Aqueous Biphasic Systems Comprising Natural Organic Acid-Derived Ionic Liquids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
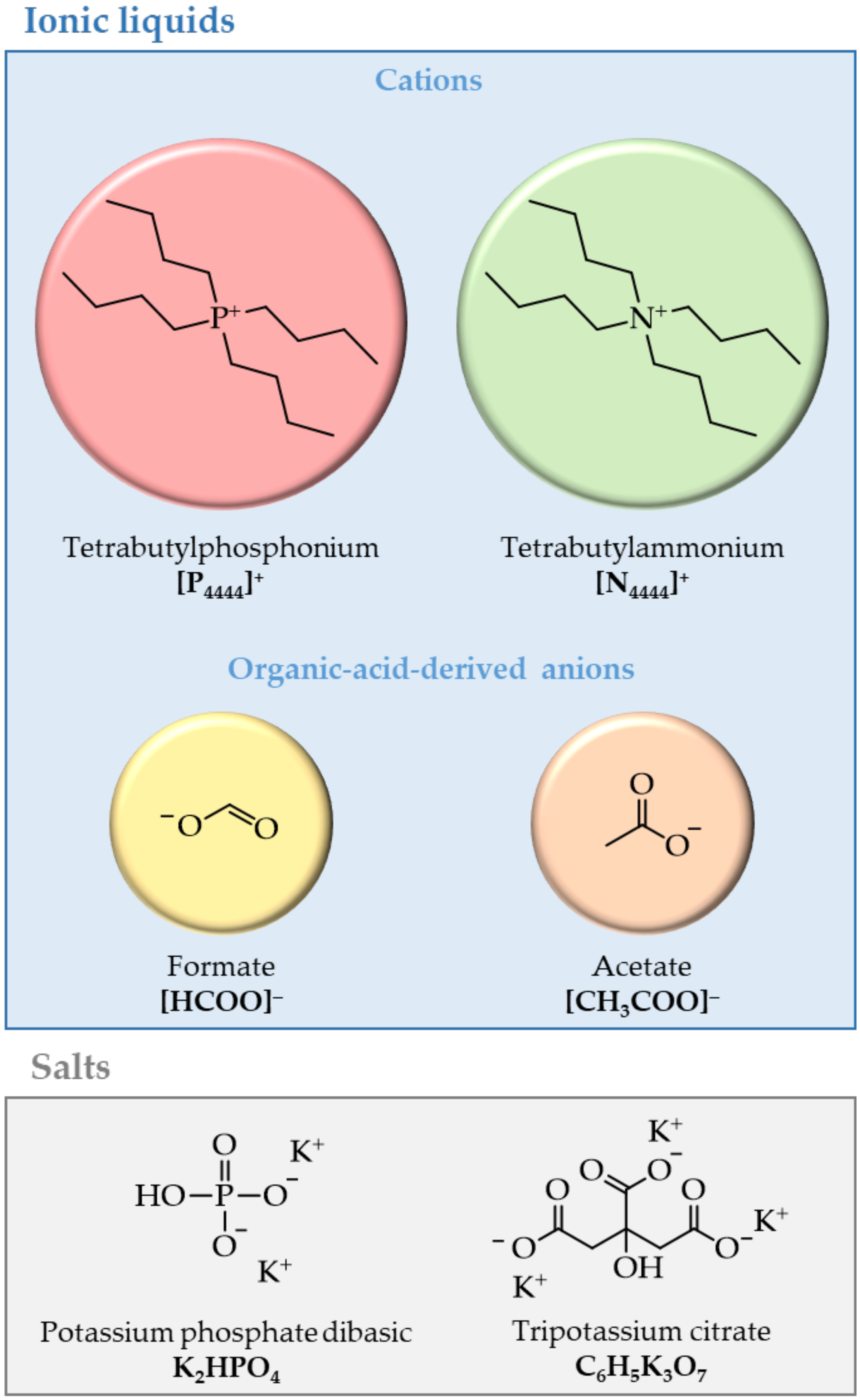
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Ionic Liquids
2.3. Determination of ABSs Phase Diagrams
2.4. Extraction of Human Transferrin
2.5. Molecular Docking
3. Results and Discussion
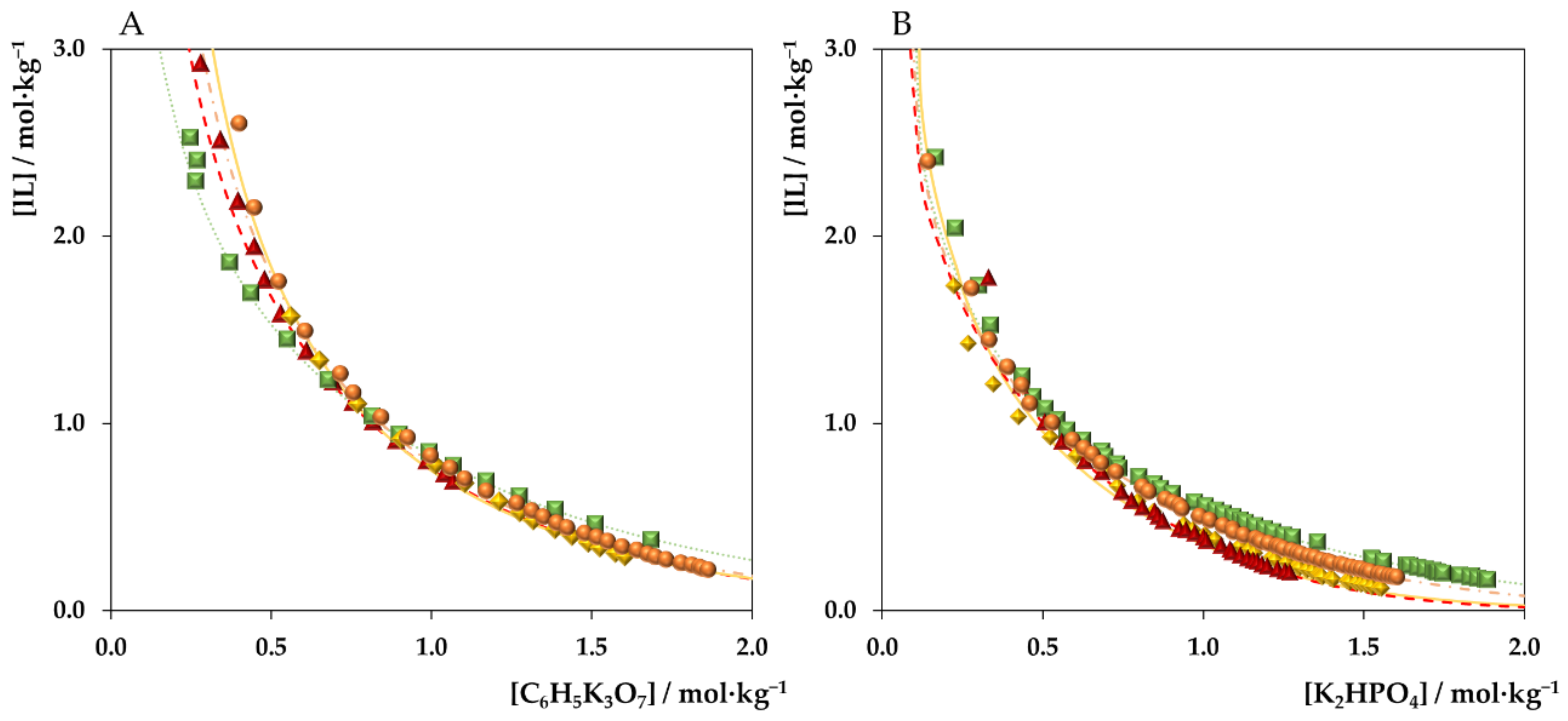
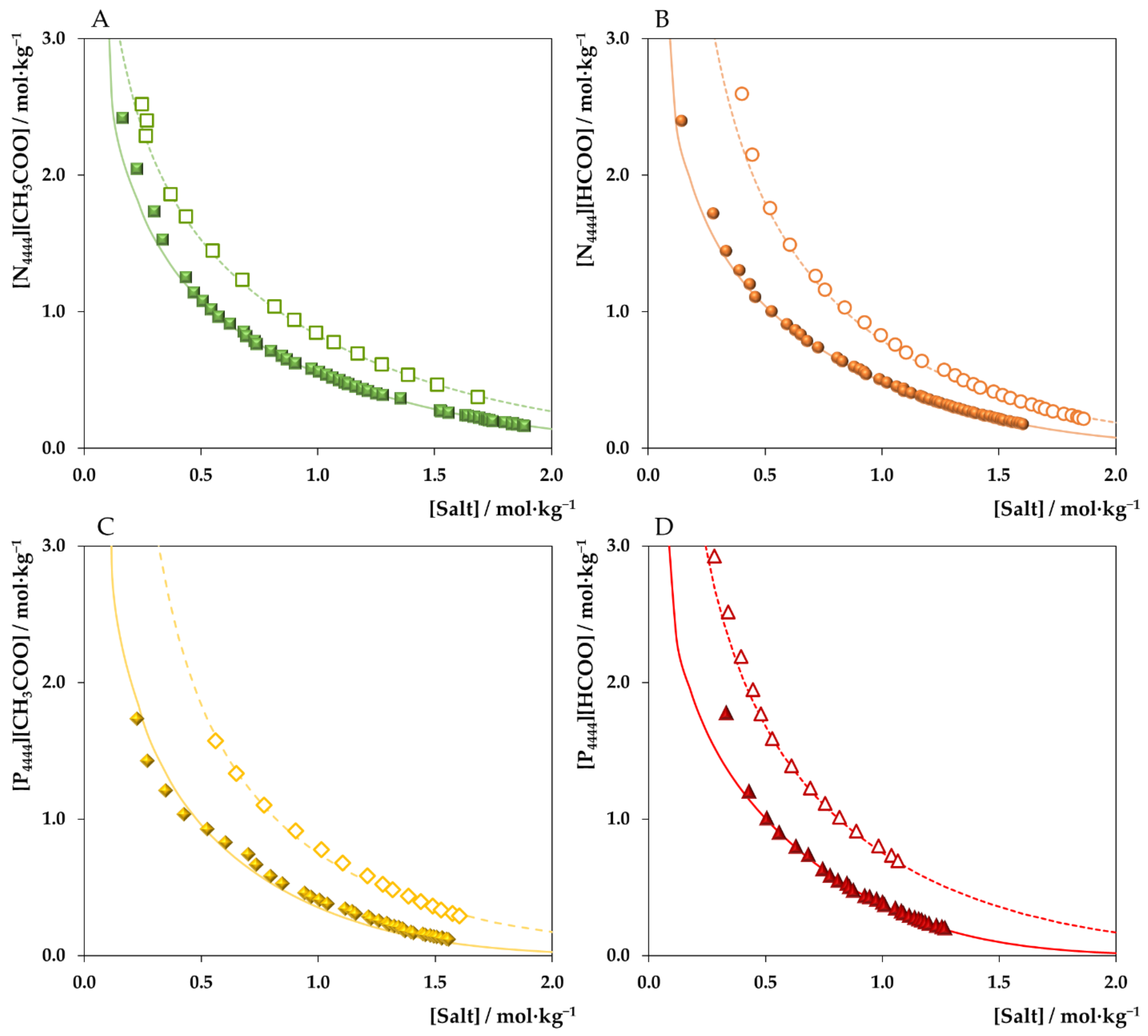
3.1. ABSs Phase Diagrams
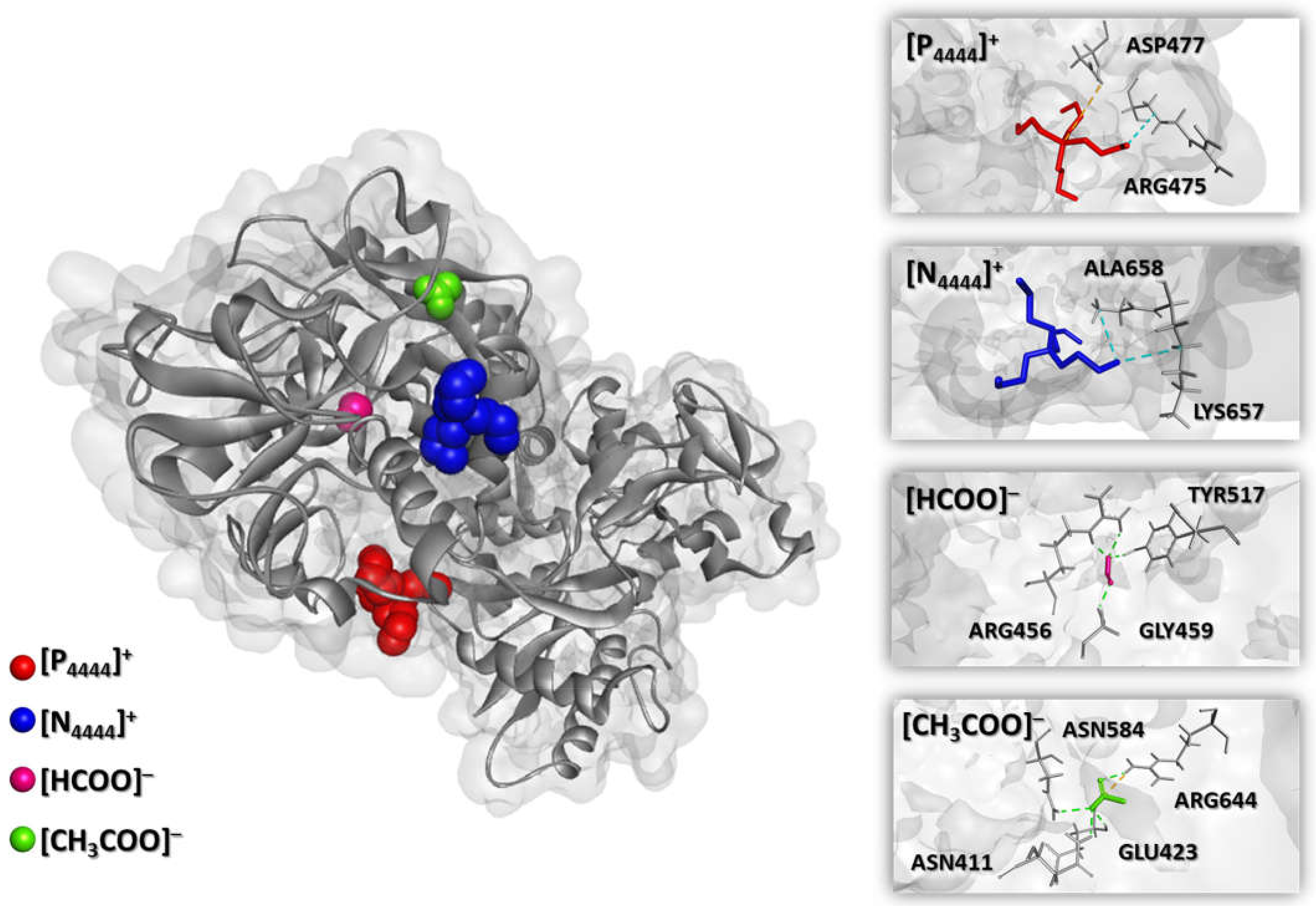
3.2. Extraction of Transferrin
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albertsson, P.-Å. Partition of Proteins in Liquid Polymer–Polymer Two-Phase Systems. Nature 1958, 182, 709–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, R.R.G.; Azevedo, A.M.; Van Alstine, J.M.; Aires-Barros, M.R. Partitioning in aqueous two-phase systems: Analysis of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 10, 1158–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Tao, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Peng, D.; Sattar, A.; Shabbir, M.A.B.; et al. Aqueous two-phase system (ATPS): An overview and advances in its applications. Biol. Proced. Online 2016, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutowski, K.E.; Broker, G.A.; Willauer, H.D.; Huddleston, J.G.; Swatloski, R.P.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Controlling the Aqueous Miscibility of Ionic Liquids: Aqueous Biphasic Systems of Water-Miscible Ionic Liquids and Water-Structuring Salts for Recycle, Metathesis, and Separations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 6632–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basaiahgari, A.; Gardas, R.L. Ionic liquid–based aqueous biphasic systems as sustainable extraction and separation techniques. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 27, 100423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, T. Ionic liquids: A brief history. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, K.; Forsyth, M.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Reid, R.W.; Elliott, G.D. Unexpected improvement in stability and utility of cytochrome c by solution in biocompatible ionic liquids. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2006, 94, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, R.; Izgorodin, A.; Ganesh, V.; Surianarayanan, M.; MacFarlane, D.R. Long-Term Structural and Chemical Stability of DNA in Hydrated Ionic Liquids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 1631–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazid, R.R.; Divisekera, U.; Yang, W.; Ranganathan, V.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Cortez-Jugo, C.; Cheng, W. Biological stability and activity of siRNA in ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 13457–13460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Khoiroh, I.; Ooi, C.W.; Ling, T.C.; Show, P.L. Recent Advances in Protein Extraction Using Ionic Liquid-based Aqueous Two-phase Systems. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2017, 46, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.M.; Silva, S.S.; Reis, R.L. Biocompatible ionic liquids: Fundamental behaviours and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 4317–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulsbosch, J.; De Vos, D.E.; Binnemans, K.; Ameloot, R. Biobased Ionic Liquids: Solvents for a Green Processing Industry? ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2917–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkovic, M.; Ferguson, J.L.; Gunaratne, H.Q.N.; Ferreira, R.; Leitão, M.C.; Seddon, K.R.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Pereira, C.S. Novel biocompatible cholinium-based ionic liquids—toxicity and biodegradability. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Donne, A.; Bodo, E. Cholinium amino acid-based ionic liquids. Biophys. Rev. 2021, 13, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parajó, J.J.; Macário, I.P.E.; De Gaetano, Y.; Dupont, L.; Salgado, J.; Pereira, J.L.; Gonçalves, F.J.M.; Mohamadou, A.; Ventura, S.P.M. Glycine-betaine-derived ionic liquids: Synthesis, characterization and ecotoxicological evaluation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gaetano, Y.; Mohamadou, A.; Boudesocque, S.; Hubert, J.; Plantier-Royon, R.; Dupont, L. Ionic liquids derived from esters of Glycine Betaine: Synthesis and characterization. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 207, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Fernández, I.; Pino, V.; Ayala, J.H.; Afonso, A.M. Guanidinium ionic liquid-based surfactants as low cytotoxic extractants: Analytical performance in an in-situ dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction method for determining personal care products. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1559, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Arritt, S.W.; Twamley, B.; Shreeve, J.M. Guanidinium-Based Ionic Liquids. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 1704–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavhane, R.J.; Madkar, K.R.; Kurhe, D.N.; Dagade, D.H. Room Temperature Ionic Liquids from Purine and Pyrimidine Nucleobases. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 5823–5827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletti, L.; Chiappe, C.; Lay, L.; Pieraccini, D.; Polito, L.; Russo, G. Glucose-derived ionic liquids: Exploring low-cost sources for novel chiral solvents. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayachandra, R.; Reddy, S.R. A remarkable chiral recognition of racemic Mosher’s acid salt by naturally derived chiral ionic liquids using 19 F NMR spectroscopy. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 39758–39761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, K.S.; Seitkalieva, M.M.; Posvyatenko, A.V.; Ananikov, V.P. An unexpected increase of toxicity of amino acid-containing ionic liquids. Toxicol. Res. 2015, 4, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlin, N.; Courty, M.; Gatard, S.; Spulak, M.; Quilty, B.; Beadham, I.; Ghavre, M.; Haiß, A.; Kümmerer, K.; Gathergood, N.; et al. Biomass derived ionic liquids: Synthesis from natural organic acids, characterization, toxicity, biodegradation and use as solvents for catalytic hydrogenation processes. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 6150–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, M.-L.; Mirjafari, A.; McCabe, J.R.; O’Brien, R.A.; Essi, D.F.; Baum, L.; West, K.N.; Davis, J.H. Synthesis and thermophysical properties of ionic liquids: Cyclopropyl moieties versus olefins as Tm-reducing elements in lipid-inspired ionic liquids. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, S.; Chowdhury, M.R.; Wakabayashi, R.; Kamiya, N.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Goto, M. Lipid based biocompatible ionic liquids: Synthesis, characterization and biocompatibility evaluation. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 13756–13759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feder-Kubis, J.; Wnętrzak, A.; Chachaj-Brekiesz, A. Terpene-Based Ionic Liquids from Natural Renewable Sources as Selective Agents in Antifungal Therapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 3832–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feder-Kubis, J.; Zabielska-Matejuk, J.; Stangierska, A.; Przybylski, P.; Jacquemin, J.; Geppert-Rybczyńska, M. Toward Designing “Sweet” Ionic Liquids Containing a Natural Terpene Moiety as Effective Wood Preservatives. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 15628–15639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, C.C.; Neves, C.M.S.S.; Quental, M.V.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Separation of immunoglobulin G using aqueous biphasic systems composed of cholinium-based ionic liquids and poly (propylene glycol). J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Pei, Y.; Wang, J.; He, M. Design of environmentally friendly ionic liquid aqueous two-phase systems for the efficient and high activity extraction of proteins. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.; Sharma, M.; Quental, M.V.; Tavares, A.P.M.; Prasad, K.; Freire, M.G. Suitability of bio-based ionic liquids for the extraction and purification of IgG antibodies. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 6071–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafarani-Moattar, M.T.; Shekaari, H.; Jafari, P. Design of Novel Biocompatible and Green Aqueous two-Phase Systems containing Cholinium L-alaninate ionic liquid and polyethylene glycol di-methyl ether 250 or polypropylene glycol 400 for separation of bovine serum albumin (BSA). J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 254, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, H.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Ionic liquid solutions as extractive solvents for value-added compounds from biomass. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 4786–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, N.J.; Gutowski, K.E.; Rogers, R.D. Investigation of aqueous biphasic systems formed from solutions of chaotropic salts with kosmotropic salts (salt–salt ABS). Green Chem. 2007, 9, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomme, P.T.; McCann, K.B.; Bertolini, J. Transferrin: Structure, function and potential therapeutic actions. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D.; Sato, G. Serum-free cell culture: A unifying approach. Cell 1980, 22, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskey, J.; Webb, I.; Schulman, H.M.; Ponka, P. Evidence that transferrin supports cell proliferation by supplying iron for DNA synthesis. Exp. Cell Res. 1988, 176, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Ann, D.K.; Shen, W.-C. Recombinant granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-transferrin fusion protein as an oral myelopoietic agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 7292–7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.-Q.; Qu, Y.-H.; Ke, W.-L.; Zhu, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; Jiang, C. Efficient gene delivery targeted to the brain using a transferrin-conjugated polyethyleneglycol-modified polyamidoamine dendrimer. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshi, K.; Ito, H.; Abe, E.; Fuwa, T.J.; Kanno, M.; Murakami, Y.; Abe, M.; Murakami, T.; Yoshihara, A.; Ugawa, Y.; et al. Transferrin Biosynthesized in the Brain Is a Novel Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Disease. Metabolites 2021, 11, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atallah, G.A.; Abd Aziz, N.H.; Teik, C.K.; Shafiee, M.N.; Kampan, N.C. New Predictive Biomarkers for Ovarian Cancer. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Bonsdorff, L.; Tölö, H.; Lindeberg, E.; Nyman, T.; Harju, A.; Parkkinen, J. Development of a Pharmaceutical Apotransferrin Product for Iron Binding Therapy. Biologicals 2001, 29, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rivat, C.; Sertillanges, P.; Patin, E.; Stoltz, J.F. Single-step method for purification of human transferrin from a by-product of chromatographic fractionation of plasma. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1992, 576, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, K.B.; Hughes, B.; Wu, J.; Bertolini, J.; Gomme, P.T. Purification of transferrin from Cohn supernatant I using ion-exchange chromatography. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2005, 42, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inman, J.K.; Coryell, F.C.; McCall, K.B.; Sgouris, J.T.; Anderson, H.D. A Large-Scale Method for the Purification of Human Transferrin. Vox Sang. 1961, 6, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, S. Transferrin: The Iron Carrier; CRC Press, Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1992; ISBN 978-0849367939. [Google Scholar]
- Passos, H.; Ferreira, A.R.; Cláudio, A.F.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Characterization of aqueous biphasic systems composed of ionic liquids and a citrate-based biodegradable salt. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 67, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchuk, J.C.; Andrews, B.A.; Asenjo, J.A. Aqueous two-phase systems for protein separation studies on phase inversion. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 1998, 711, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Rosell, G.; Giorgino, T.; De Fabritiis, G. PlayMolecule ProteinPrepare: A Web Application for Protein Preparation for Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos, H.; Dinis, T.B.V.; Cláudio, A.F.M.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Hydrogen bond basicity of ionic liquids and molar entropy of hydration of salts as major descriptors in the formation of aqueous biphasic systems. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 14234–14241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnia, K.A.; Lima, F.; Cláudio, A.F.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Hydrogen-bond acidity of ionic liquids: An extended scale. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 18980–18990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Xu, K. Design of functional guanidinium ionic liquid aqueous two-phase systems for the efficient purification of protein. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 815, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berton, P.; Tian, H.; Rogers, R.D. Phase Behavior of Aqueous Biphasic Systems with Choline Alkanoate Ionic Liquids and Phosphate Solutions: The Influence of pH. Molecules 2021, 26, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriari, S.; Neves, C.M.S.S.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Role of the Hofmeister Series in the Formation of Ionic-Liquid-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 7252–7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liang, X.; Woodley, J.M.; Kontogeorgis, G.M. Modelling study on phase equilibria behavior of ionic liquid-based aqueous biphasic systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 247, 116904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnia, K.A.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Effect of Polyvalent Ions in the Formation of Ionic-Liquid-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takátsy, A.; Hodrea, J.; Majdik, C.; Dan Irimie, F.; Kilár, F. Role of chemical structure in molecular recognition by transferrin. J. Mol. Recognit. 2006, 19, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, M.F.; Emmel, G.N.; Yang, E.J.; Lee, E.; Paek, J.H.; Wu, B.M.; Kamei, D.T. Ionic Liquid Aqueous Two-Phase Systems for the Enhanced Paper-Based Detection of Transferrin and Escherichia coli. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.G.; Neves, C.M.S.S.; Marrucho, I.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Fernandes, A.M. Hydrolysis of Tetrafluoroborate and Hexafluorophosphate Counter Ions in Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 3744–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaiahgari, A.; Priyanka, V.P.; Ijardar, S.P.; Gardas, R.L. Aqueous biphasic systems of amino acid-based ionic liquids: Evaluation of phase behavior and extraction capability for caffeine. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2020, 506, 112373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Berton, P.; Rogers, R.D. Choline-based aqueous biphasic systems: Overview of applications. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2019, 502, 112258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, R.J.; Borges, M.F.; Rosa, M.F.; Castro-Gómez, R.J.H.; Spinosa, W.A. Acetic Acid Bacteria in the Food Industry: Systematics, Characteristics and Applications. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 56, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Vera, R.; Crawford, J.; Dou, C.; Bura, R.; Gustafson, R. Techno-Economic Analysis of Producing Glacial Acetic Acid from Poplar Biomass via Bioconversion. Molecules 2020, 25, 4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quental, M.V.; Pereira, M.M.; Silva, F.A.e.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Aqueous Biphasic Systems Comprising Natural Organic Acid-Derived Ionic Liquids. Separations 2022, 9, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9020046
Quental MV, Pereira MM, Silva FAe, Coutinho JAP, Freire MG. Aqueous Biphasic Systems Comprising Natural Organic Acid-Derived Ionic Liquids. Separations. 2022; 9(2):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9020046
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuental, Maria V., Matheus M. Pereira, Francisca A. e Silva, João A. P. Coutinho, and Mara G. Freire. 2022. "Aqueous Biphasic Systems Comprising Natural Organic Acid-Derived Ionic Liquids" Separations 9, no. 2: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9020046
APA StyleQuental, M. V., Pereira, M. M., Silva, F. A. e., Coutinho, J. A. P., & Freire, M. G. (2022). Aqueous Biphasic Systems Comprising Natural Organic Acid-Derived Ionic Liquids. Separations, 9(2), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9020046






