Magnetic Ionic Liquids in Sample Preparation: Recent Advances and Future Trends
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Phase Microextraction
2.1. Direct Use of MILs
2.1.1. Procedures for Organic Compounds Determination in Environmental Samples
2.1.2. Procedures for the Determination of Organic Substances in Food Samples
2.1.3. Procedures for the Determination of Organic Substances in Biological Samples
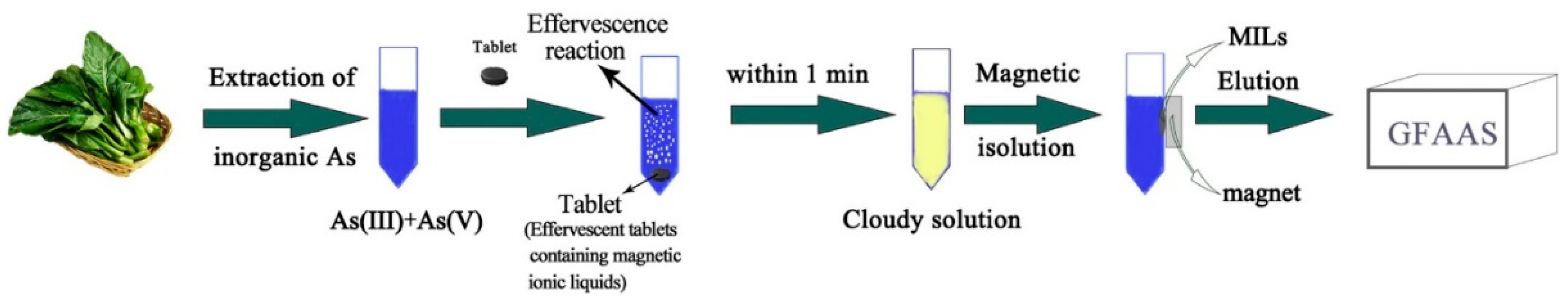
2.1.4. Procedures for Metal Species Determination in Food Samples
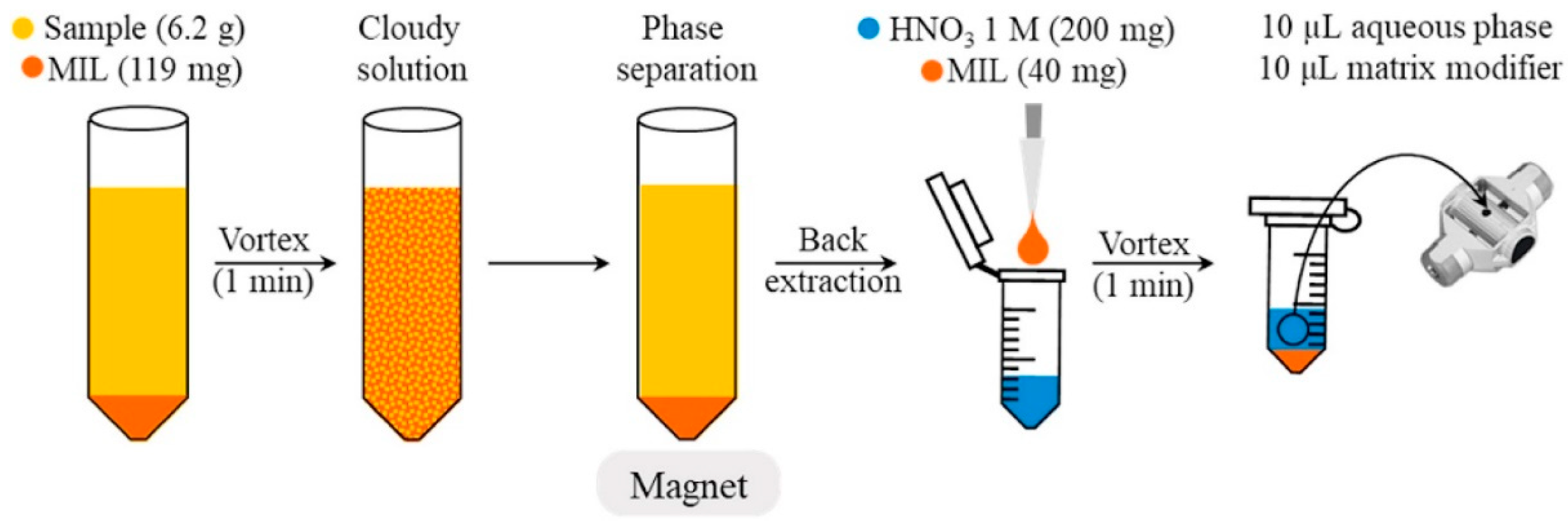
2.1.5. Procedures for Metal Species Determination in Environmental Samples
2.2. In-Situ Formation of MILs
2.3. Single Drop Microextraction Procedures
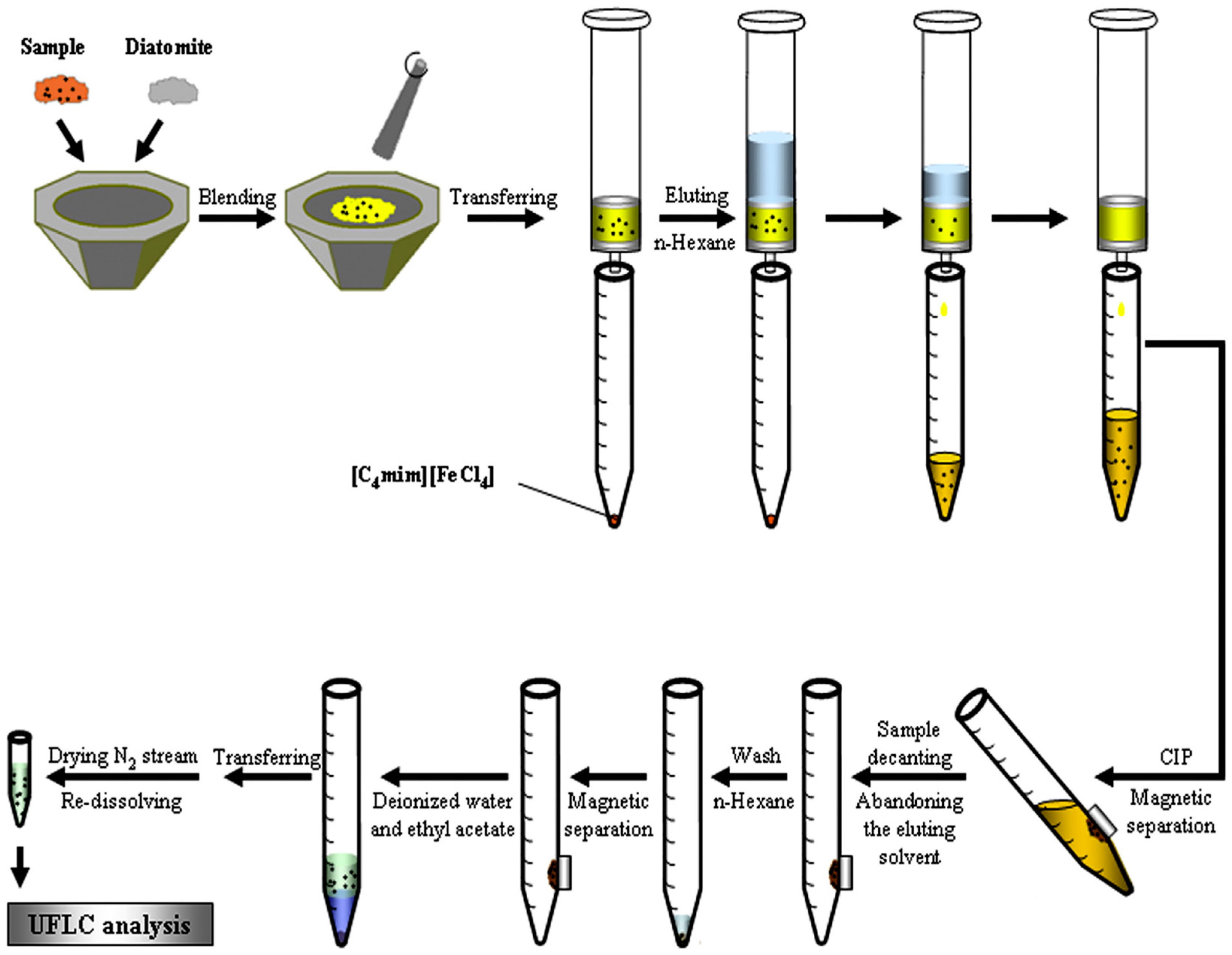
2.4. Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion Procedures
2.5. Stir-Bar Dispersive Procedures
2.6. Other Procedures
3. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reyes-Garcés, N.; Gionfriddo, E.; Gómez-Ríos, G.A.; Alam, N.; Boyacı, E.; Bojko, B.; Singh, V.; Grandy, J.; Pawliszyn, J. Advances in solid phase microextraction and perspective on future directions. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 302–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-T.; Zheng, X.; Li, H.-F.; Lin, J.-M. Application of carbon-based nanomaterials in sample preparation: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 784, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M. Magnetic ionic liquids in analytical sample preparation: A literature review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzimitakos, T.; Stalikas, C. Carbon-based nanomaterials functionalized with ionic liquids for microextraction in sample preparation. Separations 2017, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, J.; Loussala, H.M.; Han, S.; Ji, X.; Li, C.; Sun, M. Recent advances of ionic liquids in sample preparation. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 125, 115833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Aceituno, L.; Sanz, M.; Ramos, L. Use of ionic liquids in analytical sample preparation of organic compounds from food and environmental samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 43, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yavir, K.; Konieczna, K.; Marcinkowski, Ł.; Kloskowski, A. Ionic liquids in the microextraction techniques: The influence of ILs structure and properties. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 130, 115994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.D.; Emaus, M.N.; Varona, M.; Bowers, A.N.; Anderson, J.L. Ionic liquids: Solvents and sorbents in sample preparation. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 209–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzimitakos, T.G.; Pierson, S.A.; Anderson, J.L.; Stalikas, C.D. Enhanced magnetic ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of triazines and sulfonamides through a one-pot, pH-modulated approach. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1571, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo-Rodríguez, M.J.; Anderson, J.L. In situ generation of hydrophobic magnetic ionic liquids in stir bar dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with headspace gas chromatography. Talanta 2019, 196, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merib, J.; Spudeit, D.A.; Corazza, G.; Carasek, E.; Anderson, J.L. Magnetic ionic liquids as versatile extraction phases for the rapid determination of estrogens in human urine by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4689–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-Rodríguez, M.J.; Nacham, O.; Clark, K.D.; Pino, V.; Anderson, J.L.; Ayala, J.H.; Afonso, A.M. Magnetic ionic liquids as non-conventional extraction solvents for the determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 934, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maximino, C.; de Brito, T.M.; da Silva Batista, A.W.; Herculano, A.M.; Morato, S.; Gouveia, A., Jr. Measuring anxiety in zebrafish: A critical review. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 214, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, A.C.; Mafra, G.; Spudeit, D.; Merib, J.; Carasek, E. Magnetic ionic liquids as an efficient tool for the multiresidue screening of organic contaminants in river water samples. Sep. Sci. Plus 2019, 2, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Yao, S. Magnetic ionic liquid aqueous two-phase system coupled with high performance liquid chromatography: A rapid approach for determination of chloramphenicol in water environment. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1481, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, T.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Peng, L.; Liu, Y.; Du, K. Extractive resolution of racemic phenylalanine and preparation of optically pure product by chiral magnetic ionic liquid aqueous two-phase system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 274, 119024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Li, M.; Zhao, L.; Lu, C.; de Rooy, S.L.; Warner, I.M. Highly efficient extraction of phenolic compounds by use of magnetic room temperature ionic liquids for environmental remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Merib, J.; Anderson, J.L. Faster dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction methods using magnetic ionic liquids as solvents. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1463, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berton, P.; Siraj, N.; Das, S.; de Rooy, S.; Wuilloud, R.G.; Warner, I.M. Efficient low-cost procedure for microextraction of estrogen from environmental water using magnetic ionic liquids. Molecules 2020, 26, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzimitakos, T.; Binellas, C.; Maidatsi, K.; Stalikas, C. Magnetic ionic liquid in stirring-assisted drop-breakup microextraction: Proof-of-concept extraction of phenolic endocrine disrupters and acidic pharmaceuticals. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 910, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, Z.; Xue, S.; Zhang, L. Novel functionalized magnetic ionic liquid green separation technology coupled with high performance liquid chromatography: A rapid approach for determination of estrogens in milk and cosmetics. Talanta 2020, 209, 120542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, X.; Jin, R.; Zhang, H.; Song, D. Magnetic ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the determination of triazine herbicides in vegetable oils by liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1373, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Reyes, J.F.; Ferrer, C.; Thurman, E.M.; Fernández-Alba, A.R.; Ferrer, I. Analysis of herbicides in olive oil by liquid chromatography time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6493–6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, C.; Gómez, M.J.; García-Reyes, J.F.; Ferrer, I.; Thurman, E.M.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Determination of pesticide residues in olives and olive oil by matrix solid-phase dispersion followed by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1069, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, E.; Báez, M.E.; Quiñones, A. Suitability of microwave-assisted extraction coupled with solid-phase extraction for organophosphorus pesticide determination in olive oil. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1207, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Chen, X.; Wei, X.; Pan, S.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, M. Dispersive solid-phase extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of ricinine in cooking oil. Food Chem. 2014, 158, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-X.; Yang, T.-J.; Li, Z.-G.; Jong, T.-T.; Lee, M.-R. A novel method of ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled to liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry for the determination of trace organoarsenic compounds in edible oil. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 690, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wu, S.; Wang, C.; Yi, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wang, H.; Li, F.; Tan, Z. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction of sinomenine from Sinomenium acutum using magnetic ionic liquids coupled with further purification by reversed micellar extraction. Process Biochem. 2017, 58, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; Yao, S. Systematic investigation for extraction and separation of polyphenols in tea leaves by magnetic ionic liquids. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 4550–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, K.Z.; Yamini, Y.; Seidi, S. Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction using magnetic room temperature ionic liquid for extraction of ultra-trace amounts of parabens. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 9735–9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, C.; Omena, E.; Corazza, G.; Bernardi, G.; Merib, J.; Carasek, E. Expanding the applicability of magnetic ionic liquids for multiclass determination in biological matrices based on dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and HPLC with diode array detector analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 2657–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, M.A.; Mansour, F.R.; Danielson, N.D. A gadolinium-based magnetic ionic liquid for dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.A.; Tanimu, A.; Alhooshani, K. Iron and cobalt-containing magnetic ionic liquids for dispersive micro-solid phase extraction coupled with HPLC-DAD for the preconcentration and quantification of carbamazepine drug in urine and environmental water samples. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 336, 116370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentini, E.F.; Escudero, L.B.; Wuilloud, R.G. Magnetic ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction technique for preconcentration and ultra-trace determination of Cd in honey. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4715–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentini, E.F.; Canizo, B.V.; Wuilloud, R.G. Determination of As in honey samples by magnetic ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 2019, 198, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentini, E.F.; Oviedo, M.N.; Wuilloud, R.G. Ultra-trace Cr preconcentration in honey samples by magnetic ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2020, 169, 105879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentini, E.F.; Botella, M.B.; Wuilloud, R.G. A simple preconcentration method for highly sensitive determination of Pb in bee products by magnetic ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 95, 103661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, P.; Cao, L.; Xu, G.; Yang, S.; Fang, Y.; Wang, G.; Hong, X. Selenium speciation in rice samples by magnetic ionic liquid-based up-and-down-shaker-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled to graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Pang, L.; Lin, C. Ultrasound-assisted surfactant-enhanced emulsification microextraction using a magnetic ionic liquid coupled with micro-solid phase extraction for the determination of cadmium and lead in edible vegetable oils. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, G.; Guo, X.; Chen, X.; Duan, J.; Gao, Z.; Zheng, B.; Shen, Q. Effervescent tablets containing magnetic ionic liquids as a non-conventional extraction and dispersive agent for speciation of arsenite and arsenate in vegetable samples. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 272, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, G.; Chen, P.; Liu, X.; Fang, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, G. Arsenic speciation analysis in environmental water, sediment and soil samples by magnetic ionic liquid-based air-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 110247–110254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo, M.N.; Fiorentini, E.F.; Lemos, A.A.; Wuilloud, R.G. Ultra-sensitive Sb speciation analysis in water samples by magnetic ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and multivariate optimization. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre, M.Á.; Canals, A.; López-García, I.; Hernández-Córdoba, M. Determination of cadmium in used engine oil, gasoline and diesel by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry using magnetic ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. Talanta 2020, 220, 121395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo-Rodríguez, M.J.; Anderson, J.L. In situ formation of hydrophobic magnetic ionic liquids for dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1588, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, C.; Huelsmann, R.D.; Mafra, G.; Merib, J.; Anderson, J.L.; Carasek, E. High-throughput approach for the in situ generation of magnetic ionic liquids in parallel-dispersive droplet extraction of organic micropollutants in aqueous environmental samples. Talanta 2021, 223, 121759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, A.N.; Trujillo-Rodríguez, M.J.; Farooq, M.Q.; Anderson, J.L. Extraction of DNA with magnetic ionic liquids using in situ dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 7375–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Du, K. Simultaneous determination of sulfonamides in milk: In-situ magnetic ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with HPLC. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Xu, X.; Xue, S.; Feng, X.; Zhang, L. An in situ derivatization combined with magnetic ionic liquid-based fast dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for determination of biogenic amines in food samples. Talanta 2019, 199, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Fu, J. Weighing paper-assisted magnetic ionic liquid headspace single-drop microextraction using microwave distillation followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the determination of essential oil components in lavender. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Rahn, K.L.; Anderson, J.L. Headspace single drop microextraction versus dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction using magnetic ionic liquid extraction solvents. Talanta 2017, 167, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trujillo-Rodríguez, M.J.; Pino, V.; Anderson, J.L. Magnetic ionic liquids as extraction solvents in vacuum headspace single-drop microextraction. Talanta 2017, 172, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahromi, Z.; Mostafavi, A.; Shamspur, T.; Mohamadim, M. Magnetic ionic liquid assisted single-drop microextraction of ascorbic acid before its voltammetric determination. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 4041–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, E.; Vidal, L.; Canals, A. Hydrophilic magnetic ionic liquid for magnetic headspace single-drop microextraction of chlorobenzenes prior to thermal desorption-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 410, 4679–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Song, D. Matrix solid-phase dispersion coupled with magnetic ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the determination of triazine herbicides in oilseeds. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 888, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzimitakos, T.G.; Anderson, J.L.; Stalikas, C.D. Matrix solid-phase dispersion based on magnetic ionic liquids: An alternative sample preparation approach for the extraction of pesticides from vegetables. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1581–1582, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Xiao, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Cheng, M. Ionic liquid magnetic bar microextraction and HPLC determination of carbamate pesticides in real water samples. Microchim. Acta 2012, 179, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedé, J.L.; Anderson, J.L.; Chisvert, A. Trace determination of volatile polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in natural waters by magnetic ionic liquid-based stir bar dispersive liquid microextraction. Talanta 2018, 176, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisvert, A.; Benedé, J.L.; Anderson, J.L.; Pierson, S.A.; Salvador, A. Introducing a new and rapid microextraction approach based on magnetic ionic liquids: Stir bar dispersive liquid microextraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 983, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, L.; Su, A.; Zhang, H. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of phenolic compounds from vegetable oils using a magnetic ionic liquid. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 3130–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Gao, N.; Fu, J.; Yue, X.; Lv, X.; Zhong, F.; Tang, J.; Wang, T. Facile synthesis of magnetic ionic liquids/gold nanoparticles/porous silicon composite SERS substrate for ultra-sensitive detection of arsenic. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 545, 148992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakkori, P.; Erdem, P.; Bozkurt, S.S. Molecularly imprinted polymer based on magnetic ionic liquid for solid phase extraction of phenolic acids. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2017, 40, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Ionic Liquid | Extraction Technique | Matrix | Target Analytes | LOD (μg·kg−1 or μg·L−1) | Recoveries (%) | Analytical Instrumental System | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [P6,6,6,14+][Dy(III)(hfacac)4−] | MIL-DLLME | water samples | sulfonamides and triazines | 0.011–0.029 and 0.013–0.030 | 90–101 and 89–98 | HPLC-DAD | [9] |
| [Ni(C8IM)42+]2[NTf2−] | SBSDME | tap and mineral water | organic pollutants | <10 | 72.5–102 | HS-GC-MS | [10] |
| trihexyltetradecylphosphonium tetrachloromanganate (II) ([P6,6,6,14+]2[MnCl42−]) | DLLME | human urine | estriol, 17-β-estradiol, 17-α-ethynylestradiol, and estrone | 2 | 67.5–115.6 | HPLC | [11] |
| benzyltrioctylammonium bromotrichloroferrate (III) | magnet-based microextraction | aqueous sample | benzo(a)anthracene (BaA), chrysene (Chy), benzo(a)pyrene (BaPy), benzo(b)fluoranthene (BbF) and benzo(k)fluoranthene (BkF) | 0.005–0.02 | 91.5–119 | HPLC-FID | [12] |
| [P6,6,6,14+]2[MnCl42−] | DLLME | river water | estrone, estradiol, 17-α-hydroxyprogesterone, chloromadinone 17-acetate, megestrol 17-acetate and medroxyprogesterone 17-acetate | 1.5–15.1 | 56-123 | HPLC-DAD | [14] |
| [P6,6,6,14+]2[CoCl42−] | DLLME | milk and cosmetics | estrone, estradiol, 17-α-hydroxyprogesterone, chloromadinone 17-acetate, megestrol 17-acetate and medroxyprogesterone 17-acetate | 5–15 | 98.5–109.3 and 96.3–111.4 | HPLC | [21] |
| [TMG][TEMPO OSO3] | MILATPs | environmental waters | chloramphenicol | 0.14 | 94.6–99.72 | HPLC | [15] |
| [C4MIM-Tempo][L-Pro] | aqueous two-phase (ATPs) system | - | phenylalanine (D-L) | - | - | HPLC | [16] |
| trihexyltetradecylphosphonium [MnCl42−] ([P6,6,6,14+]2[MnCl42−])] | DLLME | tap water, wastewater, and a tea infusion | pharmaceutical drugs, phenolics, insecticides, and polycyclicaromatic hydrocarbons | 0.25–1.00 | 53.8–114.7 (spiking 5 μg·L−1 for phenanthrene) 106.7–150 (spiking 37.5 μg·L−1 for phenanthrene) | HPLC, UV | [18] |
| 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachlo-roferrate ([C6mim][FeCl4]) | liquid–liquid microextraction technique (DLLME) | vegetable oils, two soybean oils, three maize oils and two sunflower seed oils | triazine herbicides | 1.31–1.49 | 81.8–114.2 | HPLC | [22] |
| [P6,6,6,14+][Cl−] | Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction | human urine | carbofuran, atrazine, simazine, diuron, metalochlor, ethinylestradiol, estrone, diclofenac | 75–130 | HPLC | [31] | |
| 1-ethoxyl-3-methyl-imidazoliumtetrachloroferrate [C2OHmim]FeCl4 | UAE | sinomenium acutum | sinomenine (SIN) | - | 81.3 | HPLC | [28] |
| C3MIMFeCl4 | tea leaves | polyphenols | - | 99.8 | HPLC-UV-Vis | [29] | |
| [P6,6,6,14+]3[GdCl63−] | MIL-DLLME | river and tap water | four antihypertensive drugs | - | 82.5–101.48 | HPLC-UV | [32] |
| [P6,6,6,14]3[Fe(CN)6] | IL-on SBME | environmental water | four estrogens | 0.2–0.5 | 88.5–99.6 and 88.4–99.9 | HPLC-UV | [19] |
| methyltrioctylammonium tetrachloroferrate (N8,8,8,1[FeCl4]) | SADBME | aqueous matrices | phenols and acidic pharmaceuticals | 1.05–33.0 | 89–94 | HPLC-DAD | [20] |
| methyltrioctylammonium tetrachloroferrate ([N1,8,8,8+][FeCl4]) | MIL-DLLME | water, beer and beverage samples | parabens | 300–500 | 95–103 | HPLC-UV | [30] |
| [OA]FeCl | D-μSPE | human urine and wastewater samples | carbamazepine drug | 0.51 | 85.5–98 | HPLC-DAD | [33] |
| trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium tetrachloroferrate(III) ([P6,6,6,14]FeCl4) | MIL-DLLME | honey | Cd | 0.0004 | 95.5–102 | ETAAS | [34] |
| trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium tetrachloroferrate (III) ([P6,6,6,14]FeCl4) | DLLME | honey | As | 0.012 | 95.2–102 | ETAAS | [35] |
| exyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium ([P6,6,6,14]FeCl4) | DLLME | honey | Cr | 0.005 | 94.0–101 | ETAAS | [36] |
| trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium tetrachloromanganate (II) ([P6,6,6,14]2MnCl4) | DLLME | honey, mead, honey vinegar and honey beer | Pb | 0.003 | 94.8–101 | ETAAS | [37] |
| 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroferrate [C4mim][FeCl4] | MIL-UDSA-DLLME | rice | Se | 18 | 94.9–104.8 | GFAAS | [38] |
| 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroferrate ([C4mim][FeCl4]) | AALLME | environmental water, sediment and soil samples | As | 29 | 93.0–108.5 | GFAAS | [41] |
| trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium tetrachloroferrate ([P6,6,6,14]FeCl4) | DLLME | n tap, dam, mineral, wetland, underground, rain and river water samples | Sb | 0.02 | 94.0–100 | ETAAS | [42] |
| bis(1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium) tetrathiocyanatocobaltate (II) [Emim]2[Co(SCN)4] | DLLME | engine oil, gasoline and diesel | Cd | 0.084 | 95–110 | ETAAS | [43] |
| butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetra-chloroferrate ([C4mim] [FeCl4]) | UASEME | vegetable oil | Cd, Pb | 0.002, 0.02 | 95.0–105.8 | GFAAS | [39] |
| 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroferrate ([C4mim][FeCl4] | ETA-MILs-ME | vegetable samples | As | 7 | 97.9–105.8 | GFAAS | [40] |
| ([Ni(C4IM)42+]2[Cl−] and [Ni(BeIM)42+]2[Cl−] | in situ MIL-DLLME | aqueous samples | polar and non-polar pollutants | 0.13–5.2 and 0.012–1.6 | 67.7–120 and 86.5–96.6 | HPLC-DAD | [44] |
| [Co(C4IM)+24]2[NTf2] | in situ Pa-DDE/MIL | aqueous environmental samples | organic micropollutants | 7.5 | 53.9–129.1 | HPLC-DAD | [45] |
| [P6,6,6,14+][Ni(II)(hfacac)3−] | in situ MIL-DLLME | - | long and short double-stranded DNA | - | - | fluorescence emission spectroscopy | [46] |
| [C4MIM-TEMPO]Cl | in-situ MIL-DLLME | milk samples | sulfonamides | 0.534–0.891 | 95–105 | HPLC-UV | [47] |
| [P6,6,6,14+]2[CoCl42−] | in situ derivatization- MIL-DLLME | wine and fish samples | six biogenic amines | 1.3–3.9 and 1.2–3.8 | 93.2–103.1 and 94.5–102.3 | LC-UV | [48] |
| 1-octyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroferrate ([C8MIM]FeCl4) | weighing paper-assisted magnetic ionic liquid headspace single-drop microextraction (WP-MIL-HS-SDME) | 16 lavender samples | 39 volatile compounds | - | - | GC-MS | [49] |
| ([P6,6,6,14+]2[MnCl42−]) and ([Aliquat+]2[MnCl42−]) | HS-SDME, DLLME | lake water samples | twelve aromatic compounds and four polyaromatic hydrocarbons | 0.04–1.0 and 0.05–1.0 | 70.2–109.6 and 68.7–104.5 | HPLC | [50] |
| [P6,6,6,14+][Mn(hfacac)3−] | vacuum MIL-HS-SDME | milk samples | free fatty acids (FFAs) | 14.5–70.3 | 79.5–111 | GC-MS | [51] |
| aliquat tetrachloromanganate (II) [Aliquat+]2[MnCl42−] | single-drop microextraction | aqueous samples | ascorbic acid | 0.042–48.7 | 101.0–104.1 | voltammetric determination | [52] |
| 1-ethyl-3- methylimidazolium tetraisothiocyanatocobaltate(II) ([Emim]2[Co(NCS)4]) | magnetic headspace single-drop microextraction (Mag-HS-SDME) | water samples | 1,2-dichlorobenzene,1,3-dichlorobenzene, 1,4-dichlorobenzene, 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene, 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene, 1,3,5-trichlorobenzene,1,2,3,4-tetrachlorobenzene, 1,2,4,5-tetrachlorobenzene, and pentachlorobenzene | 0.003–0.152 | 82–114 | GC-MS | [53] |
| 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroferrate ([C4 MIM][FeCl4]) | MSPD-MIL-DLLME | oilseeds | triazine herbicides | 1.20–2.72 | 82.9–113.7 | UFLC-UV | [54] |
| [P6,6,6,14+][Co(II)(hfacac)3−] | MSPD | raw vegetables | ten pesticides | - | 65–85 | HPLC-DAD | [55] |
| [C6MIM][PF6] | ILMB-ME | water samples | carbamate pesticides | 1.4–3.4 | 85–98.0 (spiking 5 μg·L−1), 80–98 (spiking 50 μg·L−1) | HPLC-DAD | [56] |
| [P6,6,6,14+][Ni(II)(hfacac)3−] | SBDLME | natural water samples | polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) | 0.0005–0.0087 | 84–115 | GC-MS | [57] |
| [P6,6,6,14+][Ni(hfacac)3−] | SBDLME | environmental water samples | lipophilic organic UV filters | 0.0099–0.027 | 87–113 (river water), 91–117 (sea-water), 89–115 (swimming pool water) | TD-GC-MS | [58] |
| 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroferrate ([C6MIM][FeCl4]) | DLLME | vegetable oil | bisphenol A and 4-nonylphenol | 0.1 and 0.06 | 70.4–112.3 | HPLC-MS/MS | [59] |
| 1-methyl-3-hexyl imidazole ferric tetrachloride ([C6MIM]FeCl4) | immersion method | water samples | arsenic | 0.500 | - | - | [60] |
| 1-allyl-3-octylimidazolium tetrachloroferrate | SPE | apple samples | phenolic acids | 0.31–1.72 | 81–100 | HPLC-DAD | [61] |
| trihexyltetradecylphosphonium tetrachloroferrate (III) ([3C6PC14][FeCl4]) | magnetic room temperature ionic liquid | soil samples | phenol (Ph), 4-nitrophenol (4-NP), 2-chlorophenol (2-CP), 4-chlorophenol (4-CP), 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP), 3,5-dichlorophenol (3,5-DCP), pentachlorophenol (penta-CP), and 2-benzyl-4-chlorophenol (2-Bn-4-CP) | - | - | UV-Vis-NIR spectrometer, HPLC | [17] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chatzimitakos, T.; Anagnostou, P.; Constantinou, I.; Dakidi, K.; Stalikas, C. Magnetic Ionic Liquids in Sample Preparation: Recent Advances and Future Trends. Separations 2021, 8, 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8090153
Chatzimitakos T, Anagnostou P, Constantinou I, Dakidi K, Stalikas C. Magnetic Ionic Liquids in Sample Preparation: Recent Advances and Future Trends. Separations. 2021; 8(9):153. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8090153
Chicago/Turabian StyleChatzimitakos, Theodoros, Phoebe Anagnostou, Ioanna Constantinou, Kalliroi Dakidi, and Constantine Stalikas. 2021. "Magnetic Ionic Liquids in Sample Preparation: Recent Advances and Future Trends" Separations 8, no. 9: 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8090153
APA StyleChatzimitakos, T., Anagnostou, P., Constantinou, I., Dakidi, K., & Stalikas, C. (2021). Magnetic Ionic Liquids in Sample Preparation: Recent Advances and Future Trends. Separations, 8(9), 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8090153








