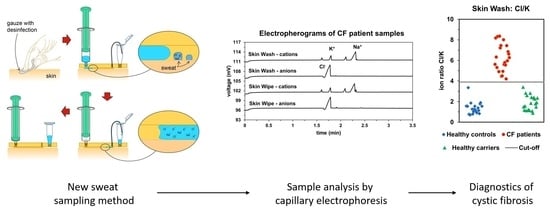
3D Printed Skin-Wash Sampler for Sweat Sampling in Cystic Fibrosis Diagnosis Using Capillary Electrophoretic Ion Ratio Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Standards
2.2. Capillary Electrophoresis System
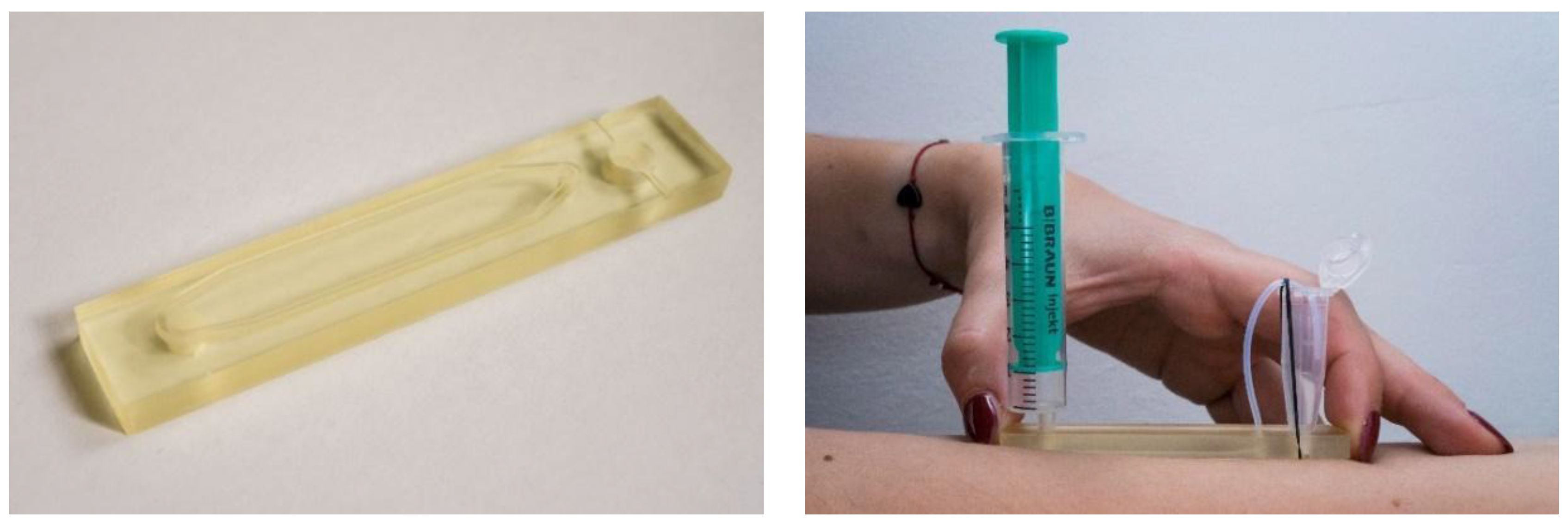
2.3. D-Printed Sampling Device Fabrication
2.4. Sampling
2.4.1. Skin-Wipe Samples
2.4.2. Skin-Wash Samples
2.4.3. Macroduct Sampling
2.5. Study Subjects
3. Results and Discussion
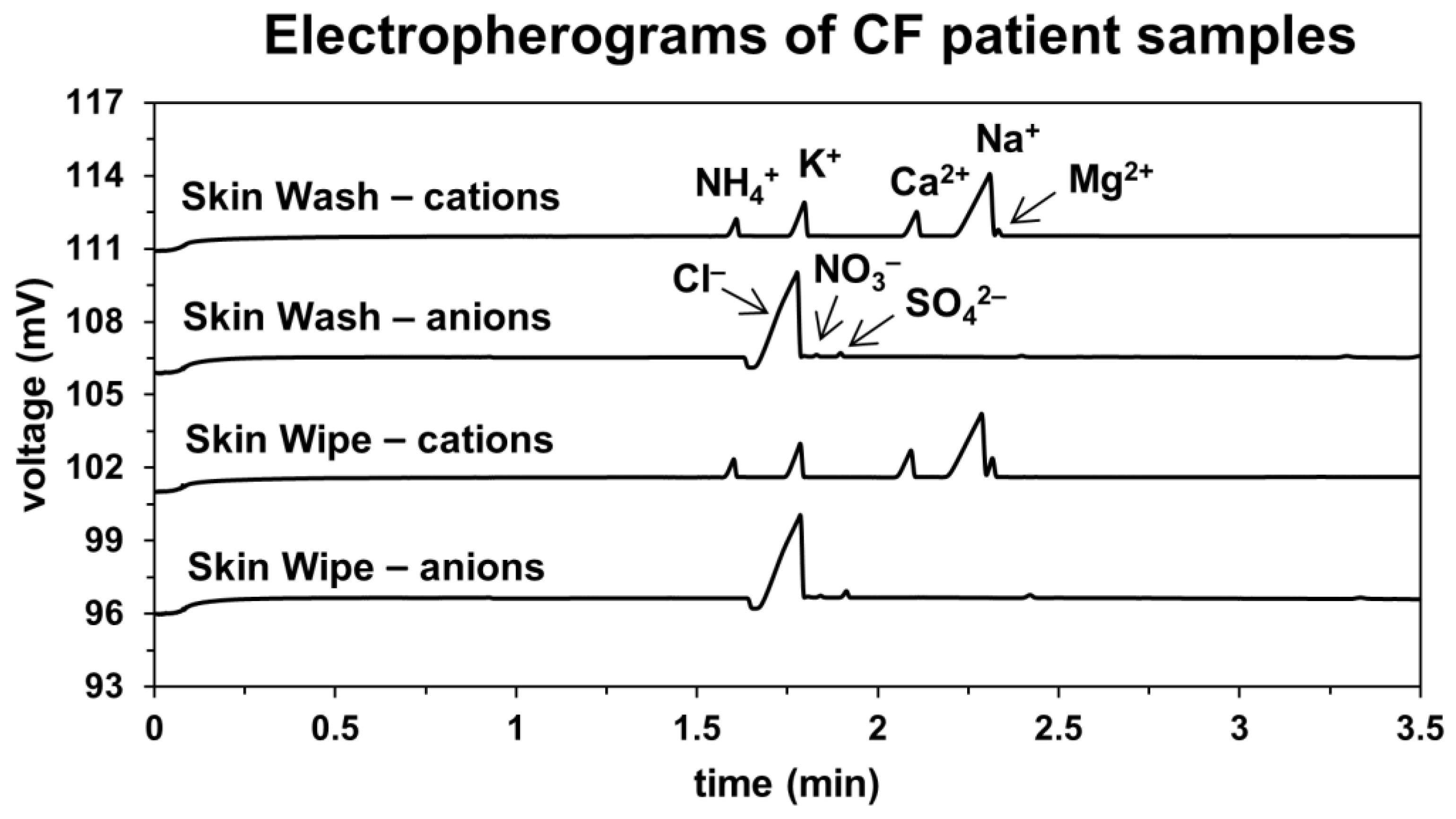
3.1. Capillary Electrophoretic Analysis of Sweat Samples
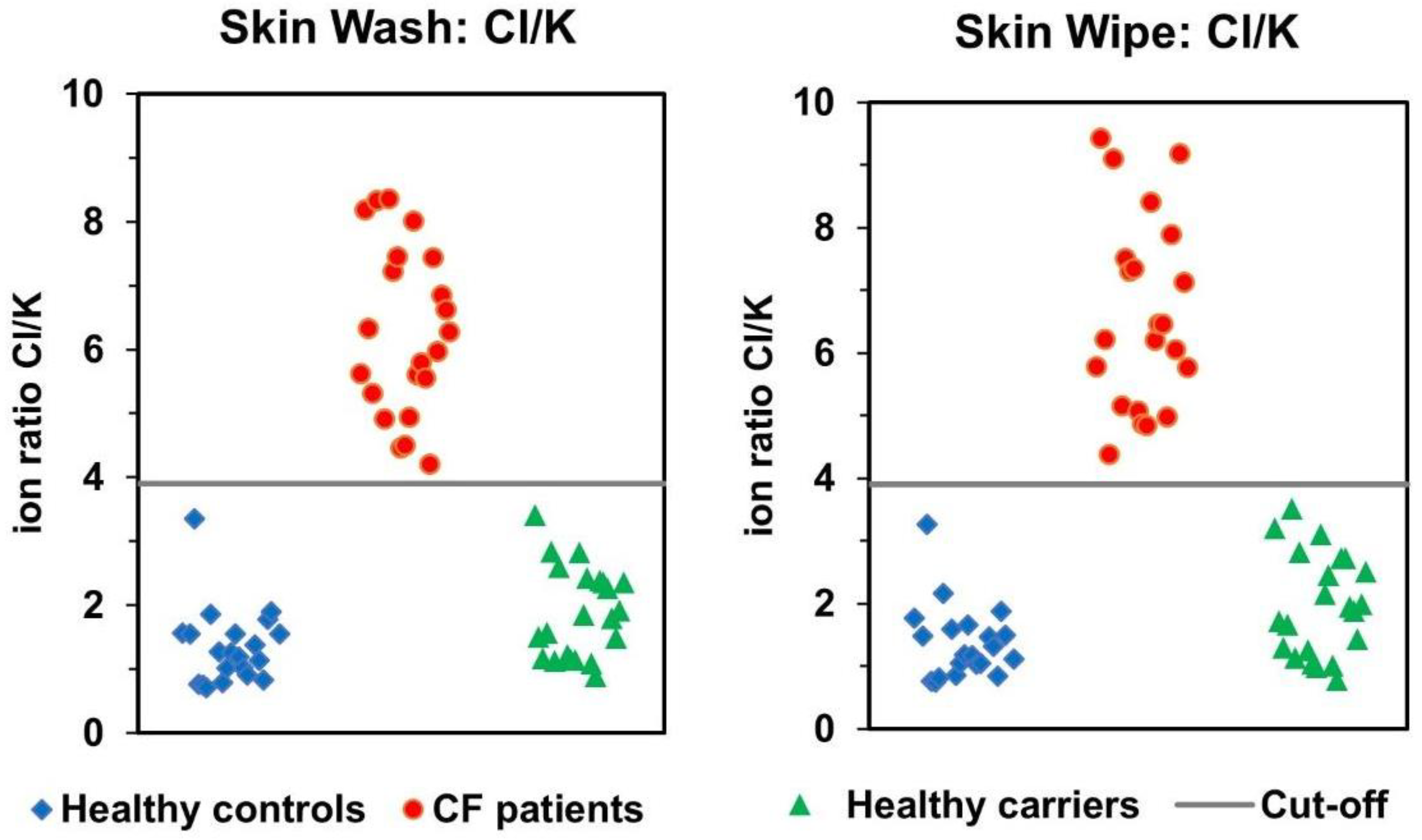
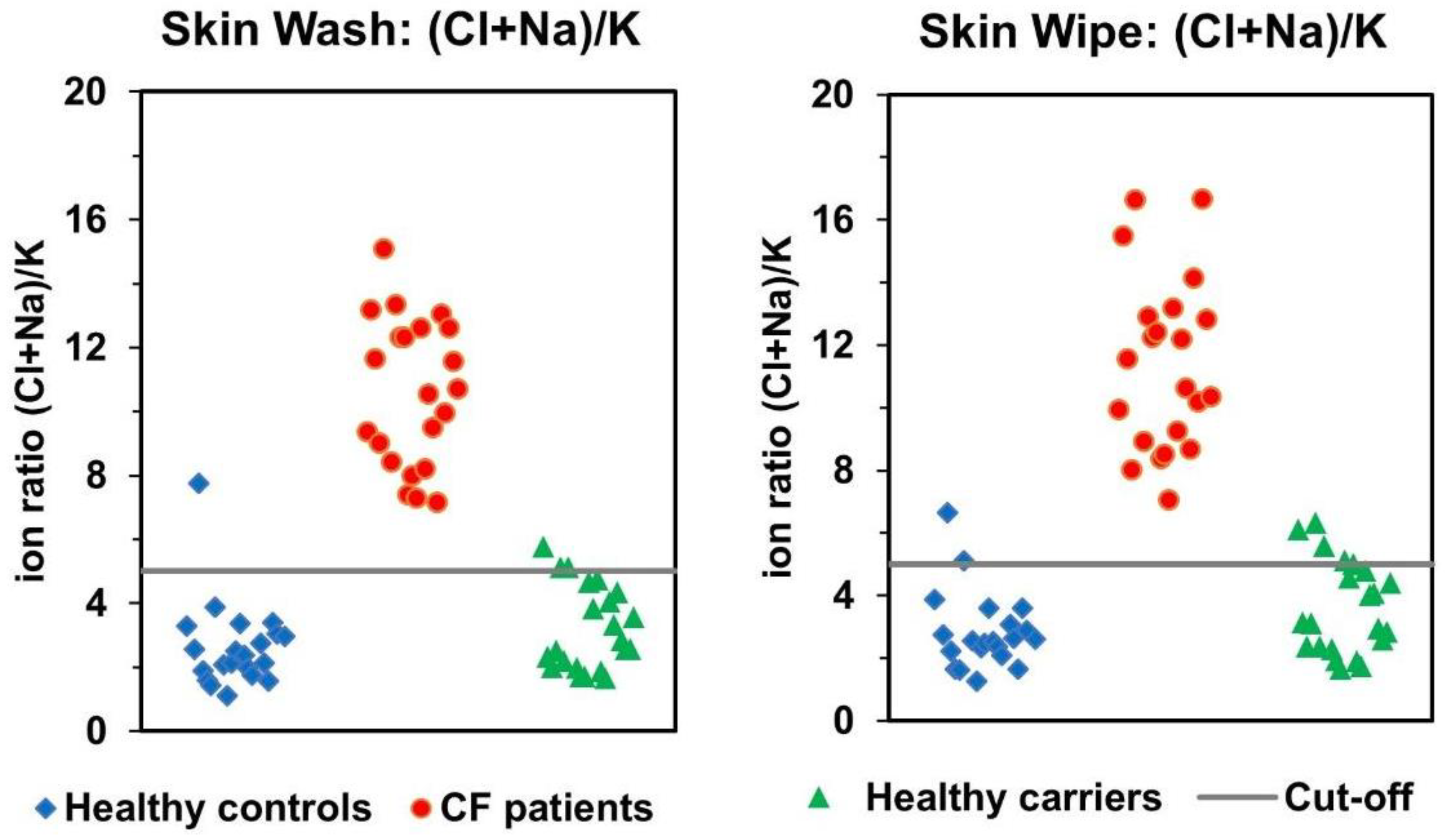
3.2. Comparison of Skin-Wash and Skin-Wipe Sampling
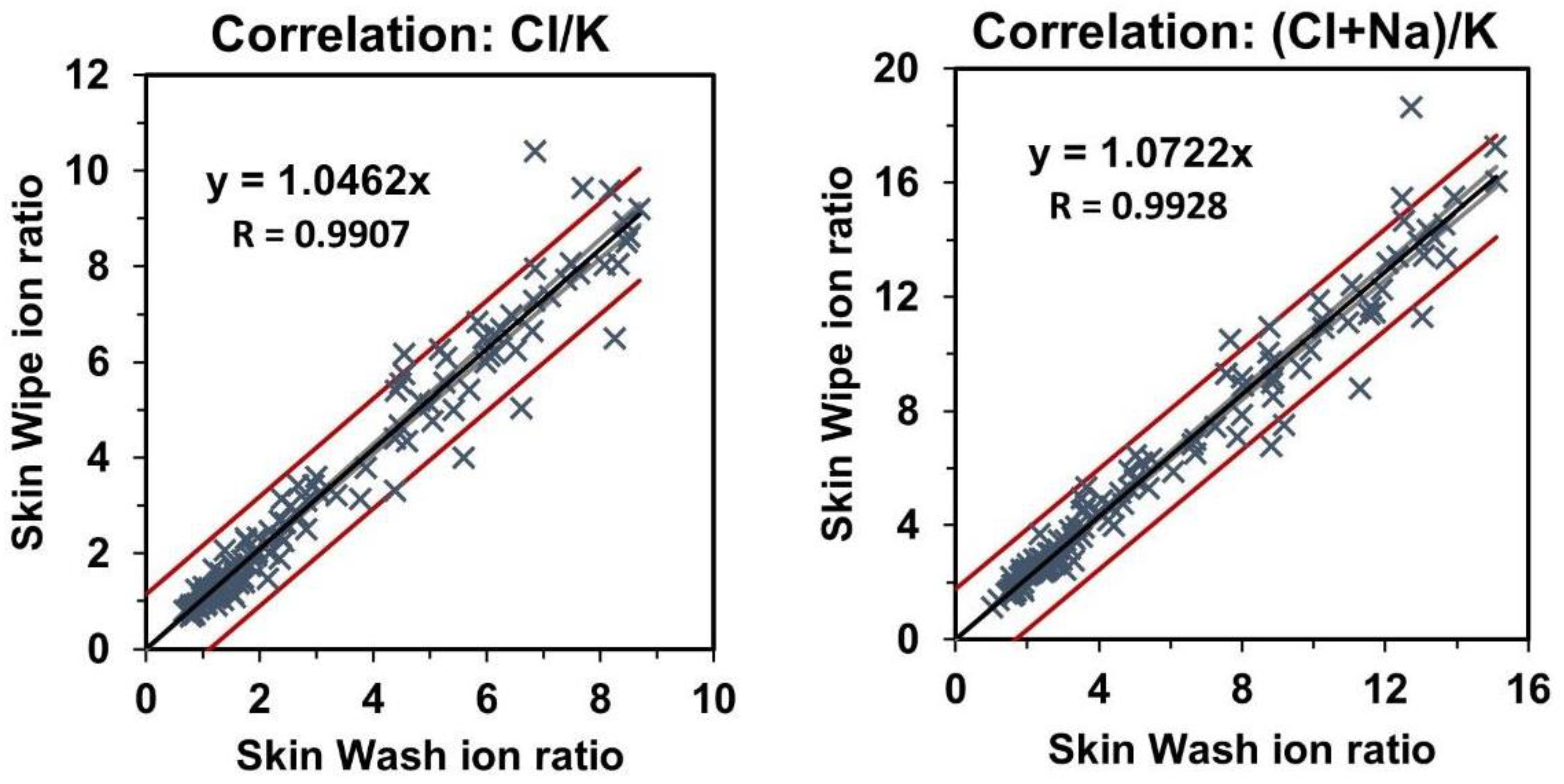
3.3. Correlation of Skin-Wash and Skin-Wipe Samples
3.4. Analysis of Ion Ratios after Sweat Stimulation with Pilopcarpine
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le Grys, V.A. Sweat testing for the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis: Practical considerations. J. Pediatr. 1996, 129, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P.M.; Rosenstein, B.J.; White, T.B.; Accurso, F.J.; Castellani, C.; Cutting, G.R.; Durie, P.R.; LeGrys, V.A.; Massie, J.; Parad, R.B.; et al. Guidelines for diagnosis of cystic fibrosis in newborns through older adults: Cystic fibrosis foundation consensus report. J. Pediatr. 2008, 153, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellani, C.; Massie, J.; Sontag, M.; Southern, K.W. Newborn screening for cystic fibrosis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elitech Group. Macroduct Sweat Collection System. Available online: https://www.elitechgroup.com/products/sweat-testing/sweat-collection (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Cirilli, N.; Southern, K.W.; Buzzetti, R.; Barben, J.; Nährlich, L.; Munck, A.; Wilschanski, M.; De Boeck, K.; Derichs, N.; ECFS Diagnostic Network Working Group. Real life practice of sweat testing in Europe. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2018, 17, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lezana, J.L.; Vargas, M.H.; Karam-Bechara, J.; Aldana, R.S.; Furuya, M.E. Sweat conductivity and chloride titration for cystic fibrosis diagnosis in 3834 subjects. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2003, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernooij-van Langen, A.; Dompeling, E.; Yntema, J.B.; Arets, B.; Tiddens, H.; Loeber, G.; Dankert-Roelse, J. Clinical evaluation of the Nanoduct sweat test system in the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis after newborn screening. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2015, 174, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Greaves, R.; Massie, J. The limitation of sweat electrolyte reference intervals for the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis: A systemic review. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2007, 28, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Traeger, N.; Shi, Q.; Dozor, A.J. Relationship between sweat chloride, sodium and age in clinically obtained samples. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2014, 13, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.H.; Kim, J.S.; Cutting, G.R.; Searson, P.C. Wearable potentiometric chloride sweat sensor: The critical role of the salt bridge. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 12241–12247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.H.; Thaxton, A.; cheol Jeong, I.; Kim, K.; Sosnay, P.R.; Cutting, G.R.; Searson, P.C. Sweat test for cystic fibrosis: Wearable sweat sensor vs. standard laboratory test. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2018, 17, e35–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, M.J.; Makholm, L.; Eickhoff, J. A new method of sweat testing: The CF quantum (R) sweat test. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2014, 13, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kubáň, P.; Greguš, M.; Pokojova, E.; Skrickova, J.; Foret, F. Double opposite end injection capillary electrophoresis withcontactless conductometric detection for simultaneous determinationof chloride, sodium and potassium in cystic fibrosis diagnosis. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1358, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ďurč, P.; Foret, F.; Pokojová, E.; Homola, L.; Skřičková, J.; Herout, V.; Dastych, M.; Vinohradská, H.; Kubáň, P. New approach for cystic fibrosis diagnosis based on chloride/potassium ratio analyzed in non-invasively obtained skin-wipe sweat samples by capillary electrophoresis with contactless conductometric detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 3507–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ďurč, P.; Foret, F.; Homola, L.; Malá, M.; Pokojová, E.; Vinohradská, H.; Dastych, M.; Krausová, D.; Nagy, D.; Bede, O.; et al. Skin wipe test: A simple, inexpensive, and fast approach in the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Union. Directive (EU) 2019/904 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 5 June 2019 on the Reduction of the Impact of Certain Plastic Products on the Environment. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2019/904/oj (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Dubot, P.; Liang, J.; Dubs, J.; Missiak, Y.; Sarazin, C.; Couderc, F.; Causse, E. Sweat chloride quantification using capillary electrophoresis. Pract. Lab. Med. 2009, 13, e00114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellani, C.; Duff, A.J.; Bell, S.C.; Heijerman, H.G.; Munck, A.; Ratjen, F.; Sermet-Gaudelus, I.; Southern, K.W.; Barben, J.; Flume, P.A.; et al. ECFS best practice guidelines: The 2018 revision. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2018, 17, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemann, A.J. Sub-minute separations of organic and inorganic anions with co-electroosmotic capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 1997, 787, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainelli, A.; Hauser, P.C. Fast electrophoresis in conventional capillaries by employing a rapid injection device and contactless conductivity detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 382, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GreyScan. ETD-100 Portable Explosive Detector. Available online: https://greyscandetection.com/products/details/18/etd-100-portable-explosive-detector.html (accessed on 29 November 2021).

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malá, M.; Itterheimová, P.; Homola, L.; Vinohradská, J.; Kubáň, P. 3D Printed Skin-Wash Sampler for Sweat Sampling in Cystic Fibrosis Diagnosis Using Capillary Electrophoretic Ion Ratio Analysis. Separations 2021, 8, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8120234
Malá M, Itterheimová P, Homola L, Vinohradská J, Kubáň P. 3D Printed Skin-Wash Sampler for Sweat Sampling in Cystic Fibrosis Diagnosis Using Capillary Electrophoretic Ion Ratio Analysis. Separations. 2021; 8(12):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8120234
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalá, Miriam, Petra Itterheimová, Lukáš Homola, Jana Vinohradská, and Petr Kubáň. 2021. "3D Printed Skin-Wash Sampler for Sweat Sampling in Cystic Fibrosis Diagnosis Using Capillary Electrophoretic Ion Ratio Analysis" Separations 8, no. 12: 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8120234
APA StyleMalá, M., Itterheimová, P., Homola, L., Vinohradská, J., & Kubáň, P. (2021). 3D Printed Skin-Wash Sampler for Sweat Sampling in Cystic Fibrosis Diagnosis Using Capillary Electrophoretic Ion Ratio Analysis. Separations, 8(12), 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8120234