Synthesis of Gum Arabic Magnetic Nanoparticles for Adsorptive Removal of Ciprofloxacin: Equilibrium, Kinetic, Thermodynamics Studies, and Optimization by Response Surface Methodology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Instrumentations
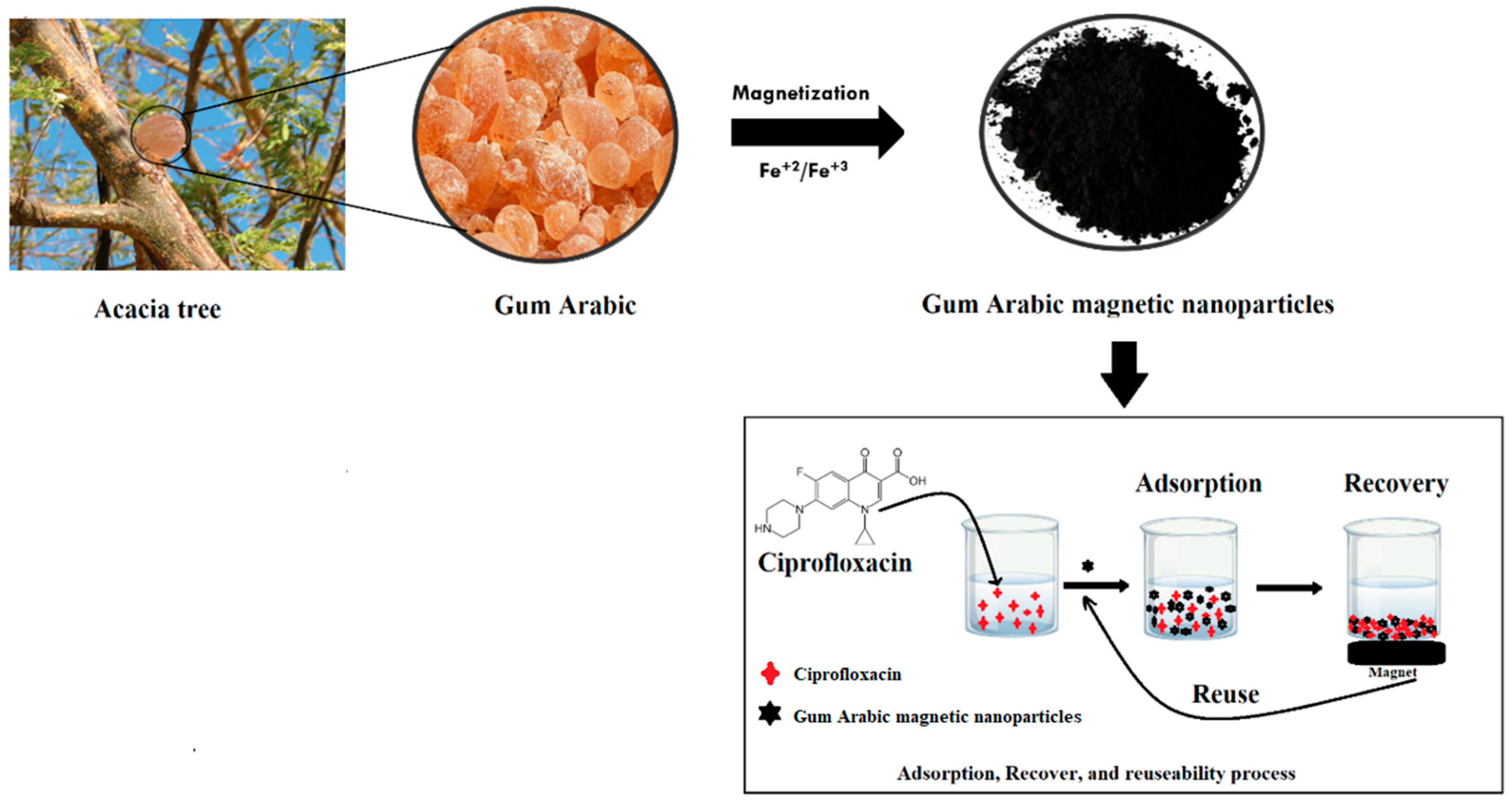
2.3. Synthesis of Gum Arabic Magnetite Nanoparticles (GA-MNPs)
2.4. Batch Adsorption Experiment
2.5. Response Surface Methodology (RSM)
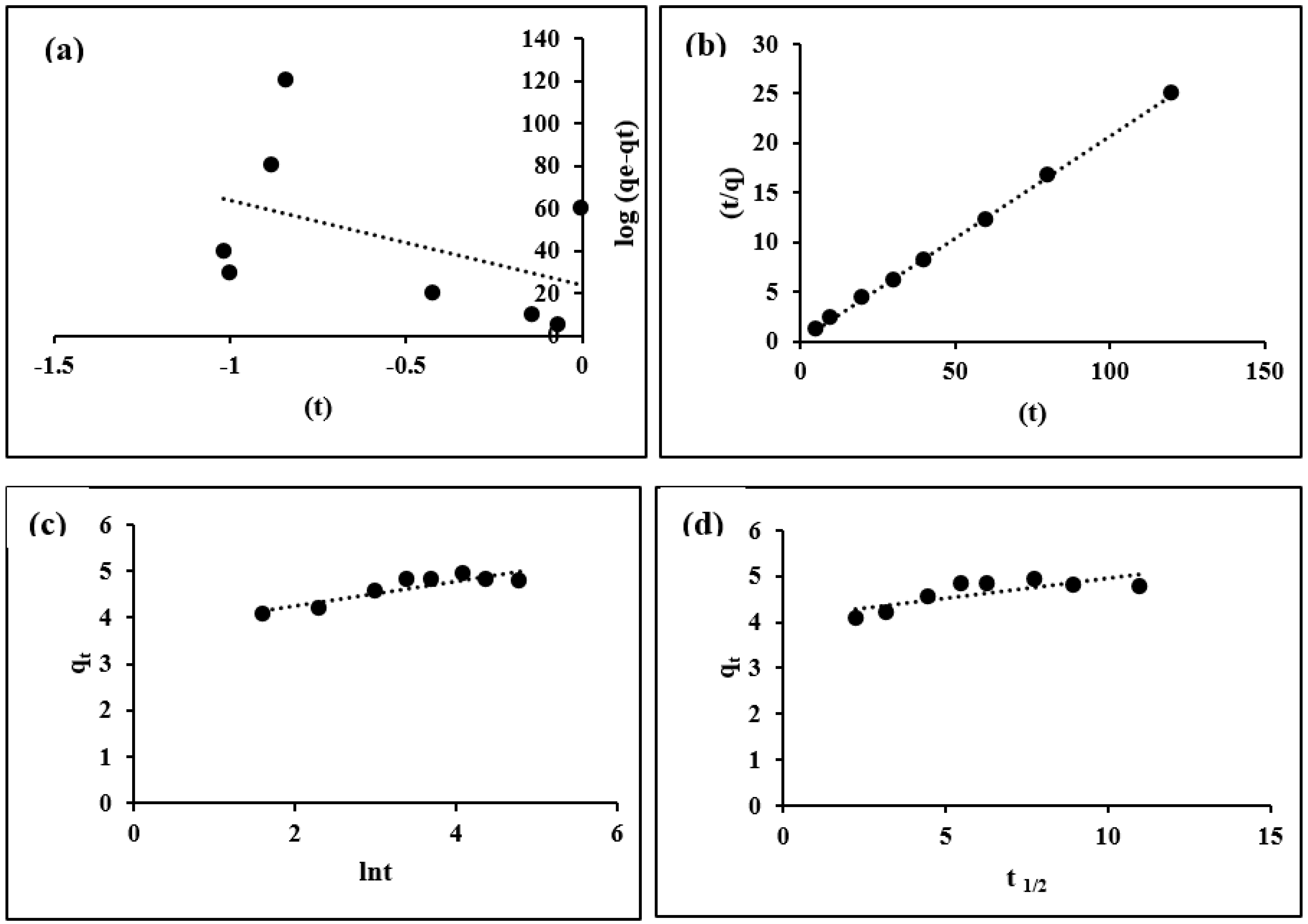
2.6. Adsorption Kinetics
2.7. Adsorption Isotherms
2.8. Thermodynamic Studies
3. Results and Discussion
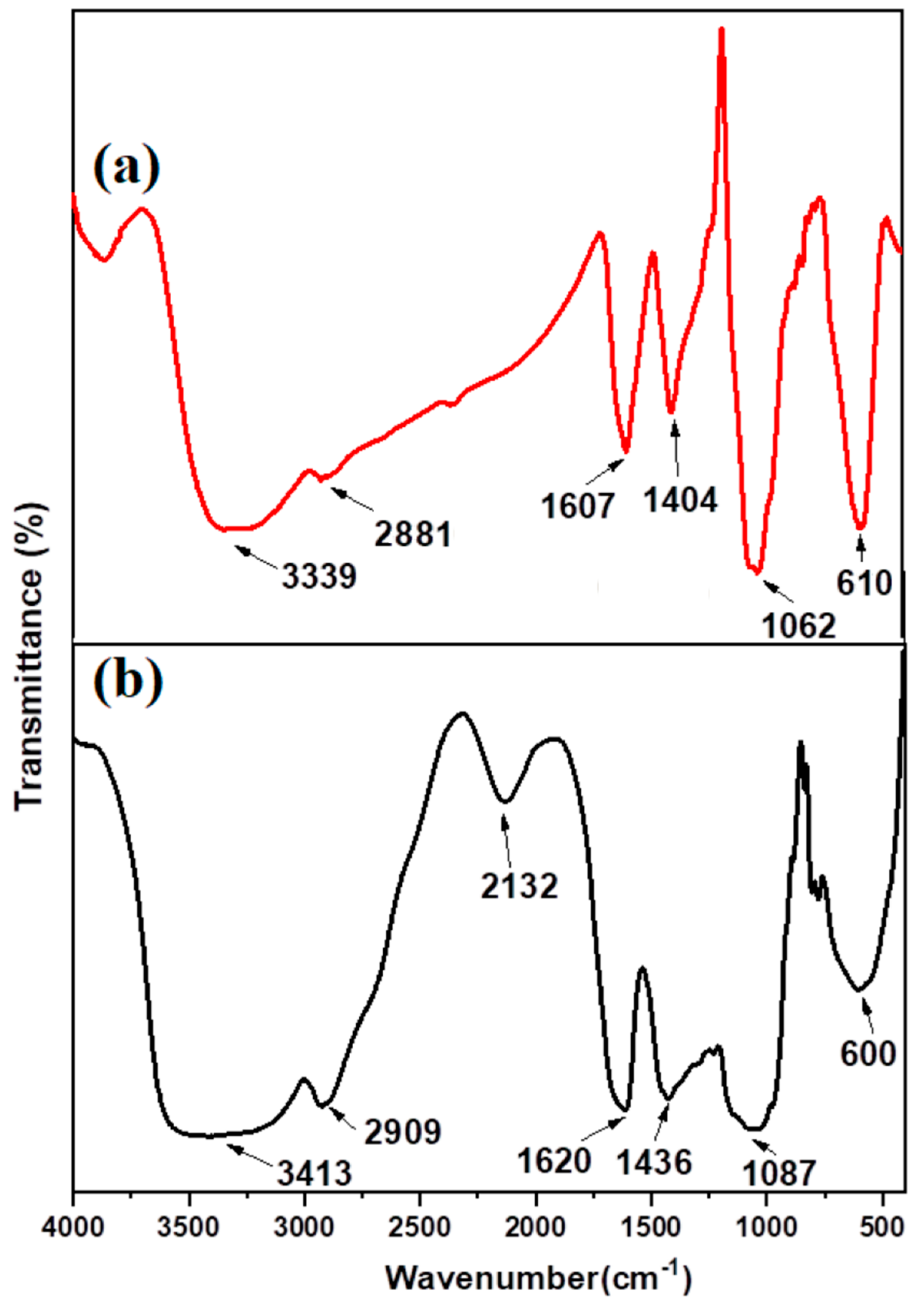
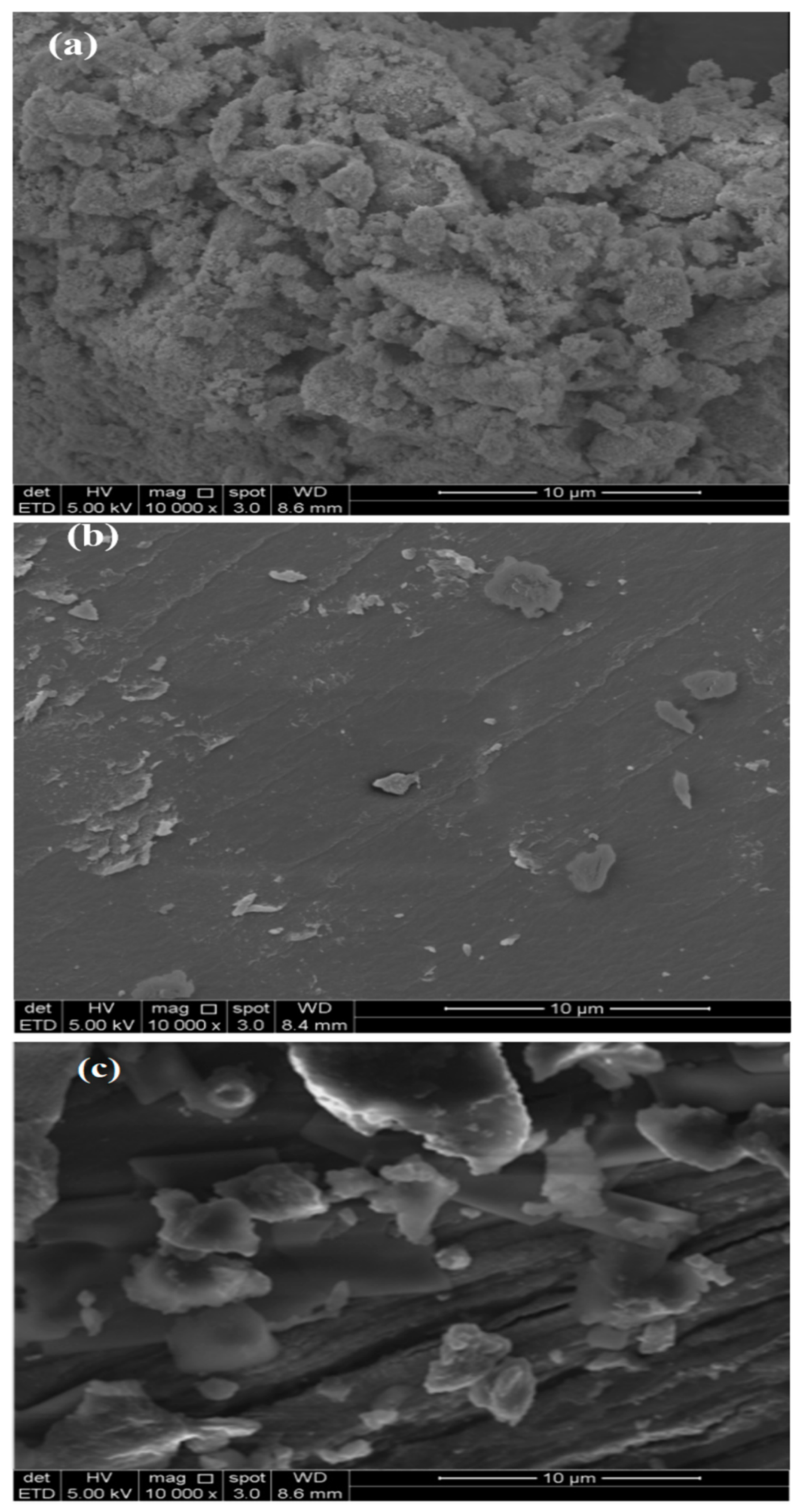
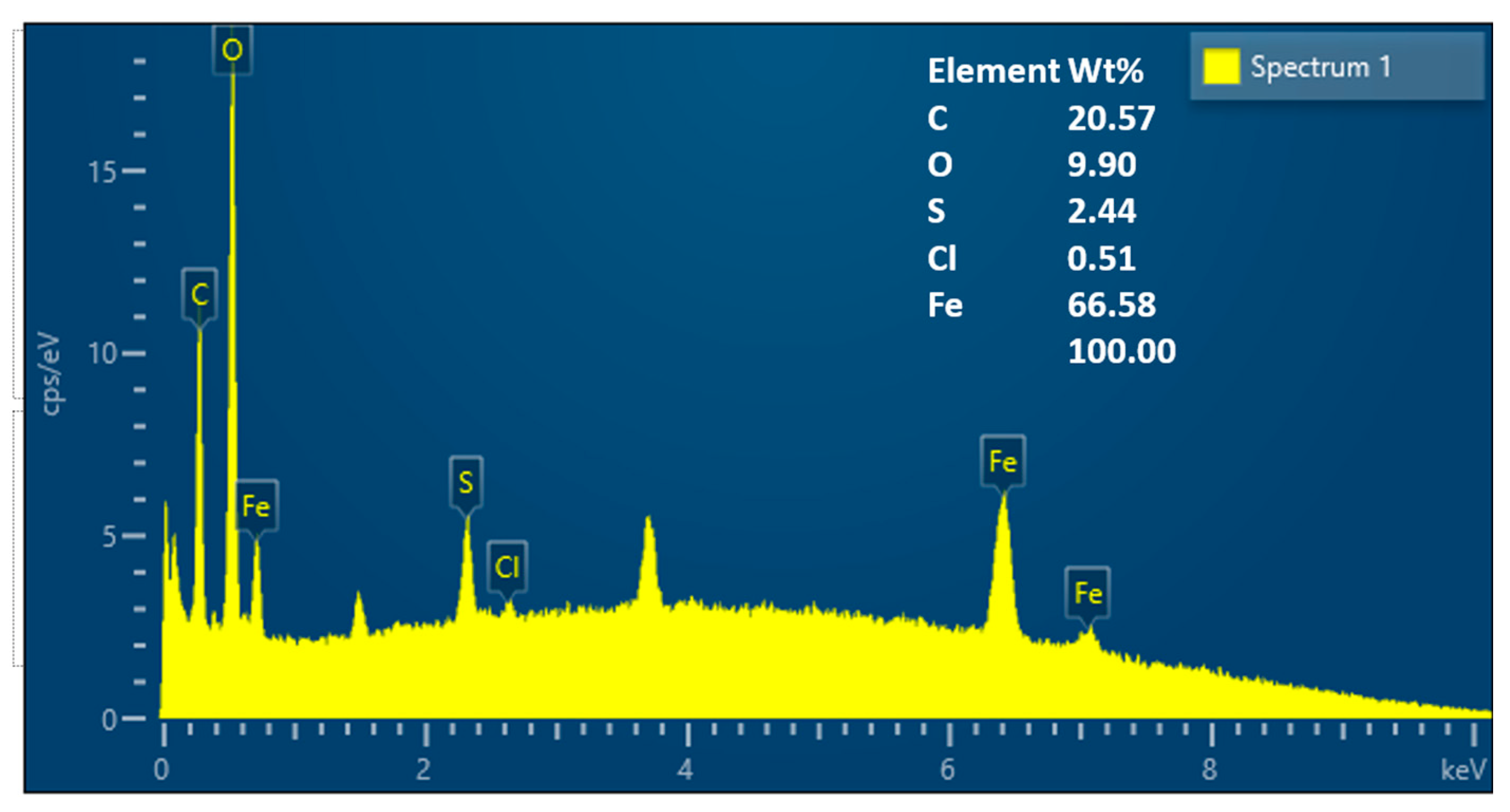
3.1. Characterization of GA-MNPs
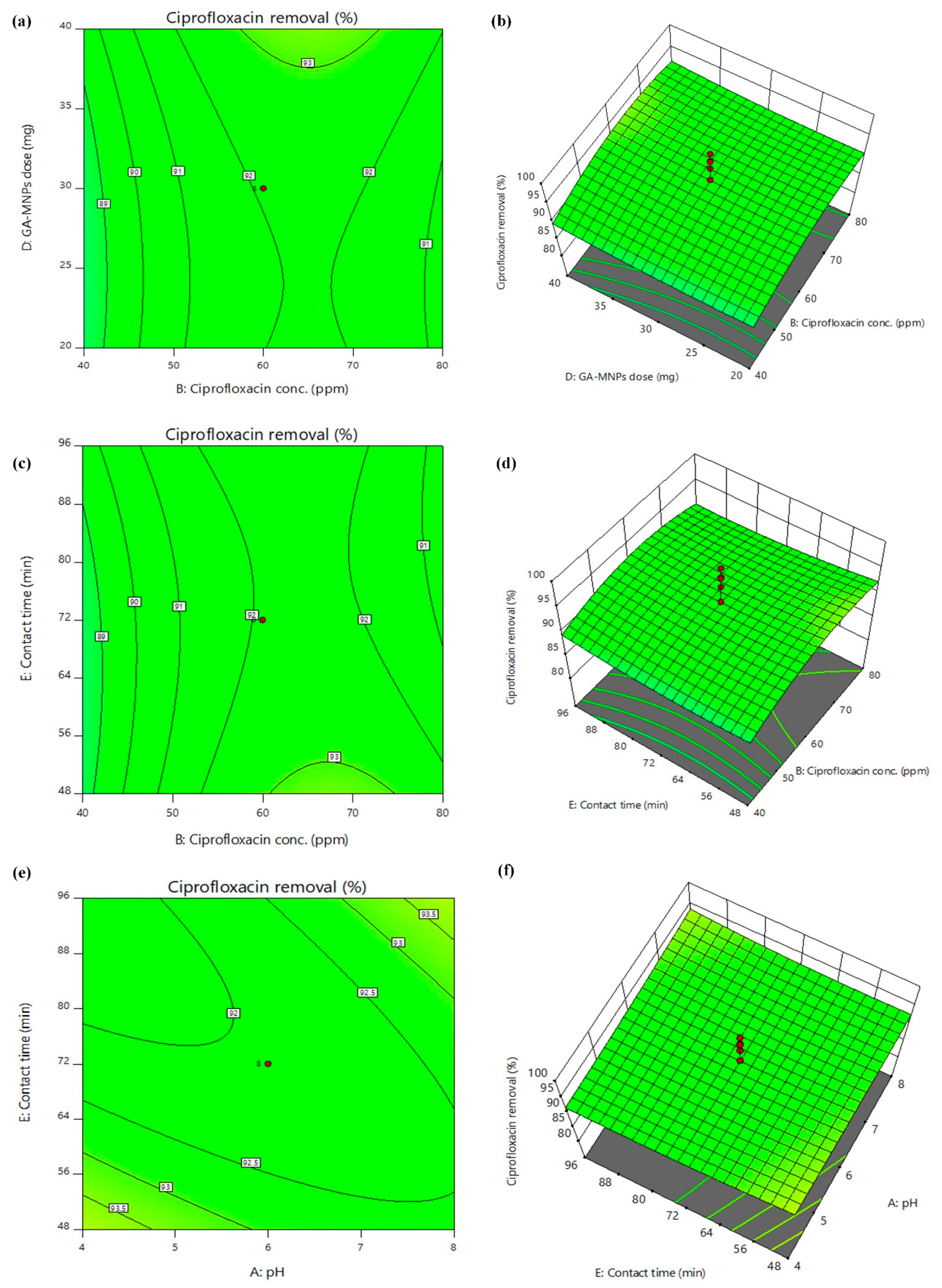
3.2. Effects of Interactive Variables during Process Optimization by RSM
3.2.1. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
3.2.2. D Surface Plots
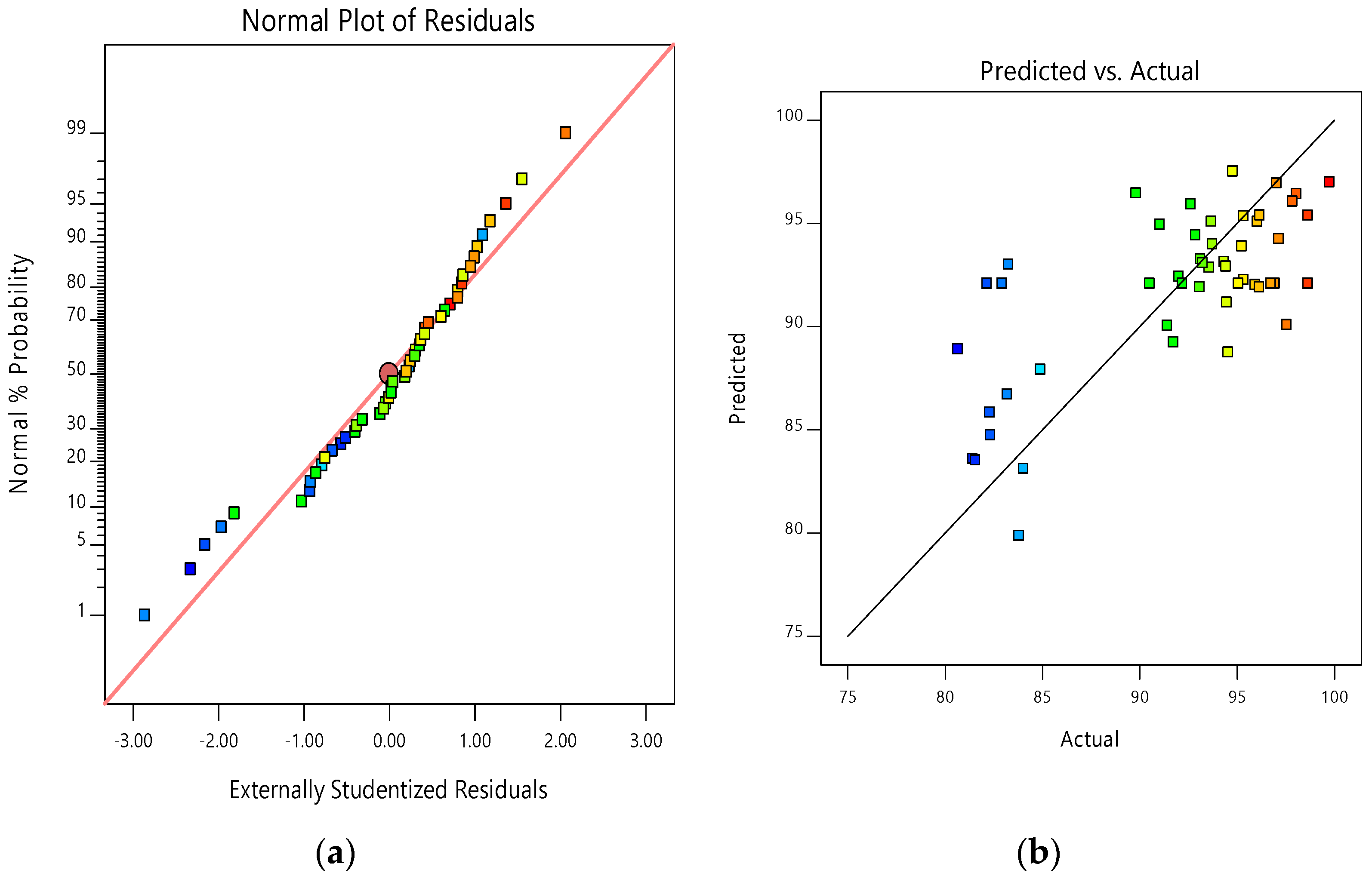
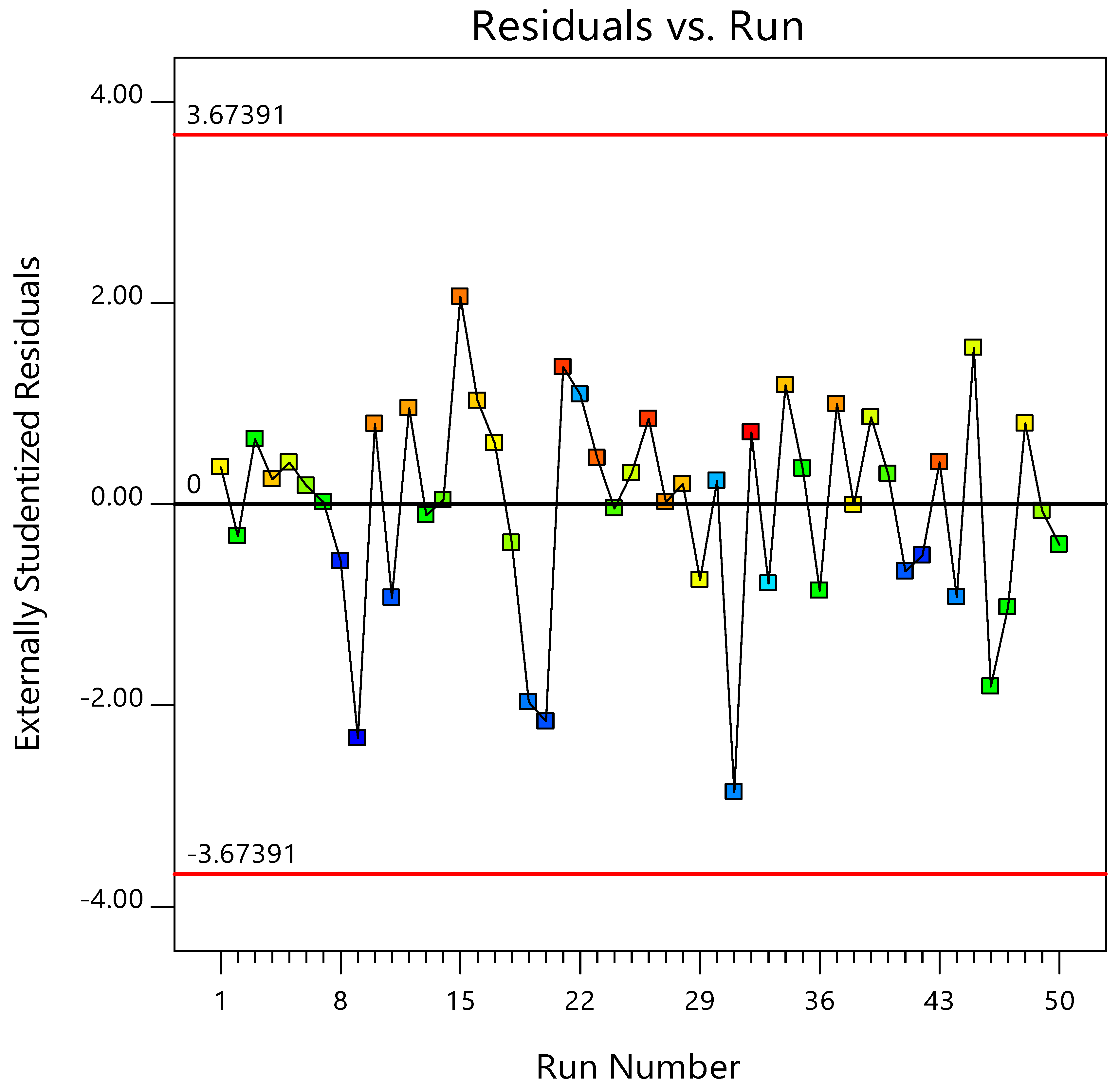
3.2.3. Normal and Predicted Plots
3.3. Sorption Kinetics
3.4. Adsorption Isotherm
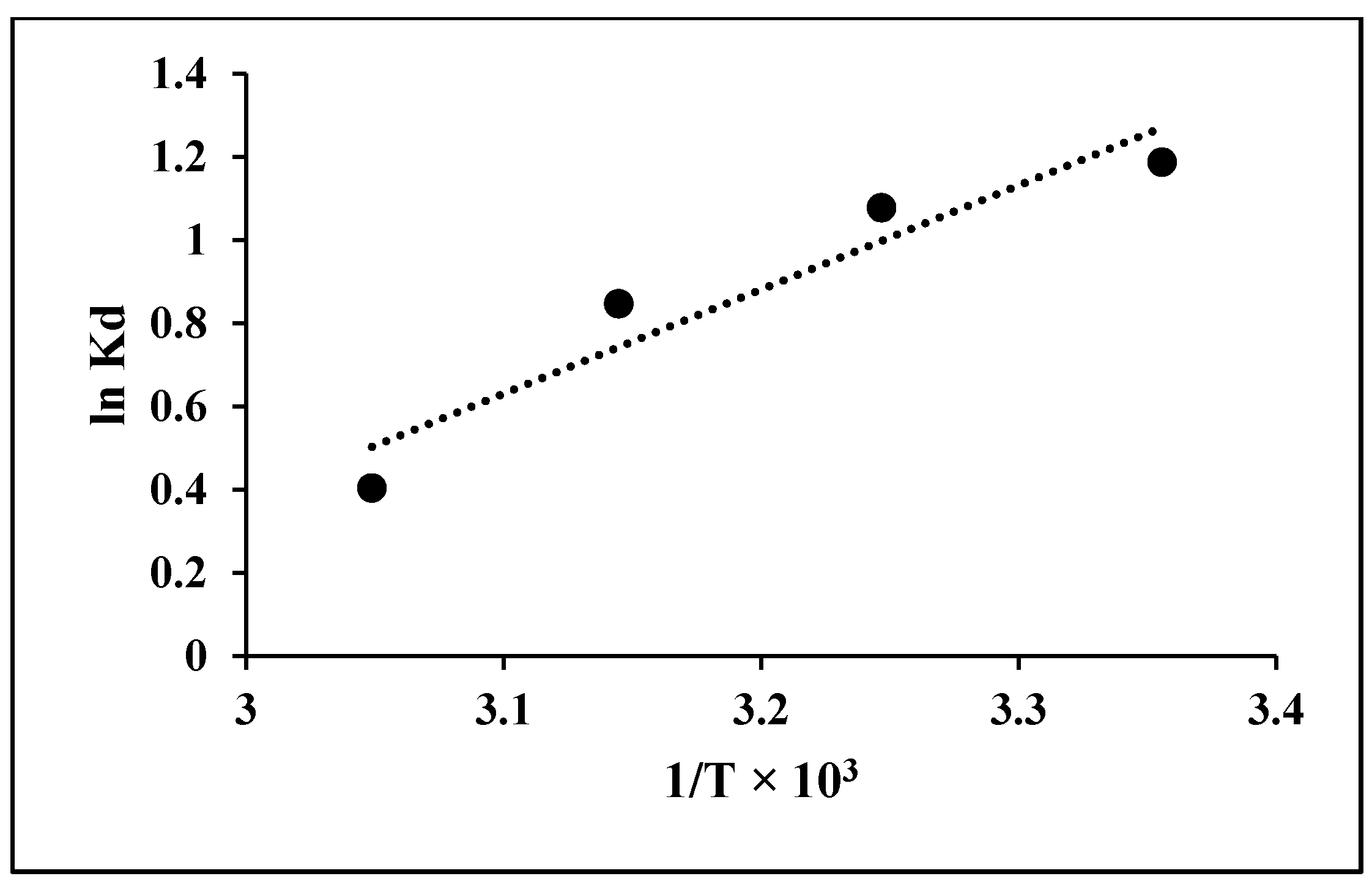
3.5. Thermodynamics Studies
3.6. Adsorption Mechanism
3.7. Comparison of the GA-MNPs with Other Reported Adsorbents
3.8. Adsorbent Regeneration and Reusability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almeida, C.M. Overview of Sample Preparation and Chromatographic Methods to Analysis Pharmaceutical Active Compounds in Waters Matrices. Separations 2021, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anucha, C.B.; Altin, I.; Bacaksız, E.; Kucukomeroglu, T.; Belay, M.H.; Stathopoulos, V.N. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of CuWO4 doped TiO2 photocatalyst towards carbamazepine removal under UV irradiation. Separations 2021, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, S.S.A.; Musa, H.; Habibu, S.; Birniwa, A.H.; Mohammad, R.E.A. Facile synthesis and dyeing performance of some disperse monomeric and polymeric dyes on nylon and polyester fabrics. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2021, 35, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Kumar, A.; Naushad, M.; García-Peñas, A.; Ala’a, H.; Ghfar, A.A.; Sharma, V.; Ahamad, T.; Stadler, F.J. Fabrication and characterization of Gum arabic-cl-poly (acrylamide) nanohydrogel for effective adsorption of crystal violet dye. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 202, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, E.; Arigò, A.; Vento, F.; Micalizzi, G.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L. Influence of citrus flavor addition in brewing process: Characterization of the volatile and non-volatile profile to prevent frauds and adulterations. Separations 2021, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, S.S.; Birniwa, A.H.; Chadi, A.S.; Mohammad, R.E.A.; Mamman, S. Effect of Fiber Surface Modification on the Mechanical Properties of Rice Husk/Glass Fiber Reinforcement Epoxy Resin Hybrid Composite. Niger. Res. J. Chem. Sci. 2020, 8, 147–162. [Google Scholar]
- Fadzli, F.S.; Bhawani, S.A.; Mohammad, R.E. Microbial fuel cell: Recent developments in organic substrate use and bacterial electrode interaction. J. Chem. 2020, 2021, 4570388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Abubakar, S.; Birniwa, A.H.; Lawal, I.M.; Umaru, I.; Usman, A.K.; Yaro, N.S.A.; Al-Zaqri, N.; Al-Maswari, B.M.; et al. Synthesis, Characterization, and Performance Evaluation of Hybrid Waste Sludge Biochar for COD and Color Removal from Agro-Industrial Effluent. Separations 2022, 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.; Yahya, W.Z.N.; Nasef, M.M.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Ghumman, A.S.M.; Afolabi, H.K. Boron removal by glucamine-functionalized inverse vulcanized sulfur polymer. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 177, 105311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birniwa, A.H.; Abubakar, A.S.; Huq, A.O.; Mahmud, H.N.M.E. Polypyrrole-polyethyleneimine (PPy-PEI) nanocomposite: An effective adsorbent for nickel ion adsorption from aqueous solution. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A Pure Appl. Chem. 2021, 58, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.T.; Chang, P.H.; Wang, Y.S.; Tsai, Y.; Jean, J.S.; Li, Z.; Krukowski, K. Removal of ciprofloxacin from water by birnessite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 250, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Isa, M.H.; Ghaleb, A.A.S.; Lawal, I.M.; Usman, A.K.; Birniwa, A.H.; Noor, A.; Abubakar, S.; Umaru, I.; et al. Toxic Effects of Xenobiotic Compounds on the Microbial Community of Activated Sludge. ChemBioEng Rev. 2022, 9, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, S.S.; Musa, H.; Habibu, S.; Birniwa, A.H.; Mohammad, R.E.A. Comparative study and dyeing performance of as-synthesized azo heterocyclic monomeric, polymeric, and commercial disperse dyes. Turk. J. Chem. 2022, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Alqadami, A.A.; Naushad, M.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Alsuhybani, M.; Algamdi, M. Excellent adsorptive performance of a new nanocomposite for removal of toxic Pb (II) from aqueous environment: Adsorption mechanism and modeling analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.Y.; Kang, I.; Kang, H.K.; Ryu, B.G. Synthesis of carboxymethylated nanocellulose fabricated ciprofloxacine–montmorillonite composite for sustained delivery of antibiotics. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 567, 118502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birniwa, A.H.; Abubakar, A.S.; Mahmud, H.N.M.E.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Jagaba, A.H.; Abdullahi, S.S.A.; Zango, Z.U. Application of agricultural wastes for cationic dyes removal from wastewater. In Textile Wastewater Treatment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 239–274. [Google Scholar]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Lawal, I.M.; Aminu, N.; Noor, A.; Al-dhawi, B.N.S.; Usman, A.K.; Batari, A.; Abubakar, S.; Birniwa, A.H.; et al. Diverse sustainable materials for the treatment of petroleum sludge and remediation of contaminated sites: A review. Clean. Waste Syst. 2022, 2, 100010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Que, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Yin, K.; Hong, H. Photodegradation of ciprofloxacin adsorbed in the intracrystalline space of montmorillonite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Noor, A.; Affam, A.C.; Ghfar, A.A.; Usman, A.K.; Lawal, I.M.; Birniwa, A.H.; Kankia, M.U.; Afolabi, H.K. Parametric optimization and kinetic modelling for organic matter removal from agro-waste derived paper packaging biorefinery wastewater. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Garg, A. Degradation of ciprofloxacin using Fenton’s oxidation: Effect of operating parameters, identification of oxidized by-products and toxicity assessment. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Hu, F.; Lam, F.L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Dai, H. Adsorption behavior and mechanisms of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solution by ordered mesoporous carbon and bamboo-based carbon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 460, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, A.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Jagaba, A.H.; Yusuf, M.; Akram, M.W.; Adil, M.R.; Ahmad, N.; Jamal, M. Kinetic modelling of nutrient removal of petroleum industry wastewater remediation. In Proceedings of the 2021 Third International Sustainability and Resilience Conference: Climate Change, Virtual Event, 15–16 November 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 216–220. [Google Scholar]
- Afolabi, H.K.; Nasef, M.M.; Nordin, N.A.H.M.; Ting, T.M.; Harun, N.Y.; Saeed, A.A.H. Isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamics of boron adsorption on fibrous polymeric chelator containing glycidol moiety optimized with response surface method. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naushad, M.; Ahamad, T.; Sharma, G.; Ala’a, H.; Albadarin, A.B.; Alam, M.M.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Alshehri, S.M.; Ghfar, A.A. Synthesis and characterization of a new starch/SnO2 nanocomposite for efficient adsorption of toxic Hg2+ metal ion. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcı, A.; İnci, İ.; Baylan, N. Adsorption of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride on multiwall carbon nanotube. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1206, 127711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcı, A.; İnci, İ.; Baylan, N.A. Comparative adsorption study with various adsorbents for the removal of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride from water. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, T.; Naushad, M.; Al-Shahrani, T.; Al-Hokbany, N.; Alshehri, S.M. Preparation of chitosan based magnetic nanocomposite for tetracycline adsorption: Kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakat, D.; Barik, P.; Bhattacharjee, A. Electrical conductivity behavior of Gum Arabic biopolymer-Fe3O4 nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 112, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; He, L.; Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, X.; Sang, S.; Huang, X. Cyclodextrin derivatives used for the separation of boron and the removal of organic pollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, H.; Morajkar, P.P.; Al Alili, A.; Alhassan, S.M. In-situ synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using gum arabic based hydrogels as a self-template for effective malachite green dye adsorption. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 1637–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renjini, M.; Bindhu, B. An in-depth study on the application of Gum Arabic: A Biopolymer. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2019, 2019, 1120–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Birniwa, A.H.; Abdullahi, S.S. Study on physico-mechanical behaviour of acacia nilotica (gum tree) and glass fiber blend reinforced epoxy resin composite. ChemSearch J. 2019, 10, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Mcnamee, B.F.; O’Riorda, E.D.; O’Sullivan, M. Emulsification and microencapsulation properties of gum arabic. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 4551–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Noor, A.; Isah, A.S.; Lawal, I.M.; Birniwa, A.H.; Usman, A.K.; Abubakar, S. Kinetics of Pulp andPaper Wastewater Treatment by High Sludge Retention Time Activated Sludge Process. J. Hunan Univ. Nat. Sci. 2022, 49, 242–251. [Google Scholar]
- Roque, A.C.; Bicho, A.; Batalha, I.L.; Cardoso, A.S.; Hussain, A. Biocompatible and bioactive gum Arabic coated iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 144, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaro, N.; Napiah, M.; Sutanto, M.; Usman, A.; Jagaba, A.; Mani, A.; Ahmad, A. Geopolymer utilization in the pavement industry-An overview. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Zhuhai, China, 19–21 November 2022; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2022; p. 012025. [Google Scholar]
- Birniwa, A.H.; Abdullahi, S.S.; Yakasai, M.Y.; Ismaila, A. Studies on physico-mechanical behaviour of kenaf/glass fiber reinforced epoxy hybrid composites. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2021, 35, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roque, A.C.A.; Wilson, O.C., Jr. Adsorption of gum Arabic on bioceramic nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2008, 28, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, K.; Baloo, L.; Kutty, S.R.B.; Al Madhoun, W.; Kankia, M.U.; Jagaba, A.H.; Singa, P.K. Optimization of palm oil mill effluent final discharge as biostimulant for biodegradation of tapis light crude petroleum oil in seawater. J. Sea Res. 2022, 188, 102268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.S.; Chen, D.H. Fast removal of copper ions by gum arabic modified magnetic nano-adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birniwa, A.H.; Mahmud, H.N.M.E.; Abdullahi, S.S.; Habibu, S.; Jagaba, A.H.; Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Ahmad, A.; Alshammari, M.B.; Parveen, T.; Umar, K. Adsorption Behavior of Methylene Blue Cationic Dye in Aqueous Solution Using Polypyrrole-Polyethylenimine Nano-Adsorbent. Polymers 2022, 14, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Sagbas, S.; Sahiner, M.; Siddiq, M.; Turk, M.; Aktas, N.; Sahiner, N. Synthesis, characterization, and modification of Gum Arabic microgels for hemocompatibility and antimicrobial studies. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horst, M.F.; Coral, D.F.; van Raap, M.B.F.; Alvarez, M.; Lassalle, V. Hybrid nanomaterials based on gum Arabic and magnetite for hyperthermia treatments. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 74, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasef, S.M.; Badawy, N.; Hafez, F.; Slim, S.; El Nesr, E.M. Preparation and characterization of magnetic nanocomposite based on gum arabic/2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate using gamma irradiation for use in biomedical application. Arab J. Nucl. Sci. Appl. 2019, 52, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaleb, A.; Kutty, S.; Ho, Y.; Jagaba, A.; Noor, A.; Al-Sabaeei, A.; Kumar, V.; Saeed, A. Anaerobic co-digestion for oily-biological sludge with sugarcane bagasse for biogas production under mesophilic condition. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, 10–13 September 2020; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; p. 012084. [Google Scholar]
- Chockalingam, A.M.; Babu, H.K.R.R.; Chittor, R.; Tiwari, J.P. Gum arabic modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles cross linked with collagen for isolation of bacteria. J. Nanobiotechnology 2010, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, A.M.; Dey, R.; Eltaweil, A.S.; Abd El-Monaem, E.M.; Ziora, Z.M. Insights into recent advances of chitosan-based adsorbents for sustainable removal of heavy metals and anions. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.A.H.; Harun, N.Y.; Sufian, S.; Bilad, M.R.; Zakaria, Z.Y.; Jagaba, A.H.; Ghaleb, A.A.S.; Mohammed, H.G. Pristine and magnetic kenaf fiber biochar for Cd2+ adsorption from aqueous solution. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movasaghi, Z.; Yan, B.; Niu, C. Adsorption of ciprofloxacin from water by pretreated oat hulls: Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 127, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, E. Gum Arabic-coated magnetic nanoparticles for methylene blue removal. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2014, 3, 15118–15129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Noor, A.; Birniwa, A.H.; Affam, A.C.; Lawal, I.M.; Kankia, M.U.; Kilaco, A.U. A systematic literature review of biocarriers: Central elements for biofilm formation, organic and nutrients removal in sequencing batch biofilm reactor. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-dhawi, B.N.S.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Baloo, L.; Almahbashi, N.M.Y.; Ghaleb, A.A.S.; Jagaba, A.H.; Kumar, V.; Saeed, A.A.H. Treatment of synthetic wastewater by using submerged attached growth media in continuous activated sludge reactor system. Int. J. Sustain. Build. Technol. Urban Dev. 2022, 2022, 2–10. [Google Scholar]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Baloo, L.; Noor, A.; Abubakar, S.; Lawal, I.M.; Umaru, I.; Usman, A.K.; Kumar, V.; Birniwa, A.H. Effect of hydraulic retention time on the treatment of pulp and paper industry wastewater by extended aeration activated sludge system. In Proceedings of the 2021 Third International Sustainability and Resilience Conference: Climate Change, Virtual Event, 15–16 November 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 221–224. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, R.E.A.; Elbashir, A.A.; Karim, J.; Yahaya, N.; Rahim, N.Y.; Miskam, M. Adsorptive performances of magnetic graphene oxide adsorbent for the removal of fluoroquinolones in the Langat River Basin, Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 2021, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Hayder, G.; Baloo, L.; Noor, A.; Yaro, N.S.A.; Saeed, A.A.H.; Lawal, I.M.; Birniwa, A.H.; Usman, A.K. A systematic literature review on waste-to-resource potential of palm oil clinker for sustainable engineering and environmental applications. Materials 2021, 14, 4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Naushad, M.; Lawal, I.M.; Noor, A.; Affam, A.C.; Birniwa, A.H.; Abubakar, S.; Soja, U.B.; Abioye, K.J. Removal of nutrients from pulp and paper biorefinery effluent: Operation, kinetic modelling and optimization by response surface methodology. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 114091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.A.; Najam, T.; Shah, S.S.A.; Hussain, E.; Ali, H.; Hussain, S.; Shaheen, A.; Ahmad, K.; Ashfaq, M. Development of Mn-PBA on GO sheets for adsorptive removal of ciprofloxacin from water: Kinetics, isothermal, thermodynamic and mechanistic studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 245, 122737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, R.E.A.; Elbashir, A.A.; Karim, J.; Yahaya, N.; Rahim, N.Y.; Miskam, M. Deep Eutectic Solvent Functionalized Graphene Oxide Based Ferrofluid for the Liquid Phase Microextraction of Fluoroquinolones from Water Samples. Key Eng. Mater. 2022, 920, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, I.M.; Bertram, D.; White, C.J.; Jagaba, A.H.; Hassan, I.; Shuaibu, A. Multi-criteria performance evaluation of gridded precipitation and temperature products in data-sparse regions. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lian, J.; Liu, M. Highly efficient and selective removal of low-concentration antibiotics from aqueous solution by regenerable Mg(OH)2. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 87, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Shan, C.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Yao, B.; Gong, G.; Jin, X.; Wang, S. Characterization and Mechanistic Study of Heavy Metal Adsorption by Facile Synthesized Magnetic Xanthate-Modified Chitosan/Polyacrylic Acid Hydrogels. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2022, 19, 11123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, A.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, H.; Sun, P.; Yao, B.; Zang, Y.; Du, X.; Dong, L. Xanthate-Modified Magnetic Fe3O4@ SiO2-Based Polyvinyl Alcohol/Chitosan Composite Material for Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water. Polymers 2022, 14, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Baloo, L.; Birniwa, A.H.; Lawal, I.M.; Aliyu, M.K.; Yaro, N.S.A.; Usman, A.K. Combined treatment of domestic and pulp and paper industry wastewater in a rice straw embedded activated sludge bioreactor to achieve sustainable development goals. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2022, 6, 100261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqadami, A.A.; Naushad, M.; Abdalla, M.A.; Ahamad, T.; AlOthman, Z.A.; Alshehri, S.M.; Ghfar, A.A. Efficient removal of toxic metal ions from wastewater using a recyclable nanocomposite: A study of adsorption parameters and interaction mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 156, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surgutskaia, N.S.; di Martino, A.; Zednik, J.; Ozaltin, K.; Lovecká, L.; Bergerová, E.D.; Kimmer, D.; Svoboda, J.; Sedlarik, V. Efficient Cu2+, Pb2+ and Ni2+ ion removal from wastewater using electrospun DTPA-modified chitosan/polyethylene oxide nanofibers. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 247, 116914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Xu, Z.; Shi, J.; Shen, L.; He, Z. Adsorption characteristics of ciprofloxacin on the schorl: Kinetics, thermodynamics, effect of metal ion and mechanisms. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2018, 8, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Pan, C.; Zheng, X.; Liu, S.; Hu, F.; Xu, L.; Xu, G.; Peng, X. Removal of ciprofloxacin with aluminum-pillared kaolin sodium alginate beads (CA-Al-KABs): Kinetics, isotherms, and BBD model. Water 2020, 12, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnamvand, N.; Ahmadi, S.; Mostafapour, F.K. Kinetic and isotherm studies on ciprofloxacin an adsorption using magnesium oxide nanoparticle. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 7, 079–083. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, A.; Zahoor, M.; Alam, S. Removal of ciprofloxacin from water through magnetic nanocomposite/membrane hybrid processes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 137, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.A.H.; Harun, N.Y.; Sufian, S.; Ghaleb, A.A.S.; Jagaba, A.H.; Mohammed, H.G.; Abdulrab, H.Q.A. Removal of Cadmium (II) from Aqueous Solution by Rice Husk Waste. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Congress of Advanced Technology and Engineering (ICOTEN), Virtual Event, 4–5 July 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Khokhar, T.S.; Memon, F.N.; Memon, A.A.; Durmaz, F.; Memon, S.; Panhwar, Q.K.; Muneer, S. Removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solution using wheat bran as adsorbent. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1278–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Du, C. Halloysite nanotubes as an effective and recyclable adsorbent for removal of low-concentration antibiotics ciprofloxacin. Minerals 2018, 8, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, H.G.; Baloo, L.; Kutty, S.R.; Altaf, M. Post Synthetic Modification of NH2-(Zr-MOF) via Rapid Microwave-Promoted Synthesis for Effective Adsorption of Pb (II) and Cd (II). Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, H.; Yavuz, E.; Sismanoglu, T.; Senkal, B. Functionalization of gum arabic including glycoprotein and polysaccharides for the removal of boron. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 225, 115139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baloo, L.; Isa, M.H.; Sapari, N.B.; Jagaba, A.H.; Wei, L.J.; Yavari, S.; Razali, R.; Vasu, R. Adsorptive removal of methylene blue and acid orange 10 dyes from aqueous solutions using oil palm wastes-derived activated carbons. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 5611–5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolabi, H.K.; Nasef, M.M.; Nordin, N.A.H.M.; Ting, T.M.; Harun, N.Y.; Abbasi, A. Facile preparation of fibrous glycidol-containing adsorbent for boron removal from solutions by radiation-induced grafting of poly (vinylamine) and functionalisation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2021, 188, 109596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | CIP |
|---|---|
| Molecular structure | 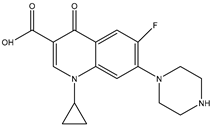 |
| Formula | C17H18FN3O3 |
| Family | Fluoroquinolone |
| Molecular weight (g/mol) | 331.346 |
| pKa | 5.76–8.68 |
| Log P | −0.81 |
| Independent Variables | Symbol | Ranges and Codes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | −α | Low | Centre | High | +α | |
| pH | ka | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| CIP concentration (ppm) | kb | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 |
| Temperature (°C) | kc | 25 | 35 | 45 | 55 | 65 |
| GA-MNPs dose (g) | kd | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
| Contact time (min) | ke | 24 | 48 | 72 | 96 | 120 |
| Factors | Contaminant Removal | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Run | pH | CIP Concentration (ppm) | Temp. (°C) | GA-MNPs Dose (mg) | Contact Time (min) | CIP Removal (%) |
| 1 | 10 | 60 | 45 | 30 | 72 | 95.24 |
| 2 | 6 | 60 | 45 | 30 | 72 | 90.51 |
| 3 | 8 | 40 | 35 | 40 | 96 | 91.73 |
| 4 | 4 | 40 | 55 | 20 | 48 | 96.04 |
| 5 | 6 | 60 | 45 | 10 | 72 | 94.43 |
| 6 | 8 | 80 | 35 | 40 | 48 | 93.57 |
| 7 | 6 | 60 | 45 | 30 | 72 | 92.18 |
| 8 | 4 | 40 | 35 | 20 | 48 | 81.42 |
| 9 | 8 | 40 | 35 | 20 | 96 | 80.65 |
| 10 | 6 | 60 | 45 | 30 | 120 | 97.14 |
| 11 | 4 | 40 | 35 | 20 | 96 | 82.29 |
| 12 | 6 | 60 | 45 | 30 | 72 | 96.74 |
| 13 | 4 | 80 | 35 | 20 | 48 | 92.01 |
| 14 | 2 | 60 | 45 | 30 | 72 | 93.23 |
| 15 | 4 | 40 | 35 | 40 | 96 | 97.54 |
| 16 | 4 | 80 | 35 | 20 | 96 | 95.93 |
| 17 | 6 | 60 | 45 | 30 | 72 | 95.07 |
| 18 | 6 | 60 | 45 | 30 | 24 | 93.68 |
| 19 | 6 | 60 | 45 | 30 | 72 | 82.92 |
| 20 | 6 | 60 | 45 | 30 | 72 | 82.15 |
| 21 | 6 | 60 | 45 | 30 | 72 | 98.64 |
| 22 | 6 | 20 | 45 | 30 | 72 | 83.79 |
| 23 | 8 | 40 | 55 | 20 | 96 | 97.84 |
| 24 | 4 | 80 | 55 | 20 | 48 | 93.11 |
| 25 | 8 | 80 | 55 | 40 | 48 | 94.33 |
| 26 | 4 | 80 | 55 | 40 | 48 | 98.64 |
| 27 | 4 | 80 | 35 | 40 | 48 | 97.03 |
| 28 | 8 | 80 | 35 | 20 | 96 | 96.17 |
| 29 | 6 | 60 | 65 | 30 | 72 | 94.78 |
| 30 | 8 | 40 | 35 | 20 | 48 | 84.02 |
| 31 | 4 | 40 | 55 | 40 | 96 | 83.25 |
| 32 | 4 | 40 | 55 | 40 | 48 | 99.74 |
| 33 | 4 | 40 | 35 | 40 | 48 | 84.89 |
| 34 | 6 | 60 | 25 | 30 | 72 | 96.14 |
| 35 | 8 | 80 | 55 | 40 | 96 | 91.41 |
| 36 | 8 | 80 | 35 | 40 | 96 | 92.63 |
| 37 | 6 | 60 | 45 | 30 | 72 | 96.94 |
| 38 | 6 | 60 | 45 | 50 | 72 | 95.33 |
| 39 | 4 | 40 | 55 | 20 | 96 | 94.47 |
| 40 | 8 | 80 | 55 | 20 | 96 | 93.08 |
| 41 | 6 | 100 | 45 | 30 | 72 | 82.32 |
| 42 | 8 | 40 | 35 | 40 | 48 | 81.55 |
| 43 | 8 | 40 | 55 | 20 | 48 | 98.04 |
| 44 | 4 | 80 | 55 | 20 | 96 | 83.19 |
| 45 | 4 | 80 | 55 | 40 | 96 | 94.54 |
| 46 | 4 | 80 | 35 | 40 | 96 | 89.81 |
| 47 | 8 | 80 | 55 | 20 | 48 | 91.03 |
| 48 | 8 | 80 | 35 | 20 | 48 | 95.34 |
| 49 | 8 | 40 | 55 | 40 | 96 | 93.73 |
| 50 | 8 | 40 | 55 | 40 | 48 | 92.87 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 777.01 | 20 | 38.85 | 1.44 | 0.1834 | significant |
| A-pH | 1.64 | 1 | 1.64 | 0.0607 | 0.8071 | |
| B-CIP concentration. | 59.56 | 1 | 59.56 | 2.20 | 0.1488 | |
| C-Temp. | 78.43 | 1 | 78.43 | 2.90 | 0.0994 | |
| D-GA-MNPs dose | 14.92 | 1 | 14.92 | 0.5512 | 0.4638 | |
| E-Contact time | 1.79 | 1 | 1.79 | 0.0659 | 0.7992 | |
| AB | 0.1969 | 1 | 0.1969 | 0.0073 | 0.9326 | |
| AC | 6.67 | 1 | 6.67 | 0.2464 | 0.6234 | |
| AD | 30.67 | 1 | 30.67 | 1.13 | 0.2959 | |
| AE | 25.12 | 1 | 25.12 | 0.9278 | 0.3434 | |
| BC | 226.05 | 1 | 226.05 | 8.35 | 0.0072 | |
| BD | 0.0770 | 1 | 0.0770 | 0.0028 | 0.9578 | |
| BE | 14.08 | 1 | 14.08 | 0.5203 | 0.4765 | |
| CD | 11.53 | 1 | 11.53 | 0.4260 | 0.5191 | |
| CE | 75.68 | 1 | 75.68 | 2.80 | 0.1053 | |
| DE | 0.0109 | 1 | 0.0109 | 0.0004 | 0.9841 | |
| A² | 3.97 | 1 | 3.97 | 0.1467 | 0.7045 | |
| B² | 190.94 | 1 | 190.94 | 7.05 | 0.0127 | |
| C² | 13.88 | 1 | 13.88 | 0.5127 | 0.4797 | |
| D² | 8.44 | 1 | 8.44 | 0.3118 | 0.5809 | |
| E² | 13.36 | 1 | 13.36 | 0.4934 | 0.4880 | |
| Residual | 785.07 | 29 | 27.07 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 503.05 | 22 | 22.87 | 0.5676 | 0.8537 | not significant |
| Pure Error | 282.02 | 7 | 40.29 | |||
| Cor Total | 1562.08 | 49 |
| Model Comparison Statistics | Fit Statistics | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PRESS | 2165.67 | Std. Dev. | 5.20 |
| −2 Log Likelihood | 279.58 | Mean | 91.86 |
| BIC | 361.73 | C.V. % | 5.66 |
| AICc | 354.58 | R² | 0.4974 |
| Adjusted R² | 0.1508 | ||
| Predicted R² | −0.3864 | ||
| Adeq Precision | 5.2332 | ||
| Coefficient Estimate | df | Standard Error | 95% Cl Low | 95% Cl High | VIF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 92.08 | 1 | 1.80 | 88.39 | 95.77 | |
| A2212 pH | 0.2027 | 1 | 0.8227 | 2212 1.48 | 1.89 | 1.0000 |
| B2212 CIP concentration | 1.22 | 1 | 0.8227 | 2212 0.4623 | 2.90 | 1.0000 |
| C2212 Temp. | 1.40 | 1 | 0.8227 | 2212 0.2823 | 3.08 | 1.0000 |
| D2212 GA2212 MNPs dose | 0.6107 | 1 | 0.8227 | 2212 1.07 | 2.29 | 1.0000 |
| E2212 Contact time | −0.2113 | 1 | 0.8227 | −1.89 | 1.47 | 1.0000 |
| AB | 0.0784 | 1 | 0.9198 | −1.80 | 1.96 | 1.0000 |
| AC | 0.4566 | 1 | 0.9198 | −1.42 | 2.34 | 1.0000 |
| AD | −0.9791 | 1 | 0.9198 | −2.86 | 0.9021 | 1.0000 |
| AE | 0.8859 | 1 | 0.9198 | −0.9952 | 2.77 | 1.0000 |
| BC | −2.66 | 1 | 0.9198 | −4.54 | −0.7767 | 1.0000 |
| BD | 0.0491 | 1 | 0.9198 | −1.83 | 1.93 | 1.0000 |
| BE | −0.6634 | 1 | 0.9198 | −2.54 | 1.22 | 1.0000 |
| CD | −0.6003 | 1 | 0.9198 | −2.48 | 1.28 | 1.0000 |
| CE | −1.54 | 1 | 0.9198 | −3.42 | 0.3433 | 1.0000 |
| DE | −0.0184 | 1 | 0.9198 | −1.90 | 1.86 | 1.0000 |
| A² | 0.3523 | 1 | 0.9198 | −1.53 | 2.23 | 1.0000 |
| B² | −2.44 | 1 | 0.9198 | −4.32 | −0.5615 | 1.0000 |
| C² | 0.6586 | 1 | 0.9198 | −1.22 | 2.54 | 1.0000 |
| D² | 0.5136 | 1 | 0.9198 | −1.37 | 2.39 | 1.0000 |
| E² | 0.6461 | 1 | 0.9198 | −1.24 | 2.53 | 1.0000 |
| Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | Elovich | Intraparticle Diffusion | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe exp | 4.929 | qe cal | 4.8473 | qe cal | 19.6405 | ||
| qe cal | 1.3799 | K2 | 0.3118 | β | 3.7693 | C | 4.1065 |
| K1 | 91.0905 | h | 7.3266 | 0.7007 | K | 0.0844 | |
| R2 | 0.1936 | R2 | 0.9984 | R2 | 0.7939 | R2 | 0.6099 |
| Langmuir | Freundlich | Temkin | Dubinin–Radushkevich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax | 54.6449 | KF | 6.982 | KT | 3.196 | qmax | 25.2065 |
| RL | 0.1007 | nF | 1.542 | b | 275.24 | E | 4.7114 |
| R2 | 0.9026 | R2 | 0.9836 | R2 | 0.9025 | R2 | 0.8613 |
| T (K) | Enthalpy, ∆H (kJ mol−1) | Entropy, ∆S (J mol−1 K−1) | Gibbs Energy, ∆G (kJ mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | −20.79 | −59.21 | −2945.0376 |
| 308 | −2764.2747 | ||
| 318 | −2241.324 | ||
| 328 | −1102.7939 |
| Adsorbent | pH | Isotherm Models | Kinetic Models | Percentage Removal (%R) | qe (mg g−1) | Equilibrium Time | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schorl | 5.5 | Freundlich | pseudo-second-order | - | 8.49 | 720 min | [66] |
| Magnesium Oxide Nanopartices | 5.7 | Langmuir | pseudo-second-order | 85 | 3.46 | 60 min | [68] |
| Oat hulls | 7 | Freundlich | pseudo-second-order | - | 83 | - | [51] |
| Aluminum-Pillared Kaolin Sodium Alginate Beads | 4 | Langmuir | pseudo-first-order | - | 68.36 | 1440 min | [67] |
| magnetic Nanocomposite/membrane | 7 | - | pseudo-first-order | 96 | - | 80 min | [69] |
| Multiwall carbon nanotube | - | Freundlich | pseudo-first-order | 91.84 | 1.7446 | 120 min | [25] |
| Birnessite | 6 | Freundlich and Langmuir | pseudo-first-order | - | 72 | 1440 min | [11] |
| Biochar | 8 | Freundlich | pseudo-second-order | - | - | 1440 min | [70] |
| Activated carbon | - | Freundlich | pseudo-second-order | 93.39 | 0.4680 | 200 min | [26] |
| Wheat bran | 3 | Langmuir and D-R | pseudo-second-order | - | 159 | 60 min | [71] |
| Halloysite Nanotubes | 6 | Langmuir | pseudo-second-order | - | 1.0172 | 90 min | [72] |
| GA-MNPs | 7 | Freundlich | pseudo-second-order | 96.34 | 54.6449 | 60 min | This study |
| Contaminant | Adsorbent | No. of Regeneration Cycles | Maximum Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Initial Removal Efficiency | Final Removal Efficiency | % Loss | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boron | Poly saccharide derivative functional hollow silica sphere (HSGUM) | 4 | 217.4 | 88 | 63 | 25 | [74] |
| Pb(II) | Fe3O4@TATS@ ATA | 4 | 205.2 | 91 | 78 | 13 | [14] |
| Crystal violet dye. | Gum arabic-cl-poly(acrylamide) nanohydrogel | 6 | 90.90 | 79 | 67 | 12 | [4] |
| Pb(II) | UiO-66-NH2 modified by Glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) | 5 | 238.80 | 84 | 80.53 | 3.47 | [73] |
| Cd(II) | 208.45 | 90 | 83.67 | 6.33 | |||
| Boron | Polymeric chelator containing glycidol moiety | 5 | 25.7 | 98.94 | 95.21 | 3.73 | [23] |
| Methylene blue dyes | Oil palm wastes-derived activated carbon | 5 | 54.00 | 98.09 | 72.21 | 25.88 | [75] |
| Acid orange 10 dyes | 36.75 | 78.58 | 60.11 | 18.47 | |||
| CIP | GA-MNPs | 7 | 54.64 | 96.34 | 82.99 | 13.35 | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Birniwa, A.H.; Mohammad, R.E.A.; Ali, M.; Rehman, M.F.; Abdullahi, S.S.; Eldin, S.M.; Mamman, S.; Sadiq, A.C.; Jagaba, A.H. Synthesis of Gum Arabic Magnetic Nanoparticles for Adsorptive Removal of Ciprofloxacin: Equilibrium, Kinetic, Thermodynamics Studies, and Optimization by Response Surface Methodology. Separations 2022, 9, 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9100322
Birniwa AH, Mohammad REA, Ali M, Rehman MF, Abdullahi SS, Eldin SM, Mamman S, Sadiq AC, Jagaba AH. Synthesis of Gum Arabic Magnetic Nanoparticles for Adsorptive Removal of Ciprofloxacin: Equilibrium, Kinetic, Thermodynamics Studies, and Optimization by Response Surface Methodology. Separations. 2022; 9(10):322. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9100322
Chicago/Turabian StyleBirniwa, Abdullahi Haruna, Rania Edrees Adam Mohammad, Mujahid Ali, Muhammad Faisal Rehman, Shehu Sa’ad Abdullahi, Sayed M. Eldin, Suwaiba Mamman, Abubakar Chadi Sadiq, and Ahmad Hussaini Jagaba. 2022. "Synthesis of Gum Arabic Magnetic Nanoparticles for Adsorptive Removal of Ciprofloxacin: Equilibrium, Kinetic, Thermodynamics Studies, and Optimization by Response Surface Methodology" Separations 9, no. 10: 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9100322
APA StyleBirniwa, A. H., Mohammad, R. E. A., Ali, M., Rehman, M. F., Abdullahi, S. S., Eldin, S. M., Mamman, S., Sadiq, A. C., & Jagaba, A. H. (2022). Synthesis of Gum Arabic Magnetic Nanoparticles for Adsorptive Removal of Ciprofloxacin: Equilibrium, Kinetic, Thermodynamics Studies, and Optimization by Response Surface Methodology. Separations, 9(10), 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9100322








