Abstract
This study aimed to evaluate the optical performance of a rotationally asymmetric intraocular lens (IOL) when it is decentered relative to the visual axis. The FEMTIS Comfort IOL (Teleon Surgical B.V., Spankeren, The Netherlands) was assessed using ray tracing software in the Atchison model eye at apertures of 3.0 mm and 4.5 mm. The metric used for assessment was the through-the-focus area under the modulation transfer function (TF-MTFa). Decentrations of 0.2 mm and 0.4 mm were considered. Our results indicated that the MTFa defocus curves exhibited significant differences depending on the direction of vertical decentration. Downward decentrations shifted the MTFa curve towards virtual vergences, resulting in improved optical quality at far distances but decreased optical quality at intermediate and near vision. Conversely, upward decentrations produced the opposite effect. Since, on one hand, this lens is fixed within the capsulorhexis during surgery, demonstrating excellent stability, and on the other hand, the precise centration of the capsulorhexis can be made accurately off the visual axis, these results provide surgeons with the opportunity to plan various clinical scenarios to optimize surgical outcomes with this IOL by selecting the optimal location for capsulorhexis centration in each patient.
1. Introduction
The rise in life expectancy has led to a surge in the number of presbyopic patients. As modern-day activities and visual demands have evolved [1], the need for effective treatment options for presbyopia has become increasingly important. While the traditional approach involved replacing the crystalline lens with a multifocal intraocular lens (MIOL) only in cases of cataract [2], it is now even more frequent and recommended in some pathological cases, such as dysfunctional lens syndrome [3,4].
There is a broad selection of commercially available MIOLs with varying designs. Depending on the number of focal points produced by the IOL, they can be categorized as monofocal, bifocal, trifocal, or extended depth of focus (EDoF) lenses [2,5,6]. While bifocal and trifocal lenses provide multiple focal points, EDoF lenses are defined differently by The American Academy of Ophthalmology working group. According to their clinical criteria, an EDoF lens is one that extends the focus by at least 0.50 D beyond that of a monofocal IOL at a visual acuity (VA) of 0.2 logMAR [7]. Among EDoF lenses, refractive rotationally asymmetric multifocal IOLs have been preferred in clinical trials due to the superior contrast sensitivity they provide compared to MIOLs with concentric rings [6,8].
Achieving optimal visual performance MIOL often requires precise centration on the visual axis [8,9]. However, several clinical studies measuring IOL decentration after lens implantation have reported an average decentration of approximately 0.20 mm in the horizontal direction [10,11,12]. The severity of the consequences of these decentrations on visual quality depends on the design of the IOL. Studies have shown that symmetrical MIOLs (with rings around the optical axis) can tolerate decentration of up to 0.2–0.3 mm without significantly affecting image quality [13,14]. However, for MIOLs with asymmetrical designs, the effects of these decentrations are much more severe [15,16]. To address this issue, some commercial MIOL models have introduced new haptic designs. For example, the FEMTIS Comfort IOL (Teleon Surgical B.V., Spankeren, The Netherlands) incorporates four flaps that secure the optic within the capsulorhexis [17,18]. A recent multicenter clinical study [19] demonstrated that this design significantly improves stability compared to conventional IOLs placed in the capsular bag.
On the other hand, with the advent of femtosecond laser cataract surgery, surgeons can now create a capsulorhexis with precise size and centration. This fact, together with the above-mentioned features of the FEMTIS Comfort IOL, suggests its potential as a suitable platform for customized surgeries. To achieve this goal, it has become necessary to be able to predict the effect of decentrations precisely. To the best of our knowledge, such an analysis has not been conducted to date. Therefore, the objective of this study is to use the ray tracing software ZEMAX™ OpticStudio (EE version 18.7, ZEMAX Development Corporation, Bellevue, WA, USA) to evaluate the potential impact of small decentrations from the visual axis of the FEMTIS Comfort IOL in a model eye. We will explore the effects on visual quality indicators closely related to VA, specifically the area under the modulation transfer function (MTFa).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Multifocal Intraocular Lens
The FEMTIS Comfort IOL is a biconvex IOL with a singular bifocal refractive design, having an angular region with an addition of 1.5 D power (see Figure 1). It has an optical zone diameter of 5.7 mm and a plate-haptic design with four clip haptics to fix the optic to the capsulorhexis [17]. It is made of a copolymer consisting of hydrophilic acrylates with a hydrophobic surface. In a previous study, we assessed the optical performance of this lens in vitro using an optical bench under polychromatic light. Our findings demonstrated that the through-focus modulation transfer function (TF-MTF) curves (at 50 cycles/mm) displayed a bifocal profile, effectively creating an EDoF design in practical terms [20].
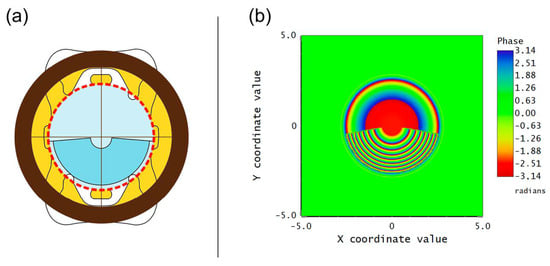
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic diagram illustrating FEMTIS Comfort IOL fixed in a centered 6 mm-diameter capsulorhexis (dashed red line). The optical zone diameter is represented in blue; the upper part corresponds to the distance vision, while the lower angular sector corresponds to the addition of power. (b) Phase map of the FEMTIS Comfort IOL (obtained with ZEMAX™ OpticStudio), related to the angular distribution of lens powers of the IOL.
2.2. Numerical Evaluation
To assess the performance of the FEMTIS Comfort IOL, we utilized the ray tracing software ZEMAX™ Optic Studio in which the Atchison model eye was programmed [21,22]. This eye model was constructed using clinical biometric data obtained from 121 healthy individuals with both emmetropic and myopic conditions. The mean spherical refraction ranged from +0.75 D to −12.38 D. Individuals included in the study had astigmatism lower than 0.75 D and at least 20/20 corrected visual acuity in the tested eye. To obtain this clinical data, that study adhered to the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki, and the study was approved by both the QUT University Human Research Ethics Committee and the Prince Charles Hospital Human Research Ethics Committee [21].
This model eye, which consists of perfectly centered optical elements, has been previously employed for numerical assessments of the optical quality achieved after IOL implantation in different scenarios: it has been employed to evaluate the decentration and tilt of aspheric IOLs with different haptic designs [23]. Similarly, it has been used to quantify modifications in ocular aberrations resulting from positional errors of the IOL (decentration, tilt, and axial translation) in eyes with myopia and emmetropia [24]. Furthermore, it has been employed to investigate the impact of glistenings on the quality of retinal imaging in pseudophakic eyes, using models of microvacuoles of varying sizes [25].
By employing this model in our study, we were able to isolate the effects of IOL decentration while minimizing the potential influence of other intrinsic eye geometrical parameters on vision, particularly variations in angle kappa. In our analysis, the IOL was positioned on the first surface of the crystalline lens, which was removed to simulate the outcome of cataract surgery where this IOL is fixed within the capsulorhexis [17]. Table 1 shows the parameters of the model eye with the IOL replacing the crystalline lens. The first surface of the IOL was configured with the FEMTIS Comfort IOL profile using the “Grid Sag” Surface. On the other hand, at the posterior surface of the IOL, we have set an asphericity of −1.275 to neutralize the spherical aberration of the lens, as stated by the manufacturer. The evaluations were conducted using monochromatic light at 555 nm wavelength. The IOL power was set to 20 D, and it was oriented as shown in Figure 1a Two pupil diameters were considered, namely, 3.0 mm and 4.5 mm, to simulate photopic and mesopic conditions, respectively.

Table 1.
Atchison model eye and IOL parameters.
To assess the performance of the IOL, we first obtained the modulation transfer function (MTF) in both tangential and sagittal directions. Each MTF was computed for vergences ranging from +0.50 D to −2.50 D in steps of 0.10 D. These measurements were conducted for the IOL located in different positions: centered, decentered by 0.20 mm horizontally and 0.20 mm vertically, and decentered by 0.40 mm horizontally and 0.40 mm vertically. Then, by averaging the tangential and sagittal MTFs across frequencies ranging from 0 to 50 cycles/mm, the MTFas were finally computed for each of the 30 points within the range of vergences assessed. This metric has been demonstrated to be a reliable predictor of VA values in prior studies [26,27,28].
3. Results
Figure 2 and Figure 3 show the predicted MTFa defocus curves of the FEMTIS Comfort IOL for horizontal and vertical decentrations under photopic (3.0 mm pupil) and mesopic (4.5 mm pupil) conditions. In these figures, the horizontal dashed lines represent the logMAR values of the VA predicted by the following semi-empirical equation proposed by Vega et al. [26],
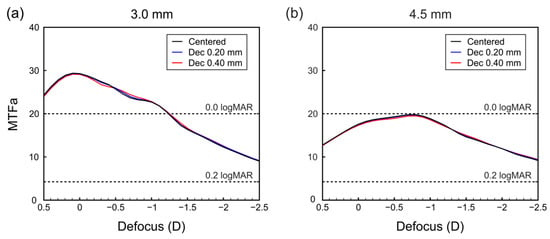
Figure 2.
MTFa defocus curves of the IOL centered and horizontally decentered towards the temporal side for (a) 3.00 mm pupil and (b) 4.50 mm pupil. Horizontal dashed lines are the logMAR values of the VA predicted by Equation (1).
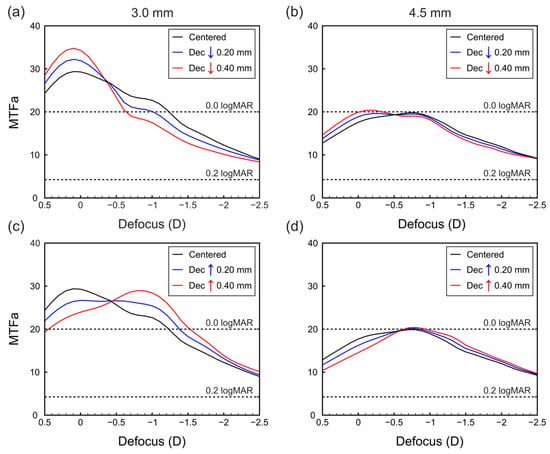
Figure 3.
MTFa defocus curves of the IOL when vertically decentered (a) downward for 3.00 mm pupil, (b) downward for 4.50 mm pupil, (c) upward for 3.00 mm pupil, and (d) upward for 4.50 mm pupil. Horizontal dashed lines are the logMAR values of the VA predicted by Equation (1).
Since the authors of that paper found a high correlation () between the VA measured in patients implanted with several commercial multifocal IOLs and the monochromatic MTFa obtained on an optical bench, the conditions for which Equation (1) was derived are met in the current analysis because our simulations were made with green monochromatic light, and the model eye used induces spherical aberration similar to that of the human cornea [21]. Once the MTFa values are ≥20, there is no improvement in the average calculated VA, regardless of increased MTFa values [26].
In Figure 2, we have represented the MTFas for the lens centered, and with a decentration of 0.2 mm and 0.4 mm in the temporal direction. In this case, it can be observed that, for both pupils, the effect of the decentrations in the MTFa (and consequently in the predicted VA) are negligible. For the small pupil, the bifocal character of the lens can be seen, with two very close foci overlapping, thus achieving the expected effect of an EDoF IOL. However, for the larger pupil, the near focus becomes more prominent than the far focus, although the EDoF effect is maintained in the same range of vergences. This means that in the photopic condition the IOL provides a better MTFa than in mesopic conditions in the range [0.00 D; −1.00 D], but in both cases, the predicted VA is better than 0.2 logMAR in the range [0.00 D; −2.00 D]. As the IOL is symmetric in the horizontal meridian, the same results were found when the IOL was nasally decentered (not shown).
Figure 3 presents the results for the lens when vertically decentered. It can be observed that the MTFa defocus curves exhibit significant differences depending on the direction of decentration. Downward decentrations shift the MTFa curve towards virtual vergences (Figure 3a,b), resulting in improved optical quality at far distances but decreased optical quality at intermediate and near vision. Conversely, upward decentrations produce the opposite effect (Figure 3c,d); that is, for upward decentrations, the curve shifts towards real vergences, leading to improved MTFa values corresponding to intermediate and near vision.
4. Discussion
The issue of IOL decentration following implantation has gained significant interest among ophthalmologists, especially for multifocal designs. However, from a theoretical point of view, it is a complex topic that is discussed unevenly in the literature, and it is particularly complicated for IOLs without rotational symmetry, like the FEMTIS Comfort IOL. Previous clinical studies have concluded that this IOL is very stable over time [17] due to its capsulorhexis fixation, which offers superior control over lens centration, rotation, and effective lens position compared to other IOLs with different haptic designs [15,18]. Considering this attribute and taking into account that the surgeon can perform the capsulorhexis at various positions relative to the visual axis, this study aimed to analyze how small decentrations may impact the visual performance of the FEMTIS Comfort IOL. The goal is to avoid potential negative consequences of IOL decentration and improve the performance of this lens for each individual patient based on their specific visual needs.
Our findings of the TF-MTFa indicate that horizontal decentrations (lateral movement relative to the orientation of the segment) do not significantly affect the optical performance of the IOL (see Figure 2). However, vertical decentrations (superior or inferior relative to the orientation of segment) have noticeable effects on optical performance, especially in photopic conditions (see Figure 3a,c), resulting in improved vision at either far or intermediate distances, depending on the decentration direction. This result is a consequence of the ratio between the areas with far and near powers covered by the pupil when the lens is decentered.
While the findings from this study cannot be directly applied to clinical expectations, it is important to consider previous results that discuss the decentration of this IOL. In the first study that reported outcomes after insertion of the FEMTIS Comfort IOL, Darian-Smith and Versace [17] found that the binocular logMAR VA obtained with this IOL was as follows: −0.05 ± 0.09, at 0 D, 0.03 ± 0.1 at −1 D, and 0.39 ± 0.17 at 2.5 D; according to Equation (1), these values correspond approximately to MTFa = 20, for 0.0 D and −1.0 D defocus values, respectively, and MTFa = 8 for −2.5 D. These values are in agreement with those represented here in Figure 2 for the centered IOL, taking into account that, on the one hand, the VA values obtained with Equation (1) are numerical approximations that are within a margin of error caused by the fitting parameters in the equation [26], and, on the other hand, no control over the pupil diameters was reported in Ref. [17].
In this work, we have adhered to the principle suggested by Atchison and Thibos that “the best model (eye) is the simplest fit for the task” [29]. Therefore, while the results presented in this study serve as a good starting point for understanding the effect of decentering in a lens without symmetry with respect to the optical axis, more sophisticated eye models, such as the Liou–Brennan model eye [30], which considers the kappa angle, or other model eyes with realistic corneal biometric data after refractive surgery [31,32], will provide complementary information about the potential behavior of this type of lenses in real eyes. Additionally, the assessment of other variables during IOL implantation, such as tilt, oblique decentrations, and segment orientation, will be useful in predicting clinical outcomes.
In this line, Radhakrishnan et al. [33] used a visual simulator to investigate how positioning a lens with similar geometry to the FEMTIS Comfort IOL (i.e., the LENTIS M-plus) in various orientations affected the visual performance of real patients. Their findings indicated that patients had different visual preferences for specific IOL orientations. Hence, further evaluation is necessary to determine the combined impact of asymmetric IOL decentrations and rotations. Therefore, considering that, to some extent, customized surgery could be performed with this type of IOL, the results presented in this work, along with the use of adaptive optics visual simulators, could greatly assist surgeons in identifying the optimal location for capsulorhexis, especially in patients with irregular corneas, or in inducing slight decentrations (as shown in Figure 3) to improve vision at the required distances.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, despite the mentioned limitations, the results presented in this article provide valuable objective insights for surgeons regarding the performance of a MIOL without rotational symmetry in the presence of small decentrations. Moreover, these findings suggest that programming these lenses in adaptive optics simulators can greatly benefit pre-surgery studies, enabling customization to meet the visual needs of each patient and prevent unfavorable outcomes. Such an assessment plays a crucial role in making informed decisions.
The optical performance of the FEMTIS Comfort IOL is not affected when it is horizontally decentered with respect to the visual axis. However, when the lens is decentered in the vertical direction, there are differences in the calculated MTFa defocus curve. Depending on the direction of decentration, either distance or intermediate vision may be improved. The advantage of computer simulation is the ability to predict several clinical conditions, including decentration in different orientations, independently. This could be useful to optimize the surgical outcome of each patient by selecting the optimal location for the capsulorhexis centration.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.G., L.S. and S.G.-D.; Methodology, S.G., L.S., A.M.-E. and V.F.; Validation, S.G., L.S. and S.G.-D.; Formal analysis, S.G., L.S., S.G.-D. and V.F.; Resources, S.G., L.S. and S.G.-D.; Data curation, A.M.-E. and V.F.; Writing – original draft, S.G., A.M.-E. and V.F.; Writing – review & editing, S.G., L.S. and S.G.-D.; Supervision, S.G.-D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Spain (Grant PID2019-107391RB-I00) and by Generalitat Valenciana, Spain, (Grant CIPROM/2022/30). A. M.-E. acknowledges financial support from Universitat de València (programa Atracció de Talent 2021).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, S.G.-D., upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Charman, W.N. Developments in the Correction of Presbyopia II: Surgical Approaches. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2014, 34, 397–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatinel, D.; Houbrechts, Y. Comparison of Bifocal and Trifocal Diffractive and Refractive Intraocular Lenses Using an Optical Bench. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2013, 39, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durrie, D.S.; Moshifar, M. Dysfunctional lens syndrome. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of ISRS. Pursuit of Perfection. Section II: Intraocular Refractive Surgery Topics, Chicago, IL, USA; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Durrie, D.S. Dysfunctional Lens Syndrome, a New Way to Educate Patients—American Academy of Ophthalmology. Available online: https://www.aao.org/eyenet/academy-live/detail/dysfunctional-lens-syndrome-educate-patients (accessed on 9 March 2023).
- Rampat, R.; Gatinel, D. Multifocal and Extended Depth-of-Focus Intraocular Lenses in 2020. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, e164–e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Y. Efficacy and Safety of Extended Depth of Focus Intraocular Lenses in Cataract Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Ophthalmol. 2019, 19, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacRae, S.; Holladay, J.T.; Glasser, A.; Calogero, D.; Hilmantel, G.; Masket, S.; Stark, W.; Tarver, M.E.; Nguyen, T.; Eydelman, M. Special Report: American Academy of Ophthalmology Task Force Consensus Statement for Extended Depth of Focus Intraocular Lenses. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Zhao, T.-Y.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Wang, W. Tilt and Decentration with Various Intraocular Lenses: A Narrative Review. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 3639–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Merino, P.; Marcos, S. Effect of Intraocular Lens Decentration on Image Quality Tested in a Custom Model Eye. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2018, 44, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, G.; Wang, W.; Xiao, W.; Jin, G.; Wang, L.; Dai, Y.; Ruan, X.; Liu, Z.; et al. Determinants of Intraocular Lens Tilt and Decentration after Cataract Surgery. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, S.; Morizane, Y.; Shiode, Y.; Hirano, M.; Doi, S.; Toshima, S.; Fujiwara, A.; Shiraga, F. Assessment of Tilt and Decentration of Crystalline Lens and Intraocular Lens Relative to the Corneal Topographic Axis Using Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyales, F.; Garzón, N.; Rozema, J.J.; Romero, C.; de Zárate, B.O. Stability of a Novel Intraocular Lens Design: Comparison of Two Trifocal Lenses. J. Refract. Surg. 2016, 32, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashena, Z.; Maqsood, S.; Ahmed, S.N.; Nanavaty, M.A. Effect of Intraocular Lens Tilt and Decentration on Visual Acuity, Dysphotopsia and Wavefront Aberrations. Vision 2020, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; He, W.; Rong, X.; Miao, A.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, X. Decentration and Tilt of Plate-Haptic Multifocal Intraocular Lenses in Myopic Eyes. Eye Vis. 2020, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Xie, L.; Huang, Y. Effects of Decentration and Tilt at Different Orientations on the Optical Performance of a Rotationally Asymmetric Multifocal Intraocular Lens. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2019, 45, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alió, J.L.; Plaza-Puche, A.B.; Javaloy, J.; Ayala, M.J.; Vega-Estrada, A. Clinical and Optical Intraocular Performance of Rotationally Asymmetric Multifocal IOL Plate-Haptic Design Versus C-Loop Haptic Design. J. Refract. Surg. 2013, 29, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darian-Smith, E.; Versace, P. Visual Performance and Positional Stability of a Capsulorhexis-Fixated Extended Depth-of-Focus Intraocular Lens. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2020, 46, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shajari, M.; Sonntag, R.; Niermann, T.; Holland, D.; Kohnen, T.; Priglinger, S.; Mayer, W.J. Determining and Comparing the Effective Lens Position and Refractive Outcome of a Novel Rhexis-Fixated Lens to Established Lens Designs. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 213, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auffarth, G.U.; Friedmann, E.; Breyer, D.; Kaymak, H.; Holland, D.; Dick, B.; Petzold, A.; Shah, S.; Ladaria, L.S.; Garcia, S.A.; et al. Stability and Visual Outcomes of the Capsulotomy-Fixated FEMTIS-IOL After Automated Femtosecond Laser–Assisted Anterior Capsulotomy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 225, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, S.; Salvá, L.; García-Delpech, S.; Martínez-Espert, A.; Ferrando, V.; Montagud-Martínez, D. Polychromatic Assessment of a Refractive Segmented EDOF Intraocular Lens. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchison, D.A. Optical Models for Human Myopic Eyes. Vis. Res. 2006, 46, 2236–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchison, D.A.; Smith, G. Chromatic Dispersions of the Ocular Media of Human Eyes. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2005, 22, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remón, L.; Cabeza-gil, I. Influence of Material and Haptic Design on the Mechanical Stability of Intraocular Lenses by Means of Finite-Element Modeling. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Goncharov, A.; Dainty, C. Intraocular Lens Implantation Position Sensitivity as a Function of Refractive Error. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2012, 32, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geniusz, M.; Kazimierska, M.; Zając, M. Impact of Glistenings on Optical Image Quality of Intraocular Lenses—A Preliminary Study. Photonics Lett. Pol. 2015, 7, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, F.; Millán, M.S.; Garzón, N.; Altemir, I.; Poyales, F.; Larrosa, J.M. Visual Acuity of Pseudophakic Patients Predicted from In-Vitro Measurements of Intraocular Lenses with Different Design. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcon, A.; Canovas, C.; Rosen, R.; Weeber, H.; Tsai, L.; Hileman, K.; Piers, P. Preclinical Metrics to Predict Through-Focus Visual Acuity for Pseudophakic Patients. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.; Rodríguez-Vallejo, M.; Martínez, J.; Burguera, N.; Piñero, D.P. Prediction of Visual Acuity and Contrast Sensitivity From Optical Simulations with Multifocal Intraocular Lenses. J. Refract. Surg. 2019, 35, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchison, D.A.; Thibos, L.N. Optical Models of the Human Eye. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2016, 99, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, H.-L.; Brennan, N.A. Anatomically Accurate, Finite Model Eye for Optical Modeling. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1997, 14, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Marshall, J.; Fitzke, F.W. Model for Predicting the Optical Performance of the Eye in Refractive Surgery. Refract. Corneal Surg. 1993, 9, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, C.; Camps, V.J.; Caballero, M.T.; Piñero, D.P.; Tañá, P.; Tello, C.; Miret, J.J. Comparison of the Optical Quality Vision between Real Post-LASIK Myopic Laser Surgery and the Simulated Implantation of a Phakic IOL in Low Myopia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, A.; Dorronsoro, C.; Marcos, S. Differences in Visual Quality with Orientation of a Rotationally Asymmetric Bifocal Intraocular Lens Design. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2016, 42, 1276–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).