Abstract
Developing effective and green methods for food analysis and separation has become an urgent issue regarding the ever-increasing concern of food quality and safety. Ionic liquids (ILs) are a new chemical medium and soft functional material developed under the framework of green chemistry and possess many unique properties, such as low melting points, low-to-negligible vapor pressures, excellent solubility, structural designability and high thermal stability. Combining ILs with extraction techniques not only takes advantage of ILs but also overcomes the disadvantages of traditional extraction methods. This subject has attracted intensive research efforts recently. Here, we present a brief review of the current research status and latest developments regarding the application of IL-assisted microextraction, including dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) and solid-phase microextraction (SPME), in food analysis and separation. The practical applications of ILs in determining toxic and harmful substances in food specimens with quite different natures are summarized and discussed. The critical function of ILs and the advantages of IL-based microextraction techniques over conventional extraction techniques are discussed in detail. Additionally, the recovery of ILs using different approaches is also presented to comply with green analytical chemistry requirements.
1. Introduction
With the increasingly prominent environmental problems, food quality and safety related issues have been recognized as common global concerns. Many environmental pollution problems such as pesticide residue, antibiotics abuse, soil and water pollution, illegal addition of prohibited substances, etc., directly or indirectly lead to food contamination and safety problems that endanger human health [1,2,3,4,5,6]. In order to ensure food safety and avoid the dangers of environmental pollution, it is necessary to develop a sensitive, efficient and reliable analytical method to monitor hazardous and noxious substances in food samples [7,8]. However, food analysis and separation are still encumbered by various challenges, which are not only related to the composition of the food matrix, but also to the particular physical-chemical properties and content of analytes. On one hand, the denomination “food” encompasses an enormous, diverse group of matrices with different compositions. On the other hand, external contaminants in food raw materials are often found in trace amounts [9]. The sample pretreatment takes almost two-thirds of the entire analysis process and any mistake occurring in sample processing could lead to substantial errors in the final results. The pretreatment method and sample quality not only determine the speed, sensitivity and accuracy of the food analysis, but also affect the service life of the analytical instrument. Within this context, sample pretreatment is particularly important for the determination of trace analytes. Undoubtedly, more attention should be paid to the selection or invention of a simple, rapid and sensitive sample preparation method [10].
Traditional sample pretreatment methods mainly include Soxhlet extraction, distillation, centrifugation, precipitation separation, ion exchange, etc. These methods are time-consuming, cumbersome to operate and inefficient. More importantly, they require the extensive use of organic solvents, which are often expensive, toxic and harmful to the environment. With the continuous development of analytical technology, various sample pretreatment techniques have been developed for the determination of noxious contaminants in food samples. Extraction is an important pretreatment method, which mainly includes solid-phase extraction (SPE), liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) and aqueous two-phase extraction (ATPE) [11,12,13,14,15]. Among them, the most popular, SPE and LLE, have been successfully applied in the preconcentration and clean-up of samples in analysis procedures. Miniaturized preconcentration has a high analyte extraction efficiency as well as a high-speed during food analysis. Therefore, microextraction has been identified as a green sample pretreatment technique and has greatly improved sample pretreatment quality and efficiency. As a consequence, liquid–liquid microextraction (LLME) and solid phase microextraction (SPME) have emerged in recent years [16,17,18,19]. However, there are still some disadvantages to these techniques, including the use of organic solvents, high costs, their long extraction times and low separation selectivity [20,21,22,23]. For these reasons, there is still a need to develop new, better sample pretreatment methods.
Ionic liquids (ILs) and their analogues are a new medium and soft functional material developed under the framework of green chemistry in recent years. They have the characteristics of non-volatilization, low melting points, good thermal and electrical conductivity, wide range of liquid, chemical stability, strong solubility and adjustable design [24,25,26]. These unique properties make them attractive alternatives to replace environmentally unfriendly organic solvents that produce volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Additionally, they can be structurally tailored for specific applications. Thus, ILs have also successfully been applied in many areas of fundamental and applied chemistry. Especially [27], the use of ILs in different extraction and microextraction processes has attracted tremendous attention [28,29,30,31,32]. So far, the application of ILs in the extraction of metal ion, drug residues and organic compounds from aqueous environmental samples have been reviewed and summarized. Food is a complex system composed of various chemicals with different properties. In food analysis and separation, a huge challenge is to extract analytes from raw foods due to the complexity of food matrices [33]. The trend of analytical chemistry is to design a reliable analysis scheme that can reduce or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. For food analysis, the application of ILs-assisted extraction conforms to this green chemistry trend. Recently, there has been an increasing number of studies employing ILs as extractants in sample pretreatment processes to extract or enrich analytes from food samples. Nevertheless, there are a few review articles on the systematical discussion of ILs-based extraction methods in food analysis and separation [24,34,35,36].
This review mainly focuses the application status and latest progress of DLLME and SPME in food analysis. The practical application of ILs in the detection of all kinds of contaminants in different food matrices is summarized and discussed in detail. The performance of the methods involving ILs is also compared with other extraction procedures. Furthermore, the property determined by the structure of ILs is analyzed and the effect of the property of ILs on extraction is discussed. Additionally, the recyclability of ILs by different approaches is presented and analyzed. This review hopes to provide meaningful and valuable information to related fields and thus promote further research and the application of the reported methods.
2. Structures, Properties and Recyclability of ILs
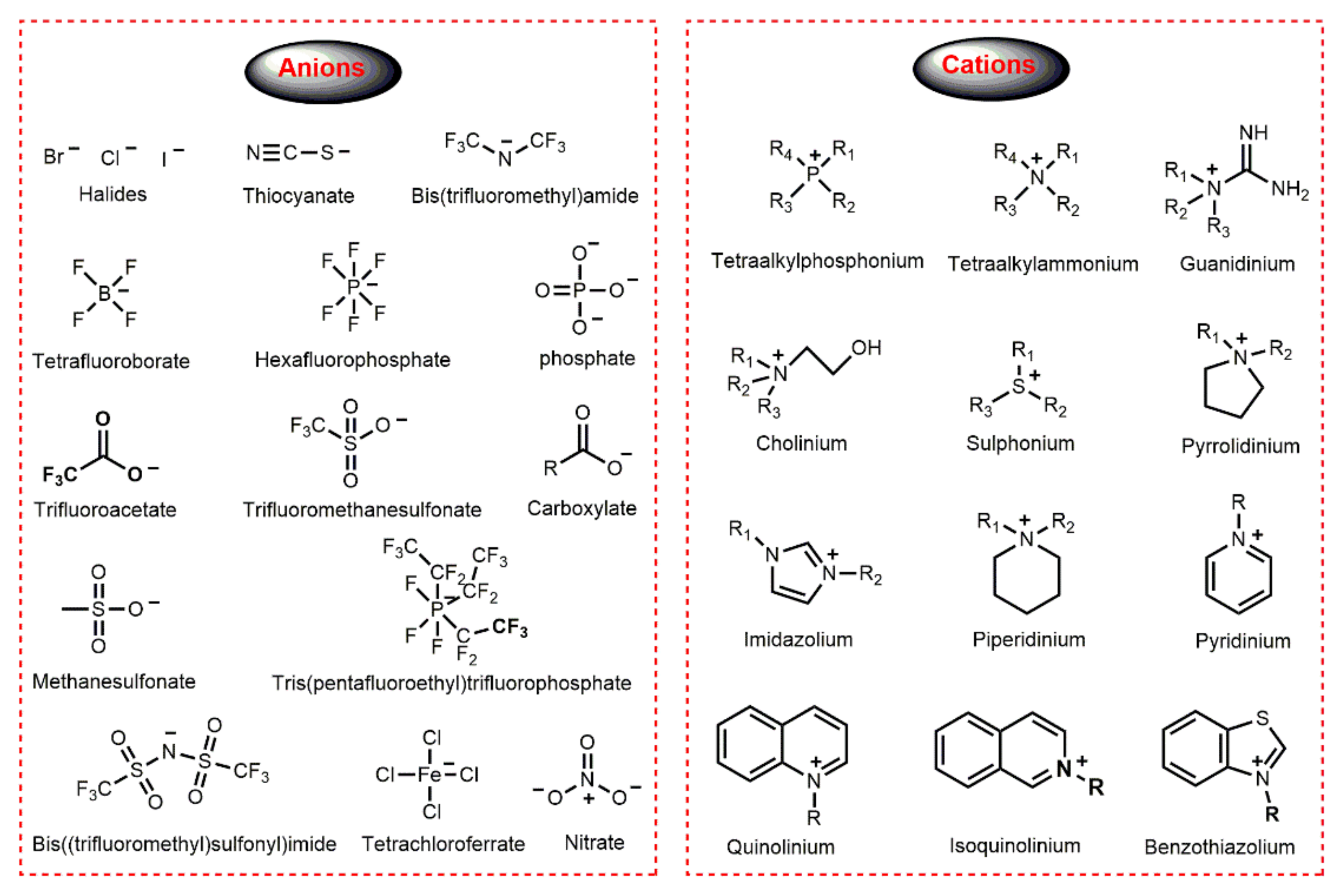
ILs are inorganic salts completely composed of ions; in general, organic cations containing heteroatoms and either inorganic or organic anions. The structure of some common anions and cations for ILs preparation are shown in Figure 1. It is a historical fact that ILs with halides and fluorine-containing anions or imidazolium cation are among the most widely used and well-studied. For example, the first-generation ILs consisted of Cl− and Br− anions and organic cations such as 1-alkyl imidazolium [37]. With the advancement of the study of ILs, halides anions have been gradually replaced with tetrafluoroborate (BF4−), hexafluorophosphate (PF6−), nitrate (NO3−), sulfate (SO42−) or phosphate (PO43−) to obtain more stable ILs. Furthermore, ILs with trifluoromethanesulfonate (CF3SO3−) or bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (NTf2−) as anions are generally more hydrophobic. According to the head group in the cation, ILs can be categorized into different structural types, such as aromatic (imidazolium, quinolinium, benzothiazolium, pyridinium, e.g.,) and alicyclic (pyrrolidinium, piperidinium, e.g.,) head group. Furthermore, other important ILs are based on quaternary ammonium salts (cholinium, tetraalkylammonium, guanidinium, e.g.,) and quaternary phosphonium salts [38].
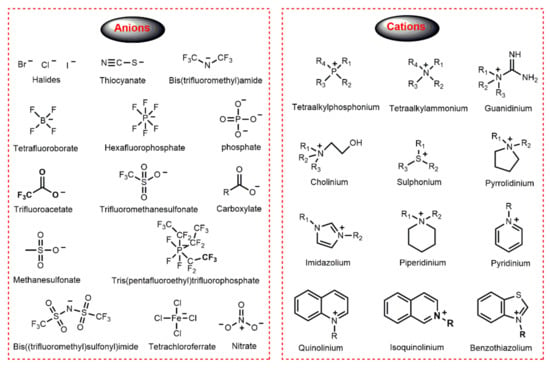
Figure 1.
Structure of some common anions and cations of ILs.
As the structures of ILs determine their physicochemical properties, ILs have a significant impact on extracting analytes. The incorporation of functional groups of different polarity onto the IL structure might promote different interactions with solutes, even permitting high solvation capabilities for both polar and nonpolar compounds [39]. For example, Zeng et al. [40] used four kinds of limidazolium-based ILs with different anions, including bromide ([Br]), chloride ([Cl]), tetrafluoroborate ([BF4]), p-methylbenzene sulfonate ([TsO]), as the extraction solvent in IL-based microwave-assisted extraction (ILMAE). The results indicated that the addition of ILs to water could greatly enhance the extraction efficiencies of rutin from Chinese medicinal plants (S. chinensis and Flos Sophorae). The main reasons are as follows: On one hand, ILs had strong solvation power and multiple interactions with analytes, such as hydrogen bonding, polarity, π-π, π-n and ionic/charge-charge. On the other hand, based on the ILs structure containing organic cations and inorganic or organic anions, they can efficiently absorb and transfer microwave energy and, consequently, make the solvent and the sample warming rapidly. Both of the above causes contribute to raising the solubility of rutin in ILs aqueous solutions, which immensely improves the extraction efficiency. Furthermore, authors also investigated the effect of these ILs with same cations but different anions on extraction efficiency. Overall, [C4mim][Br] and [C4mim][TsO] were more efficient than other two ILs in the ILMAE of rutin. Additionally, the acidities of [C4mim][Br] or [C4mim][TsO] aqueous solutions were higher than those of the others. Therefore, the subacidity of ILs was favorable for the extraction. Furthermore, when the concentration of the IL aqueous solution exceeded a certain value, the extraction efficiency decreased instead. This was probably related to the viscosity of the IL solution. Lower viscosities are required to increase the rate of mass transfer in solution. High viscosity of ILs is not conducive to the penetration into the interior of sample matrixes. Therefore, the greater the IL concentration is, the greater the viscosity and the poorer the diffusion capacity of IL solution are. Additionally, the unique structure of ILs make it easier to form interactions the with target analytes. In general, one or more unsaturated functional groups in the structure of ILs entitle them to form π-π interaction with aromatic hydrocarbons, leading to a peculiar affinity of aromatic hydrocarbons for ILs. Furthermore, the relatively strong polarity of ILs can induce a small solubility of alkanes. In this field, Meindersma’s research group significant efforts to investigate the extraction of aromatics from aromatic/aliphatic mixtures [41,42,43,44]. In their research, the separation selectivity when using IL as extractant could be 1.5 to 2.5 times higher than that when using an organic solvent (sulfolane). The results indicated that the increase in polarity of ILs (i.e., the reduction in alkyl length on the cation, introduction of polar functional groups such as hydroxyl group) could improve selectivity, leading to better extraction efficiency.
As a kind of acknowledged extraction separation medium, ILs are actually not totally environmentally friendly and pollution-free. Moreover, ILs are not easily biodegradable due to their stable chemical properties [45]. Therefore, recycling ILs is a non-negligible process that involves recovering them from coexisting systems for repeated use, which is very crucial for its “green” feature. Many methods have shown promising performances in the recycling of ILs, such as distillation, extraction, membrane evaporation, adsorption and magnetic separation. Extraction is considered the most common method for recycling ILs when ILs are used as the extraction solvent, which is based on the solubility difference for ILs and specific objects. Polar solvents (such as water) are usually selected to separate hydrophobic IL from hydrosoluble compounds. On the contrary, organic solvents are used to recycle ILs from the hydrophobic compounds. For example, Blanchard et al. used chloroform, methylene chloride and butanol as extractants in LLE to recycle the IL [C4mim][Cl] from the IL-caffeine aqueous solution. Additionally, the IL can be reused at least three times without reaching saturation [46]. However, the use of organic solvents to recover the IL may diminish the “green” feature of IL due to the cross-contamination in many conditions. Although supercritical fluid is considered as an alternative green solvent to recover IL, the facility requirement, complex operation and high costs could inevitably restrict its application in the recovery of IL [47]. Previous studies reported the adsorption of ILs from water onto different adsorbents [48,49,50]. These adsorption methods are found useful to recycle ILs and regenerate the adsorbent. In research on He and co-workers, five ion-exchange resins were selected as adsorbents to recover three kinds of benzothiazolium-based ILs from coexisting glucose [51]. After the ILs were applied in the extraction of saccharides in Lycium barbarum L. and hydrolysis of pretreated bagasse cellulose, the adsorption ratio of ILs was over 90% using the recovery method. That is, the used resins were found to exhibit excellent adsorption amounts and strong interaction for these ILs. The adsorption method has high selectivity and operational simplicity. Furthermore, other methods, such as distillation, membrane separation and magnetic separation, are also appropriate for recycling ILs. In the distillation method, the volatile compounds are often distilled, whereas the IL is retained [52]. Compared with other recovery methods, the greatest weakness of distillation is the high energy consumption. Thus, this technique is usually applied as the final step in most of the recycling process of ILs. To overcome this shortcoming, microwave-assisted vacuum distillation can be developed as a more efficient method for the recovery of ILs. In addition, membrane separation is suitable for the recovery of ILs by removing the nonvolatile compounds together with tiny particles. For instance, Krockel and Kragl investigated the use of flat sheet membranes to separate IL from the mixture containing bromophenol blue and [Amim][MeSO4] [53]. The result found that the large volume and multiply charge of the IL could lead to high retention. As a commercially available technique, membrane separation is energy-saving and easier to control and scale-up. For magnetic separation, it is specially designed for the magnetic ILs, which are responsive to the external magnetic field [54]. This recover method must be strong enough to respond to the external magnetic field in the recovery process, or the immobilization of the common IL to the magnetic supporters (e.g., ferroferric oxide).
3. ILs in Liquid–Liquid Microextraction
As an important chemical separation unit operation, the liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) method is widely used in the field of food separation and analysis. LLE involves the partitioning of an analyte(s) between two immiscible liquids (usually aqueous and organic), and partitioning depends on the degree of analyte solubility in the extraction solvent. Therefore, in the traditional LLE, the selection of appropriate extractant is critical. Normally, a large number of organic solvents are used as extractants in order to improve the extraction efficiency. This not only increases solvent recovery costs, but also brings to light environmental and security issues in the use of volatile, flammable, toxic organic solvents. In recent years, it has been a development trend for LLE to choose efficient and green solvents instead of organic solvents with the rise in the green chemical industry. Much attention is paid to very popular ILs. Compared to traditional organic solvents, ILs have the advantages of high melting points, low volatility and excellent thermal stability, which play an important role in LLE [55,56,57]. As ideal alternative extractants, ILs-based LLE has been applied in food separation and analysis. Although LLE is the most commonly used extraction, it is more time-consuming, uses large amounts of toxic organic solvents and is not sensitive enough for trace analysis. Liquid–liquid microextraction (LLME) can effectively avoid the use of an excess amount of organic solvents. However, there are still some shortcomings, such as long extraction time, low sensitivity and poor reproducibility. Thus, the development of effective extraction methods that overcome these drawbacks are very necessary.
At present, the LLME technique is the most widely used in food analysis. In the last few decades, a number of LLME modes and their applications have been developed, making it very difficult to choose a correct mode, let alone choosing an appropriate extractant for a particular application. To recognize this process, LLME can be classified into three major micro solvent extraction modes: single drop microextraction (SDME) [58,59], hollow fiber liquid–liquid microextraction (HF-LLME) [60] and dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) [61,62,63,64]. Among them, DLLME is one of the most common LLME methods. As an improvement of the LLME, DLLME was first proposed by Rezaee and coworkers in 2006 [65]. Since then, massive research achievements related to the application of the DLLME method have been made [66,67]. DLLME involves the distribution of the target analyte between a sample solution and a small volume of extractants. In DLLME, the emulsion system of water/dispersant/extractant is formed by adding micro-upgrade of extractants and milli-upgrade of dispersants to the aqueous phase sample matrix. After centrifugation, the extraction layer can be absorbed and directly injected for analysis. Thus, the mechanism of DLLME is mainly based on the partitioning of an analyte(s) between two immiscible liquids, and partitioning depends on the degree of analyte solubility in the extraction solvent. DLLME is a ternary solvent system in which the disperser solvent serves as a bridge between the sample solution and extractant, due to its excellent solubility/miscibility with most polar and non-polar solvents [68]. Furthermore, the volume of the disperser solvent must be higher than the extractant to obtain satisfactory extraction results. Except for the disperser solvents, syringes are used to inject rapidly the mixture of disperser solvent and extractant, which can offer air-assisted dispersion through the sample solution. DLLME has great application value and extensive prospects due to its simplicity, rapidness, low sample volume, cost effectiveness, high precision, excellent enrichment capacity and recovery for analytes [69]. Recent advancements in DLLME methods are mainly focus on the use of greener solvents to meet the requirements of green analytical chemistry. ILs belong to the class of green solvents, and many researchers have used ILs-based DLLME during the pre-concentration in food samples. Several techniques have been developed and discussed briefly in each of the following sub-classified DLLME modes. Some application examples of IL in DLLME for the extraction of food analysis are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Some representative applications of ILs in DLLME.
3.1. Conventional IL-DLLME
In the conventional DLLME method, a dispersive agent is used to form a “dispersed phase” or “emulsion” to improve mass transfer and facilitate the contact between the extraction solvent and the compound to be extracted. However, the extraction solvent spreads over the surface of the sample, leading to difficulty in solvent removal. To overcome this problem, special narrow neck centrifuge tubes and extraction solvents with the melting points below room temperature are recommended. After centrifugation, the centrifuge tube is placed in an ice-water bath to solidify or precipitate the extraction solvent. Very few extraction solvents are appropriately melted to meet the requirements. However, there are many ILs with melting points in the ranges necessary, which prove useful in this technique. As the simplest IL-DLLME method, it only utilizes ILs as extractants instead of organic solvents. The samples containing analytes were extracted/preconcentrated by simply mixing the sample aqueous with the IL and the dispersive solvent. Usually, the dispersive solvents used in this method are organic solvents, especially methanol [95]. This conventional IL-DLLME method was often used for pesticide residue analysis in food samples. As is well-known, herbicides can control the growth of grasses and broadleaf weeds in agricultural field, which are extensively used around the world. However, their residues have been found in the environment and pose a threat to public health problems due to their high toxicity. In consideration of the long-term persistence of herbicides in the environment, it is very likely that they can be introduced to our lives by food during its production. Therefore, an analytical method with high sensitivity is favored by researchers.
As previously indicated, ILs can be used as extraction solvents in DLLME that are also increasingly being employed in food analysis due to their lower toxicity and volatility compared to conventional solvents. However, in the conventional IL-DLLME method, the anion of most ILs used for this purpose is [PF6]−. They should have low solubility in water. Thus, food analysis by IL-DLLME usually requires the use of disperser solvents. In this sense, IL-DLLME was used for the first time to extract multiclass pesticides from different matrices (i.e., bananas, grapes and plums) [97]. In the long term, the use of pesticides such as insecticides, fungicides and herbicides for agriculture can contaminate the environment. Pesticide residues may reach humans through the food chain and cause chronic exposure and long-term toxicity effects. As a kind of natural food, today’s honey is produced in an environment polluted by different sources of contamination, which results in the direct or indirect pollution of honey. Since honey is a complicated matrix containing organic and inorganic constituents, especially saccharides, pre-concentration steps for the extraction and enrichment of analytes are very important to obtain reliable results. Therefore, the IL 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([C6MIM][PF6]) is often used as an extractant in conventional IL-DLLME combined with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to detect the triazine herbicides in honey [98]. The extraction procedure is as follows: a mixture of IL and dispersant is rapidly injected into the sample solution. After shaking for 10 min, high recovery and enrichment factor can be obtained under the optimal conditions. On the one hand, the imidazolium cation of the IL is conducive to the formation of the interactions between IL and triazine compounds, mainly including hydrogen bonding, electrostatic forces and π-π interaction. On the other hand, when the anion of the IL is [PF4], it tends to be hydrophobic. Moreover, the hydrophobicity of IL increases with the length of the alkyl chain on the cation. Thus, the selected IL is suitable for the extraction of triazine herbicides, which is beneficial to the separation of extraction phase and raffinate phase.
In addition to imidazolium-based ILs, other types of ILs can also be used as extractants. For example, the IL trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium bistriflamide [(C6)3C14P][NTf2] was employed as the extractant for the analysis of aryloxyphenoxy-propionate herbicides in soy-based foods. The density of the used IL is higher than that of the water. Therefore, the convenience of this work is that it is easy to take the extractant from the bottom of a conical tube due to the low viscosity, very low water solubility and higher density [79]. Meanwhile, compared to ILs with the anion [PF6], the ILs with [NTf2] as the anion are generally more hydrophobic. Even more to the point, a novel IL tetra butyl phosphonium phosphate ionic liquid ([TBP][PO4]) was used as an extraction solvent in DLLME for the preconcentration of nickel (II) and copper (II) ions from vegetable oils [87]. Generally, phosphate ions have strong coordination ability and can form soluble complexes with many metal ions. These ILs with the anion [PO4] are often applied to the extraction of metal ions from the food matrix. Finally, the scheme of conventional IL-DLLME is depicted in Figure 2A.
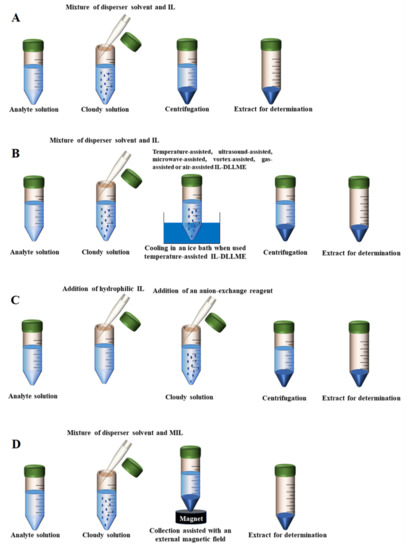
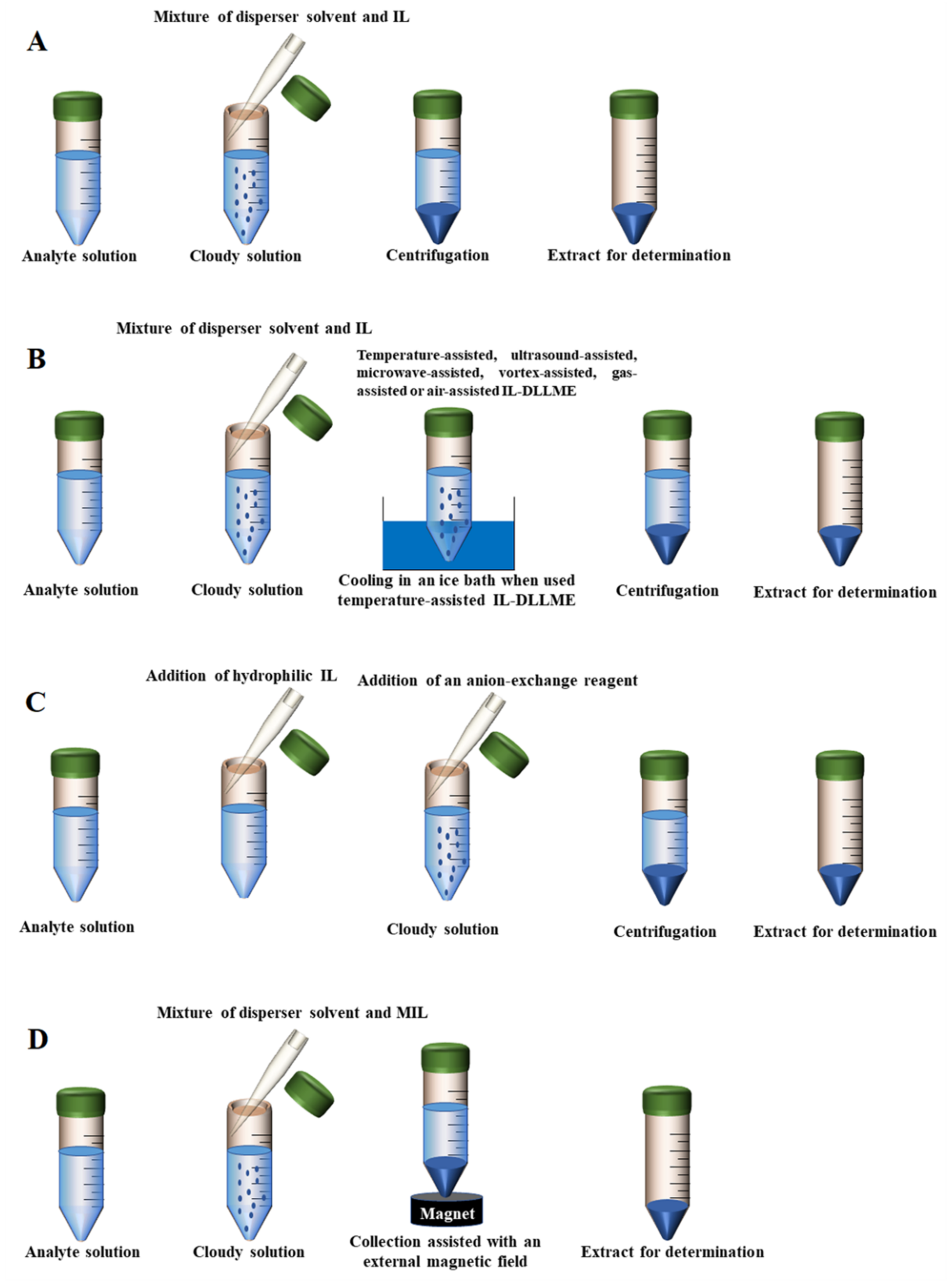
Figure 2.
The scheme of different DLLME modes. (A) Conventional IL-DLLME; (B) External assisted IL-DLLME; (C) in situ IL-DLLME; (D) MIL-DLLME.
3.2. External Assisted IL-DLLME
Although small volumes of liquid samples (1~20 mL) and extraction solvents (0.5~25 µL) are expected in the DLLME method, relatively large volumes (20~50 mL) of water samples, with correspondingly large volumes of extraction solvents and dispersion solvents (200~500 µL) are often used in published DLLME procedures, especially in solvent dispersion-assisted DLLME [99]. Large volumes of samples are used to not only lower the limits of quantification, but also lead to the excessive use of extraction or dispersion solvents, such as acetone, chloroform, acetonitrile and methanol. If these solvents cannot be recycled, they may result in serious environmental pollution. In addition, ILs are usually so viscous that it is necessary to use an additional dispersal method to completely disperse these solvents [100]. IL-DLLME modes not requiring solvent dispersion assistance mainly include the following types: temperature-assisted IL-DLLME, ultrasound-assisted IL-DLLME, microwave-assisted IL-DLLME, vortex-assisted IL-DLLME, gas-assisted IL-DLLME and air-assisted IL-DLLME. Compared with conventional IL-DLLME, these modes can facilitate the mixing of the IL and the sample solution. In the temperature-assisted IL-DLLME method, the heating of a mixture containing the sample solution analytes and the hydrophobic IL is required to ensure the adequate formation of fine droplets. Additionally, the applications of vortex, microwaves, ultrasounds, gas and air are also accompanied by an increase in temperature. Notably, the dispersive solvents are not needed in most cases.
Drug residue is the most serious problem in food safety. As a kind of dietary food for humans, milk may be contaminated by residual drugs, such as oxytetracycline, estrogen and sulfonamides. Massive consumption of milk which contains residual drugs may have a tremendous influence on human health, especially on the endocrine system. There is an urgent need to establish a rapid, effective and highly sensitive method for the detection of contaminants in milk. The most common sample pretreatment methods reported for IL-DLLME are ultrasound-assisted, microwave-assisted and vortex-assisted procedures. In the study reported by Gao et al., two ILs were used in the same ultrasound-assisted IL-DLLME for the extraction of sulfonamides in infant formula milk powder samples, where the hydrophobic ILs ([C4MIM][PF6], [C6MIM][PF6] and [C8MIM][PF6]) served as the extractant and the hydrophilic ILs ([C2MIM][BF4] and [C4MIM][BF4]) served as the disperser solvent [101]. According to the experimental results, the solubility of ILs in water may affect their extraction recoveries when used as extractants. The solubility of [C4MIM][PF6], [C6MIM][PF6] and [C8MIM][PF6] in water was 18.8, 7.5 and 2.0 mg L−1, respectively. The extraction recovery obtained with [C4MIM][PF6] was lower than those obtained with [C6MIM][PF6] and [C8MIM][PF6]. That is, the higher the solubility, the worse the extraction effect. For the selection of the dispersion solvent, the main criterion is its miscibility with the extractant and aqueous solution. The hydrophilic IL is miscible with the hydrophobic IL and water. When the hydrophilic IL is added into the aqueous solution containing hydrophobic IL, a distinct cloudy solution can be formed in a short time. Therefore, hydrophilic ILs are suitable as dispersion solvents when hydrophobic ILs are employed as extractants. Zhang et al. compared the extraction efficiency of conventional, ultrasound-assisted and temperature-assisted IL-DLLME methods for pyrethroid pesticides in honey samples [73]. The results indicated that ultrasound-assisted IL-DLLME had the best extraction efficiency. The experimental conditions, especially ultrasonic time, were examined. Under the optimized conditions, the mixture underwent ultrasonic treatment for only 2 min and was required to obtain high enrichment factors (506~515) and good recoveries (101.2~103.0%) when 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate [C8MIM][PF6] was used as the extraction solvent and methanol was used as the disperser solvent. For same analytes, Wang and co-workers used microwave-assisted IL-DLLME by using the ILs trioctylmethylammonium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide ([N8881][NTf2]) and HPLC to separate and detect them. Similarly, under the optimal microwave extraction conditions of 200 W applied for 60 s, excellent recoveries were achieved compared to DLLME alone [74]. Most recently, a simple and effective method, namely ultrasound-enhanced temperature-controlled IL-DLLME, was developed for the extraction of five pyrethroid residues in herbal tea [84]. The use of ultrasonication and heating was found to improve the ability of the IL ([C6MIM][PF6]) to extract the analytes. The above results have shown that the presence of ILs in externally assisted IL-DLLME methods can significantly improve extraction efficiencies for their applications. However, these studies did not investigate the mechanism between the external energy and IL interactions, which led to higher extraction efficiencies. Based on the ILs structure containing organic cations and inorganic or organic anions, they can efficiently absorb and transfer microwave/ultrasound energy and, consequently, rapidly warm the solvent and the sample, suggesting very high heating rates [102,103,104]. Additionally, external energy (temperature, microwave or ultrasound) can accelerate or improve the dispersion of ILs in the extraction system. Therefore, ILs are very suitable for microwave or ultrasound assisted chemistry.
Additionally, vortex-assisted, gas-assisted and air-assisted IL-DLLME methods are also widely used for the extraction of food samples before analysis [90,91,92,93]. In the vortex-assisted IL-DLLME technique, mechanical dispersion of the extraction solvent can be most easily attained by simply vortexing the sample. For the gas-assisted IL-DLLME method, dispersion is conducted by bubbling fine bubbles of air or injecting an inert gas into the sample/extraction solvent mixture. Additionally, bubbles are created by adding an acid solution to the sample containing a carbonate to produce CO2 or passing compressed gas through the solution. The sample and extraction solvent are rapidly pulled into and forced out of a syringe in air assisted IL-DLLME. In the process, the vacuum is created by withdrawing the syringe plunger to produce the shearing forces and dissolved air bubbles, which will disrupt the surface tension in the water and solvent, leading to the formation of dispersion. An example involving the air assisted IL-DLLME technique used 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([C6MIM][PF6]) as an extractant to extract and preconcentrate aryloxyphenoxypropionate herbicides from aqueous and vegetable samples [76]. In addition, the viscosities of ILs used in this method should not be too high due to the incompatibilities with the syringe plunger movement. For instance, a novel and simple air-assisted IL-based DLLME technique combined with HPLC was developed for the analysis of five fungicides in juice samples by You and co-workers [77]. In their research, three ILs commonly applied in DLLME, including 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ([C6MIM][NTF2]), 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([C8MIM][PF6]) and 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([C6MIM][PF6]), were employed as extraction solvents. The results showed that [C6MIM][NTF2] had better extraction efficiency than the other two ILs, which might have resulted from its better solvation capabilities toward the target analytes. Moreover, the viscosity of [C6MIM][NTF2] was lower than the other two ILs, allowing it to more easily form a cloudy solution. The scheme is depicted in Figure 2B.
3.3. In Situ IL-DLLME
The in situ IL-DLLME, also termed in situ solvent formation microextraction based on ILs, was first proposed by Bahdadi and Shemirani in 2009 [105]. In the in situ IL-DLLME method, a hydrophilic IL is usually utilized as an extractant solvent of analytes in food samples. The hydrophilic IL can be transformed into a hydrophobic IL by a metathesis reaction, in which an anion-exchange reagent is added to facilitate the reaction. During this process, the analytes contained in sample solution are precipitated along with the hydrophobic IL [32]. This method can effectively avoid or reduce the use of the dispersion organic solvents. Moreover, the extraction is completed in a short time. In order to improve the kinetics of the metathesis reaction, vortex, microwaves, ultrasound, or shaking is generally utilized in this method.
The in situ IL-DLLME technique has been applied towards the analysis of many analytes from food samples. For instance, Fan et al. used the in situ IL-DLLME technique as the pretreatment method for the extraction of chlorophenol compounds in honey samples. The IL 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide ([C4MIM][NTf2]) was employed as the extractant and formed in situ by the addition of hydrophilic IL 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate ([C4MIM][BF4] and LiNTf2. At first, an appropriate amount of IL [C4MIM][BF4] was added to the honey sample solution and the mixture was manually stirred to ensure complete mixing. Then, an anion exchange reagent (LiNTf2) was quickly added into the above mixture to form fine droplets of [C4MIM][NTf2] [71]. Zhang and co-workers developed a simple, rapid and sensitive in situ IL-DLLME method coupled to headspace gas chromatography (GC) for the analysis of polychlorinated biphenyls and acrylamide at trace levels from food samples [29]. The results indicated that the optimized in situ IL-DLLME method exhibited good analytical precision towards the analytes. Moreover, the matrix-compatibility of the developed method was also investigated by quantitative analysis of acrylamide in brewed coffee samples.
Among the newest publications related to in situ IL-DLLME, particular attention should be paid to the research of Smirnova et al. [72]. In their study, two tetraalkylammonium-based ILs, including tetraoctylammonium N-lauroylsarcosinate (TOALS) and tetrahexylammonium dihexylsulfosuccinate (THADHSS), were obtained in the course of extraction by metathesis reaction occurring upon the mixing of IL cation (tetra-n-octylammonium bromide, i.e., TOABr or tetran-hexylammonium bromide, i.e., THABr) and anion suppliers (sodium N-lauroylsarcosinate, i.e., NaLS or sodium dihexylsulfosuccinate, i.e., NaDHSS) in an aqueous solution containing analytes. The TOALS and THADHSS formed in situ were, respectively, employed as extractants of in situ IL-DLLME to extract different dyes in a food sample. Generally, extraction with ILs formed in situ is carried out without the dispersing agents during the extraction procedure. The extraction efficiency of analytes is mainly affected by the molar ratio of cationic to anionic suppliers. Moreover, mechanism studies indicate that the recovery of anionic dyes for in situ IL formation is closely related to ion exchange of dye anion in organic phase and bromide. In this work, it is supposed that bromide emerged in the organic phase from the precursor, TOABr or THABr. However, such a mechanism may take place even for extraction, using pre-synthesized ILs because bromide may be presented in the product as an admixture. Additionally, an in situ derivatization combined with the ultrasound-assisted IL-DLLME method was developed for the extraction of biogenic amines in foods [88]. The IL 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([C4MIM][PF6]) was used as the extraction solvent and dispersed into the aqueous sample solution as fine droplets by ultrasonication. Results indicated that the developed method was eco-friendly, sensitive, rapid and cost-effective for the determination of biogenic amines in a wide range of food sample matrices. The scheme is depicted in Figure 2C.
3.4. Magnetic IL-DLLME
The use of ILs in DLLME has boosted the rise of a wide variety of modalities of the technique. However, the ILs are difficult to recycle after use. The high cost of ILs and their unknown toxicity to the environment, either by themselves or by their degradation products, greatly restrict the further application of ILs. Recently, a new idea has emerged involving introducing magnetism into the IL-DLLME. Many DLLME techniques related to magnetism have been reported, named in situ magnetic retrieval-IL-DLLME, magnetic effervescent tablet-assisted IL-DLLME (META-IL-DLLME) and magnetic ionic liquid-based DLLME (MIL-DLLME) [36].
In the in situ magnetic retrieval-IL-DLLME technique, the magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) of iron oxide (i.e., Fe3O4) are usually used for the retrieval of the in situ created IL [70]. Iron oxides used as magnetic sorbents retrieve the IL that contained the analytes. Then, the analyte is desorbed prior to analysis. Due to the large surface area, MNPs can be easily isolated from a sample solution with the assistance of an external magnetic field. Fast mass transfer resulting from the large interfacial area between the IL and the sample solution can occur [106,107]. Additionally, a dispersing solvent and centrifugation are not often required in this method to extract the analytes and separate the extracting phase. Therefore, the application of MNPs in in situ IL-DLLME is considered as another rapid, simple, effective and eco-friendly microextraction technique, which is proved to be a widely used in the pre-treatment method. In the work reported by Fan et al., the in situ IL-DLLME combined with ultra-small Fe3O4 MNPs was developed to detect pyrethroid pesticides from water samples [108]. The microextraction performance was enhanced by optimizing the experimental conditions, especially anion-exchange reagents. In fact, the proposed method is nanometer-level microextraction with the high sensitivity.
Although the magnetic retrieval of the IL was achieved by the introduction of MNPs, the solvent dispersion and recovery steps do not run synchronously. To solve this problem, a novel a novel IL-DLLME assisted by magnetic effervescent tablets named META-IL-DLLME was proposed by Yang and co-workers. This method combined IL-DLLME with the magnetic retrieval of the extractant. A magnetic effervescent tablet composed of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles, sodium carbonate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate and 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonimide) was used for extractant dispersion and retrieval. Two ILs, including 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonimide) ([C6MIM]NTF2) and 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonimide) ([C8MIM][NTF2]), were employed as extractants, which was dispersed by the effervescing agent and then retrieved by ferroferric oxide [109]. The proposed method successfully combines effervescence dispersion and magnetic recovery and reduces some limitations of the classic IL-DLLME. As a result, the dispersion and collection of the green extractant can be completed almost simultaneously, which is timesaving and environmentally friendly. Thus, this method may be a promising sample preparation technique in the field of trace analysis from food samples.
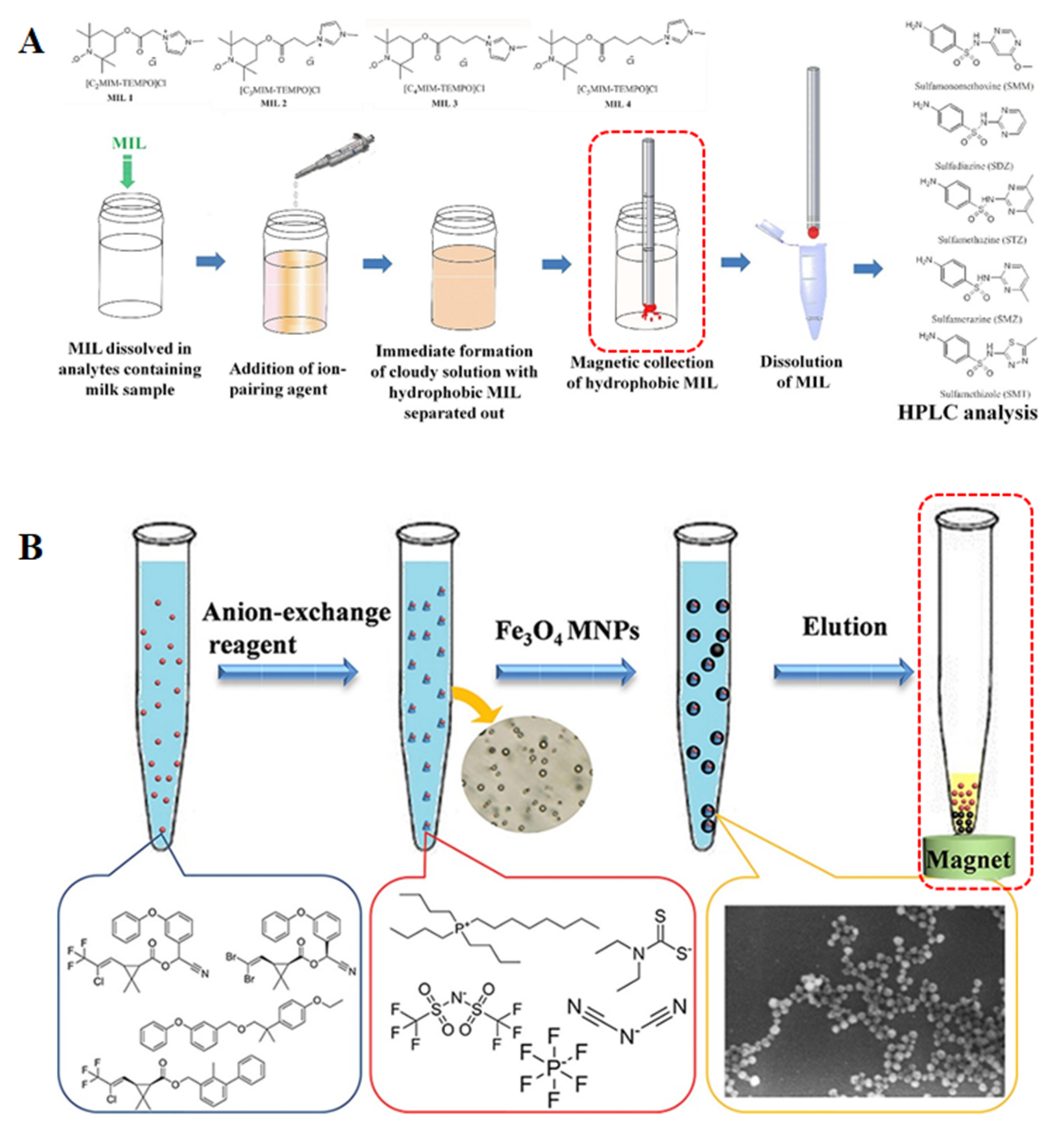
Another innovative approach for the recovery and collection of ILs is to use magnetic ionic liquids (MILs) in DLLME. MILs have an excellent response to an external magnetic field and are easy to recycle [110]. In recent decades, the development of MILs urged a new wave of research due to their unique physical and chemical properties, as well as their potential abundance of opportunities for the development of sample preparation techniques [111,112]. As effective extraction solvents, MILs have attracted interest to replace routine nonmagnetic extraction solvents in DLLME. An example of MIL-DLLME was reported by Wang and co-workers in 2014. A MIL, precisely 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroferrate [C6MIM][FeCl4], was used as the extractant for the preconcentration of triazine herbicides from vegetable oils. After extraction, phase separation was rapidly achieved by intrinsic magnetism of the MIL and external magnetic field in this method [80]. Soon afterwards, the same research group proposed a novel matrix solid-phase dispersion combined with magnetic ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (MSPD-MIL-DLLME) for the extraction of six triazine herbicides from oilseeds. In this method, the MIL 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroferrate [C4MIM][FeCl4] was employed as the extraction solvent to simplify the extraction procedure by magnetic separation. As a result, the elution and cleanup can be accomplished in one step by this method [81]. Additionally, among the most recent publications devoted to MILs, the research of Wang et al. seems to be very promising. The authors developed a novel and sensitive MIL-based up-and-down-shaker-assisted DLLME for the separation and preconcentration of inorganic selenium from various rice matrixes. As the first microextraction step, the MIL, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroferrate ([C4MIM][FeCl4]) was selected as the extractant to extract the complex of Se(IV) and 2,3-diaminonaphthalene from sample aqueous solution with the assistance of an up-and-down-shaker vortex agitator. After microextraction, the MIL containing target analytes was collected at the bottom of the tube by applying an external magnetic field around the test tube. Under the optimal extraction condition, the proposed method provides good precision and reproducibility [82]. Beiraghi et al. developed a new centrifuge-less IL-DLLME technique for the selective preconcentration of trace amounts of potassium from oil samples. In their study, a new task specific magnetic polymeric ionic liquid (TSMPIL) was employed as a chelating and extraction solvent [113]. More important points are that the proposed method provides excellent preconcentration factors in a relatively short extraction time without the need of a complexing agent and a centrifuge step. Most recently, Yao and Du proposed a novel in situ MIL-DLLME method for the simultaneous determination of sulfonamides in milk. In this method, four organic MILs, such as [C2MIM-TEMPO][PF6], [C3MIM-TEMPO][PF6], [C4MIM-TEMPO][PF6] and [C5MIM-TEMPO][PF6], were in situ formed. Compared to other DLLME methods, the extraction process of in situ MIL-DLLME is rapid, completely free of any organic solvents and realizes magnetic-assisted phase separation [85]. Several phosphonium-based MILs, including [P6,6,6,14+][FeCl4−], [P6,6,6,14+]2[MnCl42−], [P6,6,6,14+]2[CoCl42−] and [P6,6,6,14+]2[NiCl42−] combined with DLLME were synthesized and applied for the extraction of six estrogens in milk [93]. Indeed, an increasing number of MIL-DLLME applications have been reported and reviewed in recent years [114,115]. Due to the inherent magnetism, MILs gradually become excellent candidates for performing magnetic separation. Normally, the DLLME promoted by MILs is carried out without the use of centrifugation, decantation, and solidification stages. After extraction, the MIL containing analytes can be harvested by magnetic separation, making it more feasible, straightforward, and throughput the DLLME procedures. Thus, the combination of the MILs and DLLME is a powerful analytical methodology and shows the potentials of practical applications in the treatment of food samples. The scheme of MIL-DLLME is depicted in Figure 2D.
As far as we know, ILs have been successfully employed as both extraction and/or dispersive solvents in several DLLME applications. In the most classical DLLME mode, centrifugation is applied as the last step to separate the extraction solvent from the sample matrix. A microsyringe is often needed to manually collect the final microdroplet containing the preconcentrated analytes for further analysis. In order to increase sample throughput in IL-DLLME, the centrifugation should be avoided. The main strategies are as follows: the use of tailor-made dedicated extraction devices, parallel extraction, magnetic-based separation, semi-automatic or fully automatic flow injection, which involves the use of microfluidic devices and robotic equipment. Among them, magnetic separation is often performed as in the case of DLLME with magnetic retrieval. As shown in Figure 3, after application, both MILs and MNPs can be recovered by magnetic separation without centrifugation. New trends in food sample preparation using DLLME are geared towards employing ILs with greener properties to comply with green analytical chemistry requirements. In fact, ILs are not totally environmentally friendly and pollution-free. Therefore, the recycling and reuse of ILs after extraction is a non-negligible process, which is very crucial for the “green” feature.
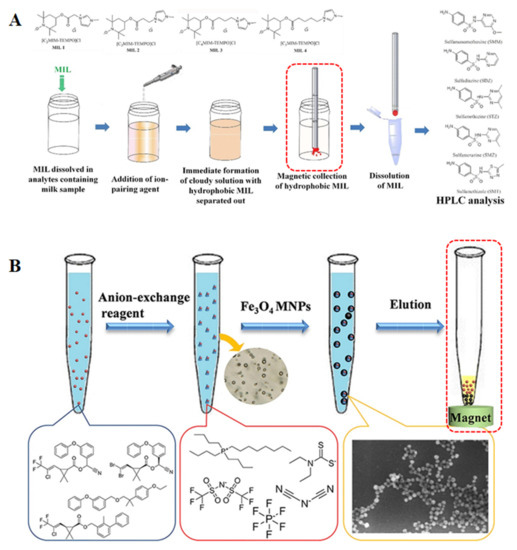
Figure 3.
Magnetic separation in the DLLME of (A) MILs and (B) Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles [85,108].
In conclusion, LLME techniques have found an important place in sample preparation due to their inherent advantages over conventional procedures. As one of the important forms of LLME, DLLME is a well-established method and commonly used in food analysis. In these methods, microliter volumes are used, and the effect of unintended solvent evaporation is magnified, which results in inaccurate quantitative results. In a word, the volatility of extraction solvents is a great concern because it affects the enrichment factor and repeatability of these methods. Thus, solvents with densities higher than water (ρ > 1) are preferred to overcome volatility issues, as they settle below sample aqueous solution. In the previous literature, more than 40% of reported DLLME methods were carried out with solvents with densities greater than 1.0 g/cm3 [114]. ILs have many of the same advantages as ILs, especially low volatility, indicating that the IL-DLLME method is a very flexible and a promising tool for trace analysis in complex food samples. Its flexibility lies in the ability to be coupled to various agitation methods (vortex, ultrasonic, microwave, etc.) and instrumental detection systems. Currently, in the IL-DLLME method, 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([CnMIM]PF6) is the IL most commonly employed, with 2–8 carbons in the alkyl chain, being hexyl and octyl the most usual alkyl groups. Their synthesis is relatively simple and they are already commercially available. Additionally, imidazolium-based ILs are conventionally more stable compared to other ILs. Moreover, they can offer a variety of properties, mainly tunable viscosity and solubility, depending on the alkyl-chain length of the imidazolium ring and the counter anion. In addition, the imidazolium cation is easier to form the interactions with target analytes, mainly including hydrogen bonding, electrostatic forces and π-π interaction. On the other hand, such ILs are usually hydrophobic, which is conducive to the separation of extraction phase and raffinate phase. Overall, the main advantages of the developed ILs-based DLLME method are ease of operation, cost-effective, eco-friendly and high extraction factor for target analytes. Nevertheless, some ILs suffer from more or less drawbacks such as toxicity, poor biodegradability and high costs. These incomplete data on their disadvantages over advantages prove the need for continuous interest and development in this area. More efforts are still needed to solve the above issues.
4. ILs in Solid-Phase Microextraction
Solid-phase microextraction (SPME) uses the sorption-based microextraction technique that has been successfully applied to the analysis of a broad range of analytes in a variety of matrices. In the SPME, fiber is often used as solid support. A thin layer of the stationary phase with different properties is coated on the surface of the fiber to form multilayered SPME fiber, which has a high surface area-to-volume ratio. The extraction mechanism of SPME is mainly based on the absorption or adsorption of the target analyte on the solid support containing the fiber coating. The extraction efficiency depends on the partition of analytes between the sample phase (food matrix) and the extraction phase (fiber coating). The fiber coating selected in SPME has a strong affinity for the extracted components, which can ensure effective enrichment and improve the sensitivity of the analysis.
Recently published reviews have summarized the most significant developments and applications of SPME as a sample preparation tool for targeted and untargeted analysis over the last decade [10,115,116,117,118]. In fact, the implementation of SPME methods for the extraction and separation of contaminants from complex food matrices is well established [80]. Introduced in the early 1990s, SPME can address several challenges in traditional sample preparation as it successfully integrates a number of analytical steps such as sampling, extraction, preconcentration and sample introduction into a single solvent-free step, when applied to capture either volatile or non-volatile analytes [119]. SPME’s main advantages are the simplicity of its workflow, high sensitivity, short process time, little or no use of organic solvents, trace analysis and easy-to-automate. The principle of SPME is based on the distribution equilibrium of analytes between the sample matrix and a fiber coated with an extraction phase. Therefore, it is very important to prepare a fiber coating with good performance, which can exhibit high selectivity and large enrichment factors for analytes. However, the limited physicochemical of commercially available extraction phases have greatly hindered its further application in food analysis. In this sense, the continuous research towards the development of new and green materials as extraction phases is a “hot topic” of investigation [120]. ILs have drawn increased attention in SPME due to their unique physical and chemical properties. The main attraction of ILs lies in their structural adjustability. That is, modifications to the composition of cations and anions can produce ILs with desired chemical properties. SPME is based on the partition of analytes between the sample phase (food matrix) and the extraction phase (the sorbent). The properties of the sorbent play a key role in the performance of SPME. Therefore, one of the most important aspects is to find an appropriate sorbent [121]. With respect to the development of new SPME sorbents, attention should be focused on the development and application of ILs. Food analysis involving ILs has been suggested in two ways: (1) functionalizing materials with IL or (2) using ILs as carriers.
4.1. ILs/PILs Sorbent Coatings
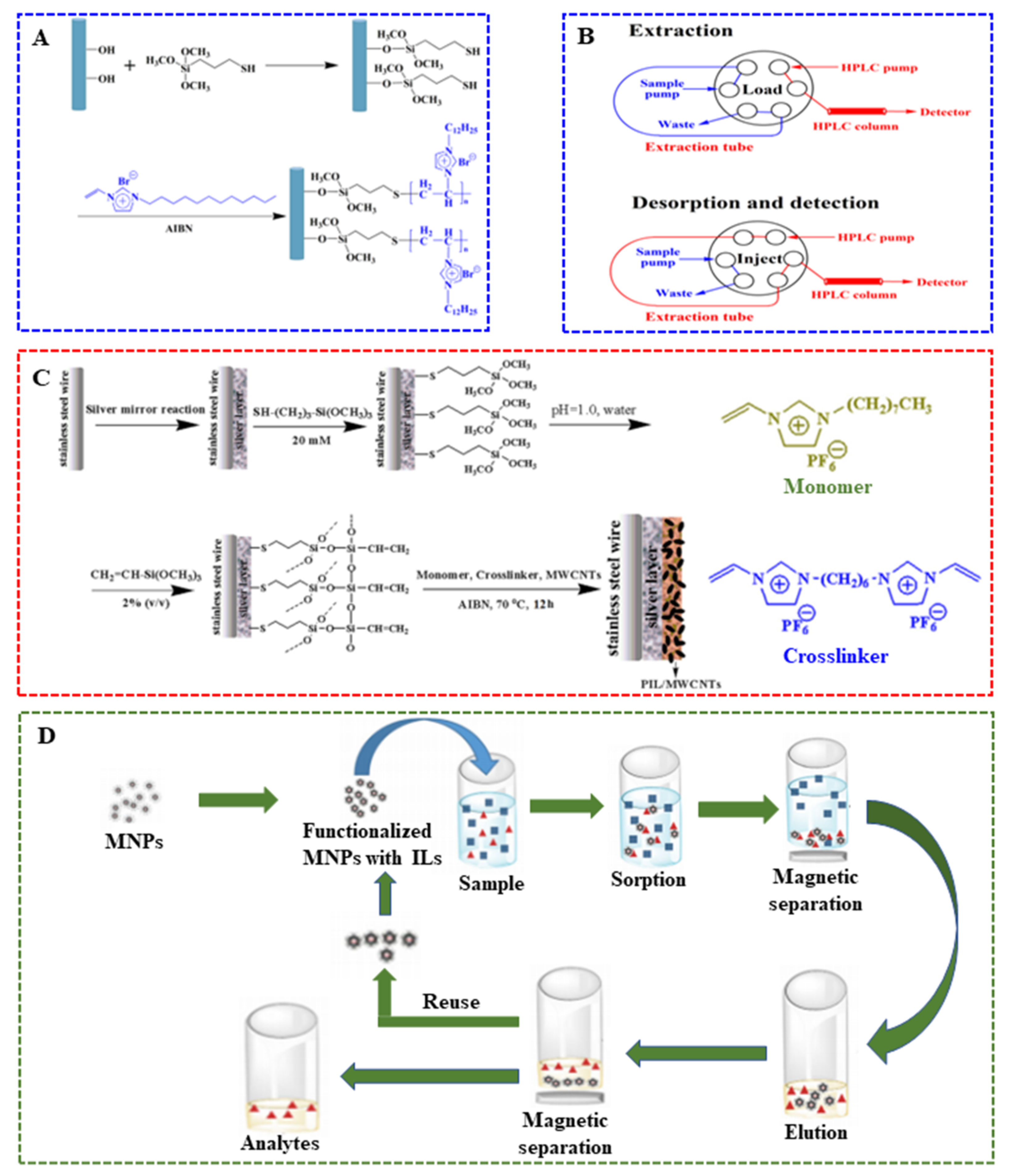
The employment of ILs in SPME sorbent coatings or membranes has grown considerably in the past decade [122]. The main advantage of employing ILs in SPME sorbent coatings or membranes are their tunable structure, which allows one to incorporate various materials selective to target analytes [123]. Several ILs-based SPME sorbent coatings have been prepared to enhance the sensitivity and lifetime of fiber. However, the use of conventional ILs in SPME is restricted by their release from the SPME coating or membrane with the organic solvent during the desorption process. Additionally, fiber re-coating after each extraction is often needed. Subsequently, in order to overcome these drawbacks, polymeric ionic liquids (PILs) have been successfully employed as sorbent coatings or membranes for SPME, leading to advantageous analytical results in comparison to commercially available coatings. As SPME coatings or membranes, cross-linked PIL based copolymers can be used in direct immersion SPME. Therefore, PILs have received considerable attention due to their chemical structure tunability and have been extensively used as SPME fiber coatings in the area of food analysis [124,125,126,127]. PIL employing as SPME coatings was first reported in 2008 by Zhao and co-workers [128]. The performances of two PIL-based SPME coatings were assessed for the extraction of pesticides and fruit metabolites in grape. In their study, two different PILs, namely poly(1-4-vinylbenzyl-3-hexadecylimidazolium) bis[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl] imide (poly([VBHDIM][NTf2]) and N,N-didecyl-N-methyl-d-glucaminium poly(2-methyl-acrylic acid 2-[1-(3-{2-[2-(3-trifluoromethanesulfonylamino-propoxy)-ethoxy]-ethoxy}-propylamino)-vinylamino]-ethyl ester) (poly([DDMGlu][MTFSI]) were used. Compared to commercially available SPME coatings, [VBHDIM][NTf2]-based coatings demonstrated a similar or better extraction performance and comparable reproducibility [8]. Task-specific PILs containing a hydrophilic group are accompanied by a monomer with a hydrophobic carbonyl functional group, providing a strong hydrophilic interaction with polar analytes in aqueous media. More recently, a PIL-based membrane was prepared via copolymerization of 1-hexyl-3-vinylimidazolium bromide (HVImBr) ionic liquid and methylmethacrylate (MMA) monomers by Sadeghi and coworker [129]. Additionally, the membrane was employed as SPME sorbent for the extraction of sulfathiazole in milk and honey aqueous samples. It is worth mentioning that five different zwitterionic sorbent coatings based on PILs were developed by the on-fiber UV co-polymerization of the zwitterionic monomers 1-vinyl-3-(alkylsulfonate)imidazolium or 1-vinyl-3-(alkylcarboxylate)imidazolium and different dicationic IL crosslinkers. Subsequently, the sorbent coatings were applied in SPME for the determination of short chain free fatty acids in wine [130]. In particular, PILs were also used as coatings of in-tube SPME (IT-SPME) system for the extraction of phthalates from bottled water to improve the durability and extraction efficiency. For instance, Feng et al. [131] prepared the basalt fibers grafted with poly(ionic liquids) coating by a two-step reaction. As shown in Figure 4A, the first step is to modify the basalt fibers with thiol groups. The second step is to the graft polymerization 1-dodecyl-3-vinylimidazolium bromide using azodiisobutyronitrile (AIBN) as the initiating agent. Meanwhile, in order to build an online SPME-HPLC system, a switchable six-port injection valve is directly connected to the analytical detection technique. In this case, the in-tube capillary containing the IL- or PIL-sorbent coating was replaced by the sample loop of the valve. That is, all the steps of the extraction/elution procedure online were preformed automatically (illustrated in Figure 4B). Moreover, the primary extraction mechanism (absorption or adsorption) was evaluated. The results indicate that sorbent coatings generated with monocationic IL monomers and silver-based IL monomers revealed an absorption-type and adsorptive-type extraction mechanism, respectively [132,133]. Therefore, it is concluded that PILs can be chemically tuned to extract analytes via absorption- or adsorption-type mechanisms by simple changes in the composition of the IL monomer. Nowadays, ILs are explored as sorbent phases for fiber-based SPME, especially using PILs. The mechanical and thermal stabilities of the PILs-based sorbent coatings can be improved by polymerization of functionalized IL monomers with cross-linkers [134,135].
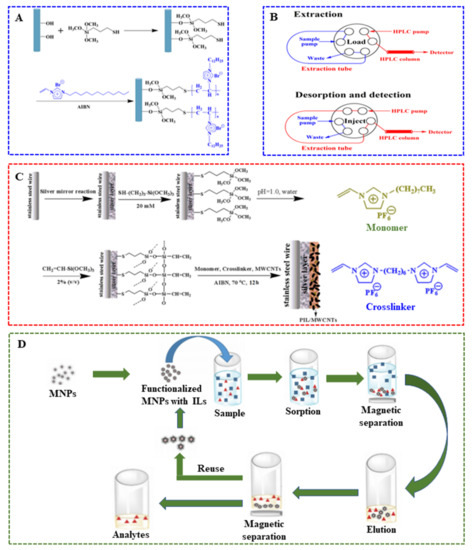
Figure 4.
(A) Non-covalent functionalization of oxidized MWCNTs with PIL; (B) Construction of in-tube SPME-HPLC online system by a switchable six-port injection valve; (C) Preparation of PIL/MWCNTs-coated SPME fiber; (D) Application of MNPs in the M-DMSPE [131,136,137].
In addition to the coat of ILs over the SPME sorbent, a flat thin film can be coated over the solid support to form a multilayered SPME fiber, which has high surface area-to-volume ratio and promoting kinetics. The thin film possesses a membrane polymer matrix with the incorporated-selective carrier. The above system is referred to as membrane-based SPME. Recently, Ferreira and co-workers prepared a PIL-based film on a stainless-steel bar via electropolymerization. The coated fiber as an SPME adsorbent was then immersed in milk samples to determine oxytetracycline residues. The proposed method achieved a low of detection (LOD) of 70 µg·mL−1 with adequate precision. Furthermore, this methodology was evaluated according to the analytical Eco-Scale approach, which was used to determine whether the analysis method was green or not. An analytical Eco-Scale score of 51 was obtained despite the multi-step character of the analytical process of the proposed method, representing an acceptable green analysis [138].
In this system, the hydrophobic external layer over the layer of the highly polar extraction phase prevents the loss of the water-soluble IL coating. Membrane-based SPME combines the benefits of both SPME and membrane separation [139]. Moreover, the double layer coating allows highly polar ILs to be used as extractants in aqueous matrices without the risk of dissolution, which is often used in isolating polar analytes from polar samples, such as aqueous media. To sum up, despite the fact that the high cost of these SPME coatings or membranes may limit their use, their unique features have led to their widespread use.
4.2. ILs/PILs-Based Functional Materials
An additional strategy to improve the selectivity of the IL or PIL SPME coatings was to modify them with specific functional materials. ILs were usually immobilized onto silica or polymeric supports to obtain supported IL phases (SILPs) in order to take advantage of the chemical functionality that ILs can possess. SILPs can therefore be considered as a new class of sorbent material in SPME. SILPs were applied as an SPME coating, in which ILs were adsorbed onto the fiber surface [140]. Although the liquid state of ILs is lost when immobilized on a solid support, ILs-based coatings can still be exploited as sorbents in SPME. A new extractive phase for SPME was reported by Tian et al. [141]. They developed a silica fiber covered by a bipyridyl IL as SPME coating to improve the extraction performance and the mechanical properties. This IL was immobilized onto silica aerogel via the covalent bond to obtain IL-hybridized silica aerogel. A hybrid material with a porous three-dimensional structure was observed and exhibited excellent extraction performance when employed as an extractive sorbent in SPME. Instead of chemical bonding to silica materials, IL 1-hexadecyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifuluoromethylsulfonyl)imide ([C16MIM][NTf2]) was confined into the network of silica-based ionogels, suggesting high loadings of IL. The hybrid material of silica-based ionogels and IL was used as an SPME fiber coating for the extraction of four organophosphorus pesticides (OPPs) from wine and juice samples. The extraction efficiency was significantly improved due to the high loadings of IL on silica-based ionogels [142].
Carbon nanomaterials (CNMs) have also been employed as sorbents in sample preparation due to their strong absorbability. Additionally, the study showed the CNMs-ILs coated fibers can provide excellent adsorption capacity and selectivity for analytes from complex matrix. There are two kinds of bingding ILs to CNMs, including covalent and non-covalent functionalization. As a simple and nondestructive method, non-covalent functionalization is a mode of modifying the surface of CNMs using a physical method, such as the grinding method and polymerization. These methods provide a facile pathway to modify the surface of CNMs without destroying their chemical structure. When the structure of IL contains imidazolium cation, the main mechanism for non-covalent functionalization is attributed to the cation-π or CH-π interaction between the imidazolium cation and the π-network of CNMs. However, due to the weak interaction between CNMs and ILs, ILs can be leached upon exposure to an organic solvent. To overcome the above problem, covalent functionalization is introduced, which involves the functionalization of CNMs by ILs via the covalent method to produce the CNMs-ILs composite. In this method, ILs are regarded as chemically linked ligands on the surface of CNMs. This approach offers some advantages, such as leaching avoidance of ILs, excellent durability and higher thermal and chemical stability. However, compared to non-covalent functionalization, several functionalization steps are needed, which will damage the extended π-networks of the CNMs and thus impair their desired mechanical and electrical properties. Additionally, the unique properties of ILs and CNMs can be retained in the CNMs-IL composite. In short, compared to single materials and other traditional commercial materials, CNMs-ILs composites possess higher mechanical and thermal stability, as well as a longer life span [143]. Therefore, CNMs-ILs composites are often used as SPME coatings for extraction and the determination of different compounds in food samples. Even more to the point, the composites of CNMs-ILs with other materials (such as PANI, Nafion and MOFs) were formed, which could also be used as novel SPME fiber coatings [144,145,146]. Feng et al., prepared a novel MWCNTs-doped PIL fiber through in situ polymerization, i.e., the polymerization of oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) with 1-vinyl-3-ethylimidazolium bromide monomer and anion exchange of PILs with PF6¯. Then, the prepared fiber was used as the SPME coating for the extraction of 2-naphthol from fruit sample [136]. In their study, non-covalent functionalization of oxidized MWCNTs with poly(VEIm+ PF6−) was performed to obtain the MWCNTs-PIL composite. Then, PIL/MWCNTs-coated SPME fiber was prepared with 1,1′-(1,6-hexanediyl)bis(1-vinylimidazolium) bishexafluorophosphate as the crosslinking agent (Figure 4C). Due to the presence of MWCNTs and PILs, there was a stronger π-π interaction between the analyte and SPME sorbent, demonstrating higher extraction efficiency for analytes, especially polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Moreover, the extraction performances of fibers with different anions were investigated. The results indicated that the hydrophobicity of the MWCNTs-PILs coating was increased when the Br¯ anion of IL was exchanged into NTf2¯ anion, which was beneficial to the extraction of n-alkanes. When the Br¯ anion was substituted for 2-naphthalene-sulfonate (NapSO3¯), the extraction performances of MWCNTs-PILs for phthalate esters and halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons were improved. Therefore, the proper anion of ILs can be selected according to a variety of analytes [147].
Generally, the high fabrication cost of CNMs-ILs composites is not suitable for industrial production, which limits its application in the SPME method. As a low cost and abundant class of clay minerals, montmorillonite has excellent potential properties such as high porosity, high surface area, high adsorption capacity and enhanced mechanical properties. Thus, montmorillonite have been preferred to fabricate composite materials. This material can be modified with ILs to decrease their hydrophilic character, which is attractive as a coating material for SPME. Moreover, the interaction between montmorillonite and ILs have also been studied [148,149,150]. Most recently, Tashakkori et al., reported the preparation of novel KSF-montmorillonite composites modified with ILs containing amino terminated imidazolium cations with methyl and benzyl groups and hydrophobic anions (bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide) and hydrophilic anions (bromide and tetrafluoroborate). The montmorillonite/IL composites were applied successfully as the coating of SPME fibers to determine/extract 16 phenolic compounds from fresh fruit juices [151]. However, the overall efficiency, stability and durability of the IL coated fibers turned out to be low. These defects can be overcome by using PIL-based coatings [122]. For example, the preparation of Na-montmorillonite clay modified with a novel polythiophene-IL was reported by Pelit and co-workers. This modified material was employed as the coating for SPME fibers to extract endocrine-disruptor pesticides in fruit juices [149].
Additionally, as one of the most studied porous crystalline hybrid materials containing both organic ligands and inorganic metal ions or metal clusters, metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) modified with ILs have great potential as SPME sorbents for the analysis of different compounds, attracting great attention from researchers [152]. A vortex-assisted dispersive solid phase microextraction (VA-d-μ-SPE) method was proposed and successfully applied in the extraction and determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from vegetable and fruit juice samples using an IL-modified MOFs (IL-MIL-100(Fe)) composite as the sorbent. Mechanism research indicates that the hydrophobic and π-π interactions between IL-MIL-100(Fe) and PAHs play a dominant role in the extraction process [153]. Compared to MOFs materials without IL (MIL-100(Fe)), IL-MIL-100(Fe) demonstrated better adsorption properties for PAHs. The anion of IL is L-cysteine and it has a stabilizing effect to the π system that facilitates the interaction of IL-modified sorbent and PAHs. Till now, the use of MOFs as a coating material in SPME for the determination of complex matrixes has not been explored much.
Furthermore, molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) have the advantages of easy fabrication, selective recognition, low cost, good stability and robustness in a wide range of pH, solvents and temperature. Thus, they are considered as a valid alternative to natural receptors. MIPs are tailor made synthetic materials with artificially generated adsorptive sites to selectively recognize the target analytes. Furthermore, its synthesis is relatively cheap and easy. Typically, the main components include template molecule, functional monomer and cross-linker in the preparation of MIPs. Among them, the functional monomer plays a crucial role to establish specific interactions with the template molecule and affects the affinity of the MIP towards the target analytes [154]. As expected, PILs can act as the functional monomer or cross-linker to synthesize MIPs [155,156]. As a new adsorbent, PILs-based MIPs are often applied in the SPME method. Chen et al. utilized a PIL, 1-ally 3-vinylimidazolium chloride as the functional monomer to prepare a novel MIP. Compared with previous sorbent materials, the proposed MIP showed high hydrophilicity and selectivity for phenolic acids in fruit juice and beer samples when used as the adsorbent of multiple monolithic fiber solid-phase microextraction (MMF-SPME) [157].
4.3. Magnetic Materials
The application of ILs in magnetic microextraction technology mainly has two forms: (1) modifying magnetic materials with ILs and (2) utilizing MILs as sorbent coatings. Aside from ILs, MILs have been developed and employed as SPME coatings for the extraction of contaminants from food samples. The magnetic properties of the MIL make it possible to magnetically harvest with an ordinary magnet, negating the need for the blended mixture to be transferred and filtered out [158]. Yao et al. developed a novel ultrasound-assisted surfactant-enhanced emulsification microextraction by using a MIL coupled with micro-solid phase extraction to extract cadmium and lead in edible vegetable oils. In this system, the MIL 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroferrate ([C4MIM][FeCl4]) was employed as an extractant and Fe3O4 nanoparticles as the sorbent. Ultrasound was applied to improve the dispersion of MIL and accelerate the mass transfer process. Under the effect of an external magnetic field, the phase separation time was shortened, and the separation process was simplified. The results demonstrated that the proposed method has satisfactory sensitivity, reproducibility and recovery for the analytes [159].
Another strategy to improve phase separation efficiency was to use ILs-modified magnetic materials as SPME sorbents [160,161]. The advantages of MNPs as sorbents in SPME of food components are low cost, high extraction efficiency, low detection limits, easy to separate, fast separation speed, excellent reusability and functionalization with both organic and inorganic groups [137]. The unique properties of ILs make them part of the sorption material of SPME. The use of ILs in sorbents MNPs can significantly increase the selectivity of the extraction method. For example, an IL-coated cyclodextrin functionalized magnetic core dendrimer nanocomposite (MNP@PAMAM@CD@IL) was prepared and used as adsorbents of dispersive magnetic SPME (DM-SPME) for the determination of pyrethroids in juice samples [161]. In the same method, another IL-coated amino silanized magnetic graphene oxide (MGO@SiO2-APTES-IL) was employed as an adsorbent for the enrichment and extraction of lead (II), copper (II) and cadmium (II) in shellfish samples [162]. When the system reached adsorption equilibrium, the magnetic adsorbents were collected using a strong external magnet without centrifugation. As another miniaturized version of SPE, magnetic-based dispersive microsolid-phase extraction (M-DMSPE) has also been used for sample pretreatment prior to analysis. In conventional SPE, the sorbents are packed into cartridges or other kinds of devices. However, in the M-DMSPE scheme, the functionalized MNPs with ILs are added and mixed directly to the sample matrix. Then, the mixture can be isolated by an external magnetic field. After elution and clean-up, MNPs are dispersed with a suitable solvent and then magnetically isolated to reuse in the next analysis procedure. The whole scheme is shown in Figure 4D. In M-DMSPE, the development of new sorbents has become increasingly important in order to extract minority food components. Functionalized MNPs with ILs employed as sorbent materials in M-DMSPE was first reported in 2012 [163]. Later on, the M-DMSPE based on MNPs modified with ILs was extensively used in the selective extraction of food contaminants including pesticides [164], synthetic food dyes [165] and metal ions [166,167,168]. Mehdinia and collaborators functionalized MNPs based on Fe3O4 with tricaprylmethyl ammonium chloride thiosalicylate ([A336][TS]), which was used as a sorbent to detect cadmium in fruits (orange, apple, and banana). Under optimum microextraction conditions, satisfactory results with a low detection limit of 0.5 ng·mL−1 and high enrichment factor of 50 were obtained [166]. Finally, Table 2 exhibits some representative application examples of ILs in SPME that have emerged in recent years.

Table 2.
Representative application examples of IL-based SPME in food samples recently.
SPME was developed in order to simplify the sample preparation step, reducing the analysis time and the solvent volume used. It is an ever-growing sample preparation method in terms of new developments and has received special attention due to its simplicity, sensitivity and efficiency in the analysis of analytes in complex matrices, especially food samples. Meanwhile, selecting a suitable SPME fiber coating is the key to achieving satisfactory analysis results. The sustainable development of SPME technology largely depends on the exploitation of novel sorbent materials. As one of the excellent alternatives of conventional solvents, ILs exhibit a range of solvent properties and attract interest as green solvents for chemical processes. The introduction of ILs makes it possible to alleviate the difficulties in the SPME method caused by traditional extraction phases. ILs are usually explored as sorbent phases for fiber-based SPME, especially using PILs. The ILs-based SPME fiber coating has the advantages of high homogeneity and purity, flexibility, selectivity, easy preparation, mechanical and thermal stability. The selectivity of the IL-based coatings can be controlled by regulating the structure of the cation and anion of ILs. Although ILs are attractive as the coatings or sorbent material for SPME, the overall efficiency and durability of the IL-based fibers toward specific target analytes have been revealed to have low tunable extraction capability. Moreover, during the extraction process, the interactions between analytes and ILs are a driving force. Therefore, the study of extraction mechanism can provide a valuable reference for the development of new IL-based SPME sorbents. In a word, SPME has been widely applied for food analysis by coupling to different instruments. The future development of SPME technology, especially for SPME sorbents, still has a long road ahead, full of great challenges. Finally, the advantages and disadvantages of SPME and DLLME are listed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Advantages and disadvantages of SPME and DLLME.
5. Conclusions
Extraction is a competitive process between the extraction phase and the raffinate phase, which is essentially caused by the different strength of interactions between solute molecules and two-phase solvent molecules. The traditional techniques for food-sample preparation are time consuming and require large amounts of organic solvents due to the inherent complexity of food samples. As a structurally designable solvent, ILs can be adapted to different extraction systems by tailoring their structures. Therefore, ILs with advantageous features have been considered as excellent alternatives to traditional extraction media or materials for a range of microextraction techniques, contributing to the improvement of extraction performance and increasing the selectivity for food samples.
In the past few years, ILs-based microextraction techniques (such as DLLME and SPME) have gained prominence in the face of traditional methods, since they minimize the consumption of organic solvents and the sample volume. Although ILs have good effects and industrial prospects in extraction techniques, the high viscosity and high costs, as well as the recovery of the ILs after the extraction process, could limit the industrial application of ILs, especially for DLLME and, thus, it is still an urgent task. The viscosity of ILs can be reduced by increasing the temperature of the extraction process. However, this may lead to increased energy consumption and is not suitable for some heat-sensitive substances. Inert diluents can be considered to reduce the viscosity of ILs. To reduce the use cost of ILs, more attention should be paid to the fabricating costs of ILs, such as reducing the raw material cost, simplifying the synthesis route and optimizing the process parameters, etc. Starting with the design of ILs, it is also important to control the cost and energy consumption throughout the process. Additionally, developing the recovery technology of ILs after extraction with low energy consumption can be adopted, including distillation, extraction, membrane separation, reverse osmosis and electrodialysis and so on. However, these recovery techniques of ILs are almost in the laboratory research stage, and their large-scale industrial application has not been reported.
Current trends in food sample preparation are geared towards employing more environmentally friendly approaches to comply with green analytical chemistry requirements. Tailored ILs with greener properties should be of especial interest to achieve the above goal; for example, MILs with excellent physicochemical properties, such as lower viscosity and higher magnetic susceptibility, which are responsive to the external magnetic field. The inherent magnetism of MILs makes them excellent candidates for the separation and recovery performing magnetic separation. In brief, ILs are kind of efficient extractants. An appropriate extraction system should be selected to maximize the function of ILs. Microextraction techniques promoted by ILs are expected to provide more opportunities for the extraction of food samples in the future. Finally, we hope that this paper will serve as a guide when choosing the most effective ILs-based microextraction strategy for the determination of contaminants in complex food matrices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Writing-Original Draft Preparation (Section 1, Section 3 and Section 5), L.N.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation (Section 4), C.C.; Table editing, drawing and literature retrieval, R.G.; Writing - Review & Revision, S.Y.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation (Section 2), Z.Z.; Figures editing, Y.H.; Writing-Editing & Supervision, D.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11574346).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| TOALS | Tetraoctylammonium N-lauroylsarcosinate |
| THADHSS | Tetrahexylammonium dihexylsulfosuccinate |
| [C4MIM][PF6] | 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate |
| [C6MIM][PF6] | 1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate |
| [C8MIM][PF6] | 1-Octyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate |
| [C4MIM][NTf2] | 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide |
| [C6MIM][NTf2] | 1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide |
| [C8MIM][NTf2] | 1-Octyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide |
| [C16MIM][NTf2] | 1-Hexadecyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifuluoromethylsulfonyl)imide |
| [N8 8 8 1][NTf2] | Trioctylmethylammonium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide |
| [C2MIM][BF4] | 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate |
| [C4MIM][BF4] | 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate; |
| [(C6)3C14P][NTf2] | Trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium bistriflamide |
| [C6MIM][FeCl4] | 1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroferrate |
| [C4MIM][FeCl4] | 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroferrate |
| [C4MIM-SH]Br | 1-(4-thiol)-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide |
| [P6,6,6,14]FeCl4) | Trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium |
| [C8MIM][NTf2] | 1-Octyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide |
| [TBP][PO4] | Tetra butyl phosphonium phosphate |
| [BBIM][NTf2] | 1,3-Dibutylimidazolium bis[(trifluoromethyl)sulfony]imide |
| [HHIM][NTf2] | 1,3-dihexylimidazolium bis[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]imide |
| [P4 4 4 12][BF4] | Tributyldodecylphosphonium tetrafluoroborate |
| [C6MIM][FAP] | 1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazolium tris(pentafluoroethyl)trifluorophosphate |
| poly[VBHDIM][NTf2] | poly(1–4-vinylbenzyl-3-hexadecylimidazolium) bis[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl] imide |
| poly[DDMGlu][MTFSI] | N,N-didecyl-N-methyl-d-glucaminium poly(2-methyl-acrylic acid 2-[1-(3-{2-[2-(3-trifluoromethanesulfonylamino-propoxy)-ethoxy]-ethoxy}-propylamino)-vinylamino]-ethyl ester) |
| [HVIM][Br] | 1-Hexyl-3-vinylimidazolium bromide |
| [H2N-C3MIM][Br] | 1-(3-Aminopropyl)-3-methylimidazolium cation with bromide |
| [H2N-C3MIM][BF4] | 1-(3-Aminopropyl)-3-methylimidazolium cation with tetrafluoroborate |
| [H2N-C3MIM][NTf2] | 1-(3-Aminopropyl)-3-methylimidazolium cation with bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide anions |
| [H2N-C3BIM][Br] | 1-(3-Aminopropyl)-3-benzylimidazolium cation with bromide |
| [H2N-C3BIM][NTf2] | 1-(3-Aminopropyl)-3-benzylimidazolium cation with bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide |
| [VIM][C3SO3] | 1-Vinyl-3-(propanesulfonate)imidazolium |
| [VIM][C4SO3] | 1-Vinyl-3-(butanesulfonate)imidazolium |
| [VIM][C9COO] | 1-Vinyl-3-(nonanocarboxylate)imidazolium |
| [VIMC10][SS] | 1-Vinyl-3-decylimidazolium styrenesulfonate |
| [(VBIM)2C12]2[SS] | 1,12-Di(3-vinylbenzylimidazolium) dodecane distyrenesulfonate |
| [VC16IM][NTf2] | 1-Hexadecyl-3-vinylimidazolium bis[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]imide |
| [(VIM)2C12]2[NTf2] | 1,12-Di(3-vinylimidazolium)dodecane dibis[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]imide |
| [AVIM][Cl] | 1-Ally-3-vinylimidazolium chloride |
| [AMIM][Cl] | 1-Allyl-3-methyl imidazolium chloride |
| [C4MIM][Cys] | 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium cysteine |
| [C4MIM][Cl] | 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride |
| [VC10OHIM][Cl] | 1-Vinyl-3-(10-hydroxydecyl) chloride |
| [C12VIM][Br] | 1-Dodecyl-3-vinylimidazolium bromide |
| [C8MIM][Br] | 1-Methyl-3-octyl-imidazolium bromide |
| [C12MIM][Br] | 1-Methyl-3-undecyl-imidazolium bromide |
| [C18MIM][Br] | 1-Methyl-3-octadecyl-imidazolium bromide |
| [BeBIM][Br] | 1-Benzyl-3-butylimidazolium bromide |
| [HeOHMIM][Cl] | 1-(6-Hydroxyethyl)-3-methylimidazolium chloride |
| [BeEOHIM][Br] | 1-Benzyl-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)imidazolium bromide |
| [AMIM][MeSO4] | 1-Allyl-3-methylimidazolium methylsulfate |
| [C4mim][Br] | 1-Octyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide |
| [C4mim][TsO] | 1-Octyl-3-methylimidazolium p-methylbenzene sulfonate |
References
- Hernández, F.; Portolés, T.; Ibáñez, M.; Bustos-López, M.C.; Díaz, R.; Botero-Coy, A.M.; Fuentes, C.L.; Peñuelad, G. Use of time-of-flight mass spectrometry for large screening of organic pollutants in surface waters and soils from a rice production area in Colombia. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 439, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matějíček, D.; Kubáň, V. Enhancing sensitivity of liquid chromatographic/ion-trap tandem mass spectrometric determination of estrogens by on-line pre-column derivatization. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1192, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodré, F.F.; Pescara, I.C.; Montagner, C.C.; Jardim, W.F. Assessing selected estrogens and xenoestrogens in Brazilian surface waters by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2010, 96, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, L.; Zeng, B.; Zhao, F. Ionic liquid polymer functionalized carbon nanotubes-doped poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) for highly-efficient solid-phase microextraction of carbamate pesticides. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1444, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ji, S.; Wu, Q.; Wu, C.; Wang, Z. Determination of triazine herbicides in environmental samples by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2011, 49, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhao, G.; Song, S.; Wang, C.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z. Determination of triazine herbicides in environmental water samples by high-performance liquid chromatography using graphene-coated magnetic nanoparticles as adsorbent. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 708, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, H.; Lord, H.L.; Pawliszyn, J. Applications of solid-phase microextraction in food analysis. J. R. Soc. Chem. 2000, 880, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardencki, W.; Michulec, M.; Curyo, J. A review of theoretical and practical aspects of solid-phase microextraction in food analysis. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 39, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuela, G.; Souza-Silva, E.A.; Ho, T.D.; Anderson, J.L.; Janusz, P. Exploiting the tunable selectivity features of polymeric ionic liquid-based SPME sorbents in food analysis. Talanta 2018, 188, 522–530. [Google Scholar]
- Souza-Silva, E.A.; Emanuela, G.; Pawliszyn, J. A critical review of the state of the art of solid-phase microextraction of complex matrices II. Food analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 71, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Absalan, G.; Akhond, M.; Sheikhian, L. Extraction and high performance liquid chromatographic determination of 3-indole butyric acid in pea plants by using imidazolium-based ionic liquids as extractant. Talanta 2009, 77, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, M.; Chao, S.; El-Sepai, F.; Wang, K.; Yan, Z.; Ye, M. Ionic liquids extraction of para red and sudan dyes from chilli powder, chilli oil and food additive combined with high performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 650, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulugeta, M.; Wibetoe, G.; Engelsen, C.J.; Lund, W. Speciation analysis of As, Sb and Se in leachates of cementitious construction materials using selective solid phase extraction and ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2010, 25, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Xia, X.; Wang, D. Ammonium pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate-modified activated carbon micro-column extraction for the determination of As(iii) in water by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchim. Acta 2008, 161, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uluozlu, O.D.; Tuzen, M.; Mendil, D.; Soylak, M. Determination of As(III) and As(V) species in some natural water and food samples by solid-phase extraction on Streptococcus pyogenes immobilized on Sepabeads SP 70 and hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadfarnia, S.; Shabani, A. Recent development in liquid phase microextraction for determination of trace level concentration of metals-a review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 658, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, H.K.; Rasmussen, K.E.; Pedersen-Bjergaard, S. Environmental and bioanalytical applications of hollow fiber membrane liquid-phase microextraction, a review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 624, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, E.M.; Berton, P.; Monasterio, R.P.; Wuilloud, R.G. Emerging ionic liquid-based techniques for total-metal and metal-speciation analysis. Trac. Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Verma, K.K. Recent advances in applications of single-drop microextraction, a review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 706, 37–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jisi, Z.; Bo, L.; Jing, P.; Bing, C.; Hongjing, W.; Baiyu, Z. Vortex- and shaker-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction (VSA-LLME) coupled with gas chromatography and mass spectrome-try (GC-MS) for analysis of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in offshore produced water. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 318. [Google Scholar]
- Martinis, E.M.; Berton, P.; Wuilloud, R.G. Ionic liquid-based microextrac-tion techniques for trace-element analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 60, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaallah, R.; Massoud, K.; Elham, G.; Mohadeseh, T. Application of in-syringe dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and narrow-bore tube dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of trace amounts of BTEX in water samples. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2015, 7, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, C.; Ping, D.L.; Guo, M.J.; Yang, F.W.; Cheng, L.Z. Liquid-liquid equilibria of multi-component systems including n-hexane, n-octane, benzene, toluene, xylene and sulfolane at 298.15 K and atmospheric pressure. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2000, 173, 109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Ensafi, A.A.; Izadi, M.; Karimi-Maleh, H. Sensitive voltammetric determination of diclofenac using room-temperature ionic liquid-modified carbon nanotubes paste electrode. Ionics 2013, 19, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, R.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Bahari, A.; Taghavi, M. A novel biosensor based on ZnO nanoparticle/1,3-dipropylimidazolium bromide ionic liquid-modified carbon paste electrode for square-wave voltammetric determination of epinephrine. Phys. Chem. Liq. 2013, 51, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-Rodríguez, M.J.; Nan, H.; Varona, M.; Emaus, M.N.; Souza, I.D.; Anderson, J.L. Advances of ionic liquids in analytical chemistry. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 505–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Calero, A.; Pino, V.; Afonso, A.M. Ionic liquids as a tool for determination of metals and organic compounds in food analysis. Trac. Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 1598–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, M.; Shemirani, F. Cold-induced aggregation microextraction, a novel sample preparation technique based on ionic liquids. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 613, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.D.; Cheng, Z.; Hantao, L.W.; Anderson, J.L. Ionic liquids in analytical chemistry, fundamentals, advances, and perspectives. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 262–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Anderson, J.L. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction using an in situ metathesis reaction to form an ionic liquid extraction phase for the preconcentration of aromatic compounds from water. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Bai, H.; Xie, G.; Xiao, J. Trace determination of organophosphorus pesticides in environmental samples by temperature-controlled ionic liquid dispersive liquid-phase microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1188, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Cagliero, C.; Pierson, S.A.; Anderson, J.L. Rapid and sensitive analysis of polychlorinated biphenyls and acrylamide in food samples using ionic liquid-based in situ dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled to headspace gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1481, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buldini, P.L.; Ricci, L.; Sharma, J.L. Recent applications of sample preparation techniques in food analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 975, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulra’uf, L.B.; Lawal, A.; Sirhan, A.Y.; Tan, G.H. Review of ionic liquids in microextraction analysis of pesticide residues in fruit and vegetable samples. Chromatographia 2020, 83, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merone, G.M.; Tartaglia, A.; Rosato, E.; D’Ovidio, C.; Locatelli, M. Ionic liquids in analytical chemistry: Applications and Recent Trends. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2021, 17, 1340–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rykowska, I.; Ziemblińska, J.; Nowak, I. Modern approaches in dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) based on ionic liquids, a review. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 259, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, S.; Dinari, M. Ionic liquids as green solvents: Progress and prospects. In Green Solvents II: Properties and Applications of Ionic Liquids; Mohammad, A., Inamuddin, D., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Isosaari, P.; Srivastava, V.; Sillanpaa, M. Ionic liquid-based water treatment technologies for organic pollutants, Current status and future prospects of ionic liquid mediated technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 604–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-Rodríguez, M.J.; Pino, V.; Miró, M. High-throughput microscale extraction using ionic liquids and derivatives, A review. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 1890–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Wang, Y.; Kong, J.; Chan, N.; Yuan, Y. Ionic liquid-based microwave-assisted extraction of rutin from chinese medicinal plants. Talanta 2010, 83, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meindersma, G.W.; de Haan, A.B. (2008). Conceptual Process Design for Aromatic/Aliphatic Separation with Ionic Liquids. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2008, 86, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meindersma, G.W.; Podt, A.; de Haan, A.B. Selection of ionic liquids for the extraction of aromatic hydrocarbons from aromatic/aliphatic mixtures. Fuel Process.Technol. 2005, 87, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meindersma, G.W.; Podt, A.; de Haan, A.B. Ternary liquid-liquid equilibria for mixtures of toluene plus n-heptane plus an ionic liquid. Fluid Phase Equilibr. 2006, 247, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meindersma, G.W.; Podt, A.; Klaren, M.B.; De Haan, A.B. Separation of aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons with ionic liquids. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2006, 193, 1384–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewicz, M.; Piszora, M.; Caicedo, N.; Jungnickel, C.; Stolte, S. Toxicity of ionic liquid cations and anions towards activated sewage sludge organisms from different sources–consequences for biodegradation testing and wastewater treatment plant operation. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2921–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, L.A.; Brennecke, J.F. Recovery of organic products from ionic liquids using supercritical carbon dioxide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, L.A.; Hancu, D.; Beckman, E.J.; Brennecke, J.F. Green processing using ionic liquids and CO2. Nature 1999, 399, 28–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Mallik, A.K.; Takafuji, M.; Ihara, H.; Qiu, H. Versatile ligands for high-performance liquid chromatography: An overview of ionic liquid-functionalized stationary phases. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 887, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.D.; You, L.B.; Ping, L.S.; Yuan, X.Z.; Chu, S.Y. A novel and eco-friendly method for the preparation of ionic liquids. Synth. Stuttg. 2003, 17, 2626–2628. [Google Scholar]
- Estager, J.; Lévêque, J.M.; Cravotto, G.; Boffa, L.; Bonrath, W.; Draye, M. One-pot and solventless synthesis of ionic liquids under ultrasonic irradiation. Synlett 2007, 13, 2065–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Dong, B.; Feng, X.; Yao, S. Recovery of benzothiazolium ionic liquids from the coexisting glucose by ion-exchange resins. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 227, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Rui, W.; Yan, C.; Huiquan, L.; Jinshu, W. Recycling and reuse of ionic liquid in homogeneous cellulose acetylation. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 21, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröckel, J.; Kragl, U. Nanofiltration for the separation of nonvolatile products from solutions containing ionic liquids. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2003, 26, 1166–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, B.; Balke, B.; Felser, C.; Mudring, A.V. Dysprosium room-temperature ionic liquids with strong luminescence and response to magnetic fields. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 7635–7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Liu, X.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Multiscale studies on ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6636–6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollóczki, O.; Malberg, F.; Welton, T.; Kirchner, B. On the origin of ionicity in ionic liquids. Ion pairing versus charge transfer. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 16880–16890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihata, K.; Tsunashima, K.; Matsumiya, M. Physicochemical and electrochemical properties of room-temperature ionic liquids based on quaternary phosphonium cations and tetracyanoborate anion. ECS Trans. 2016, 72, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokosa, J.M. Recent trends in using sing-drop microextraction and related techniques in green analytical methods. Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 71, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Qi, T.; Ansah, P.D.; Fouemina, J.N.; Shen, W.; Basheer, C.; Lee, H.K. Single-drop microextraction. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 108, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, S.; Wang, P.; Yang, Y. Method development for the analysis of phthalate esters in tea beverages by ionic liquid hollow fibre liquid-phase microextraction and liquid chromatographic detection. Food Control. 2016, 67, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunay, N.; Elik, A.; Gürkan, R. Vortex assisted-ionic liquid based dispersive liquid liquid microextraction of low levels of nickel and cobalt in chocolate-based samples and their determination by FAAS. Microchem. J. 2019, 147, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.Y.; Lin, S.L.; Fuh, M.R. Determination of phenylurea herbicides in aqueous samples using partitioned dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Talanta 2009, 80, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Ba, I.X.; Xu, J. Simultaneous determination of simazine, cyanazine, and atrazine in honey samples by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 3882–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahya, P.; Meghdad, P.; Reza, A.; Toraj, A.J.; Nazir, F.; Kiomar, S.; Reza, G.H. Assessment of triazine herbicides residual in fruit and vegetables using Ultrasound assisted extraction-dispersive liquid-Liquid microextraction with solidification of floating organic drop. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2017, 28, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaee, M.; Assadi, Y.; Hosseini, M.; Aghaee, E.; Ahmadi, F.; Berijani, S. Determination of organic compounds in water using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1116, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaee, M.; Yamini, Y.; Faraji, M. Evolution of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction method. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2342–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgoła-Grzeskowiak, A.; Grzeskowiak, T. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 1382–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chormey, D.S.; Bakrdere, S. Principles and recent advancements in microextraction techniques. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2018, 81, 257–294. [Google Scholar]
- Farajzadeh, M.A.; Khoshmaram, L.; Sheykhizadeh, S. A Review on application of microextraction techniques for analysis of chemical compounds and metal ions in foodstuffs. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. Res. 2014, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Y. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction followed by magnetic solid-phase extraction for determination of four parabens in beverage samples by ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Li, N.; Cao, X. Determination of chlorophenols in honey samples using in-situ ionic liquid-dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction as a pretreatment method followed by high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 2015, 174, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, S.V.; Lyskovtseva, K.A.; Pletnev, I.V. Extraction and determination of synthetic food dyes using tetraalkylammonium based liquid-liquid extraction-ScienceDirect. Microchem. J. 2020, 162, 105833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, H.; Bing, P.; Li, S.; Zhou, Z. Comparison of the performance of conventional, temperature-controlled, and ultrasound-assisted ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography in analyzing pyrethroid pesticides in honey samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 6621–6629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiong, J.; Baker, G.A.; Jiji, R.D.; Baker, S.N. Developing microwave-assisted ionic liquid microextraction for the detection and tracking of hydrophobic pesticides in complex environmental matrices. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 17113–17119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Min, L.; Yang, M.; Peng, B.; Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Gao, H.; Lu, R. Magnetic retrieval of ionic liquids, fast dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the determination of benzoylurea insecticides in environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1254, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajzadeh, M.A.; Bamorowat, M.; Mogaddam, M.A. Ionic liquid-based air-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction for the extraction and preconcentration of aryloxyphenoxypropionate herbicides from aqueous and vegetable samples followed by HPLC-DAD. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.W.; Chen, X.C.; Liu, F.M.; Hou, F.; Li, Y.Q. Ionic liquid-based air-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction followed by high performance liquid chromatography for the determination of five fungicides in juice samples. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gure, A.; Lara, F.J.; Garcia-Campana, A.M.; Megersa, N.; del Olmo-Iruela, M. Vortex-assisted ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the determination of sulfonylurea herbicides in wine samples by capillary high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 2015, 170, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubomirsky, E.; Padró, J.M.; Reta, M.R. Development of a dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction technique for the analysis of aryloxyphenoxy-propionate herbicides in soy-based foods. Microchem. J. 2016, 129, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, X.; Jin, R.; Zhang, H.; Song, D. Magnetic ionic liquid–based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the determination of triazine herbicides in vegetable oils by liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1373, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ying, S.; Bo, X.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Song, D. Matrix solid-phase dispersion coupled with magnetic ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of triazine herbicides in oilseeds. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 888, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, P.; Cao, L.; Xu, G.; Yang, S.; Fang, Y.; Wang, G.; Hong, X. Selenium speciation in rice samples by magnetic ionic liquid-based up-and-down-shaker-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled to graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, M.; Tan, C.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, H. Development and optimization of a thiol imidazolium-based ionic liquid for ultrasonic assisted liquid-liquid microextraction combined with HPLC-FLD for determination of bisphenols in milk and juice samples. LWT 2019, 111, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, S.; Dan, L.; Wu, L.; Jing, H.; Lian, W.; Wang, K.; Yang, H. Determination of triazine herbicides in juice samples by microwave-assisted ionic liquid/ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 2950–2958. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Du, K. Simultaneous determination of sulfonamides in milk, in-situ magnetic ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with HPLC. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ran, L.; Xu, M.; Ren, D.; Yi, L. In situ ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with ultra high performance liquid chromatography for determination of neonicotinoid insecticides in honey samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 1930–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhami, K.; Asadollahzadeh, H.; Ghazizadeh, M. Preconcentration and determination of nickel (II) and copper (II) ions, in vegetable oils by [TBP][PO4] IL-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction technique, and flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 89, 103457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bani, S.M.; Saaid, M.; Saad, B. An in situ dansylation ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on ionic liquid for determination of biogenic amines in foods. Food Anal. Methods 2020, 13, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tan, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wen, Y.; Fan, S.; Liu, C. Determination of pyrethroid residues in herbal tea using temperature-controlled ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction by high performance liquid chromatography. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Z.; Jin, S.; Gao, L.; He, L.; Jiang, X. A simple one-step transferred sample preparation for effective purification and extraction of auramine o in bean product by combining air-assisted ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, J.; Feng, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H. In-syringe temperature-controlled liquid–liquid microextraction based on solidifed floating ionic liquid for the simultaneous determination of triazine and phenylurea pesticide in vegetable protein drinks. J. Chromatogr. B 2021, 1174, 122721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, B.R.; Hantao, L.W.; Ho, T.D.; Augusto, F.; Anderson, J.L. A chemometric approach toward the detection and quantification of coffee adulteration by solidphase microextraction using polymeric ionic liquid sorbent coatings. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1346, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, Z.; Xue, S.; Zhang, L. Novel functionalized magnetic ionic liquid green separation technology coupled with high performance liquid chromatography, a rapid approach for determination of estrogens in milk and cosmetics. Talanta 2020, 209, 120542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, S.; Nasehi, Z. Simultaneous determination of brilliant green and crystal violet dyes in fish and water samples with dispersive liquid-liquid micro-extraction using ionic liquid followed by zero crossing first derivative spectrophotometric analysis method. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 201, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentini, E.F.; Oviedo, M.N.; Wuilloud, R.G. Ultra-trace cr preconcentration in honey samples by magnetic ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry-ScienceDirect. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2020, 169, 105879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Ji, Q.; Hu, Z. Detection of organophosphorus pesticides in wheat by ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with HPLC. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ravelo-Pérez, L.M.; Hernández-Borges, J.; Asensio-Ramos, M.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.Á. Ionic liquid based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the extraction of pesticides from bananas. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 7336–7345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; You, J.; Ren, R.; Yao, X.; Gao, S.; Zhang, H.; Yu, A. Determination of triazines in honey by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 4241–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokosa, J.M. Selecting an extraction solvent for a greener liquid phase microextraction (LPME) mode-based analytical method. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoś, P.; Przyjazny, A.; Boczkaj, G. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents as “green” extraction media for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aqueous samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1570, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Xiao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H. Ultrasound-assisted ionic liquid/ionic liquid-dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of sulfonamides in infant formula milk powder using high-performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 2012, 99, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, F.; Beletskaya, I.P.; Yus, M. Non-conventional methodologies for transition-metal catalysed carbon–carbon coupling, a critical overview. Part 1, the heck reaction. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 11771–11835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, F.; Beletskaya, I.P.; Yus, M. Non-conventional methodologies for transition-metal catalysed carbon–carbon coupling, a critical overview. Part 2, the suzuki reaction. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 3047–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leveque, J.M.; Cravotto, G. Microwaves, power ultrasound, and ionic liquids. a new synergy in green organic synthesis. Chimia 2006, 60, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, M.; Shemirani, F. In situ solvent formation microextraction based on ionic liquids, a novel sample preparation technique for determination of inorganic species in saline solutions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 634, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, H.; Zandi, O.; Aghakhani, A. Magnetic nanoparticle-based micro-solid phase extraction and GC-MS determination of oxadiargyl in aqueous samples. Chromatographia 2011, 74, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, I.P.; Chisvert, A.; Canals, A. Dispersive solid-phase extraction based on oleic acid-coated magnetic nanoparticles followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for UV-filter determination in water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 2467–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Liang, Y.; Dong, H.; Ding, G.; Zhang, W.; Tang, G.; Yang, J.; Kong, D.; Wang, D.; Cao, Y. In-situ ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction using a new anion exchange reagent combined Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for determination of pyrethroid pesticides in water samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 975, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wu, X.; Jia, Y.; Xi, X.; Yang, X.; Lu, R.; Zhang, S.; Gao, H.; Zhou, W. Use of magnetic effervescent tablet-assisted ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction to extract fungicides from environmental waters with the aid of experimental design methodology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 906, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Hamaguchi, H.O. Discovery of a magnetic ionic liquid [BMIM]FeCl4. Chem. Lett. 2004, 33, 1590–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Li, M.; Zhao, L.; Lu, C.; de Rooy, S.L.; Warner, I.M. Highly efficient extraction of phenolic compounds by use of magnetic room temperature ionic liquids for environmental remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.; Albo, J.; Irabien, A. Magnetic ionic liquids, synthesis, properties and applications. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 40008–40018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiraghi, A.; Shokri, M. A novel task specific magnetic polymeric ionic liquid for selective preconcentration of potassium in oil samples using centrifuge-less dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction technique and its determination by flame atomic emission spectroscopy. Talanta 2018, 178, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campillo, N.; Vias, P.; Andrejová, J.; Andruch, V. Ten years of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and derived techniques. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2016, 52, 267–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojko, B.; Reyes-Garces, N.; Bessonneau, V.; Gorynski, K.; Mousavi, F.; Souza-Silva, E.A.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid-phase microextraction in metabolomics. Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 61, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Garces, N.; Emanuela, G.; Gomez-Ríos, G.A.; Alam, M.N.; Boyacl, E.; Bojko, B.; Singh, V.; Grandy, J.; Pawliszyn, J. Advances in solid phase microextraction and perspective on future directions. Anal. Chem. 2017, 90, 302–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, C.Z.; Xia, Z.; Yuan, C.S. Solid-phase microextraction technology for in vitro and in vivo metabolite analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 80, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkle, S.; Kleeberg, K.; Fritsche, J. Recent developments and applications of solid phase microextraction (SPME) in food and environmental analysis—A review. Chromatography 2015, 2, 293–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, C.L.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid phase microextraction with thermal desorption using fused silica optical fibers. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 2145–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zheng, J.; Tian, J.; Zhu, F.; Zeng, F.; Su, C.; Ouyang, G. New materials in solid phase microextraction. Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 47, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. A zeolitic imidazolate framework based nanoporous carbon as a novel fiber coating for solid-phase microextraction of pyrethroid pesticides. Talanta 2017, 166, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Ho, T.D.; Anderson, J.L. Ionic liquid and polymeric ionic liquid coatings in solid phase microextraction. Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 45, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Khaled, N.M.; Rutkowska, M.; Szczepańska, N.; Namieśnik, J.; Płotka-Wasylka, J. Solid phase microextraction, apparatus, sorbent materials, and application. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2018, 49, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagliero, C.; Ho, T.D.; Zhang, C.; Bicchi, C.; Anderson, J.L. Determination of acrylamide in brewed coffee and coffee powder using polymeric ionic liquid-based sorbent coatings in solid-phase microextraction coupled to gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1449, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crucello, J.; Miron, L.F.O.; Ferreira, V.H.C.; Nan, H.; Marques, M.O.M.; Ritschel, P.S.; Zanus, M.C.; Anderson, J.L.; Poppi, R.J.; Hantao, L.W. Characterization of the aroma profile of novel Brazilian wines by solid-phase microextraction using polymeric ionic liquid sorbent coatings. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4749–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.D.; Ho, T.D.; Cole, W.; Anderson, J.L. Determination of polychlorinated biphenyls in ocean water and bovine milk using crosslinked polymeric ionic liquid sorbent coatings by solid-phase microextraction. Talanta 2014, 118, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-Rodríguez, M.J.; Yu, H.; Cole, W.T.S.; Ho, T.D.; Pino, V.; Anderson, J.L.; Afonso, A.M. Polymeric ionic liquid coatings versus commercial solid-phase microextraction coatings for the determination of volatile compounds in cheeses. Talanta 2014, 121, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Meng, Y.; Anderson, J.L. Polymeric ionic liquids as selective coatings for the extraction of esters using solid-phase microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1208, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.; Oliaei, S. Microextraction of sulfathiazole from milk and honey samples using a polymeric ionic liquid membrane followed by fluorometric determination. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 97, 103774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Fernández, I.; Trujillo-Rodríguez, M.J.; Kuroda, K.; Holen, A.L.; Jensen, M.B.; Anderson, J.L. Zwitterionic polymeric ionic liquid-based sorbent coatings in solid phase microextraction for the determination of short chain free fatty acids. Talanta 2019, 200, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, T.; Luo, C.; Sun, M. Basalt fibers grafted with a poly(ionic liquids) coating for in-tube solid-phase microextraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 3267–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.D.; Cole, W.T.S.; Augusto, F.; Anderson, J.L. Insight into the extraction mechanism of polymeric ionic liquid sorbent coatings in solid-phase microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1298, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-Rodríguez, M.J.; Anderson, J. Silver-based polymeric ionic liquid sorbent coatings for solid-phase microextraction, Materials for the selective extraction of unsaturated compounds. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1047, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.D.; Emaus, M.N.; Varona, M.; Bowers, A.N.; Anderson, J.L. Ionic liquids, solvents and sorbents in sample preparation. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 209–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavir, K.; Konieczna, K.; Marcinkowski, U.; Kloskowski, A. Ionic liquids in the microextraction techniques, the influence of ILs structure and properties. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 130, 115994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Sun, M.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Duan, H.; Luo, C. Multiwalled carbon nanotubes-doped polymeric ionic liquids coating for multiple headspace solid-phase microextraction. Talanta 2014, 123, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Hernández, A.A.; Álvarez-Romero, G.A.; Contreras-López, E.; Aguilar-Arteaga, K.; Castañeda-Ovando, A. Food analysis by microextraction methods based on the use of magnetic nanoparticles as supports: Recent advances. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 2974–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.A.; Flores-Aguilar, J.F.; Santos, E.M.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Ibarra, I.S. New poly(ionic liquid) based fiber for determination of oxytetracycline in milk samples by application of SPME-CE technique. Molecules 2019, 24, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rynkowska, E.; Fatyeyeva, K.; Kujawski, W. Application of polymer-based membranes containing ionic liquids in membrane separation processes, a critical review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 341–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Shi, Y.; Chen, J. Carbon nanotubes-reinforced hollow fibre solid-phase microextraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography for the determination of carbamate pesticides in apples. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Feng, J.; Wang, X.; Luo, C.; Sun, M. Ionic liquid functionalized silica aerogel as coating for solid-phase microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1583, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, L.; Yang, P.; Pang, R.; Lu, X.; Xiao, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J. Ionogel-based ionic liquid coating for solid-phase microextraction of organophosphorus pesticides from wine and juice samples. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jon, C.S.; Meng, L.Y.; Li, D. Recent review on carbon nanomaterials functionalized with ionic liquids in sample pretreatment application. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 120, 115641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Wu, M.; Li, L.; Zhao, F.; Zeng, B. Highly selective and effective solid phase microextraction of benzoic acid esters using ionic liquid functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes-doped polyaniline coating. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1437, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wu, M.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zeng, B. Doping of three-dimensional porous carbon nanotube-graphene-ionic liquid composite into polyaniline for the headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography determination of alcohols. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 948, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Chen, G.; Liu, P.; Zhou, W.; Jia, Q. Preparation of porous aromatic framework/ionic liquid hybrid composite coated solid-phase microextraction fibers and their application in the determination of organochlorine pesticides combined with GC-ECD detection. Analyst 2016, 141, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Sun, M.; Bu, Y.; Luo, C. Facile modification of multi-walled carbon nanotubesepolymeric ionic liquids-coated solid-phase microextraction fibers by on-fiber anion exchange. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1393, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano, D.F.; Casanova, H.; Cardona, W.I.; Giraldo, L.F. Functionalization of montmorillonite with ionic liquids based on 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium, effect of anion and length chain. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 198, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelit, F.O.; Pelit, L.; Dizdas, T.N.; Aftata, C.; Ertas, H.; Yalcinkaya, E.E.; Turkmen, H.; Ertas, F.N. A novel polythiophene-ionic liquid modified clay composite solid phase microextraction fiber, Preparation, characterization and application to pesticide analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 859, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Xing, X.; Xia, B.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Z. Study on the adsorption behaviour between an imidazolium ionic liquid and Na-Montmorillonite. Molecules 2019, 24, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakkori, P.; Tagaç, A.A.; Merdivan, M. Fabrication of montmorillonite/ionic liquid composite coated solid-phase microextraction fibers for determination of phenolic compounds in fruit juices by gas chromatography and liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1635, 461741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocío-Bautista, P.; Pino, V.; Ayala, J.H.; Pasán, J.; Ruiz-Pérez, C.; Afonso, A.M. A magnetic-based dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction method using the metal-organic framework HKUST-1 and ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection for determining polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in waters and fruit tea infusions. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1436, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Nasrollahpour, A.; Moradi, S.E.; Baniamerian, M.J. Vortex-assisted dispersive solid-phase microextraction using ionic liquid-modified metal-organic frameworks of PAHs from environmental water, vegetable, and fruit juice samples. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 2815–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speltini, A.; Scalabrini, A.; Maraschi, F.; Sturini, M.; Profumo, A. Newest applications of molecularly imprinted polymers for extraction of contaminants from environmental and food matrices: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 974, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, S.; Moore, L., Jr.; Lejeune, J.; Hasan, F.; Carlisle, T.K.; Bara, J.E.; Gin, D.L.; LaFrate, A.L.; Noble, R.D.; Spivak, D.A.; et al. Ionic liquid crosslinkers for chiral imprinted nanogumbos. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 463, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhirvel, P.; Azenha, M.; Shinde, S.; Schillinger, E.; Silva, A.F. Imidazolium-based functional monomers for the imprinting of the anti-inflammatory drug naproxen, comparison of acrylic and sol-gel approaches. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1314, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, X. Preparation and application of a poly (ionic liquid)-based molecularly imprinted polymer for multiple monolithic fiber solid-phase microextraction of phenolic acids in fruit juice and beer samples. Analyst 2017, 142, 4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzimitakos, T.G.; Anderson, J.L.; Stalikas, C.D. Matrix solid-phase dispersion based on magnetic ionic liquids, an alternative sample preparation approach for the extraction of pesticides from vegetables. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1581, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Liu, H.T.; Wang, X.; Xu, W.Z.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Wang, H.; Pang, L.Y.; Lin, C.W. Ultrasound-assisted surfactant-enhanced emulsification microextraction using a magnetic ionic liquid coupled with micro-solid phase extraction for the determination of cadmium and lead in edible vegetable oils. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, Y.H.; Zain, N.N.M.; Mohamad, S.; Osman, H.; Raoov, M. Magnetic poly(β-cyclodextrin-ionic liquid) nanocomposites for micro-solid phase extraction of selected polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rice samples prior to GC-FID analysis. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yang, X.; Wu, X.; Xi, X.; Gao, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, W.; Lu, R. A dispersive magnetic solid phase microextraction based on ionic liquid-coated and cyclodextrin-functionalized magnetic core dendrimer nanocomposites for the determination of pyrethroids in juice samples. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Gao, X.; Song, J.; Zhao, L. A novel dispersive magnetic solid phase microextraction using ionic liquid-coated amino silanized magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite for high efficient separation/preconcentration of toxic ions from shellfish samples. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 130023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontanals, N.; Borrull, F.; Marcé, R.M. Ionic liquids in solid-phase extraction. Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 41, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, X. Ionic liquid coated magnetic core/shell Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles for the separation/analysis of linuron in food samples. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 137, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, H.; Liu, Z.; Gao, N.; Du, L.; Fu, Y. Ionic liquid-magnetic nanoparticle microextraction of safranin T in food samples. Food Anal. Methods 2015, 8, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdinia, A.; Shegefti, S.; Shemirani, F. A novel nanomagnetic task specific ionic liquid as a selective sorbent for the trace determination of cadmium in water and fruit samples. Talanta 2015, 144, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramandi, N.F.; Shemirani, F. Selective ionic liquid ferrofluid based dispersive-solid phase extraction for simultaneous preconcentration/separation of lead and cadmium in milk and biological samples. Talanta 2015, 131, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soylak, M.; Yilmaz, E. Determination of cadmium in fruit and vegetables by ionic liquid magnetic microextraction and flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal. Lett. 2015, 48, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amde, M.; Temsgen, A.; Dechassa, N. Ionic liquid functionalized zinc oxide nanorods for solid-phase microextraction of aflatoxins in food products. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 91, 103528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Merib, J.; Anderson, J.L. Crosslinked polymeric ionic liquids as solid-phase microextraction sorbent coatings for high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1438, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).