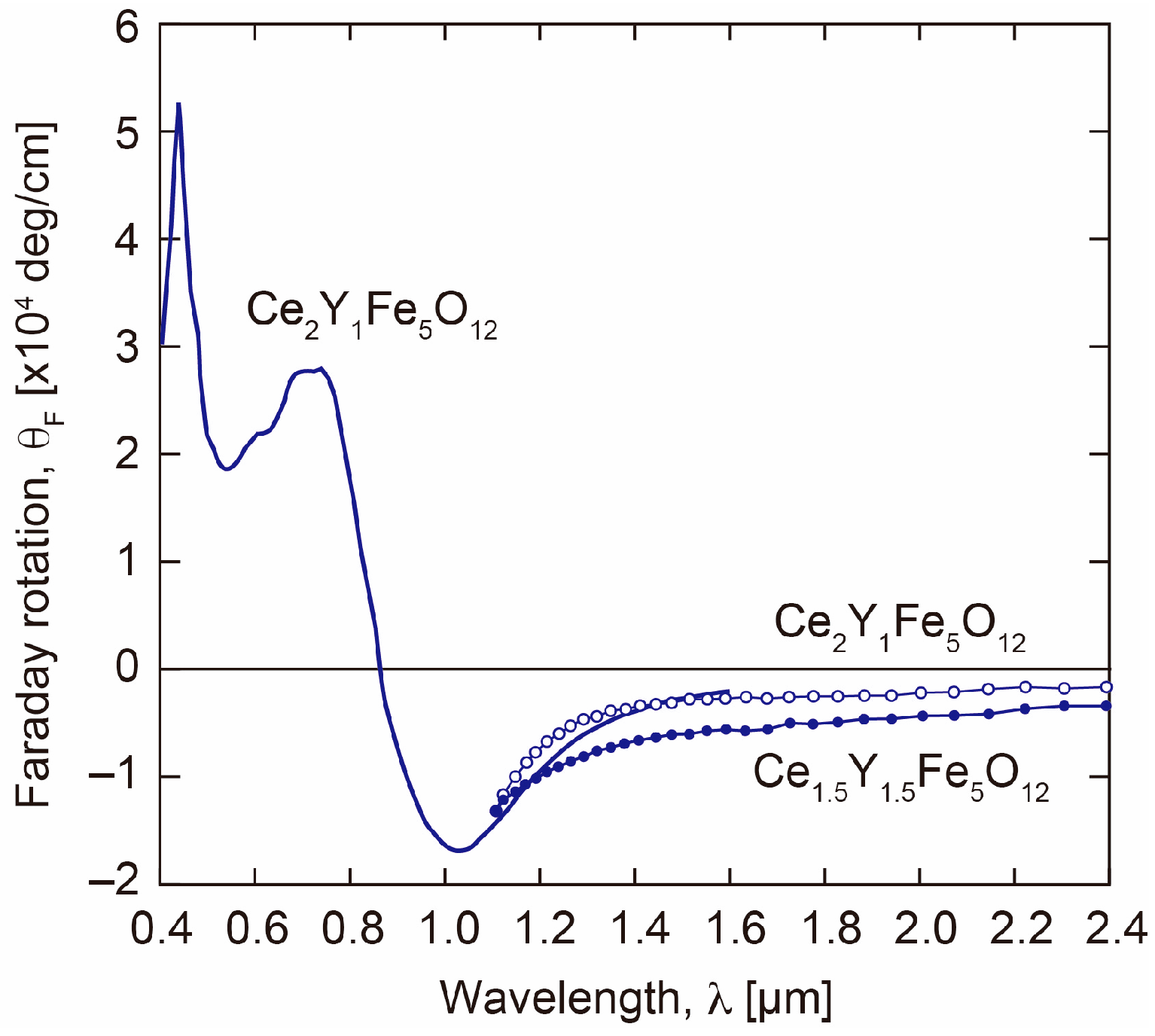
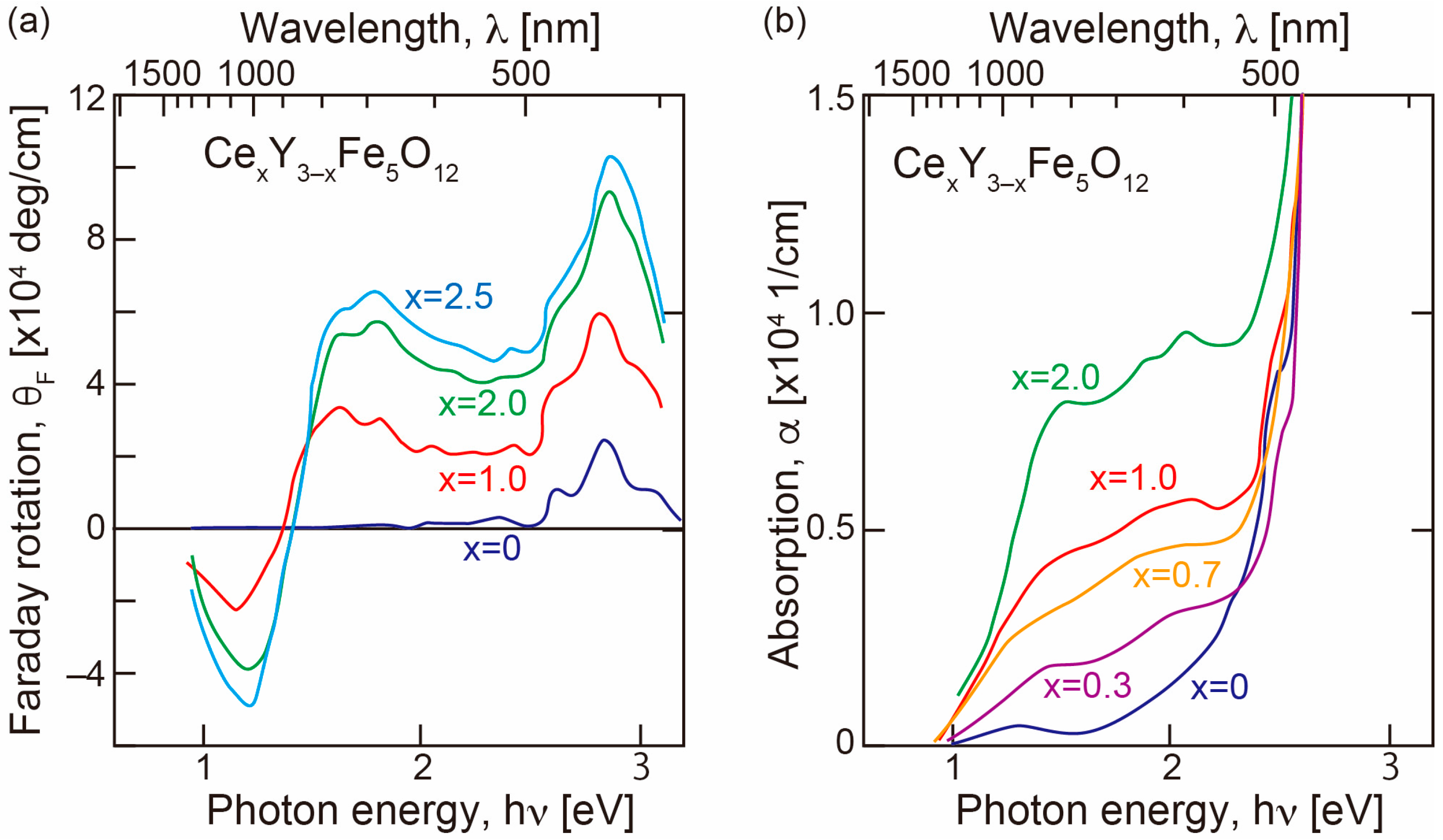
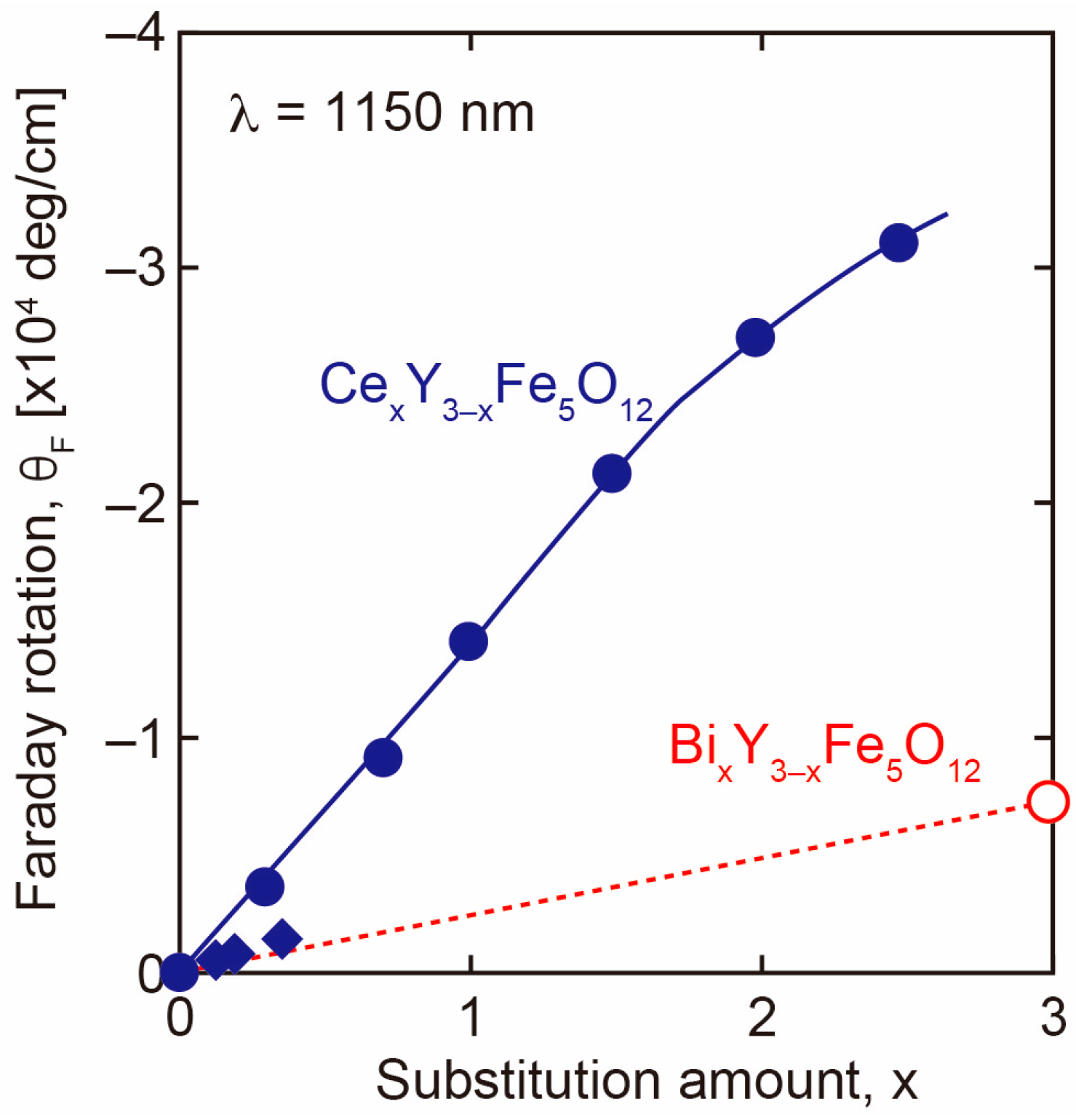
3.1.2. Effect of Ce Substitution
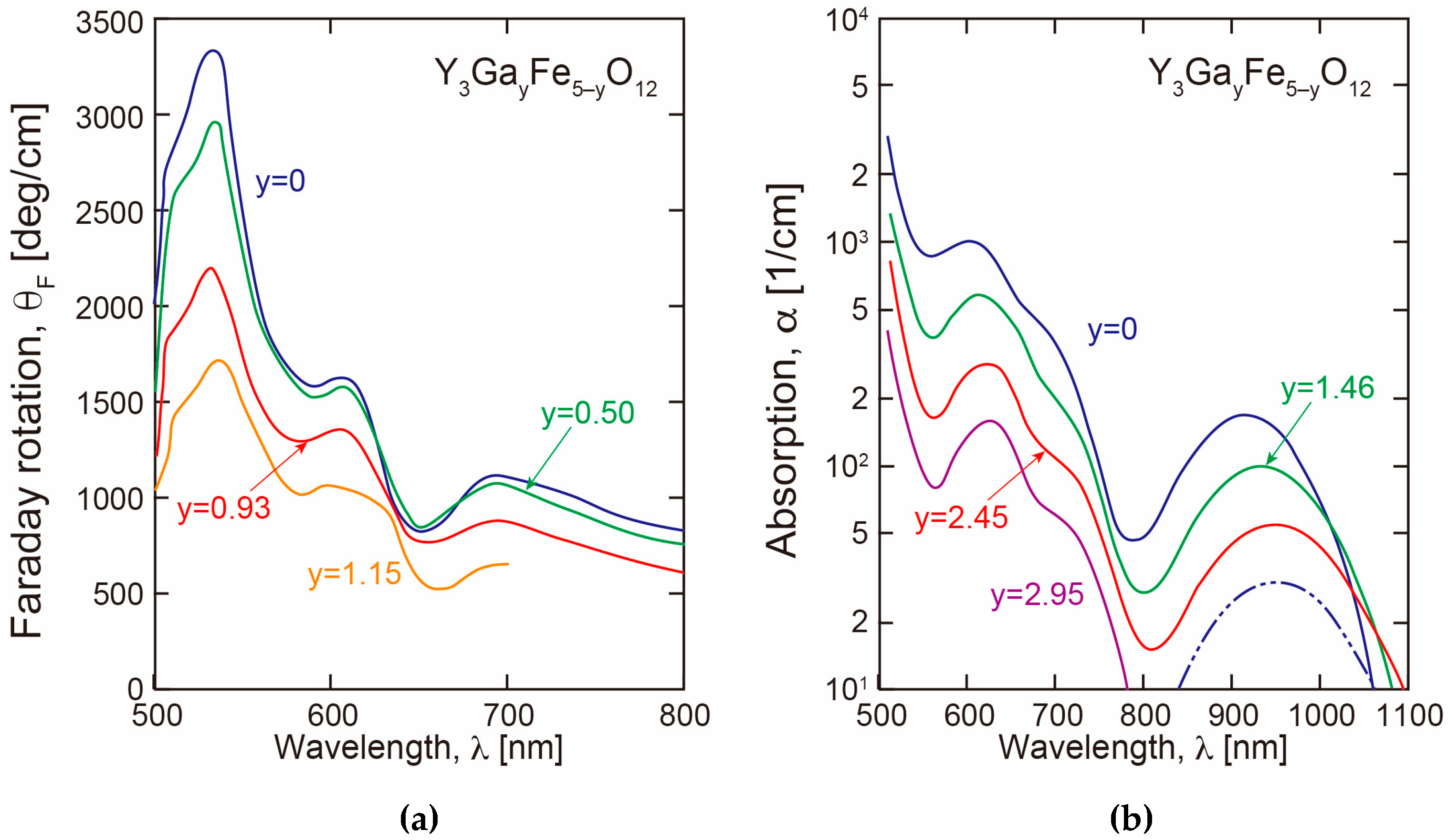
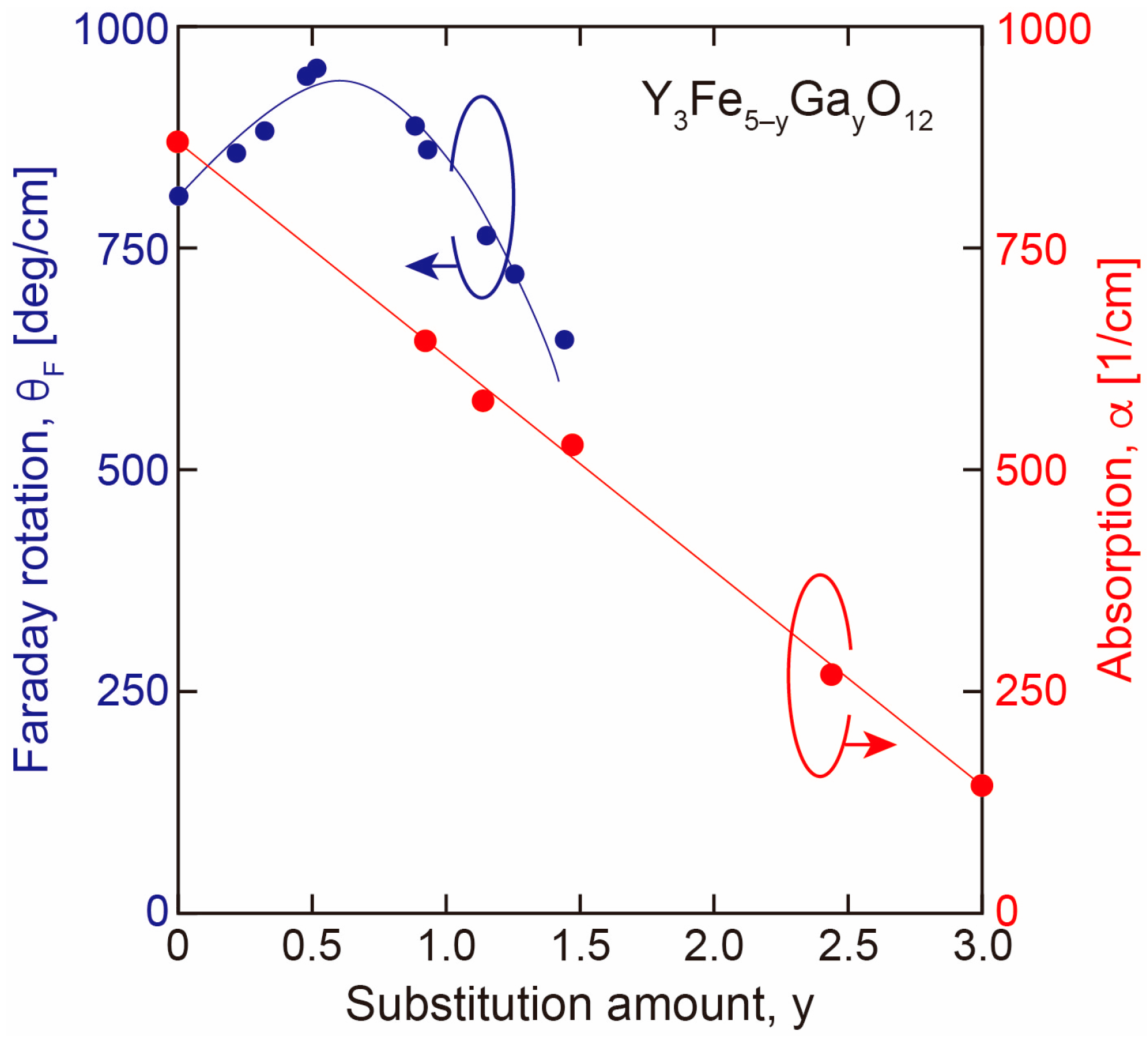
3.2. Effect of Fe Site Substitution
4. Applications
4.1. Isolator
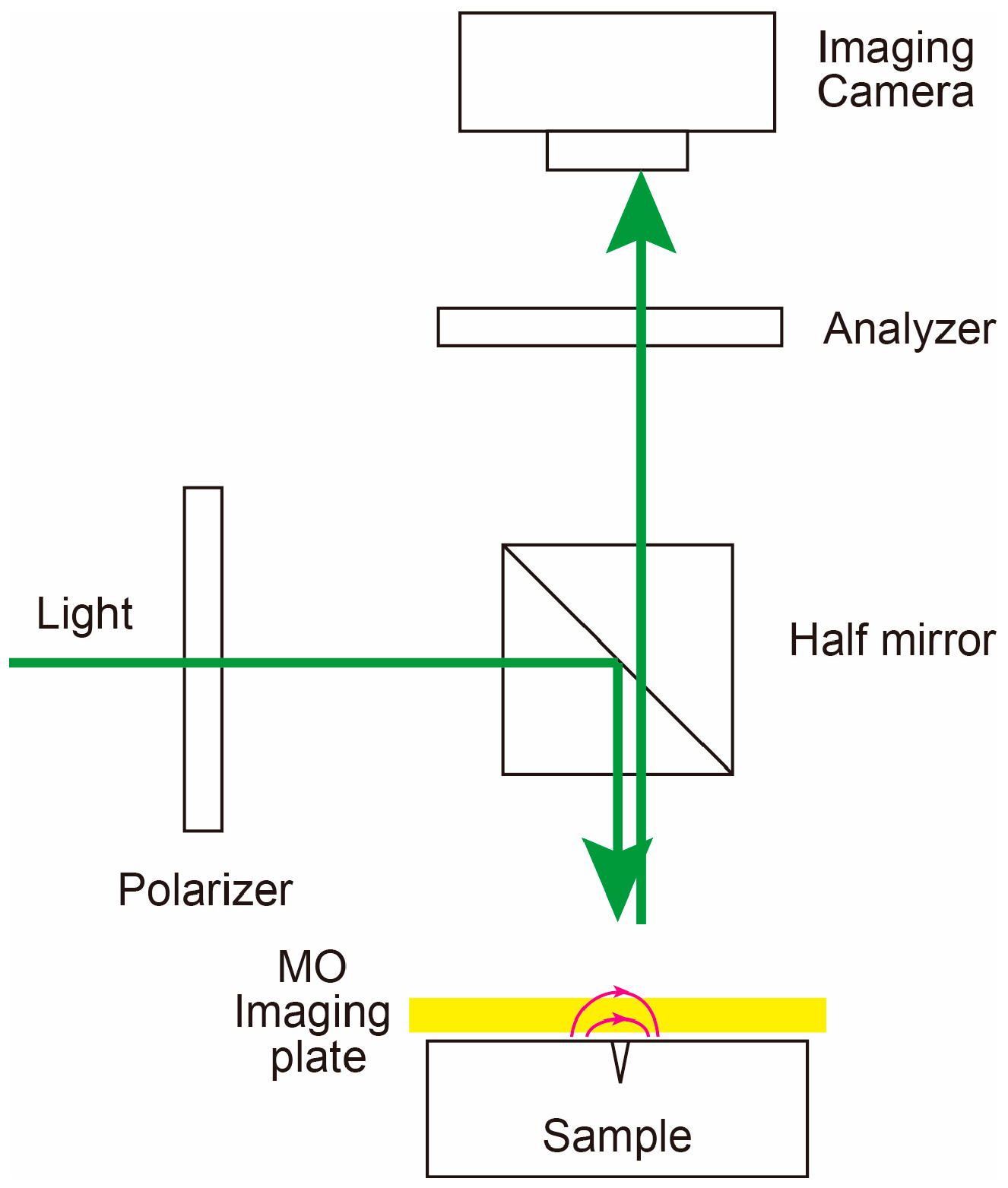
4.2. Imaging
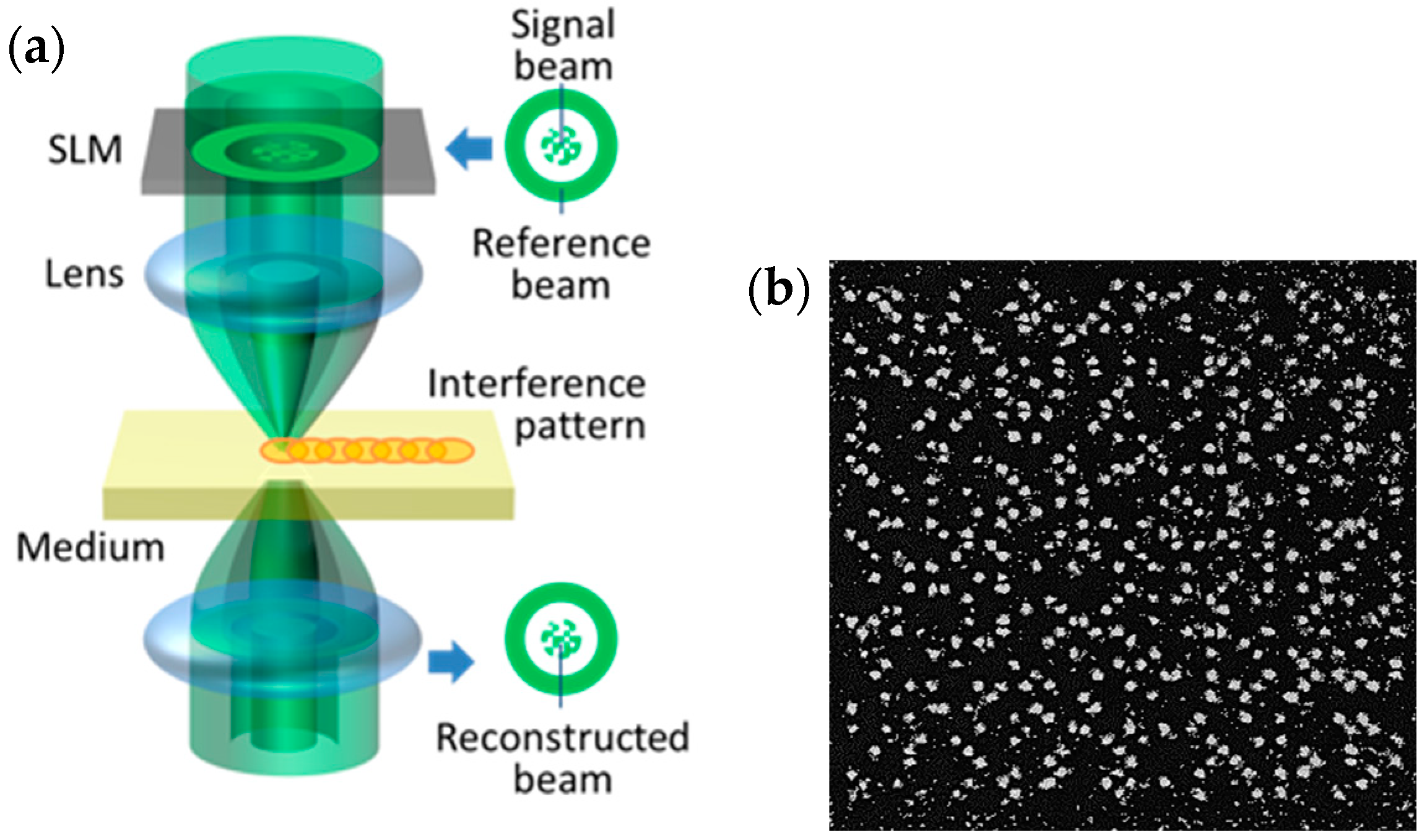
4.3. Magnetic Holography
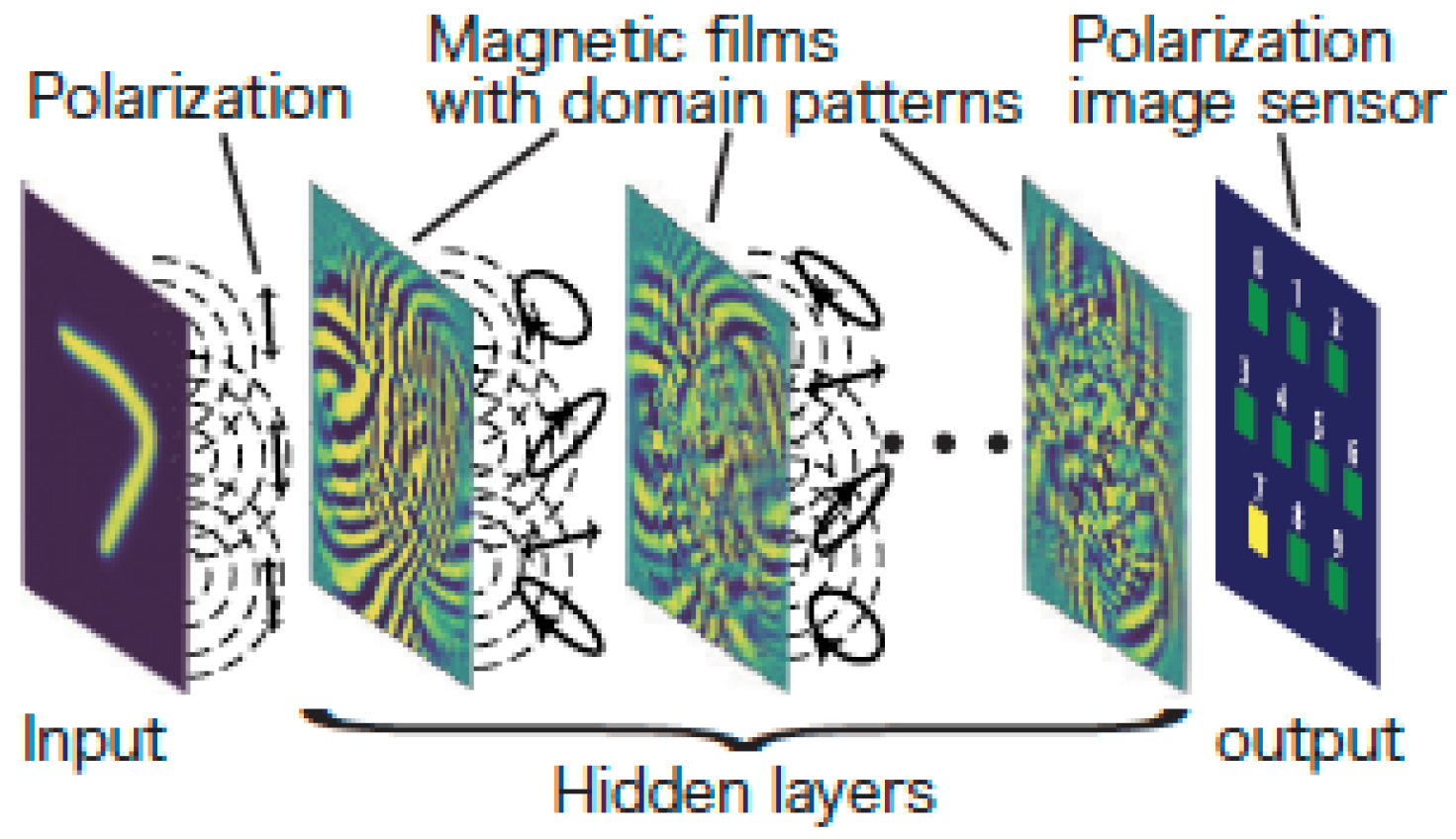
4.4. MO Neural Network
4.5. Other Applications
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shinagawa, K. Faraday and Kerr Effects in Ferromagnets. In Magneto-Optics; Sugano, S., Kojima, N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 137–178. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdi, B.M.; Goyallon, M.-L.; Bitsch, T.; Kastner, A.; Schlott, M.; Alff, L. Transparent magnetic oxide thin films of Fe3O4 on glass. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 2531–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, M.W.; Huffman, D.R. Matrix-mediated synthesis of nanocrystalline γ-Fe2O3: A New optically transparent magnetic material. Science 1992, 257, 219–222. [Google Scholar]
- Ohkoshi, S.; Namai, A.; Imoto, K.; Yoshikiyo, M.; Tarora, W.; Nakagawa, K.; Komine, M.; Miyamoto, Y.; Nasu, T.; Oka, S.; et al. Nanometer-size hard magnetic ferrite exhibiting high optical-transparency and nonlinear optical-magnetoelectric effect. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, N.; Masumoto, H.; Takahashi, S.; Maekawa, S. Optically transparent ferromagnetic nanogranular films with tunable transmittance. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, N.; Ikeda, K.; Gu, B.; Takahashi, S.; Masumoto, H.; Maekawa, S. Giant Faraday rotation in metal-fluoride nanogranular films. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, N.; Ikeda, K.; Arai, K. Giant Faraday effect of FeCo-BaF and FeCo-SiN nanogranular films. Electron. Comm. Jpn. 2021, 104, e12308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Arai, K. Large Faraday effect in nanogranular films with a high refractive index matrix. Opt. Mater. Express 2022, 12, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, H.; Endo, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Nojima, T.; Kobayashi, N.; Ohnuma, S.; Masumoto, H.; Ikeda, K. Shape effect of Co nanoparticles on the electric and magnetic properties of Co–SiO2 nanogranular films. AIP Adv. 2022, 12, 035229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Liu, T.; Ota, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Iwamoto, S. Enhanced magneto-optical effects in epsilon-near-zero indium tin oxide at telecommunication wavelengths. Adv. Optical Mater. 2024, 12, 2301320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.N.; Sulong, A.B.; Khan, M.A.; Ahmad, M.; Murtaza, G.; Raza, M.R.; Raza, R.; Saleem, M.; Kashif, M. Structural and magnetic properties of yttrium iron garnet (YIG) and yttrium aluminum iron garnet (YAIG) nanoferrites prepared by microemulsion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 401, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Song, Y.-Y.; Chang, H.; Kabatek, M.; Jantz, M.; Schneider, W.; Wu, M.; Schultheiss, H.; Hoffmann, A. Growth and ferromagnetic resonance properties of nanometer-thick yttrium iron garnet films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 152405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanjani, S.M.; Onbasli, M.C. Thin film rare earth iron garnets with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy for spintronic applications. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 035024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, V.; Serga, A.A.; Leven, B.; Hillebrands, B.; Stamps, R.L.; Kostylev, M.P. Realization of spin-wave logic gates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 022505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, N.; Goto, T.; Sekiguchi, K.; Granovsky, A.B.; Ross, C.A.; Takagi, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Inoue, M. Demonstration of a robust magnonic spin wave interferometer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, T.; Yoshimoto, T.; Iwamoto, B.; Shimada, K.; Ross, C.A.; Sekiguchi, K.; Granovsky, A.B.; Nakamura, Y.; Uchida, H.; Inoue, M. Three port logic gate using forward volume spin wave interference in a thin yttrium iron garnet film. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionne, F.D. Magnetic Oxide; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 175–184. [Google Scholar]
- Özgür, Ü.; Alivov, Y.; Morkoç, H. Microwave ferrites, part 1: Fundamental properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2009, 20, 789–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilleo, M.A.; Geller, S. Crystallographic properties of substituted yttrium-iron garnet. Phys. Rev. 1958, 110, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller, S.; Williams, H.J.; Espinosa, G.P.; Sherwood, R.C. Importance of intrasublattice magnetic interactions and of substitutional ion type in the behavior of substituted yttrium iron garnets. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1964, 42, 565–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.; Krumme, J.-P. Magnetic and magneto-optical properties of garnet films. Thin Solid Films 1984, 114, 69–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krinchik, G.S.; Chetkin, M.V. Magneto-optical properties of garnet ferrites in the infrared region. Sov. Phys. JETP 1961, 13, 509–511. [Google Scholar]
- Crossley, W.A.; Cooper, R.W.; Page, J.L. Faraday rotation in rare-earth iron garnets. Phys. Rev. 1969, 181, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, U.V.; Zvezdin, A.K.; Krinchik, G.S.; Levitin, R.Z.; Mukimov, K.M.; Popov, A.I. Faraday effect of rare-earth iron garnets in strong magnetic fields. Sov. Phys. JETP 1983, 58, 181–189. [Google Scholar]
- Booth, R.C.; White, E.A.D. Magneto-optic properties of rare earth iron garnet crystals in the wave length range 1.1–1.7 µm and their use in device fabrication. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1984, 17, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinagawa, K.; Tobita, E.; Saito, T.; Tsushima, T. Faraday effect in (Pb2+, Th4+)-substituted magnetic garnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1998, 177–181, 251–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudiar, T.; Capraro, S.; Rouiller, T.; Blanc-Mignon, M.-F.; Payet-Gervy, B.; Le Berre, M.; Rousseau, J.-J. YIG thin films for magneto-optical and microwave applications. Phys. Status Solidi C 2004, 1, 3347–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Ciubotariu, O.T.; Matthes, P.; Okano, S.; Zviagin, V.; Kalbáčová, J.; Gemming, S.; Himcinschi, C.; Grundmann, M.; Zahn, D.R.T.; et al. Optical and magneto-optical properties of pulsed laser-deposited thulium iron garnet thin films. Appl. Res. 2024, 3, e202200064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Shen, H.; Ma, Y.; Liao, S.; Xia, S.; Tian, T.; Zhou, D.; Ma, Y.; Xu, J. Growth, optical dispersion and magnetic behavior of Dy3+ doped yttrium iron garnet crystals. J. Rare Earths 2024, 42, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikesue, A.; Aung, Y.L.; Wang, J. Progress of magneto-optical ceramics. Prog. Quantum Electron. 2022, 86, 100416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, H.; Ito, S.; Mikami, I.; Taniguchi, S. Faraday rotation and optical absorption of a single crystal of bismuth-substituted gadolinium iron garnet. J. Appl. Phys. 1973, 44, 4789–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, H. The Faraday effect of bismuth substituted rare-earth iron garnet. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1975, 14, 1903–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.; Witter, K.; Tolksdorf, W. Magnetic and magneto-optic properties of lead- and bismuth-substituted properties of lead- and bismuth-substituted yttrium iron garnet films. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 27, 6608–6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratello, V.J.; Licht, S.J.; Brandle, C.D. Innovative improvements in bismuth-doped rare-earth iron garnet Faraday rotators. IEEE Trans. Mag. 1996, 32, 4102–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, T.; Kosaka, T.; Naganuma, M.; Nomura, T. Magneto-optical properties of Bi-substituted yttrium iron garnet films by metal-organic decomposition method. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2010, 200, 112002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Oishi, K.; Nishi, T.; Ishibashi, T. Nd3−xBixFe4GaO12 (x = 2, 2.5) films on glass substrates prepared by MOD method. EPJ Web Conf. 2014, 75, 05009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongquoc, V.; Kuchi, R.; Van, P.C.; Yoon, S.-G.; Jeong, J.-R. Effects of heating rate on the magneto-optical properties of bismuth-substituted yttrium iron garnet films prepared via modified metal-organic decomposition. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2018, 18, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Syvorotka, I.; Wang, F.; Yang, S.; Wen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Q. Giant reduced magnetic anisotropy in magneto-optical garnet. Results Phys. 2024, 60, 107625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, M.Y.; Lo, F.-Y.; Liu, D.-R.; Yang, K.; Liaw, J.-S. Red shift of Faraday rotation in thin films of completely bismuth-substituted iron garnet Bi3Fe5O12. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 38, 6687–6689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, A.; Leitenmeier, S.; Kömer, T.; Lux, R.; Herbort, M.; Strtzker, B. Pulsed laser deposition and growth studies of Bi3Fe5O12 on Gd3Ga5O12 and SiO2. J. Magn. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 30, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vertruyen, B.; Cloots, R.; Abell, J.S.; Jackson, T.J.; Silva, R.C.; Popova, E.; Keller, N. Curie temperature, exchange integrals, and magneto-optical properties in off-stoichiometric bismuth iron garnet epitaxial films. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 094429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahl, S.; Grishin, A.M. Pulsed laser deposition of Y3Fe5O12 and Bi3Fe5O12 films on garnet substrates. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 6945–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J. Fabrication of Bismuth- and aluminum-substituted dysprosium iron garnet films for magneto-optic recording by pyrolysis and their magnetic and magneto-optic properties. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 1995, 1, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Musa, M.A.; Azis, R.S.; Osman, N.H.; Hassan, J.; Zangina, T. Structural and Magnetic Properties of Yttrium Iron Garnet (YIG) and Yttrium Aluminum Iron Garnet (YAlG) Nanoferrite via Sol-Gel Synthesis. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohaidat, Q.I.; Lataifeh, M.; Hamasha, K.; Mahmood, S.H.; Bsoul, I.; Awawdeh, M. The structural and the magnetic properties of aluminum substituted yttrium iron garnet. Mater. Res. 2018, 21, e20170808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borade, R.B.; Kadam, S.B.; Wagare, D.S.; Kadam, R.H.; Shirsath, S.E.; Nimbore, S.R.; Kadam, A.B. Fabrication of Bi3+ substituted yttrium aluminum iron garnet (YAIG) nanoparticles and their structural, magnetic, optical and electrical nvestigations. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electro. 2019, 30, 19782–19791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, F.; Ru, Z.; Xiang, F.; Sun, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. In-plane magnetic properties and anisotropy of scandium substituted thulium iron garnet thin films for fluxgate magnetometer. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2024, 598, 171993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffler, D.; Steuer, O.; Zhou, S.; Siegl, L.; Goennenwein, S.T.B.; Lammel, M. Aluminium substituted yttrium iron garnet thin films with reduced Curie temperature. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2023, 7, 094405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, L.R.F.; Guerra, Y.; Padrón-Hernández, E.; Rodrigues, A.R.; Santos, F.E.P.; Peña-Garcia, R. Structural and Magnetic Properties of Yttrium Iron Garnet Nanoparticles Doped with Copper Obtained by Sol Gel Method. Mater. Lett. 2019, 236, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Li, Z. Study on the Structure, Magnetic Properties and Mechanism of Zn-Doped Yttrium Iron Garnet Nanomaterial Prepared by the Sol-Gel Method. Gels 2022, 8, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.; Witter, K. Magneto-optical properties of gallium-substituted yttrium iron garnets. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 27, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidoh, H.; Yashima, H.; Morimoto, A.; Shimizu, T. Magneto-optical characteristics of Bi-substituted rare-earth iron garnet films prepared by laser ablation. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 3, 4094–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Nanpei, S.; Inoue, M.; Arai, K.I. Preparation of high bismuth and gallium substituted yttrium iron garnet films by coating gel on glass substrates. J. Magn. Soc. Jpn. 1998, 22, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, M.; Lou, G.; Liu, Q.; Ninomiya, M.; Kato, T.; Iwata, S.; Ishibashi, T. Nd0.5Bi2.5Fe5−yGayO12 thin films on Gd3Ga5O12 substrates prepared by metal–organic decomposition. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 55, 055501. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.I.; Waqas, M.; Naeem, M.A.; Hasan, M.S.; Iqbal, M.; Mahmood, A.; Ramay, S.M.; Al-Masry, W.; Abubshait, S.A.; Abubshait, H.A.; et al. Magnetic Behavior of Ga Doped Yttrium Iron Garnet Ferrite Thin Films Deposited by Sol-Gel Technique. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 27318–27325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.S.; Khan, M.I.; Ali, S.S.; Brahmia, A.; Ihtisham-ul-Haq. Influence of Gallium on Structural, Optical and Magnetic Properties of Bi-YIG Thin Films. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2024, 301, 117180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.M.; Wittekoek, S.; Popma Th, J.A.; Bongers, P.F. Preparation and Optical Properties of Single Crystal Thin Films of Bismuth Substituted Iron Garnets for Magneto-Optic Applications. Appl. Phys. 1973, 2, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, G.B.; Lacklison, D.E. Magnetooptic properties and applications of bismuth substituted iron garnets. IEEE Trans Mag. 1976, 12, 292–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.; Witter, K.; Tolksdorf, W. Magnetic and magneto-optical properties of bismuth-substituted magneto-optical properties of bismuth-substituted gadolinium iron garnet films. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 27, 4375–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomi, M.; Tanida, T.; Abe, M. rf sputtering of highly Bi-substituted garnet films on glass substrates for magneto-optic memory. J. Appl. Phys. 1985, 57, 3888–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Koshizuka, N.; Hayashi, K.; Takahashi, T.; Kotani, H.; Yamamoto, H. Epitaxial growth of Bi-substituted yttrium iron garnet films by ion beam sputtering. J. Magn. Soc. Jpn. 1987, 11, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Koshizuka, N.; Hayashi, K.; Takahashi, T.; Kobani, H.; Yamamoto, H. Faraday rotation in highly Bi-substituted yttrium iron garnet films prepared by ion beam sputtering. IEEE Trans. Mag. 1987, 23, 3491–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezawa, M.; Yokoyama, Y.; Koshizuka, N. Temperature dependence of Faraday rotation in Bi-substituted terbium iron garnet films. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 63, 3113–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Katayama, S.; Tominaga, K. Preparation and magneto-optic properties of Bi-substituted yttrium iron garnet thin films by metalorganic chemical vapor deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 69, 3566–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvorotka, I.M.; Ubizskii, S.B.; Kucera, M.; Kuhn, M.; Vértesy, Z. Growth and characterization of Bi, Pr-and Bi, Sc-substituted lutetium iron garnet films with planar magnetization for magneto-optic visualization. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2001, 34, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huanga, M.; Xu, Z.-C. Liquid phase epitaxy growth of bismuth-substituted yttrium iron garnet thin films for magneto-optical applications. Thin Solid Films 2004, 450, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistora, I.; Holthaus, C.; Mayergoyz, I.D.; Krafft, C. Development of liquid phase epitaxy-grown (Bi, Gd, Lu)-substituted thin-film iron garnets. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 08M702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongquoc, V.; Thi, T.N.; Van, P.C.; Viet, D.C.; Ahn, H.-Y.; Kim, E.-T.; Park, S.-Y.; Jeong, J.-R. Enhancing the magnetic and magneto-optical properties of praseodymium-substituted Bi-YIG thin film on glass substrate prepared by metal-organic decomposition. J. Magn. 2021, 26, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urakawa, R.; Asano, W.; Nishikawa, M.; Kawahara, M.; Nishi, T.; Oshima, D.; Kato, T.; Ishibashi, T. Magneto-optical property and magnetic anisotropy of (100) oriented R0.5Bi2.5Fe5O12 (R = Eu, Sm, and Pr) thin films prepared by metal–organic decomposition. AIP Adv. 2022, 12, 095322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhara, M.C.; Singh, M.R. Fabrication and characterization of Bismuth-Cerium composite iron garnet epitaxial films for magneto optical applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 083525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomi, M.; Furuyama, H.; Abe, M. Strong magneto-ooptical enhancement in highly Ce-substituted iron garnet films prepared by sputtering. J. Apply. Phys. 1991, 91, 7065–7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintaku, T.; Tate, A.; Mino, S. Ce-substituted yttrium iron garnet films prepared n Gd3Sc2Ga3O12 garnet substrates by sputter epitaxy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1997, 71, 1640–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhang, S.-Y. Growth and characterization of cerium-substituted yttrium iron garnet single crystals for magneto-optical applications. Appl. Phys. A 2002, 74, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, M.C.; Hwang, J.-Y.; Ferrera, M.; Linzon, Y.; Razzari, L.; Harnagea, C.; Zaezjev, M.; Pignolet, A.; Morandotti, R. Strong enhancement of the Faraday rotation in Ce and Bi commodified epitaxial iron garnet thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 181916. [Google Scholar]
- Goto, T.; Onbaşh, M.C.; Ross, C.A. Magneto-optical properties of cerium substituted yttrium iron garnet films with reduced thermal budget for monolithic photonic integrated circuits. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 28507–28517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onbasli, M.C.; Beran, L.; Zahradník, M.; Kučera, M.; Antoš, R.; Mistrík, J.; Dionne, G.F.; Veis, M.; Ross, C.A. Optical and magneto-optical behavior of cerium yttrium iron garnet thin films at wavelengths of 200–1770 nm. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, E.; Beran, L.; Quindeau, A.U.; Ohnoutek, L.; Kucera, M.; Antos, R.; Sani, S.R.; Dionne, G.F.; Veis, M.; Ross, C.A. Temperature-dependent Faraday rotation and magnetization reorientation in cerium-substituted yttrium iron garnet thin films. APL Mater. 2017, 5, 036104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.T.; Liang, X.; Peng, B.; Lu, H.P.; Zhou, P.H.; Zhang, L.; Xie, J.X.; Deng, L.J.; Zahradnik, M.; et al. Enhanced magneto-optical effect in Y1.5Ce1.5Fe5O12 thin films deposited on silicon by pulsed laser deposition. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 703, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhrul, T.; Tazlaru, S.; Khurana, B.; Beran, L.; Bauer, J.; Vančík, M.; Marchese, A.; Tsotsos, E.; Kučera, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. High figure of merit magneto-optical Ce- and Bi-substituted terbium iron garnet films integrated on Si. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2021, 9, 2100512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, Y.; Ishiyama, K.; Watanabe, T.; Lim, P.B.; Ross, C.A.; Goto, T.; Inoue, M. Growth of magnetooptical cerium-substituted yttrium iron garnet on yttrium aluminum garnet using ion beam sputtering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023, 123, 112404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minemoto, H.; Kamada, O.; Matsuda, K.; Ishizuka, S. Improvement of temperature dependence of Faraday rotation using two layer epitaxial films in (biR)IG for optical isolators. J. Mag. Soc. Jpn. 1987, 11, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Chen, J.; Tian, Y.; Shen, S.; Yanga, X.; Zhou, S.; Liu, J.; He, Z.; Yu, T.; Wang, Z.; et al. Characteristics of Y3Fe5O12 ceramic at mid-infrared wavelengths and its Faraday isolator application. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 181, 111829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, Y.; Mizumoto, T. Magneto-optical non-reciprocal devices in silicon photonics. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2014, 15, 014602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.Y.; Du, Q.; Goto, T.; Onbasli, M.C.; Kim, D.H.; Aimon, N.M.; Hu, J.; Ross, C.A. Single-step deposition of cerium-substituted yttrium iron garnet for monolithic on-chip optical isolation. ACS Photonics 2015, 2, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, Y.; Mizumoto, T. Silicon Waveguide Optical Isolator with Directly Bonded Magneto-Optical Garnet. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Du, Q.; Wnag, C.; Fakhrul, T.; Liu, S.; Deng, L.; Huang, D.; Pintus, P.; Bowers, J.; Ross, C.A.; et al. Monolithic integration of broadband optical isolators for polarization-diverse silicon photonics. Optica 2019, 6, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, S.; Kang, T.; Yang, W.; Qin, J.; Deng, L.; Bi, L. Waveguide-integrated high-performance magneto-optical isolators and circulators on silicon nitride platforms. Optica 2020, 7, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saker, K.; Lahoubi, M.; Pu, S. Optimized magneto-optical isolator design based on cerium-substituted yttrium iron garnet fiber. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2021, 53, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yan, W.; Qin, J.; Deng, L.; Bi, L. Dysprosium substituted Ce:YIG thin films for temperature insensitive integrated optical isolator applications. Materials 2022, 15, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shoji, Y.; Mizumoto, T. TE-mode magneto-optical isolator based on an asymmetric microring resonator under a unidirectional magnetic field. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 9934–9943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minemura, D.; Kou, R.; Sutoh, Y.; Murai, T.; Yamada, K.; Shoji, Y. Compact magneto-optical isolator by μ-transfer printing of magneto-optical single-crystal film on silicon waveguides. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 27821–27829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, K.; Stadler, B.J.H. Review of integrated magneto-optical isolators with rare-earth iron garnets for polarization diverse and magnet-free isolation in silicon photonics. Opt. Mater. Express 2022, 12, 697–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoh, S.; Koshizuka, N.; Yoshida, M.; Murakami, M.; Tanaka, S. Direct observation of flux behavior in high-Tc oxide superconductors using the Faraday effect of iron garnet films. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 29, L1083–L1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görnert, P.; Aichele, T.; Lorenz, A.; Hergt, R.; Taubert, J. Liquid phase epitaxy (LPE) grown Bi, Ga, Al substituted iron garnets with huge Faraday rotation for magneto-optic applications. Phys. Stat. Sol. 2004, 201, 1398–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, T.; Lou, G.; Meguro, A.; Hashinaka, T.; Sasaki, M.; Nishi, T. Liquid phase epitaxy (LPE) grown Bi, Ga, Al substituted iron garnets with huge Faraday rotation for magneto-optic applications. Sens. Mater. 2015, 27, 965–970. [Google Scholar]
- Galstyan, O.; Lee, H.; Babajanyan, A.; Hakhoumian, A.; Friedman, B.; Lee, K. Magneto-optical visualization by Bi:YIG thin films prepared at low temperatures. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 163914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagakubo, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Meguro, S.; Nishikawa, M.; Ishibashi, T. Magneto-optical imaging plate with backlight for quantitative measurement of magnetic field distribution. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 57, 09TC02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, T. Magneto-optical imaging using bismuth-substituted iron garnet films prepared by metal-organic decomposition. J. Mag. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 44, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagakubo, Y.; Baba, Y.; Liu, Q.; Low, G.; Ishibashi, T. Development of MO imaging plate for MO color imaging. J. Mag. Soc. Jpn. 2017, 41, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, G.; Yoshida, T.; Ishibashi, T. Magneto-optical properties of Nd0.5Bi2.5Fe4GaO12 thin films on glass substrates with various thicknesses prepared using metal-organic decomposition. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 17A749. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, H.; Yonezawa, T.; Takagi, H.; Goto, T.; Endo, H.; Nishimizu, A.; Inoue, M. Defect depth estimation using magneto optical imaging with magnetophotonic crystal. J. Mag. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 39, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Song, Y.; Ye, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Gao, X. Magneto-optical imaging detection and reconstruction of complex-shaped weld defects. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1986, 012050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xu, G.; He, J.; Cheng, Y.; Dong, W.; Ma, L. Research on rail crack detection technology based on magneto-optical imaging principle. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2196, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, R.; Itaya, T.; Uchida, H.; Funaki, Y.; Fukuchi, S. Properties of magnetic garnet films for flexible magneto-optical indicators fabricated by spin-coating Method. Materials 2022, 15, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharmawan, I.D.M.O.; Lee, J.; Sim, S. Defect shape classification using transfer learning in deep convolutional neural network on magneto-optical nondestructive inspection. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, H.; Oya, R.; Wada, S.; Matsumura, T.; Saito, H.; Ishibashi, T. 3D magnetic field vector measurement by magneto-optical imaging. J. Mag. Soc. Jpn. 2022, 46, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y. Magnetic holography and its application to data storage. Photonics 2021, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Takagi, H.; Lim, P.B.; Inoue, M. Magnetic volumetric hologram memory with magnetic garnet. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 16439–16444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Takagi, H.; Lim, P.B.; Inoue, M. Effect of recording condition on the diffraction efficiency of magnetic hologram with magnetic garnet films. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 10316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isogai, R.; Suzuki, S.; Nakamura, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Takagi, H.; Goto, T.; Lim, P.B.; Inoue, M. Collinear volumetric magnetic holography with magnetophotonic microcavities. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 13153–13158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isogai, R.; Nakamura, Y.; Takagi, H.; Goto, T.; Lim, P.B.; Inoue, M. Thermomagnetic writing into magnetophotonic microcavities controlling thermal diffusion for volumetric magnetic holography. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Shirakashi, Z.; Takagi, H.; Goto, T.; Lim, P.B.; Uchida, H.; Inoue, M. Error-free reconstruction of magnetic hologram via improvement of recording conditions in collinear optical system. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 15349–15357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakashi, Z.; Goto, T.; Takagi, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Lim, P.B.; Uchida, H.; Inoue, M. Reconstruction of non-error magnetic hologram data by magnetic assist recording. Sci. Rep. 2019, 7, 12835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Lim, P.B.; Goto, T.; Uchida, H.; Inoue, M. Development of heat dissipation multilayer media for volumetric magnetic hologram memory. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Lim, P.B.; Goto, T.; Uchida, H.; Inoue, M. Recording and reconstruction of volumetric magnetic hologram using multilayer medium with heat dissipation layers. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 27573–27579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Lim, P.B.; Goto, T.; Uchida, H.; Inoue, M. Development of heat dissipation multilayer media for magnetic hologram memory. Electron. Commun. Jpn. 2020, 103, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, Q.; Sui, X.; Chen, Q.; Gu, G.; Wang, L.; Li, S. Research progress in optical neural networks: Theory, applications and developments. PhotoniX 2021, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Sakaguchi, H.; Zhang, J.; Nonaka, H.; Sumi, S.; Awano, H.; Ishibashi, T. Magneto-optical diffractive deep neural network. Opt. Express 2022, 20, 36889–36899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, H.; Fujita, T.; Zhang, J.; Sumi, S.; Awano, H.; Nonaka, H.; Ishibashi, T. Development of Fabrication Techniques for Magneto-Optical Diffractive Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Mag. 2023, 59, 2500704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T.; Morimoto, R.; Pritchard, J.W.; Mina, M.; Takagi, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Lim, P.B.; Taira, T.; Inoue, M. Magneto-optical Q-switching using magnetic garnet film with micromagnetic domains. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 17636–17643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, R.; Goto, T.; Pritchard, J.; Takagi, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Lim, P.B.; Uchida, H.; Mina, M.; Taira, T.; Inoue, M. Magnetic domains driving a Q-switched laser. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, R.; Goto, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Lim, P.B.; Uchida, H.; Inoue, M. Crystalline and magnetooptical characteristics of (Tb,Bi)3(Fe,Ga)5O12 deposited on (Y,Nd)3Al5O12. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 57, 061101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, T.; Mito, S. Random number generation using magnetic domain images of magneto-optical materials. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 59, SEEA07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowa, J.; Ciéslak, J.; Zajusza, M.; Mózdzierz, M.; Berent, K.; Mikuła, A.; Stępié, A.; Swierczek, K. Structure and transport properties of the novel (Dy,Er,Gd,Ho,Y)3Fe5O12 and (Dy,Gd,Ho,Sm,Y)3Fe5O12 high entropy garnets. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 3844–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Yang, Y.; Chen, C.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C. Structure and magnetism of novel high-entropy rare-earth iron garnet ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 9862–9867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieslak, J.; Reissner, M.; Dabrowa, J.; Zielinska, K. Magnetization measurements of multicomponent iron garnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 582, 170987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, H.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, Z. Effects of different light and heavy rare-earth compositions on structure and magnetic properties of high-entropy garnet ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2024, 35, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhanga, X.; Bao, A.; Qi, X. Effects of Fe2+ on dielectric and magnetic properties in rare earth garnet type high entropy oxides. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 27453–27461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Torres, C. Low-dimensional multiplexing: The magneto- optical Kerr effect in an individual FeCoCu nanowire. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 032501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Ding, B.; Liu, B. Magneto-optic effect of two-dimensional materials and related applications. Nano. Select. 2020, 1, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Xia, S.; Yang, W.; Wang, H.; Yan, W.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Liu, W.; Luo, Y.; Deng, L.; et al. Nanophotonic devices based on magneto-optical materials: Recent developments and applications. Nanophotonics 2022, 11, 2639–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Jin, Z.; Chen, J. A review: Magneto-optical sensor based on magnetostrictive materials and magneto-optical material. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2023, 5, 100152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; Zhu, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, G.; Wen, Z.; Xiang, J.; Chen, G. Strong transverse magneto-optical Kerr effect at normal incidence based on hybrid bound states in the continuum. Phys. Rev. B 2023, 108, 235314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-B.; Wu, H.; Tan, P.-H. Magneto-optical interactions in layered magnets. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2312214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Parameters | Properties | |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Substitution sites Substitution elements Substitution amounts | Faraday rotation Transmittance or absorption |
| Wavelength Temperature | ||
| Applications | Important Properties |
|---|---|
| Isolator | Large Faraday rotation (45 deg) High transmittance |
| Imaging | Perpendicular or in-plane magnetization Small coercivity (soft magnetic garnets) |
| Magnetic hologram memory | Perpendicular magnetization Large residual Faraday rotation High coercivity |
| MO neural network | Perpendicular magnetization |
| MO Q-switch | Fine magnetic domain |
| Random number generator | Fine magnetic domain |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakamura, Y.; Chauhan, S.B.S.; Lim, P.B. Magneto–Optical Properties and Applications of Magnetic Garnet. Photonics 2024, 11, 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11100931
Nakamura Y, Chauhan SBS, Lim PB. Magneto–Optical Properties and Applications of Magnetic Garnet. Photonics. 2024; 11(10):931. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11100931
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakamura, Yuichi, Sumiko Bharti Singh Chauhan, and Pang Boey Lim. 2024. "Magneto–Optical Properties and Applications of Magnetic Garnet" Photonics 11, no. 10: 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11100931
APA StyleNakamura, Y., Chauhan, S. B. S., & Lim, P. B. (2024). Magneto–Optical Properties and Applications of Magnetic Garnet. Photonics, 11(10), 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11100931