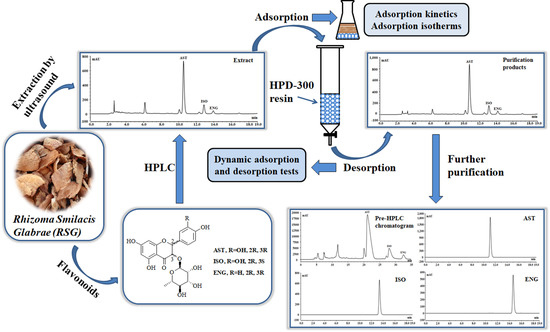
Adsorption Properties and Preparative Separation of Flavonoids from Rhizoma Smilacis Glabrae Using Macroporous Resins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Extration of RSG
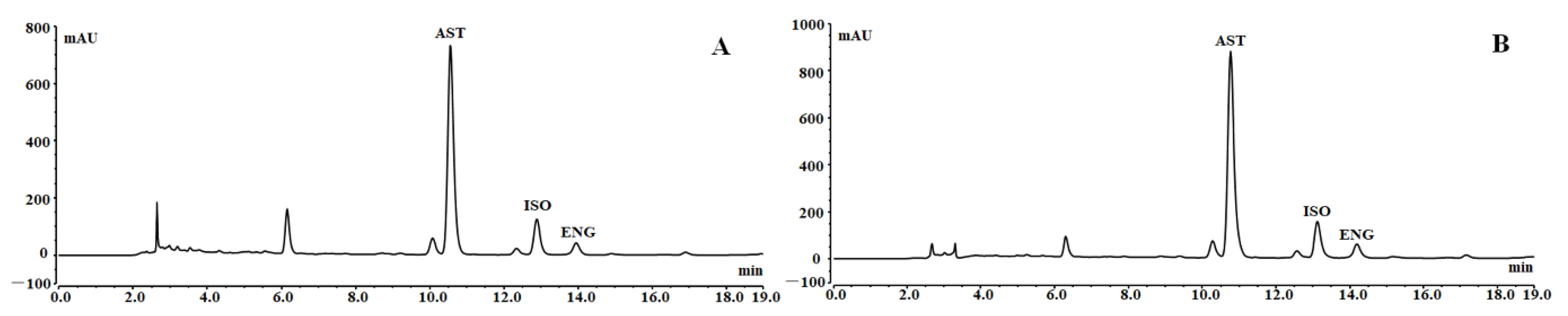
2.3. HPLC Analysis of the Three Flavonoids
2.4. Adsorption Kinetics
2.5. Adsorption Isotherms
2.6. Dynamic Adsorption and Desorption Tests
2.7. The Purification of Flavonoids by Preparative HPLC and Silica Gel Column Chromatography
2.8. Data Processing
3. Results and Discusstion
3.1. Adsorption Kinetics
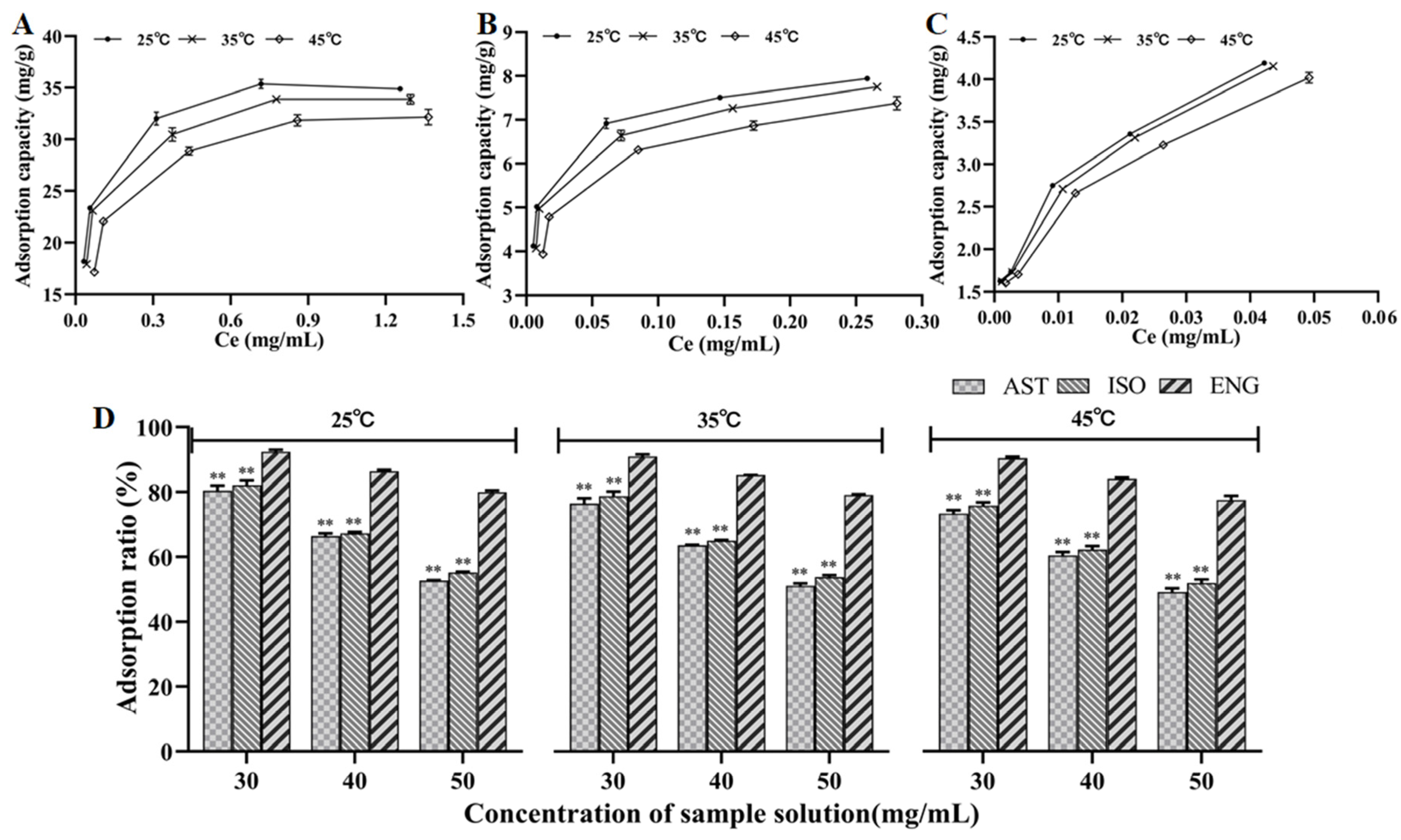
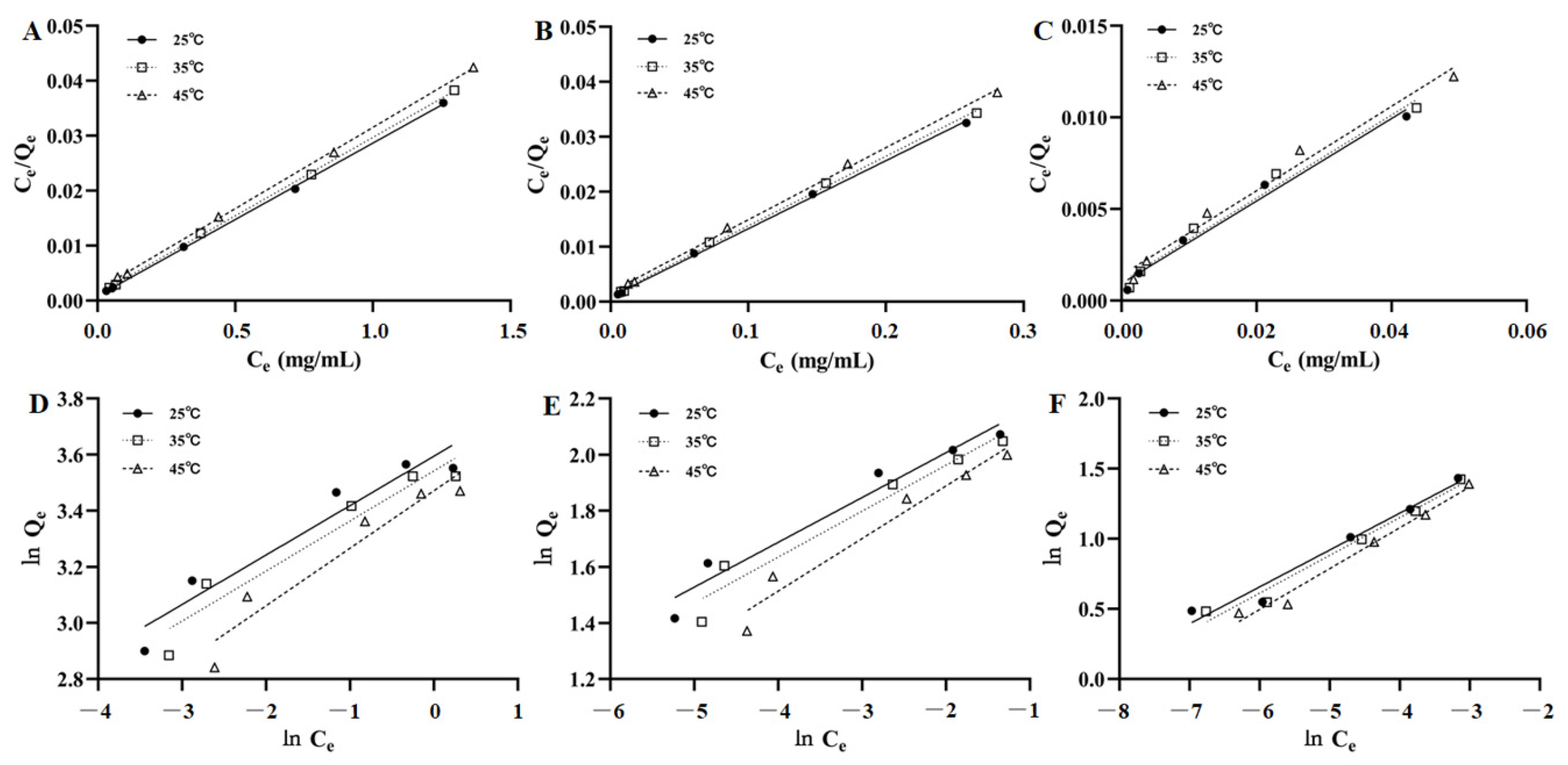
3.2. Adsorption Isotherms
3.3. Dynamic Adsorption Tests
3.4. Dynamic Desorption Tests
3.5. The Further Purification of AST, ISO, and ENG with High Purities
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gegentana; Xu, F.; Li, F.C.; Zhang, Y.F.; Shen, S.J.; Yang, P.; Yang, X.X.; Shang, M.Y.; Liu, G.X.; Li, Y.L.; et al. Discovery of the active compounds of Smilacis Glabrae Rhizoma by utilizing the relationship between the individual differences in blood drug concentration and the pharmacological effect in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 258, 112886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, J.; Li, L.; Zhou, M.; Yu, J.; Peng, C.; Shao, F.; Liu, R.; Zhu, G.; Huang, H. Three new flavonoid glycosides from Smilax Glabra and their anti-inflammatory activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1760–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pharmacopoeia Commission of PRC. Ch.P; Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020; Volume I, p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Yin, Y.; Yi, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, T. Simultaneous quantification of five major bioactive flavonoids in Rhizoma Smilacis Glabrae by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 43, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, Q.F. Purification of total flavonoids from Rhizoma Smilacis Glabrae through cyclodextrin-assisted extraction and resin adsorption. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Li, L.; Shi, Y.; Chen, R.; Liu, G.; Wang, M.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, N. Simultaneous ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry determination of six components in rat plasma after oral administration of Smilacis Glabrae Roxb. extract. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Q.Y.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, C.F.; Wang, C.Z.; Yuan, C.S. Therapeutic effects of Smilax Glabra and Bolbostemma Paniculatum on rheumatoid arthritis using a rat paw edema model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, B.; Zong, X.; Li, L. Preparative separation of flavonoids in plant extract of Smilacis Glabrae Roxb. by high performance counter-current chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Shang, M.Y.; Liu, G.X.; Xu, F.; Wang, X.; Shou, C.C.; Cai, S.Q. Chemical constituents from the rhizomes of Smilax Glabra and their antimicrobial activity. Molecules 2013, 18, 5265–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.F. Isomerization of astilbin and its application for preparation of the four stereoisomers from Rhizoma Smilacis Glabrae. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 155, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Zhu, J.; Du, H.; Nong, H.; He, X.; Chen, X. Astilbin from Smilax Glabra Roxb. attenuates inflammatory responses in complete freund’s adjuvant-Induced arthritis rats. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2017, 2017, 8246420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Gupta, S.; Chauhan, S.; Nair, A.; Sharma, P. Astilbin: A promising unexplored compound with multidimensional medicinal and health benefits. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 158, 104894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Xu, M.; Yin, L. Pharmacokinetic, bioavailability and tissue distribution study of astilbin in rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Gao, Z.; Xu, F.; Liu, L.; Luo, Q.; Shen, Y.; Wu, X.; Wu, X.; Sun, Y.; Wu, X.; et al. A novel combination of astilbin and low-dose methotrexate respectively targeting A2AAR and its ligand adenosine for the treatment of collagen-induced arthritis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 153, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Pang, Z.; Qi, G.; Hua, B.; Yan, Z.; Yuan, H. Engeletin protects against TNF-α-Induced apoptosis and reactive oxygen species generation in chondrocytes and alleviates osteoarthritis in vivo. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Ji, H.; Shi, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhi, Z. Engeletin attenuates Aβ1-42-Induced oxidative stress and neuroinflammation by Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Inflammation 2020, 43, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, R.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tian, C.; Xia, D. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of six flavonoids from Smilax Glabra Roxb. Molecules 2020, 25, 5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippenaar, C.; Shimbo, H.; Okon, K.; Miller, N.; Joubert, E.; Yoshida, T.; de Beer, D. Anti-allergic and antioxidant potential of polyphenol-enriched fractions from Cyclopia subternata (Honeybush) produced by a scalable process. Separations 2022, 9, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charpe, T.W.; Rathod, V.K. Separation of glycyrrhizic acid from licorice root extract using macroporous resin. Food Bioprod. Process 2015, 93, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Xiong, S.; Xie, Y.; Liang, X. The separation and purification of ellagic acid from Phyllanthus urinaria L. by a combined mechanochemical-macroporous resin adsorption method. Separations 2021, 8, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che Zain, M.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Teo, C.Y.; Shaari, K. Adsorption and desorption properties of total flavonoids from oil palm (Elaeis Guineensis Jacq.) mature leaf on macroporous adsorption resins. Molecules 2020, 25, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lin, H.; Zhang, J.; Deng, X.; Li, J. An efficient procedure for preparing high-purity pingyangmycin and boanmycin from Streptomyces verticillus var. pingyangensis fermentation broth via macroporous cation-exchange resin and subsequent reversed-phase preparative chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1136, 121883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.J.; Hou, G.G.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhao, F.; Cong, W.; Wang, C.H. Preparative separation of phloridzin from apple leaves using macroporous resins followed by preparative high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 3918–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.J.; Shi, J.L.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, C.H.; Hou, G.G.; Cong, W.; Zhao, F. Purification of spinosin from Ziziphi Spinosae Semen using macroporous resins followed by preparative high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 3134–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.J.; Su, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, D.X.; Hou, G.G.; Zhao, F.; Sun, J.F.; Cong, W.; Wang, C.H.; Li, H.J. Separation of three chromones from Saposhnikovia Divaricata using macroporous resins followed by preparative high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 3287–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

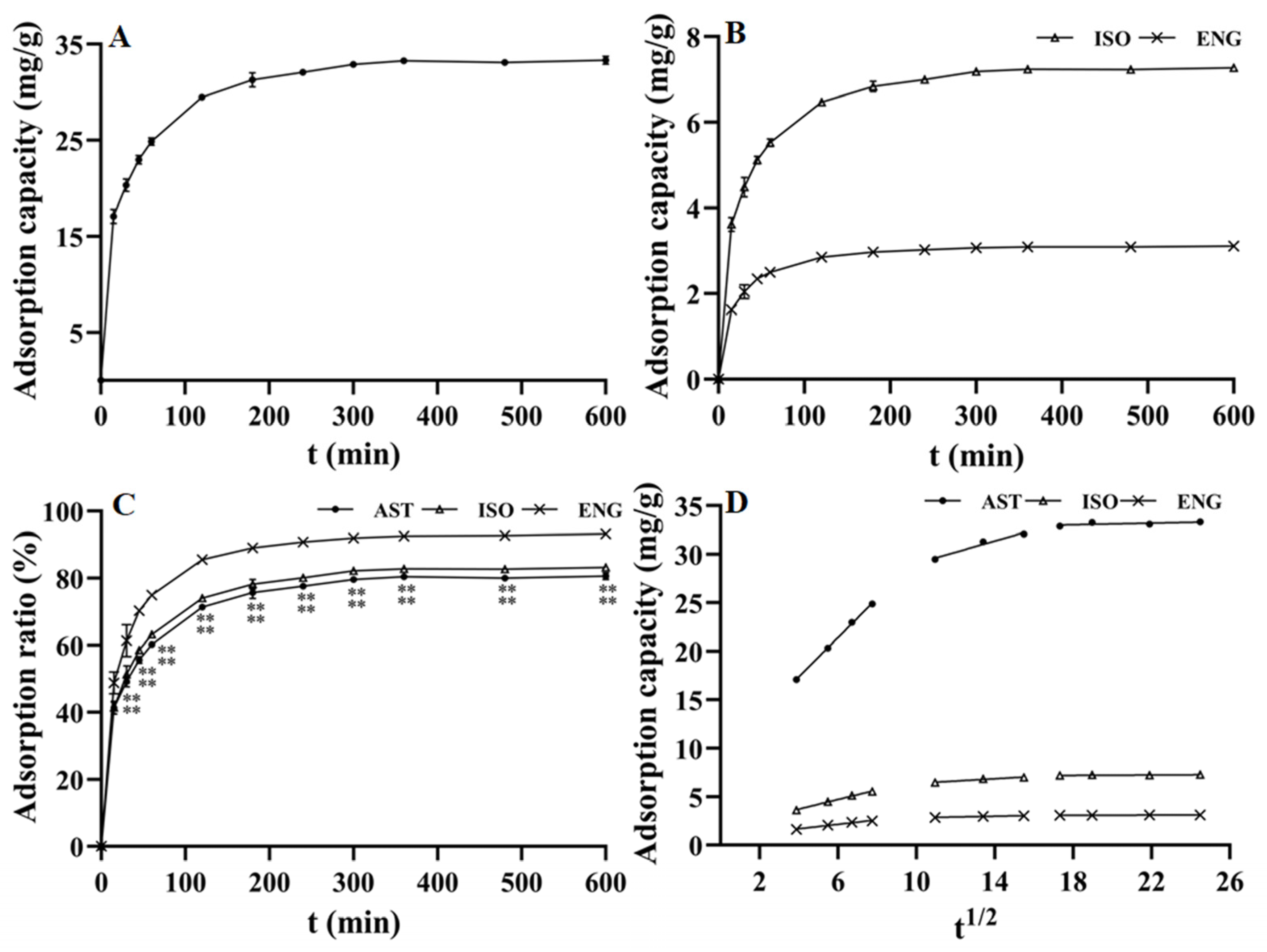


| Kinetics Equations | Dynamic Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order model | Coumpound | Qe (mg/g) | K1 | R2 |
| AST | 18.33 | 0.0121 | 0.9925 | |
| ISO | 3.94 | 0.0123 | 0.9895 | |
| ENG | 1.40 | 0.0122 | 0.9853 | |
| Pseudo-second-order model | Qe (mg/g) | K2 | R2 | |
| AST | 34.60 | 0.0015 | 0.9997 | |
| ISO | 7.54 | 0.0070 | 0.9998 | |
| ENG | 3.20 | 0.0208 | 0.9999 | |
| Intraparticle diffusion model (0–60 min) | C | Ki | R2 | |
| AST | 9.24 | 2.0280 | 0.9993 | |
| ISO | 1.72 | 0.4979 | 0.9958 | |
| ENG | 0.76 | 0.2295 | 0.9891 | |
| Compounds | Temperature (K) | Langmuir Equation | Freundlich Equation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax | KL | R2 | KF | 1/n | R2 | ||
| AST | 298 | 35.97 | 34.75 | 0.9996 | 36.39 | 0.1763 | 0.9264 |
| 308 | 35.09 | 23.75 | 0.9996 | 34.53 | 0.1785 | 0.9269 | |
| 318 | 33.78 | 15.58 | 0.9997 | 32.17 | 0.2051 | 0.9223 | |
| ISO | 298 | 8.07 | 137.67 | 0.9991 | 10.24 | 0.1598 | 0.9577 |
| 308 | 7.91 | 115.00 | 0.9985 | 9.88 | 0.1639 | 0.9528 | |
| 318 | 7.63 | 72.83 | 0.9985 | 9.62 | 0.1876 | 0.9575 | |
| ENG | 298 | 4.44 | 250.22 | 0.9844 | 9.34 | 0.2630 | 0.9675 |
| 308 | 4.41 | 206.09 | 0.9811 | 9.30 | 0.2697 | 0.9756 | |
| 318 | 4.33 | 164.79 | 0.9831 | 9.43 | 0.2915 | 0.9829 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Hou, G.; Li, H. Adsorption Properties and Preparative Separation of Flavonoids from Rhizoma Smilacis Glabrae Using Macroporous Resins. Separations 2022, 9, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9120431
Su X, Zhang X, Wang C, Hou G, Li H. Adsorption Properties and Preparative Separation of Flavonoids from Rhizoma Smilacis Glabrae Using Macroporous Resins. Separations. 2022; 9(12):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9120431
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Xiangyi, Xuan Zhang, Chunhua Wang, Guige Hou, and Hongjuan Li. 2022. "Adsorption Properties and Preparative Separation of Flavonoids from Rhizoma Smilacis Glabrae Using Macroporous Resins" Separations 9, no. 12: 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9120431
APA StyleSu, X., Zhang, X., Wang, C., Hou, G., & Li, H. (2022). Adsorption Properties and Preparative Separation of Flavonoids from Rhizoma Smilacis Glabrae Using Macroporous Resins. Separations, 9(12), 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9120431