Protective Effects of Dietary Supplement Spirulina (Spirulina platensis) against Toxically Impacts of Monosodium Glutamate in Blood and Behavior of Swiss mouse
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Design
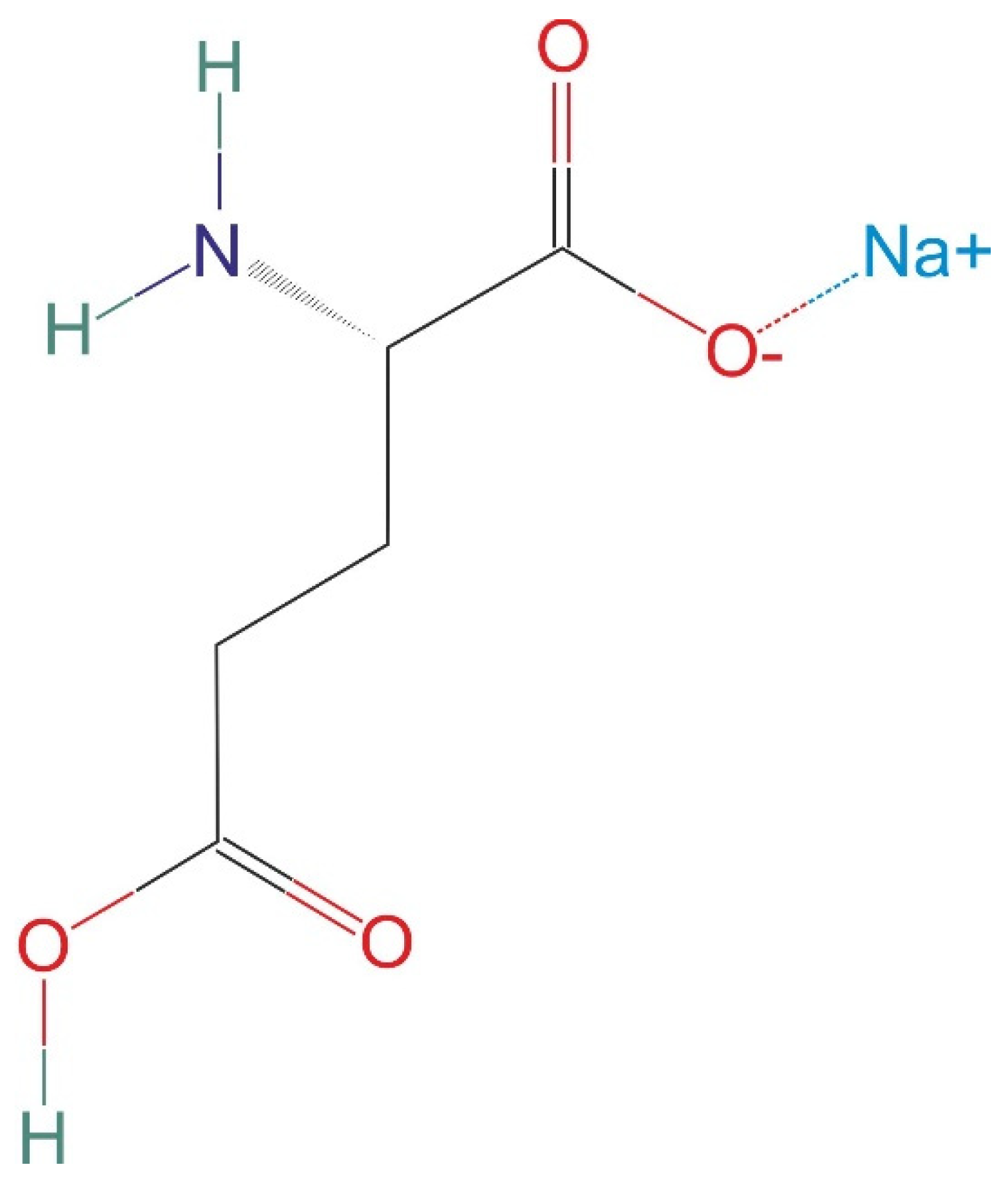
2.3. Chemicals
2.4. Organ and Blood Sample Collection
2.5. Biochemical Analysis of Blood
2.6. Histopathological Analysis
2.7. FTIR Measurements
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. MSG’s Influence on Blood Biochemical Parameters in Swiss Mice
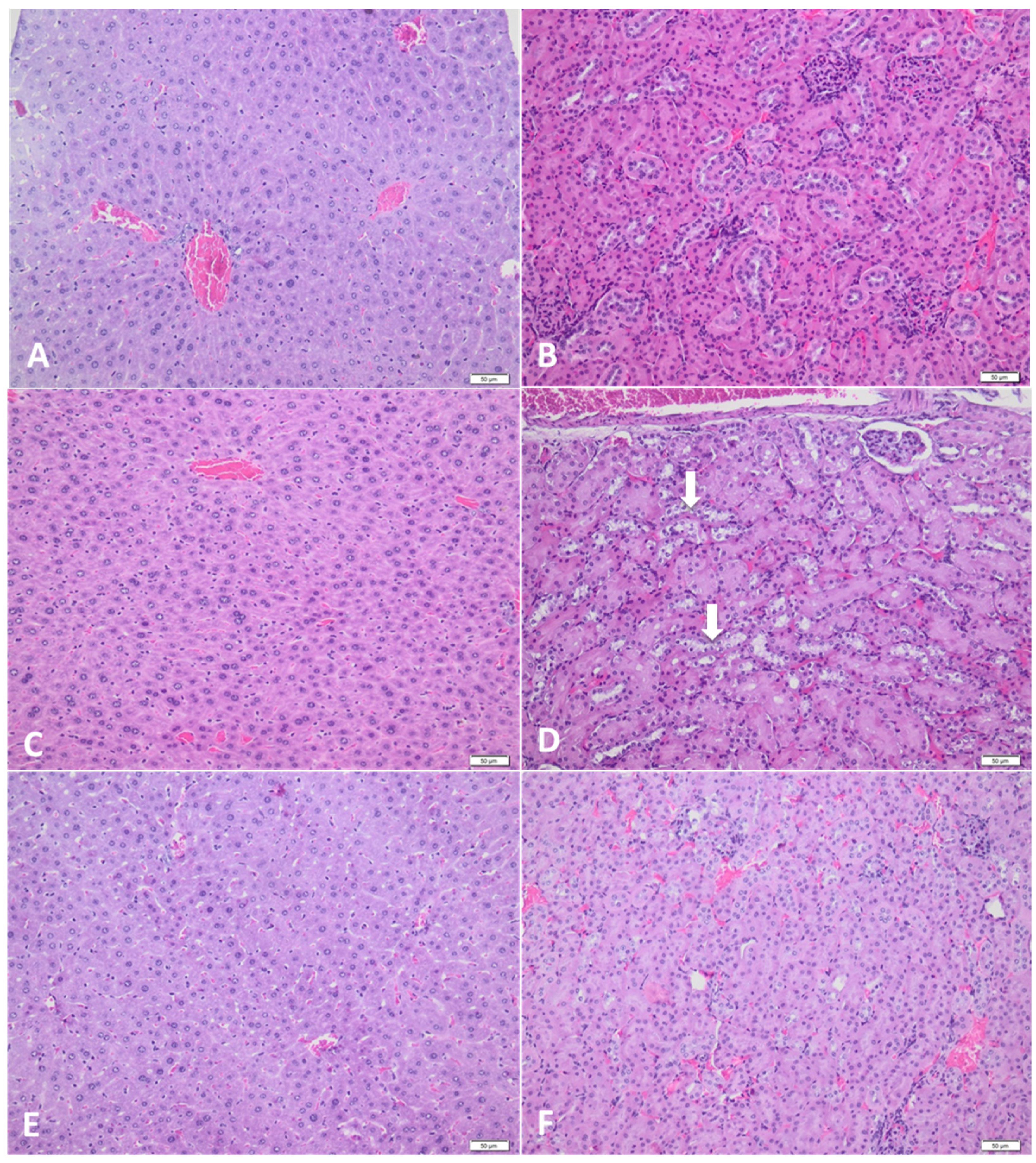
3.2. Histopathological Assay
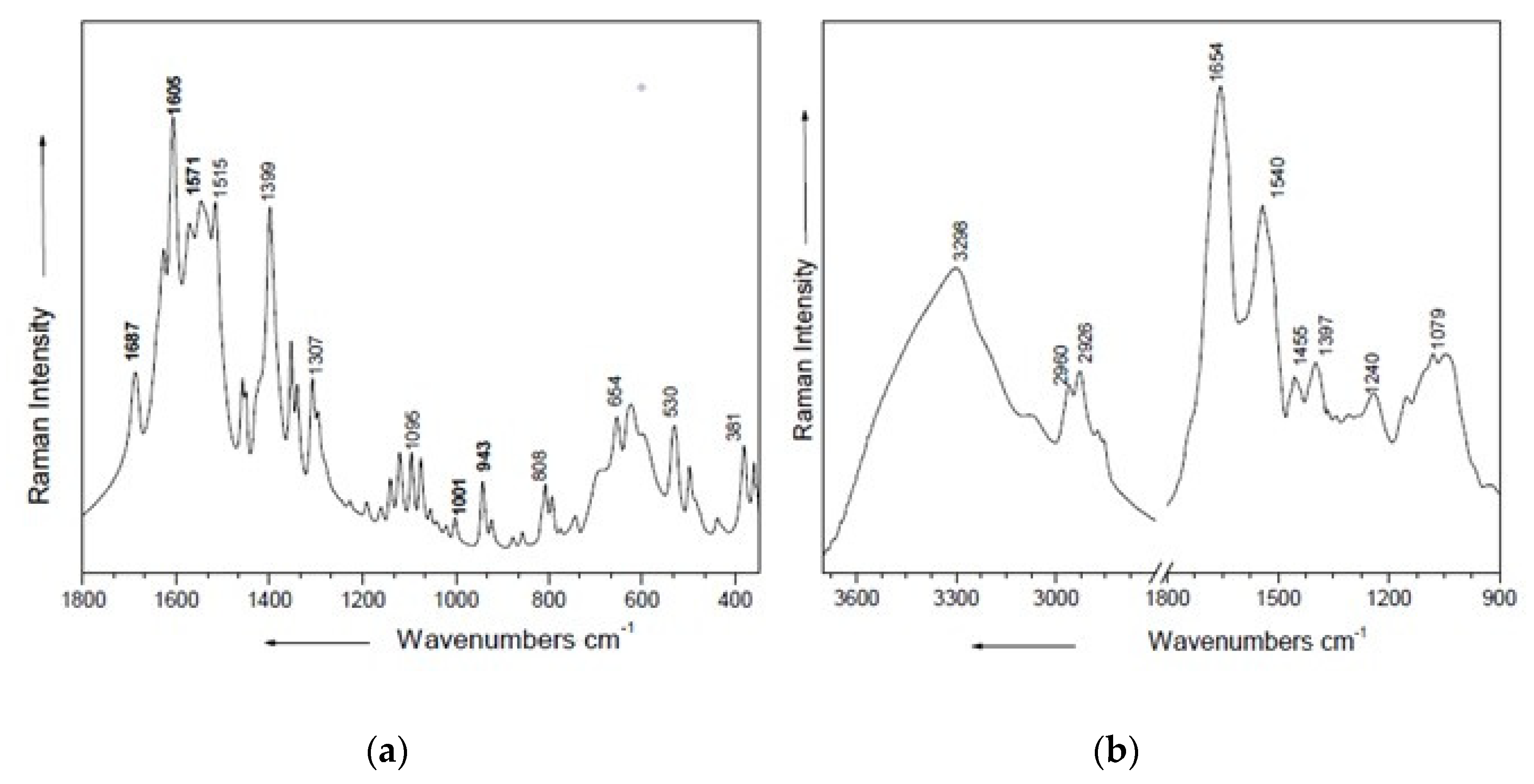
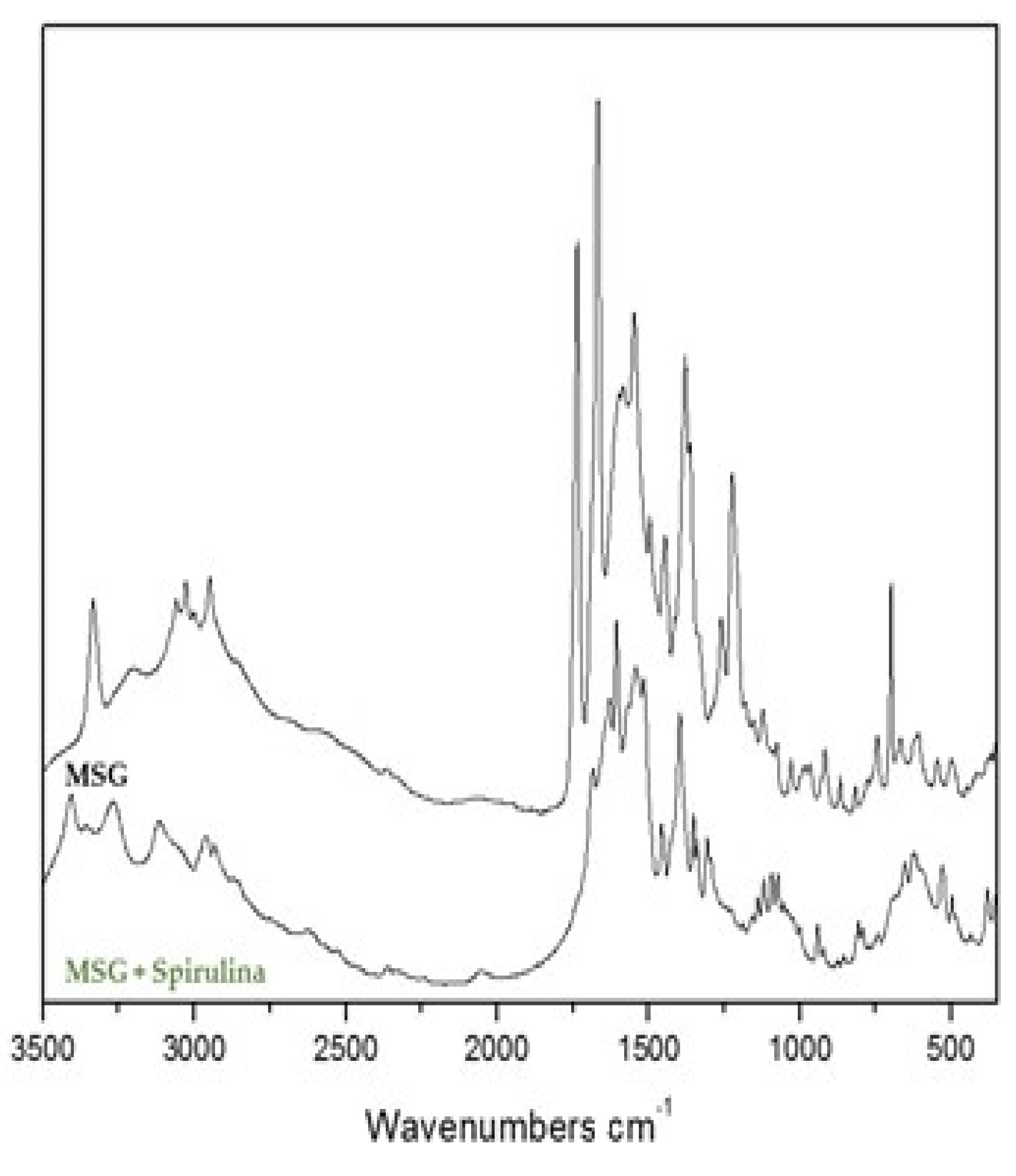
3.3. Spectroscopic Investigations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burt, S. Essential oils: Their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods-a review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 94, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.A.; Paula, A.T.; Casarotti, S.N. Lactic Acid Bacteria Antimicrobial Compounds: Characteristics and Applications. Food Eng. Rev. 2012, 4, 124–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, I.; Brinzan, L.; Stratakos, A. Geraniol and Linalool Loaded Nanoemulsions and Their Antimicrobial Activity. Bull. UASVM Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 74, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pasca, C.; Coroian, A.; Socaci, S. Risks and Benefits of Food Additives-Review. Bull. UASVM Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 75, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidi, M.; Moini Ashraf Alipoor, E.; Rezvan, N.; Gorgani-Firuzjaee, S.; Yaseri, M.; Hosseinzadeh-Attar, M. The effects of quercetin supplementation on metabolic and hormonal parameters as well as plasma concentration and gene expression of resistin in overweight or obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2282–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onaolapo, A.Y.; Onaolapo, O.J.; Mosaku, T.J. A Histological Study of the Hepatic and Renal Effects of Subchronic Low Dose Oral Monosodium Glutamate in Swiss Albino Mice. Br. J. Med. Med Res. 2013, 3, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Campbell, A. Monosodium Glutamate (MSG). In Encyclopedia of Toxicology, Collection in Biomedical Sciences, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 391–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alalwani, A.D. Monosodium glutamate induced testicular lesions in rats (histological study). Middle East Fertil. Soc. J. 2014, 19, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaolapo, O.J.; Onaolapo, A.Y.; Akanmu, M. Changes in Spontaneous Working-memory, Memory-recall and Approach-avoidance following “Low Dose” Monosodium Glutamate in Mice. AIMS Neurosci. 2016, 3, 317–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smriga, M. Food-added monosodium glutamate does not alter brain structure or antioxidant status. Pathophysiology 2016, 23, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry-Unaeze, H.N. Update on food safety of monosodium l-glutamate (MSG). Pathophysiology 2017, 24, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaolapo, O.J.; Onaolapo, A.Y.; Akanmu, M.A. Evidence of alterations in brain structure and antioxidant status following ‘low-dose’ monosodium glutamate ingestion. Pathophysiology 2016, 23, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaolapo, A.Y.; Odetunde, I.; Akintola, A.S. Dietary composition modulates impact of food-added monosodium glutamate on behaviour, metabolic status and cerebral cortical morphology in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallavi, R. The effect of monosodium glutamate on planarian memory retention. South Carol. Jr. Acad. Sci. 2018, 211. Available online: https://scholarexchange.furman.edu/scjas/2018/all/211 (accessed on 4 November 2021).
- Bhandari, U. Effect of Embelin in Monosodium Glutamate Induced Obesity in Male Neonatal Wistar Rats. Artheroscler. Suppl. 2018, 32, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubaidi, F.F.; Mathialagan, R.D.; Noor, M.M. Monosodium glutamate daily oral supplementation: Study of its effects on male reproductive system on rat model. Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med. 2019, 65, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, D.D.; Bossche, F.V.D.; Thanh, N.L. Synergistic effect of a monosodium glutamate/aspartame mixture on zebrafish larval neurobehavioral in comparison with the ADHD symptoms. In Proceedings of the Conference: Belgian Brain Congress 2018—Belgian Brain Council, Liege, Belgium, 19 October 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, M.; El-Nassag, D.; Gasser, M. Potential Protective Effects of Propolis against Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity Induced by Monosodium Glutamate in Rabbits. Alex. Sci. Exch. J. 2019, 40, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shenawy, N.S.; Hamza, R.Z.; Al-Salmi, F.A. Evaluation of the Effect of Nanoparticles Zinc Oxide/Camellia sinensis Complex on the Kidney of Rats Treated with Monosodium Glutamate: Antioxidant and Histological Approaches. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2019, 20, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, A.; Baad-Hansen, L.; Castrillon, E. Differential effects of repetitive oral administration of monosodium glutamate on interstitial glutamate concentration and muscle pain sensitivity. Nutrition 2015, 31, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, M.G.; Vaz, B.S.; Morais, E.G. Biological Effects of Spirulina (Arthrospira) Biopolymers and Biomass in the Development of Nanostructured Scaffolds. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, G.; Salazar, M.; Favila, L. Pharmacology and toxicology of Spirulina alga. Rev. Invest. Clin. 1966, 48, 389–399. [Google Scholar]
- Blé-Castillo, J.L.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, A.; Miranda-Zamora, R. Arthrospira maxima prevents the acute fatty liver induced by the administration of simvastatin, ethanol and a hypercholesterolemic diet to mice. Life Sci. 2002, 70, 2665–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.T. Filamentous tropical marine cyanobacteria: A rich source of natural products for anticancer drug discovery. J. Appl. Phycol. 2010, 22, 659–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobón-Velasco, J.C.; Palafox-Sanchez, V.; Mendieta, L. Antioxidant effect of Spirulina (Arthrospira) maxima in a neurotoxic model caused by 6-OHDA in the rat stratum. J. Neural Transm. 2013, 120, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionov, V.A.; Basova, M.M. Use of blue-green micro-seaweed Spirulina platensis for the correction of lipid and hemostatic disturbances in patients with ischemic heart disease. Vopr. Pitan. 2003, 72, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shalaby, E.A.; Shanab, M.M.; Singh, V. Salt stress enhancement of antioxidant and antiviral efficiency of Spirulina platensis. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 2622–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Canchihuamán, J.C.; Pérez-Méndez, O.; Hernández-Muñoz, R. Protective effects of Spirulina maxima on hyperlipidemia and oxidative-stress induced by lead acetate in the liver and kidney. Lipids Health Dis. 2010, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Bhadouria, P.; Bisen, P.S. Nutritional and therapeutic potential of Spirulina. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2005, 6, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, R.; Chow, T.J. Hypolipidemic, Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Activities of Microalgae Spirulina. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2011, 28, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, T.; Tanaka, M.; Ooike, M. Antioxidant activities of phycocyanobilin prepared from Spirulina platensis. J. Appl. Phycol. 2000, 12, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, J.E.P.; Bescos, P.B.; Villar del Fresno, A.M. Antioxidant activity of different fractions of Spirulina platensis protean extract. II Farm. 2001, 56, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Pan, B.; Sheng, J. Antioxidant activity of Spirulina platensis extracts by supercritical carbon dioxide extraction. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinanoglu, O.; Yener, A.N.; Ekici, S. The protective effects of spirulina in cyclophosphamide induced nephrotoxicity and urotoxicity in rats. Urology 2012, 80, 1392.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalaby, E.A.; Shanab, S.M.M. Comparison of DPPH and ABTS assays for determining antioxidant potential of water and methanol extracts of Spirulina platensis. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2013, 42, 556–564. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, A.E.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Modulating Effects of Spirulina platensis against Tilmicosin-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Mice. Cell J. 2015, 17, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, M.J. Protective effects of spirulina on hippocampal injury in exercise-fatigue mice and its mechanism. Chin. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 34, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Daim, M.; El-Bialy, B.E.; Rahman, H.G.A. Antagonistic effects of Spirulina platensis against sub-acute deltamethrin toxicity in mice: Biochemical and histopathological studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 77, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zhong, Z.; Hu, F. The protective effects of selenium-enriched Spirulina platensis on chronic alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 3155–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Ryu, G.H.; Choi, W.Y. Protective Effect of Water Extracted Spirulina maxima on Glutamate-induced Neuronal Cell Death in Mouse Hippocampal HT22 Cell. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2018, 14, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltantawy, F.M.; Sobh, M.A.A.; El-Waseef, A.M. Protective effect of Spirulina against cyclophosphamide-induced urotoxicity in mice. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2018, 5, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronie, L.; Coroian, A.; Miresan, V. Results Obtained by Investigating Saffron Ussing FT-IR Spectroscopy. Bull. UASVM Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 73, 238–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Keseru, A.; Andronie, L.; Pop, I. Rotaru, A.; Maniutiu, D.; Coroian, A.; Raducu, C. Characterization of momordica charantia ussing FT-IR spectroscopy. Bull. UASVM Holticulture For. 2016, 73, 245–246. [Google Scholar]
- Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the Protection of Animals Used for Scientific Purposes. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A32010L0063 (accessed on 3 November 2021).
- Gonciarov, M.; Coman, C. General principles concerning the harmonization of Romanian Legislation with the European Union in the field of protection of animals used for scientific scope. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2015, 6, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Windmueller, H.G.; Spaeth, A.E. Intestinal Metabolism of Glutamine and Glutamate from the Lumen as Compared to Glutamine from Blood. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1975, 171, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windmueller, H.G.; Spaeth, A.E. Respiratory Fuels and Nitrogen Metabolism in Vivo in Small Intestine of Fed Rats. Quantitative Importance of Glutamine, Glutamate, and Aspartate. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehad, R.; Elyazji, I.; Osama, S.; Lubbad, A.M. Effects of Monosodium Glutamate on Some Biochemical and Hematological Parameters in Adult Rabbits and Potential Protective Effect of Soybean Oil. J. Biol. Chem. Res. 2014, 32, 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Agnes, W.; Boots Guido, R.M.; Haenen, M.; Bast, A. Health effects of quercetin: From antioxidant to nutraceutical. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 585, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAnlis, G.T.; McEneny, J.; Pearce, J.; Young, I.S. Absorption and antioxidant effects of quercetin from onions in man. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 53, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskowitz, H.; Hartmann, J. Consumer research: Creating a solid base for innovative strategies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS Institute JMP 12 Statistical Software; SAS Institute Inc., Cary: Lerida, Spain, 2014.
- Seiva, F.R.F.; Chuffa, L.G.A.; Braga, C.P. Quercetin ameliorates glucose and lipid metabolism and improves antioxidant status in postnatally monosodium glutamate-induced metabolic alterations. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3556–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, I.; Sevastre, B.; Mireșan, V. Protective effect of blackthorn fruits (Prunus spinosa) against tartrazine toxicity development in albino Wistar rats. BMC Chem. 2019, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, K.M.; Tamanna, N.; Haque, A. Biochemical and histopathological profiling of Wistar rat treated with Brassica napus as a supplementary feed. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2018, 7, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuraman, P.; Senthikumar, R.; Srikumar, K. Alterations in beta-islets of Langerhans in alloxan-induced diabetic rats by marine Spirulina platensis. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2009, 24, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbo, S.L.; Bonfleur, M.L.; Carneiro, E.M. Parasympathetic activity changes insulin response to glucose and neurotransmitters. Diabetes Metab. 2002, 28, 3S13-7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andreazzi, A.E.; Scomparin, D.X.; Mesquita, F.P. Swimming exercise at weaning improves glycemic control and inhibits the onset of monosodium L-glutamate-obesity in mice. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 201, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macho, L.; Ficková, M.; Jezova, Z.S. Late effects of postnatal administration of monosodium glutamate on insulin action in adult rats. Physiol. Res. 2000, 48, S79–S85. [Google Scholar]
- Prentki, M.; Nolan, C.J. Islet beta cell failure in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1802–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyema, O.O.; Farombi, E.O.; Emerole, G.O. Effect of vitamin E on monosodium glutamate induced hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2006, 43, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, M.M.; Mohamed, N.E. Impact of Flax Seed and Canola Oils Mixture Supplementation on The Physiological and Biochemical Changes Induced by Monosodium Glutamate in Rats. J. Rad. Res. Appl. Sci. 2010, 3, 943–964. [Google Scholar]
- Takasaki, Y. Studies on brain lesions after administration of monosodium L-glutamate to mice. II. Absence of brain damage following administration of monosodium L-glutamate in the diet. Toxicology 1978, 9, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peláez, B.; Blázquez, J.L.; Pastor, F.E. Lectinhistochemistry and ultrastructure of microglial response to monosodium glutamate-mediated neurotoxicity in the arcuate nucleus. Histol. Histopathol. 1999, 14, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera-Cervantes, M.C.; Torres, J.S.; Feria-Velasco, A. NMDA and AMPA receptor expression and cortical neuronal death are associated with p38 in glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in vivo. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 76, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, M.L.; Lee, T.C.; Fitzgerald, V.; Snyder, F. A specific acetyl hydrolase for I-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (a hypotensive and platelet-activating lipid). J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif-Lehrer, L.; Bergenthal, J.; Hanninen, L. Effects of monosodium glutamate on chick embryo retina in culture. Investig. Ophthalmol. 1975, 14, 114–124. [Google Scholar]
- Blanks, J.C.; Reif-Lehrer, L.; Casper, D. Effects of monosodium glutamate on the isolated retina of the chick embryo as a function of age: A morphological study. Exp. Eye Res. 1981, 32, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndman, A.G.; Adler, R. Analysis of glutamate uptake and monosodium glutamate toxicity in neural retina monolayer cultures. Dev. Brain Res. 1981, 2, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, P.C. Neuroglial Responses to Elevated Glutamate in the Medial Basal Hypothalamus of the Infant Mouse. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karwowska, M.; Kononiuk, A. Nitrates/Nitrites in Food—Risk for Nitrosative Stress and Benefits. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Control | MSG 0.5 | MSG1 | MSG1 + S | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COL mg/dL | 78.40 ± 1.23 c | 86.80 ± 6.47 b | 108.20 ± 3.43 a | 67.40 ± 3.39 d | *** |
| TG mg/dL | 86.20 ± 2.01 b | 86.80 ± 5.20 b | 106.00 ± 2.44 a | 72.20 ± 2.84 c | *** |
| CRE mg/dL | 0.07 ± 0.01 b | 0.08 ± 0.01 b | 0.12 ± 0.01 a | 0.06 ± 0.01 b | *** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lia Longodor, A.; Coroian, A.; Balta, I.; Taulescu, M.; Toma, C.; Sevastre, B.; Marchiș, Z.; Andronie, L.; Pop, I.; Matei, F.; et al. Protective Effects of Dietary Supplement Spirulina (Spirulina platensis) against Toxically Impacts of Monosodium Glutamate in Blood and Behavior of Swiss mouse. Separations 2021, 8, 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8110218
Lia Longodor A, Coroian A, Balta I, Taulescu M, Toma C, Sevastre B, Marchiș Z, Andronie L, Pop I, Matei F, et al. Protective Effects of Dietary Supplement Spirulina (Spirulina platensis) against Toxically Impacts of Monosodium Glutamate in Blood and Behavior of Swiss mouse. Separations. 2021; 8(11):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8110218
Chicago/Turabian StyleLia Longodor, Adina, Aurelia Coroian, Igori Balta, Marian Taulescu, Corina Toma, Bogdan Sevastre, Zamfir Marchiș, Luisa Andronie, Ioana Pop, Florica Matei, and et al. 2021. "Protective Effects of Dietary Supplement Spirulina (Spirulina platensis) against Toxically Impacts of Monosodium Glutamate in Blood and Behavior of Swiss mouse" Separations 8, no. 11: 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8110218
APA StyleLia Longodor, A., Coroian, A., Balta, I., Taulescu, M., Toma, C., Sevastre, B., Marchiș, Z., Andronie, L., Pop, I., Matei, F., Tamas-Krumpe, O. M., & Maris, S. (2021). Protective Effects of Dietary Supplement Spirulina (Spirulina platensis) against Toxically Impacts of Monosodium Glutamate in Blood and Behavior of Swiss mouse. Separations, 8(11), 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8110218








