Selective Separation and Analysis of Catecholamines in Urine Based on Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction by Mercaptophenylboronic Acid Functionalized Fe3O4-NH2@Au Magnetic Nanoparticles Coupled with HPLC
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Chromatography Conditions
2.4. Preparation of Phenylboronic Acid-Functionalized Fe3O4-NH2@Au (Fe3O4-NH2@Au-MPBA)
2.5. Sample Collection
2.6. Sample Pretreatment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
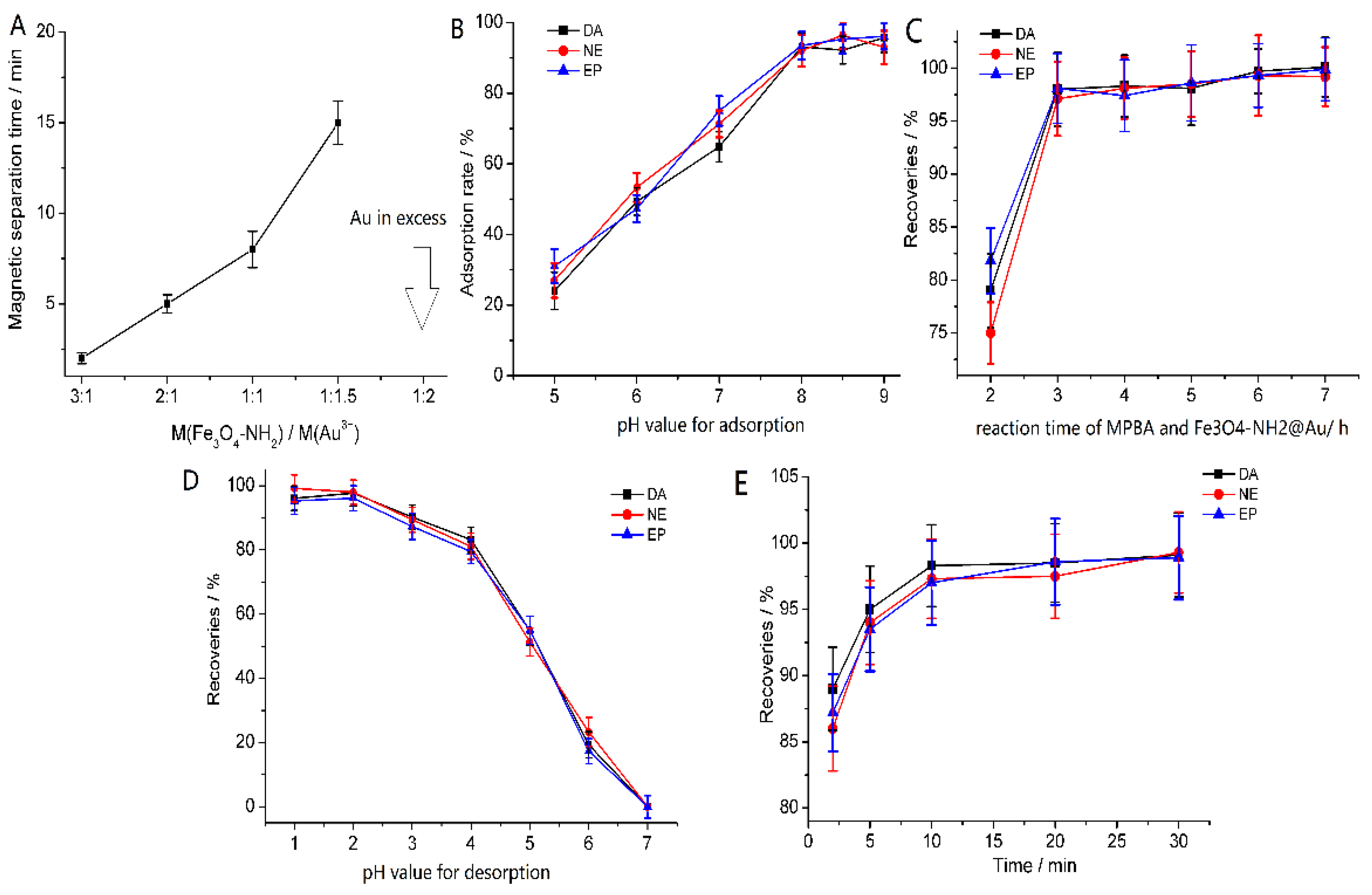
3.2. Optimization of the Extraction Condition
3.2.1. Optimizing the Mass Ratio of Au3+ and Fe3O4-NH2
3.2.2. Optimizing the pH Value of the Adsorption Solution
3.2.3. Optimizing Reaction Time of MPBA and Fe3O4-NH2@Au
3.2.4. The pH Value of Desorption Solvent
3.2.5. Exploring the Elution Time
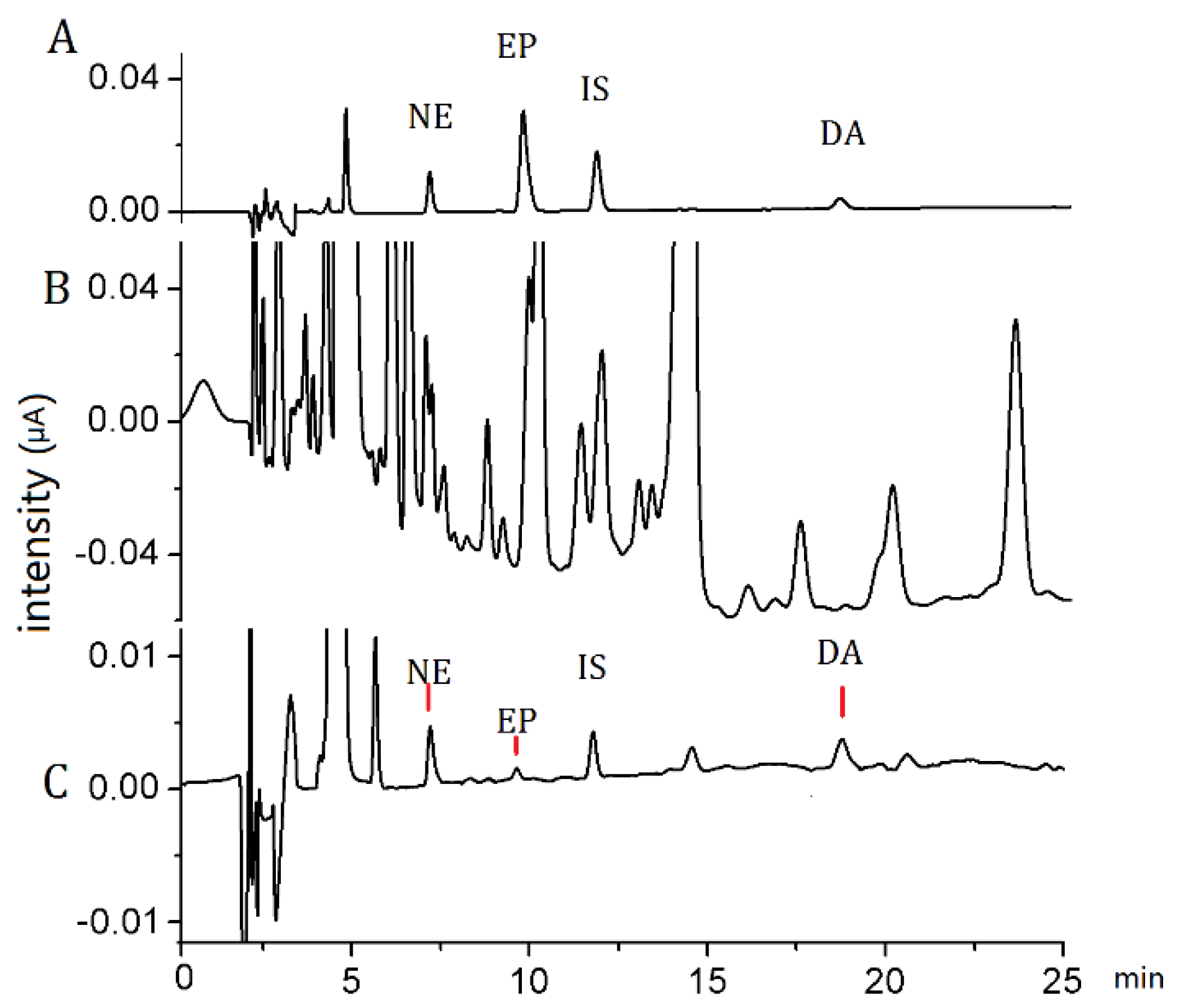
3.3. Method Evaluation
3.4. Reproducibility and Stability
3.5. Application of the Method to Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barnes, M.A.; Carson, M.J.; Nair, M.G. Non-traditional cytokines: How catecholamines and adipokines influence macrophages in immunity, metabolism and the central nervous system. Cytokine 2015, 72, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, D.S.; Kopin, I.J.; Sharabi, Y. Catecholamine autotoxicity. Implications for pharmacology and therapeutics of Parkinson disease and related disorders. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 144, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhofer, G.; Peitzsch, M. Laboratory Evaluation of Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. Clin. Chem. 2014, 60, 1486–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, J.; Vogelgesang, A.; Dressel, A. Catecholamines, steroids and immune alterations in ischemic stroke and other acute diseases. Aging Dis. 2014, 5, 327–339. [Google Scholar]
- Bergquist, J.; Ściubisz, A.; Kaczor, A.; Silberring, J. Catecholamines and methods for their identification and quantitation in biological tissues and fluids. J. Neurosci. Methods 2002, 113, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangubotla, R.; Kim, J. Recent trends in analytical approaches for detecting neurotransmitters in Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 105, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.; Soni, S.; Agrawal, P.; Balhara, Y.P.S.; Jain, U. Recent advancement in nanosensors for neurotransmitters detection: Present and future perspective. Process. Biochem. 2020, 91, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranwal, A.; Chandra, P. Clinical implications and electrochemical biosensing of monoamine neurotransmitters in body fluids, in vitro, in vivo, and ex vivo models. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 121, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokinoya, K.; Shishikura, Y.; Sekine, N.; Aoyagi, A.; Yoshida, Y.; Aita, Y.; Sugasawa, T.; Nabekura, Y.; Takekoshi, K. Plasma free metanephrine and normethanephrine levels correlated toplasma catecholamine after acute running in amateur runner. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2021, 19, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, A.M.D.; Gould, E.A.M.; Penfold, S.A.; Lambert, G.W.; Pratama, P.R.; Dai, A.; Gray, S.P.; Head, G.; Jandeleit-Dahm, K.A. Diabetes and Hypertension Differentially Affect Renal Catecholamines and Renal Reactive Oxygen Species. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomae, A.; Nantaphol, S.; Kondo, T.; Chailapakul, O.; Siangproh, W.; Panchompoo, J. Simultaneous determination of beta-agonists by UHPLC coupled with electrochemical detectioin based on palladium nanoparticles modified BDD electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 840, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Guo, X.-F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.-S. Analysis of catecholamines and related compounds in one whole metabolic pathway with high performance liquid chromatography based on derivatization. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, J.-X.; Cui, W.-Q.; Zhang, J.-W.; Wu, D.-Q.; Yu, X.-R.; Luo, Y.-B.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Zhu, F.-P.; Hussain, D.; et al. A simultaneous extraction/derivatization strategy coupled with liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of free catecholamines in biological fluids. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1654, 462474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torul, H.; Gumustas, M.; Urguplu, B.; Uzunoglu, A.; Boyaci, I.H.; Celikkan, H.; Tamer, U. Disposable electrochemical flow cell with paper-based electrode assemble. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 891, 115268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhu, A.; Shi, G. Selective extraction and analysis of catecholamines in rat blood microdialysate by polymeric ionic liquid-diphenylboric acid-packed capillary column and fast separation in high-performance liquid chromatography-electrochemical detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1409, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, H.; Hayashi, T. High-performance liquid chromatographie analysis of catecholamines in biological samples by liquid/liquid extraction prepurification. J. Pharmacol. Methods 1990, 23, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Betzabeth, E.B.M.; Fabienne, M.; Jérome, R.; Claire, D.; Vincent, D. Evaluation of boronate affinity solid-phase extraction coupled in-line to capillary isoelectric focusing for the analysis of catecholamines in urine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1034, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, H.I.; Yang, J.S.; Oh, H.J.; Cho, Y.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.-D.; Lee, S.-Y. A simple and rapid analytical method based on solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for the simultaneous determination of free catecholamines and metanephrines in urine and its application to routine clinical analysis. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 49, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicker, J.; Fortuna, A.; Alves, G.; Falcão, A. Liquid chromatographic methods for the quantification of catecholamines and their metabolites in several biological samples—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 768, 12–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Shen, J.; Zhang, W. High-throughput and selective solid-phase extraction of urinary catecholamines by crown ether-modified resin composite fiber. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1561, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, H.; Hu, M. An intensive study on the magnetic effect of mercapto-functionalizednano-magnetic Fe3O4 polymers and their adsorption mechanism for the removal of Hg (II) from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 210, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Qin, P.; Lei, M.; Zeng, Q.; Song, H.; Yang, J.; Shao, J.; Liao, B.; Gu, J. Modifying Fe3O4 nanoparticles with humic acid for removal of Rhodamine B in water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 209–210, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.; Xue, D.; Tan, N.; Zheng, B.; Jia, M.; Zhang, W. Pt supported on octahedral Fe 3 O 4 microcrystals as a catalyst for removal of formaldehyde under ambient conditions. Chin. J. Catal. 2018, 39, 1534–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhao, A.; He, Q.; Chen, P.; Wei, Y.; Chen, X.; Hu, H.; Wang, M.; Huang, H.; Wang, R. Multifunctional Fe3O4@mTiO2@noble metal composite NPs as ultrasensitive SERS substrates for trace detection. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 2017–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, M.; Yu, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, H. Facile synthesis of highly ordered mesoporous Fe3O4 with ultrasensitive detection of dopamine. Talanta 2019, 201, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddaoui, M.; Sola, C.; Raouafi, N.; Korri-Youssoufi, H. E-DNA detection of rpoB gene resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis in real samples using Fe3O4/polypyrrole nanocomposite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 128, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, H. Fe3O4@rGO doped molecularly imprinted polymer membrane based on magnetic field directed self-assembly for the determination of amaranth. Talanta 2014, 123, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babamiri, B.; Hallaj, R.; Salimi, A. Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for determination of hepatitis B virus surface antigen using CdTe@CdS-PAMAM dendrimer as luminescent labels and Fe3O4 nanoparticles as magnetic beads. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 254, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, S.; Prabaharan, M. Multi-functional core-shell Fe3O4@Au nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 174, 252–259. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, H.; Liu, B.; Gong, D.; Peng, B.; Han, B.; Zhang, N. Direct electrochemical enhanced detection of dopamine based on peroxidase-like activity of Fe3O4@Au composite nanoparticles. Microchem. J. 2021, 164, 105943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, S.; Aghaei, H.; Ghaedi, M.; Asfaram, A.; Monajjemi, M.; Bazrafshan, A.A. Synthesis of nanocomposites of iron oxide/gold (Fe3O4/Au) loaded on activated carbon and their application in water treatment by using sonochemistry: Optimization study. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 41, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, N.; Khenkin, A.M.; Hailegnaw, B.; Neumann, R. Depolymerization of Cellulose in Water Catalyzed by Phenylboronic Acid Derivatives. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 5799–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dutta, D.; Sailapu, S.K.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Ghosh, S.S. Phenylboronic Acid Templated Gold Nanoclusters for Mucin Detection Using a Smartphone-Based Device and Targeted Cancer Cell Theranostics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 3210–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahlberg, C.; Linares, M.; Norman, P.; Uvdal, K. Phenylboronic Ester- and Phenylboronic Acid-Terminated Alkanethiols on Gold Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 116, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ye, F.; Wang, H.; Admassu, H.; Feng, Y.; Hua, X.; Yang, R. Phenylboronic Acid Functionalized Adsorbents for Selective and Reversible Adsorption of Lactulose from Syrup Mixtures. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9269–9281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, G.; Desikan, R.; Thundat, T. Label-Free Sugar Detection Using Phenylboronic Acid-Functionalized Piezoresistive Microcantilevers. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 4860–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankoh, S.; Thammakhet, C.; Numnuam, A.; Limbut, W.; Kanatharana, P.; Thavarungkul, P. 4-mercaptophenylboronic acid functionalized gold nanoparticles for colorimetric sialic acid detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cheng, C.; Chang, Y.; Ma, H.; Hao, Y. Two sensitive electrochemical strategies for the detection of protein kinase activity based on the 4-mercaptophenylboronic acid-induced in situ assembly of silver nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 248, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, G.; He, X.; Zhou, C.; Ya, D.; Feng, J.; Yu, C.; Deng, B. A novel ECL sensor based on a boronate affinity molecular imprinting technique and functionalized SiO2@CQDs/AuNPs/MPBA nanocomposites for sensitive determination of alpha-fetoprotein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-Q.; Wang, Y.; Qu, J.-S.; Deng, J.-J.; Kang, X.-J. Selective extraction of catecholamines by packed fiber solid-phase using composite nanofibers composing of polymeric crown ether with polystyrene. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, N.; Çakır, A.; Somtürk, B. Boronic acid functionalized polymeric microspheres for catecholamine isolation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 445, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Chen, L.; Gu, P.; Wei, L.; Kang, X. A Convenient Method for Extraction and Analysis with High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography of Catecholamine Neurotransmitters and Their Metabolites. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 133, e56445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
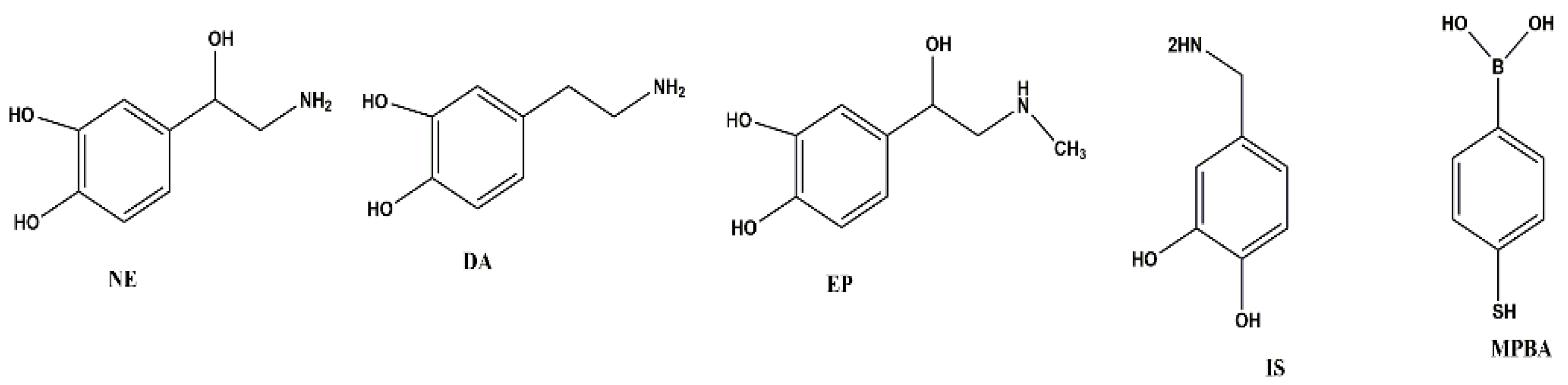
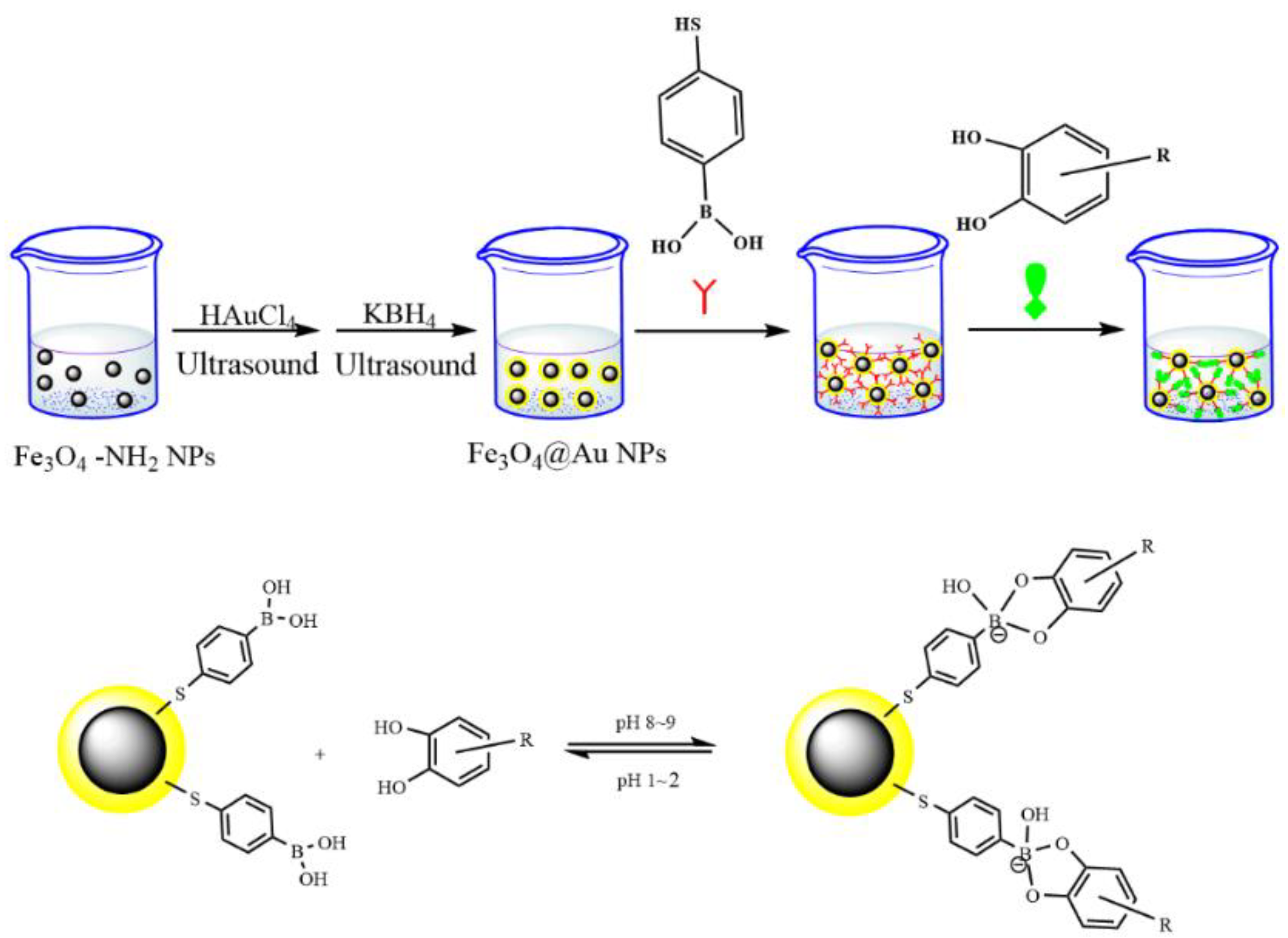
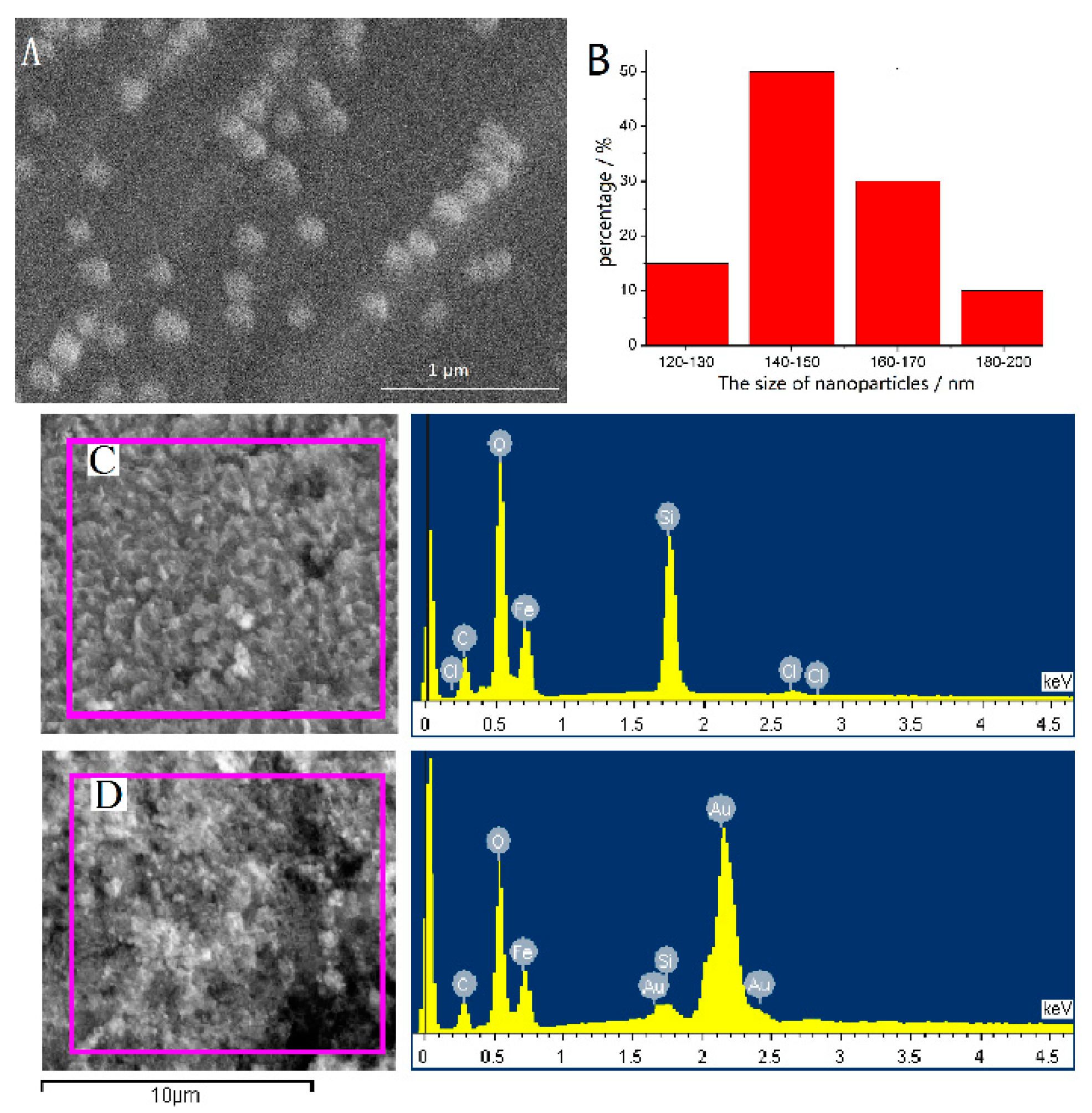
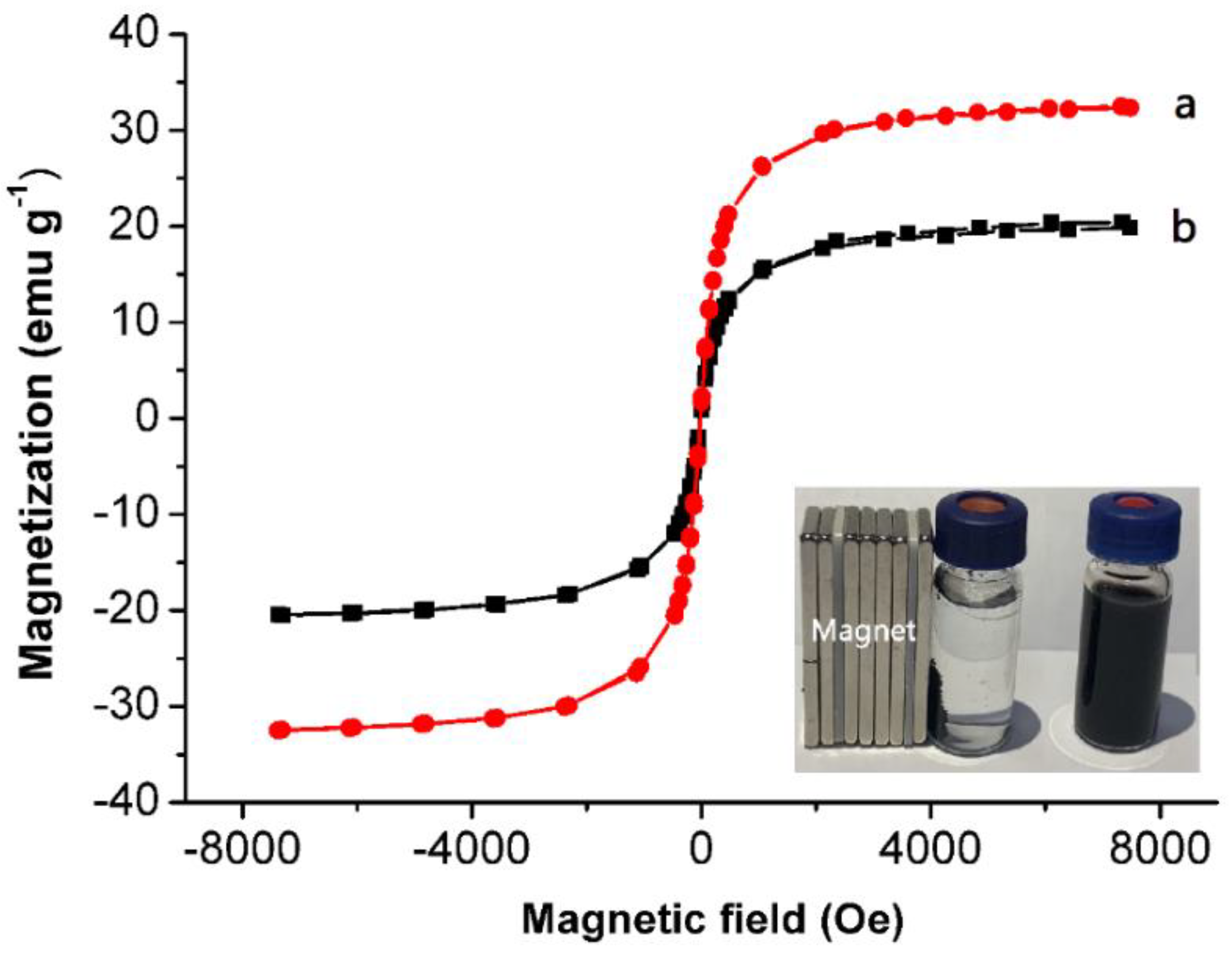
| Catecholamines | Linear Range (ng mL−1) | r2 | Spiked Concentration (ng mL−1) | Recovery (%) | LOD (ng mL−1) | LOQ (ng mL−1) | Intraday (RSD, %) | Interday (RSD, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.5–500.0 | 0.9907 | 10.0 | 85.4 | 0.60 | 2.0 | 8.2 | 9.3 | |
| DA | 50.0 | 93.2 | 7.7 | 8.8 | ||||
| 200.0 | 95.7 | 6.1 | 7.4 | |||||
| 2.5–500.0 | 0.9911 | 10.0 | 88.1 | 0.39 | 1.3 | 7.9 | 11.5 | |
| NE | 50.0 | 96.3 | 8.4 | 8.1 | ||||
| 200.0 | 97.1 | 6.6 | 9.0 | |||||
| 2.5–500.0 | 0.9935 | 10.0 | 89.6 | 0.27 | 0.9 | 10.7 | 8.6 | |
| EP | 50.0 | 98.3 | 8.3 | 7.9 | ||||
| 200.0 | 105.2 | 8.9 | 8.1 |
| Samples | Level of Catecholamines (M + SD, ng/mL) (n = 3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| NE | EP | DA | |
| 1 | 13.2 ± 0.7 | 10.8 ± 0.3 | 81.1 ± 9.9 |
| 2 | 26.3 ± 1.1 | 25.3 ± 1.5 | 99.1 ± 10.1 |
| 3 | 65.8 ± 5.4 | 21.1 ± 1.7 | 279.3 ± 21.6 |
| 4 | 52.6 ± 4.1 | 43.2 ± 3.5 | 135.1 ± 14.7 |
| 5 | 65.8 ± 6.7 | 22.6 ± 1.9 | 9.0 ± 0.8 |
| 6 | 11.2 ± 0.8 | 2.7 ± 0.1 | 15.1 ± 1.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Q.; Wu, X.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Kang, X.; Zhu, H. Selective Separation and Analysis of Catecholamines in Urine Based on Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction by Mercaptophenylboronic Acid Functionalized Fe3O4-NH2@Au Magnetic Nanoparticles Coupled with HPLC. Separations 2021, 8, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8110196
Han Q, Wu X, Cao Y, Zhang H, Zhao Y, Kang X, Zhu H. Selective Separation and Analysis of Catecholamines in Urine Based on Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction by Mercaptophenylboronic Acid Functionalized Fe3O4-NH2@Au Magnetic Nanoparticles Coupled with HPLC. Separations. 2021; 8(11):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8110196
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Qing, Xiaoxiao Wu, Yi Cao, Hua Zhang, Yuqin Zhao, Xuejun Kang, and Huaiyuan Zhu. 2021. "Selective Separation and Analysis of Catecholamines in Urine Based on Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction by Mercaptophenylboronic Acid Functionalized Fe3O4-NH2@Au Magnetic Nanoparticles Coupled with HPLC" Separations 8, no. 11: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8110196
APA StyleHan, Q., Wu, X., Cao, Y., Zhang, H., Zhao, Y., Kang, X., & Zhu, H. (2021). Selective Separation and Analysis of Catecholamines in Urine Based on Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction by Mercaptophenylboronic Acid Functionalized Fe3O4-NH2@Au Magnetic Nanoparticles Coupled with HPLC. Separations, 8(11), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8110196





