Abstract
In this paper, the laser pulse time compression technique, based on stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) and passive laser–induced breakdown (LIB) series technology, is investigated. By doping a SiC nanowire in a CCl4 solution of an LIB breakdown medium, the LIB generation threshold is reduced, and the stability of the LIB compression output is improved. When OD is 0.2, the output pulse width is 254.4 ps, and the corresponding energy conversion efficiency and pulse compression rate are 34.2% and 50.2%, respectively. Our experiment proves the feasibility of this scheme.
1. Introduction
Ultrashort–pulse lasers are widely used in laser processing, spectral measurement, and high–energy physics [1,2,3]. The traditional method of generating an ultrashort–pulse laser through mode locking makes it difficult to generate a high–energy short–pulse laser due to the limitation of the damage threshold of the locking mirror [4,5,6]. Another method is to generate a nanosecond laser through Q–switching and then compress the laser to a picosecond level using SBS pulse–width compression technology, which has the advantages of a low cost, high energy conversion efficiency, phase conjugation, and high beam quality [7,8]. However, SBS pulse–width compression technology can only compress the pulse leading edge to obtain the laser pulse output in the order of a hundred picoseconds. In order to achieve a narrower pulse width, further post–pulse compression must be combined with other technical solutions.
The existing SBS and SRS series compression technology schemes [9,10], SBS and saturated gain switch series compression technology schemes [11], and SBS and LIB series compression technology schemes have been proven to be feasible [12]. The SBS and SRS series compression technology is the earliest technological combination to realize ultra–short pulses, which has been proved in a large number of studies, and that can achieve high repetition frequency output. However, after injecting the high peak power laser pulse output produced by the SBS pulse–width compression technology into the SRS medium, the SRS pulse–width compression technology will generate high–order Stokes light. The stability and energy conversion efficiency of the whole system are affected, making the scheme difficult to apply in high–power laser generation. The SBS and saturated gain switch series compression technology can generate a ps–level ultrashort–pulse laser, and the energy conversion efficiency is noteworthy. But, the saturated gain switch is only suitable for gas lasers, and this technology is only used in KrF lasers. The SBS and LIB series compression technology scheme combines pulse leading–edge compression technology with trailing–edge compression technology to yield complementary results. In addition, the high peak power Stokes light output from SBS pulse–width compression technology is injected into the LIB plasma switch, which is beneficial to the excitation of the plasma.
In 2017, Liu et al. [13] proposed a scheme of combining SBS and LIB compressions to simultaneously compress the leading and trailing edges of pulses, achieving a synchronous compression of the leading and trailing edges of the pulse and breaking through the limitation of SBS phonon lifetime. However, using pure water as a medium is affected by various nonlinear effects, while the LIB effect is not stable enough for practical applications. In this paper, CCl4 is used as the medium to significantly improve the stability of LIB, and the stability and efficiency of the system are significantly enhanced by doping SiC nanowires. In addition, the commercial Faraday optical isolator is used to achieve optical isolation between the seed laser source and the amplifier. Meanwhile, the optical wedge is used to adjust the horizontal and vertical directions of the beam in the experimental setup, which improves the stability of the experimental setup and further improves the engineering application ability of the combined SBS and LIB pulse compression technology.
In this letter, in view of the limitation that SBS can only compress the leading edge of the injected light pulse, we proposed a scheme combining SBS leading–edge pulse compression technology with LIB trailing–edge compression technology in series and successfully realized the simultaneous compression of the leading and trailing edges of the injected light pulse. By doping the SiC nanowire into the CCl4 solution to reduce the LIB threshold and improve the system stability, ultra–narrow pulse width and high–intensity laser outputs are finally achieved.
2. Material Preparation
The introduction of impure particles into a pure liquid medium can also significantly reduce the LIB threshold of the medium and improve the stability of the LIB [12]. LIB enhancement based on the thermal effect is a mechanism that enhances the performance of LIB through the doping of solid particles [14], where the selected doped solid particle materials are required to have a large difference in the thermal conductivity of the medium. The SiC material has significant nonlinear optical properties, excellent mechanical properties, and electrical conductivity. Its thermal conductivity is 100~200 W/m·K [15]. The SiC nanowire preparation method includes the following: Si and SiO2 powders were mixed by ball milling according to the designed proportion (molar ratio of 1:1). The mixed Si and SiO2 powders were placed at the bottom of the graphite crucible and covered with the porous carbon material. The graphite crucible was put into the center of the tube furnace, heated to 1400 °C at a rate of ~5 °C/min, and held at 1400 °C for 1 h under an argon gas environment.
The prepared SiC nanowire was characterized by electron microscopy, as shown in Figure 1. Figure 1a is a 1500× magnification image, and Figure 1b is a 4000× magnification image. SiC nanowire was integrated into the CCl4 solution and dispersed homogeneously by ultrasound, and suspensions with OD values of 0.1, 0.15, and 0.2 were obtained, respectively. CCl4 is a liquid organic solvent at room temperature. Its chemical properties are stable under natural conditions [16,17]. Then, suspensions with OD values of 0.1, 0.15, and 0.2 were injected into the LIB pool for narrow pulse–width compression experiments by combining SBS and LIB switches in series.
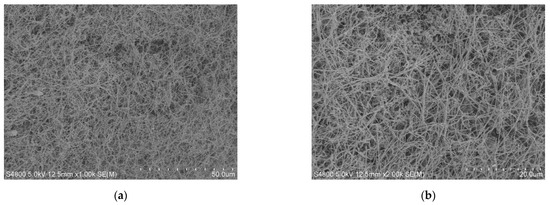
Figure 1.
SEM image of SiC nanowire: (a) 1500× magnification; (b) 4000× magnification.
3. Experiment
The experimental setup for the narrow–pulse width compression of a Nd:YAG single–longitudinal–mode laser using a structure of SBS and LIB switches in series is shown in Figure 2. During the experiment, the SBS is used for the first–stage compression; then, the LIB compression is performed with the steep rising–edge pulse output from the SBS. The Nd:YAG single–longitudinal–mode laser serves as a seed laser, with an output pulse width of 8 ns and a central wavelength of 1064 nm. The maximum output energy is 7 mJ at a repetition rate of 1 Hz. The optical Faraday isolator is used to avoid damage to the seed laser caused by backward light. The max beam diameter and isolation of the optical Faraday isolator are 9 mm and 40 dB, respectively. Lenses M1 and M2 are used to adjust the spot size of the optical Faraday isolator. Optical wedge pairs W1~W5 are used for beam adjustment, while right–angle prisms RM1~RM4 are used for beam reflection. Optical wedge pairs utilize the relative rotation of the two optical wedges. The output beam can be positioned in any direction in the corner cone with the input beam as the axis. Its advantages include an easy system assembly, stable structure, and easy realization of the engineering of optical systems. The deflection angle parameter of the optical wedge is 1°. The right–angle prism uses critical angle characteristics to achieve the efficient total reflection of the incident beam inside the right–angle prism. Compared with ordinary mirrors, the advantages of a right–angle prism include easy installation and high mechanical stress strength. A dual–pass amplifier structure is applied in the first–stage Nd:YAG amplifier. A half–wave plate and a polarizer P1 are used to control the energy injected into the Nd:YAG amplifier crystal. Lenses M3 and M4 are used to adjust the beam diameter in the Nd:YAG amplifier crystal. A compact dual–pool compression structure is employed in the SBS compression section, including an amplification pool and a generation pool, both of which are 60 cm in length, and the SBS medium is FC–43. The FC–43 medium is one of the perfluorocarbon media. As an SBS medium, FC–43 has the characteristics of a high breakdown threshold, short phonon lifetime, large gain coefficient, and low absorption [18,19]. The phonon lifetime, SBS frequency shift, gain coefficient, and optical breakdown threshold of FC–43 medium are 200 ps, 1.3 cm/GW, 1073 MHz, and 178 GW/cm2, respectively. In the single–pass amplification, the seed laser energy is amplified to 60 mJ. The amplified beam enters the amplification pool after passing through the quarter–wave waveplate and is focused into the generating pool by the lens M5 with a focal length of 300 mm. The Stokes light generated near the focal area is compressed and amplified in the amplification pool by extracting the input energy in a backward direction. Stokes light is transformed into the s–polarized light through the quarter–wave plate and then further amplified in the Nd:YAG amplifier crystal, which is reflected by polarizer P1 and the right–angle prism RM3. The output beam passes through a half–wave plate and is incident to a type I phase–matched LiB3O5 (LBO) crystal for frequency doubling, producing green light in the 532 nm wavelength range. For the laser beam, the center wavelength, pulse width, and repetition rate are 1064 nm, 10 ns, and 10 Hz, respectively. The damage threshold of LBO crystal is better than 1 GW/cm2. Dichroic mirror DM1 is used to separate the 532 nm beam, and the 1064 nm beam is recovered using an optical trash can. Lens M6 is used for focusing the 532 nm beam into the LIB generation pool with a length of 40 cm. The beam through the LIB pool is collimated by lens M7. The forward–stimulated Raman component and compressed transmitted light are separated by a dichroic mirror DM2 with high transmission for the 650 nm light and high reflectivity for the 532 nm light.
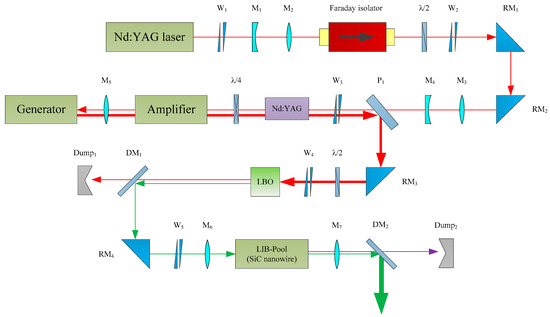
Figure 2.
Optical path diagram of SBS and LIB switch series combination compression experiment.
4. Results and Discussion
The output Stokes beam compressed by SBS is focused into the LIB pool as a pump source for LIB compression after frequency doubling with LBO. After the occurrence of laser–induced plasma breakdown, the pulse width of the output waveform changes with the input energy, as shown in Figure 3. A total of 100 pulses recorded by a detection system using a photoelectric detector (Ultrafast UPD–50–UP) and a digital oscilloscope (Tektronix, DPO71254C, bandwidth: 12.5 GHz; sampling rate: 100 Gs/s) are captured for statistical analysis. The output laser energy is measured by an energy meter (ORHIR, PE50DIF–ER).
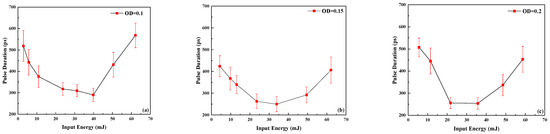
Figure 3.
Pulse duration as a function of the input energy after the LIB pulse compression stage: (a) OD = 0.1; (b) OD = 0.15; (c) OD = 0.2.
Taking Figure 3c as an example, when the input energy reaches 21.7 mJ, the output pulse width gradually decreases, and the shortest pulse width is 255.7 ps. When the input energy is increased to 35.7 mJ, the output pulse width remains basically unchanged, and the output pulse width is 254.4 ps. When the input energy continues to be increased to 58.7 mJ, the output pulse width gradually increases, and the longest output pulse width is 453.2 ps.
The reason for this change is that the pulse width of the LIB output is affected by the pulse width of the Stokes beam after SBS compression and due to the LIB switching properties. The pulse width of the Stokes beam compressed by SBS is affected by the output power density of the Nd:YAG pumping source. When the output power density of the Nd:YAG laser is less than a specific value, the pulse width of the Stokes beam rapidly shortens and eventually saturates to a minimum value. The output power density of the Nd:YAG laser is further increased, and the pulse width of the Stokes beam is slowly broadened. In terms of stability, the pulse–width stability is optimal when the output pulse width is the shortest, and the stability gradually deteriorates by further increasing the pump power density [20,21,22,23]. By comparing Figure 3a–c, it can be seen that the minimum pulse width of the LIB output and its stability, and the corresponding input energy, are affected by the OD value of LIB, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Influence of different OD values on the minimum pulse output by LIB.
In the CCl4 solution doped with the SiC nanowire, the curves of LIB compression output energy and energy conversion efficiency with input energy are shown in Figure 4. Taking Figure 4c as an example, when the input energy is 5 mJ, a stable LIB shutdown phenomenon begins to appear. This is because SiC nanowires can reduce the breakdown threshold of LIB, causing LIB to occur at low energy, significantly suppressing the occurrence of SBS and SRS, making LIB dominant in the competition for nonlinear effects. As the input energy increases, the output energy of LIB gradually increases. Before entering the saturation gain region, the energy conversion efficiency increases rapidly as the input energy rises. When entering the saturation gain region, the energy conversion efficiency gradually tends to saturate and stabilize at about 50% [24,25,26]. At the same time, the variance in the output energy is also continuously increasing.
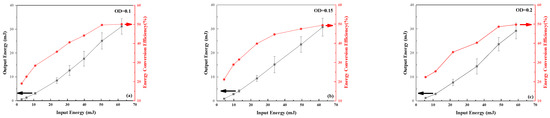
Figure 4.
Relationship between output energy and energy conversion efficiency with input energy: (a) OD = 0.1; (b) OD = 0.15; (c) OD = 0.2.
By comparing Figure 4a–c, it can be seen that the output energy and energy conversion efficiency follow the same trend as the input energy. After experiencing a small signal gain under low input energy, the final energy conversion efficiency is saturated at about 50%. This is because the media selected in the LIB pool are the same, resulting in the same phonon lifetime. The change in OD value from 0.1 to 0.2 has a relatively small impact on the gain coefficient. The maximum energy output of LIB and its saturation energy conversion efficiency, the corresponding input energy, are affected by the OD value of the LIB, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Influence of different OD values on the output energy by LIB.
After SBS compression, the output laser energy is 35.7 mJ, and the corresponding energy conversion efficiency and pulse width are 55% and 506.8 ps, respectively. For the LIB pool with an OD value of 0.2, when the input energy is 35.7 mJ, the statistical histogram of LIB output energy stability is shown in Figure 5. The corresponding average value and R2 value are 12.2 mJ and 92.3%, respectively.
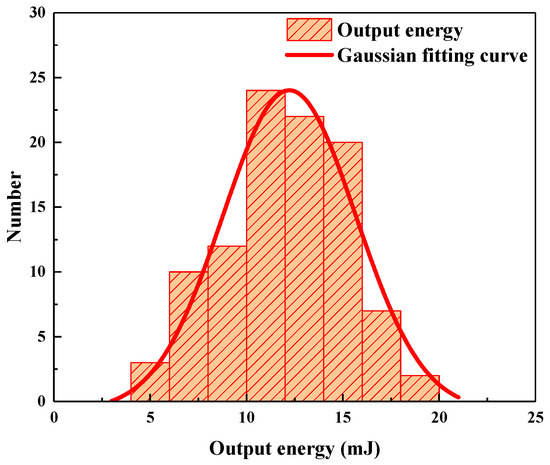
Figure 5.
Output energy stability statistical histogram at OD value of 0.2 and input energy of 35.7 mJ.
The comparison of pulse waveforms before and after LIB compression is shown in Figure 6. The black curve represents the pump pulse before LIB compression, and the red curve represents the short pulse after compression. It can be seen that the leading edges of the two pulses are essentially coincident, which indicates that the LIB plasma switch preserves the leading–edge portion of the compression pulse more completely. The trailing edge after the peak is almost absorbed, causing compression. After compression, the slope of the trailing edge of the pulse is basically the same as that of the front edge, forming a short pulse with symmetric front and trailing edges. Due to the effective suppression of other nonlinear effects, the compression effect here is changed from a combination of multiple nonlinear effects in the pure media to a single LIB compression. The final output pulse width is 254.4 ps, and the compression rate of 50.2% is achieved via SBS compression.
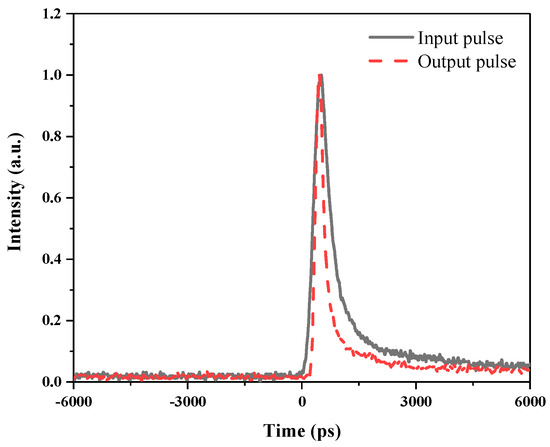
Figure 6.
Temporal profiles of unclipped pulse (solid line) and clipped pulse (dash line).
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, we proposed a novel narrow pulse–width compression scheme that combined SBS pulse–width compression technology with LIB switching. The LIB threshold is decreased by doping a SiC nanowire into a CCl4 solution. The nonlinear effects of SBS and SRS are suppressed to improve the stability of the system. For the LIB switch with an OD value of 0.2, the optimal output is obtained when the input energy is 35.7 mJ. For a LIB switch with an OD value of 0.2, the minimum pulse–width output of 254.4 ps is obtained when the input energy is 35.7 mJ. The corresponding energy conversion efficiency and pulse compression rate are 34.2% and 50.2%, respectively. The produced optical pulse provides a spatial resolution that is well suited for LIDAR Thomson scattering diagnostics.
Author Contributions
Validation, L.F.; writing—original draft preparation, L.F.; writing—review and editing, D.S. and Y.Z.; supervision, L.F., D.S., Y.Z. and W.Z.; project administration, W.Z.; funding acquisition, W.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ishii, N.; Turi, L.; Yakovlev, V.S.; Fuji, T.; Krausz, F.; Baltuška, A.; Butkus, R.; Veitas, G.; Smilgevičius, V.; Danielius, R.; et al. Multimillijoule chirped parametric amplification of few–cycle pulses. Opt. Lett. 2000, 30, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolotti, M. High–order Harmonic Generation in Laser Plasma Plumes by Rashid Ganeev. Contemp. Phys. 2015, 56, 88–89. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, M.J.; Beurskens, M.; Carolan, P.G.; Gilbert, M.; Loughlin, M.; Morris, A.W.; Riccardo, V.; Xue, Y.; Huxford, R.B.; Walker, C.I. Design challenges and analysis of the iter core lidar thomson scattering system. Review of Scientific Instruments. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2006, 77, 1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, J.A.D.; Spühler, G.J.; Südmeyer, T.; Paschotta, R.; Hövel, R.; Moser, M.; Erhard, S.; Karszewski, M.; Giesen, A.; Keller, U. 16.2–W average power from a diode–pumped femtosecond Yb:YAG thin disk laser. Opt. Lett. 2000, 25, 859–861. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Izumida, S.; Ono, S.; Ohtake, H.; Sarukura, N. High–repetition–rate, high–average–power, mode–locked Ti:sapphire laser with an intracavity continuous–wave amplification scheme. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 74, 3622–3623. [Google Scholar]
- Beddard, T.; Sibbett, W.; Reid, D.T.; Garduno-Mejia, J.; Jamasbi, N.; Mohebi, M. High–average–power, 1–MW peak–power self–mode–locked Ti: Sapphire oscillator. Opt. Lett. 1999, 24, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayhowski, J.J.; Dill, I.C. Diode–pumped passively Q–switched picosecond microchip lasers. Opt. Lett. 1994, 19, 1427–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, B.; Kärtner, F.X.; Zhang, G.; Moser, M.; Keller, U. 56–ps passively Q–switched diode–pumped microchip laser. Opt. Lett. 1997, 22, 381–383. [Google Scholar]
- Kulagin, O.V.; Gorbunov, I.A.; Sergeev, A.M.; Valley, M. Picosecond Raman Compression Laser at 1530 nm with Aberration Compensation. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 3237–3240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kubeček, V.; Hamal, K.; Procházka, I.; Valach, P.; Buzelis, R.; Dementev, A. Compression of the Nd: YAP Laser Pulse by Two–Stage Stimulated Backward Scattering. Opt. Commun. 1989, 73, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, K.; Takahashi, E.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kato, S.; Owadano, Y. Short–Pulse Generation by Saturated KrF Laser Amplification of a Steep Stokes Pulse Produced by TwoStep Stimulated Brillouin Scattering. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2000, 17, 1943–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasi, W.L.J.; Lu, Z.W.; Lu, H.H.; Fu, M.L.; Gong, S.; Lin, D.Y.; He, W.M.; Gao, W. Investigation on Pulse Compression Based on Stimulated Brillouin Scattering and Optical Breakdown. Appl. Phys. B 2010, 98, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Bai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; He, W.; Lin, D.; Lu, Z. Pulse temporal compression by two–stage stimulated Brillouin scattering and laser–induced breakdown. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 241108. [Google Scholar]
- Noack, J.; Vogel, A. Laser–Induced Plasma Formation in Water at Nanosecond to Femtosecond Time Scales: Calculation of Thresholds, Absorption Coefficients, and Energy Density. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1999, 35, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, M.; Baliga, B.J. Comparison of 6H–SiC, 3C–SiC, and Si for power devices. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1993, 40, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, D.P. Long–range correlation of intra–molecular and inter–molecular vibration in liquid CCl4. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 154, 034502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.; Rai, S.N. Depolarization ratio and correlation between the relative intensity data and the abundance ratio of various isotopes of liquid carbon tetrachloride at room temperature. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2005, 62, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwahara, K.; Takahashib, E.; Matsumoto, Y.; Matsushima, I.; Okuda, I.; Kato, S.; Owadano, Y. High Intensity Pulse Generation by Saturated Amplification of Stokes Pulse with Steep Leading Edge. In Proceedings of the ECLIM 2000: 26th European Conference on Laser Interaction with Matter, Prague, Czech Republic, 12–16 June 2000; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2011; Volume 4424, pp. 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, A.; Yoshida, H.; Fujita, H.; Nakatsuka, M. Sub Nanosecond Pulse Generation by Stimulated Brillouin Scattering Using FC–75 in an Integrated with Laser Energy up to 1.5 J. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 45, 1607–1611. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.; Xu, X.; Diels, J.C. High–Energy Sub–Phonon Lifetime Pulse Compression by Stimulated Brillouin Scattering in Liquids. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 12421–12434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frings, H. Compact Temporal–Pulse–Compressor Used in Fused–Silica Glass at 1064 nm Wavelength. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 46, L80–L82. [Google Scholar]
- Dane, C.B.; Neuman, W.A.; Norton, M.A. Energy Scaling of SBS Pulse Compression. Proc. SPIE 1992, 1626, 297–307. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, T.J. Principles of Phase Conjugation. Opt. Acta Int. J. Opt. 1986, 33, 685–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Bai, Z.; Cui, C.; Liu, R.; Zhang, H.; Hasi, W. Fluctuation Initiation of Stokes Signal and Its Effect on Stimulated Brillouin Scattering Pulse Compression. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 14378–14388. [Google Scholar]
- Hasi, W.; Zhong, Z.; Qiao, Z.; Guo, X.; Li, X.; Lin, D.; He, W.; Fan, R.; Lü, Z. The Effects of Medium Phonon Lifetime on Pulse Compression Ratio in the Process of Stimulated Brillouin Scattering. Opt. Commun. 2012, 285, 3541–3544. [Google Scholar]
- Gorbunov, V. Formation and Amplification of Ultrashort Optical Pulses as a Result of Stimulated Scattering in Opposite Directions. Sov. J. Quantum Electron. 1984, 14, 1066–1069. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).