Sensitivity Increase in Headspace Analysis of Hydrocarbons in Water by Using Online Selective Elimination of Gas Extractant
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
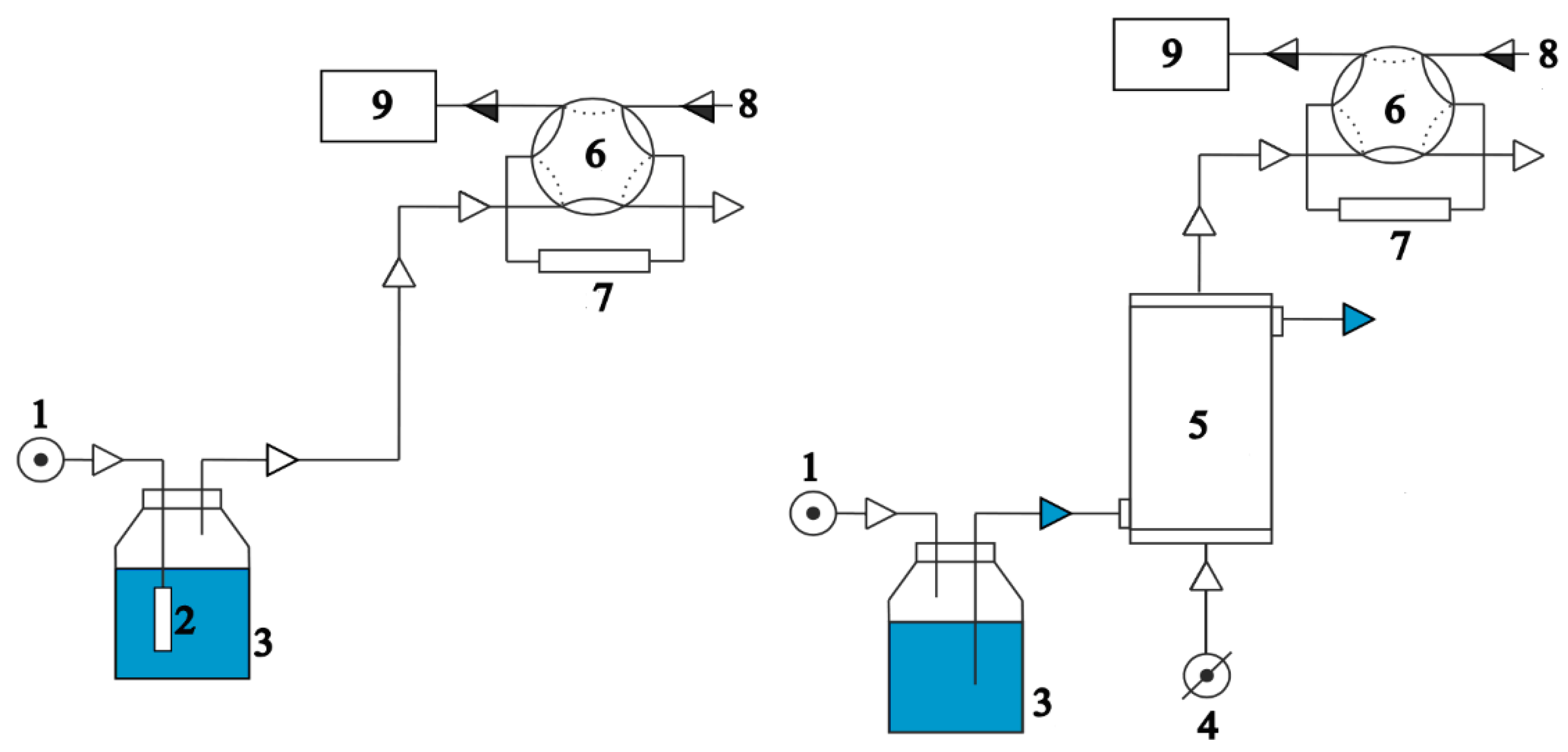
2.1. Theoretical Background
2.2. Reagents
2.3. Instrumentation
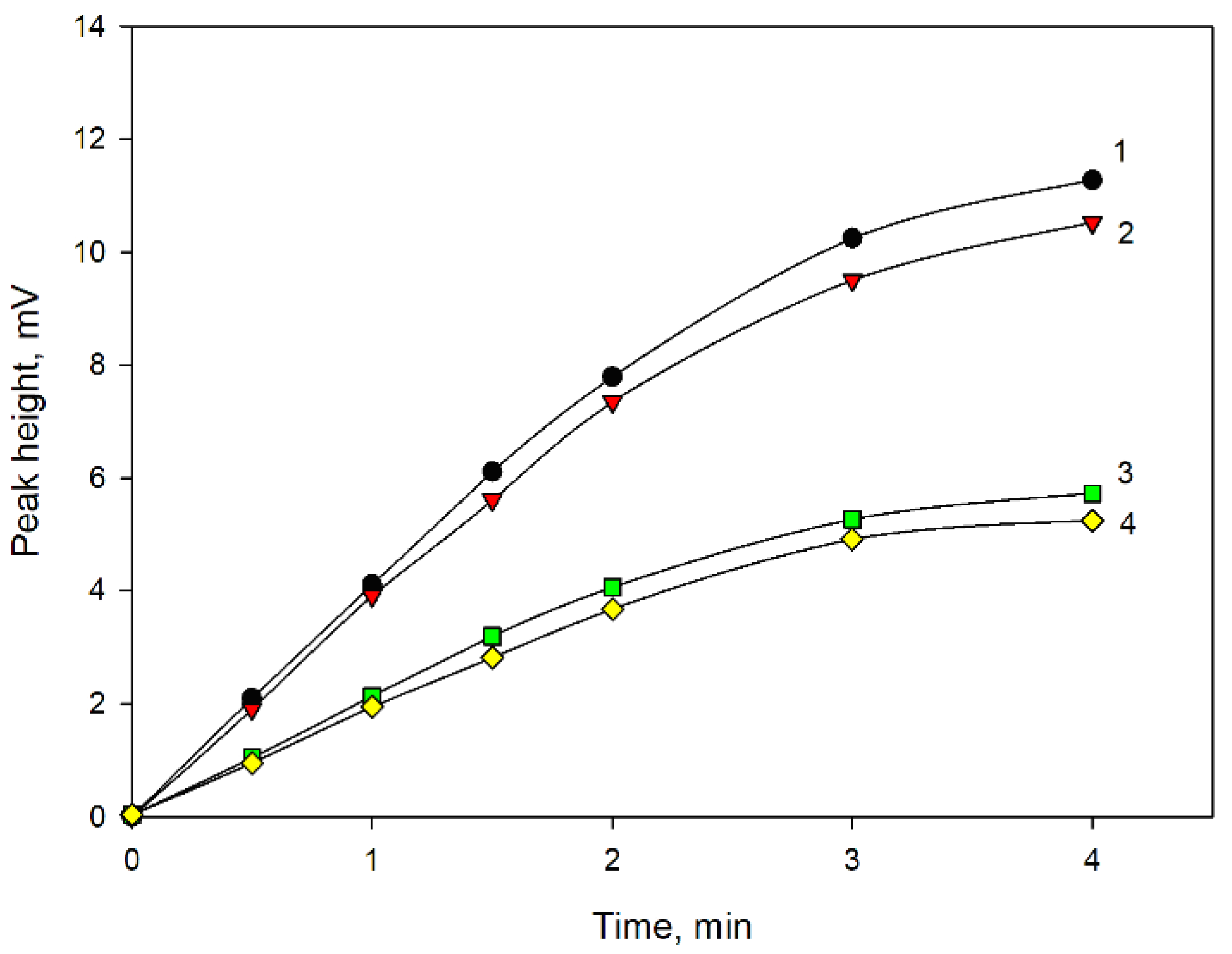
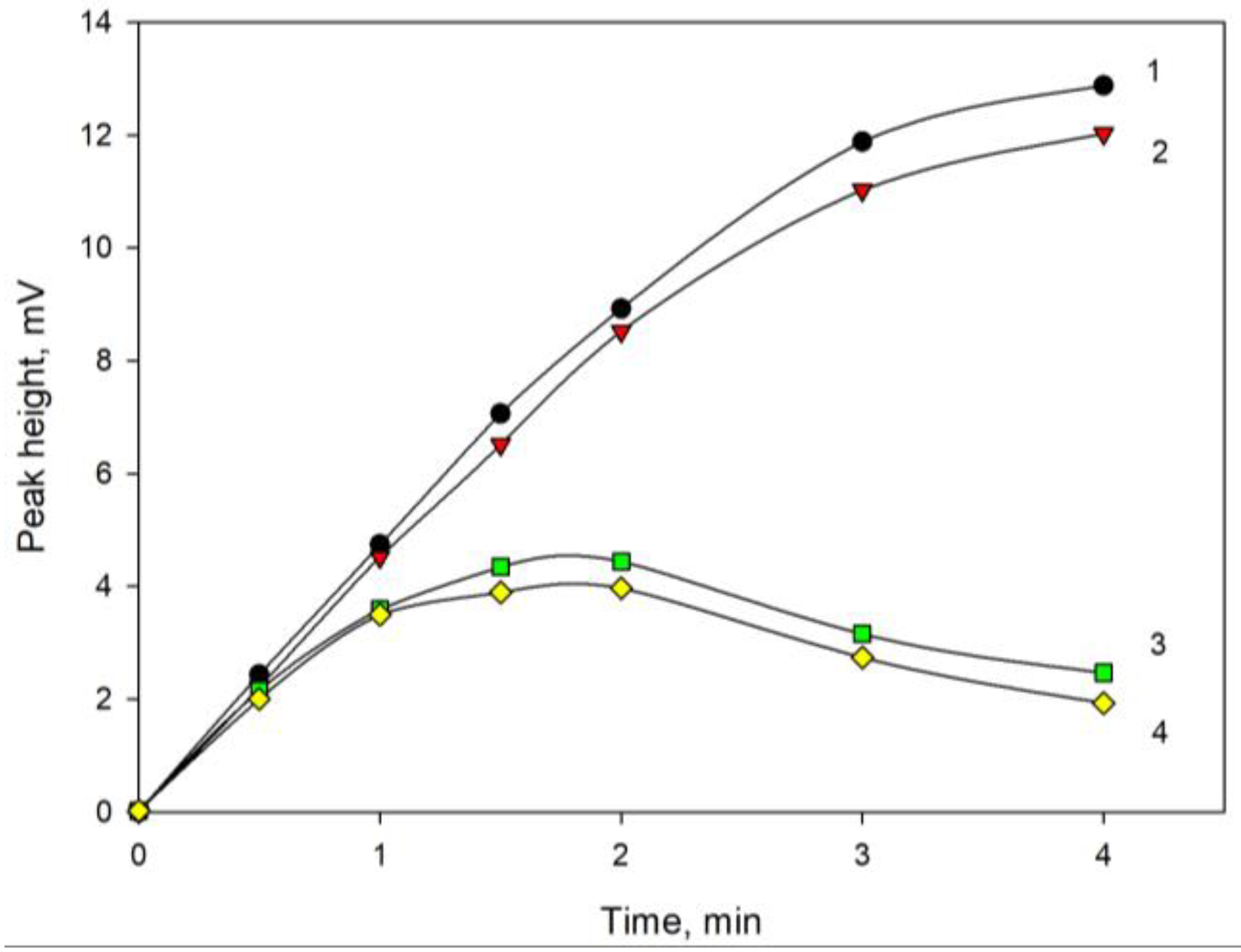
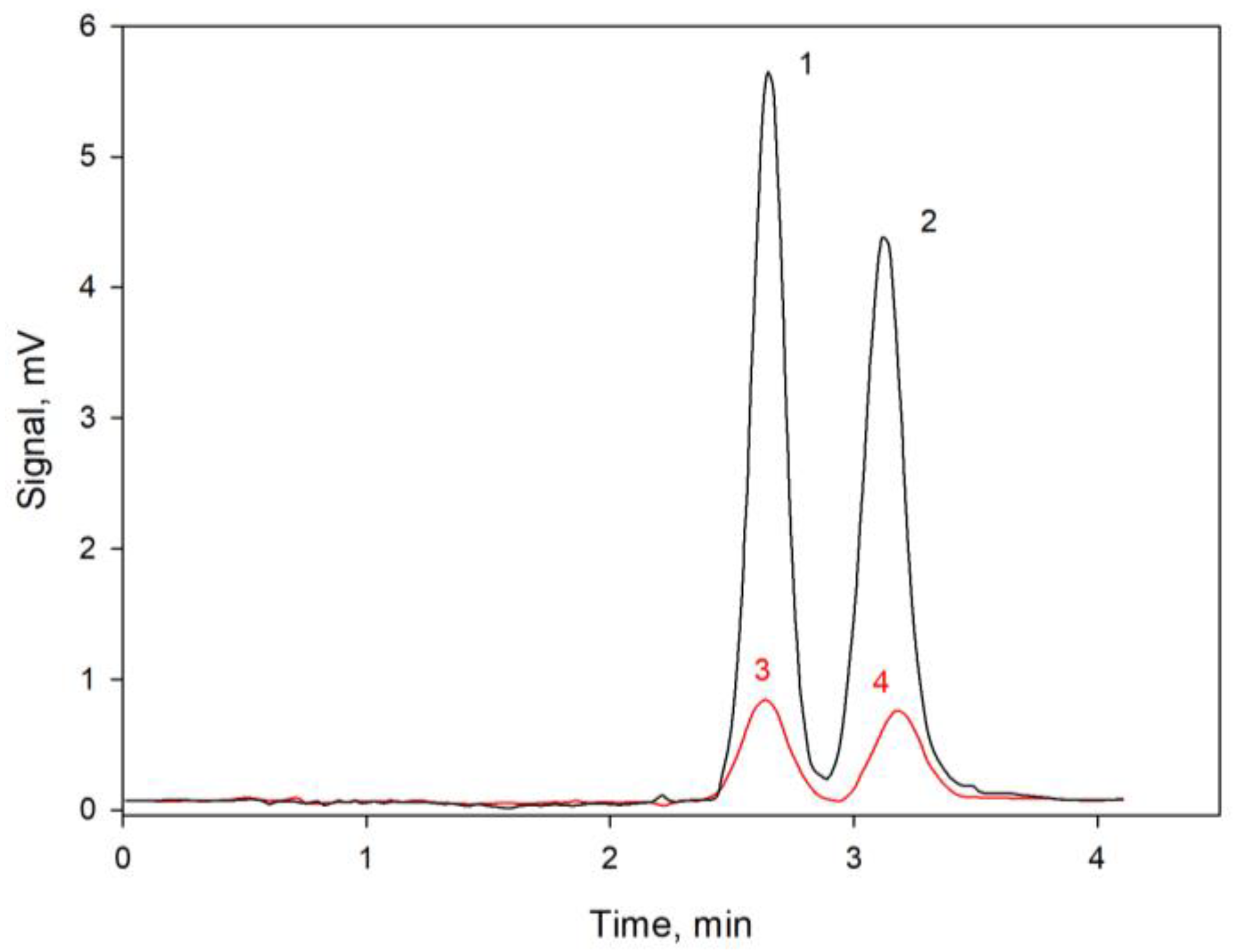
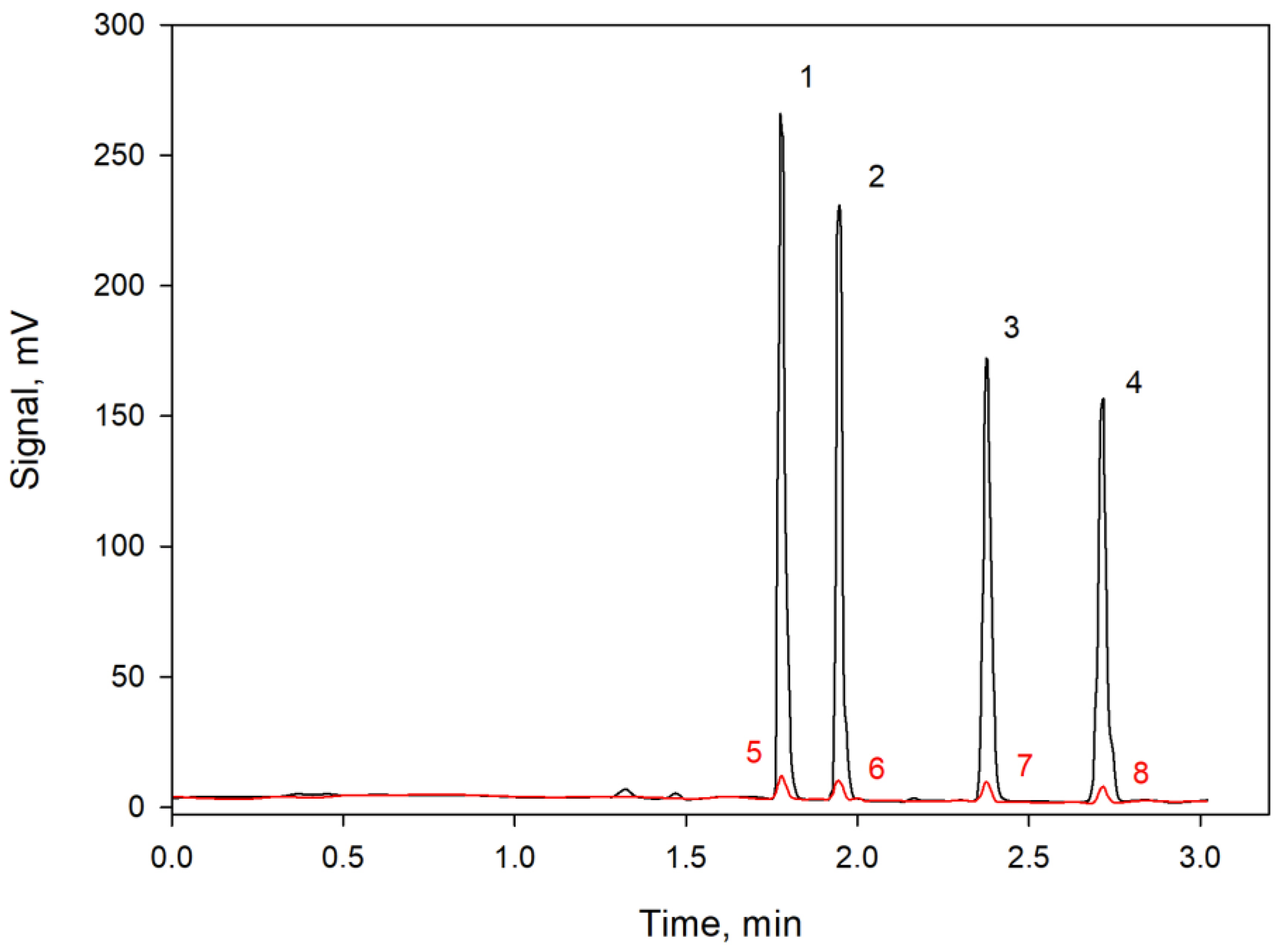
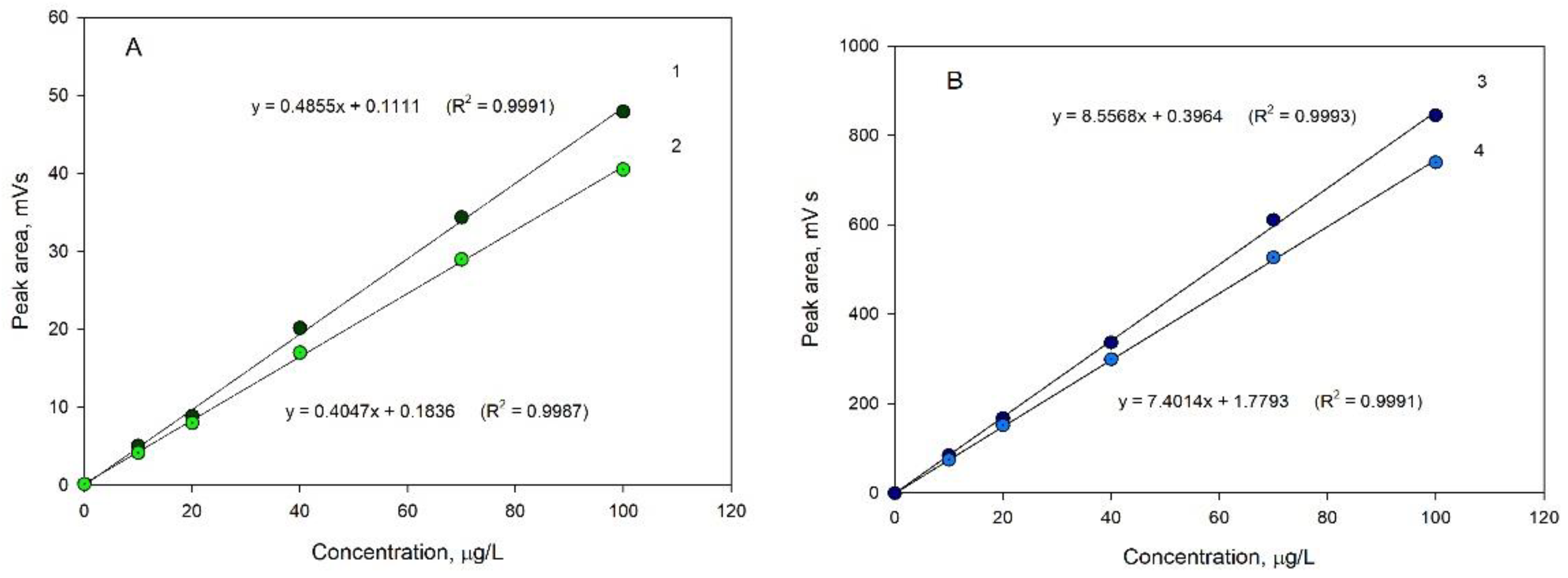
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Demestere, K.; De Wulf, J. Sample preparation for the analysis of volatile organic compounds in air and water matrices. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1153, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, X.; Qiu, C. Sample preparation. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1184, 191–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chary, N.S.; Fernandez-Alba, A. Determination of volatile organic compounds in drinking and environmental waters. Trend Anal. Chem. 2012, 32, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, C.V.; Koukouraki, E.; Diamadopoulos, E. Determination of chlorinated volatile organic compounds in water and municipal wastewater using headspace-solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1132, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Huang, P.; Zhang, M.; Li, W.-Q. A purge and trap gas chromatographic method for detection of chlorofluorocarbons in seawater. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 41, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodinkov, O.; Bugaichenko, A.; Moskvin, L. Static head space analysis and its status. J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 75, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwan, A.; Singh, B.; Roychowdhury, T.; Yan, D.D.; Tedone, L.; Nesterenko, P.N.; Paull, B.; Sevy, E.T.; Shellie, R.A.; Kaykhaii, M.; et al. Porous, high capacity coatings for solid phase microextraction (SPME) by sputtering. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambropoulou, D.A.; Konstantinou, I.K.; Albanis, T.A. Recent developments in headspace microextraction techniques for the analysis of environmental contaminants in different matrices. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1152, 70–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara-Gonzalo, A.; Sanchez-Urıa, J.E.; Segovia-Garcıa, E.S.; Sanz-Medel, A.S. Critical comparison of automated purge and trap and solid-phase microextraction for routine determination of volatile organic compounds in drinking waters by GC-MS. Talanta 2008, 74, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrington, J.; Gomez-Ríos, G.; Myers, C.; Stidsen, G.; Bell, D. Hunting molecules in complex matrices with SPME arrows: A review. Separations 2002, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paiva, C.; Crucello, J.; Porto, N.; Hantao, L. Fundamentals of and recent advances in sorbent-based headspace extractions. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 139, 116252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueta, I.; Razaka, N.; Mizuguchia, A.; Kawakuboa, S.; Saitob, Y.; Jinno, K. Needle-type extraction device for the purge and trap analysis of 23 volatile organic compounds in tap water. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1317, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojnowski, W.; Majchrzak, T.; Dymerski, T.; Gebicki, J.; Namiesnik, J. Dynamic headspace sampling as an initial step for sample preparation in chromatographic analysis. J. AOAC Inter. 2017, 100, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; Miller, S.; Emmert, G.L. On-line purge and trap gas chromatography for monitoring of trihalomethanes in drinking water distribution systems. Anal. Chem. Acta 2007, 592, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saridara, C.; Brukh, R.; Mitra, S. Development of continuous on-line purge and trap analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2006, 29, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, N.R.; Manzke, B.U.; Schulz-Bull, D.E. Development of a purge and trap continuous flow system for the stable carbon isotope analysis of volatile halogenated organic compounds in water. J. Chromatogr. 2006, 1131, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyötyläinen, T. Principles, developments and applications of on-line coupling of extraction with chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1153, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyötyläinen, T. On-line coupling of extraction with gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1186, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, L. Critical overview of selected contemporary sample preparation techniques. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1221, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenarsari, S.D.; Yang, D.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Russell, A.G.; Wei, Q.; Fan, M. Review of recent advances in carbon dioxide separation and capture. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 22739–22773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhan, H.; Fu, S.; Liu, M.; Chai, X.-S. Rapid determination of methanol in black liquors by full evaporation headspace gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1175, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodinkov, O.V.; Zhuravljova, G.A.; Vaskova, E.A.; Platonov, I.A. Potassium fluoride as a selective moisture trapping agent for SPE-TD-GC-FID determination of volatile organic compounds in air. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, L.L.; Davis, B.H. Review of absorption and adsorption in the hydrogen-palladium system. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2006, 310, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorini, D.; Boarelli, M.C. Solid-phase microextraction may catalize hydrogenation when using hydrogen as carrier in gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1453, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kianpour, M.; Sobati, M.; Shahhosseini, S. Experimental and modeling of CO2 capture by dry sodium hydroxide carbonation. Chem. Eng. Res. Design 2012, 90, 2041–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskvin, L.N.; Rodinkov, O.V. Continuous chromatomembrane headspace analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 1996, 725, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskvin, L.N.; Rodinkov, O.V.; Moskvin, A.L.; Spivakovskii, V.; Vlasov, A.Y.; Bugaichenko, A.S.; Samokhin, A.S.; Nesterenko, P.N. Chromatomembrane preconcentration of phenols using a new 3D printed microflow cell followed by reversed-phase HPLC determination. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 2449–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D.R. (Ed.) Aqueous Solubility and Henry’s Law Constants of Organic Compounds. In CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics; Internet Version 2005; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, B.V.; Vitenberg, A.G. Head-Space Analysis and Related Methods in Gas Chromatography; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Lazarev, N.V.; Levina, E.N. Harmful substances in industry. In Handbook for Chemists, Engineers and Doctors; Organic Substances; Khimiya: Saint Petersburg, Russia, 1976; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Toluene in drinking-water. In WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- Benzene in drinking-water. In WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- GN 2.1.5.2280-07; Maximum Allowable Concentrations (MAC) of Chemical Substances in Water of Water Objects of Domestic and General Water Use; Hygiene Standards: Moscow, Russia, 2008.
- Golfinopoulos, S.K.; Lekkas, T.D.; Nikolaou, A.D. Comparison of methods for determination of volatile organic compounds in drinking water. Chemosphere 2001, 45, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Analyte | Boiling Temperature, °C [28] | Solubility in Water (25 °C), g/L [28] | K 1, at 25 °C [29,30] | Maximum Allowable in Water, μg/L | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WHO [31,32] | Russia [33] | ||||
| Benzene | 80.1 | 1.78 | 4.0 [29] | 10 | 1.0 |
| Toluene | 110.6 | 0.531 | 3.6 [29] | 700 | 24 |
| n-Hexane | 69.0 | 0.11 | 0.021 [30] | - | |
| n-Heptane | 98.4 | 0.024 | 0.019 [30] | - | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodinkov, O.V.; Pisarev, A.Y.; Moskvin, L.N.; Bugaichenko, A.S.; Nesterenko, P.N. Sensitivity Increase in Headspace Analysis of Hydrocarbons in Water by Using Online Selective Elimination of Gas Extractant. Separations 2022, 9, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9010015
Rodinkov OV, Pisarev AY, Moskvin LN, Bugaichenko AS, Nesterenko PN. Sensitivity Increase in Headspace Analysis of Hydrocarbons in Water by Using Online Selective Elimination of Gas Extractant. Separations. 2022; 9(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodinkov, Oleg V., Alexey Y. Pisarev, Leonid N. Moskvin, Aleksandra S. Bugaichenko, and Pavel N. Nesterenko. 2022. "Sensitivity Increase in Headspace Analysis of Hydrocarbons in Water by Using Online Selective Elimination of Gas Extractant" Separations 9, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9010015
APA StyleRodinkov, O. V., Pisarev, A. Y., Moskvin, L. N., Bugaichenko, A. S., & Nesterenko, P. N. (2022). Sensitivity Increase in Headspace Analysis of Hydrocarbons in Water by Using Online Selective Elimination of Gas Extractant. Separations, 9(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9010015








