Advanced Treatment of Palm Oil Mill Effluent Using Thermally Activated Persulfate Oxidation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Treated POME Characteristics
2.2. Setup of Laboratory-Scale Thermally Activated AOP System
2.3. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
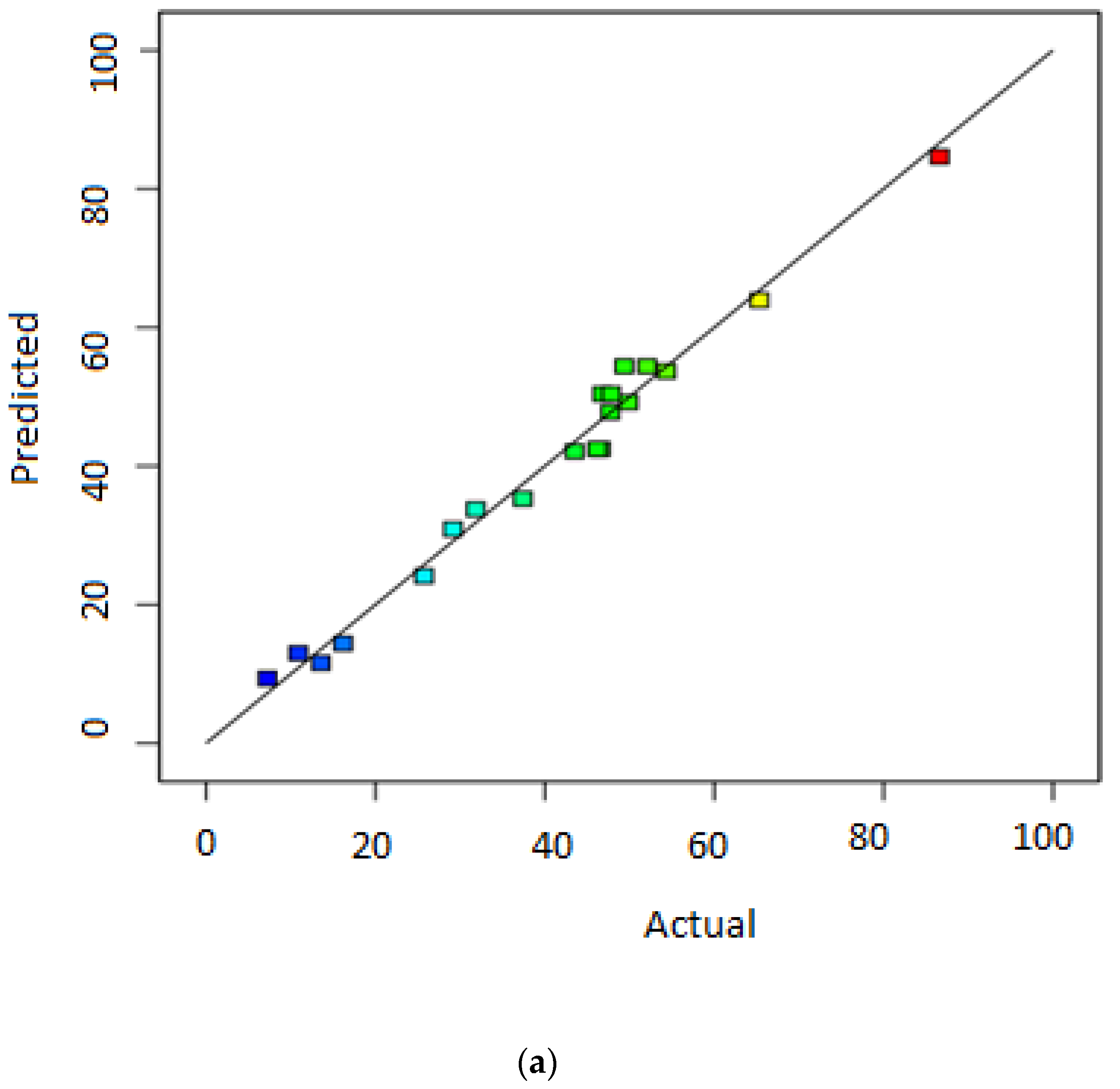
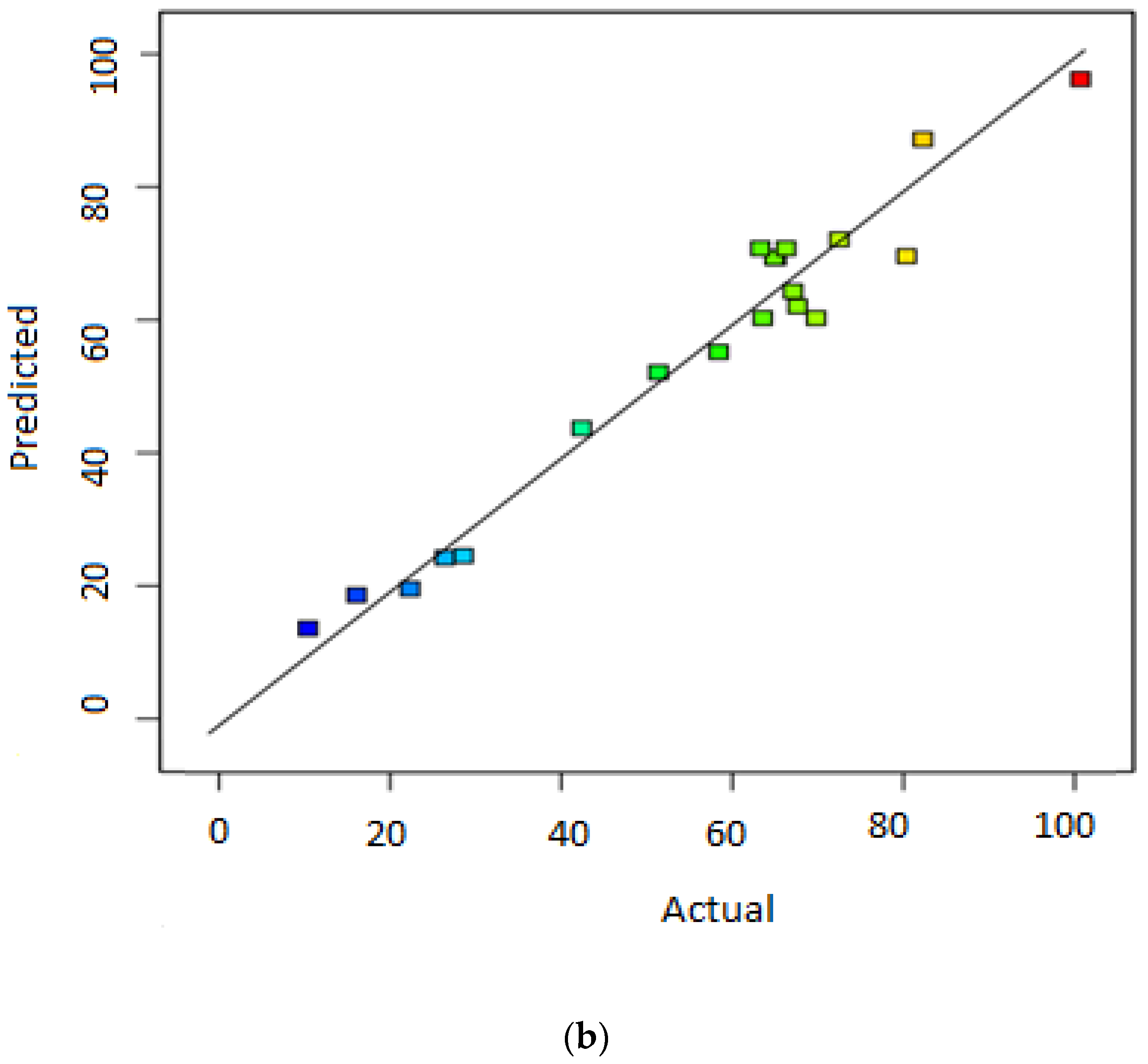
3.1. Statistical Significance of Responses’ Models
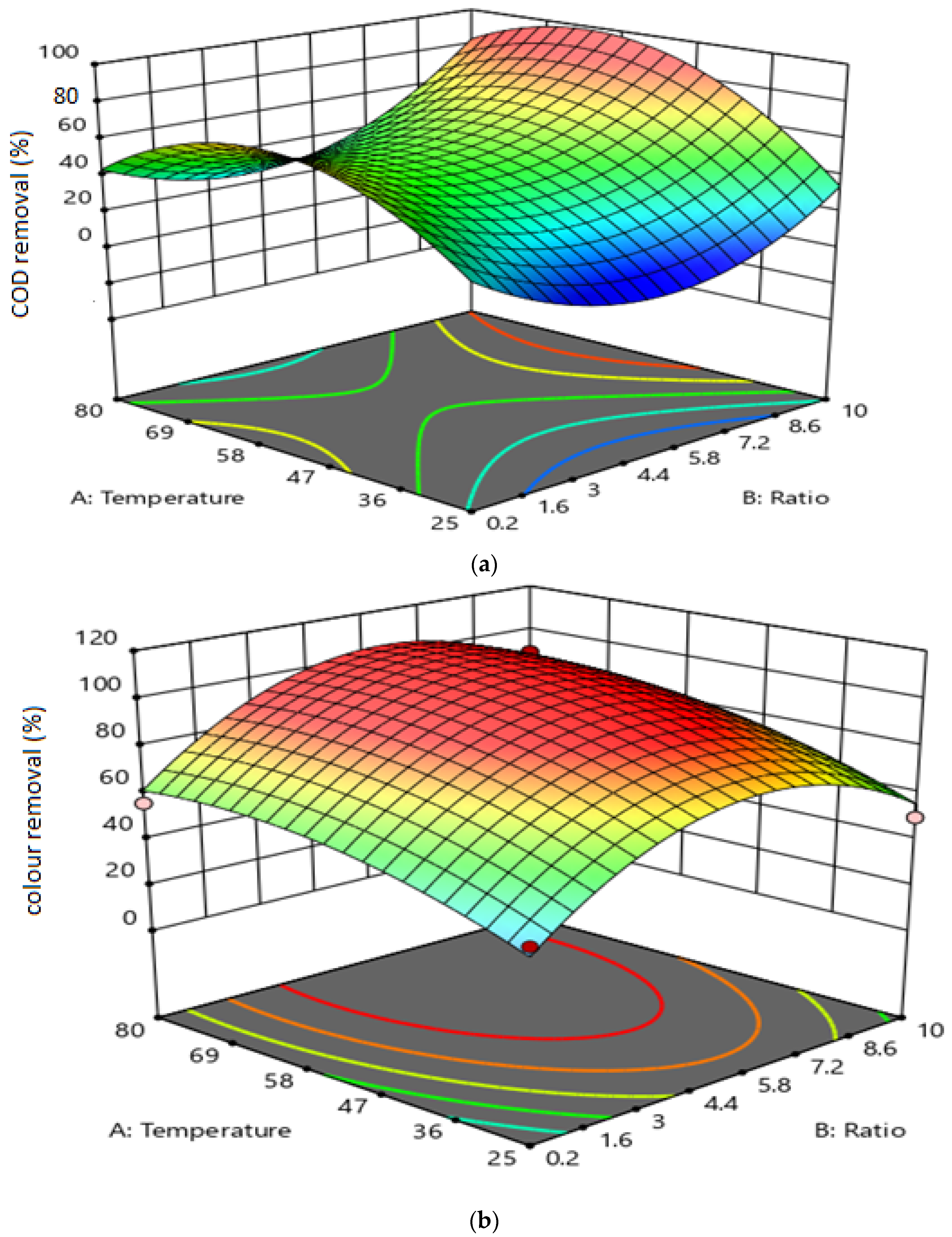
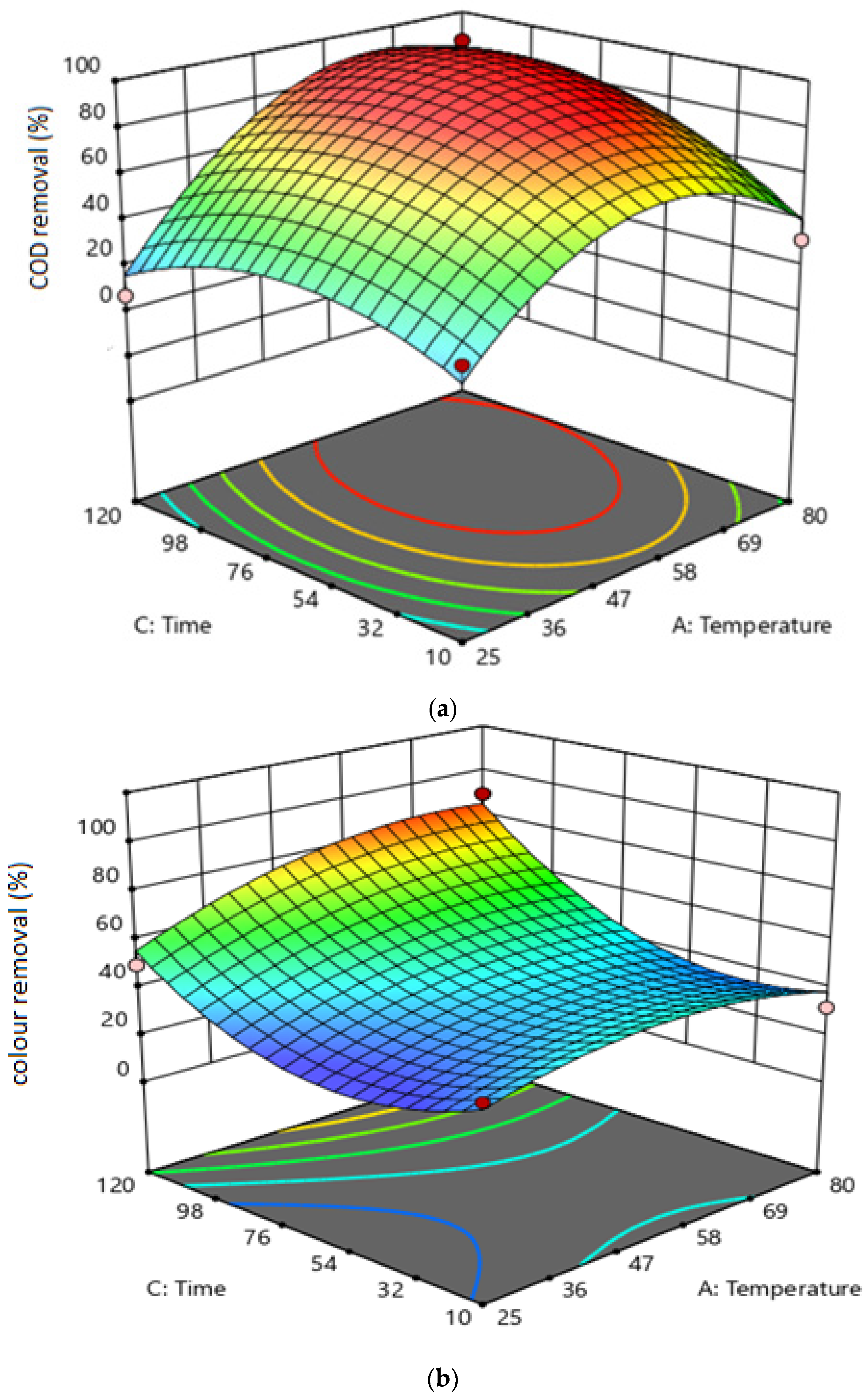
3.2. The Effect of Variable Interactions on Responses
3.3. Optimizing the Interactions between Process Variables in the Electrocoagulation Process
3.4. Analysis of the Operational Cost
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soybean Buyers Turn Attention to Brazil’s 2021 Harvest; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; pp. 4–33.
- Isa, M.H.; Wong, L.P.; Bashir, M.J.; Shafiq, N.; Kutty, S.R.; Farooqi, I.H.; Lee, H.C. Improved anaerobic digestion of palm oil mill effluent and biogas production by ultrasonication pretreatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.K.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Abu Amr, S.S.; Sim, L.C. Post treatment of palm oil mill effluent (POME) using combined persulphate with hydrogen peroxide (S2O82−/H2O2) oxidation. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 2675–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Idris, I.; Chan, C.Y.; Ismail, S. Reclamation from palm oil mill effluent using an integrated zero discharge membrane-based process. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2010, 17, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bashir, M.J.K.; Hong, L.J.; Amr, S.S.A.; Wong, L.P.; Sim, Y.-L. Post treatment of Palm Oil Mill Effluent Using Electro-coagulation-peroxidation (ECP) Technique. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.K.M.; Norsalwani, T.L.T.; Asmah, M.S.; Badrulhisham, Z.Y.; Easa, A.M.; Omar, F.M.; Hossain, S.; Zuknik, M.H.; Norulaini, N.A.N. Implementation of the supercritical carbon dioxide technology in oil palm fresh fruits bunch sterilization: A review. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 25, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.J.; Mau Han, T.; Jun Wei, L.; Choon Aun, N.; Abu Amr, S.S. Polishing of treated palm oil mill effluent (POME) from ponding system by electro-oxidation process. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 2704–2712. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Onn, S.W.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Sethupathi, S.; Amr, S.S.A.; Nguyen, T.T. Colour and COD Removal from Mature Landfill Leachate Using Electro-persulphate Oxidation Process. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 31, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-Rodríguez, S.; Rodríguez, E.; Singh, D.N.; Rodríguez-Chueca, J. Assessment of sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment: A review. Water 2018, 10, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Guven, G.; Perendeci, A.; Tanyolac, A. Electrochemical treatment of deproteinated whey wastewater and optimization of treatment conditions with response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, M.J.K.; Aziz, H.A.; Yusoff, M.S.; Adlan, M.N. Application of response surface methodology (RSM) for optimization of ammoniacal nitrogen removal from semi-aerobic landfill leachate using ion exchange resin. Desalination 2010, 254, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajeri, S.; Aziz, H.A.; Isa, M.H.; Zahed, M.A.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Adlan, M.N. Application of the central composite design for condition optimization for semi-aerobic landfill leachate treatment using electrochemical oxidation. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, M.J.; Aziz, H.A.; Aziz, S.Q.; Abu Amr, S.S. An overview of electro-oxidation processes performance in stabilized landfill leachate treatment. Desalin. Water Treat 2013, 51, 2170–2184. [Google Scholar]
- Bashir, M.J.; Isa, M.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Bin Awang, Z.; Aziz, H.A.; Mohajeri, S.; Farooqi, I.H. Landfill leachate treatment by electrochemical oxidation. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2534–2541. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, R.H.; Montgomery, M.D.; Anderson-Cook, C.M. Response Surface Methodology, Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments, 3rd ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Azmi, N.B.; Bashir, M.J.; Sethupathi, S.; Wei, L.J.; Aun, N.C. Stabilized landfill leachate treatment by sugarcane bagasse derived activated carbon for removal of color, COD and NH3-N–Optimization of preparation conditions by RSM. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabalak, E. Treatment of agrochemical wastewater by thermally activated persulfate oxidation method: Evaluation of energy and reagent consumption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X. Sulfate radicals induced degradation of Triclosan in thermally activated persulfate system. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokoohi, R.; Salari, S.B.M.; Shabanloo, A. Thermochemical degradation of furfural by sulfate radicals in aqueous solution: Optimization and synergistic effect studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 8914–8927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norzaee, S.; Taghavi, M.M.; Djahed, B.; Mostafapour, F.K. Degradation of Penicillin G by heat activated persulfate in aqueous solution. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 215, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, A.; Makoś, P.; Boczkaj, G. Treatment of bitumen post oxidative effluents by sulfate radicals based advanced oxidation processes (S-AOPs) under alka-line pH conditions. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Quality (Prescribed Premises) (Crude Palm Oil) Regulation 1977. Malaysia Sewage and Industrial Effluent Discharge Standards. In Malaysia’s Environmental Law, Environmental Quality Act; 1974; Available online: https://www.env.go.jp/en/recycle/asian_net/Country_Information/Law_N_Regulation/Malaysia/Malaysia_mal13278.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Ghauch, A.; Tuqan, A.M.; Kibbi, N. Ibuprofen removal by heated persulfate in aqueous solution: A kinetics study. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 197, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Unit | Average Value |
|---|---|---|
| COD | mg/L | 4020.0 |
| N-NH3 | mg/L | 4810.0 |
| Color | PtCo | 5400.0 |
| Turbidity | NTU | 1280 |
| BOD5 | mg/L | 444.5 |
| pH | - | 7.6 |
| Temperature | °C | 32.9 |
| Run | Process Variables | Responses | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | S2O82−/COD Ratio | Reaction Time (min) | COD (%) | Color (%) | |
| 1 | 25.0 | 0.20 | 10.0 | 10.90 | 27.96 |
| 2 | 25.0 | 0.20 | 120.0 | 16.19 | 40.37 |
| 3 | 25.0 | 10.00 | 10.0 | 25.75 | 38.89 |
| 4 | 25.0 | 10.00 | 120.0 | 7.24 | 49.81 |
| 5 | 80.0 | 10.00 | 10.0 | 31.84 | 31.85 |
| 6 | 80.0 | 10.00 | 120.0 | 86.62 | 89.63 |
| 7 | 80.0 | 0.20 | 10.0 | 13.56 | 36.11 |
| 8 | 80.0 | 0.20 | 120.0 | 29.15 | 55.93 |
| 9 | 52.5 | 2.65 | 65.0 | 54.35 | 60.74 |
| 10 | 52.5 | 5.10 | 65.0 | 46.62 | 68.52 |
| 11 | 52.5 | 5.10 | 65.0 | 46.19 | 64.26 |
| 12 | 52.5 | 5.10 | 65.0 | 52.09 | 65.19 |
| 13 | 52.5 | 5.10 | 65.0 | 49.38 | 65.37 |
| 14 | 52.5 | 5.10 | 65.0 | 47.84 | 66.11 |
| 15 | 52.5 | 5.10 | 92.5 | 49.90 | 77.04 |
| 16 | 52.5 | 7.55 | 65.0 | 65.35 | 66.67 |
| 17 | 66.3 | 5.10 | 65.0 | 47.74 | 70.37 |
| 18 | 38.8 | 5.10 | 65.0 | 37.39 | 67.04 |
| 19 | 52.5 | 5.10 | 37.5 | 43.51 | 75.74 |
| 20 | 52.5 | 5.10 | 65.0 | 46.79 | 64.07 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | DF | Mean Square | F Value | Prob > F | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD Removal Efficiency | ||||||
| Model | 5638.00 | 9 | 626.44 | 41.83 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A | 1328.37 | 1 | 1328.37 | 88.70 | <0.0001 | |
| B | 893.44 | 1 | 893.44 | 59.65 | <0.0001 | |
| C | 428.41 | 1 | 428.41 | 28.60 | 0.0006 | |
| A2 | 234.20 | 1 | 234.20 | 15.63 | 0.0042 | |
| B2 | 210.80 | 1 | 210.80 | 14.07 | 0.0056 | |
| C2 | 66.45 | 1 | 66.45 | 4.43 | 0.0682 | |
| AB | 609.87 | 1 | 609.87 | 40.72 | 0.0002 | |
| AC | 873.41 | 1 | 873.41 | 58.32 | <0.0001 | |
| BC | 29.60 | 1 | 29.60 | 1.97 | 0.1971 | |
| Residual | 119.80 | 8 | 14.97 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 115.51 | 5 | 23.10 | 16.16118 | 0.0222 | |
| Pure Error | 4.28 | 3 | 1.42 | |||
| R2 = 0.9792, Adjusted R2 = 0.9559, Predicted R2 = −0.2774, C.V. = 9.5745%, Adequate Precision = 25.1211 | ||||||
| Final equation in terms of coded factors: COD removal efficiency = 49.093 + 12.50A + 10.25B + 7.10C − 35.48A2 + 33.66 B2 − 18.90C2 + 8.73AB + 10.45AC | ||||||
| Source | Sum of Squares | DF | Mean Square | F Value | Prob > F | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color Removal Efficiency | ||||||
| Model | 3637.440 | 9 | 404.16 | 15.07 | 0.0004 | significant |
| A | 397.8828 | 1 | 397.88 | 14.83 | 0.0048 | |
| B | 327.6707 | 1 | 327.67 | 12.21 | 0.0081 | |
| C | 1213.94 | 1 | 1213.94 | 45.26 | 0.0001 | |
| A2 | 18.56 | 1 | 18.56 | 0.69 | 0.4295 | |
| B2 | 167.33 | 1 | 167.33 | 6.23 | 0.0370 | |
| C2 | 80.10 | 1 | 80.10 | 2.98 | 0.1221 | |
| AB | 10.28 | 1 | 10.28 | 0.38 | 0.5529 | |
| AC | 368.15 | 1 | 368.15 | 13.72 | 0.0059 | |
| BC | 166.25 | 1 | 166.25 | 6.19 | 0.0375 | |
| Residual | 214.55 | 8 | 26.81 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 203.38 | 5 | 40.67 | 10.92 | 0.0384 | |
| Pure Error | 11.17 | 3 | 3.72 | |||
| R2 = 0.9443, Adjusted R2 = 0.8816, Predicted R2 = −1.0842, C.V. = 8.7651%, Adequate Precision = 14.012 | ||||||
| Final equation in terms of coded factors: COD removal efficiency = 66.987 + 6.84A + 6.21B + 11.95C + 1.13AB + 6.78AC + 4.56BC | ||||||
| Response | Predicted Value | Actual Value | Percentage of Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| COD (%) | 86.62 | 85.65 | 1.2 |
| Color (%) | 87.39 | 85.74 | 1.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bashir, M.J.K.; Sheen, O.S.; Ng, C.A.; Abujazar, M.S.S.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Abu Amr, S.S. Advanced Treatment of Palm Oil Mill Effluent Using Thermally Activated Persulfate Oxidation. Separations 2022, 9, 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9070171
Bashir MJK, Sheen OS, Ng CA, Abujazar MSS, Alazaiza MYD, Abu Amr SS. Advanced Treatment of Palm Oil Mill Effluent Using Thermally Activated Persulfate Oxidation. Separations. 2022; 9(7):171. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9070171
Chicago/Turabian StyleBashir, Mohammed J. K., Ong Sue Sheen, Choon Aun Ng, Mohammed Shadi S. Abujazar, Motasem Y. D. Alazaiza, and Salim S. Abu Amr. 2022. "Advanced Treatment of Palm Oil Mill Effluent Using Thermally Activated Persulfate Oxidation" Separations 9, no. 7: 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9070171
APA StyleBashir, M. J. K., Sheen, O. S., Ng, C. A., Abujazar, M. S. S., Alazaiza, M. Y. D., & Abu Amr, S. S. (2022). Advanced Treatment of Palm Oil Mill Effluent Using Thermally Activated Persulfate Oxidation. Separations, 9(7), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9070171










