Selective Accumulation of Rare-Earth and Heavy Metal Ions by a Fucoidan-Inorganic Composite Material
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Preparation of Fucoidan-Inorganic Composite Material
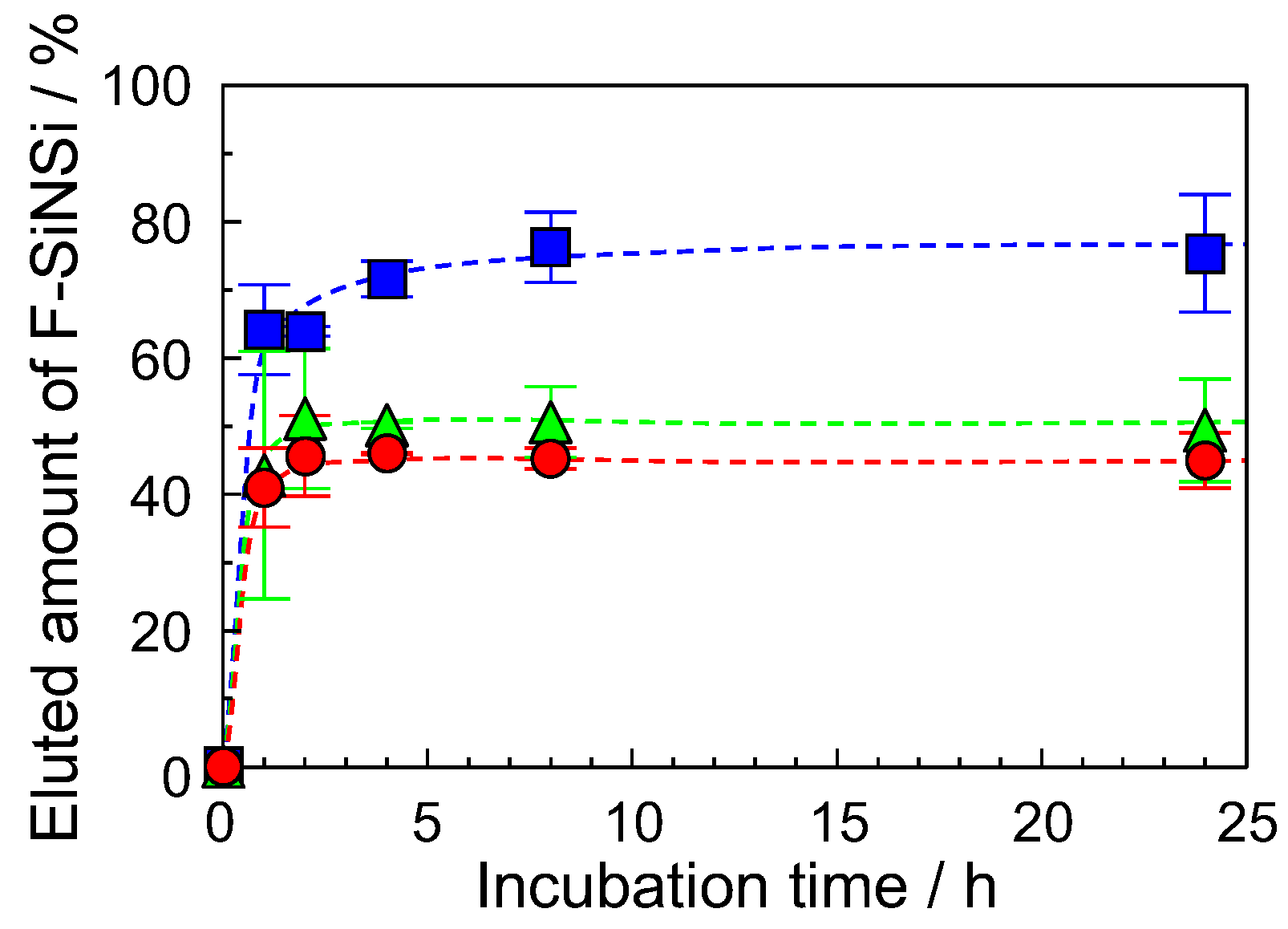
2.3. Water Stability of F-SiNSi Composite Material
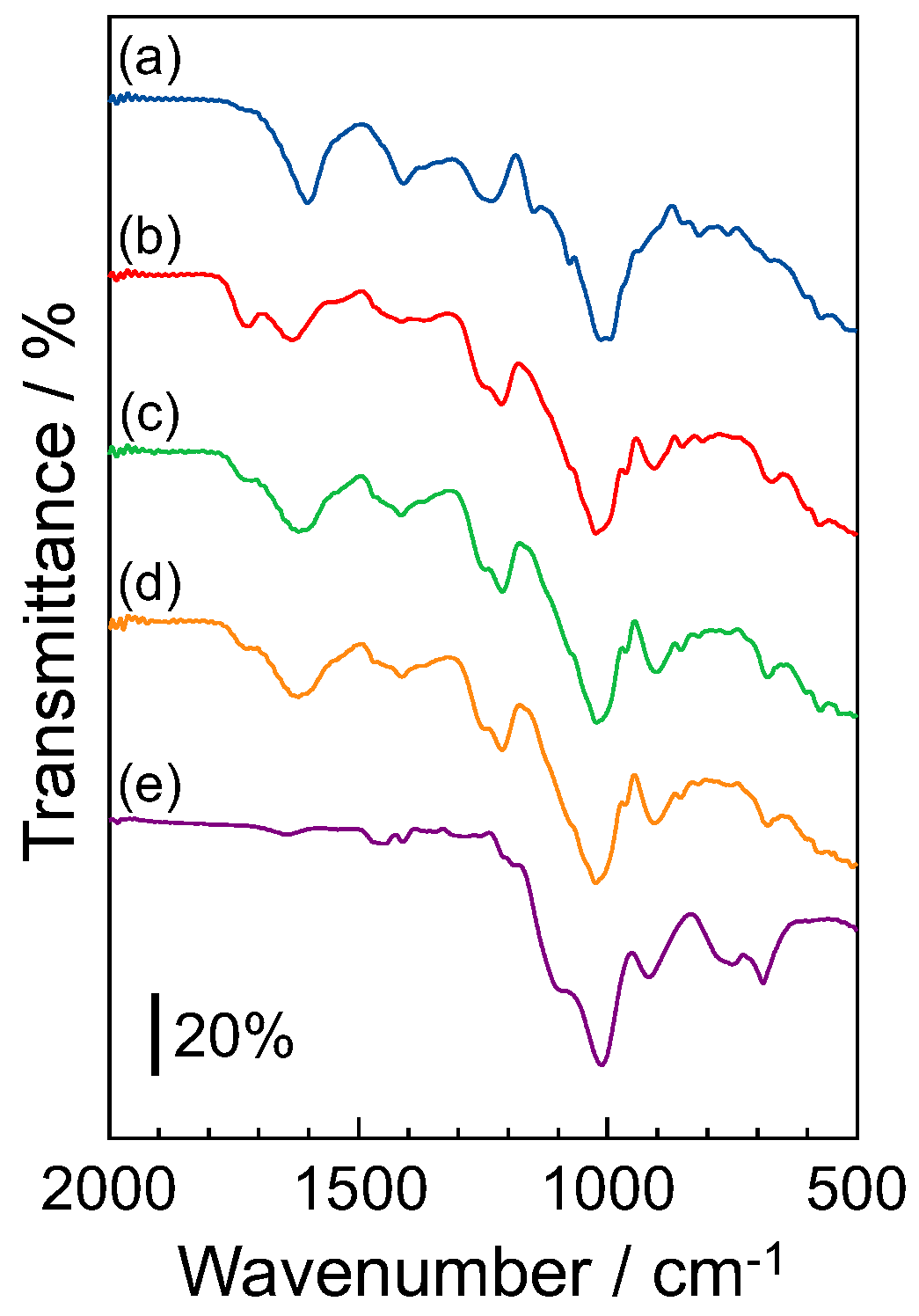
2.4. Structural and Thermal Analyses of F-SiNSi Composite Material
2.5. Accumulation of Metal Ions by F-SiNSi Composite Film
2.6. IR Measurements of Metal Ion-Accumulated F-SiNSi Composite Material
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of F-SiNSi Composite Material
3.2. Molecular Structure of F-SiNSi Composite Material
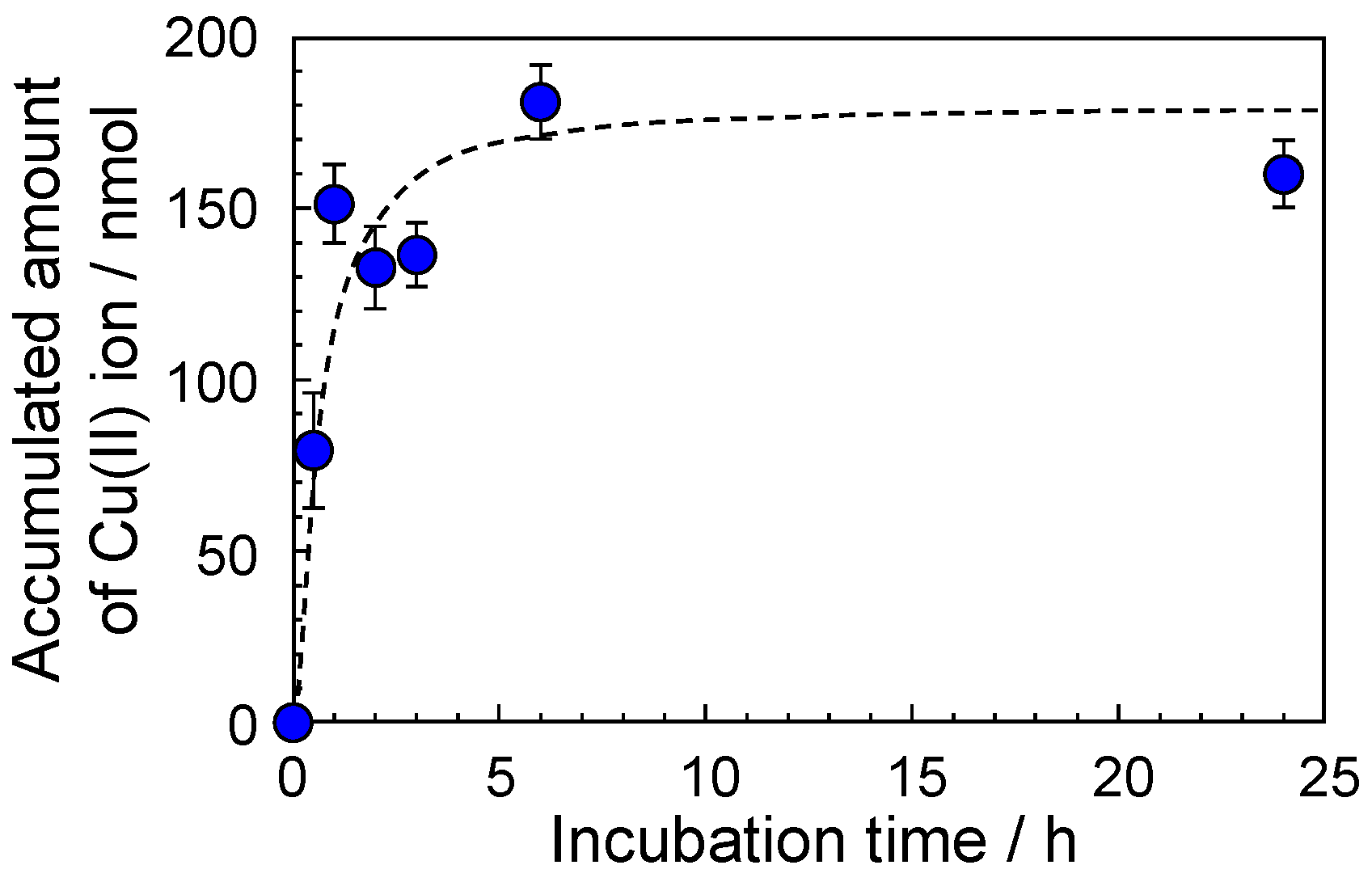
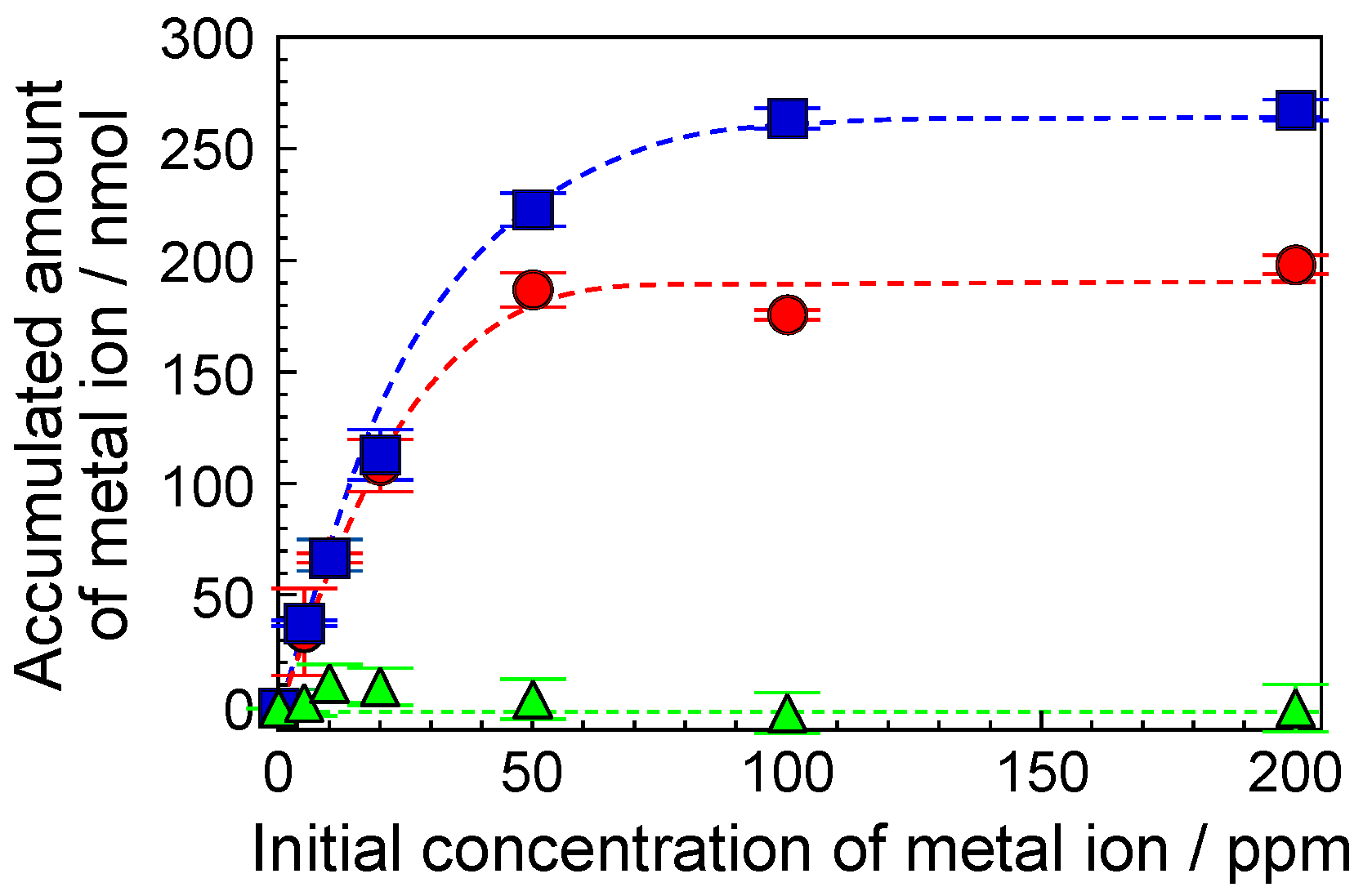
3.3. Accumulation of Metal Ions by the F-SiNSi Composite Material
3.4. Accumulative Mechanism of Metal Ions by F-SiNSi Composite Material
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, A.P.; Aris, A.Z. A review on economically adsorbents on heavy metals removal in water and wastewater. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 13, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M.; Bakar, N.K.A.; Bakar, A.F.A.; Ashraf, M.A. Chemical speciation and bioavailability of rare earth elements (REEs) in the ecosystem: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 22764–22789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbatenko, A.A.; Revina, E.I. A review of instrumental methods for determination of rare earth elements. Inorg. Mater. 2015, 51, 1375–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naila, A.; Meerdink, G.; Jayasen, V.; Sulaiman, A.Z.; Aji, A.B.; Berta, G. A review on global metal accumulators—Mechanism, enhancement, commercial application, and research trend. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 26449–26471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Hu, Y.H. Design, synthesis, and performance of adsorbents for heavy metal removal from wastewater: A review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 1047–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borji, H.; Ayoub, G.M.; Bilbeisi, R.; Nassar, N.; Malaeb, L. How effective are nanomaterials for the removal of heavy metals from water and wastewater? Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, B. Potential of biological materials for removing heavy metals from wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 1614–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C. Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 195–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, V.H.; Cameron, N.R.; Saito, K. Synthesis, properties and performance of organic polymers employed in flocculation applications. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolisetty, S.; Peydayesh, M.; Mezzenga, R. Sustainable technologies for water purification from heavy metals: Review and analysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 463–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumashi, A.; Ushakova, N.A.; Preobrazhenskaya, M.E.; D’Incecco, A.; Piccoli, A.; Totani, L.; Tinari, N.; Morozevich, G.E.; Berman, A.E.; Bilan, M.I.; et al. A comparative study of the anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant, antiangiogenic, and antiadhesive activities of nine different fucoidans from brown seaweeds. Glycobiology 2007, 17, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ale, M.T.; Meyer, A.S. Fucoidans from brown seaweeds: An update on structures, extraction techniques and use of enzymes as tools for structural elucidation. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 8131–8141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, F.; Wei, X.; Zhao, R. Fucoidan: Structure and bioactivity. Molecules 2008, 13, 1671–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, J.; Anil, S.; Kim, S.K.; Shim, M.S. Seaweed polysaccharide-based nanoparticles: Preparation and applications for drug delivery. Polymers 2016, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, T.A.; Voleskya, B.; Mucci, A. A review of the biochemistry of heavy metalbiosorption by brown algae. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4311–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidi, F.; Shamsabadi, A.A.; Amooghin, A.E.; Saeb, M.R.; Xiao, H.; Jin, Y.; Rezakazemi, M. Biopolymer-based membranes from polysaccharides for CO2 separation: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1083–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titirici, M.M.; White, R.J.; Brun, N.; Budarin, V.L.; Su, D.S.; Monte, F.; Clark, J.H.; MacLachlang, M.J. Sustainable carbon materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 250–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samiey, B.; Cheng, C.H.; Wu, J. Organic-inorganic hybrid polymers as adsorbents for removal of heavy metal ions from solutions: A review. Materials 2014, 7, 673–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erigoni, A.; Diaz, U. Porous silica-based organic-inorganic hybrid catalysts: A review. Catalysts 2021, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Mishra, S.B. Sol-gel derived organic–inorganic hybrid materials: Synthesis, characterizations and applications. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2011, 59, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.; Julián, B.; Belleville, P.; Popall, M. Applications of hybrid organic–inorganic nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 3559–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Aono, H. DNA-inorganic hybrid material as selective absorbent for harmful compounds. Polymer 2008, 49, 4658–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Tohyama, C.; Yamada, T. Preparation of water-insoluble and biochemically-stable RNA hybrid material. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 2890–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Ogino, T. Anhydrous proton conductor consisting of pectin-inorganic composite material. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42433–42439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Kametani, Y. Preparation of gellan gum-inorganic composite film and its metal ion accumulation property. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, N.; Fukuda, T.; Ono, K. Change in the structure of heat-treated siloxane oligomers as observed by FT-IR. Kobunshi Ronbunshu 2000, 57, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plueddemann, E.P. Silane Coupling Agents, 2nd ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Webster, F.X. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ptak, S.H.; Sanchez, L.; Fretté, X.; Kurouski, D. Complementarity of Raman and infrared spectroscopy for rapid characterization of fucoidan extracts. Plant Methods 2021, 17, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Gunasekaran, S. Preparation of pectin–ZnO nanocomposite. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtaki, H. Preparation and characterization of heteropolytungstates containing group 3a elements. Rev. Inorg. Chem. 1982, 4, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Caminiti, R.; Licheri, G.; Piccaluga, G.; Pinna, G.; Magini, M. Structural properties of lead-iron phosphate glasses by X-ray diffraction. Rev. Inorg. Chem. 1979, 1, 333. [Google Scholar]
- Cotton, F.A.; Wilkinson, G.; Gaus, P.L. Basic Inorganic Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.S.; Wertz, D.L. Solute structuring in aqueous lanthanum(III) chloride solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 2365–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habenschuss, A.; Spedding, F.H. The coordination (hydration) of rare earth ions in aqueous chloride solutions from X-ray diffraction. II. LaCl3, PrCl3, and NdCl3. J. Chem. Phys. 1979, 70, 3758–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist-Reis, P.; Lamble, K.; Pattanaik, S.; Persson, I.; Sandström, M. Hydration of the yttrium(III) ion in aqueous solution. An X-ray diffraction and XAFS structural study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamada, M.; Shimanouchi, Y. Selective Accumulation of Rare-Earth and Heavy Metal Ions by a Fucoidan-Inorganic Composite Material. Separations 2022, 9, 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9080219
Yamada M, Shimanouchi Y. Selective Accumulation of Rare-Earth and Heavy Metal Ions by a Fucoidan-Inorganic Composite Material. Separations. 2022; 9(8):219. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9080219
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamada, Masanori, and Yuta Shimanouchi. 2022. "Selective Accumulation of Rare-Earth and Heavy Metal Ions by a Fucoidan-Inorganic Composite Material" Separations 9, no. 8: 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9080219
APA StyleYamada, M., & Shimanouchi, Y. (2022). Selective Accumulation of Rare-Earth and Heavy Metal Ions by a Fucoidan-Inorganic Composite Material. Separations, 9(8), 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9080219





