Lanthanum Diffusion in Fluorapatite at 400 °C, 50 MPa and 4–16 wt %
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Instruments and Sample Pretreatment
2.2. Experimental Process Control
2.3. Sample Analysis after Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
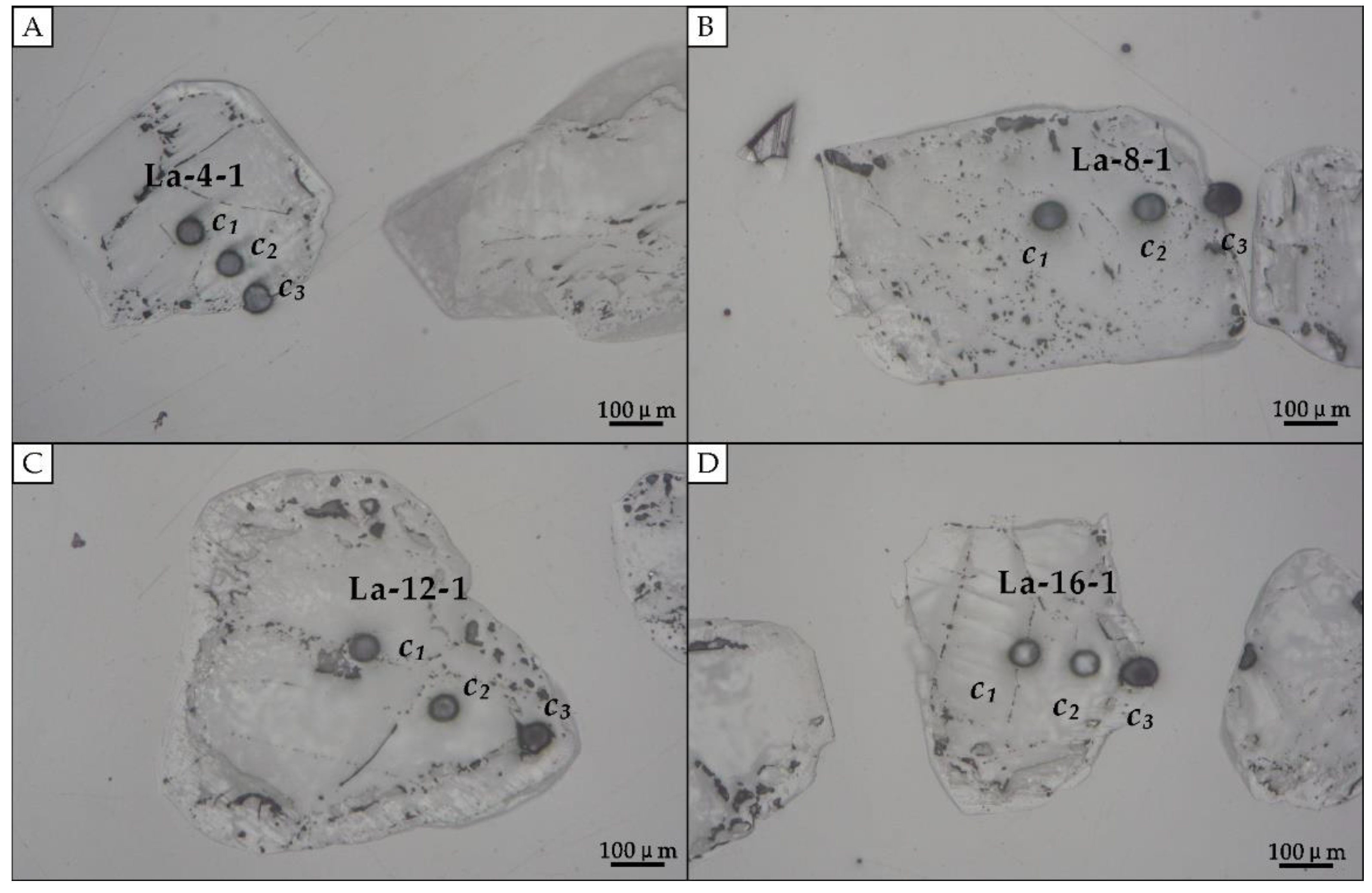
3.1. Experimental Result
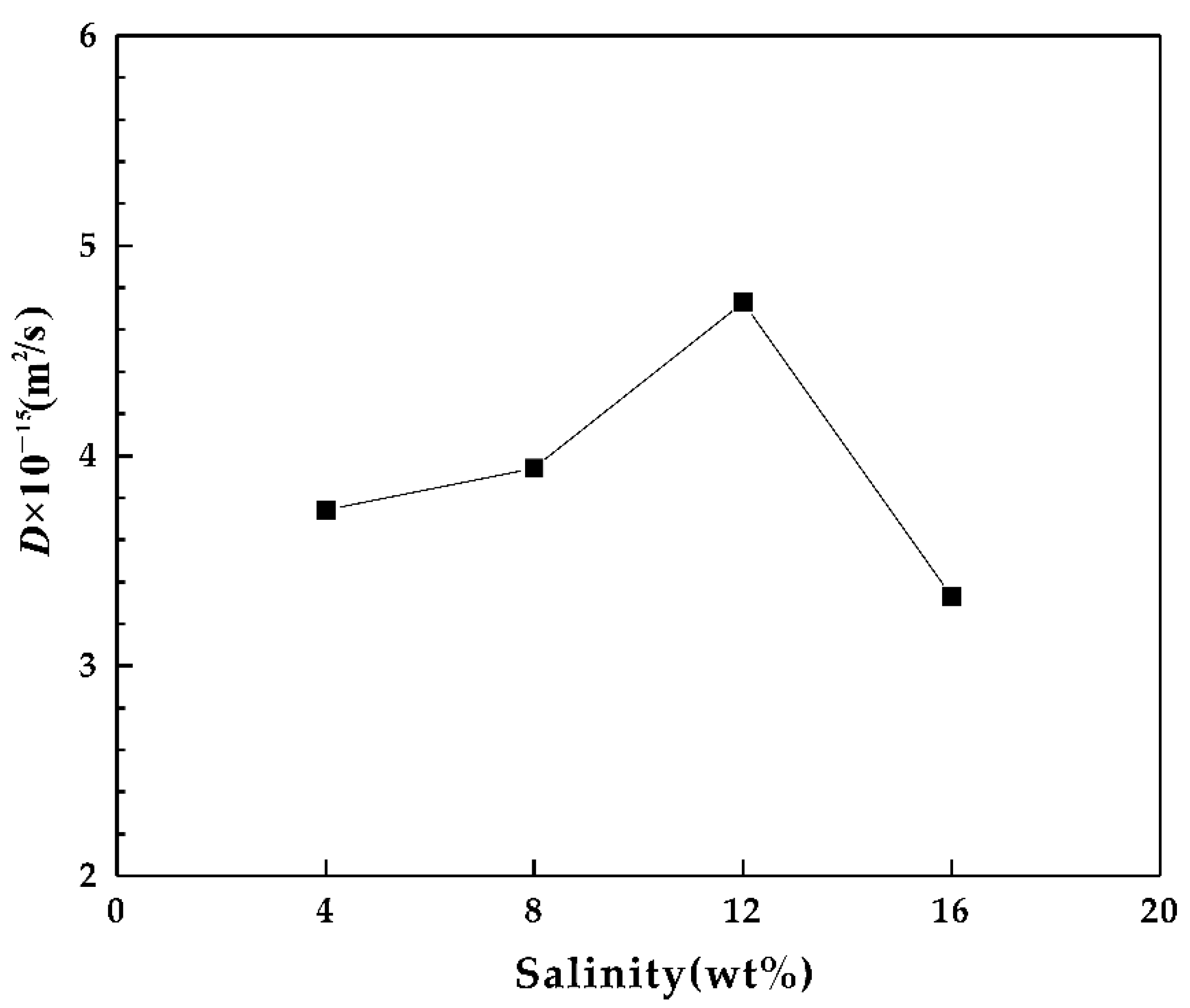
3.2. Diffusion Coefficient of La in Fluroapatite
3.3. Geological Implications
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, M.; Henderson, P.; Campbell, L. Fractionation of the REE during hydrothermal processes: Constraints from the Bayan Obo Fe-REE-Nb deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 3141–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlov, D.E.; Förster, H.-J. Fluid-induced nucleation of (Y+REE)-phosphate minerals within apatite: Nature and experiment. Part II. Fluorapatite. Am. Mineral. 2004, 88, 1209–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynard, B.; Lecuyer, C.; Grandjean, P. Crystal-chemical controls on rare-earth element concentrations in fossil biogenic apatites and implications for paleoenvironmental reconstructions. Chem. Geol. 1999, 155, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, Y.; Terada, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Nutman, A.P. Origin of life from apatite dating? Nature 1999, 400, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouch, J.E.; Hole, M.J.; Trewin, N.H.; Chenery, S.; Morton, A.C. Authigenic Apatite in a Fluvial Sandstone Sequence: Evidence for Rare-Earth Element Mobility During Diagenesis and a Tool for Diagenetic Correlation. J. Sediment. Res. 2002, 72, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenberg, S.N.; Nadeau, P.H. Postdepositional Sm/Nd Fractionation in Sandstones: Implications for Neodymium-Isotope Stratigraphy. J. Sediment. Res. 2002, 72, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchelt, H.; Emmermann, R. Bearing of rare earth patterns of apatites from igneous and metamorphic rocks. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1976, 31, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y. REE Geochemical Characteristic of Apatite: Implications for Ore Genesis of the Zhijin Phosphorite. Minerals 2020, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsbo, P.; McLaughlin, P.I.; Breit, G.N.; du Bray, E.A.; Koenig, A.E. Rare earth elements in sedimentary phosphate deposits: Solution to the global REE crisis? Gondwana Res. 2015, 27, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, I. Phosphorite geochemistry: State-of-the-art and environmental concerns. Eclogae Geol. Helv. 1995, 87, 643–700. [Google Scholar]
- Piper, D.Z. Trace Elements and Major-Element Oxides in the Phosphoria Formation at Enoch Valley, Idaho Permian Sources and Current Reactivities1; No. 99-163; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1999.
- Long, K.R.; Van Gosen, B.S.; Foley, N.K.; Cordier, D. The Principal Rare Earth Elements Deposits of the United States: A Summary of Domestic Deposits and a Global Perspective. In Non-Renewable Resource Issues; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosu, L.; Lepland, A.; Kirsimäe, K.; Romashkin, A.E.; Roberts, N.M.W.; Martin, A.P. The REE-composition and petrography of apatite in 2 Ga Zaonega Formation, Russia: The environmental setting for phosphogenesis. Chem. Geol. 2015, 395, 88–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.; Seymour, R.S.; Shaw, H.F.; Clark, D.L. REE and Nd isotopes in conodont apatite: Variations with geological age and depositional environment. Spec. Pap. Geol. Soc. Am. 1984, 196, 325–340. [Google Scholar]
- Morad, S. Identification of primary Ce-anomaly signatures in fossil biogenic apatite: Implication for the Cambrian oceanic anoxia and phosphogenesis. Sediment. Geol. 2001, 143, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.E.; Scher, H.D. Preservation of seawater Sr and Nd isotopes in fossil fish teeth: Bad news and good news. Earth. Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 220, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, A.V. Rare-earth geochemistry of ‘old’ phosphorites and probability of syngenetic precipitation and accumulation of phosphate. Chem. Geol. 1998, 144, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, G.; Stille, P. Diagenetic constraints on the use of cerium anomalies as palaeoseawater redox proxies: An isotopic and REE study of Cambrian phosphorites. Chem. Geol. 2001, 175, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, G.A.; Webb, G.E. Has the REE composition of seawater changed over geological time? Chem. Geol. 2004, 204, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaby, E.; Gros, K.; Förster, H.-J.; Wudarska, A.; Birski, Ł.; Hamada, M.; Götze, J.; Martin, H.; Jayananda, M.; Moyen, J.-F. Mineral–fluid interactions in the late Archean Closepet granite batholith, Dharwar Craton, southern India. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2019, 489, 293–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzari, F.; Hart, C.; Bissig, T.; Barker, S. Hydrothermal Alteration Revealed by Apatite Luminescence and Chemistry: A Potential Indicator Mineral for Exploring Covered Porphyry Copper Deposits. Econ. Geol. 2016, 111, 1397–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krneta, S.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Cook, N.J.; Ehrig, K.; Kontonikas-Charos, A. Rare Earth Element Behaviour in Apatite from the Olympic Dam Cu–U–Au–Ag Deposit, South Australia. Minerals 2017, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, C.N.; Watts, K.E.; Gross, J. Apatite trace element geochemistry and cathodoluminescent textures—A comparison between regional magmatism and the Pea Ridge IOAREE and Boss IOCG deposits, southeastern Missouri iron metallogenic province, USA. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 116, 103129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, M.-F. Multiple stages of hydrothermal REE remobilization recorded in fluorapatite in the Paleoproterozoic Yinachang Fe–Cu–(REE) deposit, Southwest China. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 166, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, K.; Słaby, E.; Förster, H.-J.; Michalak, P.P.; Munnik, F.; Götze, J.; Rhede, D. Visualization of trace-element zoning in fluorapatite using BSE and CL imaging, and EPMA and μPIXE/μPIGE mapping. Mineral. Petrol. 2016, 110, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orman, J.; Grove, T.L.; Shimizu, N. Rare earth element diffusion in diopside: Influence of temperature, pressure, and ionic radius, and an elastic model for diffusion in silicates. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2001, 141, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, W.J.; Wood, B.J. An experimental investigation of the partitioning of REE between garnet and liquid with reference to the role of defect equilibria. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1980, 72, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, J.; Tirone, M.; Hervig, R. Diffusion kinetics of samarium and neodymium in garnet, and a method for determining cooling rates of rocks. Science 1998, 281, 805–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusebauch, C.; John, T.; Whitehouse, M.J.; Klemme, S.; Putnis, A. Distribution of halogens between fluid and apatite during fluid-mediated replacement processes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 170, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Hu, Z.C.; Zong, K.Q.; Gao, C.G.; Chen, H.H. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Mernagh, T.P.; Lan, T.; Tang, Y.; Wygralak, A. Intrusion related gold deposits in the Tanami and Kurundi-Kurinelli goldfields, Northern Territory, Australia: Constraints from LA-ICPMS analysis of fluid inclusions. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freer, R. Diffusion in silicate minerals and glasses: A data digest and guide to the literature. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1981, 76, 440–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, M.H. Closure temperature in cooling geochronological and petrological systems. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1973, 40, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherniak, D. Rare earth element diffusion in apatite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 3871–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.I.; Jiang, S.-Y. A LA-ICP-MS analysis of rare earth elements on phosphatic grains of the Ediacaran Doushantuo phosphorite at Weng’an, South China: Implication for depositional conditions and diagenetic processes. Geol. Mag. 2017, 154, 1381–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, S.J.; Harouiya, N.; Chaïrat, C.; Oelkers, E.H. Experimental studies of REE fractionation during water–mineral interactions: REE release rates during apatite dissolution from pH 2.8 to 9.2. Chem. Geol. 2005, 222, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
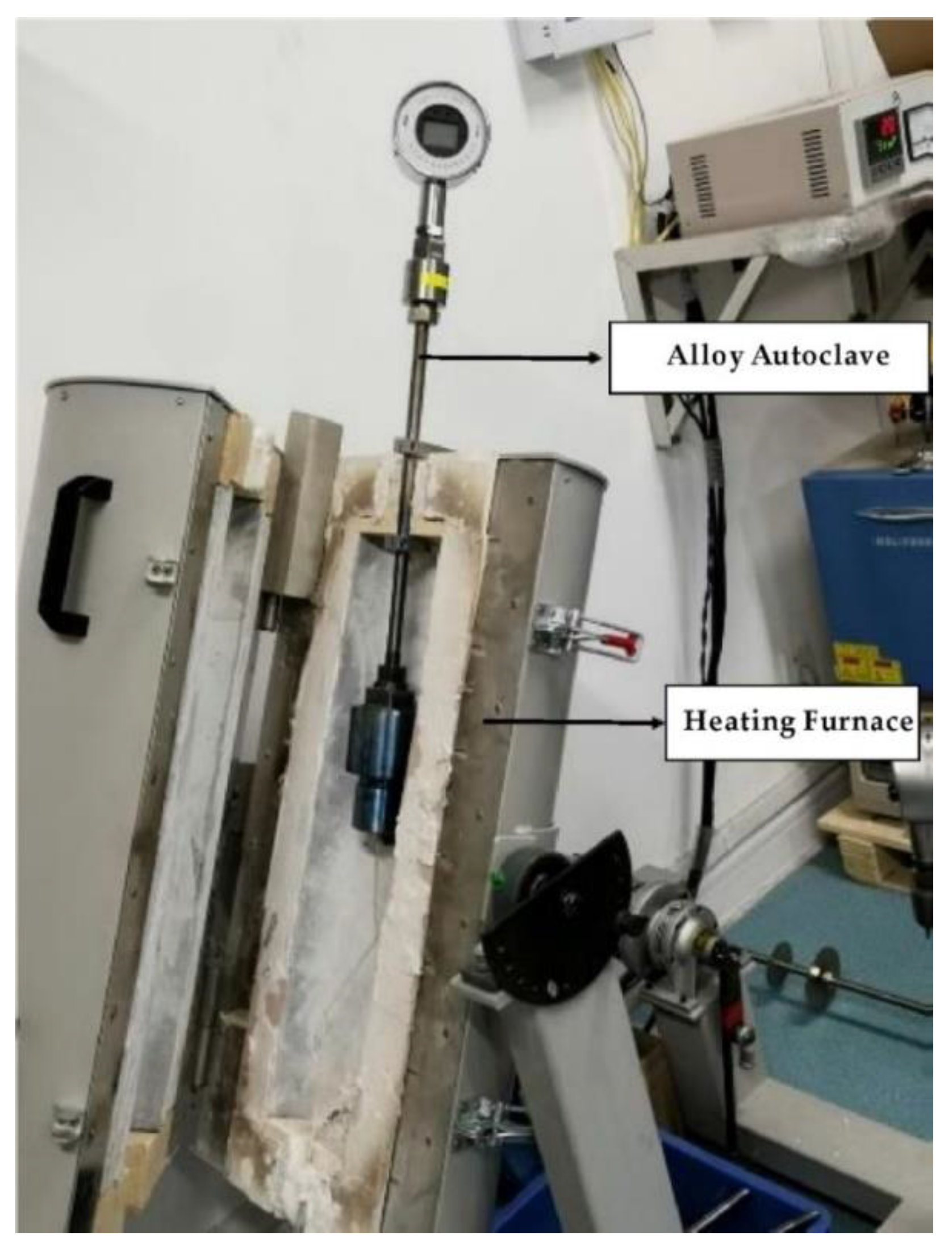


| Laser Ablation System | |
|---|---|
| Instrument | GeoLasPro 193 nm |
| Energy Density (J/cm2) | 10 |
| Safety level | IIIb |
| Frequency (Hz) | 10 |
| Spot Size (μm) | 40 |
| Confidence level | 95% |
| Blank time (s) | 18 |
| Denudation time (s) | 50 |
| Detection limit of REE (ppm) | 0.03–0.4 |
| ICP–MS system | Agilent 7900 |
| Monitored isotope | 44Ca, 89Y, 139La, 140Ce, 141Pr, 146Nd, 147Sm, 153Eu, 160Gd, 159Tb, 163Dy, 165Ho, 166Er, 165Ho, 166Er, 169Tm, 172Yb and 175Lu. |
| Reference material | NIST610, NIST612, NIST614 and Durago apatite |
| Samples | C1/ppm | x1/μm | C2/ppm | x2/μm | D/m2/s | D/m2/s (AVG) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La-4-1 | 3.45 | 160 | 14.58 | 90 | 3.33 × 10−15 | 3.74 × 10−15 |
| La-4-2 | 3.06 | 170 | 8.02 | 100 | 4.67 × 10−15 | |
| La-4-3 | 0.2 | 190 | 0.89 | 130 | 3.24 × 10−15 | |
| La-8-1 | 0.33 | 230 | 0.44 | 220 | 4.04 × 10−15 | 3.94 × 10−15 |
| La-8-2 | 15.45 | 200 | 48.72 | 150 | 3.83 × 10−15 | |
| La-12-1 | 9.07 | 240 | 31.63 | 170 | 5.88 × 10−15 | 4.73 × 10−15 |
| La-12-2 | 36.71 | 190 | 252.20 | 100 | 3.58 × 10−15 | |
| La-16-1 | 2.53 | 240 | 10.09 | 120 | 3.57 × 10−15 | 3.33 × 10−15 |
| La-16-2 | 0.37 | 240 | 1.20 | 150 | 2.81 × 10−15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y. Lanthanum Diffusion in Fluorapatite at 400 °C, 50 MPa and 4–16 wt %. Separations 2021, 8, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8060072
Liu X, Zhang H, Liu Y. Lanthanum Diffusion in Fluorapatite at 400 °C, 50 MPa and 4–16 wt %. Separations. 2021; 8(6):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8060072
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiqiang, Hui Zhang, and Yunlong Liu. 2021. "Lanthanum Diffusion in Fluorapatite at 400 °C, 50 MPa and 4–16 wt %" Separations 8, no. 6: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8060072
APA StyleLiu, X., Zhang, H., & Liu, Y. (2021). Lanthanum Diffusion in Fluorapatite at 400 °C, 50 MPa and 4–16 wt %. Separations, 8(6), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8060072







