Review of New Approaches for Fouling Mitigation in Membrane Separation Processes in Water Treatment Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Strategies for Mitigation of Fouling
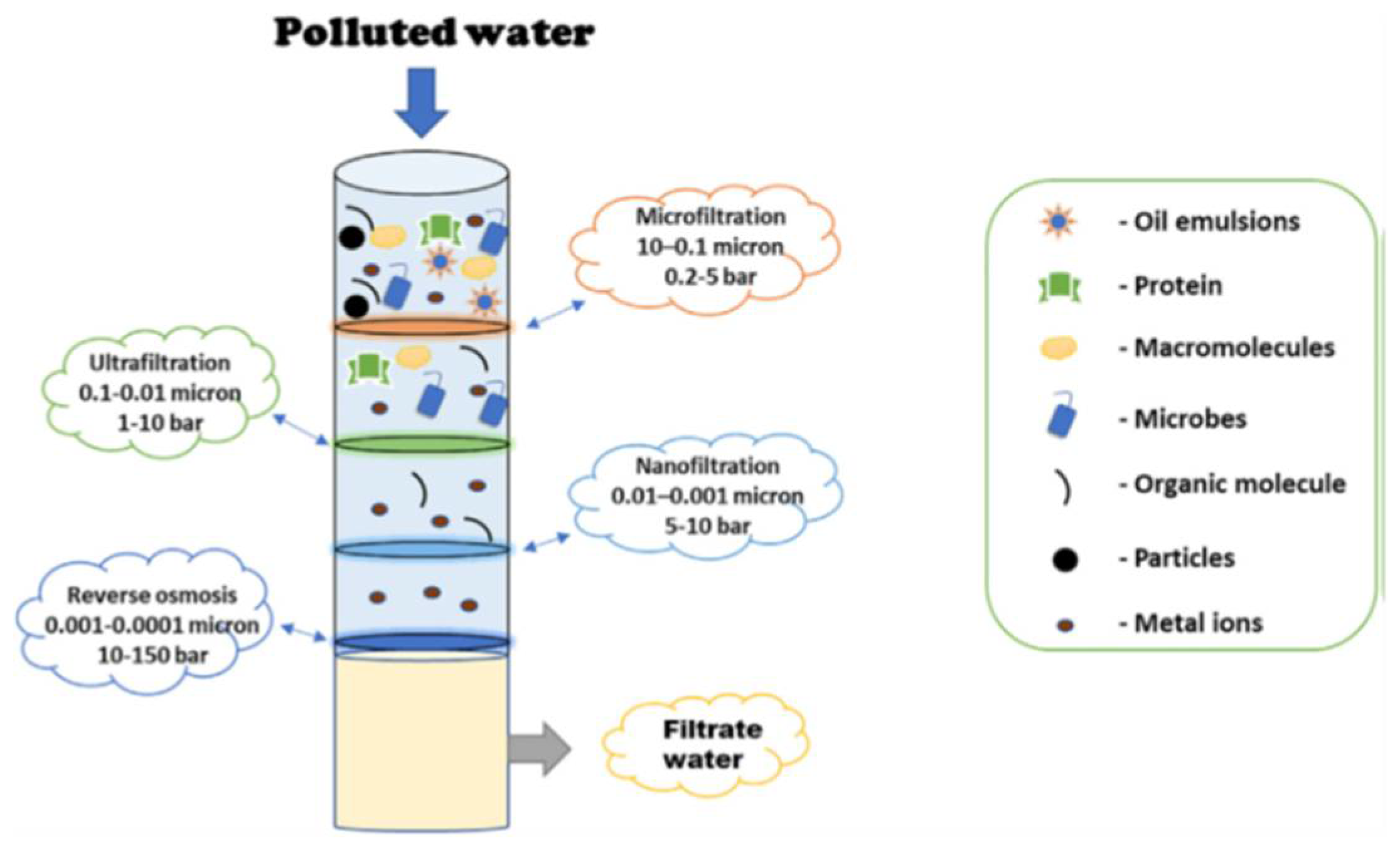
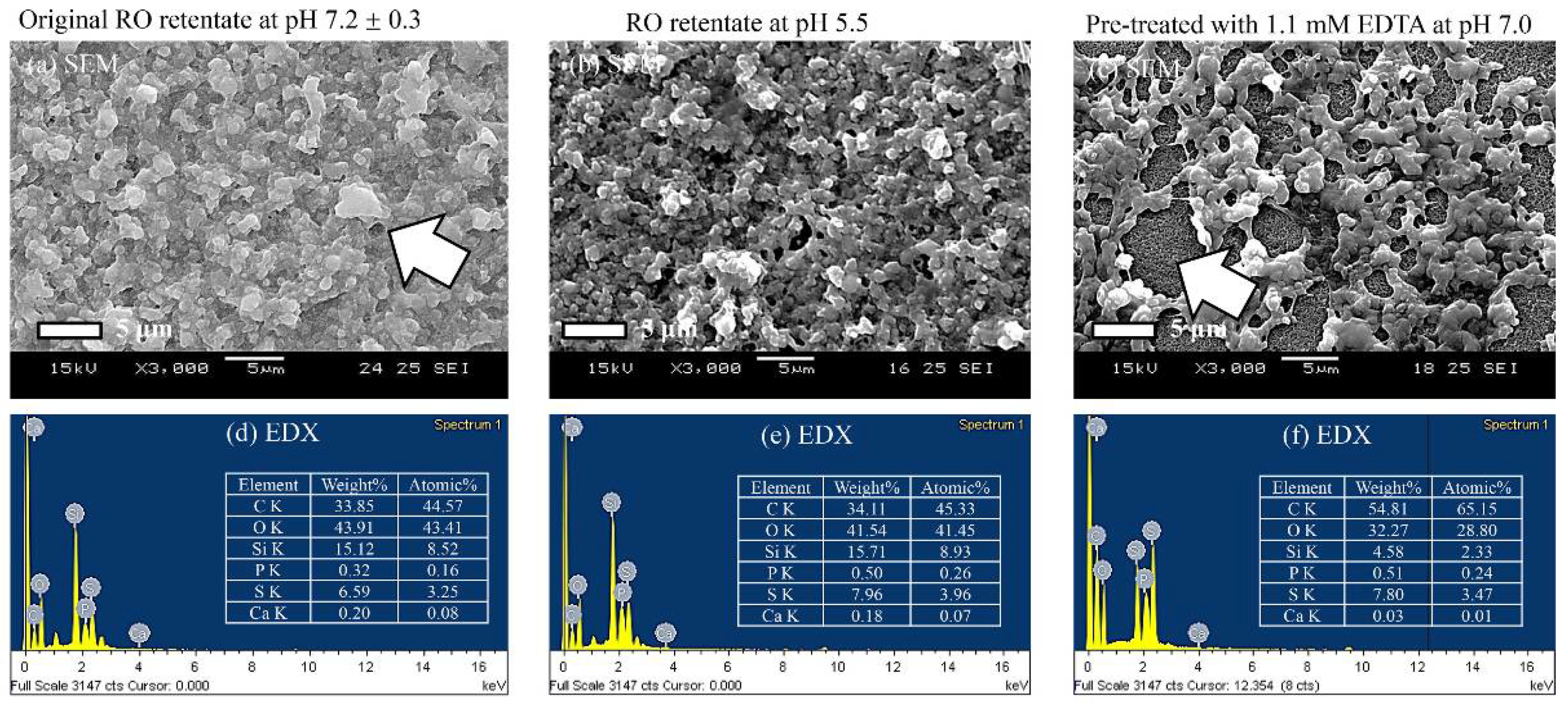
2.1. Pressure Driven Membrane Processes
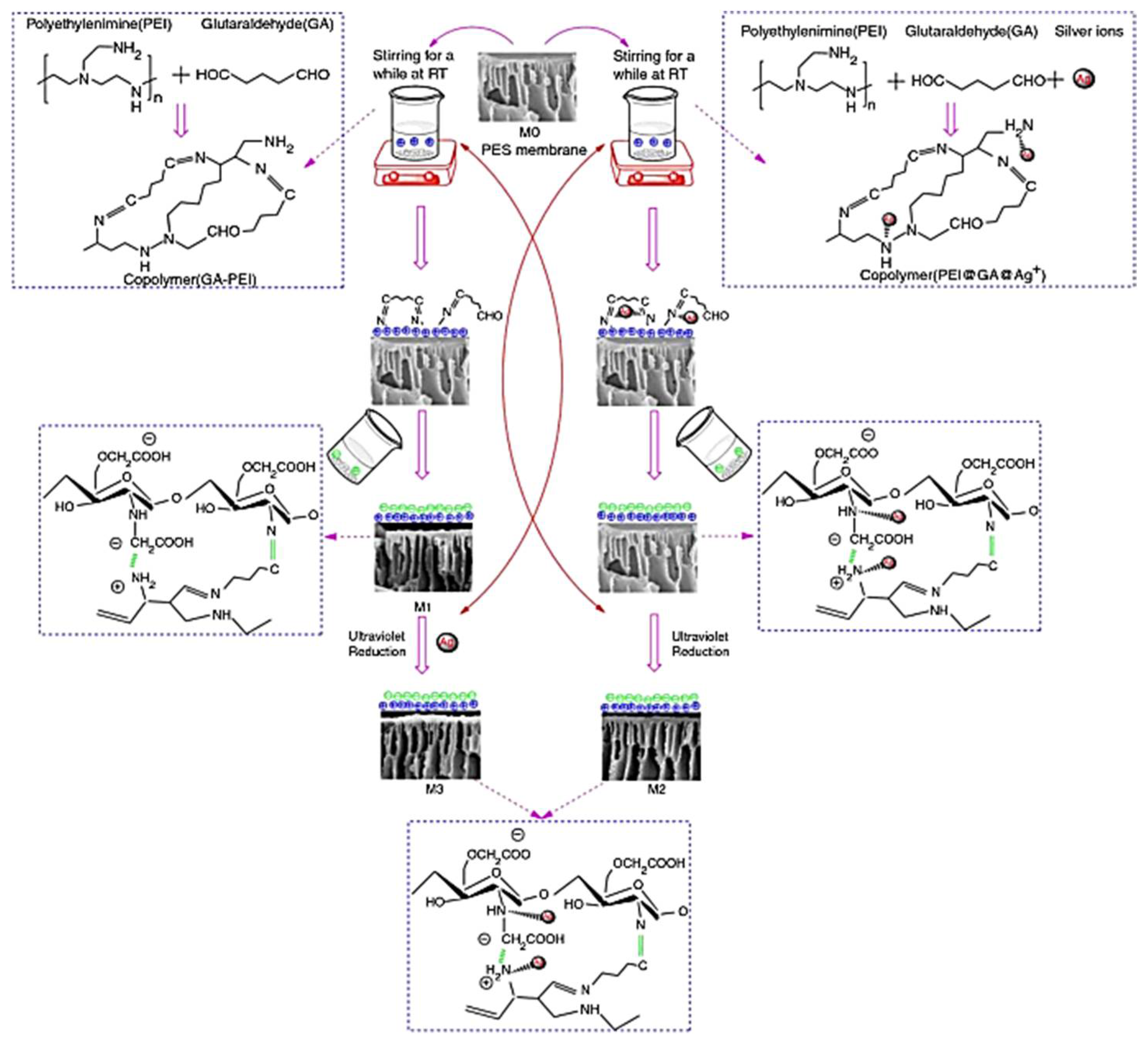
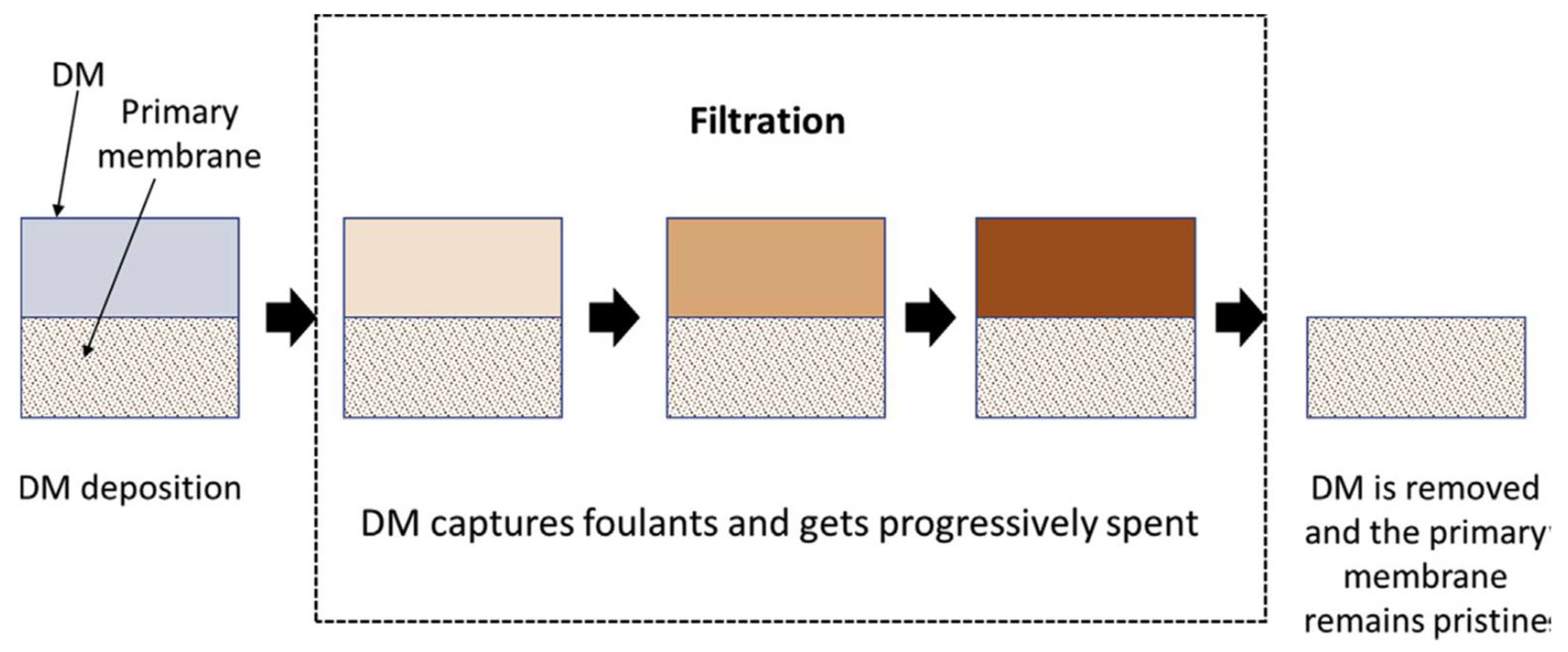
2.2. Low Pressure-Driven Membranes
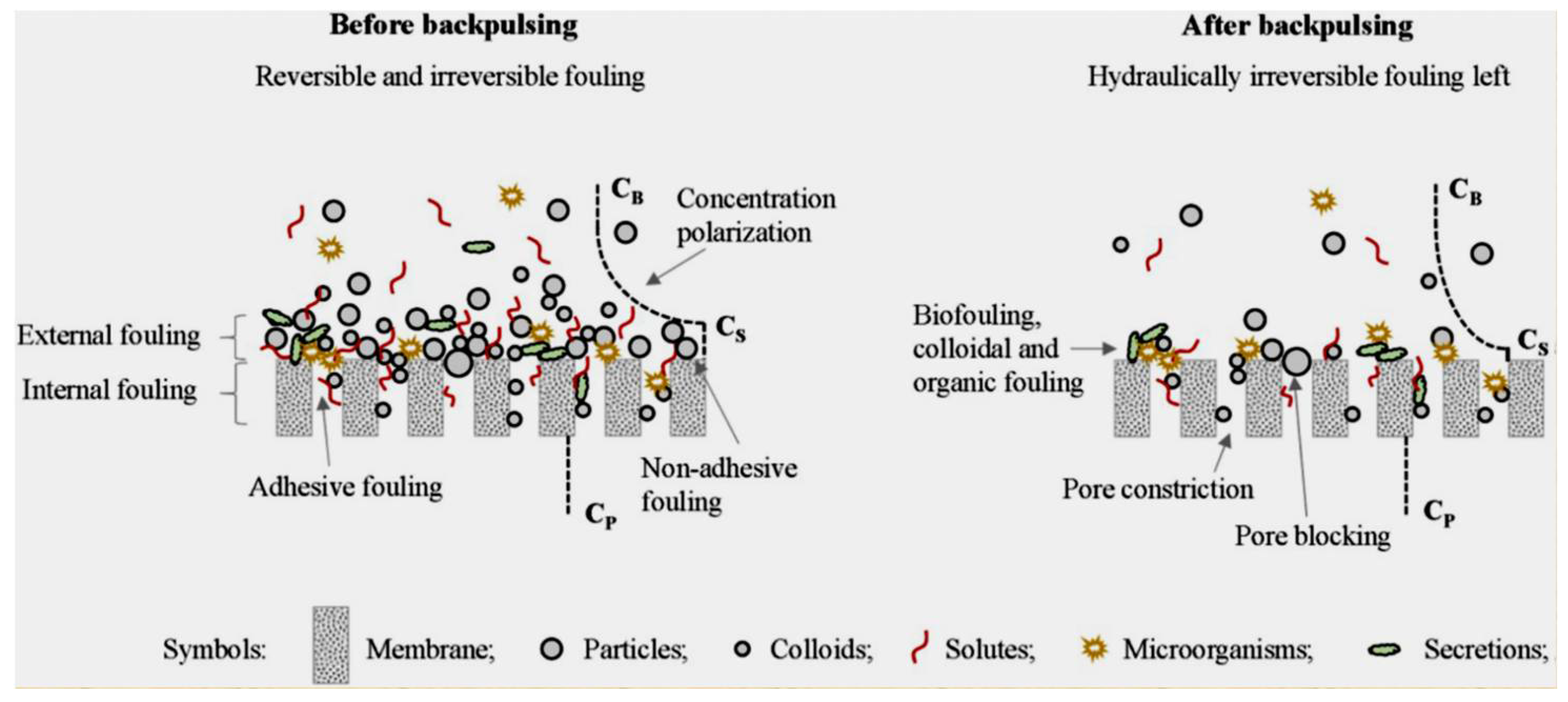
- Feeding characteristics. The types of foulants present in the feed solution have a direct impact on the types of membrane fouling. Backpulsing is more effective at removing non-adhesive and external fouling. The higher the concentration of foulants, the more severe the fouling of the membrane and the lower the cleaning efficiency of backpulsing.
- Membrane characteristics. Because of the elasticity of polymeric membranes, the cleaning capability of backpulsing may be caused by membrane vibration caused by the rapid reverses of TMP rather than reverse flow. Membrane surface modification can alter the types of fouling formation, making backpulsing more effective. Furthermore, membrane pore sizes are related to membrane fouling types and backpulsing efficiency.
- The operational parameters. It is critical to perform backpulsing under optimal conditions, such as amplitude, duration, and frequency. It is also advantageous to investigate the three backpulsing parameters as a backpulsing strategy. In addition, the traditional filtration parameters are TMP/flux and CFV [97].
2.3. Membrane Fouling Mitigation in Membrane Distillation (MD)
2.4. Ion Exchange Membrane (IEM)
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| 2D | two-dimensional |
| AEM | anion exchange membrane |
| AFM | atomic force microscopy |
| AgNPs | silver nanoparticles |
| AOM | algal organic matter |
| APAM | anion polyacrylamide |
| AT-FTIR | attenuated total reflectance-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| AV | alternating voltage |
| BAC | biological activated carbon |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| CECP | cake-enhanced concentration polarisation |
| CEM | cation exchange membrane |
| CFV | crossflow velocity |
| CIP | clean-in-place |
| CNFs | carbon nanofibers |
| CNT | carbon nanotube |
| CP | concentration polarization |
| DCMD | direct contact membrane distillation |
| DI | deionized water |
| DOC | dissolved organic carbon |
| DO–HS | direct osmosis–high salinity |
| DOMs | dissolved organic matters |
| EC | electrocoagulation |
| ED | electrodialysis |
| EDTA | ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| EDX | energy dispersive X-ray |
| EfOM | effluent organic matter |
| EIS | electrochemical impedance spectroscopy |
| FO | forward osmosis |
| FRR | flux recovery ratio |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| GA | glutaraldehyde |
| GAC | granular activated carbon |
| GO | graphene oxide |
| HA | humic acid |
| IEM | ion exchange membrane |
| LbL | layer-by-layer |
| LMHB | L/m2-h-bar |
| MBR | membrane bioreactors |
| MD | membrane distillation |
| MF | microfiltration |
| MFI | modified fouling index |
| MLSS | mixed liquor suspended solids |
| MW | molecular weight |
| MWCNT | multi-walled carbon nanotube |
| MWCO | membrane molecular weight cut-off |
| NF | nanofiltration |
| NO-CMC | negatively charged carboxymethyl chitosan |
| NOMs | natural organic matters |
| NTU | nephelometric turbidity unit |
| n-ZnO | zinc oxide nanoparticle |
| OCT | optical coherence tomography |
| PA | polyamide |
| PAA | poly acrylic acid |
| PAC | powder activated carbon |
| PACl | poly-aluminium chloride or alum |
| PEES | poly(ether sulfone) |
| PEI | polyethylenimine |
| PES | polyethersulfone |
| PolyDMDAAC | poly dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride |
| PPSU | polyphenylsulfone |
| PSf | polysulfone |
| PTFE | polytetrafluoroethylene |
| PVA | poly vinyl alcohol |
| PVDF | polyvinylidenefluoride |
| RO | reverse osmosis |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
| SMPs | soluble microbial products |
| SWRO | seawater RO |
| TEPs | transparent exopolymer particles |
| TFC | thin film composite |
| TMEP | transmembrane electric potential |
| TMP | transmembrane pressure |
| TrOCs | trace organic compounds |
| TSS | total suspended solids |
| UF | ultrafiltration |
| VETOS | vinyltriethoxy |
| WRR | water recovery rates |
| WWRO | wastewater RO |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
References
- Alexander, K. World Water Development. In What Leaving No One Behind Means to CARE; UNICEF: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Teodosiu, C.; Gilca, A.F.; Barjoveanu, G.; Fiore, S. Emerging pollutants removal through advanced drinking water treatment: A review on processes and environmental performances assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 1210–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Huang, M.; Gul, S.; Jiang, H. Solar-Intensified Ultrafiltration System Based on Porous Photothermal Membrane for Efficient Water Treatment. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 4889–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fane, A.G.; Wang, R.; Jia, Y. Membrane Technology: Past, Present and Future BT-Membrane and Desalination Technologies; Wang, L.K., Chen, J.P., Hung, Y.-T., Shammas, N.K., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1–45. ISBN 978-1-59745-278-6. [Google Scholar]
- El Batouti, M.; Al-Harby, N.F.; Elewa, M.M. A Review on Promising Membrane Technology Approaches for Heavy Metal Removal from Water and Wastewater to Solve Water Crisis. Water 2021, 13, 3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Ryu, J.; Yu, Y.; Kweon, J. Characteristics of organic fouling, reversibility by physical cleaning and concentrates in forward osmosis membrane processes for wastewater reclamation. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmawati, R.; Bilad, M.R.; Nawi, N.I.M.; Wibisono, Y.; Suhaimi, H.; Shamsuddin, N.; Arahman, N. Engineered spacers for fouling mitigation in pressure driven membrane processes: Progress and projection. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhou, W.; Wu, D.; Luo, C.; Jia, R.; Li, P.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, X.; Liang, H. Pre-deposition layers for alleviating ultrafiltration membrane fouling by organic matter: Role of hexagonally and cubically ordered mesoporous carbons. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 240, 116599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motsa, M.M.; Mamba, B.B.; Verliefde, A.R.D. Forward osmosis membrane performance during simulated wastewater reclamation: Fouling mechanisms and fouling layer properties. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 23, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nthunya, L.N.; Bopape, M.F.; Mahlangu, O.T.; Mamba, B.B.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Quist-Jensen, C.A.; Richards, H. Fouling, performance and cost analysis of membrane-based water desalination technologies: A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Ngo, H.-H.H.; Li, J. A mini-review on membrane fouling. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Ladewig, B.P. A review of reverse osmosis membrane fouling and control strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geise, G.M.; Lee, H.S.; Miller, D.J.; Freeman, B.D.; McGrath, J.E.; Paul, D.R. Water purification by membranes: The role of polymer science. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 1685–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Yuan, J.; Ma, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y. Polymeric nanocomposite membranes for water treatment: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1539–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhaveri, J.H.; Murthy, Z.V.P. A comprehensive review on anti-fouling nanocomposite membranes for pressure driven membrane separation processes. Desalination 2016, 379, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Sharma, A.; Awasthi, K.K.; Awasthi, A. Metal oxides nanocomposite membrane for biofouling mitigation in wastewater treatment. Mater. Today Chem. 2021, 21, 100532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschner, A.Y.; Cheng, Y.H.; Paul, D.R.; Field, R.W.; Freeman, B.D. Fouling mechanisms in constant flux crossflow ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 574, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goh, P.S.; Lau, W.J.; Othman, M.H.D.; Ismail, A.F. Membrane fouling in desalination and its mitigation strategies. Desalination 2018, 425, 130–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochkodan, V.; Hilal, N. A comprehensive review on surface modified polymer membranes for biofouling mitigation. Desalination 2015, 356, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichardo-Romero, D.; Garcia-Arce, Z.P.; Zavala-Ramírez, A.; Castro-Muñoz, R. Current Advances in Biofouling Mitigation in Membranes for Water Treatment: An Overview. Processes 2020, 8, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antony, A.; Low, J.H.; Gray, S.; Childress, A.E.; Le-Clech, P.; Leslie, G. Scale formation and control in high pressure membrane water treatment systems: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 383, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabelas, A.J.; Karanasiou, A.; Sioutopoulos, D.C. Experimental study on the effect of polysaccharides on incipient membrane scaling during desalination. Desalination 2017, 416, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsinger, D.M.; Swaminathan, J.; Guillen-Burrieza, E.; Arafat, H.A.; Lienhard, V.J.H. Scaling and fouling in membrane distillation for desalination applications: A review. Desalination 2015, 356, 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Xu, S. Thermodynamics and Characteristics of Heterogeneous Nucleation on Fractal Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 27426–27433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyadasa, C.; Ridgway, H.F.; Yeager, T.R.; Stewart, M.B.; Pelekani, C.; Gray, S.R.; Orbell, J.D. The application of electromagnetic fields to the control of the scaling and biofouling of reverse osmosis membranes—A review. Desalination 2017, 418, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavala, R.; Sohn, J.-S.; Han, J.-H.; Her, N.-G.; Yoon, Y.-M. Pretreatment in Reverse Osmosis Seawater Desalination: A Short Review. Environ. Eng. Res. 2011, 16, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.W.; Gallego, S.; Chesters, S.P. Removing Biofilm from Membranes—A Practical Approachitle; Genesys International Limited: Middlewich, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, S.; Liu, Y. New insights into transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) formation from precursor materials at various Na+/Ca2+ ratios. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berman, T. TEP, an Ubiquitous Constituent of NOM Is an Important Factor in Membrane Biofouling. In Proceedings of the 2011 IWA Specialty Conference on Natural Organic Matter, Costa Mesa, CA, USA, 27–29 July 2011; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri, M.; Mirbagheri, S.A. Critical review of fouling mitigation strategies in membrane bioreactors treating water and wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 258, 318–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.R.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, D.J. Membrane fouling during water or wastewater treatments: Current research updated. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 94, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, F.C.; Shang, R.; Rietveld, L.C.; Heijman, S.J.G. Fouling control in ceramic nanofiltration membranes during municipal sewage treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 237, 116373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mat Nawi, N.I.; Bilad, M.R.; Zolkhiflee, N.; Nordin, N.A.H.; Lau, W.J.; Narkkun, T.; Faungnawakij, K.; Arahman, N.; Mahlia, T.M.I. Development of A Novel Corrugated Polyvinylidene difluoride Membrane via Improved Imprinting Technique for Membrane Distillation. Polymers 2019, 11, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rana, D.; Matsuura, T. Surface modifications for antifouling membranes. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2448–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeberl, P.; Brik, M.; Bertoni, M.; Braun, R.; Fuchs, W. Optimization of operational parameters for a submerged membrane bioreactor treating dyehouse wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 44, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Su, Z.; Lin, R.; Lin, X.; Xu, R.; Chen, W. Influence of Membrane Materials and Operational Modes on the Performance of Ultrafiltration Modules for Drinking Water Treatment. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 2016, 6895235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.S.; Liu, Y.; El-Din, M.G. The effects of pretreatment on nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membrane filtration for desalination of oil sands process-affected water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 81, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.T.; Busch, M.; Molina, V.G.; Emwas, A.-H.; Aubry, C.; Croue, J.-P. How different is the composition of the fouling layer of wastewater reuse and seawater desalination RO membranes? Water Res. 2014, 59, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenlee, L.F.; Lawler, D.F.; Freeman, B.D.; Marrot, B.; Moulin, P. Reverse osmosis desalination: Water sources, technology, and today’s challenges. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2317–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enfrin, M.; Lee, J.; Fane, A.G.; Dumée, L.F. Mitigation of membrane particulate fouling by nano/microplastics via physical cleaning strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enfrin, M.; Wang, J.; Merenda, A.; Dumée, L.F.; Lee, J. Mitigation of membrane fouling by nano/microplastics via surface chemistry control. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 633, 119379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippers, J.C.; Verdouw, J. The modified fouling index, a method of determining the fouling characteristics of water. Desalination 1980, 32, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnélye, V.; Guey, L.; Del Castillo, J. UF/MF as RO pre-treatment: The real benefit. Desalination 2008, 222, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elimelech, M.; Gregory, J.; Jia, X.; Williams, R.A. Particle Deposition & Aggregation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; ISBN 9780750670241. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.Y.; Chong, T.H.; Fane, A.G. Colloidal interactions and fouling of NF and RO membranes: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 164, 126–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Lisdonk, C.A.C.; van Paassen, J.A.M.; Schippers, J.C. Monitoring scaling in nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membrane systems. Desalination 2000, 132, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilron, J.; Hasson, D. Calcium sulphate fouling of reverse osmosis membranes: Flux decline mechanism. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1987, 42, 2351–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzotzi, C.; Pahiadaki, T.; Yiantsios, S.G.; Karabelas, A.J.; Andritsos, N. A study of CaCO3 scale formation and inhibition in RO and NF membrane processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 296, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, C.-H. Analysis of CaSO4 scale formation mechanism in various nanofiltration modules. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 163, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervov, A.G. Scale formation prognosis and cleaning procedure schedules in reverse osmosis systems operation. Desalination 1991, 83, 77–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempter, A.; Gaedt, T.; Boyko, V.; Nied, S.; Hirsch, K. New insights into silica scaling on RO-membranes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lueptow, R.M. Control of scale formation in reverse osmosis by membrane rotation. Desalination 2003, 155, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, R.J. Scaling Indices. In Mineral Scales and Deposits; Amjad, Z., Demadis, K.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 721–735. ISBN 9780444632289. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, T.A. Mechanisms of Scale Formation and Inhibition. In Mineral Scales and Deposits; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 47–83. [Google Scholar]
- Remize, P.-J.; Laroche, J.-F.; Leparc, J.; Schrotter, J.-C. A pilot-scale comparison of granular media filtration and low-pressure membrane filtration for seawater pretreatment. Desalin. Water Treat. 2009, 5, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amy, G. Fundamental understanding of organic matter fouling of membranes. Desalination 2008, 231, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoa, A.F.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Fortunato, L. Membrane Fouling in Algal Separation Processes: A Review of Influencing Factors and Mechanisms. Front. Chem. Eng. 2021, 3, 687422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvi, A.G.I.; Al-Rasheed, R.; Javeed, M.A. Studies on organic foulants in the seawater feed of reverse osmosis plants of SWCC. Desalination 2000, 132, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W. Humic acid fouling during microfiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 157, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Manolarakis, S.A.; van der Hoek, J.P.; van Paassen, J.A.M.; van der Meer, W.G.J.; van Agtmaal, J.M.C.; Prummel, H.D.M.; Kruithof, J.C.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Quantitative biofouling diagnosis in full scale nanofiltration and reverse osmosis installations. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4856–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.-C. Reverse osmosis membrane biofouling. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 1997, 14, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, T.H.; Wong, F.S.; Fane, A.G. Implications of critical flux and cake enhanced osmotic pressure (CEOP) on colloidal fouling in reverse osmosis: Experimental observations. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 314, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.; Amy, G.L.; Chung, T.-S.S. Membrane fouling and anti-fouling strategies using RO retentate from a municipal water recycling plant as the feed for osmotic power generation. Water Res. 2016, 88, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Northcott, K.; Duke, M.; Scales, P.; Gray, S.R. Influence of pre-treatment combinations on RO membrane fouling. Desalination 2016, 393, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucera, J. Desalination: Water from Water; Kucera, J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; ISBN 9781118904855. [Google Scholar]
- Fortunato, L.; Bucs, S.; Linares, R.V.; Cali, C.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Leiknes, T. Spatially-resolved in-situ quantification of biofouling using optical coherence tomography (OCT) and 3D image analysis in a spacer filled channel. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gohil, J.M.; Suresh, A.K. Chlorine attack on reverse osmosis membranes: Mechanisms and mitigation strategies. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 541, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, R.; Gómez, V.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Chlorine-resistance of reverse osmosis (RO) polyamide membranes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 72, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glater, J.; Hong, S.; Elimelech, M. The search for a chlorine-resistant reverse osmosis membrane. Desalination 1994, 95, 325–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Martin, J.; Du, J.R.; Zhang, Y.; Lawless, D.; Feng, X. Effects of chlorine exposure on nanofiltration performance of polyamide membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 487, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soice, N.P.; Maladono, A.C.; Takigawa, D.Y.; Norman, A.D.; Krantz, W.B.; Greenberg, A.R. Oxidative degradation of polyamide reverse osmosis membranes: Studies of molecular model compounds and selected membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, M.A.; Chellam, S. Electrocoagulation process considerations during advanced pretreatment for brackish inland surface water desalination: Nanofilter fouling control and permeate water quality. Desalination 2017, 410, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, K.; Matsui, Y.; Itoh, M.; Oguchi, Y.; Kondo, T.; Konno, Y.; Matsushita, T.; Magara, Y. NF membrane fouling by aluminum and iron coagulant residuals after coagulation–MF pretreatment. Desalination 2010, 254, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, C.; Huang, Z.; Ouyang, Z.; Tang, M.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Z. Improvement of the separation and antibiological fouling performance using layer-by-layer self-assembled nanofiltration membranes. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2020, 17, 731–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushothaman, M.; Arvind, V.; Saikia, K.; Vaidyanathan, V.K. Fabrication of highly permeable and anti-fouling performance of Poly(ether ether sulfone) nanofiltration membranes modified with zinc oxide nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Ibrar, I.; Samal, A.K.; Altaee, A.; Déon, S.; Zhou, J.; Ghaffour, N. Preparation of fouling resistant and highly perm-selective novel PSf/GO-vanillin nanofiltration membrane for efficient water purification. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersahin, M.E.; Ozgun, H.; Dereli, R.K.; Ozturk, I.; Roest, K.; van Lier, J.B. A review on dynamic membrane filtration: Materials, applications and future perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, G.; Yu, H. Dynamic Membrane Filtration: Formation, Filtration, Cleaning, and Applications. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2018, 41, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Malack, M.H.; Anderson, G.K. Crossflow microfiltration with dynamic membranes. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, X.C.; Ngo, H.H.; Sun, Q.; Yang, Y. Anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactor (AnDMBR) for wastewater treatment: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharaman, A.; Chun, Y.; Hua, T.; Chew, J.W.; Wang, R. Pre-deposited dynamic membrane filtration—A review. Water Res. 2020, 173, 115558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liu, T.; Crawshaw, J.; Liu, T.; Graham, N. Ultrafiltration and nanofiltration membrane fouling by natural organic matter: Mechanisms and mitigation by pre-ozonation and pH. Water Res. 2018, 139, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilal, N.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T.; Oatley-Radcliffe, D. Membrane Characterization, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 9780444637765. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, G.; Cao, Y. Application and modification of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) membranes—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 463, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hu, M.; Mi, B. Membrane surface modification with TiO2–graphene oxide for enhanced photocatalytic performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 455, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Yanilmaz, M.; Toprakci, O.; Fu, K.; Zhang, X. A review of recent developments in membrane separators for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3857–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilal, N.; Ogunbiyi, O.O.; Miles, N.J.; Nigmatullin, R. Methods Employed for Control of Fouling in MF and UF Membranes: A Comprehensive Review. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 1957–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Darwish, N.N.; Mhiyo, S.; Darwish, N.A.; Hilal, N. The use of ultrasound to mitigate membrane fouling in desalination and water treatment. Desalination 2018, 443, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naji, O.; Al-juboori, R.A.; Khan, A.; Yadav, S.; Altaee, A.; Alpatova, A.; Soukane, S.; Ghaffour, N. Ultrasound-assisted membrane technologies for fouling control and performance improvement: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 43, 102268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, C.; Durand-Bourlier, L.; Clifton, M.J.; Moulin, P.; Rouch, J.C.; Aptel, P. Use of air sparging to improve backwash efficiency in hollow-fiber modules. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 161, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenten, I.G. Mechanisms and control of fouling in crossflow microfiltration. Filtr. Sep. 1995, 32, 252–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Héran, M.; Elmaleh, S. Prediction of cross-flow microfiltration through an inorganic tubular membrane with high-frequency retrofiltration. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2001, 56, 3075–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Héran, M.; Elmaleh, S. Cross-flow microfiltration with high frequency reverse flow. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, V.G.J.; Sparks, R.E. Effect of transmembrane pressure pulsing on concentration polarization. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 68, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.D.; Weitzel, S.; Rodgers, V.G.J. Reduction of membrane fouling in the presence of high polarization resistance. J. Membr. Sci. 1993, 76, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondhi, R.; Lin, Y.S.; Alvarez, F. Crossflow filtration of chromium hydroxide suspension by ceramic membranes: Fouling and its minimization by backpulsing. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 174, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Qin, J.; Wang, Z.; Østerhus, S.W. Backpulsing technology applied in MF and UF processes for membrane fouling mitigation: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 587, 117136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, J.; Tang, C.Y.; Kimura, K.; Wang, Q.; Han, X. Membrane cleaning in membrane bioreactors: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 276–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A.; Gupta, V.K. Membrane Fouling and Strategies for Cleaning and Fouling Control. In Nanomaterial and Polymer Membranes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 25–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Song, H.; Zhang, D.; Wang, G.; Zeng, Z.; Xue, Q. Negatively charged polysulfone membranes with hydrophilicity and antifouling properties based on in situ cross-linked polymerization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 498, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yu, S.; Yang, H.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, B.; Li, L.; Liu, Z. Molecular Mechanisms of Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling in Polymer-Flooding Wastewater Treatment: Role of Ions in Polymeric Fouling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidu, G.; Jeong, S.; Vigneswaran, S.; Hwang, T.-M.; Choi, Y.-J.; Kim, S.-H. A review on fouling of membrane distillation. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 10052–10076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Qi, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, M.; Miao, S.; Li, W.; Liu, R.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Moderate KMnO4-Fe(II) pre-oxidation for alleviating ultrafiltration membrane fouling by algae during drinking water treatment. Water Res. 2018, 142, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribau Teixeira, M.; Rosa, M.J. pH adjustment for seasonal control of UF fouling by natural waters. Desalination 2003, 151, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, C.-C.; Genuino, D.A.D.; Rivera, K.K.P.; de Luna, M.D.G. Ultrasonic cleaning of polytetrafluoroethylene membrane fouled by natural organic matter. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 497, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Qiu, M.; Chen, X.; Verweij, H.; Fan, Y. Fabrication and in-situ fouling mitigation of a supported carbon nanotube/γ-alumina ultrafiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 550, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshasayee, M.S.; Yu, Z.; Arthanareeswaran, G.; Das, D.B. Preparation of nanoclay embedded polymeric membranes for the filtration of natural organic matter (NOM) in a circular crossflow filtration system. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Gao, B.; Guo, K.; Yue, Q. Characterization and influence of floc under different coagulation systems on ultrafiltration membrane fouling. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Ji, M.; Li, R. Effects of different Ca2+ behavior patterns in the electric field on membrane fouling formation and removal of trace organic compounds. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 111, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, W.; Gryta, M. Application of ultrafiltration ceramic membrane for separation of oily wastewater generated by maritime transportation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 261, 118259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
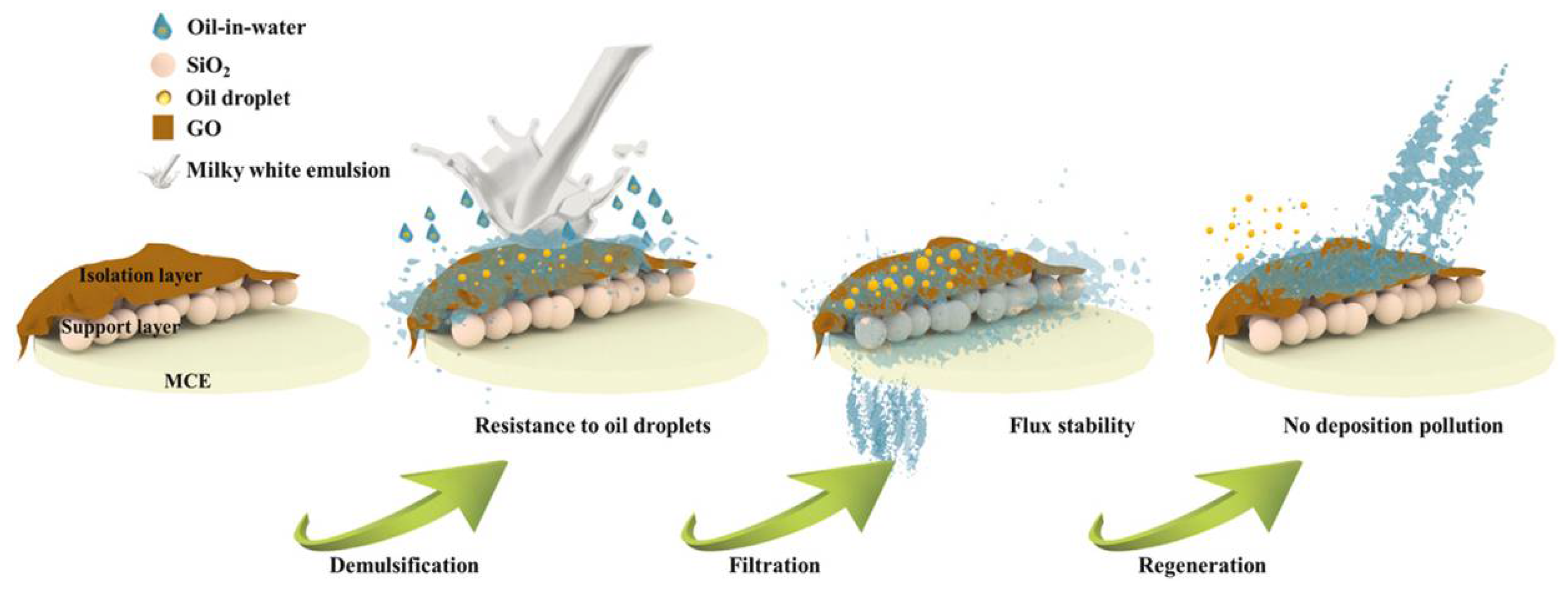
- Feng, L.; Gao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Dan, H.; Qi, Y.; Wang, S.; Yin, F.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B. A dual-functional layer modified GO@SiO2 membrane with excellent anti-fouling performance for continuous separation of oil-in-water emulsion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Sun, W.; Lu, Z.; Ao, X.; Li, S. Ceramic nanocomposite membranes and membrane fouling: A review. Water Res. 2020, 175, 115674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, C.; Farris, K.; Kilduff, J. Membrane Fouling, Modelling and Recent Developments for Mitigation. In Emerging Membrane Technology for Sustainable Water Treatment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 433–462. ISBN 9780444633125. [Google Scholar]
- Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Kruithof, J.C. A novel scenario for biofouling control of spiral wound membrane systems. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3890–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, P.A.; Kruithof, J.C.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. The potential of standard and modified feed spacers for biofouling control. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 403–404, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.J.; Araújo, P.A.; Correia, P.B.; Ramsey, M.M.; Kruithof, J.C.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Freeman, B.D.; Paul, D.R.; Whiteley, M.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Short-term adhesion and long-term biofouling testing of polydopamine and poly(ethylene glycol) surface modifications of membranes and feed spacers for biofouling control. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3737–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algoufily, Y. Wastewater Treatment Plant Optimization: Development of Membrane Bioreactor Fouling Monitoring Tool and Prediction of Transmembrane Pressure Using Artificial Neural Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology KAUST, Thuwal, Saudi Arabia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, K.; Heo, S.; Rhee, G.; Kim, M.; Yoo, C. Dual-objective optimization for energy-saving and fouling mitigation in MBR plants using AI-based influent prediction and an integrated biological-physical model. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 626, 119208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Tian, Y.; Sun, L.; Zuo, W.; Li, H.; Li, A.; Wiesner, M.R. A novel approach for fouling mitigation in anaerobic-anoxic-oxic membrane bioreactor (A2O-MBR) by integrating worm predation. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Ren, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Roddick, F.A.; Fan, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Yao, P. A review of the current in-situ fouling control strategies in MBR: Biological versus physicochemical. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 98, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buakaew, T.; Ratanatamskul, C. Effects of novel anaerobic baffled biofilm membrane bioreactor configurations on membrane fouling mitigation and microbial community in treating liquor condensate. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 335, 125310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahi, N.; Ghalamchi, L.; Vatanpour, V.; Khataee, A. Photocatalytic-membrane technology: A critical review for membrane fouling mitigation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 93, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokulakrishnan, S.A.; Arthanareeswaran, G.; László, Z.; Veréb, G.; Kertész, S.; Kweon, J. Recent development of photocatalytic nanomaterials in mixed matrix membrane for emerging pollutants and fouling control, membrane cleaning process. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wan, Y.; Luo, J.; Darling, S.B. Drawing on Membrane Photocatalysis for Fouling Mitigation. ACS Appl. Mater. & Interfaces 2021, 13, 14844–14865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Xu, Y.; Jakaj, G.; Lin, H. Polymeric Membranes Incorporated With ZnO Nanoparticles for Membrane Fouling Mitigation: A Brief Review. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horseman, T.; Yin, Y.; Christie, K.S.; Wang, Z.; Tong, T.; Lin, S. Wetting, Scaling, and Fouling in Membrane Distillation: State-of-the-Art Insights on Fundamental Mechanisms and Mitigation Strategies. ACS ES&T Eng. 2021, 1, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chung, T.-S. Recent advances in membrane distillation processes: Membrane development, configuration design and application exploring. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 474, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, D.; Amigo, J.; Suárez, F. Membrane distillation: Perspectives for sustainable and improved desalination. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 238–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, D.L.M.; Castel, C.; Lemaitre, C.; Favre, E. Improved performances of vacuum membrane distillation for desalination applications: Materials vs process engineering potentialities. Desalination 2019, 452, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eykens, L.; Reyns, T.; De Sitter, K.; Dotremont, C.; Pinoy, L.; Van der Bruggen, B. How to select a membrane distillation configuration? Process conditions and membrane influence unraveled. Desalination 2016, 399, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madalosso, H.B.; Machado, R.; Hotza, D.; Marangoni, C. Membrane Surface Modification by Electrospinning, Coating, and Plasma for Membrane Distillation Applications: A State-of-the-Art Review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2021, 23, 2001456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhatib, A.; Ayari, M.A.; Hawari, A.H. Fouling mitigation strategies for different foulants in membrane distillation. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2021, 167, 108517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, W.; Gryta, M. Application of Capillary Polypropylene Membranes for Microfiltration of Oily Wastewaters: Experiments and Modeling. Fibers 2021, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, L.M.; Dumée, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.-d.; Duke, M.; Gomez, J.; Gray, S. Advances in membrane distillation for water desalination and purification applications. Water 2013, 5, 94–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, W.; Shen, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, Y. An ultrathin, porous and in-air hydrophilic/underwater oleophobic coating simultaneously increasing the flux and antifouling property of membrane for membrane distillation. Desalination 2018, 445, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, E.; Lee, Y.T. Preparation of an omniphobic nanofiber membrane by the self-assembly of hydrophobic nanoparticles for membrane distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 259, 118134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryta, M.; Tomczak, W. Stability of Ar/O2 Plasma-Treated Polypropylene Membranes Applied for Membrane Distillation. Membranes 2021, 11, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naddeo, V.; Borea, L.; Belgiorno, V. Sonochemical control of fouling formation in membrane ultrafiltration of wastewater: Effect of ultrasonic frequency. J. Water Process Eng. 2015, 8, e92–e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Fan, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, H. Humic acid fouling mitigation by ultrasonic irradiation in membrane distillation process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 154, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, C.; Fan, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, H. Ultrasonic irradiation control of silica fouling during membrane distillation process. Desalination 2016, 386, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naim, M.M.; El Batouti, M.; Elewa, M.M. Novel heterogeneous cellulose-based ion-exchange membranes for electrodialysis. Polym. Bull. 2021, 51, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreeva, M.A.; Loza, N.V.; Pis’menskaya, N.D.; Dammak, L.; Larchet, C. Influence of Surface Modification of MK-40 Membrane with Polyaniline on Scale Formation under Electrodialysis. Membranes 2020, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, K.S.; Scarazzato, T.; Pérez-Herranz, V.; Espinosa, D.C.R. Treatment of Cyanide-Free Wastewater from Brass Electrodeposition with EDTA by Electrodialysis: Evaluation of Underlimiting and Overlimiting Operations. Membranes 2020, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.-J.; Park, J.-S.; Kang, M.-S.; Moon, S.-H. Effects of silica sol on ion exchange membranes: Electrochemical characterization of anion exchange membranes in electrodialysis of silica sol containing-solutions. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2003, 20, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelle, M.T. Colloidal fouling of reverse osmosis membranes. Desalination 1980, 32, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouy, M. Sur la constitution de la charge électrique à la surface d’un électrolyte. J. Phys. Theor. Appl. 1910, 9, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapman, D.L. LI. A contribution to the theory of electrocapillarity. Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1913, 25, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, W.J. Zur Theorie der elektrolytischen Ventilwirkung. Z. Phys. 1932, 73, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylin, S.; Bazinet, L. Fouling on ion-exchange membranes: Classification, characterization and strategies of prevention and control. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 229, 34–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin Teng Shee, F.; Arul, J.; Brunet, S.; Bazinet, L. Chitosan solubilization by bipolar membrane electroacidification: Reduction of membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 290, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husson, E.; Araya-Farias, M.; Desjardins, Y.; Bazinet, L. Selective anthocyanins enrichment of cranberry juice by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membranes stacked. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 17, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, B.; Sistat, P.; Huguet, P.; Pourcelly, G.; Araya-Farias, M.; Bazinet, L. Application of relaxation periods during electrodialysis of a casein solution: Impact on anion-exchange membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 287, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Xiao, L.; Yu, S.; Yang, H.; Hu, J.; Liu, G.; Tang, Y. Analysis of anion exchange membrane fouling mechanism caused by anion polyacrylamide in electrodialysis. Desalination 2014, 346, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.G. Biofilm Dispersion. In Biofilm Highlights; Flemming, H.-C., Wingender, J., Szewzyk, U., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–28. ISBN 978-3-642-19940-0. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.Y.; Yu, J.W.; Kweon, J.H. Electrodialysis for desalination of brackish groundwater in coastal areas of Korea. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 6230–6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, A.C.M. Prevention and Control of Membrane Fouling: Practical Implications and Examining Recent Innovations. 2009. Available online: https://www.yumpu.com/en/document/read/15294589/prevention-and-control-of-membrane-fouling-practical-implications- (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Chang, D.I.; Choo, K.H.; Jung, J.H.; Jiang, L.; Ahn, J.H.; Nam, M.Y.; Kim, E.S.; Jeong, S.H. Foulant identification and fouling control with iron oxide adsorption in electrodialysis for the desalination of secondary effluent. Desalination 2009, 236, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin Teng Shee, F.; Angers, P.; Bazinet, L. Microscopic approach for the identification of cationic membrane fouling during cheddar cheese whey electroacidification. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 322, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, P.; Cong, W. Cation-exchange membrane fouling and cleaning in bipolar membrane electrodialysis of industrial glutamate production wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 79, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Geluwe, S.; Braeken, L.; Robberecht, T.; Jans, M.; Creemers, C.; Van der Bruggen, B. Evaluation of electrodialysis for scaling prevention of nanofiltration membranes at high water recoveries. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 56, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, L.; Montpetit, D.; Ippersiel, D.; Amiot, J.; Lamarche, F. Identification of Skim Milk Electroacidification Fouling: A Microscopic Approach. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 237, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes-Araya, N.; Pourcelly, G.; Bazinet, L. Impact of pulsed electric field on electrodialysis process performance and membrane fouling during consecutive demineralization of a model salt solution containing a high magnesium/calcium ratio. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 361, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, K.C.; Teow, Y.H.; Mohammad, A.W.; Ang, W.L.; Lee, P.H. Development of graphene oxide (GO)/multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) nanocomposite conductive membranes for electrically enhanced fouling mitigation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 552, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Han, M.; Dong, T.; Yao, J.; Han, L. Fouling dynamics of anion polyacrylamide on anion exchange membrane in electrodialysis. Desalination 2021, 507, 115036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, J.J.; Jana, A.; Getachew, B.A.; Bergsman, D.S.; Gariepy, Z.; Smith, B.D.; Lu, Z.; Grossman, J.C. Conductive carbonaceous membranes: Recent progress and future opportunities. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 3270–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Fan, S.; Zhou, Q.; Shao, H.; Hu, W.; Li, C.; Tong, L.; Kumar, R.R.; et al. Membrane fouling mitigation by coupling applied electric field in membrane system: Configuration, mechanism and performance. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 287, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, J.; Rajalakshmi, M.; Phani, A.R.; Padaki, M. Pretreatment processes for seawater reverse osmosis desalination systems—A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32, 100926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]































| Property | Affects | Typical Values (Commercial Membranes) | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contact angle (θ) | Wetting resistance | 80°–160° | >90° as high as possible |
| LEP (bar) | Wetting resistance | 0.5–4.6 | >2.5 |
| Thickness (δ) (μm) | Flux, energy efficiency, strength | 20–400 | Low salinity: 30–60 High salinity: 2–700 |
| Porosity (ϵ) | Flux, energy efficiency, strength | 39–90% | >80% |
| Thermal conductivity (km) (W/m k) | Flux, energy efficiency | 0.031–0.057 | As low as possible |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | Strength | 3.4–57.9 | As high as possible |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Batouti, M.; Alharby, N.F.; Elewa, M.M. Review of New Approaches for Fouling Mitigation in Membrane Separation Processes in Water Treatment Applications. Separations 2022, 9, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9010001
El Batouti M, Alharby NF, Elewa MM. Review of New Approaches for Fouling Mitigation in Membrane Separation Processes in Water Treatment Applications. Separations. 2022; 9(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Batouti, Mervette, Nouf F. Alharby, and Mahmoud M. Elewa. 2022. "Review of New Approaches for Fouling Mitigation in Membrane Separation Processes in Water Treatment Applications" Separations 9, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9010001
APA StyleEl Batouti, M., Alharby, N. F., & Elewa, M. M. (2022). Review of New Approaches for Fouling Mitigation in Membrane Separation Processes in Water Treatment Applications. Separations, 9(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9010001






