Simulation of CO2 Capture Process in Flue Gas from Oxy-Fuel Combustion Plant and Effects of Properties of Absorbent
Abstract
:1. Introduction
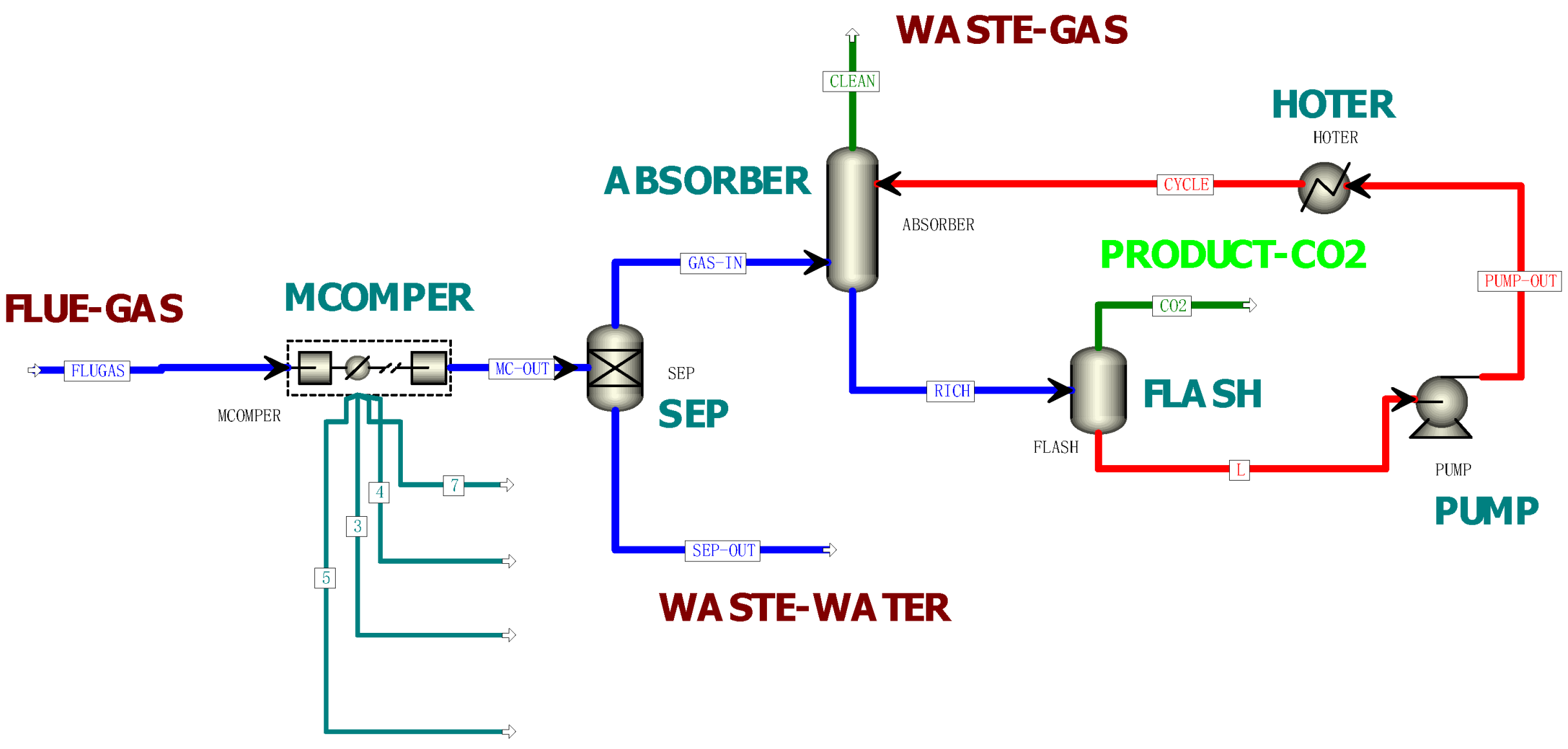
2. Materials and Methods
- A flue gas pretreatment unit:
- 2.
- An absorption unit:
- 3.
- A solvent desorption unit:
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Simulation Results of Aspen Plus
3.2. Compare between Post-Combustion Capture and Oxy-Fuel Combustion Capture
3.3. Effect of Physical Properties of Ionic Liquid on Absorption Process
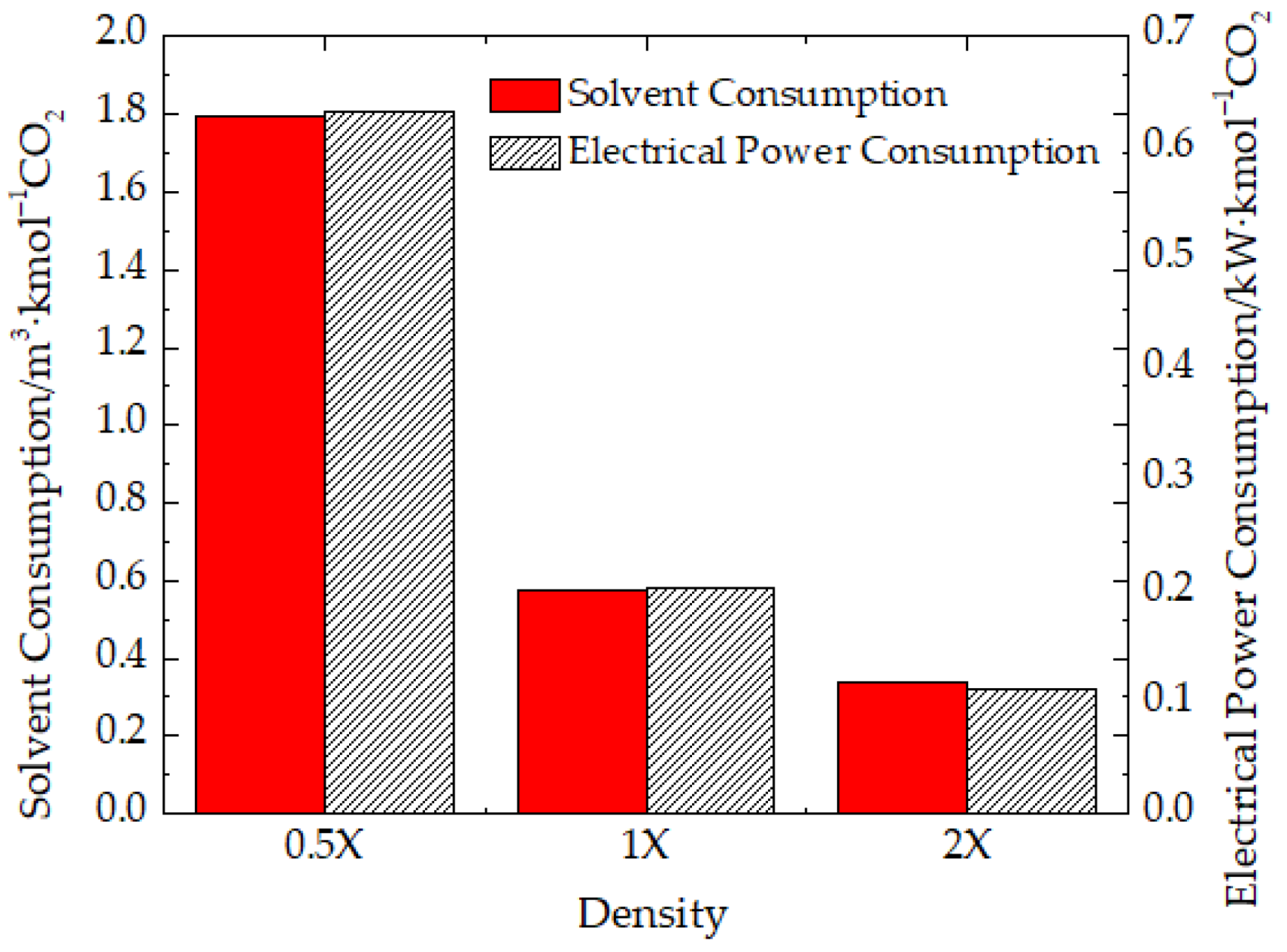
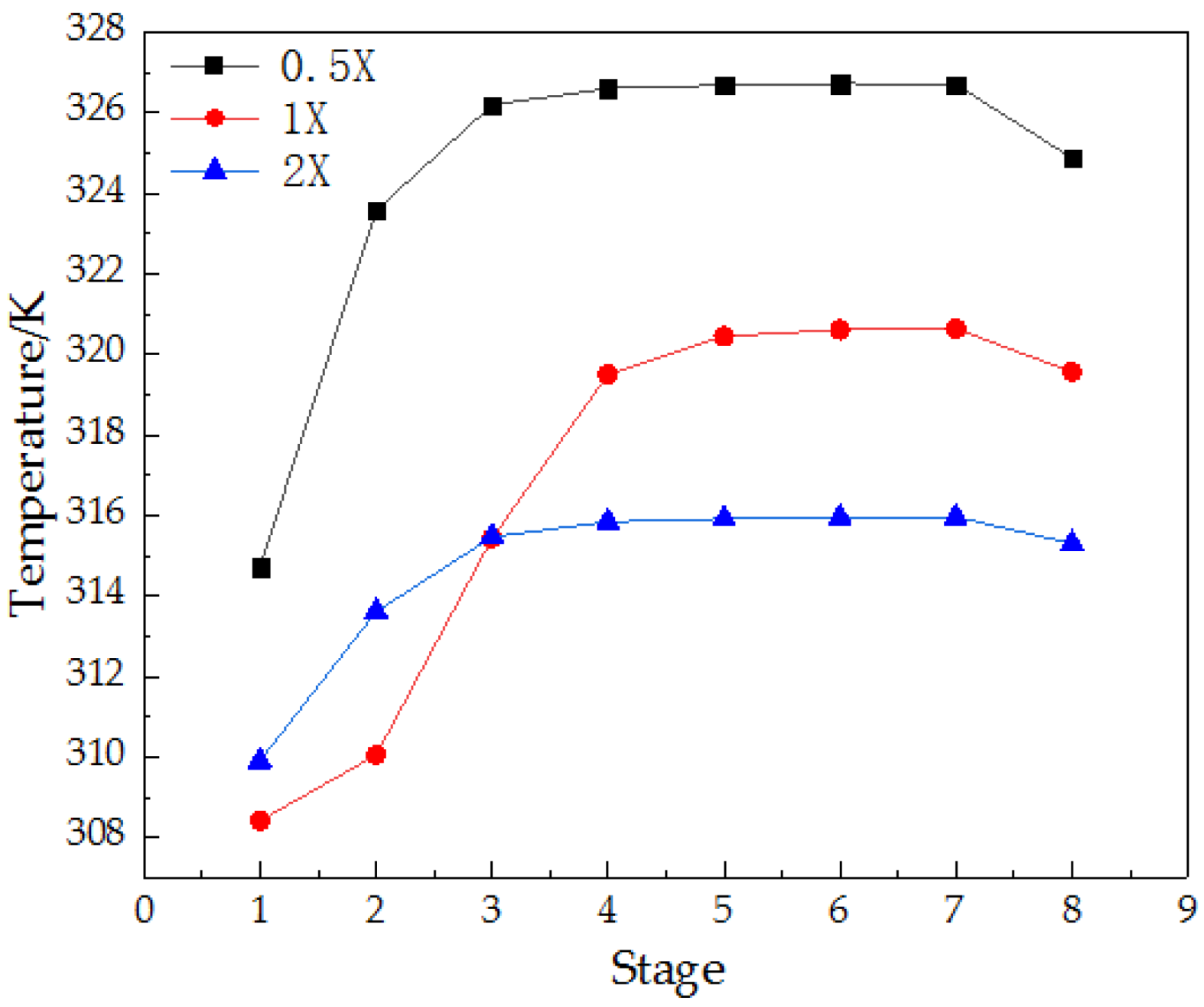
3.3.1. Density
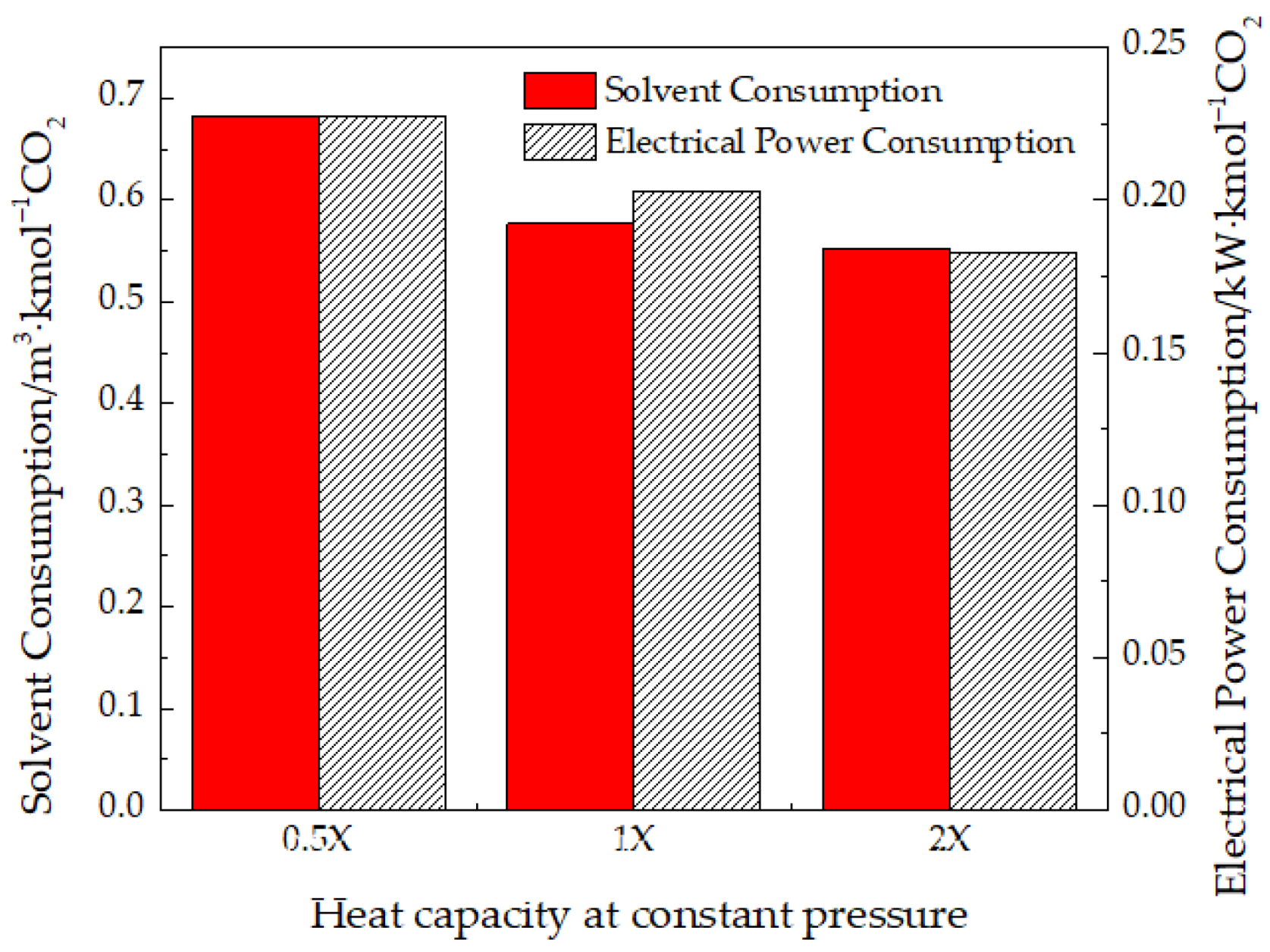
3.3.2. Heat Capacity at Constant Pressure
3.4. Influence of Physical Properties of Ionic Liquid on Heat Exchanger Design
3.4.1. Density
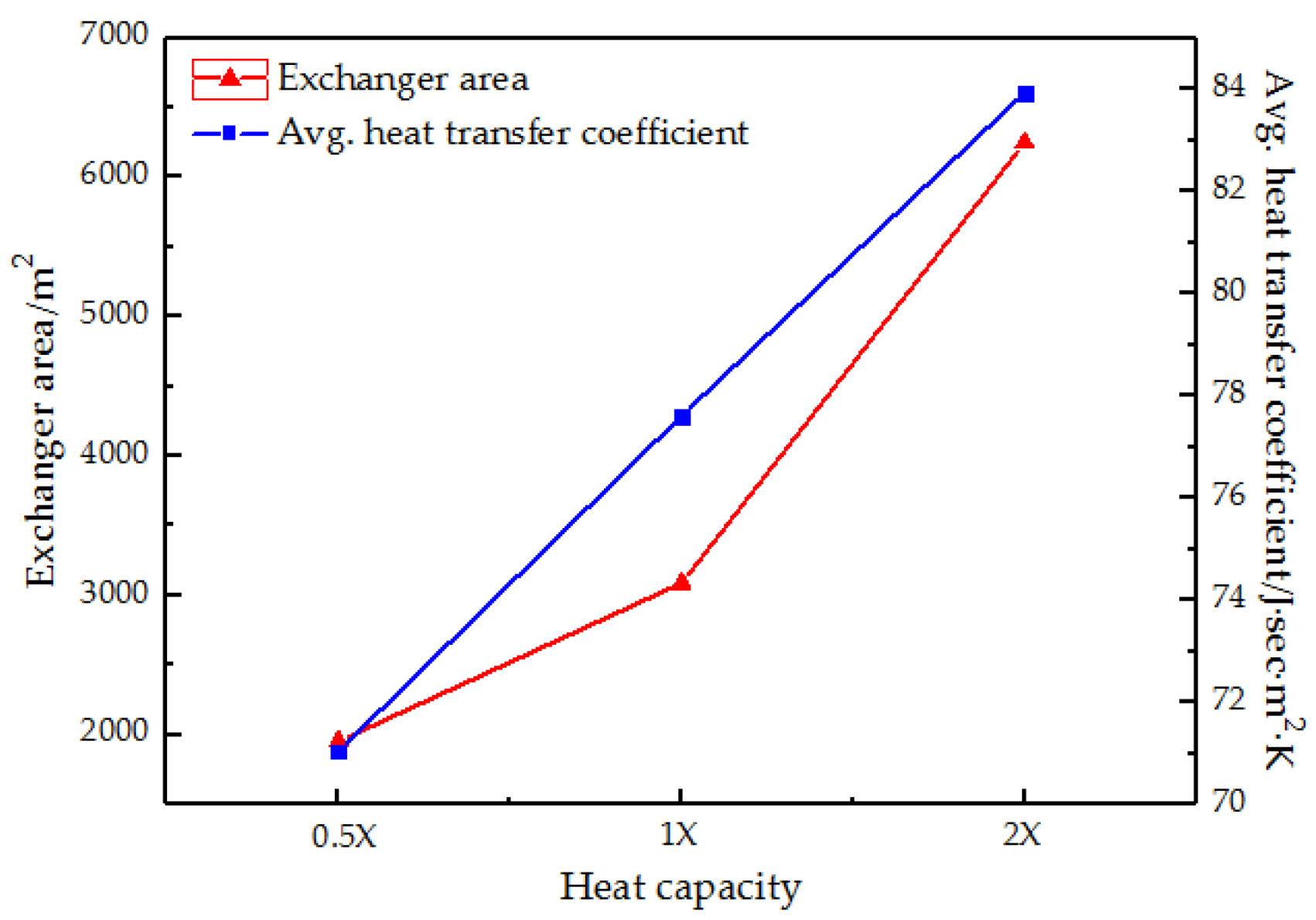
3.4.2. Heat Capacity at Constant Pressure
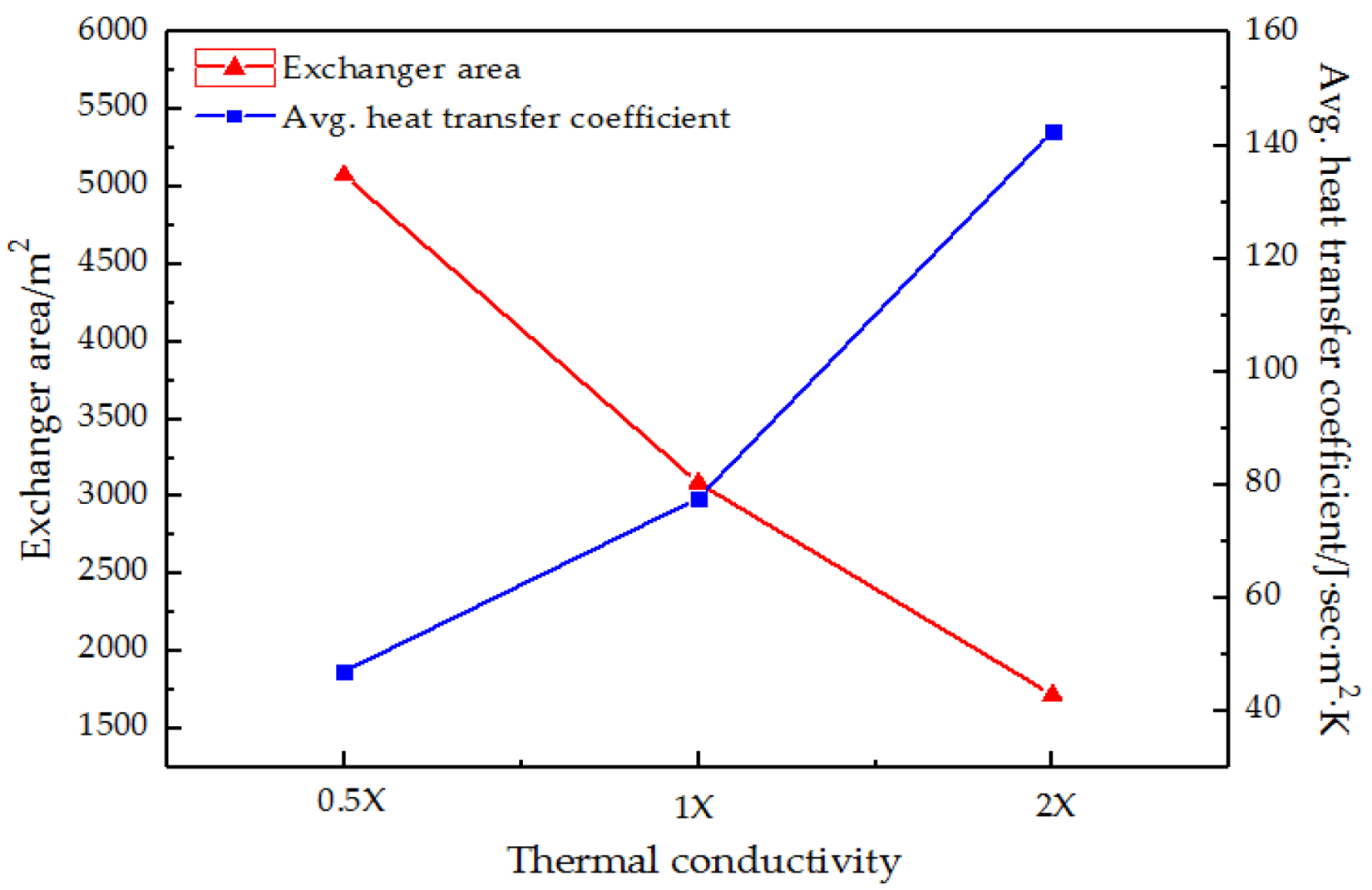
3.4.3. Heat Transfer Coefficient
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wijesiri, R.P.; Knowles, G.P.; Easmin, H.Y. Technoeconomic evaluation of a process capturing CO2 directly from air. Processes 2019, 7, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohamed Mohsin, H.; Mohd Shariff, A.; Johari, K. 3-Dimethylaminopropylamine (DMAPA) mixed with glycine (GLY) as an absorbent for carbon dioxide capture and subsequent utilization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 222, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghussain, L. Global warming: Review on driving forces and mitigation. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2019, 38, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, T.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, S.; Hai, Y.X.; Liao, H.Y. Research and application on carbon capture of coal-fired power plants. Coal Eng. 2017, 49, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, J.H. Study on CO2 Capture Combined with Sulfuric acid Nitric Acid in Biomass Oxyfuel Combustion Flue Gas. Master’s Thesis, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pehnt, M.; Henkel, J. Life cycle assessment of carbon dioxide capture and storage from lignite power plants. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2009, 3, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Otto, A.; Robinius, M.; Stolten, D. A review of post-combustion CO2 capture technologies from coal-fired power plants. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 650–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toftegaard, M.B.; Brix, J.; Jensen, P.A.; Glarborg, P.; Jensen, A.D. Oxy-fuel combustion of solid fuels. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2010, 36, 581–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portillo, E.; Alonso-Farinas, B.; Vega, F.; Cano, M.; Navarrete, B. Alternatives for oxygen-selective membrane systems and their integration into the oxy-fuel combustion process: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 229, 115708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eveloy, V. Hybridization of solid oxide electrolysis-based power-to-methane with oxyfuel combustion and carbon dioxide utilization for energy storage. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 108, 550–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhre, B.J.P.; Elliott, L.K.; Sheng, C.D.; Gupta, R.P.; Wall, T.F. Oxy-fuel combustion technology for coal-fired power generation. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2005, 31, 283–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Pan, S.C.; Ran, S.M. Development and research of 35 MW oxyfuel burning coal powder pot. Dongfang Electr. Rev. 2016, 4, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Châtel-Pélage, F.; Varagani, R.; Pranda, P.; Perrin, N.; Farzan, H.; Vecci, S.J.; Yongqi, L.; Chen, S.; Rostam-Abadi, M.; Bose, A.C. Applications of oxygen for NOx control and CO2 capture in coal-fired power plants. Therm. Sci. 2006, 10, 119–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbassov, Y.; Duan, L.B.; Manovic, V.; Anthony, E.J. Sulfur trioxide formation/emissions in coal-fired air- and oxy-fuel combustion processes: A review. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 402–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemitallah, M.A.; Habib, M.A.; Badr, H.M.; Said, S.A.; Jamal, A.; Ben-Mansour, R.; Mokheimer, E.M.A.; Mezghani, K. Oxy-fuel combustion technology: Current status, applications, and trends. Int. J. Energy Res. 2017, 41, 1670–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditaranto, M.; Hals, J. Combustion instabilities in sudden expansion oxy–fuel flames. Combust. Flame 2006, 146, 493–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, Y.B.; Chen, Y.B. Experimental study on integrated combustion desulfurization and denitrification of oxy-combustion simulated flue gas. Electr. Power 2016, 49, 170. [Google Scholar]
- Herzog, H.; Golomb, D.; Zemba, S. Feasibility, modeling and economics of sequestering power plant CO2 emissions in the deep ocean. Environ. Prog. 1991, 10, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cau, G.; Tola, V.; Ferrara, F.; Porcu, A.; Pettinau, A. CO2-free coal-fired power generation by partial oxy-fuel and post-combustion CO2 capture: Techno-economic analysis. Fuel 2018, 214, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaddix, C.R.; Molina, A. Particle imaging of ignition and devolatilization of pulverized coal during oxy-fuel combustion. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2009, 32, 2091–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.; Rasmussen, C.L.; Giselsson, T.; Glarborg, P. Global combustion mechanisms for use in CFD modeling under oxy-fuel conditions. Energ Fuel 2009, 23, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, K.Q.; Trinh, T.N.; Bach, Q.V. Development of a biomass torrefaction process integrated with oxy-fuel combustion. Bioresour. Technol 2016, 199, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.B.; Chen, M.Q.; Li, Y.; Xue, F. Evaluation on the oxy-fuel combustion behavior of dried sewage sludge. Fuel 2016, 178, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Kim, T.S.; Sohn, J.L.; Lee, Y.D. An integrated power generation system combining solid oxide fuel cell and oxy-fuel combustion for high performance and CO2 capture. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glarborg, P.; Bentzen, L.L.B. Chemical effects of a high CO2 concentration in oxy-fuel combustion of methane. Energ Fuel 2008, 22, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Kumar, P.; Yang, A.; Fennell, P. Energy and exergy analysis of chemical looping combustion technology and comparison with pre-combustion and oxy-fuel combustion technologies for CO2 capture. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2104–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fytianos, G.; Ucar, S.; Grimstvedt, A.; Hyldbakk, A.; Svendsen, H.F.; Knuutila, H.K. Corrosion and degradation in MEA based post-combustion CO2 capture. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2016, 46, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, O.M.; Keller, M.J.; Luebke, D.R.; Resnik, K.P.; Morsi, B.I. Development of a conceptual process for selective CO2 capture from fuel gas streams using [hmim][Tf2N] ionic liquid as a physical solvent. Energ Fuel 2013, 27, 3905–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, A.J.; Pereda, S.; Tavares, F.W. A molecular dynamics study of the solvation of carbon dioxide and other compounds in the ionic liquids [emim][B(CN)4] and [emim][NTf2]. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2019, 491, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, T.; Wang, J.; Du, Z. A process simulation study of CO2 capture by ionic liquids. Int. J. Greenh. Gas. Con. 2017, 58, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayraghavan, R.; Pas, S.J.; Izgorodina, E.I. Diamino protic ionic liquids for CO2 capture. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 19994–19999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaban, V.V.; Andreeva, N.A. Amination of five families of room-temperature ionic liquids: Computational thermodynamics and vibrational spectroscopy. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2016, 61, 1917–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanyi, S. Chemical Process Simulation Training—Aspen Plus Tutorial, 2nd ed.; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Huang, X.; Jiang, Q.; Xia, L.; Wang, J.; Ai, N. New process development and process evaluation for capturing CO2 in flue gas from power plants using ionic liquid [emim][Tf2N]. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 28, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilderman, A.M.; Raeissi, S.; Peters, C.J. Solubility of carbon dioxide in the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis (trifluoromethylsulfonyl) imide. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2007, 260, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, T.; Kanakubo, M.; Masuda, Y.; Umecky, T.; Suzuki, A. CO2 absorption properties, densities, viscosities, and electrical conductivities of ethylimidazolium and 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium ionic liquids. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2014, 362, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Argyle, M.D.; Dellenback, P.A.; Fan, M. Progress in O2 separation for oxy-fuel combustion–A promising way for cost-effective CO2 capture: A review. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2018, 67, 188–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Shah, K.; Song, H.; Zanganeh, J.; Doroodchi, E.; Moghtaderi, B. Integration options and economic analysis of an integrated chemical looping air separation process for oxy-fuel combustion. Energ Fuel 2016, 30, 1741–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Moghtaderi, B.; Wall, T. Effect of flue gas impurities on the performance of a chemical looping based air separation process for oxy-fuel combustion. Fuel 2013, 103, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Chung, Y.G.; Kang, J.H.; Song, H. CO2 absorption characteristics of amino group functionalized imidazolium-based amino acid ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, 111825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Guo, R.F.; Tang, Y.Q.; Zhu, J.M.; Liu, M.Y.; Chen, J.Q.; Xu, Y. Properties of aqueous amine based protic ionic liquids and its application for CO2 quick capture. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 239, 116531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Property | Units | Correlation | Parameters | Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density | g·cm−3 | 0.272 | ||
| Heat Capacity | J·mol−1·K−1 | 329.328 | ||
| 0.849 | ||||
| −0.000768 | ||||
| Viscosity | mPa·s | −138.104 | ||
| 9054.914 | ||||
| 19.524 | ||||
| Vapor Pressure | MPa | 28.375 | ||
| −15130 | ||||
| Thermal Conductivity | W·m−1·K−1 | 0.134 | ||
| −6.13 × 10−5 | ||||
| 4.957 × 10−8 | ||||
| Surface Tension | mN·m−1 | 103.234 | ||
| 15.613 | ||||
| −92.955 | ||||
| 234.092 | ||||
| −204.914 |
| Component i | Component A | aiA | biA | ciA | diA | eiA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | [emim][Tf2N] | 82.149 | 0.00517 | −12.954 | 0.00517 | −874,200 |
| Component i | Component A | aij | aji | bij | bji |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | [emim][Tf2N] | 1.267 | −4.903 | −671.282 | 1685.225 |
| Components | Flue Gas V [%] |
|---|---|
| N2 | 7 |
| CO2 | 80 |
| O2 | 6.5 |
| H2O | 6.5 |
| Description | Unit |
|---|---|
| Absorption tower | |
| Stages | 8 |
| Pressure drop | 0.02 MPa |
| IL-IN feeding position | On stage 1 |
| Feeding position | On stage 8 |
| Flash tank | |
| Heat load | 0 kW |
| Multi-stage compressor unit | |
| Compressor stage | 5 |
| Interstage cooler temperature | 308 K |
| Types | Mcompr(Isentropic) |
| Net work | 101.41 kW·t−1 CO2 |
| Pump | |
| Net work | 4.246 kW·t−1 CO2 |
| Exchanger | |
| Net work | 6.62 kW·t−1 CO2 |
| Post-Combustion Capture | Oxy-Fuel Combustion Capture | |
|---|---|---|
| Load efficiency | 0.36 mol CO2·mol−1 IL | 0.45 mol CO2·mol−1 IL |
| Product purity | 99.9% | 99.9% |
| Lean circulation | 191.1 kmol·h−1·t−1 CO2 | 46.65 kmol·h−1·t−1 CO2 |
| Energy consumption | 604.2 kW·h·t−1 CO2 | 112.276 kW·h·t−1 CO2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Ai, N.; Li, L.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Ren, J.; Wang, J. Simulation of CO2 Capture Process in Flue Gas from Oxy-Fuel Combustion Plant and Effects of Properties of Absorbent. Separations 2022, 9, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9040095
Huang X, Ai N, Li L, Jiang Q, Wang Q, Ren J, Wang J. Simulation of CO2 Capture Process in Flue Gas from Oxy-Fuel Combustion Plant and Effects of Properties of Absorbent. Separations. 2022; 9(4):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9040095
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xiaoting, Ning Ai, Lan Li, Quanda Jiang, Qining Wang, Jie Ren, and Jiawei Wang. 2022. "Simulation of CO2 Capture Process in Flue Gas from Oxy-Fuel Combustion Plant and Effects of Properties of Absorbent" Separations 9, no. 4: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9040095
APA StyleHuang, X., Ai, N., Li, L., Jiang, Q., Wang, Q., Ren, J., & Wang, J. (2022). Simulation of CO2 Capture Process in Flue Gas from Oxy-Fuel Combustion Plant and Effects of Properties of Absorbent. Separations, 9(4), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9040095







