Abstract
This paper demonstrates the capability of sub-nanosecond, high peak power Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 passively Q-switched Raman microchip lasers at 1134 nm operated in multiple pulses mode under quasi-continuous-wave (QCW) pumping. Total pulse energy for the Stokes laser was 1.8 mJ with a 4 mm YVO4 crystal and TOC = 16%. The corresponding pulse repetition rate reached 225 kHz within a single pumping pulse. By employing a compact plane-concave cavity and 5 mm YVO4 crystal, the single pulse energy for the Raman laser was further scaled up to 44 μJ. The corresponding peak power was 95 kW. A highest output pulse repetition rate of 87.8 kHz and shortest pulse duration of 464 ps were found for the Raman laser. The results indicate that the Raman microchip laser configuration under QCW LD pumping is a promising approach for developing high peak power, commercial and portable Raman lasers with a pulse duration of several hundred-picoseconds at a pulse repetition rate of hundred kilohertz.
1. Introduction
Many applications, such as laser induced plasma ignition (LIPI) [1], lidar [2], laser micro processing [3] and planar laser induced fluorescence (PLIF) imaging [4], require high energy sub-nanosecond laser sources with high repetition rates. For example, sub-nanosecond laser sources with a repetition rate of hundred kilohertz provide high detection precision in the area of lidar and laser detection. In laser processing applications, this type of laser also has an improved processing accuracy, compared to nanosecond lasers. A variety of approaches have been explored to generate sub-nanosecond pulses. Currently, laser diode (LD) end-pumped passively Q-switched (PQS) microchip lasers using Cr4+:YAG crystals as saturable absorbers have the merits of low intracavity losses, good stabilities, low costs and are insensitive to misalignment, which can provide sub-nanosecond laser pulses with relative high pulse energy and peak power [2].
Ytterbium (Yb3+)-doped laser gain media exhibit a variety of intrinsic benefits, such as broad absorption spectral bands, relatively simple energy level structures, low quantum defects and long upper state lifetimes [5]. These features motivate producing sub-nanosecond laser pulses with a relatively high pulse energy and peak power based on PQS microchip lasers geometry. To this end, sub-nanosecond Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG and Yb:KLu(WO4)2/Cr4+:YAG PQS microchip lasers emitting at 1.03 μm have been demonstrated [6,7,8].
Sub-nanosecond, high peak power PQS microchip lasers can be used for efficient nonlinear optical frequency conversion. Wavelength conversion from 1 μm to 532, 355, 266 and 118 nm has been investigated [2,9,10,11,12,13]. However, extension of the emission spectral range of microchip lasers from 1 μm to 1.1–1.3 μm is still a challenge. Laser radiations in the 1120–1150 nm region can produce yellow–green lasers using frequency doubling [14,15]. In many biomedical applications, yellow–green lasers are desirable for dermatological treatments, cytology, ophthalmology, and dermatology and fluorescence microscopy imaging [14,15,16,17,18,19]. Stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) is an effective solution for extending the emission range and for acquiring specific laser lines that are hard to access using the direct lasing of traditional laser gain media. YVO4 crystal demonstrates excellent optical, thermal and mechanical features, such as a high damage resistance threshold, a large Raman gain coefficient and a broad spectral transparency range, which are beneficial for constructing high energy Raman lasers [20]. In 2001, Kaminskii et al. first proposed and predicted that Yttrium vanadate (YVO4) crystal would be a promising Raman active medium [20]. Both Nd3+ or Yb3+ doped YVO4 crystals have been verified as excellent self-Raman laser materials. With the primary Raman shift line at 890 cm−1 for YVO4 crystal, the fundamental laser wavelength at 1 μm lasing from Nd-doped or Yb-doped lasers can be efficiently converted to the first order Stokes laser at 1.1–1.3 μm. In 2004, Chen et al. investigated a PQS c-cut Nd:YVO4/Cr4+:YAG self-Raman laser, achieving a maximum pulse energy of 7.2 μJ with a pulse duration of 710 ps at the first Stokes laser of 1178.6 nm [21]. In 2005, a Yb:YVO4/Cr4+:YAG self-Raman laser was shown to produce a pulse energy of 3.6 μJ at a repetition rate of 25 kHz at 1119.5 nm [22]. In 2013, Ding et al. demonstrated a c-cut Nd:YVO4/Cr4+:YAG self-Raman laser at 1178 nm with an average output power of 800 mW, a pulse width of 2.6 ns and a peak power of 7.0 kW [23]. In 2017, Jiang et al. utilized a Yb:YAG/YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YAG composite crystal and an a-cut YVO4 Raman crystal in a PQS Raman laser, which obtained multiple Stokes lines ranging from 1092.6–1290.1 nm with a pulse energy of 84.30 μJ and a pulse width of 2.20 ns at a repetition rate of 6.15 kHz [24]. Recently, Zhang et al. reported a Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQS Raman laser generated dual-pulse Raman lasers with an equal peak power of 1.7 kW at 1134 nm [25].
The concept of a passively Q-switched Raman microchip laser (PQSRML) combines the intracavity SRS effect with a PQS microchip laser technique, which is a method to extend the spectral scope of conventional PQS microchip lasers. Multiple Stokes lines at 1079–1260 nm with a sub-nanosecond pulse width of 440 ps and a high peak power of 9.2 kW have been generated from a Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML under continuous-wave (CW) pumping [26]. By optimizing the initial transmission of Cr4+:YAG crystals and the transmission of output couplers, an elevated output behavior of 24.1 μJ, 45.1 kW and 535 ps for a Raman laser at 1134 nm from a Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML was achieved [27]. However, generating Raman laser pulses with simultaneous high pulse energies and high repetition rates is relatively difficult under CW pumping due to the limiting average output power. The quasi-continuous-wave (QCW) pumping of PQSRML generates a high pump intensity and alleviates thermal loading in the laser gain medium, which is beneficial for enhancing the output pulse energy, even in an air-cooled configuration. By adjusting the pumping width and energy parameters, the output Raman laser pulses can work in a multiple pulse mode, generating several pulses oscillated within a single pumping pulse regime, which increases the output repetition rate [28,29,30]. In 2012, P.V. Shpak et al. demonstrated a Nd:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/Ba(NO3)2 PQSRML operating at 1.37 μm under QCW pumping [31], achieving a Raman pulse duration of 100 ps with a peak power of 50 kW at a pulse repetition rate of 24 kHz. In 2014, a QCW LD end-pumped Nd:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/α-BaTeMo2O9 PQS Raman laser emitting at 1177.8 nm with a pulse repetition rate of 21.6 kHz in one of the pump envelopes was demonstrated [32]. But the narrowest pulse duration of the Raman laser was 4.6 ns due to the long Raman cavity. In 2020, Bai et al. reported a PQS Raman laser based on a Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG composite crystal and c-cut YVO4 Raman crystal under QCW pumping, which achieved a single pulse energy of 50 µJ, a peak power of 56.9 kW, a pulse duration of 0.88 ns and a maximum pulse repetition rate of 42.6 kHz for the Raman laser [33].
In this work, sub-nanosecond Raman laser radiations in a multiple pulse mode emitting at 1134 nm were generated from Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRMLs utilizing Yb:YAG as the laser gain medium and YVO4 as the Raman gain material under QCW pumping. The dependence of the Raman laser behavior on the transmission of the output couplers and the length of the YVO4 crystal was studied to explore the optimal parameters for maximal Raman pulse energy and peak power. Moreover, a comparison of Raman laser performance in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML between a sandwich-type plane-parallel structure and a compact plane-concave cavity was conducted.
2. Experimental Setup
The Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML was tested with two cavity configurations. One is a sandwich-type plane-parallel structure and the other is a compact plane-concave cavity. Fiber-coupled, QCW laser diode arrays (nLIGHT Inc., Vancouver, WA, USA) with a core diameter of 200 μm and a numerical aperture of NA = 0.22 that emitted up to 100 W of peak power at 940 nm acted as the pump source. The repetition rate (R.R.) for the QCW LD was set to 10 Hz. The experimental setup of the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a sandwich-type structure is shown in Figure 1a. A 10% Yb3+ ions doped Yb:YAG crystal with a thickness of 1.2 mm was longitudinally pumped by the 940 nm LD. Figure 1c depicts the square pulse shape of the QCW fiber-coupled LD. Through an optical coupling system composed of two aspheric lenses with focal lengths of 8 mm and 11 mm, the pump radiation was focused into the Yb:YAG crystal with a beam diameter of approximately 275 µm. The transmission spectrum of the coating on the two facets of the Yb:YAG crystal is shown in Figure 1d. The entrance facet of the Yb:YAG crystal was coated for high transmission (HT) at 940 nm (T > 92%) as well as high-reflection (HR) at 1030–1100 nm (R > 99.8%) to act as the rear HR mirror of the microchip laser. The other facet of the Yb:YAG crystal was covered with an anti-reflection (AR) coating (R < 0.2%) at 940 nm and 1030 nm. The coatings on the two facets of the Yb:YAG crystal were originally optimized for the oscillation of the fundamental laser at 1.03 μm, without consideration of a specific design for the first Stokes laser at 1134 nm. As shown in Figure 1d, the reflectivity of the coating on the entrance facet of the Yb:YAG crystal was higher than 99% for 1134 nm and the transmission of the coating on the other facet of the Yb:YAG crystal was higher than 99% for the Raman laser, which means it can act as the oscillating resonator for the Raman laser. The saturable absorber was a 0.5-mm-thick Cr4+:YAG crystal with an initial transmission (T0) of 90%. Two c-cut YVO4 crystals with thicknesses of 4 mm and 5 mm were utilized as the Raman active media. These were AR coated at 1030–1100 nm (R < 0.2%) to reduce cavity Fresnel reflection losses. Two kinds of commercial BK7 plane output couplers (OCs) with partial transmissions (TOC) of 11% and 16% at 1030 nm were used in the experiment. The corresponding transmissions of the output couplers for the Raman laser wavelength at 1134 nm were 13% and 18%, respectively. The optical samples were attached tightly by two copper holders with 3 mm diameter holes in the center allowing the laser to pass through, which also acted as the heat sink to alleviate the thermal effect of the microchip laser. The total geometrical cavity length was the sum of the lengths of Yb:YAG, YVO4 and Cr4+:YAG crystals. The geometrical cavity length was 5.7 mm or 6.7 mm depending on the thickness of the YVO4 crystal. No active cooling device was used and the microchip laser was operated in a natural cooling mode.
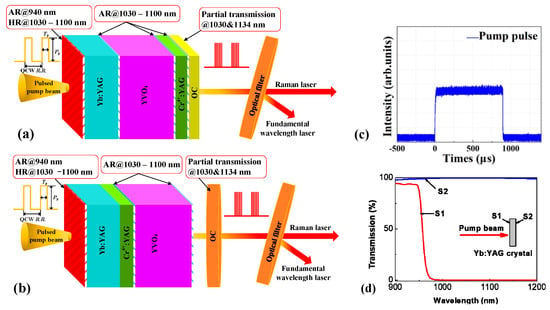
Figure 1.
(a) Experimental setup of the QCW LD end–pumped Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a sandwich–type plane–parallel structure. (b) Experimental setup of the QCW LD end–pumped Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a compact plane–concave cavity. (c) Typical pulse waveform of the QCW LD. (d) Transmission spectrum of the coating on the facets of the Yb:YAG crystal.
Figure 1b shows the experimental setup of the QCW LD end-pumped Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a compact plane-concave cavity. The pump source and coupling system were identical to those used for the plane-parallel microchip laser. A Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG composite crystal fabricated using the thermal bonding method was employed as the laser gain material and saturable absorber. The thicknesses of the Yb:YAG and Cr4+:YAG segments were 1.2 and 0.5 mm, respectively. The doping concentration of Yb3+ ions was 10% and the initial transmission was 90%. The rear surface of the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG composite crystal was HT coated at 940 nm (R < 0.2%) and HR coated at 1030–1100 nm (R > 99.8%) to serve as the HR mirror of the cavity. The other surface was AR coated (R < 0.2%) at 940 nm and 1030 nm. A c-cut YVO4 crystal with a thickness of 5 mm was selected as the Raman medium. A commercial BK7 plane-concave output coupler with a 70 mm radius of curvature and a partial transmission of 30% at 1030 nm was used. The corresponding transmission of the OC for the Raman laser wavelength at 1134 nm was measured to be 35%. The composite crystal and YVO4 crystal were tightly mounted by two copper plates with 3 mm diameter central holes. The cavity length was shortened to 13 mm. The microchip laser was also operated in a natural cooling mode.
A longpass optical filter (FEL1100, Thorlabs Inc., Newton, NJ, USA) which was HR coated (R > 99.99%) at 1030 nm and HT coated (T > 90%) at 1114–2150 nm was applied to split the Raman laser and the fundamental laser. The average output power was measured using a power meter (PM200, Thorlabs Inc., Newton, NJ, USA). An optical spectral analyzer (MS9740A, Anritsu Corp., Atsugi-shi, Japan) was used to monitor the spectral information. The laser pulse characteristics were recorded and analyzed using a digital oscilloscope (6 GHz bandwidth, TDS6604, Tektronix Inc., Beaverton, OR, USA) and a fast InGaAs photo-diode (DET08CFC/M, Thorlabs Inc., Newton, NJ, USA) was used to record and analyze the laser pulse characteristics.
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Influences of TOC on the Laser Behavior of the QCW End-Pumped Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a Sandwich-Type Plane-Parallel Structure
At first, the behavior of the QCW LD end-pumped Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a sandwich-type plane-parallel structure was investigated with TOC = 11% and 16%. The pulse width of the QCW LD was 0.9 ms, close to the upper lifetime limit of a Yb:YAG crystal (951 μs) in order to ensure sufficient energy storage time to accumulate inversion particles for the Yb3+ ions. The pumping repetition rate of the QCW LD was 10 Hz. A low duty cycle of 0.9% is recommended for the laser gain medium to have enough time to dissipate heat and reduce the thermal effect.
Figure 2 shows the typical output spectra of the QCW end-pumped Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML for TOC = 11% and 16%. The first Stokes laser was located at 1134 nm via the primary Raman shift line of 890 cm−1 for the c-cut YVO4 crystal. As illustrated in Figure 2, the number of longitudinal modes of the Stokes laser at 1134 nm is obviously less than that of the fundamental laser at 1030 nm. For example, in the case of TOC = 11%, the emission spectra for the fundamental laser exists in a multi-longitudinal mode consisting of several lines ranging from 1029.3 to 1031.5 nm because of the wide emission bands of the Yb:YAG crystal at 1.03 μm. In contrast, only a strong lasing line at 1134.8 nm together with a weak lasing line at 1132.7 nm for the Raman laser exists in the emission spectra. The SRS effect can be regarded as a longitudinal mode selection process. Only the strong lasing lines of the fundamental laser, which exceed the SRS threshold level, can be converted to Raman laser lines in the intracavity SRS conversion process. Therefore, the single longitudinal mode emission of the Raman laser is expected through further optimizing the parameters of the Raman medium under certain circumstances. The relative spectral strength of the Raman laser and the fundamental laser is related to TOC. For TOC = 11%, the spectral intensity of the Raman laser is apparently higher than that of the fundamental laser.
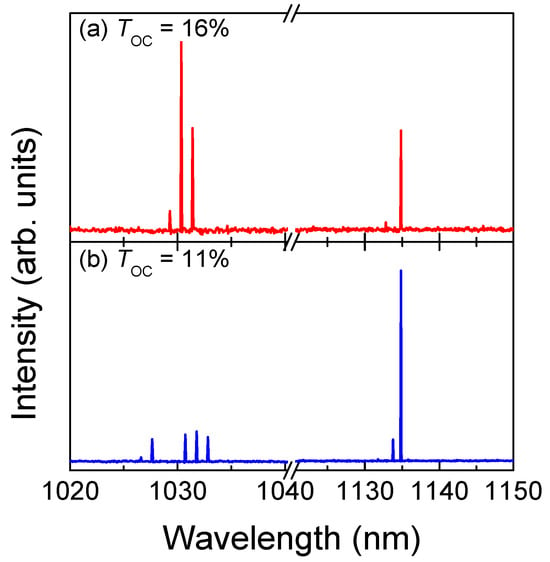
Figure 2.
Typical output spectra of the QCW LD end–pumped Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a sandwich–type plane–parallel structure for TOC = 11% and 16%. (a) TOC = 16%. (b) TOC = 11%.
Figure 3 shows the total output energy of the Raman laser in the QCW LD end-pumped Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a sandwich-type plane-parallel structure for TOC = 11% and 16% versus the incident pump energy (Ein). The output pulse energy was the total energy of several Raman laser pulses within a single pump pulse envelope. As Ein < 20 mJ, the Raman laser output energy for the case of TOC = 11% was slightly higher than for that when TOC = 16%. With further increases in Ein, the Raman laser output energy was higher when TOC = 16% than when TOC = 11%. This was attributed to the strong interaction between the Raman thermal lens effect and the Raman laser intensity during the SRS process. The Raman thermal lens effect is proportional to the time-averaged power density of the first Stokes laser [34]. According to Pheat = PS1(λS1/λL−1) (where PS1 is the time-averaged power of the first-order Stokes laser, and λL and λS1 are the fundamental and first-order Stokes laser wavelengths, respectively) [34], the higher Raman laser output energy of Ein < 20 mJ when TOC = 11% resulted in a more severe Raman thermal lens effect, which in turn restricted the growth rate of the output energy when further increasing Ein. At Ein = 38.2 mJ, the highest output energies of the Raman laser were 1.7 mJ and 1.8 mJ for TOC = 11% and 16% with corresponding optical conversion efficiencies of 4.45% and 4.7%, respectively.
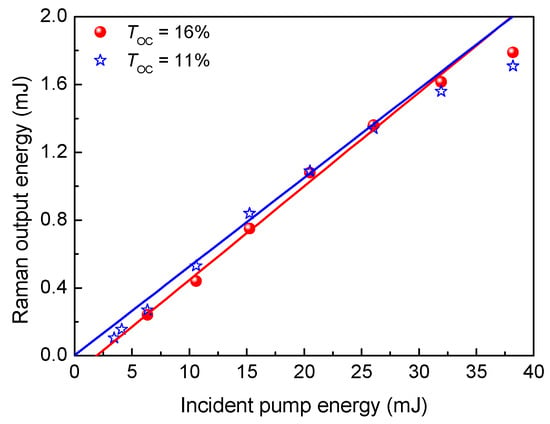
Figure 3.
The variation of the total Raman laser output energy in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a sandwich−type plane−parallel structure for TOC = 11% and 16% versus Ein.
Figure 4 depicts the variation of the pulse repetition rate, pulse duration, single pulse energy and peak power of the Raman laser for TOC = 11% and 16% in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a sandwich-type plane-parallel structure versus Ein. The repetition rate under a single pump pulse envelope increased almost linearly with Ein for both TOC = 11% and 16%. At the same pump energy, the repetition rate for TOC = 16% was lower than that when TOC = 11%. This was due to the higher transmission losses induced by higher TOC, which resulted in longer blenching time for the Cr4+:YAG crystal and a larger pulse interval. At Ein = 38.2 mJ, the maximum pulse number within a single pump width for TOC = 11% and 16% was 203 and 166, respectively. The corresponding repetition rate was 225 kHz and 184 kHz, respectively.
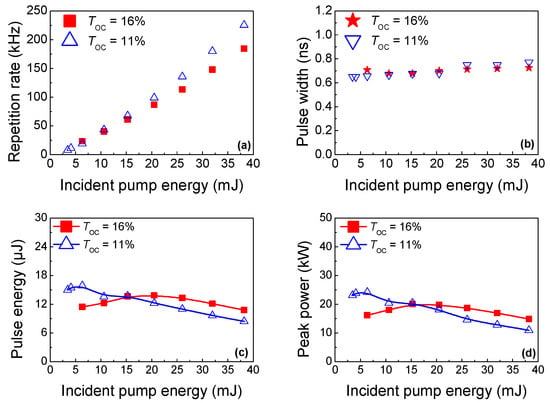
Figure 4.
The variation of output properties of the Raman laser in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a sandwich−type plane−parallel structure for TOC = 11% and 16% versus Ein. (a) Pulse repetition rate. (b) Pulse duration. (c) Single pulse energy. (d) Peak power.
The pulse duration (FWHM) exhibits a weak dependence on Ein for TOC = 11% and 16%. At Ein = 3.45 mJ, the narrowest pulse width for TOC = 11% was 650 ps. At Ein = 10.6 mJ, the narrowest pulse width for TOC = 16% was 678 ps.
The single pulse energy and peak power of the Raman laser increase slowly with Ein and then gradually decrease with a further increase of Ein for both TOC = 11% and 16%. The stimulated emission cross-section (σe) of the Yb:YAG crystal and the initial transmission of the Cr4+:YAG crystal are all affected by temperature. The thermal loading and temperature rises in the Yb:YAG crystal reduced the stimulated emission cross section of the Yb:YAG crystal [5,35], which was beneficial for the increase of the single pulse energy and the peak power with increasing Ein. With a further increase in Ein, the initial transmission of Cr4+:YAG crystal tended to slightly increase with the rising temperature [36], which led to a decrease in the single pulse energy under a high pump energy. Moreover, the severe thermal lens effect in the Raman crystal under the high pump energy levels led to a decrease in the Raman gain coefficient [37], which is also a reason for the drop in the Raman single pulse energy and peak power. The single pulse energy and peak power of the Raman laser for TOC = 11% was higher than that when TOC = 16% until Ein reached 15 mJ, and then became lower than that of TOC = 16%. This variation tendency is very similar to that presented in Figure 3, which is caused by the different Raman thermal lens effects for TOC = 11% and 16%. At Ein = 6.35 W, the highest pulse energy and peak power of the Raman laser reached 15.9 μJ and 24.2 kW for TOC = 11%. The highest pulse energy of 13.8 μJ and a peak power of 19.8 kW were obtained at Ein = 20.5 mJ for TOC = 16%. Output pulse properties of the Raman laser for different TOCs are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Output pulse properties of the Raman laser in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a sandwich-type plane-parallel structure for TOC = 11% and 16%.
Figure 5 shows the typical pulse trains and waveforms of the Raman laser in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a sandwich-type plane-parallel structure for TOC = 11% and 16%. The temporal shape of an individual pulse waveform is asymmetrical with a steep rising edge and a gentle falling edge. The instability in the intensity of the pulse trains of the Raman laser was 20.3% and 15.6% for TOC = 11% and 16%, respectively. The corresponding pulse-to-pulse timing jitters were 23.4% and 29.4%, respectively.
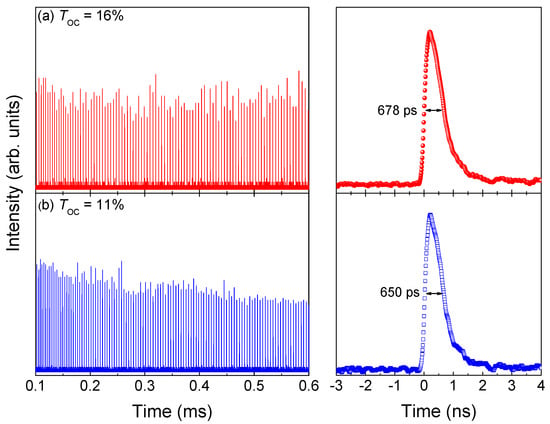
Figure 5.
Typical pulse trains and pulse waveforms of the Raman laser in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a sandwich−type plane−parallel structure for TOC = 11% and 16%. (a) TOC = 16%. (b) TOC = 11%.
3.2. Effects of Raman Crystal Length on Laser Performance of Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML
The output performance of the Raman laser in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a sandwich-type plane-parallel structure for two different Raman crystal length (lR) was investigated when TOC is 16%. Figure 6 depicts the output energy of the Raman laser in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML for lR = 4 mm and 5 mm. The Raman threshold pumping energy when lR = 5 mm was lower than that when lR = 4 mm due to the higher SRS gain introduced by the longer Raman crystal length. The total output energy of the Raman laser exhibits a nearly linear dependence on Ein for lR = 4 mm and 5 mm. Highest total output energies of 1.8 mJ and 1.65 mJ were obtained for the Raman laser with lR = 4 mm and 5 mm at Ein = 38.2 mJ, respectively. Although a longer Raman crystal possesses a higher SRS gain, an increase in the Raman crystal length also increases the cavity length, which results in greater intracity losses. Based on the combined interaction of the cavity length and Raman gain, the total output energy of the Raman laser when lR = 5 mm is slightly lower than that when lR = 4 mm.
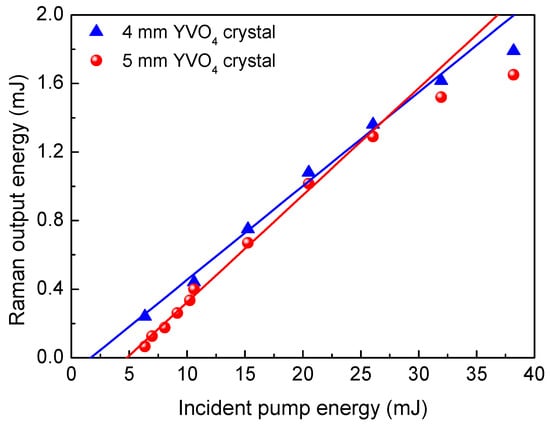
Figure 6.
The variation of the total Raman laser output energy in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a sandwich−type plane−parallel structure for lR = 4 mm and 5 mm versus Ein.
Figure 7 depicts the pulse repetition rate, pulse duration, single pulse energy and peak power of the Raman laser in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a sandwich-type plane–parallel structure for lR = 4 mm and 5 mm versus Ein. Better pulse behaviors (shorter pulse duration, and higher single pulse energy and peak power) were found with a 5 mm YVO4 crystal, indicating that the SRS conversion process was enhanced with a longer lR. The highest single pulse energy was 14.7 μJ for lR = 5 mm YVO4 crystal at Ein = 20.5 mJ. The corresponding peak power of the Raman laser was 26.4 kW.
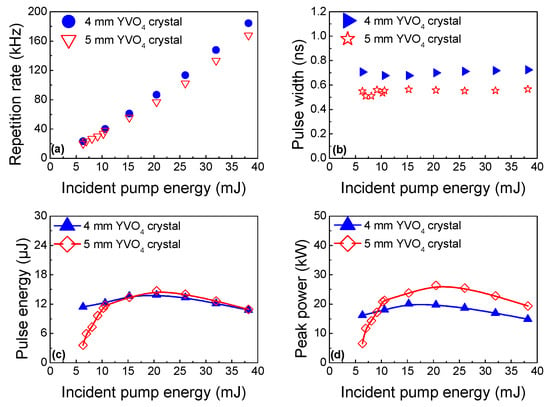
Figure 7.
The variation of output properties of the Raman laser in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a sandwich−type plane−parallel structure for lR = 4 mm and 5 mm versus Ein. (a) Pulse repetition rate. (b) Pulse duration. (c) Single pulse energy. (d) Peak power.
At Ein = 38.2 mJ, 151 pulses of the Raman laser were generated within a single pump pulse. The corresponding repetition rate was 167 kHz. The pulse duration exhibits a slight dependence on Ein for both lR = 4 mm and 5 mm YVO4 crystal. The shortest pulse duration of 510 ps was obtained for lR = 5 mm at Ein = 7 mJ. Output pulse properties of the Raman laser for different lRs are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Output pulse properties of the Raman laser in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a sandwich–type plane–parallel structure for lR = 4 mm and 5 mm.
Figure 8 shows the typical pulses trains and pulse waveforms under a single pump pulse in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML for lR = 4 mm and 5 mm YVO4 crystal. For the lR = 5 mm YVO4 crystal, the intensity instabilities and timing jitters in the pulse trains of the Raman laser were reduced to 13% and 13.9%, respectively. More stable pulse trains can be obtained with the lR = 5 mm YVO4 crystal. The longer cavity length of the lR = 5 mm YVO4 crystal had more cavity losses, which led to the suppression of the oscillations of the laser pulses with a weak gain, therefore the amplitude fluctuation and time jitters of the Raman laser pulses were reduced.
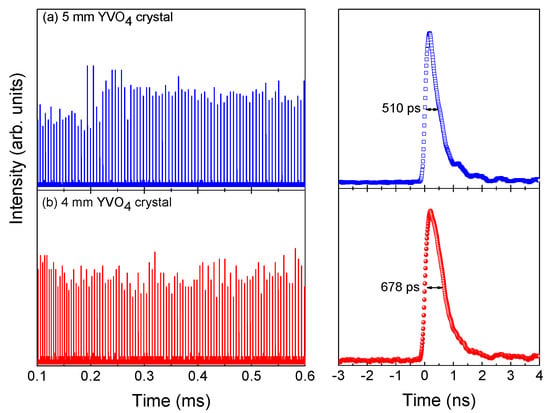
Figure 8.
Typical pulse trains and pulse waveforms of the Raman laser in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a sandwich–type plane–parallel structure for lR = 4 mm and 5 mm. (a) 5 mm YVO4 crystal. (b) 4 mm YVO4 crystal.
3.3. Laser Performance of the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a Compact Plane–Concave Cavity
With the purpose of adjusting the cavity length and flexibly optimizing the mode sizes of the fundamental and Stokes waves, a compact plane-concave cavity was utilized. The plane-concave cavity has a relatively small beam spot in the Raman crystal, which provides a sufficient pump intensity contributing to a better performance in the SRS process. Furthermore, the plane-concave cavity is convenient for placing second harmonic generation crystals, such as KTP and LBO crystals, to develop 0.56 μm yellow–green lasers. In the plane-concave cavity, a lR = 5 mm YVO4 crystal was adopted in order to enhance the intracavity SRS conversion process based on the above experimental results and analyses. An output coupler of TOC = 30% at 1030 nm was used to avoid coating damage at high peak powers.
Figure 9 depicts the variation of the total output pulse energy in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML versus Ein. First, the pulse performance of the 1030 nm fundamental laser was investigated by employing a Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG composite crystal and a plane-concave OC without YVO4 crystal. The cavity length was shortened to 10 mm. At Ein = 38.2 mJ, the highest total pulse energy was 14.5 mJ, corresponding to an optical conversion efficiency of 38%. When the YVO4 crystal was inserted into the cavity, the cavity length was increased to 13 mm. At Ein = 38.2 mJ, the total pulse energy of the fundamental laser and the Raman laser was reduced to 11.5 mJ, due to the insertion losses of the YVO4 crystal. The corresponding optical conversion efficiency was 30%. The highest total fundamental laser pulse energy was 10.34 mJ, corresponding to an optical conversion efficiency of 27%. For the 1134 nm Raman laser, the highest total pulse energy was 1.16 mJ, corresponding to an optical conversion efficiency of 3%.
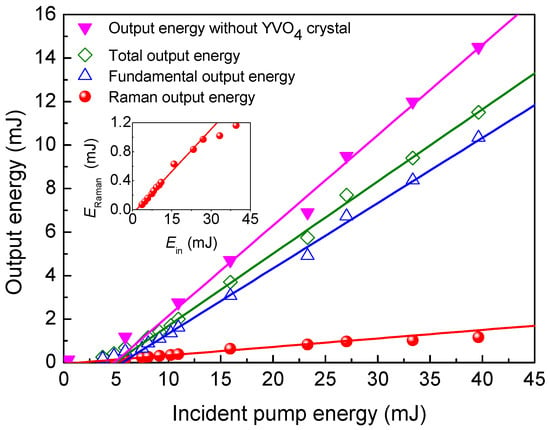
Figure 9.
Total output energy of the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a compact plane–concave cavity versus Ein.
Figure 10 shows output laser characteristics in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a plane-concave cavity versus Ein. The repetition rate within a single pump pulse increases linearly with Ein. At Ein = 38.2 mJ, 79 pulses of the Raman laser were generated within a single pump pulse and the corresponding repetition rate was 87.8 kHz.
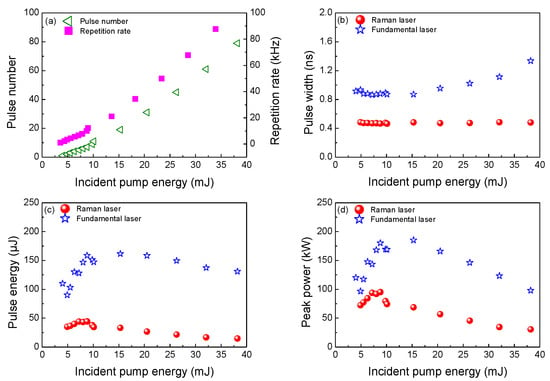
Figure 10.
Pulse performance for the fundamental laser and the Raman laser in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a compact plane–concave cavity versus Ein. (a) Pulse number and repetition rate. (b) Pulse width. (c) Single pulse energy. (d) Peak power.
The Raman laser pulse duration is constant with Ein. The narrowest Raman laser pulse duration was 464 ps at Ein = 10.1 mJ. This contrasts with the laser pulse duration of the fundamental laser increases from 900 ps to 943 ps as Ein grows. The narrowest fundamental laser pulse duration was 864 ps at Ein = 7.2 mJ.
The single pulse energy and peak power grow with Ein and then decrease with further increases in Ein for both the fundamental laser and the Raman laser. The highest single pulse energy and peak power of the Raman laser were 44 μJ and 95 kW at Ein = 8.2 mJ, respectively. For the fundamental laser, the highest single pulse energy was 161.6 μJ with a corresponding peak power of 185 kW at Ein = 15.3 mJ.
Figure 11a shows the global profile of the output Raman pulse cluster with a repetition rate of 10 Hz, which is determined by the given repetition rate of the QCW LD. Figure 11b shows the details of the output Raman pulses for an individual pulse cluster. As illustrated from Figure 11b, 79 pulses of the Raman laser appear within a single pump pulse regime of 1 ms with a corresponding repetition rate of 87.8 kHz, which was modulated by the saturable absorber. The time regime from the first Raman pulse to the last pulse was approximately 900 μs. The amplitude fluctuation and the time jitters were 16.4% and 6.37%. In comparison with the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a sandwich-type plane-parallel structure, the pulse stability improved.
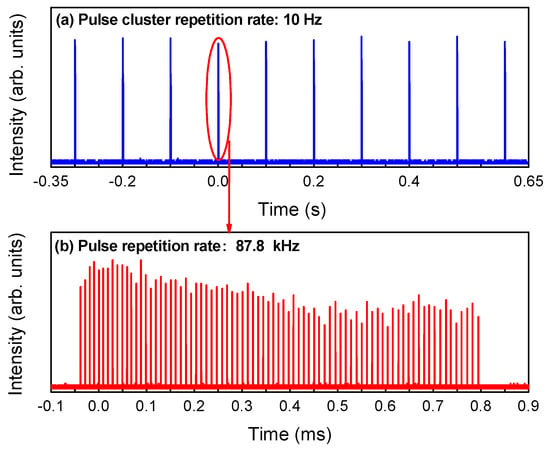
Figure 11.
Typical pulse trains of the Raman laser in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a compact plane–concave cavity. (a) Global profile of output pulse cluster. (b) Details for an individual pulse cluster.
Figure 12 shows the typical pulse profiles and emitting spectra at Ein = 8.2 mJ. The typical emitting spectra is shown in the inset of Figure 11. The pulse width of the Raman laser is nearly half of the residual fundamental laser, which is compressed in comparison with the fundamental laser.
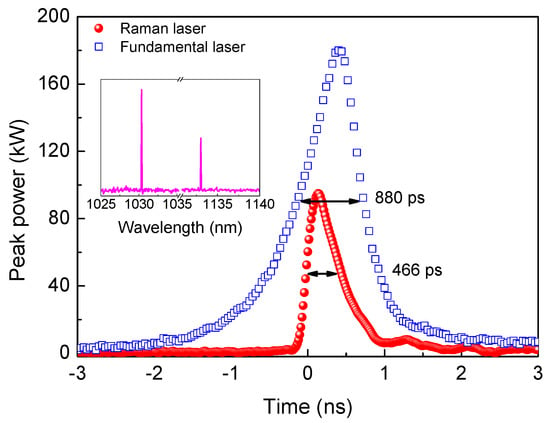
Figure 12.
Typical pulse waveforms and output spectrum in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML with a plane–concave cavity.
4. Discussion
Table 3 summarizes the output laser performance of this work and some similar miniature Cr4+:YAG passively Q-switched Raman lasers. From the above comparisons, it can be concluded that the sandwich-type plane-parallel structure of PQSRML is suitable for generating high repetition rate pulses due to a compact plane-plane laser cavity resulting in a short cavity roundtrip time. Low losses in the microchip configuration are also beneficial in improving laser efficiency and output pulse energy. A pulse repetition rate as high as 225 kHz has been demonstrated with a 4 mm YVO4 crystal and TOC = 11%. The pulse duration of the Raman laser was shortened to 510 ps at a repetition of 167 kHz with a 5 mm YVO4 crystal and TOC = 16%. In contrast, the compact plane-concave cavity used in the Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML is more suitable for boosting the output single pulse energy and peak power of the Raman laser. This work has improved upon previous implementations by demonstrating as high as 95 kW of peak power for the Raman laser based on a compact plane-concave cavity. The miniature plane-concave cavity setup of only a 13 mm cavity length is favorable for shortening the Raman laser pulse duration and improving the Raman laser peak power. In comparison with a separated laser gain medium and saturable absorber configuration, the composite Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG crystal eliminates the air gap between the gain medium and the saturable absorber to avoid interface layer damage and provide good thermal management. These features are desirable for generating high peak power pulses of the Raman laser. Moreover, Yb3+-doped laser materials possess various excellent properties, such as large energy storage capacities, low thermal loadings and permitting high concentration doping. PQSRMLs with a typical cavity length of several millimeters can provide low intracavity losses and generate sub-nanosecond pulses, which is also suitable for generating high peak power pulses of the Raman laser. For PQSRMLs using Yb3+-doped laser materials, the selection of TOC should ensure a sufficient intracavity laser intensity for the Raman conversion and also control for strong re-absorption losses of Yb3+ ions at 1.03 μm to avoid another emission line oscillation at 1.05 μm. The improvement in peak power of the Raman laser can also be attributed to the employment of a separate laser gain medium and Raman active medium configuration which allows for good thermal management to prevent serious thermal loading.

Table 3.
Summary of output properties of passively Q-switched micro Raman lasers.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, sub-nanosecond, high peak power Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRMLs based on a sandwich-type plane-parallel structure and a compact plane-concave cavity operated in multiple pulse mode under QCW pumping have been demonstrated. The highest total Raman laser energy was 1.8 mJ, obtained using a combination of 4 mm YVO4 crystal and TOC = 16% with a sandwich-type plane-parallel structure. The corresponding repetition rate reaches 225 kHz under a single LD pump pulse. By using a compact plane-concave cavity and 5 mm YVO4 crystal, the output single pulse energy and peak power of the Raman laser were increased to 44 μJ and 95 kW at a repetition rate of 87.8 kHz. The shortest Raman pulse duration was 464 ps. The sub-nanosecond, high peak power Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 PQSRML provides a promising method for developing miniature, low-cost yellow–green laser sources for biomedical applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.W. and S.F.; Investigation, Y.Z.; Methodology, C.Z. and X.M.; Supervision, W.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22104139), Jinan “20 New Universities” Funding Project (202228019) and the Qilu University of Technology (Shandong Academy of Sciences), Education and Industry Integration Pilot Project (2022PY045).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Tsunekane, M.; Inohara, T.; Ando, A.; Kido, N.; Kanehara, K.; Taira, T. High Peak Power, Passively Q-switched Microlaser for Ignition of Engines. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2010, 46, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayhowski, J.J. Passively Q-switched Nd:YAG microchip lasers and applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2000, 303–304, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerse, C.; Kalaycioglu, H.; Elahi, P.; Çetin, B.; Kesim, D.K.; Akçaalan, Ö.; Yavas, S.; Asik, M.D.; Öktem, B.; Hoogland, H.; et al. Ablation-cooled material removal with ultrafast bursts of pulses. Nature 2016, 537, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.T.; Li, X.D.; Mei, F.; Chen, D.Y.; Yan, R.P. 30 mJ, 1 kHz sub-nanosecond burst-mode Nd:YAG laser MOPA system. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 36129–36136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Bass, M.; Mao, Y.; Deng, P.; Gan, F. Dependence of the Yb3+ emission cross section and lifetime on temperature and concentration in yttrium aluminum garnet. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B Opt. Phys. 2003, 20, 1975–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Ueda, K.I.; Shirakawa, A.; Yagi, H.; Yanagitani, T.; Kaminskii, A.A. Composite Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG ceramics picosecond microchip lasers. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 14516–14523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loiko, P.; Serres, J.M.; Mateos, X.; Yumashev, K.; Yasukevich, A.; Petrov, V.; Griebner, U.; Aguiló, M.; Díaz, F. Sub-nanosecond Yb:KLu(WO4)2 microchip laser. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 2620–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Y.; Tokita, S.; Kawanaka, J. High beam quality and high peak power Yb:YAG/Cr:YAG microchip laser. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, R.; Taira, T. > 6 MW peak power at 532 nm from passively Q-switched Nd:YAG/Cr4+:YAG microchip laser. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 19135–19141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, R.; Taira, T.; Miyamoto, A.; Furukawa, Y.; Tago, T. >3 MW peak power at 266 nm using Nd:YAG/Cr4+:YAG microchip laser and fluxless-BBO. Opt. Mater. Express 2012, 2, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, R.; Tsuji, N.; Suzuki, T.; Nishifuji, M.; Taira, T. Efficient second to ninth harmonic generation using megawatt peak power microchip laser. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 28849–28855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Chen, X.; Zhou, C.L.; Huang, G.H.; He, Z.P.; Shu, R. 150 kHz, 300 ps green laser frequency doubled from a linearly polarized passively Q-switched Nd:YAG/Cr4+:YAG microchip oscillator and a Nd:YVO4 amplifier. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 147, 107708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.D.; Wang, T.Q.; Zhou, M.; Qiao, Z.D.; Liu, X.L.; Fan, Z.W. High Repetition Rate, TEM00 Mode, Compact Sub-Nanosecond 532 nm Laser. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mildren, R.P.; Convery, M.; Pask, H.M.; Piper, J.A.; McKay, T. Efficient, all-solid-state, Raman laser in the yellow, orange and red. Opt. Express 2004, 12, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.J.; Pask, H.M.; Piper, J.A.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, J.Y. An intracavity, frequency-doubled BaWO4 Raman laser generating multi-watt continuous-wave, yellow emission. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 5984–5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawley, T.S.; Telford, W.G.; Ramezani, A.; Hawley, R.G. Four-color flow cytometric detection of retrovirally expressed red, yellow, green, and cyan fluorescent proteins. BioTechniques 2001, 30, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevis, B.J.; Glick, B.S. Rapidly maturing variants of the Discosoma red fluorescent protein (DsRed). Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telford, W.; Murga, M.; Hawley, T.; Hawley, R.; Packard, B.; Komoriya, A.; Haas, F.; Hubert, C. DPSS yellow-green 561-nm lasers for improved fluorochrome detection by flow cytometry. Cytom. Part A 2005, 68A, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telford, W.G.; Babin, S.A.; Khorev, S.V.; Rowe, S.H. Green fiber lasers: An alternative to traditional DPSS green lasers for flow cytometry. Cytom. Part A 2009, 75A, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminskii, A.A.; Ueda, K.; Eichler, H.J.; Kuwano, Y.; Kouta, H.; Bagaev, S.N.; Chyba, T.H.; Barnes, J.C.; Gad, G.M.A.; Murai, T.; et al. Tetragonal vanadates YVO4 and GdVO4—New efficient χ(3)-materials for Raman lasers. Opt. Commun. 2001, 194, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F. Efficient subnanosecond diode-pumped passively Q-switched Nd:YVO4 self-stimulated Raman laser. Opt. Lett. 2004, 29, 1251–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisel, V.E.; Troshin, A.E.; Tolstik, N.A.; Shcherbitsky, V.G.; Kuleshov, N.V.; Matrosov, V.N.; Matrosova, T.A.; Kupchenko, M.I. Q-switched Yb3+:YVO4 laser with Raman self-conversion. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 2005, 80, 471–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.H.; Wang, M.Q.; Wang, S.Q.; Zhang, W.H. Investigation on LD end-pumped passively Q-switched c-cut Nd:YVO4 self-Raman laser. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 13052–13061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Li, Z.; Zhu, S.Q.; Yin, H.; Chen, Z.Q.; Zhang, G.; Chen, W.D. YVO4 Raman laser pumped by a passively Q-switched Yb:YAG laser. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 14033–14042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, L.; Miao, Y.; Dong, J. Elliptically polarized, nanosecond dual-pulse Raman laser with tunable pulse interval and pulse amplitude ratio. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 171, 110397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Wang, X.J.; Dong, J. Multiwavelength, sub-Nanosecond Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 passively Q-switched Raman microchip laser. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2018, 24, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Wang, X.J.; Dong, J. Sub-nanosecond, high peak power Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 passively Q-switched Raman micro-laser operating at 1134 nm. J. Lumin. 2021, 234, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.F.; Li, X.D.; Yu, X.; Fan, R.W.; Yan, R.P.; Peng, J.B.; Xu, X.R.; Sun, R.; Chen, D.Y. A novel miniaturized passively Q-switched pulse-burst laser for engine ignition. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 24655–24665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.F.; He, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, X.D.; Li, J.; Yan, R.P.; Peng, J.B.; Zhang, X.L.; Sun, R.; Pan, Y.B.; et al. Multiple-beam, pulse-burst, passively Q-switched ceramic Nd:YAG laser under micro-lens array pumping. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 24955–24961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdon, P.; Planchat, C.; Fleury, D.; Le Gouet, J.; Gustave, F.; Dolfi-Bouteyre, A.; Lombard, L.; Durécu, A.; Jacqmin, H. Passively cooled Cr:YAG Q-switched Yb:YAG micro-laser delivering continuously tunable high repetition rate bursts of short pulses. In Proceedings of the Conference on Solid State Lasers XXVIII—Technology and Devices, SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–7 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shpak, P.V.; Voitikov, S.V.; Demidovich, A.A.; Danailov, M.B.; Orlovich, V.A. Coupled-cavity passively Q-switched two-Stokes microchip laser. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 2012, 108, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.D.; Gao, Z.L.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, B.T.; He, J.L.; Tao, X.T. An α-BaTeMo2O9 Raman Shifting Driven by a Pulsed LD Pumped Nd:YAG Laser. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2014, 26, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.C.; Qiao, X.H.; Sun, P.; Wang, X.L.; Dong, J. High peak power, multi-wavelength, passively Q-switched Raman lasers based on Yb:YAG/Cr4+:YAG composite crystal. Laser Phys. 2020, 30, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pask, H.M. The design and operation of solid-state Raman lasers. Prog. Quantum Electron. 2003, 27, 3–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, M.; Weichman, L.S.; Vigil, S.; Brickeen, B.K. The temperature dependence of Nd3+ doped solid-state lasers. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2003, 39, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunekane, M.; Taira, T. Temperature and Polarization Dependences of Cr:YAG Transmission for Passive Q-switching. In Proceedings of the Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics/Quantum Electronics and Laser Science Conference (CLEO/QELS 2009), Baltimore, MD, USA, 2–4 June 2009; p. JTuD8. [Google Scholar]
- Zverev, P.G. The influence of temperature on Raman modes in YVO4 and GdVO4 crystals. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 92, 012073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiko, P.; Serres, J.M.; Mateos, X.; Jambunathan, V.; Yumashev, K.; Petrov, V.; Griebner, U.; Aguiló, M.; Díaz, F. Passive Q-switching and self-Raman conversion in Yb:KLu(WO4)2 microchip laser. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, Optical Society of America, Munich, Germany, 21–25 June 2015; p. CA_5b_3. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.H.; Petrov, V.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, J.Y. Power scaling of a continuous-wave and passively Q-switched Yb:KLu(WO4)2 laser end-pumped by a high-power diode. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 2007, 88, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisel, V.E.; Shcherbitsky, V.G.; Kuleshov, N.V. Efficient self-frequency Raman conversion in a passively Q-switched diode-pumped Yb:KGd(WO4)2 laser. In Proceedings of the Advanced Solid-State Photonics Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, 2–5 February 2003; pp. 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.J.; Wang, X.L.; Zheng, Z.F.; Qiao, X.H.; Dong, J. 1164.4 nm and 1174.7 nm dual-wavelength Nd:GdVO4/Cr4+:YAG/YVO4 passively Q-switched Raman microchip laser. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 3198–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).