Evaluation of Renal Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury Using Optical Coherence Tomography Based on Fractal Dimension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Protocol
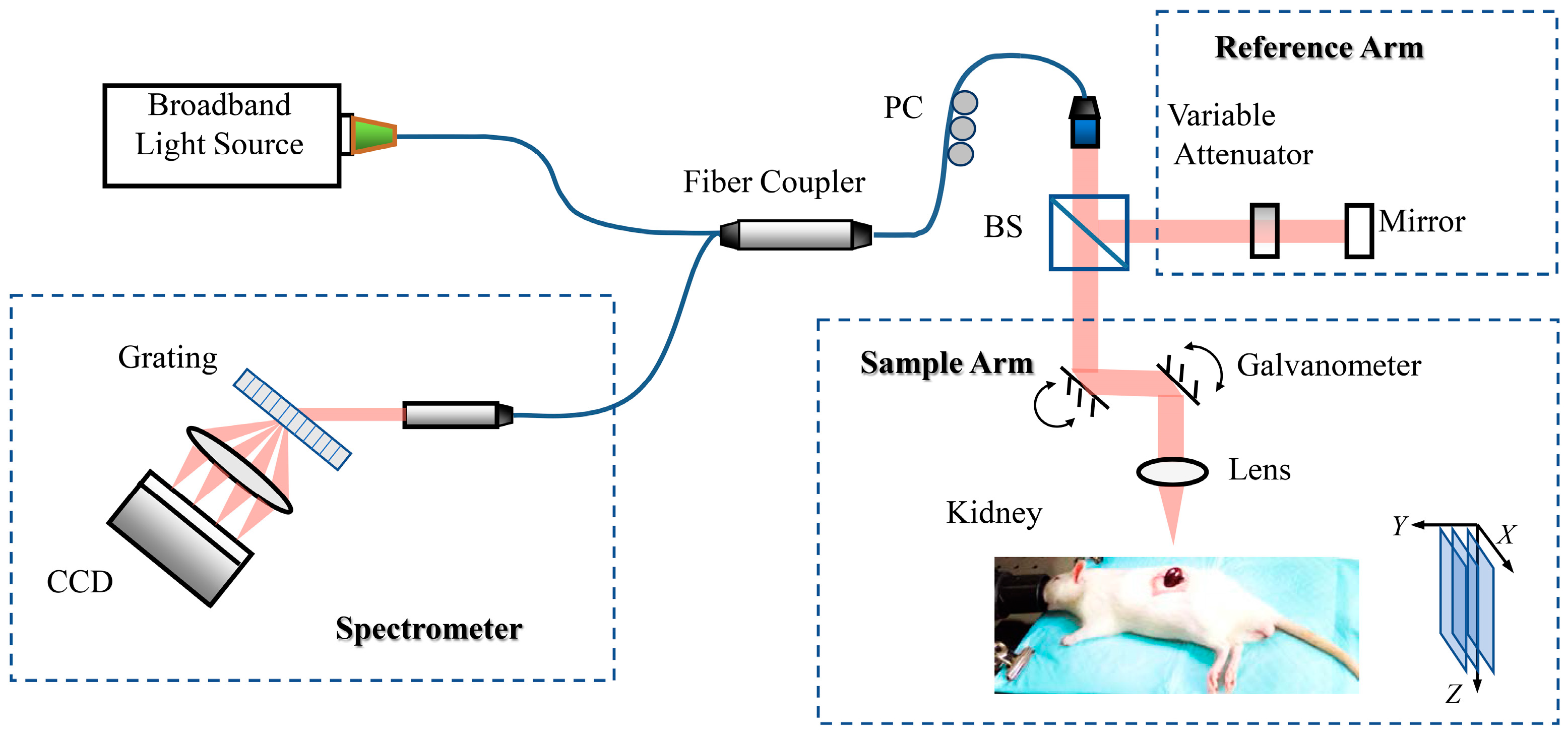
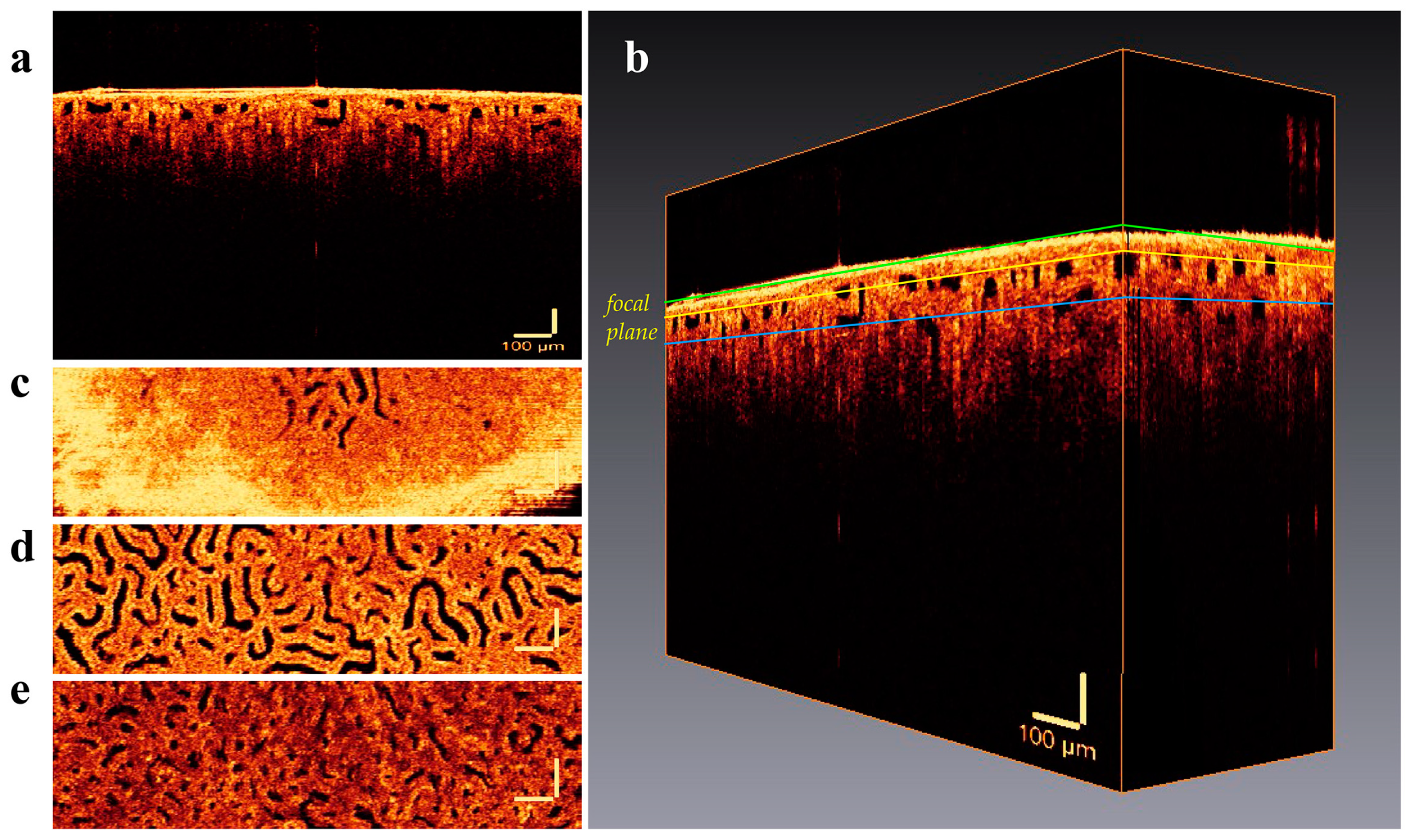
2.2. OCT Imaging of the Rat Kidney
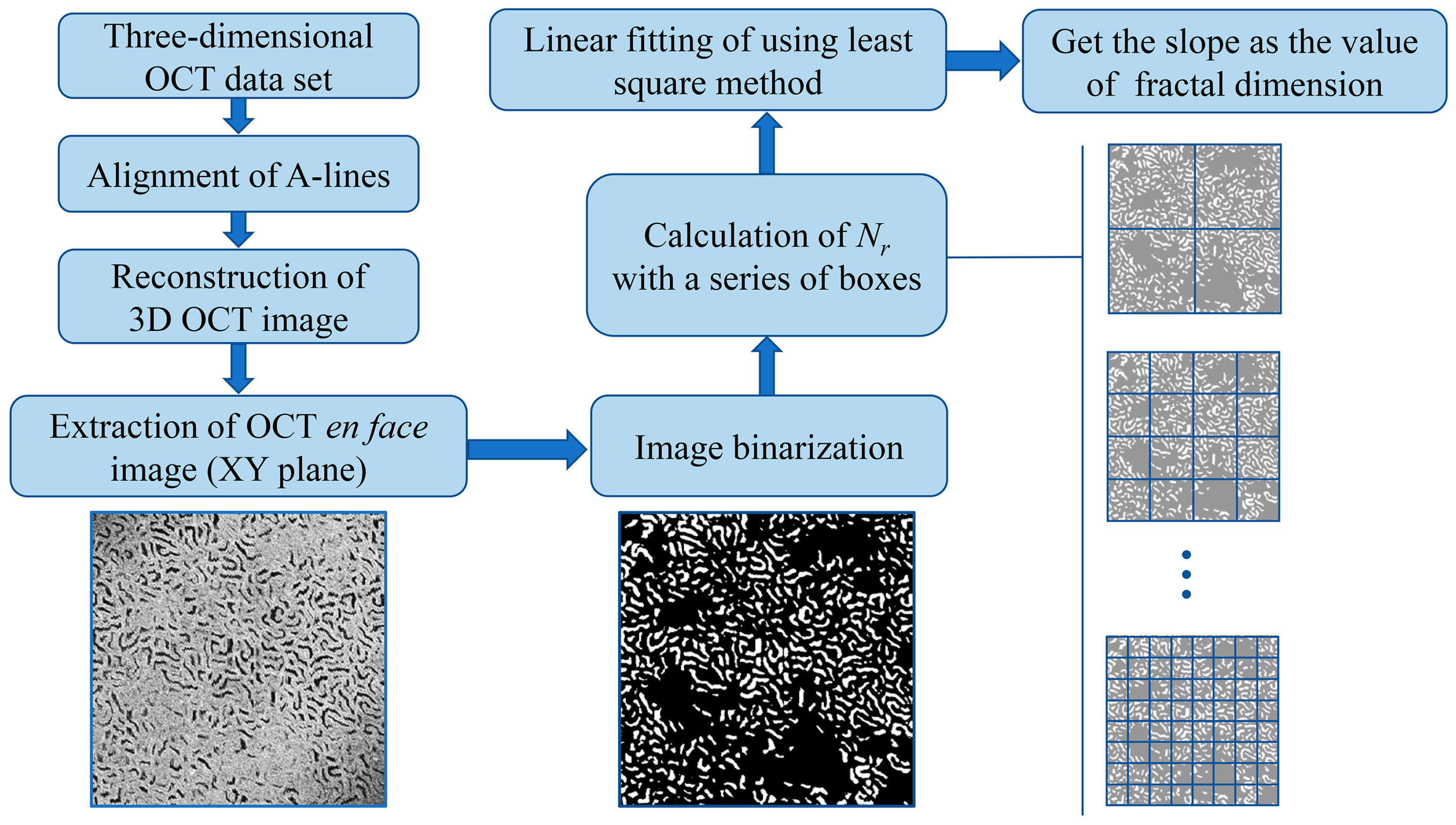
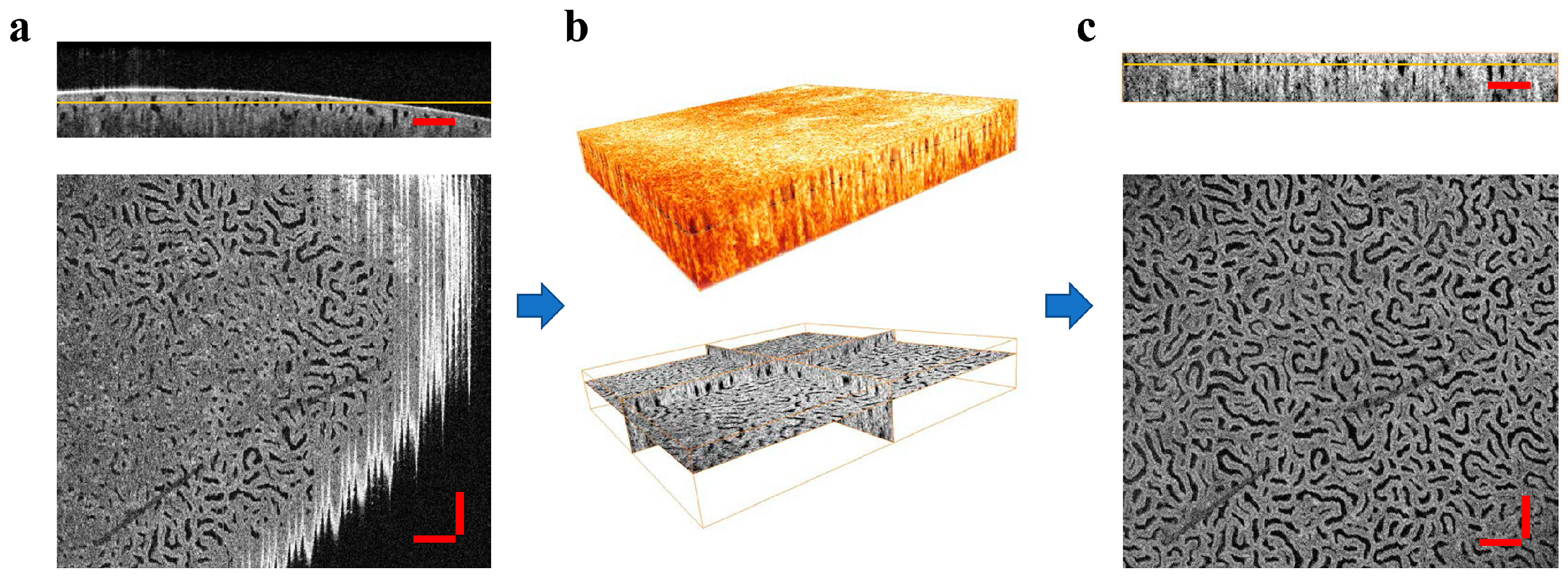
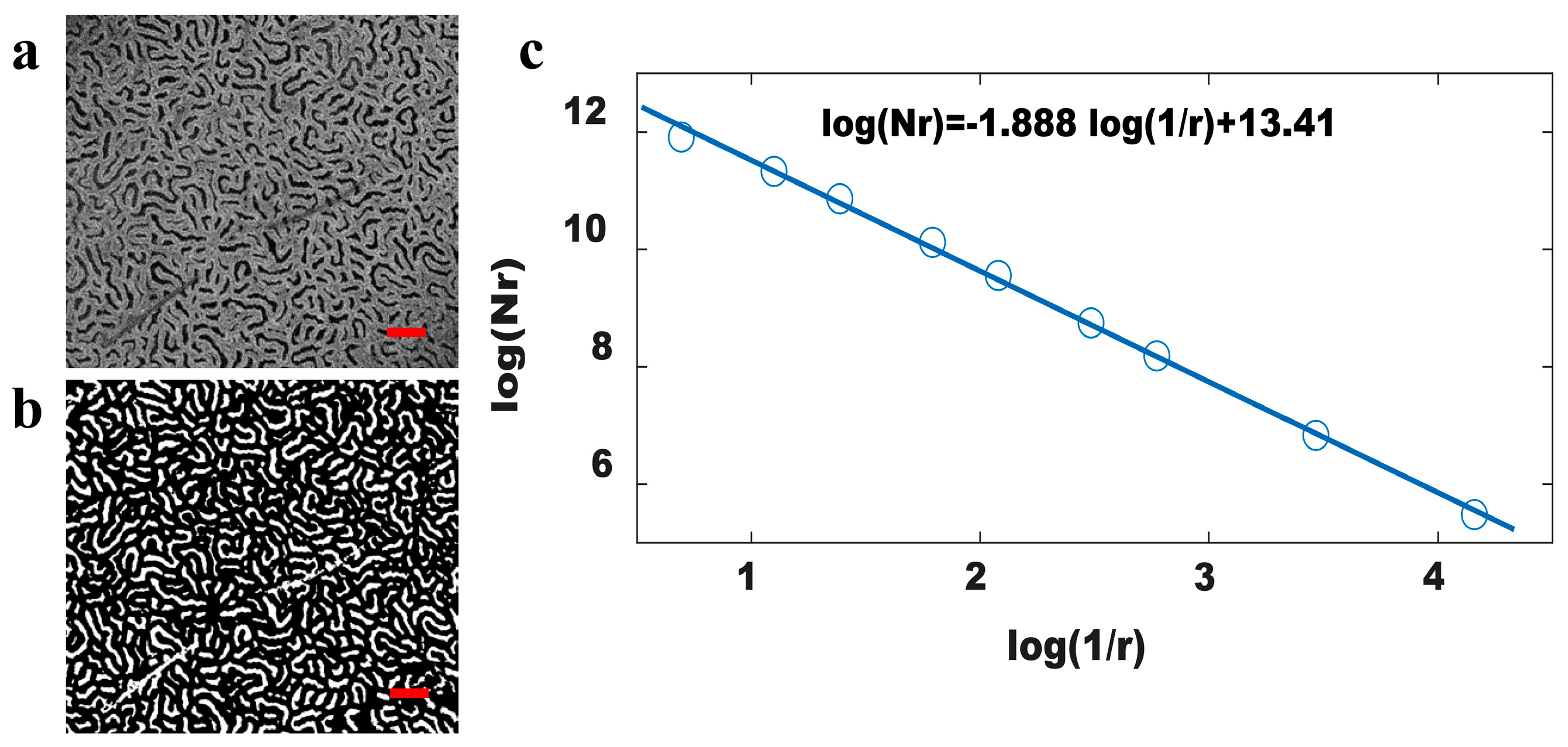
2.3. Fractal Dimension Calculation of OCT Image
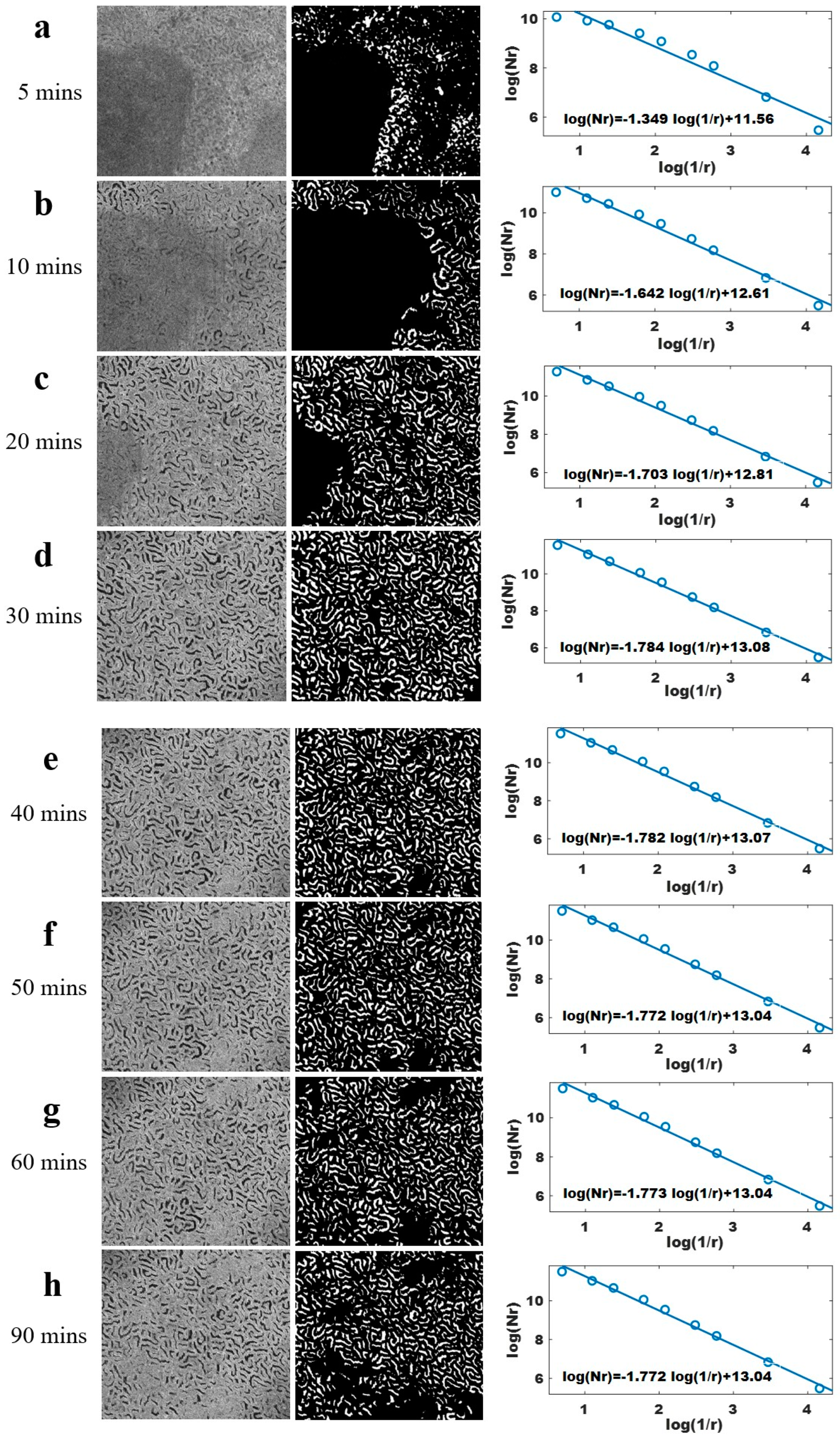
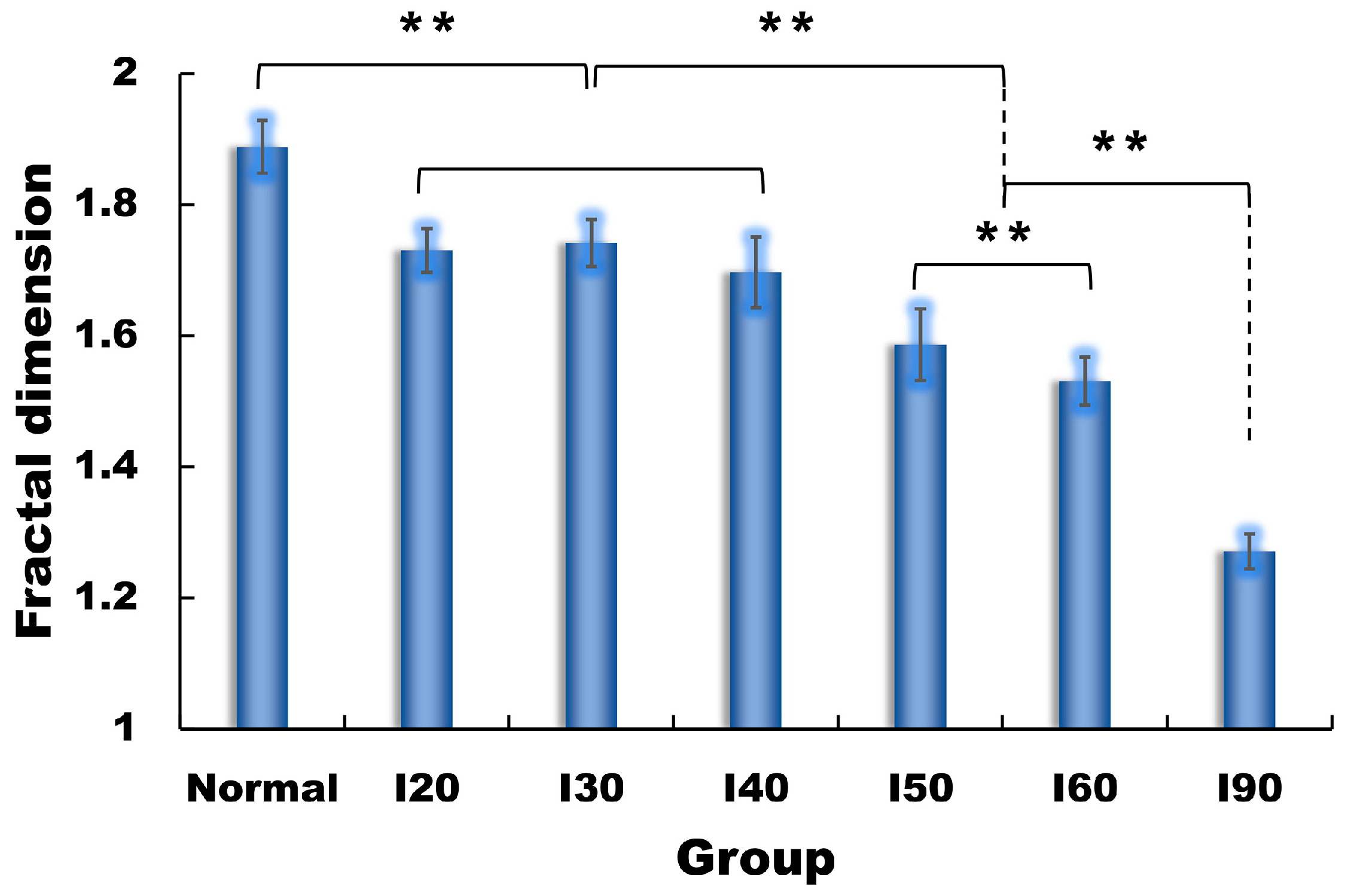
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, D.; Swanson, E.A.; Lin, C.P.; Schuman, J.S.; Stinson, W.G.; Chang, W.; Hee, M.R.; Flotte, T.; Gregory, K.; Puliafito, C.A. Optical coherence tomography. Science 1991, 254, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Mazlin, V.; Grieve, K.; Sahel, J.A. In vivo high-resolution human retinal imaging with wavefront-correctionless full-field OCT. Optica 2018, 5, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Milner, T.E.; Srinivas, S.; Wang, X.; Malekafzali, A.; van Gemert, M.J.; Nelson, J.S. Noninvasive imaging of in vivo blood flow velocity using optical doppler tomography. Opt. Lett. 1997, 22, 1119–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izatt, J.A.; Kulkarni, M.D.; Yazdanfar, S.; Barton, J.K.; Welch, A.J. In vivo bidirectional color dopplor flow imaging of picoliter blood volumes using optical coherence tomography. Opt. Lett. 1997, 22, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitgeb, R.A.; Hitzenberger, C.K.; Fercher, A.F.; Bajraszewski, T. Phase-shifting algorithm to achieve high-speed long-depth-range probing by frequency-domain optical coherence tomography. Opt. Lett. 2003, 28, 2201–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.L.; Wang, R.K. Optical coherence tomography based angiography [Invited]. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 1056–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, T.; Alam, M.; Toslak, D.; Wang, B.; Lu, Y.; Yao, X. Functional optical coherence tomography of neurovascular coupling interactions in the retina. J. Biophotonics 2018, 11, e201800089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auksorius, E.; Borycki, D.; Wojtkowski, M. Crosstalk-free volumetric in vivo imaging of a human retina with fourier-domain full-field optical coherence tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2019, 10, 6390–6407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignali, L.; Solinas, E.; Emanuele, E. Research and clinical applications of optical coherence tomography in invasive cardiology: A review. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2014, 10, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IJsselmuiden, A.J.J.; Zwaan, E.M.; Oemrawsingh, R.M.; Bom, M.J.; Dankers, F.J.; de Boer, M.J.; Camaro, C.; van Geuns, R.J.; Daemen, J.; Van Der Heijden, D.J.; et al. Appropriate use criteria for optical coherence tomography guidance in percutaneous coronary interventions: Recommendations of the working group of interventional cardiology of the Netherlands society of cardiology. Neth. Heart J. 2018, 26, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, J.A.; Saleah, S.A.; Kim, H.; Kang, D.; Seong, D.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.; Wijesinghe, R.E.; Kim, J.; Jeon, M. A Case Report on Skin Sebum Extraction Using High Lateral Resolution Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography. Photonics 2023, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Wang, R.K. Assessment of edema volume in skin upon injury in a mouse ear model with optical coherence tomography. Lasers Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adabi, S.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Noei, S.; Conforto, S.; Daveluy, S.; Clayton, A.; Mehregan, D.; Nasiriavanaki, M. Universal in vivo textual model for human skin based on optical coherence tomograms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welge, W.A.; Barton, J.K. In vivo endoscopic doppler optical coherence tomography imaging of the colon. Lasers Surg. Med. 2017, 49, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Andrews, P.M.; Aguirre, A.D.; Schmitt, J.M.; Fujimoto, J.G. High-resolution three-dimensional optical coherence tomography imaging of kidney microanatomy ex vivo. J. Biomed. Opt. 2007, 12, 034008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, P.M.; Chen, Y.; Onozato, M.L.; Huang, S.W.; Adler, D.C.; Huber, R.A.; Jiang, J.; Barry, S.E.; Cable, A.E.; Fujimoto, J.G. High-resolution optical coherence tomography imaging of the living kidney. Lab. Investig. 2008, 88, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, P.M.; Cooper, M.; Verbesey, J.; Ghasemian, S.; Chen, Y. Mannitol infusion within 15 min of cross-clamp improves living donor kidney preservation. Transplantation 2014, 98, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Boppart, S.A. Review of optical coherence tomography in oncology. J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 22, 121711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseripour, M.; Falavarjani, K.G.; Mirshahi, R.; Sedaghat, A. Optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) applications in ocular oncology. Eye 2020, 34, 1535–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onozato, M.L.; Andrews, P.M.; Li, Q.; Jiang, J.; Cable, A.; Chen, Y. Optical coherence tomography of human kidney. J. Urol. 2010, 183, 2090–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tojo, A. Optical coherence tomography in the kidney: A step toward echo microscopy. J. Urol. 2010, 183, 1669–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Guo, H.; Andrews, P.M.; Anderson, E.; Chen, Y. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) of a murine model of chronic kidney disease. Proc. SPIE Med. Imag. 2015, 9417, 94170T. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, P.M.; Wang, H.; Guo, H.; Anderson, E.; Falola, R.; Chen, Y. Optical coherence tomography of the aging kidney. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2016, 6, 617–622. [Google Scholar]
- Wierwille, J.; Andrews, P.M.; Onozato, M.L.; Jiang, J.; Cable, A.; Chen, Y. In vivo, label-free, three-dimensional quantitative imaging of kidney microcirculation using doppler optical coherence tomography. Lab. Investig. 2011, 91, 1596–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, Z.; Jung, Y.; Jia, Y.; An, L.; Wang, R.K. Highly sensitive imaging of renal microcirculation in vivo using ultrahigh sensitive optical microangiography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2011, 2, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Onozato, M.L.; Andrews, P.M.; Chen, C.W.; Paek, A.; Naphas, R.; Yuan, S.A.; Jiang, J.; Cable, A.; Chen, Y. Automated quantification of microstructural dimensions of the human kidney using optical coherence tomography (OCT). Opt. Express 2009, 17, 16000–16016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, H.; Guo, H.; Anderson, E.; Tang, Q.; Wu, T.; Falola, R.; Smith, T.; Andrews, P.M.; Chen, Y. Optical coherence tomography and computer-aided diagnosis of a murine model of chronic kidney disease. J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 22, 121706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.H.; Gong, W.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, L.Q.; Lin, H.X.; Yang, D.Y.; Xie, S.S. Research on Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury of Rat Kidney Using Optical Coherence Tomography; SPIE/COS Photonics Asia: Hangzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Benoit, B.M.; John, A.W. The fractal geometry of nature. Am. J. Phys. 1983, 51, 286. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, N.; Chaudhuri, B.B. An efficient differential box-counting approach to compute fractal dimension of image. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybernet. 1994, 24, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, G.; Curtis, K.M. Shape recognition using fractal geometry. Pattern Recogn. 1997, 30, 1957–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugihara, G.; May, R.M. Applications of fractals in ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1990, 5, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, B.B.; Sarkar, N. Texture segmentation using fractal dimension. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1995, 17, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.M.; Chen, S.; Crownover, R.M. Texture description and segmentation through fractal geometry. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1989, 45, 150–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalan, S.; Yadav, A.; Sarkar, C.; Boccaletti, S. Unveiling the multi-fractal structure of complex networks. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2017, 97, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, K.; Yang, W. Coarse iris classification using box-counting to estimate fractal dimensions. Pattern Recognit. 2005, 38, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uahabi, K.L.; Atounti, M. Applications of fractals in medicine. Ann. Univ. Craiova-Math. Comput. Sci. Ser. 2015, 42, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Saghatchi, F.; Mohseni-Dargah, M.; Akbari-Birgani, S.; Saghatchi, S.; Kaboudin, B. Cancer therapy and imaging through functionalized carbon nanotubes decorated with magnetite and gold nanoparticles as a multimodal tool. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2020, 191, 1280–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MubarakAli, D. Comprehensive review on rapid diagnosis of new infection COVID-19. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, A.; Panigrahy, C. Human authentication based on fusion of thermal and visible face images. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 30373–30395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahy, C.; Seal, A.; Mahato, N.K. Image texture surface analysis using an improved differential box counting based fractal dimension. Powder Technol. 2020, 364, 276–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | Normal | I20 | I30 | I40 | I50 | I60 | I90 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FD | 1.888 ± 0.040 1 | 1.730 ± 0.033 | 1.741 ± 0.036 | 1.697 ± 0.054 | 1.586 ± 0.055 | 1.531 ± 0.036 | 1.271 ± 0.027 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, Y.; Gong, W.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xie, S. Evaluation of Renal Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury Using Optical Coherence Tomography Based on Fractal Dimension. Photonics 2023, 10, 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10070741
Fang Y, Gong W, Huang Z, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Xie S. Evaluation of Renal Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury Using Optical Coherence Tomography Based on Fractal Dimension. Photonics. 2023; 10(7):741. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10070741
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Yuhong, Wei Gong, Zheng Huang, Yongtao Zhang, Limin Zhang, and Shusen Xie. 2023. "Evaluation of Renal Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury Using Optical Coherence Tomography Based on Fractal Dimension" Photonics 10, no. 7: 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10070741
APA StyleFang, Y., Gong, W., Huang, Z., Zhang, Y., Zhang, L., & Xie, S. (2023). Evaluation of Renal Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury Using Optical Coherence Tomography Based on Fractal Dimension. Photonics, 10(7), 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10070741





