Eco-Friendly and Sensitive HPLC and TLC Methods Validated for the Determination of Betahistine in the Presence of Its Process-Related Impurity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instruments and Software
2.3. Chromatographic Conditions
2.4. Preparation of Stock Solutions and Standards
2.5. Method Validation
2.6. Preparation of Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Method Development and Optimization
3.2. Method Validation
3.3. Pharmaceutical Formulation Application
3.4. Assessment of Analytical Greenness
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharon, J.D.; Trevino, C.; Schubert, M.C.; Carey, J.P. Treatment of Meniere’s disease. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2015, 17, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Carpena, P.; Lopez-Escamez, J.A. Current understanding and clinical management of meniere’s disease: A systematic review. In Proceedings of the Seminars in Neurology; Thieme: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 138–150. [Google Scholar]
- Devantier, L.; Hougaard, D.; Händel, M.N.; Liviu-Adelin Guldfred, F.; Schmidt, J.H.; Djurhuus, B.; Callesen, H.E. Using betahistine in the treatment of patients with Menière’s disease: A meta-analysis with the current randomized-controlled evidence. Acta Otolaryngol. 2020, 140, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basura, G.J.; Adams, M.E.; Monfared, A.; Schwartz, S.R.; Antonelli, P.J.; Burkard, R.; Bush, M.L.; Bykowski, J.; Colandrea, M.; Derebery, J. Clinical practice guideline: Ménière’s disease. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 162, S1–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.E.; Elmaaty, A.A.; El-Sayed, H.M. Determination of six drugs used for treatment of common cold by micellar liquid chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 5051–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciura, K.; Dziomba, S.; Nowakowska, J.; Markuszewski, M.J. Thin layer chromatography in drug discovery process. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1520, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Pharmacopoeia Commission. British Pharmacopoeia 2017; Stationery Office: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- United States Pharmacopoeia. USP 43-NF 38; United States Pharmacopoeia: North Bethesda, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ayad, M.M.; Hosny, M.M.; Elabassy, O.M.; Belal, F. Conductometric determination of Betahistine dihydrochloride and Heptaminol hydrochloride using silver nitrate. Zagazig J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 28, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ganjali, M.R.; Aghili, S.; Larijani, B.; Ghasemi, M.H. Potentiometric determination of betahistine in pharmaceutical formulations by drug selective sensors. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 1893–1903. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, R.; Tiwari, D.; Karolia, P. Highly sensitive and selective polyaniline–zinc oxide nanocomposite sensor for betahistine hydrochloride in solubilized system. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 196, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Yadav, R.K.; Rather, J.A. Voltammetric assay of anti-vertigo drug betahistine hydrochloride in sodium lauryl sulphate. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 366, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensafi, A.A.; Doozandeh, F.; Allafchian, A.R. Potentiometric sensor for betahistine determination in pharmaceuticals, urine and blood serum. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2010, 21, 2246–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavada, V.D.; Bhatt, N.M.; Sanyal, M.; Shrivastav, P.S. Modulation of inner filter effect of non-conjugated silver nanoparticles on blue emitting ZnS quantum dots for the quantitation of betahistine. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 240, 118575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donchenko, A.; Vasyuk, S. Betahistine dihydrochloride quantitative determination in dosage forms by the reaction with sodium 1, 2-napthoquinone-4-sulphonate. Zaporozhye Med. J. 2018, 20, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishvas, P.; Paresh, P. Development and validation of ratio spectra derivative method for the simultaneous estimation of betahistine dihydrochloride and prochlorperazine maleate in tablet dosage form. Int. J. Pharm. Drug Anal. 2014, 2, 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Anis, S.; Hosny, M.; Abdellatef, H.; El-Balkiny, M. Kinetic spectrophotometric determination of betahistine dihydrochloride and etilefrine hydrochloride in pharmaceutical formulation. Pharm. Anal. Acta 2011, 2, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Nanda, S.; Chomwal, R. Spectrophotometric estimation of betahistine hydrochloride in tablet formulations. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2010, 2, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Walily, A.; Razak, O.A.; Belal, S.; Bakry, R. Utilization of carbon disulphide for the analytical determination of betahistine hydrochloride and captopril in their pharmaceutical preparations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1999, 21, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-J.; Zheng, L.-H.; Wang, J.-W. Separation and Determination of Betahistine Hydrochloride by Capillary Electrophoresis with Eelectrochemiluminescence Detection. J. Anal. Sci. 2008, 24, 457–460. [Google Scholar]
- Mistry, V.; Mishra, R. Simultaneous estimation, validation, and forced degradation studies of betahistine dihydrochloride and domperidone in a pharmaceutical dosage form using RP-HPLC method. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2018, 11, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Soni, K.; Bhatt, C.; Singh, K.; Bhuvaneshwari, P.; Jha, A.; Patel, P.; Patel, H.; Srinivas, N.R. An LC–MS/MS assay for the quantitative determination of 2-pyridyl acetic acid, a major metabolite and key surrogate for betahistine, using low-volume human K2EDTA plasma. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2017, 31, e3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Nameh, E.S.; Abu-Shandi, K.; Mohammad, M.; Tayyem, R.; Mohammad, Y. Determination of the major metabolite of betahistine (2-pyridyl acetic acid) in human plasma by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 70, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangrade, D.; Bakshi, S. RP-HPLC Method Development and Validation for Betahistine Hydrochloride Controlled Release Tablets. Int. J. Chem. Pharm. Anal. 2014, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, R.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Xie, L.; Zhang, H.-J. Study on determination of the related substances in betahistine hydrochloride tablets. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2015, 35, 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Khedr, A.; Sheha, M. Stress degradation studies on betahistine and development of a validated stability-indicating assay method. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 869, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guideline. Guideline. ICH guidelines for Validation of analytical procedures: Text and methodology Q2 (R1). In Proceedings of the International Conference on Harmonization, Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; pp. 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Patyra, E.; Kwiatek, K. Analytical capabilities of micellar liquid chromatography and application to residue and contaminant analysis: A review. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 2206–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.E.; Elmansi, H.; Belal, F. Solvent-free mixed micellar mobile phases: An advanced green chemistry approach for reversed-phase HPLC determination of some antihypertensive drugs. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 3224–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.E.; Deeb, S.E.; Abdelhalim, E.M.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Sayed, R.A. Green Stability Indicating Organic Solvent-Free HPLC Determination of Remdesivir in Substances and Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms. Separations 2021, 8, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.; Yang, F.; Duan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y. Quantitative analysis of nine isoflavones in traditional Chinese medicines using mixed micellar liquid chromatography containing sodium dodecylsulfate/β-cyclodextrin supramolecular amphiphiles. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 3188–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attala, K.; Eissa, M.S.; Hasan, M.A.; El-Henawee, M.M.; Abd El-Hay, S.S. An enhanced first derivative synchronous spectrofluorimetric method for determination of the newly co-formulated drugs, amlodipine and celecoxib in pharmaceutical preparation and human plasma. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 240, 118533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmansi, H.; Ibrahim, A.E.; Mikhail, I.E.; Belal, F. Green and sensitive spectrofluorimetric determination of Remdesivir, an FDA approved SARS-CoV-2 candidate antiviral; application in pharmaceutical dosage forms and spiked human plasma. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 2596–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keith, L.H.; Gron, L.U.; Young, J.L. Green analytical methodologies. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2695–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gałuszka, A.; Migaszewski, Z.M.; Konieczka, P.; Namieśnik, J. Analytical Eco-Scale for assessing the greenness of analytical procedures. Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 37, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J. A new tool for the evaluation of the analytical procedure: Green Analytical Procedure Index. Talanta 2018, 181, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Wojnowski, W.; Tobiszewski, M. AGREE—Analytical GREEnness Metric Approach and Software. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10076–10082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
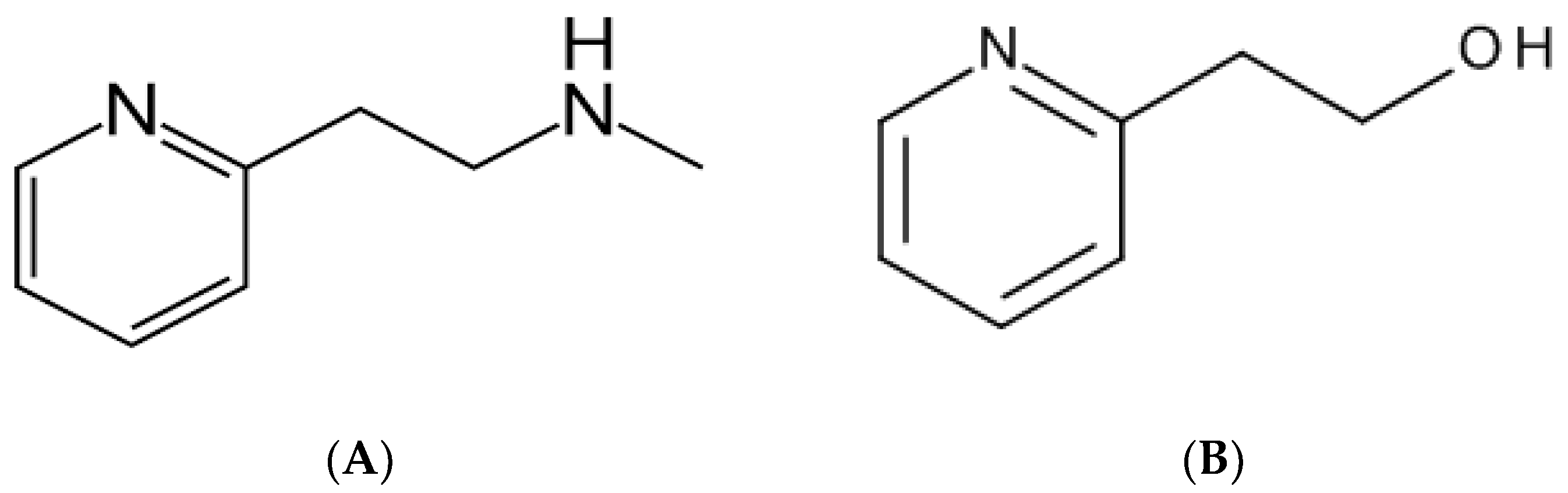

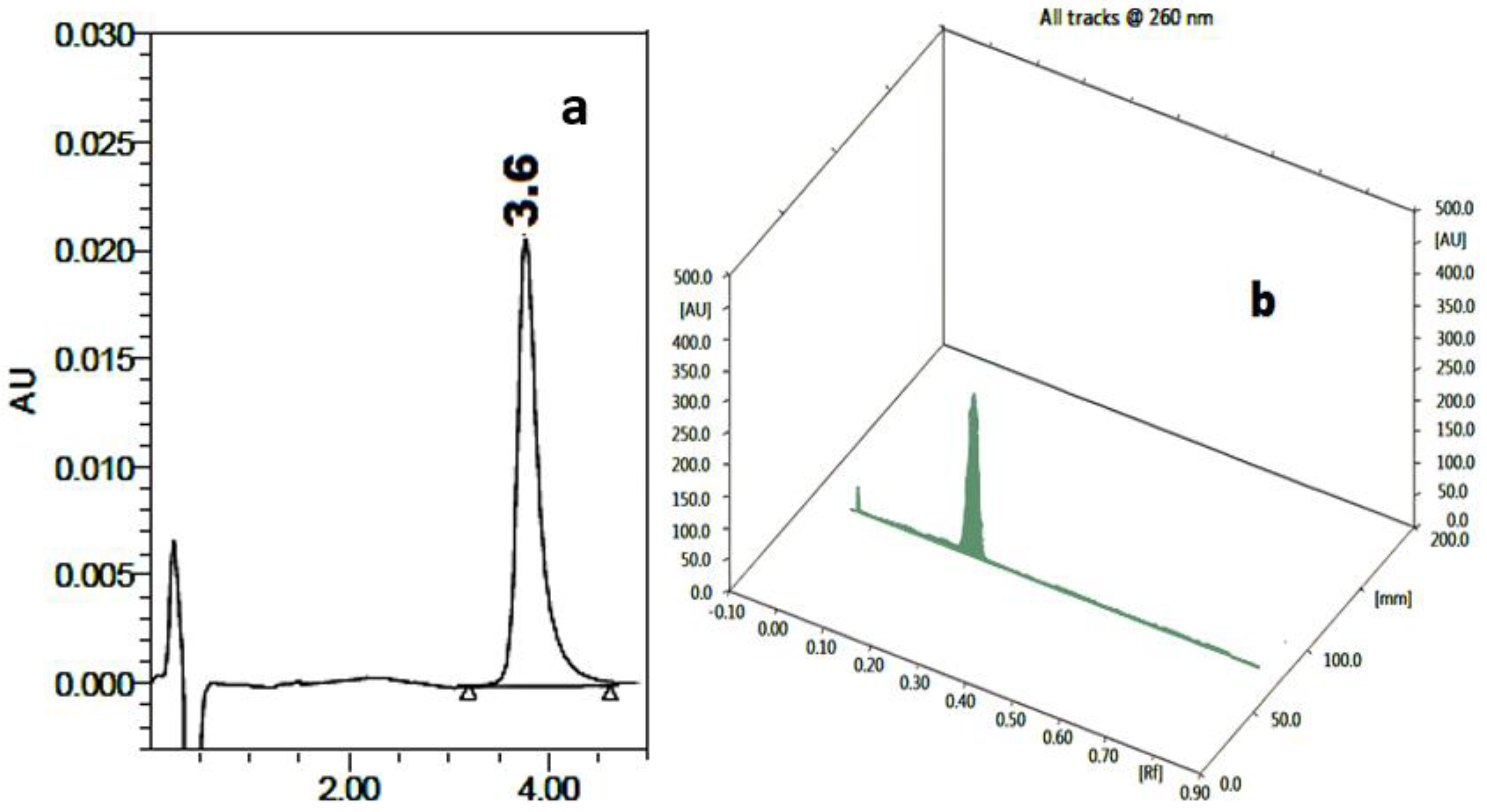
| HPLC | HPTLC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retention Time (min) | Selectivity (α) | Resolution (Rs) | Capacity Factor | Column Efficiency N a | Symmetry Factor | Retention Factor (Rf) b | |
| HEP | 1.8 | ---- | ----- | 2.47 | 1624 | 1.31 | 0.25 ± 0.02 |
| BHS | 3.5 | 2.28 | 4.79 | 5.64 | 2048 | 1.45 | 0.74 ± 0.02 |
| Parameter | HPLC | HPTLC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BHS | HEP | BHS | HEP | |
| Linearity range | 3.0–200.0 a | 0.1–5.0 a | 300.0–15,000.0 b | 25.0–250.0 b |
| R2 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 |
| LOD | 0.96 a | 0.03 a | 80.0 b | 4.0 b |
| LOQ | 2.91 a | 0.09 a | 240.0 b | 10.0 b |
| Accuracy c | 99.9 ± 0.6 | 99.52 ± 0.8 | 99.0 ± 0.7 | 99.6 ± 0.7 |
| Intra-day precision d | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.5 |
| Inter-day precision d | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.8 |
| Parameter | BHS | HEP |
|---|---|---|
| HPLC a | ||
| pH ± 0.1 | 0.54 | 0.39 |
| Column temp. ± 2°C | 0.57 | 1.29 |
| Flow rate ± 0.05 mL min−1 | 1.11 | 0.83 |
| HPTLC a | ||
| Methylene chloride (±0.1%) | 0.64 | 0.82 |
| Saturation time ± 5 min | 0.81 | 0.83 |
| Parameters | HPLC | HPTLC | Reported [7] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average BHS% | 100.52 | 99.61 | 100.22 |
| SD | 0.76 | 1.01 | 1.27 |
| Variance | 0.57 | 1.02 | 1.61 |
| n | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Student’s t-test (2.39) a | 0.17 | 1.10 | |
| F-test (6.39) a | 2.79 | 1.58 |
| Proposed Method | Proposed Method | Reported Method [25] | Reported Method [21] | Reported Method [7] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technique | HPLC-PDA | HPTLC-UV | HPLC-FLD | HPLC-UV | HPLC-UV |
| Organic phase | Totally free | Methylene chloride/methanol/ethyl acetate/ammonia | Acetonitrile | Methanol | Acetonitrile |
| Mobile phase | 0.01 M of Brij-35, 0.12 M of SDS, and 0.02 M of disodium hydrogen phosphate adjusted to a pH of 5.5 with phosphoric | Methylene chloride/methanol/ethyl acetate/ammonia (25%) (5:2:2:0.2; v/v) | 30% acetonitrile and 70% sodium acetate | Acetonitrile and mixed solution (buffer ammonium acetate with sodium lauryl sulfate at a pH of 4.7) | Acetonitrile and Solution of sodium lauryl sulfate (7:13) |
| Flow rate | 1.5 mL min−1 | ----- | 1 mL min−1 | 1 mL min−1 | 1 mL min−1 |
| Retention time | HEP: 1.8 min BHS: 3.5 min | HEP: 0.74 Rf BHS: 0.25 Rf | HEP: Not applicable BHS: 18.4 min | HEP: Not applicable BHS: 2.6 min | HEP: 0.2 min BHS: 7.0 min |
| GAPI |  |  |  | 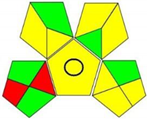 | 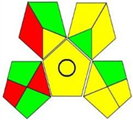 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, A.E.; El Deeb, S.; Abdellatef, H.E.; Hendawy, H.A.M.; El-Abassy, O.M.; Ibrahim, H. Eco-Friendly and Sensitive HPLC and TLC Methods Validated for the Determination of Betahistine in the Presence of Its Process-Related Impurity. Separations 2022, 9, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9020049
Ibrahim AE, El Deeb S, Abdellatef HE, Hendawy HAM, El-Abassy OM, Ibrahim H. Eco-Friendly and Sensitive HPLC and TLC Methods Validated for the Determination of Betahistine in the Presence of Its Process-Related Impurity. Separations. 2022; 9(2):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9020049
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Adel Ehab, Sami El Deeb, Hisham Ezzat Abdellatef, Hassan A. M. Hendawy, Omar M. El-Abassy, and Hany Ibrahim. 2022. "Eco-Friendly and Sensitive HPLC and TLC Methods Validated for the Determination of Betahistine in the Presence of Its Process-Related Impurity" Separations 9, no. 2: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9020049
APA StyleIbrahim, A. E., El Deeb, S., Abdellatef, H. E., Hendawy, H. A. M., El-Abassy, O. M., & Ibrahim, H. (2022). Eco-Friendly and Sensitive HPLC and TLC Methods Validated for the Determination of Betahistine in the Presence of Its Process-Related Impurity. Separations, 9(2), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9020049







