Multiple Fano Resonances in a Metal–Insulator–Metal Waveguide for Nano-Sensing of Multiple Biological Parameters and Tunable Slow Light
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
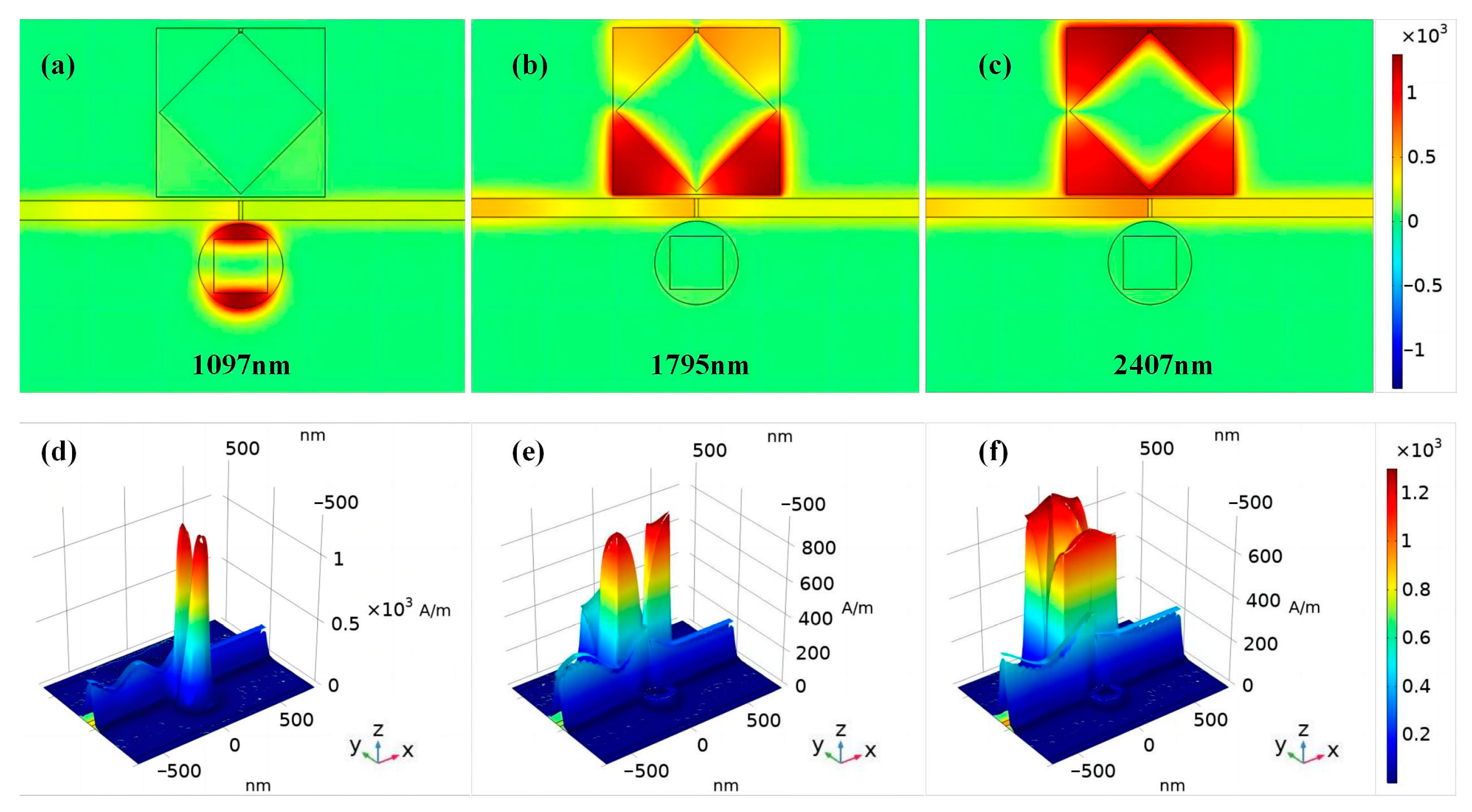
3.1. Mechanism of Fano Resonance and Distribution of Magnetic Fields
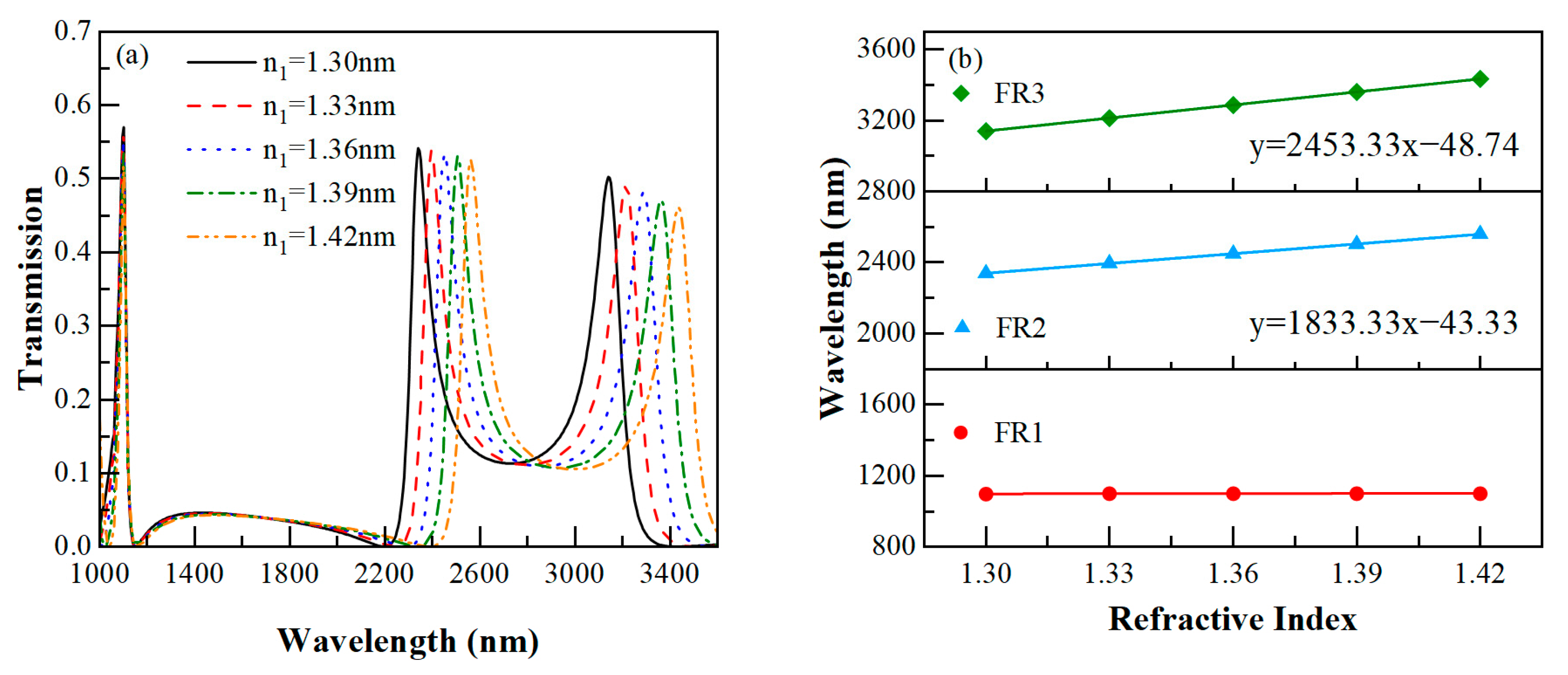
3.2. Refractive Index Sensing
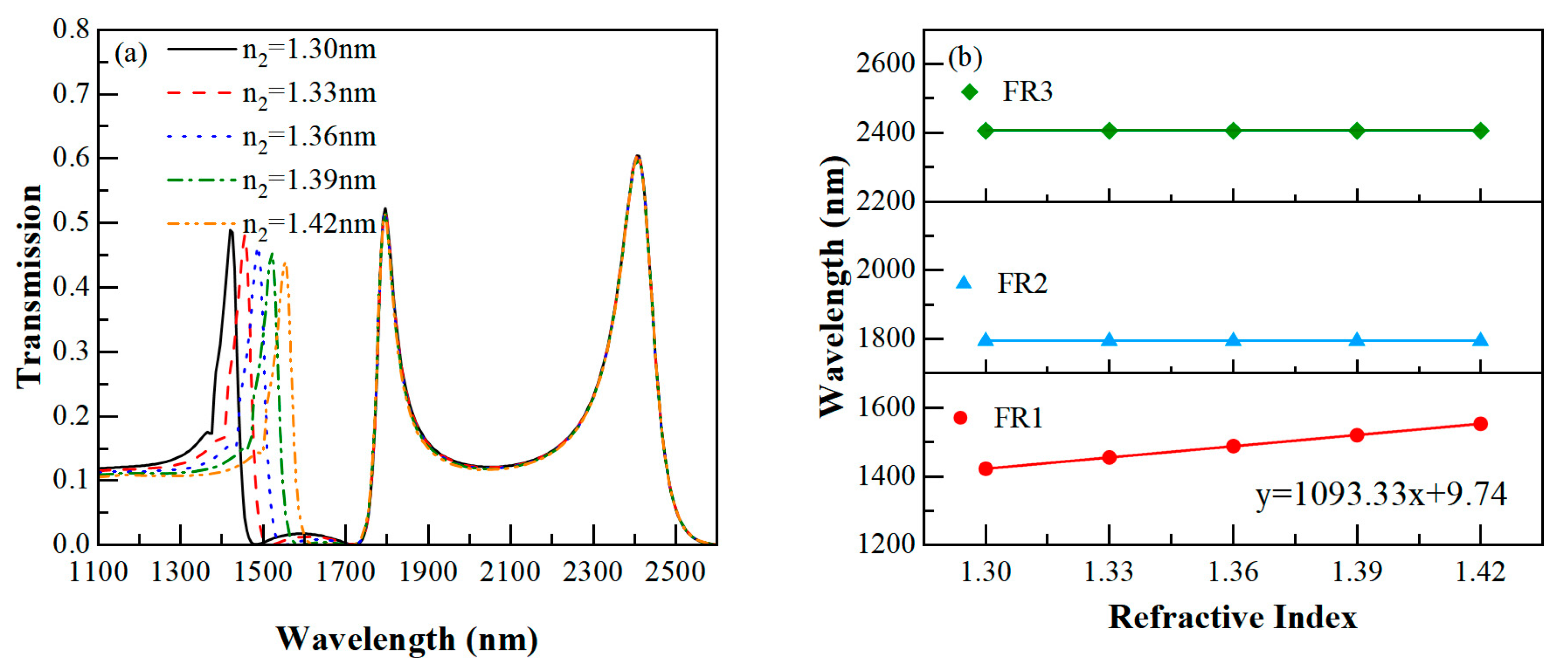
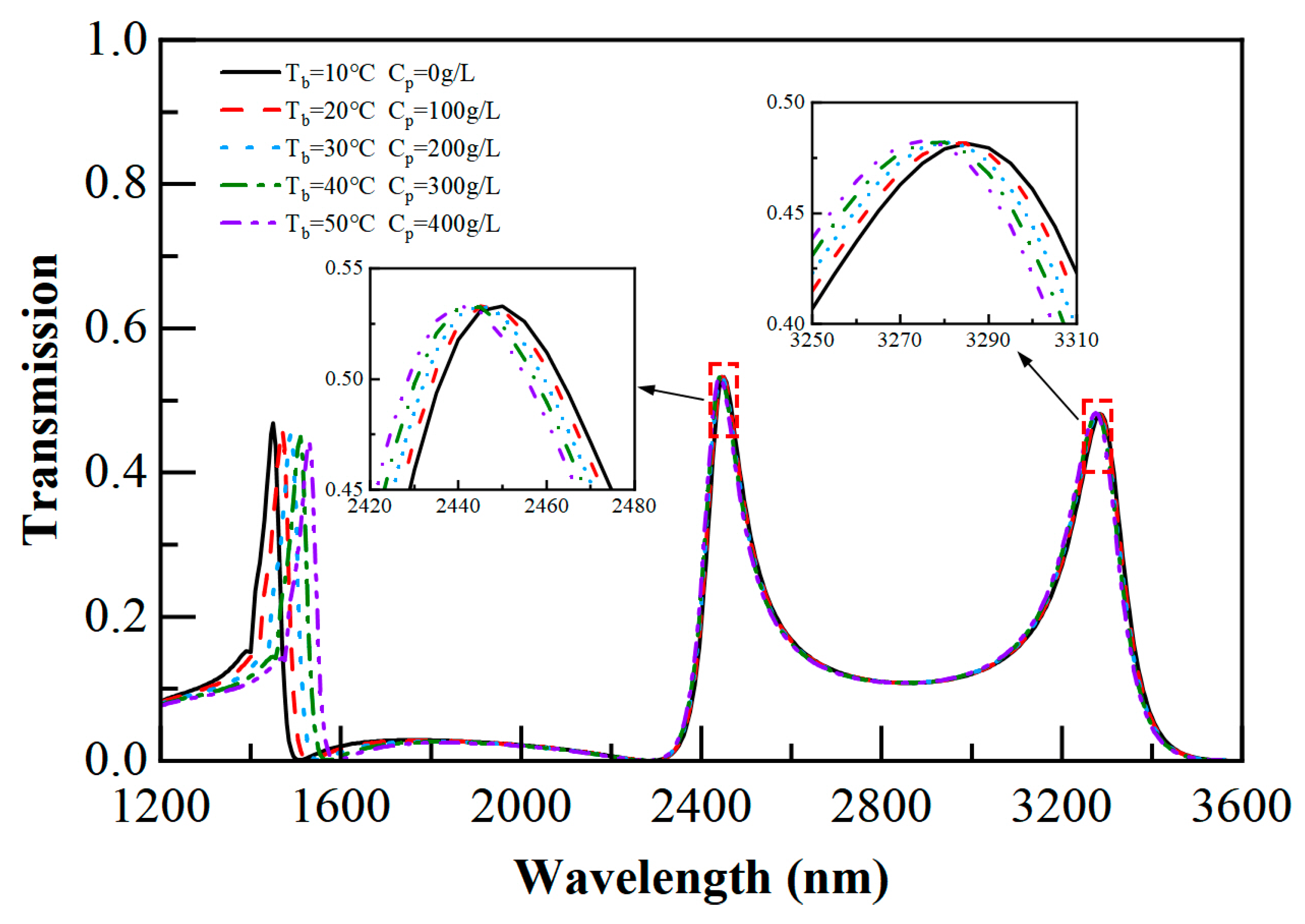
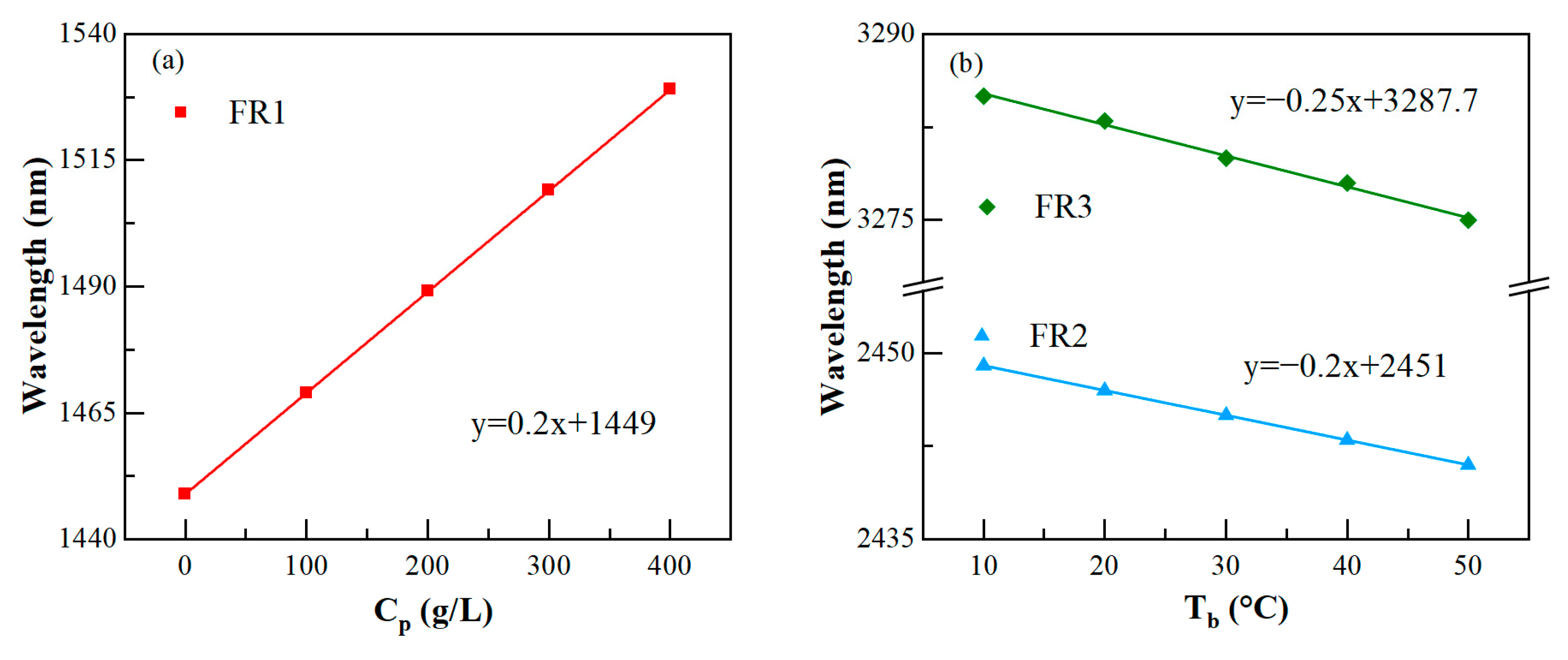
3.3. Multi-Biological Parameter Sensing
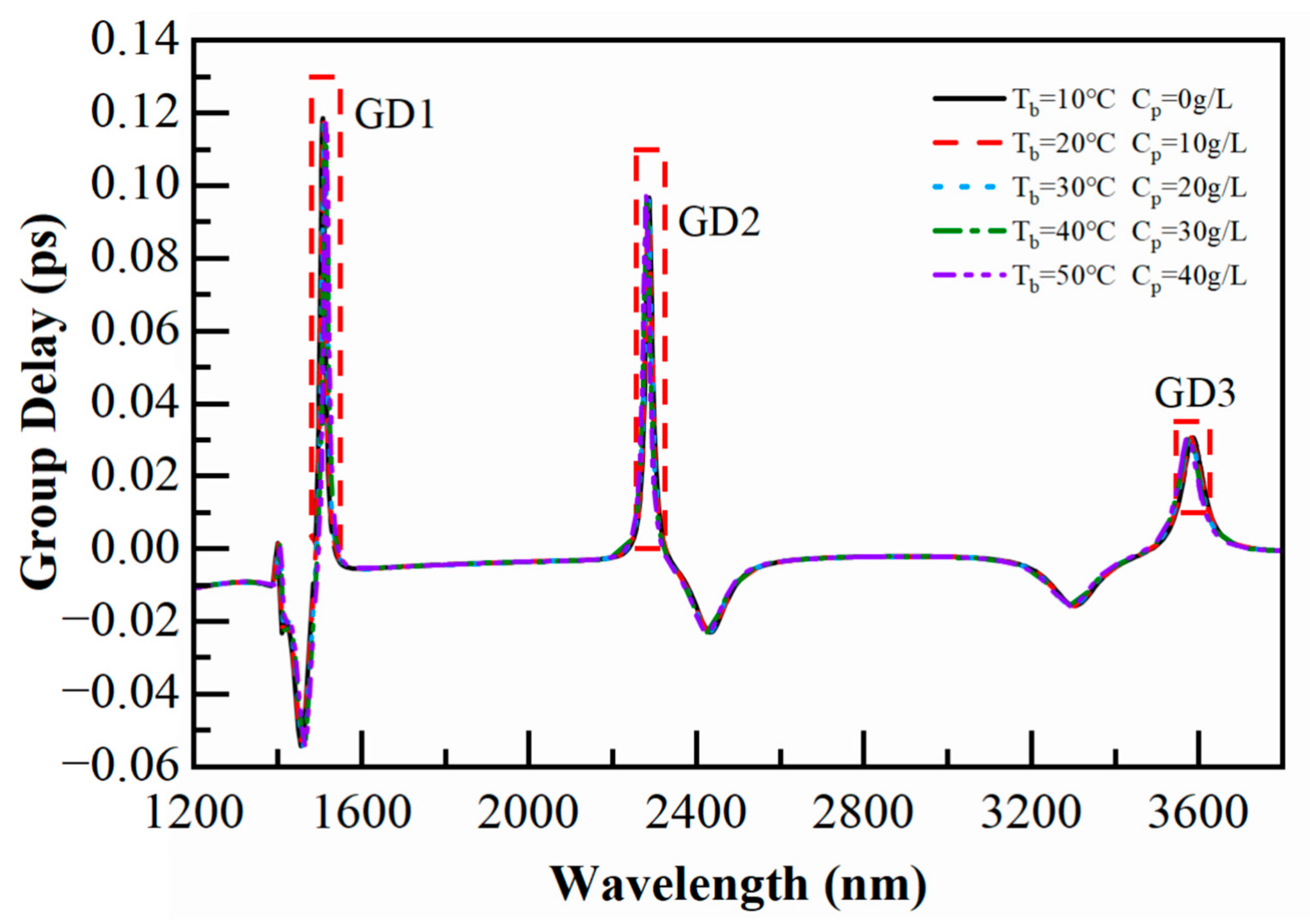
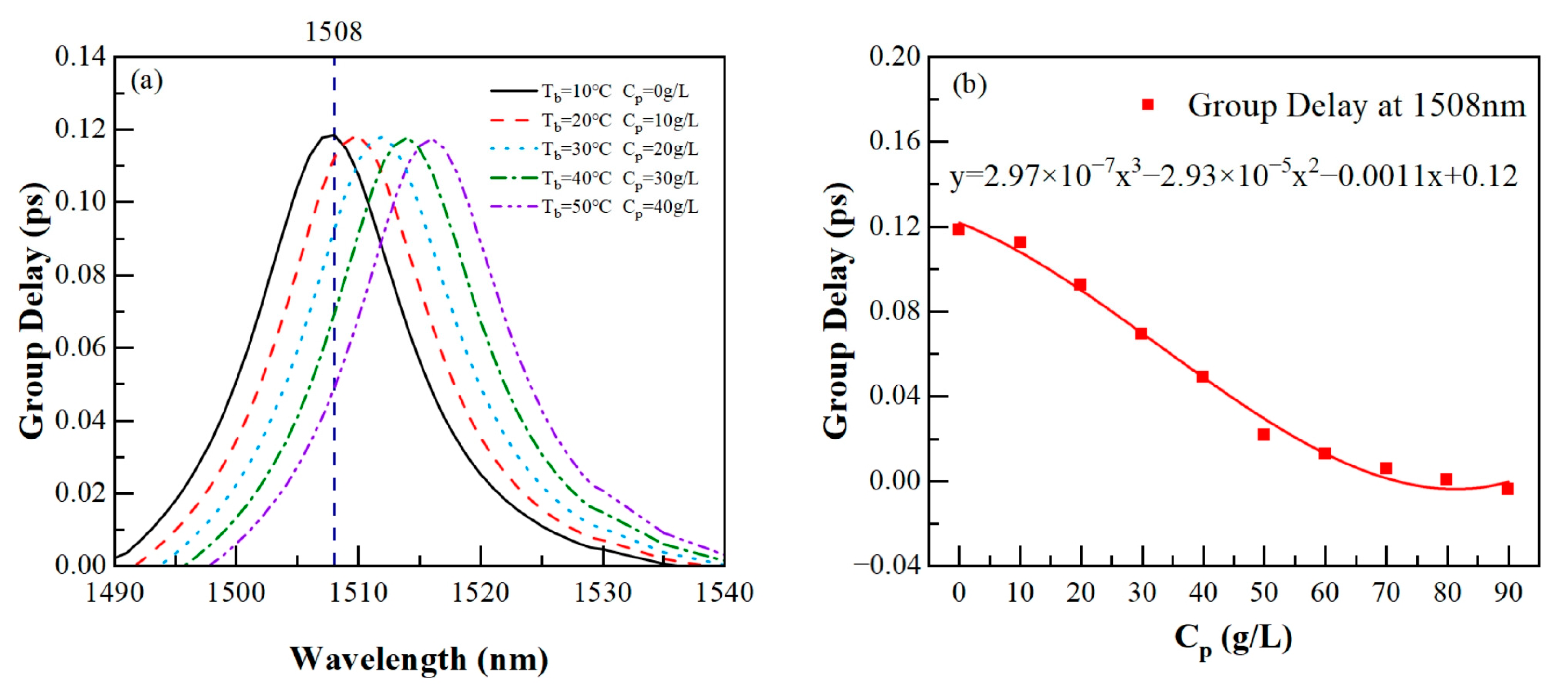
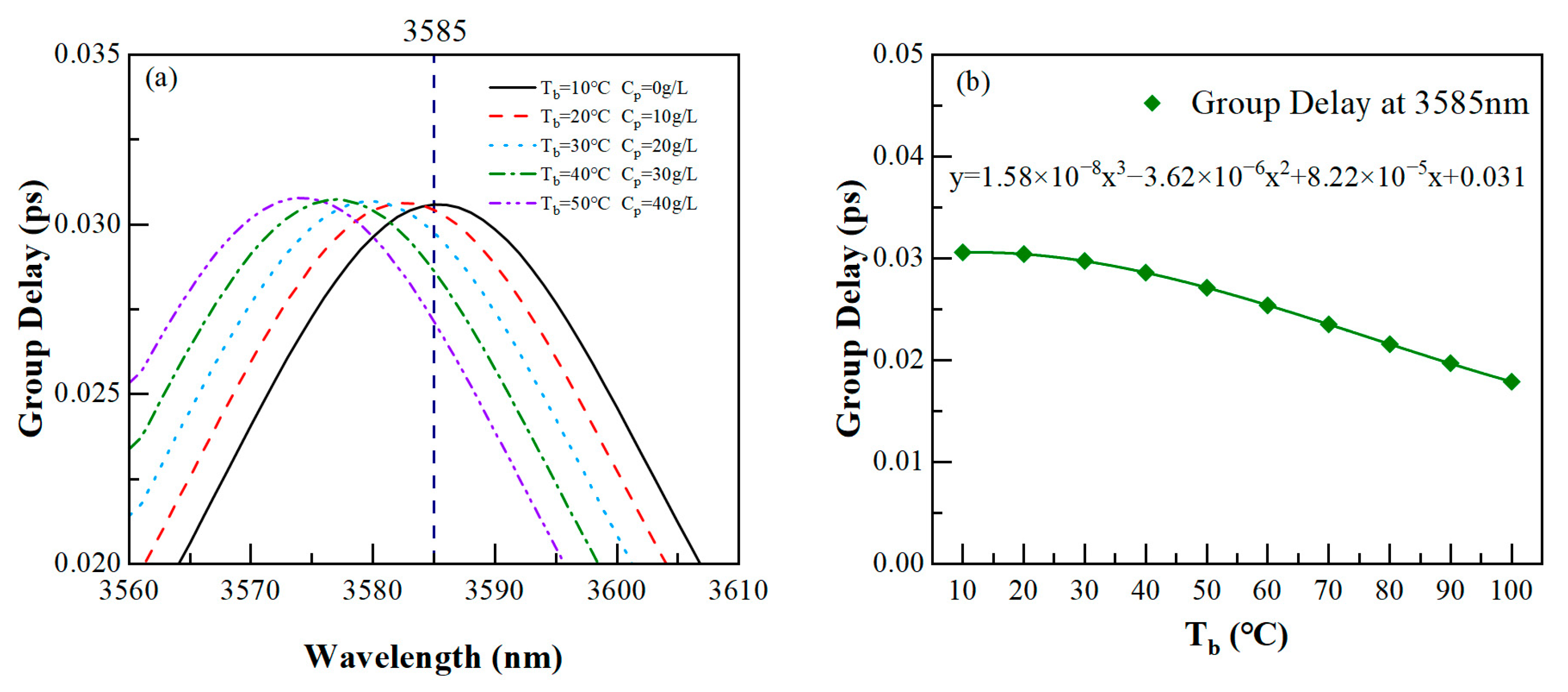
3.4. Tunable Slow Light
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fano, U. Effects of Configuration Interaction on Intensities and Phase Shifts. Phys. Rev. 1961, 124, 1866–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Ruan, B.; Xiang, Y. Self-Referenced Refractive Index Biosensing with Graphene Fano Resonance Modes. Biosensors 2021, 11, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limonov, M.F.; Rybin, M.V.; Poddubny, A.N.; Kivshar, Y.S. Fano resonances in photonics. Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk’yanchuk, B.; Zheludev, N.I.; Maier, S.A.; Halas, N.J.; Nordlander, P.; Giessen, H.; Chong, C.T. The Fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, F.; Qian, G.; Li, R.; Tang, J.; Zhang, T. High sensitivity optical waveguide accelerometer based on Fano resonance. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 6644–6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Tian, H.; Wang, J.; Cui, J.; Rohimah, S. Optical sensing based on multimode Fano resonances in metal-insulator-metal waveguide systems with X-shaped resonant cavities. Appl. Opt. 2021, 60, 5312–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziauddin, J.R.; Chaung, Y.-L.; Rahmatullah. Tunable Fano resonances via optomechanical effect and gain -loss ratio in coupled microresonators. Laser Phys. 2018, 28, 116003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, R.; Wu, Y. Actively tunable double-Fano and Ramsey-Fano resonances in photonic molecules and improved sensing performance. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 94, 063822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Cao, G.; Yang, H. Tunable Fano resonance and high-sensitivity sensor with high figure of merit in plasmonic coupled cavities. Photonics Nanostruct. Fundam. Appl. 2018, 28, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Cheng, D.; Zhang, B.; Shu, G.; Wang, J. A microwave biosensor based on spoof surface plasmon polaritons for in vivo measurement of the water content of human skin tissues. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 205401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-Q.; Yin, Z.-X.; Xia, G.-Q.; Hong, L.-L.; Hu, Y.-L.; Liu, M.-H.; Hu, X.-W.; Kudryavtsev, A.A. Pulsed microwave-driven argon plasma jet with distinctive plume patterns resonantly excited by surface plasmon polaritons. Chin. Phys. B 2015, 24, 025203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balevicius, Z. Photonic Sensors in Chemical and Biological Applications. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; Wei, H.; Zhang, S.; Xu, H. Recent Advances in Plasmonic Sensors. Sensors 2014, 14, 7959–7973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Zhai, X.; Wang, L.; Wen, S. Plasmonically induced transparency in double-layered graphene nanoribbons. Photonics Res. 2018, 6, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffato, G.; Pasqualotto, E.; Sonato, A.; Zacco, G.; Silvestri, D.; Morpurgo, M.; De Toni, A.; Romanato, F. Implementation and testing of a compact and high-resolution sensing device based on grating-coupled surface plasmon resonance with polarization modulation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 185, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, S.; Qin, J. Tunable Fano Resonance and Enhanced Sensing in Terahertz Metamaterial. Front. Phys. 2021, 8, 605125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Pile, D.F.P.; Nam, S.; Bartal, G.; Zhang, X. Compressing surface plasmons for nano-scale optical focusing. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 7519–7524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohimah, S.; Tian, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Cui, J.; Hao, Y. Tunable multiple Fano resonances based on a plasmonic metal-insulator-metal structure for nano-sensing and plasma blood sensing applications. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Cao, J.; Qian, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, S. Multiple Fano Resonance Based Optical Refractive Index Sensor Composed Of Micro-Cavity and Micro-Structure. IEEE Photonics J. 2018, 10, 6804410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Cheng, L.; Shen, Z. Formation Laws of Direction of Fano Line-Shape in a Ring MIM Plasmonic Waveguide Side-Coupled with a Rectangular Resonator and Nano-Sensing Analysis of Multiple Fano Resonances. Crystals 2021, 11, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Rohimah, S.; Tian, H.; Qi, D. Fano resonance in a MIM waveguide with double symmetric rectangular stubs and its sensing characteristics. Opt. Commun. 2021, 482, 126563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Zhai, X.; Wang, L.; Xiang, Y.; Wen, S. Plasmonically induced transparency in phase-coupled graphene nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. B 2022, 106, 075401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-B.; Wen, X.-W.; Yin, C.-P.; Wang, H.-Z. The transmission characteristics of surface plasmon polaritons in ring resonator. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 24096–24101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, H.; Lee, B. High order plasmonic Bragg reflection in the metal-insulator-metal waveguide Bragg grating. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohimah, S.; Tian, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Cui, J.; Xu, Q.; Hao, Y. Fano Resonance in the Plasmonic Structure of MIM Waveguide with r-Shaped Resonator for Refractive Index Sensor. Plasmonics 2022, 17, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Shu, C.; Ye, H. The sensing characteristics of plasmonic waveguide with a ring resonator. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 7669–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, X.-G.; Lin, X.-S.; Tao, J.; Jin, X.-P. A subwavelength coupler-type MIM optical filter. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 7549–7555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.-S.; Huang, X.-G. Tooth-shaped plasmonic waveguide filters with nanometeric sizes. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 2874–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, B.; Hu, G.; Cui, Y. Theoretical analysis of a nanoscale plasmonic filter based on a rectangular metal-insulator-metal waveguide. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 385102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Ying, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Gu, J.; Pan, D.Z.; Chen, R.T. Wavelength-division-multiplexing (WDM)-based integrated electronic-photonic switching network (EPSN) for high-speed data processing and transportation. Nanophotonics 2020, 9, 4579–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Rohimah, S.; Tian, H.; Wang, J. Fano resonance based on D-shaped waveguide structure and its application for human hemoglobin detection. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 6424–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovszki, D.; Krekic, S.; Valkai, S.; Heiner, Z.; Der, A. All-Optical Switching Demonstrated with Photoactive Yellow Protein Films. Biosensors 2021, 11, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Jiang, L.; Yu, H.; Cui, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, G. Fano resonance and slow light in hybrid optomechanics mediated by a two-level system. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 96, 053821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Tian, J.; Yang, R. Tunable Fano resonance in MDM plasmonic waveguide with a T-shaped resonator coupled to ring resonator. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 035021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; Hao, Y. Quadruple Fano resonances in MIM waveguide structure with ring cavities for multisolution concentration sensing. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 10548–10555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Lin, Y.-S. Plasmonic metamaterial using metal-insulator-metal nanogratings for high-sensitive refraction index sensor. Results Phys. 2019, 15, 102602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhshani, M.R.; Mansouri-Birjandi, M.A. High-Sensitivity Plasmonic Sensor Based on Metal-Insulator-Metal Waveguide and Hexagonal-Ring Cavity. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lian, X.; Zhao, M.; Xie, C. Multimode Fano Resonances Sensing Based on a Non-Through MIM Waveguide with a Square Split-Ring Resonance Cavity. Biosensors 2022, 12, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Qiang, W.; Xu, J.; Sun, Q. Independently tunable double Fano resonances in asymmetric MIM waveguide structure. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 14688–14695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Wen, K.; Qin, Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, B. Multiple fano resonances in an end-coupled MIM waveguide system. Opt. Commun. 2019, 452, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Tian, H.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. Multiparameter Sensing Based on Tunable Fano Resonances in MIM Waveguide Structure with Square-Ring and Triangular Cavities. Photonics 2022, 9, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc Duy, N.; Zhao, S. A new high order dispersive FDTD method for Drude material with complex interfaces. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2015, 285, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugger, H.; Jurich, M.; Swalen, J.D.; Sievers, A.J. Reply to “Comment on ‘Observation of an index-of-refraction-induced change in the Drude parameters of Ag films’”. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter 1986, 34, 1322–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, K.; Chen, L.; Zhou, J.; Lei, L.; Fang, Y. A Plasmonic Chip-Scale Refractive Index Sensor Design Based on Multiple Fano Resonances. Sensors 2018, 18, 3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xia, S.; Dong, C.; Shen, K.; Deng, C.; Luo, W.; Su, M.; et al. Numerical study on the biosensing in mid-infrared based on multiple Fano-resonance plasmonic waveguide. Optik 2022, 270, 170042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ouyang, Z.; Lin, M.; Liu, Q. Independently Tunable Fano Resonances Based on the Coupled Hetero-Cavities in a Plasmonic MIM System. Materials 2018, 11, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Rohimah, S.; Tian, H.; Wang, J. Independently tunable triple Fano resonances based on MIM waveguide structure with a semi-ring cavity and its sensing characteristics. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 20829–20838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naib, I. Terahertz Asymmetric S-Shaped Complementary Metasurface Biosensor for Glucose Concentration. Biosensors 2022, 12, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, R.; Cui, J.; Hou, Y.; Liu, W. High-sensitivity refractive index sensors based on Fano resonance in the plasmonic system of splitting ring cavity-coupled MIM waveguide with tooth cavity. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 125, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Cao, X.; Song, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, L. Side-Coupled Cavity-Induced Fano Resonance and Its Application in Nanosensor. Plasmonics 2016, 11, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Xu, Y.; Yang, H.; Ou, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Zeng, L.; Li, J. High Sensitivity Plasmonic Sensor Based on Fano Resonance with Inverted U-Shaped Resonator. Sensors 2021, 21, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, K.; Hu, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhou, J.; He, M.; Lei, L.; Meng, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, J. Fano Resonance Based on End-Coupled Cascaded-Ring MIM Waveguides Structure. Plasmonics 2017, 12, 1875–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhshani, M.R. Refractive index sensor based on concentric triple racetrack resonators side-coupled to metal-insulator-metal waveguide for glucose sensing. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B Opt. Phys. 2019, 36, 2834–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, M.; Saghir, M.Z. Empirical modelling to predict the refractive index of human blood. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Khozondar, H.J.; Mahalakshmi, P.; El-Khozondar, R.J.; Ramanujam, N.R.; Amiri, I.S.; Yupapin, P. Design of one dimensional refractive index sensor using ternary photonic crystal waveguide for plasma blood samples applications. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2019, 111, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
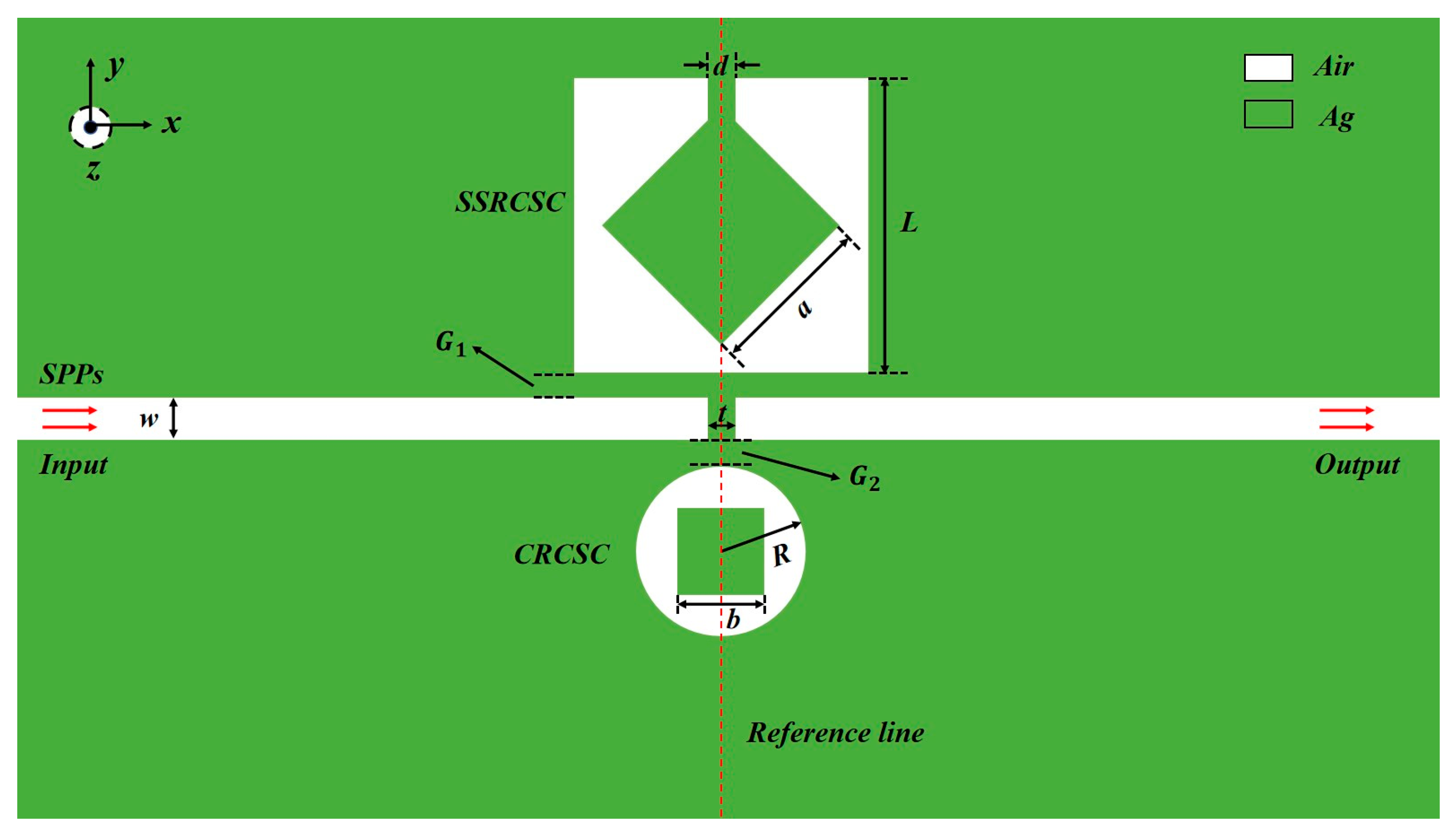


| Parameter | Symbol | Quantity | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length of the side of the external square of the SSRCSC | 440 | nm | |
| Split length of SSRCSC | 10 | nm | |
| Length of the side of the internal square of the SSRCSC | 300 | nm | |
| The separation between the bus waveguide and the SSRCSC | 10 | nm | |
| The radius of the external circle of the CRCSC | 110 | nm | |
| Length of the side of the internal square of the CRCSC | 140 | nm | |
| The separation between the bus waveguide and the CRCSC | 10 | nm | |
| The size of the bus waveguide | 50 | nm | |
| The size of the bus waveguide’s silver baffle | 10 | nm | |
| Index of refractive of bus waveguide | 1 | ||
| Index of refractive of SSRCSC | 1 | ||
| Index of refractive of CRCSC | 1 |
| Reference | Waveguide | Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|
| [6] | Baffle and an X-shaped cavity make up the MIM waveguide | 1303 nm/RIU |
| [38] | MIM waveguide containing a rectangular split-ring resonance cavity | 1290.2 nm/RIU |
| [47] | MIM waveguide containing a semi-ring cavity | 1550.38 nm/RIU |
| [49] | MIM waveguide containing ring-splitting cavity and tooth cavity coupling | 1200 nm/RIU |
| [50] | MIM waveguide-coupled structure-based simple and small plasmonic sensor | 1820 nm/RIU |
| [51] | Inverted U-shaped resonator | 840 nm/RIU |
| [52] | A MIM waveguide with an end-coupled ring-groove junction | 1050 nm/RIU |
| [53] | Three-racetrack resonators in two concentric rings with plasmonic MIM waveguides | 1618 nm/RIU |
| This paper | MIM waveguide consisting of square split-ring and circular ring cavities | 2453.33 nm/RIU |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Tian, H.; Liu, Y.; Cui, S. Multiple Fano Resonances in a Metal–Insulator–Metal Waveguide for Nano-Sensing of Multiple Biological Parameters and Tunable Slow Light. Photonics 2023, 10, 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10070703
Zhang R, Tian H, Liu Y, Cui S. Multiple Fano Resonances in a Metal–Insulator–Metal Waveguide for Nano-Sensing of Multiple Biological Parameters and Tunable Slow Light. Photonics. 2023; 10(7):703. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10070703
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ruiqi, He Tian, Yang Liu, and Shihang Cui. 2023. "Multiple Fano Resonances in a Metal–Insulator–Metal Waveguide for Nano-Sensing of Multiple Biological Parameters and Tunable Slow Light" Photonics 10, no. 7: 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10070703
APA StyleZhang, R., Tian, H., Liu, Y., & Cui, S. (2023). Multiple Fano Resonances in a Metal–Insulator–Metal Waveguide for Nano-Sensing of Multiple Biological Parameters and Tunable Slow Light. Photonics, 10(7), 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10070703






