Abstract
The benefits of ginseng have been mainly attributed to its triterpenoids, called ginsenosides. Recent genome sequencing of the Panax ginseng has paved the way for in-depth proteomic studies of this medicinal plant. The current study was conducted to deepen the proteomic information on the root proteome of Korean ginseng. Proteomic workflow was optimized by testing two different strategies, characterized by the phenol extraction procedure, the presence or the absence of SDS-PAGE fractionation step, and nano-scale liquid chromatographic tandem mass spectrometry (nLC-MS/MS) analysis. The results highlighted an evident improvement of proteome extraction by the combination of phenol extraction with SDS-PAGE before the nLC-MS/MS analysis. In addition, a dramatic impact of the steaming process (the treatment to produce red ginseng from ginseng) on protein properties was observed. Overall, the analyses of Korean ginseng permitted the characterization of a total of 2412 proteins. A large number of identified proteins belonged to the functional categories of protein and carbon/energy metabolism (22.4% and 14.6%, respectively). The primary and secondary metabolisms are major metabolic pathways, which emerged from the proteomic analysis. In addition, a large number of proteins known to play an important role in response to (a)biotic stresses were also identified. The current proteomic study not only confirmed the previous transcriptomic and proteomic reports but also extended proteomic information, including the main metabolic pathways involved in Korean ginseng.
1. Introduction
Panax ginseng Meyer, a species belonging to the Araliaceae family, is a slow-maturing perennial herb used for 5000 years in the far east for its medicinal properties. Panax ginseng was originally used for alimentary purposes and its use was extended for physical comfort later on [1]. Since an initial report about the pharmacological effects of Panax ginseng in the 1950s [2], research on this medicinal plant has surged.
Even though various efforts have been made to discover the molecular basis of ginseng’s beneficial effects, the exact mechanisms of action of its components are still unclear [3,4,5]. Among the various chemical components of Panax ginseng, the bioactivity of ginsenoside has been mostly studied. Clinical trials have demonstrated its pharmacological effects on the central nervous and cardiovascular systems, inflammation, cancer, and diabetes [6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. However, only few works have dealt with the characterization of small molecules and proteins of Panax ginseng until now.
An in-depth analysis of proteomes is essential to complement transcriptomic data and thereby to understand the molecular and biochemical basis of different metabolic pathways [13]. In 2005, a scientific report [14] described a proteomic approach to the analysis of Korean Panax ginseng: among the identified proteins in the root were four isoforms of an RNase-like major storage protein. This protein belongs to a family of proteins known to act as a reserve for the survival of plants [15]. Other proteomics studies on Panax provided the first proteome profile by the use of two-dimensional electrophoresis (2D-gel) maps that led to the identification of 20 proteins of Panax quinquefolius [16], and 17 proteins of Panax ginseng hairy roots [17]. More recently, a proteomic study was conducted with a more sensitive extraction method, which led to the identification of 207 proteins [3]. The genome sequencing of Panax ginseng paved the way for in-depth proteomic studies [18,19]. Recently, a proteomic analysis of the cauline leaf and root of Panax ginseng reported a large number of proteins, while also characterizing the biosynthetic pathway at the proteomic level [20]. According to different roles of the two organs, this study highlighted that only half of identifying proteins overlapped between two parts.
Red ginseng is a form of Panax ginseng, typically produced in Korea, whose roots are exposed to a steaming process at about 90 °C for 3 h followed by a drying process. After the steaming treatment, the roots become reddish, which is the origin of the name of red ginseng [21]. The steaming process affects the properties of ginseng, and its characteristics warrant further study in detail [22]. In this context, information about the effects induced by the streaming process on the protein profile is very scarce. Until now, no proteomics analysis on red ginseng has been performed.
A crucial step in proteomic analysis of plant tissue is the procedure adopted for protein extraction. The presence of a high concentration of interfering compounds, such as phenolics, terpenes, organic acids, ions, and carbohydrates, makes it particularly difficult to obtain a protein fraction suitable for proteomic analysis [23]. In this context, the phenol extraction method followed by ammonium acetate in methanol precipitation was found to be the most appropriate protocol up to now [23,24,25]. Moreover, the addition of SDS-PAGE step is a further possible strategy to improve both the removal of interfering compounds and the resolution of the proteomics analyses [26,27,28]. Although, these approaches permitted the improvement of the quality of protein sample of different plant materials, many studies highlighted that each plant material requires a specific optimization of the protein extraction protocol.
The first aim of this present work was to define a protocol to be used to improve the resolution of proteomics analysis for the root of Panax ginseng (i.e., white ginseng). In this context, the efficiency of in-solution or in-gel digestions strategy was evaluated. Subsequently, the elaboration of results produced by the combined experimental approach permitted the obtaining of in-depth information on the proteome of ginseng. In order to investigate the impact of the steaming procedure on the protein pattern, the same experimental procedure was also adopted to analyze the red ginseng.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
The water used for the preparation of the different buffers was purified through a purification system Milli-Q (Millipore). The 4x Laemmli sample buffer (LSB), Precision Plus Protein standard, Bio-safe Coomassie G 250, 10x Tris glycine-SDS, Bio-Rad Mini-PROTEAN System and precast Mini Protean TGX gels were from Bio-Rad Laboratories. The enzyme trypsin and Lys-C were from Roches Diagnostic S.p.A. All other analytical grade reagents were from Sigma-Aldrich S.r.l.
2.2. Experimental Material
The Korean ginseng root and red ginseng were obtained from the Korean Red ginseng Corporation.
2.3. Protein Extraction
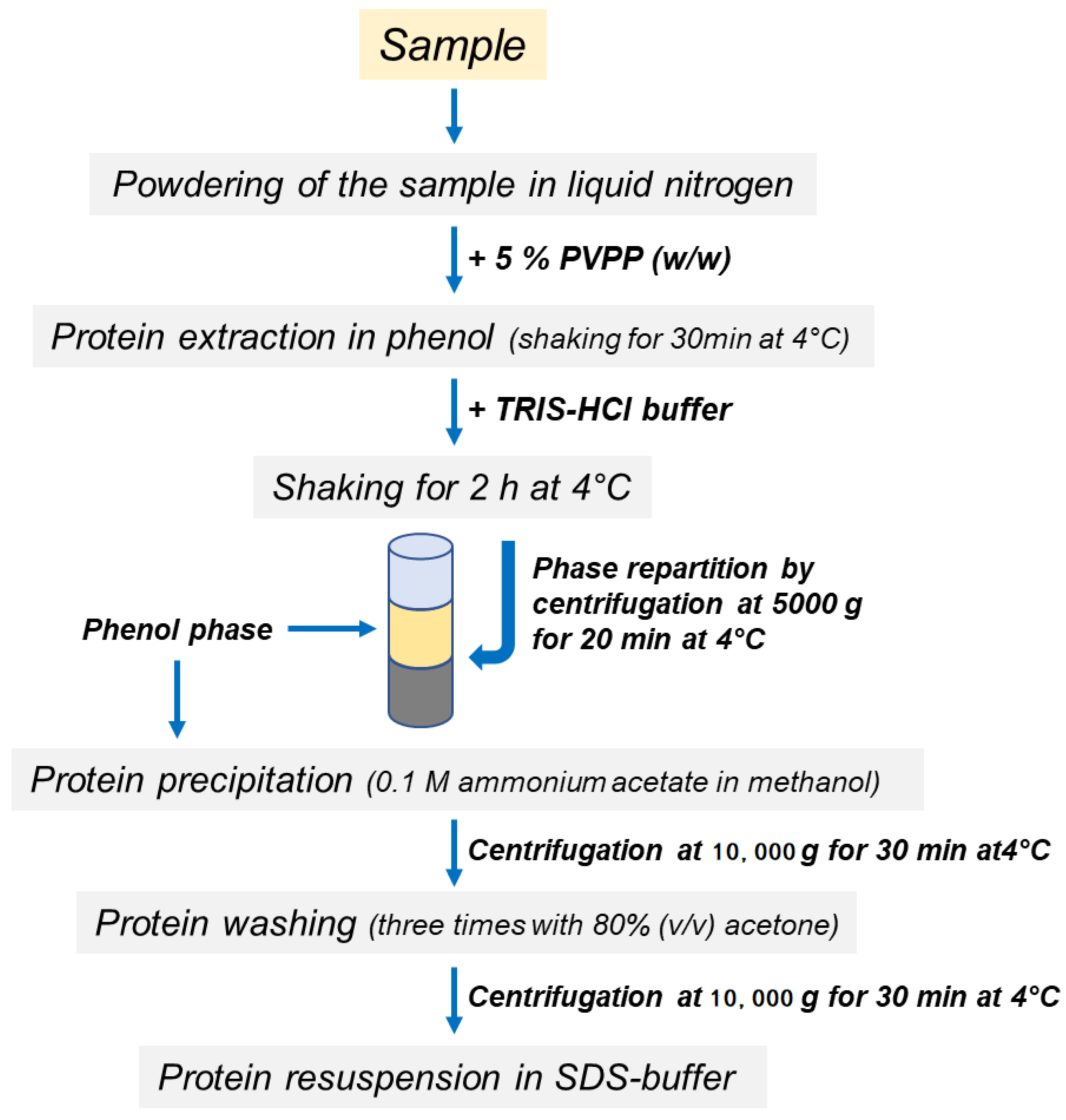
Proteins were extracted from the roots as previously described [29] with some modifications. A scheme of the protocols is shown in Figure 1. Briefly, 0.25 g of polyvinylpolypyrrolidone (PVPP) was added to 5 g of root powder and proteins were extracted in 25 mL of acidic phenol (P4557, Sigma-Aldrich, without the addition of the equilibration Buffer). The sample was incubated at 4 °C for 30 min with shaking. Other macromolecules were separated by repartition procedures after the addition of Tris-HCl buffer [0.7 M sucrose, 0.5 M Tris-HCl pH 8, 10 mM Na2-EDTA, 4 mM ascorbic acid, 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 1 µM leupeptin, 0.1 mg mL−1 Pefabloc, 0.4% (v/v) β-mercaptoethanol]. After 2 h of incubation at 4 °C in continuous agitation, phase partitioning was performed by centrifugation at 5000 g for 20 min at 4 °C and the upper phenol phase, containing protein fraction, was finally recovered. Protein samples were precipitated in five volumes of 0.1 M ammonium acetate in methanol and washed three times in 80% (v/v) acetone. The final pellet, obtained by centrifugation at 10,000 g for 30 min at 4 °C, was dissolved in 2 mL of SDS-buffer containing 150 mM Tris-HCl pH 6.8, 10% glycerol, 2% SDS, 2% β-mercaptoethanol.
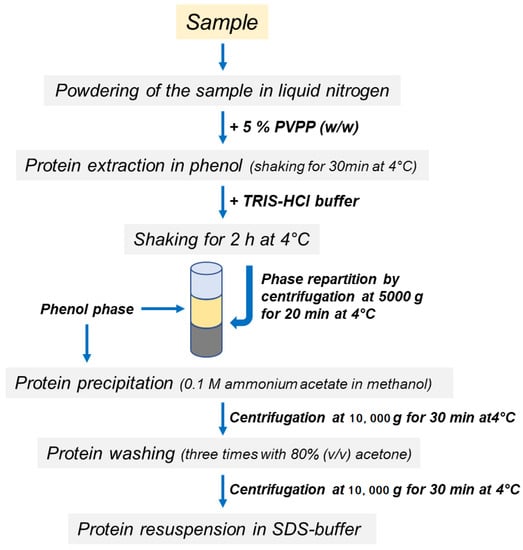
Figure 1.
Schematic workflow of protein extraction methods.
The protein content was determined by the 2-DE Quant kit (GE Healthcare) using bovine serum albumin as the standard.
2.4. SDS-PAGE
Sample aliquots were mixed with 12.5 µL of 4x Laemmli Sample Buffer (LSB) added with 50 mM dithiothreitol (DTT). Before loading onto gels, the samples were heated for 5 min at 95 °C. The electrophoresis run was performed by applying a constant voltage of 200 V for 30 min, and monitored by checking the run of Precision Plus Protein Standards Markers (Mr 10–250 kD, Bio-Rad). After electrophoresis completion, gels were stained with Bio-Safe Coomassie. Gel images were acquired using the Molecular Imager VersaDoc MP 5000 and using the software Quantity One 1-D (Bio-Rad) set to detect Coomassie staining at medium resolution. Filters were used to enhance the contrast of entire gel images.
2.5. Protein Digestion and Peptide Desalting
In-gel digestion was performed as described [30]. Each line of ginseng samples was cut into 10 regular slices, while for red ginseng samples the gel slices with visible bands was picked up. Briefly, gel slices were destained twice for 10 min with 100 µL of 50% 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate/50% acetonitrile. For cysteine reduction, gel pieces were incubated (56 °C, 60 min) with 100 µL of 10 mM DTT in 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate. After removal of the reducing solution, 100 µL of 55 mM iodoacetamide in 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate were added and samples were incubated for 45 min in the dark. Gel pieces were then washed twice with 100 µL of 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate for 10 min and incubated for dehydration with 100% acetonitrile. Samples were then incubated (overnight, 37 °C) with 1 µg of sequencing-grade trypsin dissolved in 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate. After this period, the solutions containing the digested peptides were collected in new tubes. Gel pieces were incubated with 50 µL of extraction solution (3% trifluoroacetic acid, 30% acetonitrile) for 10 min. The solution in each tube was collected and pooled with the corresponding initial peptide mixture. Gel pieces were incubated for an additional 10 min with 100% acetonitrile. The solution of each tube was collected again and pooled with the previous one.
For in-solution digestion, 100 µg of protein sample was diluted with 80 µL of 8 M urea solution. After the addition of 8 µL of the reduction buffer (10 mM DTT in 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate), the samples were incubated for 30 min at room temperature. Eight µL of 55 mM iodoacetamide in 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate were then added, after which samples were incubated for 20 min in the dark. One µg of Lys-C (enzyme concentration 0.5 µg/µL) was then added to the sample. After three hours, the samples were diluted 8-fold with digestion buffer (50 mM ammonium bicarbonate in water), and finally incubated overnight at 37 °C after the addition of 2 µg of trypsin (enzyme concentration 0.5 µg/µL).
The peptides derived from both in-gel and in-solution digestions were purified using Stage Tips, C18 (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, the solutions containing the peptides were loaded onto the Stage tips after their activation and washes. The peptides were eluted using 10 µL of 85% acetonitrile, 0.1% formic acid two times. The eluted peptides were then evaporated in a vacuum concentrator (Christ Speedvac RVC 2-25); dried peptides were stored at −20 °C until the nLC-MS/MS analysis.
2.6. NLC-MS/MS Analysis
The peptides were loaded in a 96-well plate and automatically injected by an Easy- Nlc1000 (Proxeon) with autosampler into a Q Exactive (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) mass spectrometer, which was connected on-line through a nano-ESI source. The peptides were separated by RP-LC using the same chromatographic system. For each analysis, 5 µL of sample were injected into a hand-made nano column (C18-AQ resin, 75 µm × 12 cm, particle diameter 1.9 µm, Dr. Masisch GmbH, Ammerbuch, Germany) using a nano-flow of 200 nl/min of 99% phase A (0.1% formic acid in water) and 1% phase B (0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile). After the injection, the peptides were eluted from the column by a linear gradient (10% to 70% in 55 min) of phase B, after which the column was extensively washed in 80% phase B for 5 min and re-equilibrated in phase A for 15 min. The entire chromatographic process was monitored by the software Xcalibur, Thermo (3.1.66.10 version). The flow from the column was electrosprayed using a positive voltage. During the whole process, the instrument worked in Data-Dependent-Analysis (DDA), to switch automatically between the acquisition of MS and MS/MS spectra. The spectra were acquired in Profile mode by Orbitrap analyzer in a scansion window 300–2000 m/z, with Automatic Gain Control of 3 × 106 using 35,000 (FWHM at 200 m/z) resolution. After acquisition of full MS spectra, ions (minimum charge state 2+, minimum intensity 10,000 cps) were automatically selected and fragmented in the ion trap by collision-induced dissociation (CID). In order to avoid the continuous fragmentation of the most abundant ions, the dynamic exclusion was activated, by which the ions observed twice in 30 s were excluded for 15 s.
2.7. Protein Identification
Proteome Discoverer software (version 2.2.0.338, Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), implemented with the SEQUEST algorithm, was used to compare the experimental full and tandem mass spectra with the theoretical ones obtained by the in silico proteolytic digestion of all the proteins within the Panax ginseng protein sequences_v1.1 dataset (FASTA, http://ginsengdb.snu.ac.kr/index.php (accessed on 2 April 2019)). Trypsin was selected as the cleaving protease, allowing a maximum of two missed cleavages. Peptide and fragment ion tolerances were set to 10 ppm and 0.6 Da, respectively. Cysteine carbamidomethylation was set as fix modification (+57.02147 Da), while methionine oxidation (+15.99491 Da) was allowed as a variable modification. As a quality filter, only peptide sequences assigned with an XCorr value grater then 2.2 were considered as genuine peptide identifications. To ensure the lowest number of false positives, the mass values experimentally recorded were further processed through a combined search with the Database Decoy, where the protein sequences are inverted and randomized. This operation allows the calculation of the statistical value False Discovery Rate (FDR) for PSMs (Peptide Spectral Matches), Peptide Groups, Proteins, and Protein Groups to measure the certainty of the matches at each level; all the identifications out of the FDR range of between to 0.01 (strict) and 0.05 (relaxed) were rejected. Moreover, only proteins listed with at least two unique peptides were confirmed. Each MS raw file (raw data from In-solution digestion analysis and raw data from In-gel digestion analysis) was processed to search against Panax ginseng proteome databases; all the assignments deriving from the two experiments (in-gel/in-solution digestion) computationally regarded as reliable were finally merged into a final list. In order to assign putative functions of identified proteins, sequences were matched against Arabidopsis thaliana TAIR proteome database using TAIR BLAST 2.9.0+ (https://www.arabidopsis.org/Blast/index.jsp (accessed from July 2019 to September 2020).
2.8. MapMan Visualization
Identified proteins were visualized in metabolism pathway schemes produced by the MapMan [31] software and referred to the Arabidopsis thaliana mapping file. The MapMan software (Version 3.6.0RC1) was downloaded from MapMan website (https://mapman.gabipd.org/ (accessed in September 2019)).
3. Results and Discussion
Proteomic information is a fundamental piece of the puzzle that characterizes living organisms at the biochemical and molecular levels. Moreover, these proteins and peptides may have relevant nutraceutical and medicinal properties that are valuable for humans [32]. Here, we report an extensive study to deepen the proteomic information on the root of Korean Panax ginseng.
3.1. Evaluation of Different Proteomics Analysis Strategies
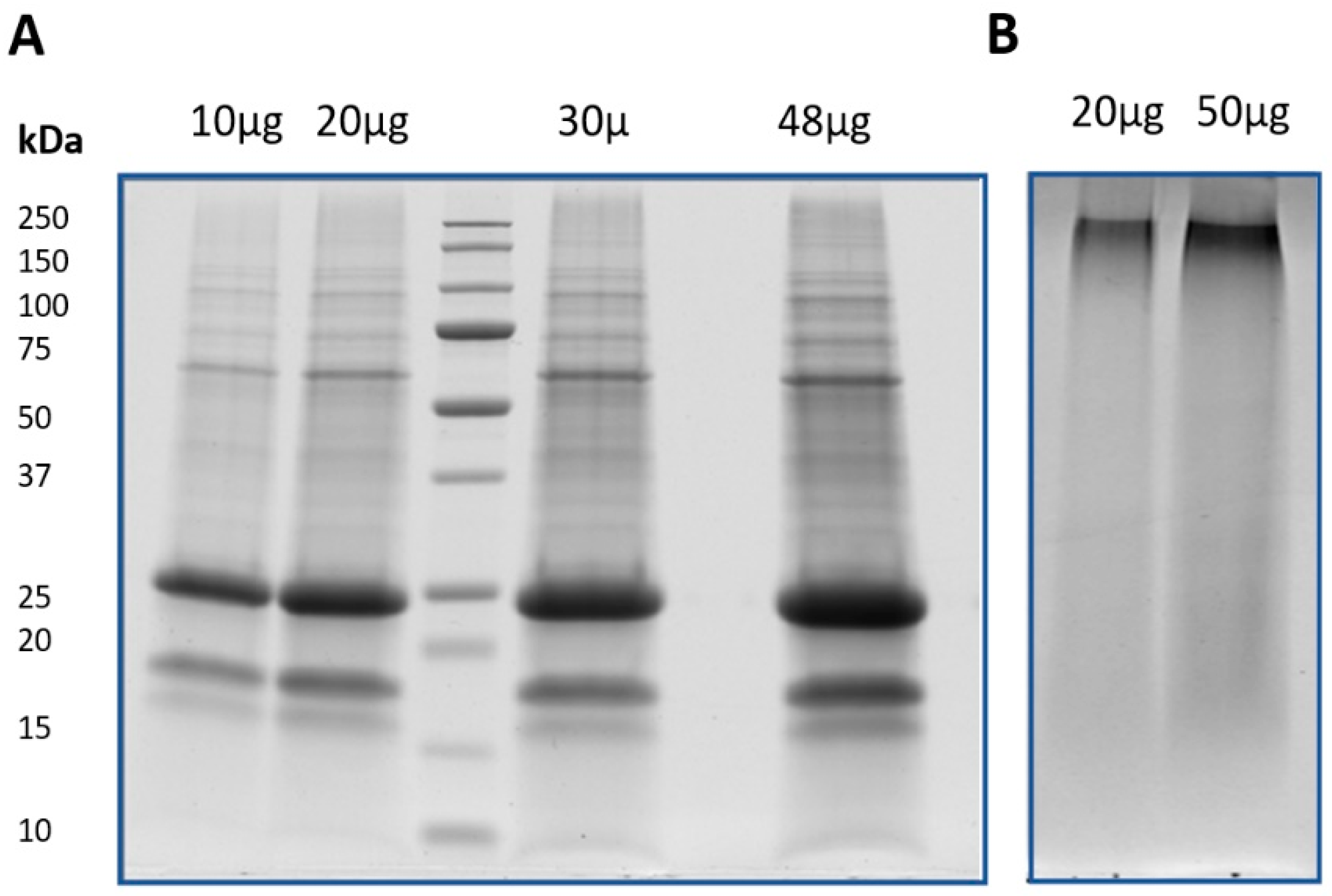
In order to obtain the protein fraction from the Korean ginseng, we adopted a phenol extraction procedure, known to efficiently remove the interfering compounds such as sugars, lipids and secondary compounds, which are known to affect the steps of both protein extraction and protein solubilization [33,34]. Firstly, the efficiency of the method was evaluated on the basis of the SDS-PAGE electrophoretic profiles. As shown in Figure 2A, protein profiles characterized by multiple well defined bands at different values of molecular weight was obtained for ginseng samples. Lane intensities were proportional with the amount of sample loaded in the gel and, in accordance with recent proteomic study conducted on ginseng, the protein profile was characterized by a very intense band with MW of ca. 25 kDa [20].
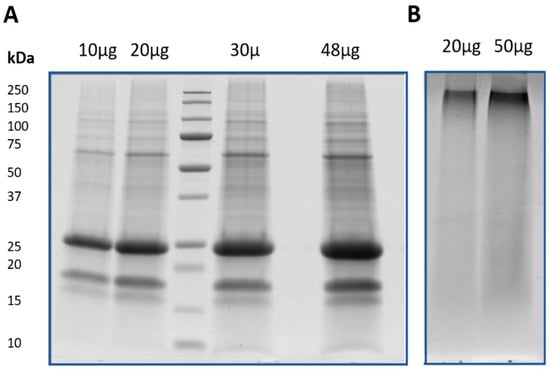
Figure 2.
Electrophoretic profiles of protein samples obtained by phenol extraction method. (A) SDS-PAGE results of ginseng loading 10, 20, 30, and 48 µg of proteins; (B) SDS-PAGE results of red Ginseng loading 20 and 50 µg of proteins.
Differently, this experimental approach did not allow for resolution of the protein profile of red ginseng (Figure 2B). For this sample, only one band at high MW (about 250 kDa) and a smear in the remaining part of the lane were observed. The results indicate that the steaming process dramatically affects the characteristics of proteins. As has long been known, high-temperature treatments affect the structure of plant proteins, changing their physical, chemical, and functional properties [35]. This conclusion was further supported by LC-MS/MS analysis, that did identify any protein from the sample obtained after digestion with trypsin of the only detectable band in red ginseng (data not shown). A better understanding of this phenomenon may be achieved by future studies on the effect(s) of heat treatments with both increasing times and/or temperature on the characteristics of ginseng root proteins. Another aspect that would be interesting to verify in future studies is the possible presence of peptides. In other words, even if the steaming process deeply affects the protein characteristics, some peptides could still be present in the red ginseng. In this view, the possible bioactive action in humans can be an interesting field to investigate [36,37].
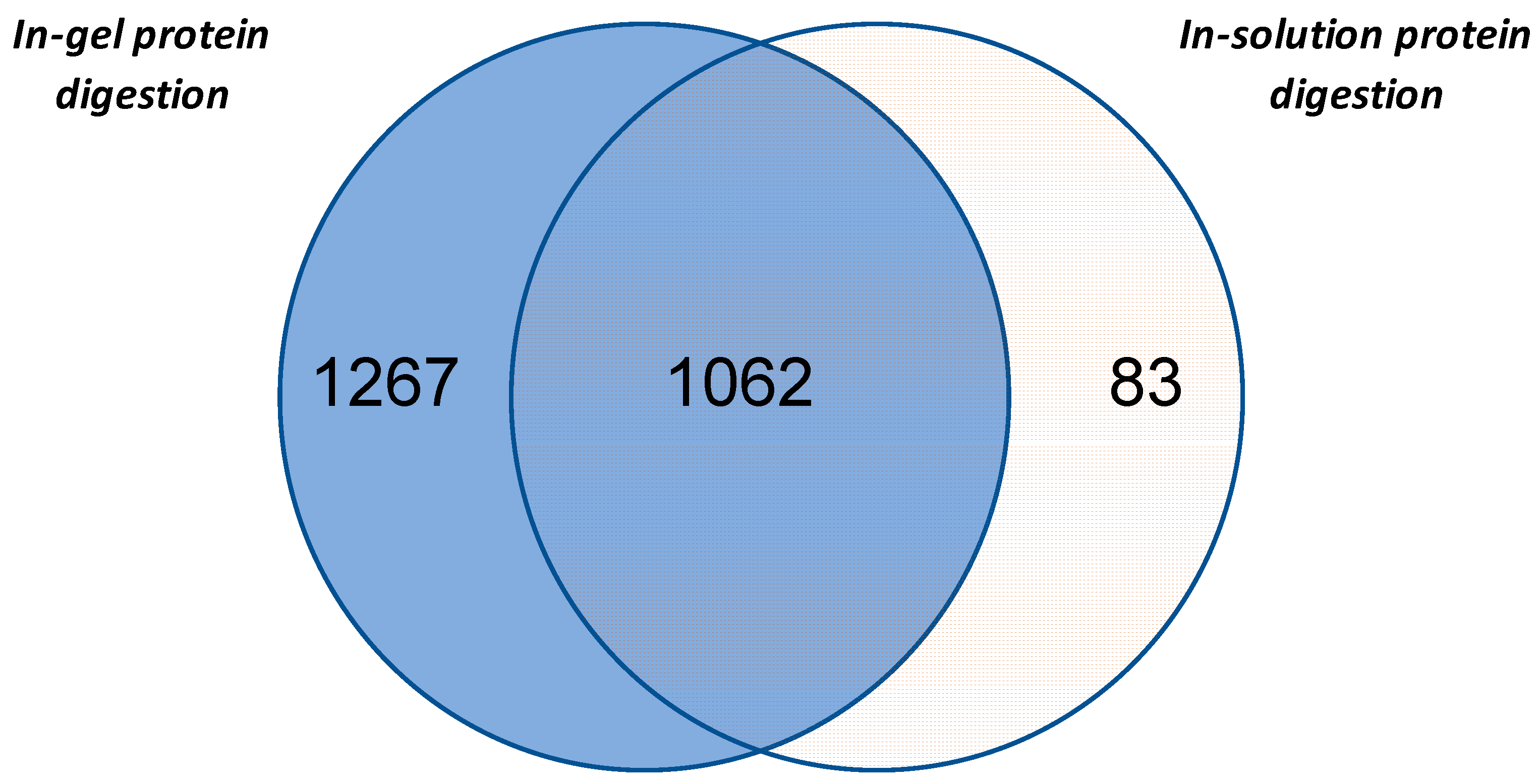
In accordance with the aim of our study, protein sample of ginseng obtained by phenol-extraction procedure were digested either in-solution or in-gel (i.e., samples obtained cutting the line into 10 regular slices) and analyzed by nLC-MS/MS. These two procedures allowed the identification of 1145 and 2329 unique proteins, respectively. Among these, 1062 proteins were identified with both methods, while 83 and 1267 were specifically found within the in-solution and in-gel digested samples, respectively (Figure 3). Moreover, the Venn diagram showed that in-gel digestion procedure in comparison with in-solution digestion left out only a small number of proteins. In total, the two analyses allowed 2412 proteins to be identified. This result was obtained, as reported in Materials and Methods, selecting the proteins identified with at least two unique peptides to obtain a highly reliable data set for the following evaluations. However, an investigative analysis was performed to also consider proteins identified as one unique peptide (Table S1a). Using this less stringent condition, a further 544 proteins were identified.
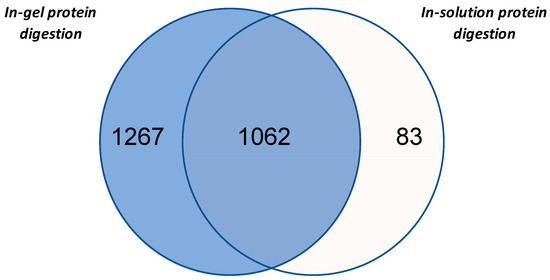
Figure 3.
The Venn diagram of the proteins identified in ginseng by in-gel protein digestion or in-solution protein digestion.
The good efficacy of the phenol extraction method is also highlighted by the comparison with that previously adopted by Li and co-workers [20]. These authors, through an in-solution digestion of samples previously extracted with Gdn-HCl lysis buffer (100mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.5 and 6 M guanidine chloride), identified 929 proteins, while the phenol method used in the present study permitted the identification of 1145 proteins. Taken together, the results further validate the efficacy of the experimental workflow in which the phenol-based extraction method is combined with SDS-PAGE fractionation in removing the interfering compounds and in isolating the protein fraction from plant roots, such as ginseng [26]. This label-free shotgun proteomics approach is a very simple, sturdy, and versatile technique that can permit the conduct of the qualitative and quantitative analyses with high confidence in recalcitrant plant materials.
3.2. Functional Distribution of the Identified Proteins
Details on the protein identification, protein annotation, and functional assignment are summarized in Tables S1–S3, respectively.
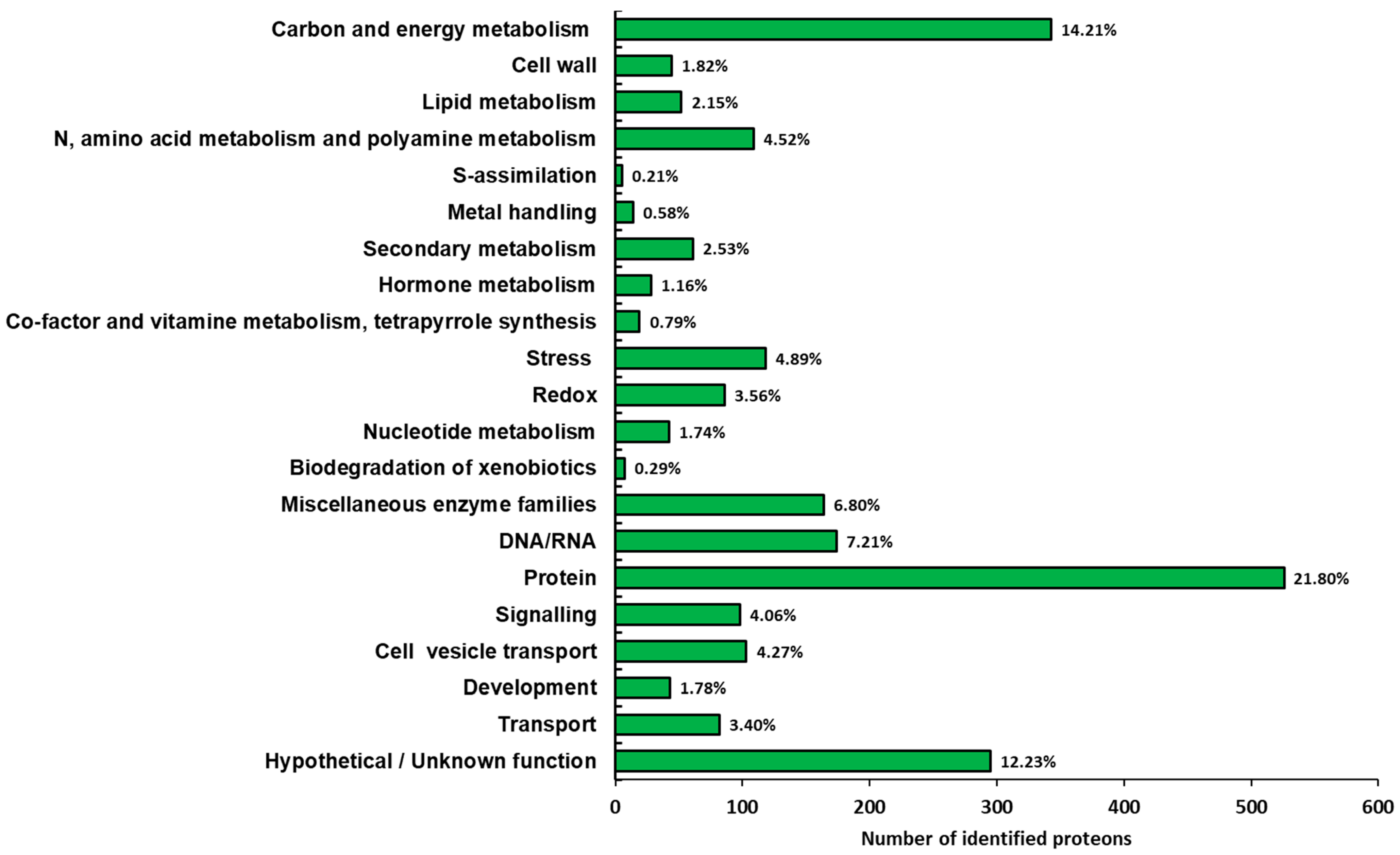
Functional classification of the identified proteins was conducted according to the bin hierarchical tree developed by MapMan ontology [31] and the results are summarized in Figure 4. A very large number of identified proteins belonged to the functional categories of protein and carbon/energy metabolism (22.4% and 14.6%, respectively). This result fits well with previous proteomic studies performed on the root of Panax ginseng [3,20]. Six functional categories, i.e., N, amino acid and polyamine metabolisms, stress, miscellaneous enzyme families, DNA/RNA, signaling and cell vesicle transport, exceeded more than 4% of the identified proteins. Finally, a representative number of proteins, corresponding to 12.6% of the identified proteins, were classified in the hypothetical/unknown function category, suggesting that further work is necessary for more detailed protein annotation.
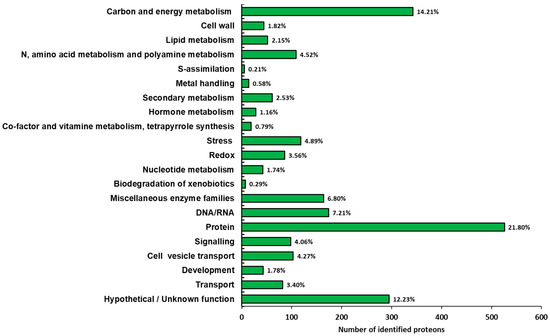
Figure 4.
Functional distribution of the identified proteins in ginseng. The identified proteins were classified into metabolic functional classes according to the BIN ontology.
Previously, Li et al. found that among the 20 most abundant proteins, classified through PSM’s parameter (total number of identified peptide spectra matched for the protein), there were five ribonuclease-like storage proteins and proteins involved in energy metabolism and in stress responses [20]. Using the same parameter, our study revealed similar results (Tables S1 and S2). We found four ribonucleases (Pg_S0091.2, Pg_S2777.2, Pg_S2925.7, Pg_S2281.6) with molecular weights (MW) of 24.1, 27.3, 24.0 and 24.1 kDa, respectively. This result appears in accordance with the electrophoretic profile, that showed a very large band at the same MW (Figure 2), confirming that ribonuclese-like proteins are abundant in ginseng [15,16,20]. Among the more abundant proteins, the presence of three enolases (Pg_S2681.1, Pg_S6078.6, Pg_S3701.1), of two ATP synthase subunits (Pg_S3187.19, Pg_S3125.6) and a β-amylase (Pg_S1798.6) was also confirmed. In addition, supporting an active carbon metabolism, we found two starch branching enzymes (Pg_S3303.10, Pg_S3613.11), a glycosyl transferase (Pg_S0808.11), an UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (Pg_S1124.2) and two phosphoglycerate kinases (Pg_S0871.3, Pg_S0624.8). Further information emerged from the analysis of whole proteomics data (see below).
3.3. Main Metabolic Pathways that Emerged from Proteomic Analysis
Proteomic analysis highlighted traits typical of both primary and secondary metabolisms in accordance with the biochemical activities previously described by transcriptomic and metabolomic studies of Panax ginseng [38].
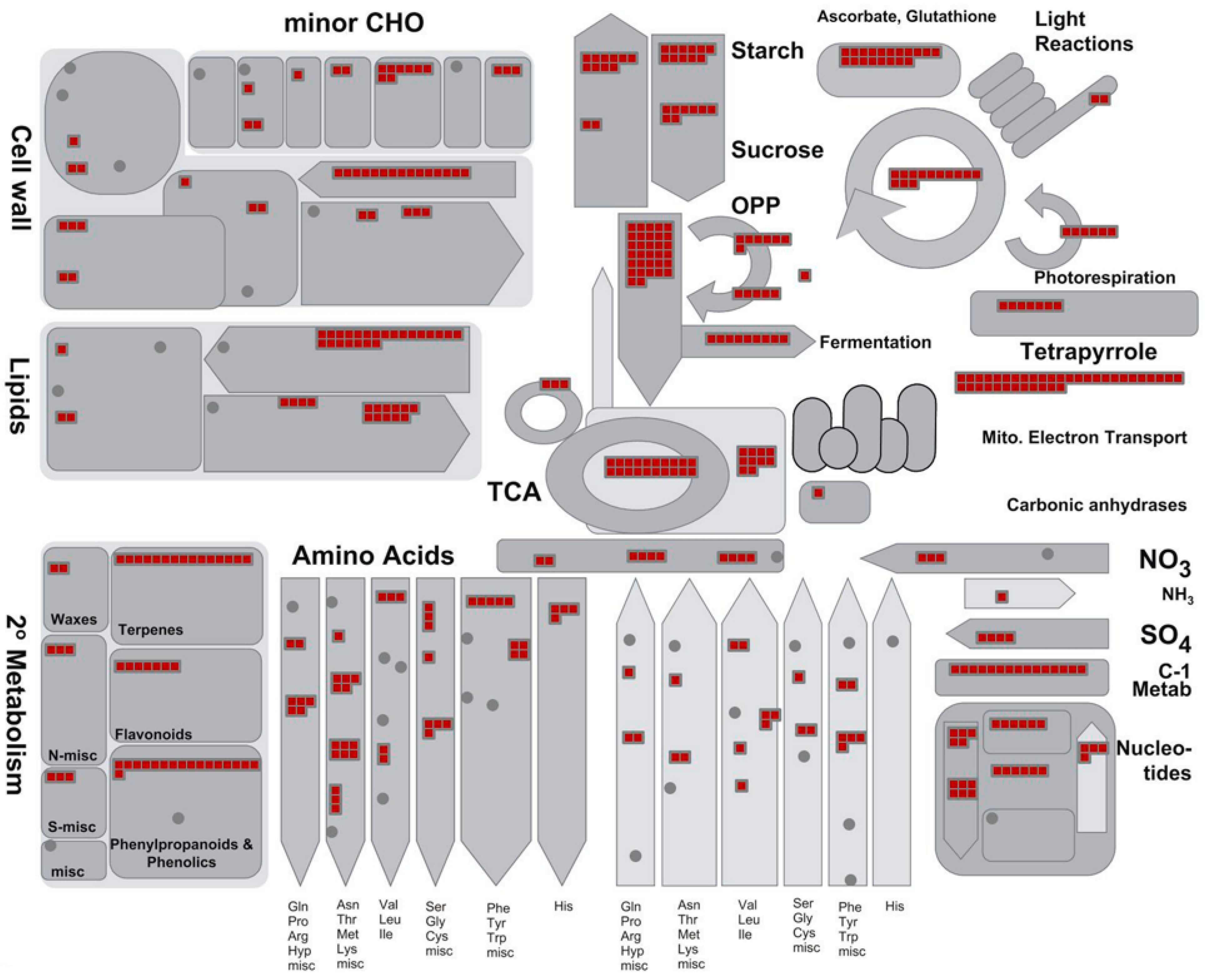
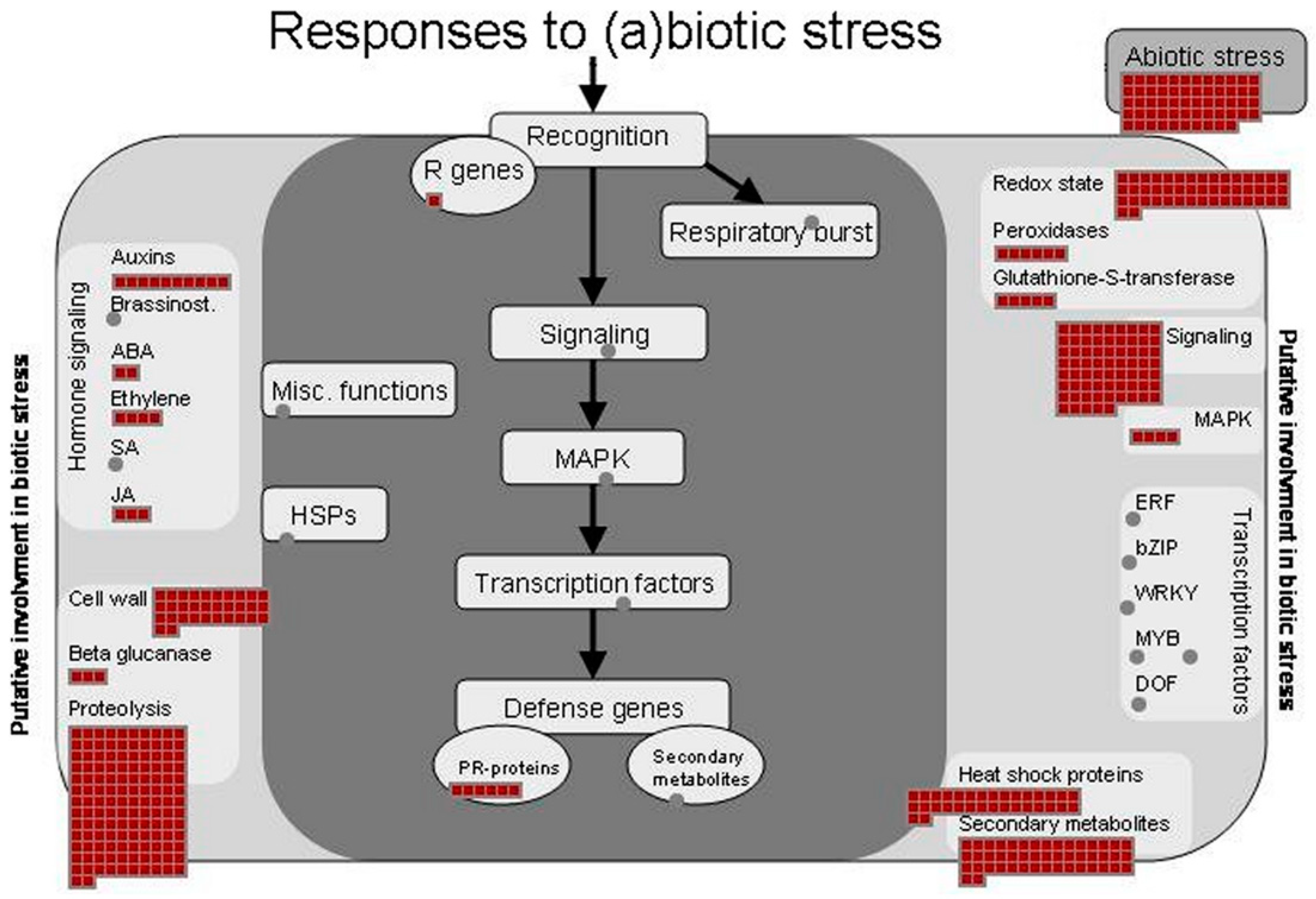
The major identified proteins were analyzed by the MapMan software to depict an overview of the main metabolic pathways (Figure 5) and to summarize the pathways involved in stress responses (Figure 6). Further information on the pathways involved in sucrose and starch metabolisms (Figure S1), TCA cycle and respiratory chain (Figure S2), protein synthesis and degradation (Figure S3), and terpenoid metabolism (Figure S4) is available as Supplementary data.
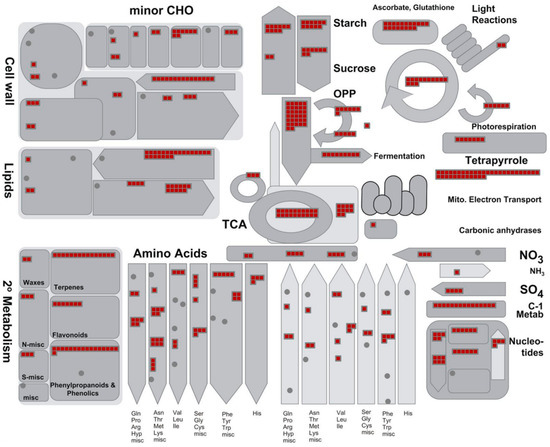
Figure 5.
Proteins identified in ginseng involved in main primary metabolic pathways. The identified proteins were classified into metabolic functional classes according to the BIN ontology. The schematic metabolic pathways were obtained by MapMan software.
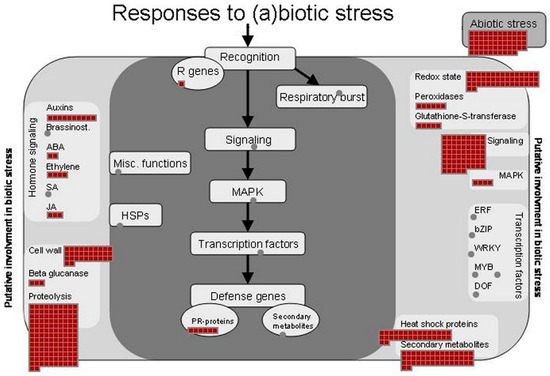
Figure 6.
Proteins identified in ginseng involved in (a)biotic stress pathways. The identified proteins were classified into metabolic functional classes according to the BIN ontology. The schematic metabolic pathways were obtained by MapMan software.
A very large part of the enzymes operating in primary C metabolism (i.e., glycolysis, pentose phosphates cycle, TCA cycle) as well as proteins of all the four respiratory complexes were identified (Figure 4 and Figure S2).
Several enzymes involved in sucrose and starch metabolism were also identified (Figure S1). In this context, it is interesting to underline that the present study revealed several (iso)forms of these enzymes, such as sucrose synthase and sucrose phosphate synthase. These enzymes, in fact, are known to play a pivotal role in the metabolism of sucrose for their involvement in the modulation of sink strength and starch accumulation. (Table S3) [39,40]. The identification of several enzymes involved in both the synthesis and degradation of sucrose and starch appears to confirm previous transcriptomic analyses underlining the importance of the sugar pathways in the root metabolism of Panax ginseng [38].
Taken together, the proteomic data presented in this study fits well in the context of an active energetic metabolism to sustain sugar import and accumulation (i.e., typical events that characterize a sink organ like the root); however, it also characterizes a tissue that is producing both the energy (i.e., ATP) and the carbon skeletons needed to sustain other metabolic pathways and/or cellular functions. Identification of several proteins involved in other activities such as the cell wall, lipid, and amino acid metabolisms also support this interpretation (Figure 5). The proteomic analysis of the present study identified various proteins involved in the different phases of protein synthesis and protein degradation allowed an in-depth description of these processes and confirmed the intense metabolic activity of the root of Panax ginseng (Figure 4, Figure S4 and Table S3). In particular, 19 proteins were involved in amino acid activation, 111 were ribosomal proteins, 31 were translation initiation factors, 17 were translation elongation factors, 3 were release factors, 36 were involved in protein folding, 53 were involved in post-translational modification activities, and 63 were involved in protein sorting. Furthermore, proteins were found to be involved in the protein degradation.
3.4. Identification of Proteins Involved in Stress Responses
Previous omic studies conducted on Panax ginseng root reported several metabolic activities involved in response to different stresses [14,20,38,39,41,42]. Accordingly, our study also found a large number of proteins known to play an important role in the responses to (a) biotic stresses (Figure 6) [43]. The main enzymes involved in the scavenging of ROS, such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, ascorbate peroxidase, and others were identified (Tables S2 and S3).
Among the proteins classified in the stress functional class, 39 were found to be heat shock proteins (HSPs) having different MW (17.6 kDa, 70.1 kDa, 101 kDa, 18.2 kDa, 81.4 kDa, 81.9 kDa and others), confirming the central role of these cytoprotective proteins in ginseng [39]. Many of these were revealed to be most abundant proteins in the present study. The important role of these molecular chaperones, involved in folding, accumulation, localization, and degradation of proteins, is well documented [44,45]. Moreover, it is known that their expression can occur in specific tissue and could be linked to specific physiological processes and/or environmental conditions [42,43]. A recent transcriptome analysis for the study of the effects of high light exposure in leaves of Panax ginseng showed the involvement of many HSPs. [46]. Our proteomics study revealed that 7 of these HSPs (Pg_S1378.3, Pg_S5690.5, Pg_S3341.2, Pg_S3045.2, Pg_S0918.3, Pg_S4966.10 and Pg_S7676.3) are expressed in the ginseng.
Moreover, we identified other proteins (MLP-like proteins, germin-like protein 10, dehydrin family proteins, stress-inducible proteins and others) that are known to be involved in the stress responses [26,47,48,49,50].
3.5. Ginsenoside Biosynthetic Pathways
The biosynthesis of ginsenosides, a series of glycosylated triterpenoids, derives from the common precursor 2,3-oxidosqualene. This compound is produced through an oxidative reaction of squalene, which is the product of the condensation of isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP). The synthesis of IPP and DMAPP can occur through both the mevalonate (MVA) pathway and the 2C-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate (MEP) pathway. In the ginsenoside biosynthesis, cythocrome P450, a complex family of enzymes, catalyze the reaction of hydroxylation, while UDP-glycosyltransferases (UGTs) are involved in the glycosylation step.
With respect to ginsenoside biosynthetic pathways, the present proteomic analysis identified proteins involved in the MVA and MEP pathways, as well as cytochrome P450 and UGTs (Table 1 and Figure S4).

Table 1.
Proteins identified in ginseng related to the ginsenoside biosynthesis pathway.
Although not all of the enzymes involved in the different steps of ginsenoside biosynthesis were identified, this study highlights that IPP and DMAPP could be synthesized mainly through this metabolic pathway. In contrast to what was recently proposed [20], we found four different UGT isoforms suggesting that glycosylation events can occur in the roots of Korean ginseng. Considering that glycosylation increases the stability of molecules and is implicated in compartmentalization events, further studies are warranted to clarify this aspect. In other words, the evidence reported by Li and coworkers suggesting that glycosylation of ginsenosides might be carried out mainly in leaf, open a crucial question. If as suggested by these authors, the glycosylated forms were transported to the root when withering occurs, the ginsenoside root composition would be strictly influenced, as previously suggested, by the physiological status of the plant. [39]. In this context, the possibility cannot be excluded that the presence of four UGTs found in the present study could be linked to a different genetic background of Korean ginseng [51]. In addition, it cannot be overlooked that the biochemical activities of ginseng could be influenced by other factors, such as environmental growth conditions.
4. Conclusions
The current study tested two different proteomic workflows for extended proteome analyses of Korean ginseng, highlighting the high performance of the phenol-based extraction method combined with SDS-PAGE fractionation. Overall, the analyses identified 2412 proteins. It should be noted however that the process of steaming Panax ginseng dramatically impacts the properties of the proteins, interfering with their electrophoretic separation as well as their identification by mass spectroscopy.
In accordance to functional classification, proteomic analyses found substantial amounts of proteins belonged to protein and carbon/energy metabolism. Further analyses visualizing the major identified proteins according to their biochemical characteristics indicate that a large number of proteins known to play an important role in the responses to (a)biotic stresses operate in ginseng. Finally, the study identified a large number of proteins involved in the biosynthesis of ginsenosides, thus highlighting some peculiar traits, such as the presence of UTGs in the Korean ginseng.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/separations8040053/s1, Figure S1: Overview of metabolic pathways involved in sucrose and starch metabolism in ginseng, Figure S2: Overview of the TCA cycle (B) and the respiratory chain (B) in ginseng, Figure S3: Overview of (A) protein synthesis and (B) ubiquitin dependent protein degradation in ginseng, Figure S4: Overview of the terpenoid metabolism in ginseng, Table S1: Protein identification, Table S2: Protein annotation, Table S3: Functional categories.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.A. and K.-J.Y.; methodology, L.E. and B.P.; formal analysis, A.A.A., B.P., and L.E.; investigation, C.B., M.C., and A.A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, C.B. and L.E.; writing—review and editing, B.P., G.A., L.E., Y.-M.L., and K.-J.Y.; supervision, G.A. and K.-J.Y.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
The Korean white ginseng was provided by the Korean Ginseng Cooperation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lee, F.C. Facts about Ginseng: The Elixir of Life; Hollym International Corporation: Elizabeth, NJ, USA, 1992; ISBN 10:0930878833. [Google Scholar]
- Petkov, W. Pharmacological Studies of the Drug P. Ginseng C.A. Meyer. Arzneim. Forsch. 1959, 9, 305–311. [Google Scholar]
- Colzani, M.; Altomare, A.; Caliendo, M.; Aldini, G.; Righetti, P.G.; Fasoli, E. The secrets of Oriental panacea: Panax ginseng. J. Proteom. 2016, 130, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attele, A.S.; Wu, J.A.; Yuan, C.-S. Ginseng pharmacology. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 58, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, D.; Lee, H.L.; Kim, C.-E.; Jung, K.; Kang, K.S. Beneficial effects of Panax ginseng for the treatment and prevention of neurodegenerative diseases: Past findings and future directions. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-L.; He, Z.-M.; Zhu, H.-Y.; Gao, Y.-G.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, L.-X. Involvement of serotonergic, noradrenergic and dopaminergic systems in the antidepressant-like effect of ginsenoside Rb1, a major active ingredient of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 204, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Jeong, J.-J.; Eun, S.-H.; Kim, D.-H. Anti-inflammatory effects of ginsenoside Rg1 and its metabolites ginsenoside Rh1 and 20(S)-protopanaxatriol in mice with TNBS-induced colitis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 762, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-H.; Song, K.-H.; Woo, J.-K.; Park, M.H.; Rhee, M.H.; Choi, C.; Oh, S.H. Ginsenoside Rp1 from Panax ginseng Exhibits Anti-cancer Activity by Down-regulation of the IGF-1R/Akt Pathway in Breast Cancer Cells. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2011, 66, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Goyal, P.K. Chemoprevention of chemical-induced skin cancer by Panax ginseng root extract. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Kim, J.-H. A review on the medicinal potentials of ginseng and ginsenosides on cardiovascular diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2014, 38, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Dou, G.; Wan, F.; Zhang, W.; Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, C.; Li, L. Anti-platelet activity of panaxatriol saponins is mediated by suppression of intracellular calcium mobilization and ERK2/p38 activation. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Kim, H.Y. Korean red ginseng stimulates insulin release from isolated rat pancreatic islets. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 120, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorrin, J.V.; Maldonado, A.M.; Castillejo, M.A. Plant proteome analysis: A 2006 update. Proteomics 2007, 7, 2947–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, M.H.; Kim, S.I.; Liu, J.R.; Yang, D.C.; Lim, Y.P.; Kwon, K.-H.; Yoo, J.S.; Park, Y.M. Proteomic analysis of Korean ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer). J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 815, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.I.; Kweon, S.-M.; Kim, E.A.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.; Yoo, J.S.; Park, Y.M. Characterization of RNase-like major storage protein from the ginseng root by proteomic approach. J. Plant Physiol. 2004, 161, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lum, J.H.-K.; Fung, K.-L.; Cheung, P.-Y.; Wong, M.-S.; Lee, C.-H.; Kwok, F.S.-L.; Leung, M.C.-P.; Hui, P.-K.; Lo, S.C.-L. Proteome of Oriental ginseng Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer and the potential to use it as an identification tool. Proteomics 2002, 2, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.I.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, E.A.; Kwon, K.-H.; Kim, K.-W.; Cho, K.; Lee, J.H.; Nam, M.H.; Yang, D.-C.; Yoo, J.S.; et al. Proteome analysis of hairy root fromPanax ginseng C. A. Meyer using peptide fingerprinting, internal sequencing and expressed sequence tag data. Proteomics 2003, 3, 2379–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.-H.; Jayakodi, M.; Lee, S.-C.; Choi, B.-S.; Jang, W.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.H.; Waminal, N.E.; Lakshmanan, M.; Van Nguyen, B.; et al. Genome and evolution of the shade-requiring medicinal herbPanax ginseng. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 1904–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakodi, M.; Choi, B.-S.; Lee, S.-C.; Kim, N.-H.; Park, J.Y.; Jang, W.; Lakshmanan, M.; Mohan, S.V.G.; Lee, D.-Y.; Yang, T.-J. Ginseng Genome Database: An open-access platform for genomics of Panax ginseng. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, X.; Liao, B.; Xu, J.; Han, X.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Z.; Hu, L. Spatial protein expression of Panax ginseng by in-depth proteomic analysis for ginsenoside biosynthesis and transportation. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Bae, B.-S.; Park, H.-W.; Ahn, N.-G.; Cho, B.-G.; Cho, Y.-L.; Kwak, Y.-S. Characterization of Korean Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer): History, preparation method, and chemical composition. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, S.-H.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, Y.-S.; Hyun, S.H.; Han, C.-K. Red ginseng monograph. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, J.K.; Bashir, S.; Giovannoni, J.J.; Jahn, M.M.; Saravanan, R.S. Tackling the plant proteome: Practical approaches, hurdles and experimental tools. Plant J. 2004, 39, 715–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, R.S.; Rose, J.K.C. A critical evaluation of sample extraction techniques for enhanced proteomic analysis of recalcitrant plant tissues. Proteomics 2004, 4, 2522–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, S.C.; Witters, E.; Laukens, K.; Deckers, P.; Swennen, R.; Panis, B. Preparation of protein extracts from recalcitrant plant tissues: An evaluation of different methods for two-dimensional gel electrophoresis analysis. Proteomics 2005, 5, 2497–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinsi, B.; Negri, A.S.; Failla, O.; Scienza, A.; Espen, L. Root proteomic and metabolic analyses reveal specific responses to drought stress in differently tolerant grapevine rootstocks. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilson, K.A.; George, I.S.; Emery, S.J.; Muralidharan, S.; Mirzaei, M.; Haynes, P.A. Analysis of Rice Proteins Using SDS-PAGE Shotgun Proteomics. In Advanced Structural Safety Studies; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; Volume 1072, pp. 289–302. [Google Scholar]
- Vadivel, A.K.A. Gel-based proteomics in plants: Time to move on from the tradition. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinsi, B.; Negri, A.S.; Quattrocchio, F.M.; Koes, R.E.; Espen, L. Proteomics of red and white corolla limbs in petunia reveals a novel function of the anthocyanin regulator ANTHOCYANIN1 in determining flower longevity. J. Proteom. 2016, 131, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilm, M.; Shevchenko, A.; Houthaeve, T.; Breit, S.; Schweigerer, L.; Fotsis, T.; Mann, M. Femtomole sequencing of proteins from polyacrylamide gels by nano-electrospray mass spectrometry. Nat. Cell Biol. 1996, 379, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimm, O.; Bläsing, O.; Gibon, Y.; Nagel, A.; Meyer, S.; Krüger, P.; Selbig, J.; Müller, L.A.; Rhee, S.Y.; Stitt, M. mapman: A user-driven tool to display genomics data sets onto diagrams of metabolic pathways and other biological processes. Plant J. 2004, 37, 914–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mine, Y.; Li-Chan, E.C.; Jiang, B. Biologically Active Food Proteins and Peptides in Health: An Overview. In Bioactive Proteins and Peptides as Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals; Wiley and Sons: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hurkman, W.J.; Tanaka, C.K. Solubilization of Plant Membrane Proteins for Analysis by Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis. Plant Physiol. 1986, 81, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faurobert, M.; Pelpoir, E.; Chaïb, J.; Valerie, M.; Catherine, D.; Michel, Z.; Hervé, T. Phenol Extraction of Proteins for Proteomic Studies of Recalcitrant Plant Tissues. In Plant Proteomics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; Volume 355, pp. 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.V.; Inglett, G.E. Denaturation of plant proteins related to functionality and food applications: A review. J. Food Sci. 1974, 39, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.; Vázquez, A. Bioactive peptides: A review. Food Qual. Saf. 2017, 1, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.P.; Goswami, A.; Kalia, K.; Kate, A.S. Plant-Derived Bioactive Peptides: A Treatment to Cure Diabetes. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2020, 26, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakodi, M.; Lee, S.-C.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, H.-S.; Kim, N.-H.; Jang, W.; Lee, H.O.; Joh, H.J.; Yang, T.-J. Comprehensive analysis of Panax ginseng root transcriptomes. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Joo, S.C.; Shi, J.; Hu, C.; Quan, S.; Hu, J.; Sukweenadhi, J.; Mohanan, P.; Yang, D.-C.; Zhang, D. Metabolic dynamics and physiological adaptation of Panax ginseng during development. Plant Cell Rep. 2017, 37, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.-L. Sucrose Metabolism: Gateway to Diverse Carbon Use and Sugar Signaling. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 33–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Sun, L.; Chen, X.; Mei, B.; Chang, G.; Wang, M.; Zhao, D. Proteomic Analyses Provide Novel Insights into Plant Growth and Ginsenoside Biosynthesis in Forest Cultivated Panax ginseng (F. Ginseng). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, G.; Zhang, L.; Du, Y.; Yu, R.; Liu, X.; Cao, F.; Chang, Q.; Deng, X.; Xia, M.; He, H. De novo assembly and comparative analysis of root transcriptomes from different varieties of Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer grown in different environments. Sci. China Life Sci. 2015, 58, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidchik, V. Mechanisms of oxidative stress in plants: From classical chemistry to cell biology. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2015, 109, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Whaibi, M.H. Plant heat-shock proteins: A mini review. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2011, 23, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, S.U.; Khan, A.; Ali, M.; Khattak, A.M.; Gai, W.-X.; Zhang, H.-X.; Wei, A.-M.; Gong, Z.-H. Heat Shock Proteins: Dynamic Biomolecules to Counter Plant Biotic and Abiotic Stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Kim, H.-Y.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, S.H. Transcriptome analysis of Panax ginseng response to high light stress. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musidlak, O.; Bałdysz, S.; Krakowiak, M.; Nawrot, R. Plant latex proteins and their functions. In Advances in Botanical Research; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 93, pp. 55–97. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Structural and Functional Dynamics of Dehydrins: A Plant Protector Protein under Abiotic Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Dai, X.-F. Cloning and characterization of the Gossypium hirsutum major latex protein gene and functional analysis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 2010, 231, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunwell, J.M.; Gibbings, J.G.; Mahmood, T.; Naqvi, S.M.S. Germin and Germin-like Proteins: Evolution, Structure, and Function. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2008, 27, 342–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Park, H.-S.; Lee, D.-K.; Jayakodi, M.; Kim, N.-H.; Koo, H.J.; Lee, S.-C.; Kim, Y.J.; Kwon, S.W.; Yang, T.-J. Integrated Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analysis of Five Panax ginseng Cultivars Reveals the Dynamics of Ginsenoside Biosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).