Abstract
Background: The metabolic changes associated with diabetes can lead to nephropathy eventually resulting in end-stage renal disease. Current antidiabetic therapies do not effectively prevent the onset of diabetic kidney diseases as well as progression. Aim: To evaluate the effect of Coccinia indica leaf extract alone and in combination with pioglitazone, an antihyperglycemic agent was used to modulate the progressive kidney damage induced by type 2 diabetes in rats. Hypotheses: Pioglitazone causes severe adverse effects when administered for long-term therapy. The hypotheses in this study is to examine the renoprotective effect of Coccinia indica leaf extract (200 mg/kg p.o.) when co-administered with low-dose pioglitazone (7 mg/kg) in type-2-diabetes-induced nephropathy in rats and simultaneously evaluate the hypoglycemic response as well. Methods: Rats (Males, Sprague Dawley) were kept on a high-fat diet and were given a single dose of streptozotocin (35 mg/kg, i.p.) to induce diabetic nephropathy. Treatment groups received either Coccinia indica leaf extract or pioglitazone or pioglitazone with Coccinia indica extract, fenofibrate, or lisinopril for 7 weeks. Blood glucose, antioxidant status, triglycerides, total cholesterol, creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, and proteinuria levels were estimated and compared with the normal control and disease control (untreated) groups. Results: The untreated diabetic rats showed increased blood glucose levels, lipid profiles, and renal oxidative stress, along with an increase in nephropathy markers such as blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, and proteinuria. Histopathological examination revealed glomerular damage. Combination treatment with Coccinia indica leaf extract and a low dose of pioglitazone normalized the nephropathic markers as well as histopathological changes. Conclusion: Coccinia indica leaf extract when co-administered with a low dose of pioglitazone as antidiabetic therapy showed good glycemic control and a beneficial renoprotective effect. Combination therapy would lower the dose of pioglitazone and also protect kidneys from drug-induced toxicity as observed from normalized nephropathic markers in a diabetic rat model.
1. Introduction
Diabetes mellitus is an endocrine dysfunction of blood sugar regulation. It is characterized by hyperglycemia either due to a deficiency in insulin due to autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing beta cells in pancreas, or due to resistance to insulin. Diabetes mellitus can lead to multiple complications, and end-stage renal failure is one of the leading causes of death due to diabetic complications [1].
Diabetic nephropathy refers to a condition with progressive kidney damage that leads to the thickening of the glomerular basement membrane, glomerulosclerosis, degrading of podocyte adhesion, mesangial cell expansion, tubulointerstitial fibrosis, and overall glomerular hypertrophy [2]. This leads to a decreased glomerular filtration rate (GFR), worsening albuminuria, peripheral edema, and increased arterial blood pressure [3]. Uncontrolled blood glucose level and persistent hypertension may lead to structural and functional changes in kidney [4]. A hyperglycemic state reduces the mRNA levels of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) in the glomeruli [5]. Progression of nephropathy in diabetic patients may be accelerated in the presence of hyperlipidemic condition and considered as an independent risk factor [6]. Thiazolidinediones such as pioglitazone have beneficial effects on glucose and lipid metabolism [7].
Recent studies indicate antioxidant use can stall the formation of free radicals and reduce its damaging effects in diabetes-induced animal models [8,9] and the severity of diabetes complications [10]. Reactive oxygen free radicals play a crucial part in renal injury among hyperglycemic patients [11,12]. Renal morphology and functional changes are specific characteristic futures of diabetic nephropathy in rats. Fenofibrate and lisinopril are renoprotective compounds that have beneficial effect in diabetic nephropathy [13,14].
Coccinia indica Cucurbitaceae is an ivy gourd native to India and is considered to be an “Indian substitute for insulin” due to its efficacy in controlling hyperglycemia [15]. Coccinia indica has been reported to have antidiabetic properties [16,17,18]. It is hypothesized that its antioxidant properties help protect renal damage and ability to control lipid peroxidation, which would increase oxidative damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetes [17]. Various parts of Coccinia indica possess different activities, such as hypoglycemia, antilipidemic, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antipyretic, antinociceptive, hepatoprotective, antimicrobial, antitussive, antilithiatic, and antimutagenic. It is also useful in curing some skin disorders, such as ring worm, psoriasis, scabies, other itchy skin eruptions, and ulcer activity [19].
There is no report on the usefulness of the combination therapy of Coccinia indica leaf extract with low-dose pioglitazone. Therefore, the present investigation is aimed at determining whether a bioflavonoid-rich extract of Coccinia indica leaf alone or in combination with pioglitazone can modulate the progressive damage of kidney induced by type 2 diabetes in rats. A low dose of pioglitazone was used to prevent the hypoglycemic effect and to examine the synergistic activity with Coccinia indica leaf extract, because glucose uptake and the tissue’s peripheral utilization by fat, liver, and muscle are necessary for proper glycemic control and to prevent the adverse effect of its conventional dosage.
2. Methods
2.1. Drugs and Chemicals
Streptozotocin (18883-66-4) was purchased from Sigma Aldrich Ltd (St Louis, MO, USA) Lisinopril was gifted by Dr. Reddy’s Laboratory, Hyderabad, India. Carboxymethyl cellulose was purchased from Quest International, Bangalore, India. Fenofibrate and pioglitazone were purchased from Ranbaxy Laboratory Ltd at Gurgaon, India. Analytical grade chemicals were used for the rest of the protocols.
2.2. Plant Material—Ethanolic Extract of Coccinia indica
Coccinia indica dried leaves were extracted with ethanol. It was extracted by heating the mass for 5–6 h within a closed system that re-pumps Coccinia indica extra into the herb bed. This process was done twice. The extracts were combined and concentrated with reduced pressure at a low temperature. This was taken to a drier unit for drying and separated the product in a powder form. This was further made into a fine powder in a multimill, and the product was blended to make a uniform and homogenous lot.
2.3. Experimental Animals and Preliminary Work
Sprague Dawley male rats weighing around 180–200 g were used with the permission of the Institutional Animal Ethical Committee. The species were stored in Vidya Siri College of Pharmacy, Bangalore, India. Laboratory conditions of twelve-hour light–dark cycles, temperature at 23 ± 2 °C and 50 ± 5% humidity, were all controlled. Water ad libitum and normal diet were provided to the animals, before the dietary interventions. Animals were bred in an institutional animal house.
Before induction of disease and the start of therapy, we conducted a preliminary experiment, wherein, the effect of low-dose pioglitazone and fenofibrate on blood glucose level and lipid profile, respectively, was studied in normal rats.
2.4. Experimental Groups
Rats were divided into seven groups (n = 10 in each group). The rats belonging to the control group (Group I) were fed with a normal diet. The remaining 60 rats (Group II–VII) were fed with a high fat diet (HFD) for two weeks. After 2 weeks of HFD, 60 rats (Groups II–VII) were given low-dose streptozotocin (STZ, i.p. 35 mg/kg) to induce diabetes mellitus [20]. Group II diabetic rats were considered the diabetic control (untreated). Diabetic rats from Groups III to VII were treated with respective drugs/extract for 7 weeks orally after induction of diabetes. The medication/extracts were dissolved in 0.5% w/v of carboxy methyl cellulose (CMC). Fenofibrate (30 mg/kg) [2], pioglitazone (7 mg/kg), Coccinia indica leaf extract (200 mg/kg)combination of Coccinia indica leaf extract 200 mg/kg plus pioglitazone and lisinopril only (1 mg/kg) [2] were administered to Groups III–VII, respectively.
2.5. Assessment of Diabetes and Lipid Profile
Glucose levels in the blood sampled from a tail vein was quantified using AccuCheck (a glucose diagnostic kit—Ser.No.GB 14561388). Rats were designated as diabetic if non-fasting blood sugars were ≥250 mg per deciliter and were forwarded for additional pharmacological studies. After 7 weeks of streptozotocin administration (end of the treatment), serum was derived from blood samples, frozen, and analyzed later for biochemical data. Serum glucose concentrations were derived using ready-made kits (Crest Biosystems, India) via a glucose oxidase peroxidase (GOD-POD) method [21]. Total serum cholesterol was quantified by using cholesterol oxidase peroxidase (CHOD/PAP) method [22]. A glycerol phosphate oxidase method was used to compute the serum triglyceride levels [23].
2.6. Pre- and Post-Prandial Glucose Measurement/Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
On oral glucose load, the rate at which glucose enters the intestine, the rate of intestinal absorption of glucose, and the rate of insulin-driven metabolism shall determine the change in the blood glucose concentration at various time intervals. A glucose tolerance test was performed before the start of the therapy in 3 groups (Group I, IV, and V; normal control, pioglitazone treatment, and Coccinia indica leaf extract treatment, respectively). This test was performed to assure the non-hypoglycemic effect of medications. OGTT was also performed after the treatment period (after 7 weeks of therapy) in five groups, Group I, II, IV, V, and VI, namely normal control, diabetes control, pioglitazone treated, Coccinia indica leaf extract treated, and combination therapy of pioglitazone and Coccinia indica leaf extract. While performing the test, the animals were fasted for 12 h and then administered with the predesignated medication. After 30 min of dose administration, 2.0 g/kg glucose was given by oral gavage. Blood glucose levels were measured at 0, 30, 60, and 120 min after glucose load. The levels of glucose were compared with normal group, diabetes control, and within the groups.
2.7. Evaluation of Diabetic Nephropathy.
Serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and proteinuria were analyzed biochemically as described below to determine the extent of diabetes-induced nephropathy.
2.7.1. Serum Creatinine
Using the alkaline picrate method [24], the serum creatinine was measured with a kit (Crescent biosystems, Goa, India). A clear supernatant was formed by adding 2 mL picric acid to 0.2 mL of serum. This mixture was centrifuged at 3000 rpm. The authors separated 100 µL of buffer reagent and added the following: 0.1 mL standard creatinine, 1.1 mL of supernatant, and 0.1 mL water (distilled) for standard, test preparation, and blank, respectively. Then, 0.1 mL reagent of picric acid was added to blank as well as to the standard. The mixture was kept undisturbed for 20 min at room temperature. Creatinine undergoes reaction with alkaline picrate, forming a reddish-orange compound that is read at 520 nm using a spectrophotometer.
2.7.2. Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
Serum urea was estimated by the Glutamate dehydrogenase (GLDH)–Urease method (end point method) with the help of Semi Auto-Analyzer Urea Reagent. Twenty microliters of standard urea (50 mg/dL) was mixed with 1000 μL of reagent. The mixture was kept aside (10 min) at 37 °C for incubation. The produced mixture aspirated and calibrated to 50 mg/dL. The fasting serum urea was measured by adding 20 μL of the serum sample to 1000 μL of the reagent. This was then mixed and incubated for 10 min at the same temperature. Absorbance was measured at 505 nm using the Auto Analyzer [25].
2.7.3. Protein in Urine
Total protein was measured using Biuret method. Hydrated copper sulphate (CuSO4·5 H2O, 3 g) and sodium–potassium tartrate (KNaC4H4O6·4H2O, 9 g) were dissolved in half a liter of distilled water. Five grams of potassium iodide (KI) was added to above copper sulphate solution. In another vessel, 24 g of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) was mixed into 300 mL of distilled water. Both solutions were combined, and the final volume was made up to 1 L with distilled water. This Biuret reagent was stored at room temperature and used within 12 weeks of preparation.
Metabolic cage was used to collect the urine. Two milliliters of urine was aliquoted into a tube per sample. Additional test tubes containing 2 mL of standard solution and a blank (distilled water) were prepared separately. To each sample, 2 mL of perchloric acid (1.5 mol/L) was mixed. This mixture was kept aside (10 min) at room temperature. The precipitate was pelleted via centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 15 min. The supernatant was discarded and 1.5 mL Biuret reagent was mixed with each sample. After 12 min, color intensity was measured and compared with the blank sample using spectrophotometry at 540 nm [26,27].
2.7.4. Histopathological Analysis of Kidneys
Kidneys were isolated at the end of the experiment after animal sacrifice and were stored in 10% phosphate buffered formalin. Tissues were dehydrated using 60% ethanol. Paraffin was used to embed the tissue (5 μM sizes). Cell structure was examined after staining the tissue with hematoxylin and eosin. Some samples were stained with acid Schiff reagent (PAS) in order to assess basement membrane changes such as thickening, glycogen deposition, or Masson’s trichome to identify possible collagen deposition within tissues. Light microscopy was performed to visualize interstitial inflammatory cell proliferation and possible lesions by the observers blinded to control vs. treatment groups [28].
2.8. Detection of Renal Oxidative Stress
2.8.1. Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Activity
Tissue homogenate was prepared by homogenizing 100 mg of kidney tissue with 10 mL of 100 mM potassium dihydrogen phosphate buffer containing 1 mM Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), pH 7.4. The obtained homogenate was centrifuged at 12,000× g for 30 min at 4 °C, and the protein concentration of the supernatant was used. Nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT, 0.4 mL), sodium carbonate (Na2CO3, 1 mL), and EDTA (0.2 mL) were added to 100 μL of kidney tissue homogenate. Spectrophotometric measurements were made at 560 nm prior to initiation of the reaction. An amount of 1 mM hydroxylamine HCl (0.4 mL) was added to begin the reaction. The solution was incubated at 25 °C for 5 min and then measured the reduction of NBT at 560 nm. A control mixture was formed without the use of tissue homogenate. Superoxide dismutase (units/mg of protein) of 1 enzymatic unit is equivalent to the protein form in 100 μL of 10% tissue homogenate needed to prevent reduction of 24 mM NBT by 50% [29].
2.8.2. Catalase Activity
Phosphate buffer (pH 7, 1.9 mL) was added to 100 µL kidney tissue homogenate, and absorbance was measured spectrophotometrically at 240 nm. One milliliter of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) was mixed with the above solution and allowed to rest for a minute at room temperature. Absorbance was measured against phosphate buffer (blank solution) at 240 nm. The authors used 1 IU (International Unit). catalase to initiate the degrading of 1mM H2O2 per minute at 37 °C and expressed as units/mg of protein [30].
2.8.3. Estimation of Lipid Peroxidation
Kidney tissue homogenate (0.5 mL) was added to a solution of 1 mL of 0.6% thiobarbituric acid (C4H4N2O2S) and 3 mL phosphoric acid (H3PO4). The mixture was boiled for 45 min using a water bath. After cooling the mixture, 4 mL n-butanol was added. The resultant mixture was centrifuged for 20 min at 20,000 rpm. The organic layer was decanted into a new test tube, and absorbance was measured at 532 nm [31].
2.9. Statistical Evaluation
All the data were expressed as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM). The data were first tested for normality and homogeneity and analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test for the within-group analysis, given the 5% significance level. A p value less than 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
3. Results
We started our experiments with a preliminary study analyzing the effect of oral administration of fenofibrate and low-dose pioglitazone to normal control, and we noted no significant effect on the lipid profile and glucose levels (results not shown). Thereafter, we proceeded to conduct our experiments as mentioned in Section 2, and the results of the same are discussed herewith. Various physiological parameters analyzed in experiments were compared with normal and diabetic control groups (Groups I and II). The results are documented systematically as follows.
3.1. Therapeutic Interventions on Blood Glucose
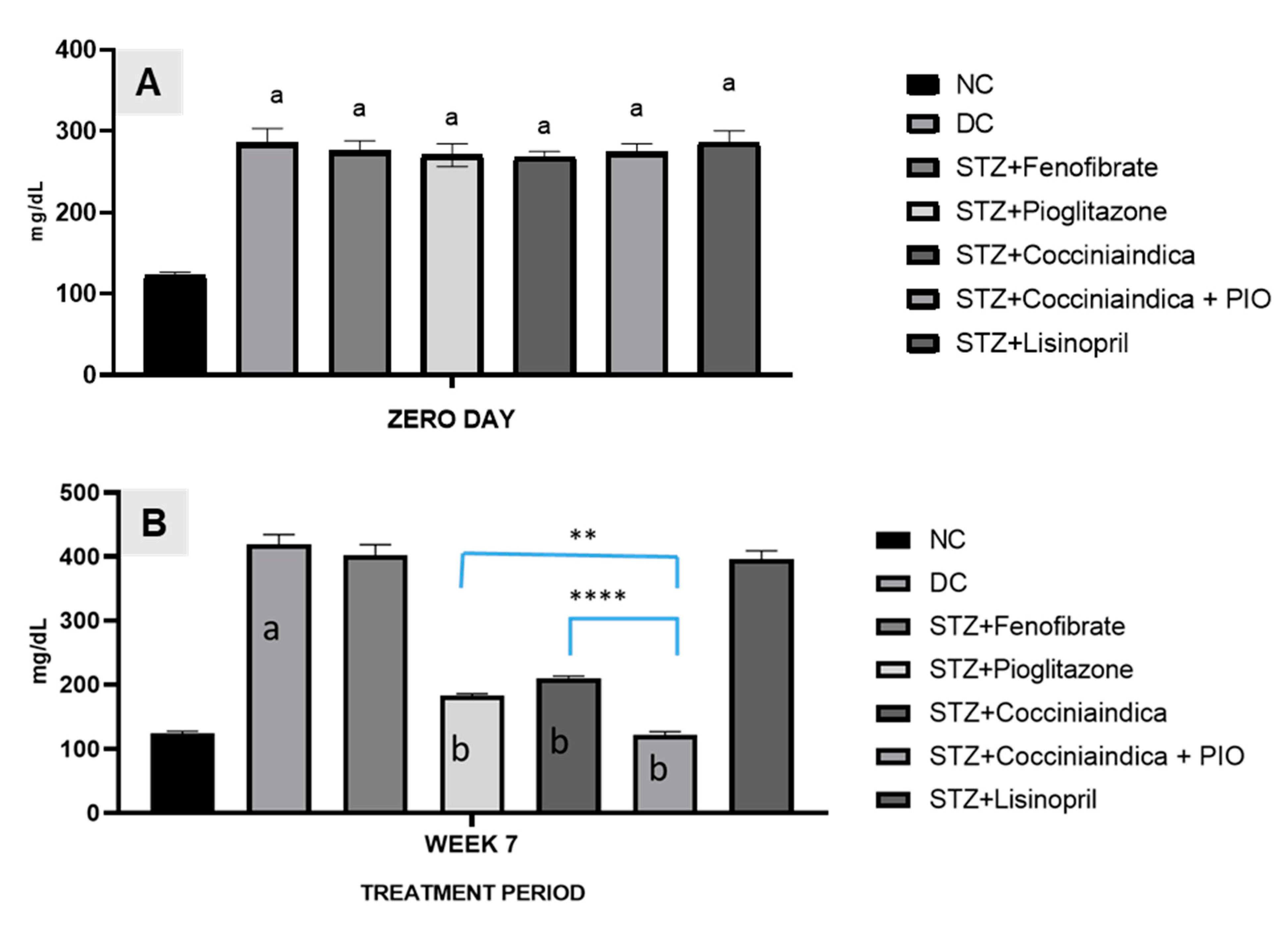
The treatment was given to diabetes-induced rats viz. Group III to Group VII, with fenofibrate, pioglitazone, Coccinia indica leaf extract, combination therapy with pioglitazone, and Coccinia indica leaf extract and lisinopril, respectively, for 7 weeks. Blood glucose levels were measured at the start of therapy and after 7 weeks. At the start of the therapy, blood glucose levels in diabetic rats (Groups II–VII) were elevated in comparison to normal control rats (Group I). After 7 weeks of treatment, fenofibrate-treated rats (Group III) showed no significant decrease, but pioglitazone-treated diabetic rats (Group IV) showed a significant reduction in blood glucose level. The treatment of Coccinia indica leaf extract (Group V) and extract co-administered with small dose of pioglitazone (Group VI) showed a decrease in blood glucose levels in comparison to groups treated with pioglitazone (Group IV); however, results were significant in Group VI. Diabetic rats treated with lisinopril alone (Group VII) did not have a significant decrease in blood glucose levels (Figure 1).
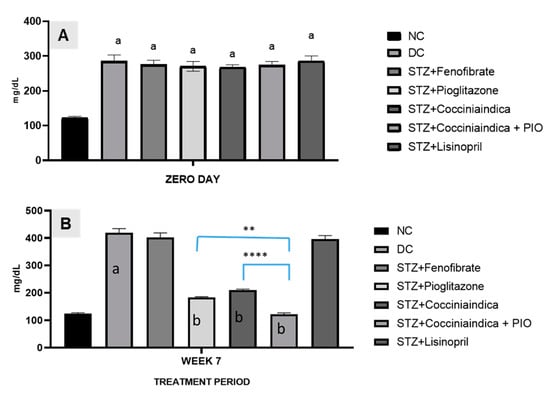
Figure 1.
(A) Blood glucose levels in different groups of rats (normal, diabetic, and different treatment groups) measured at the start of therapy (Day 0). All values are represented as mean ± SEM, n = 10/group, a p < 0.0001 when compared with normal control. (B) Blood glucose levels in different groups of rats (normal, diabetic, and different treatment groups) measured after 7 weeks of treatment. All values are represented as mean ± SEM, n = 10/group, a p < 0.001 when compared with normal control and b p < 0.0001 when compared with diabetic control. ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.001.
3.2. Pre- and Post-Prandial Glucose Measurement/OGTT
3.2.1. OGTT—Before Treatment
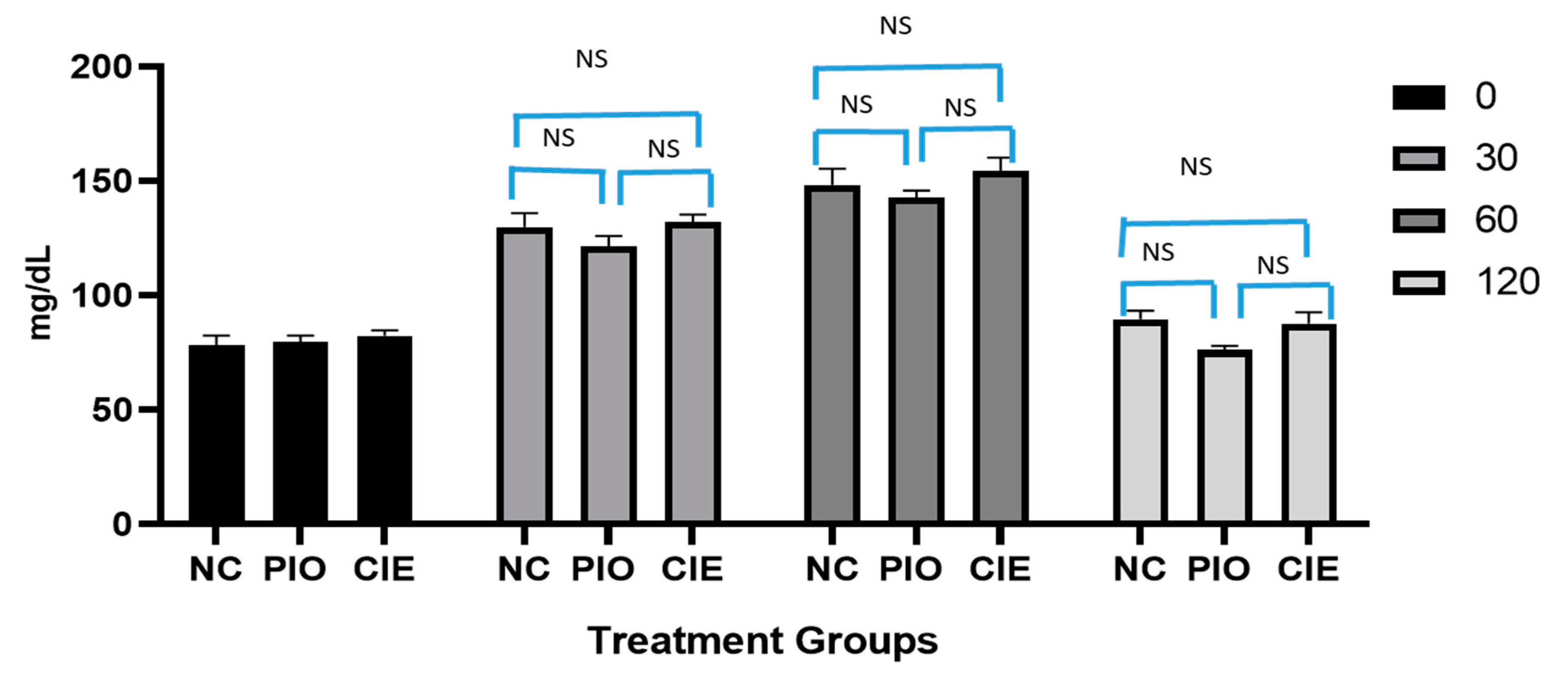
The clinical impact of Coccinia indica leaf extract and pioglitazone on oral glucose tolerance test is shown in Figure 2. It is observed that, glucose level reached to peak level, 1 h post administration and subsequently returned to normal fasting sugar level 2 h later. Similar responses were observed in pioglitazone (7 mg/kg) as well as in Coccinia indica leaf extract treated groups. The effect of increase in blood glucose level after 30 and 60 min post glucose administration, as well as lowering to a normal level after 2 h of administration, were statistically non-significant when compared with normal rats (p > 0.05) as well as within the groups. This indicates that Coccinia indica extract as well as pioglitazone do not cause hypoglycemia in normal rats.
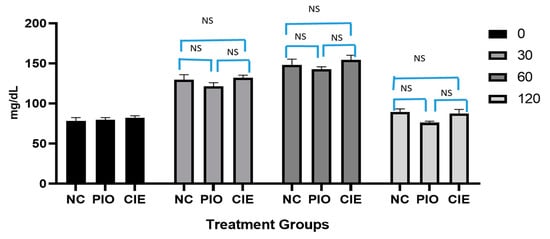
Figure 2.
Effect of Coccinia indica leaf extract (CIE) and pioglitazone (PIO) on OGTT in normal rats (before treatment) at 4 different time points, 0, 30, 60, and 120 min. All values are represented as mean ± SEM (n = 10). NC = normal control group, PIO = pioglitazone treated, CIE = Coccinia indica leaf extract treated, NS = not significant when all groups were compared with normal control group (NC) as well as between groups.
3.2.2. OGTT—After Treatment
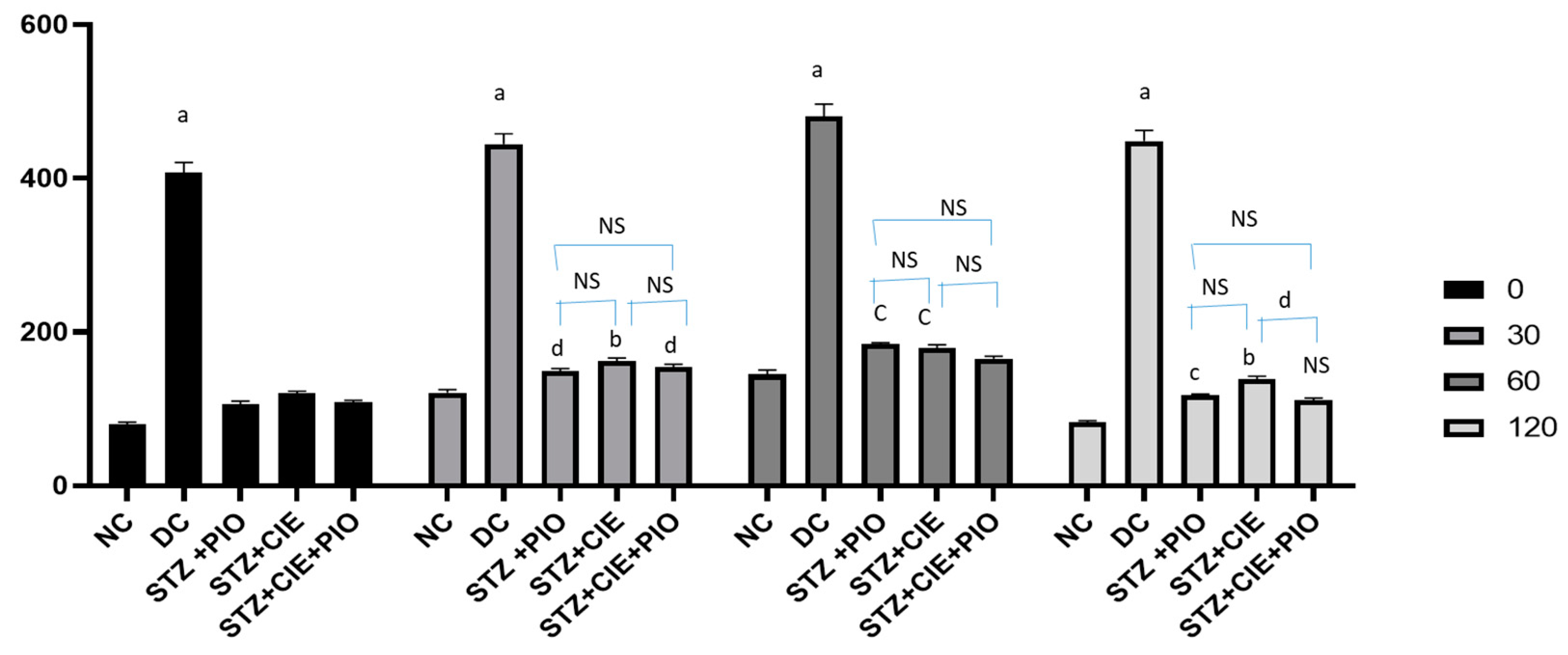
After 7 weeks of treatment with various predesignated therapies in diabetes-induced rats, OGTT was carried out. The fasting blood glucose values (mg/dL) for the rats belonging to the Groups I (normal control) and II (Diabetes control) was 79.83 ± 3.25, 407.83 ± 13.15, respectively. Diabetic rats treated with pioglitazone (Group IV), Coccinia indica leaf extract (Group V) and the combined therapy of pioglitazone plus Coccinia indica leaf extract (Group VI) showed blood glucose levels, 106.17 ± 4.20, 120.00 ± 3.01, and 108.33 ± 3.91, respectively. In Figure 3, Group I rat data showed their peak blood glucose (1 h post glucose) and returned to almost baseline 2 h from glucose loading. The untreated diabetic rats had a 10% increase in blood glucose level at the end of 2 h. The treated diabetic rats showed considerably lower peak of levels of blood glucose, 2 h after glucose load, indicating more pronounced antihyperglycemic activity. The combined therapy of pioglitazone and Coccinia indica showed a better antihyperglycemic effect than when treated alone (Figure 3).
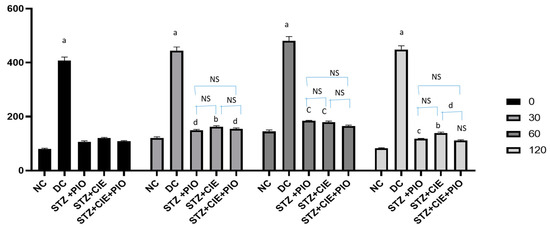
Figure 3.
Effect of Coccinia indica leaf extract alone and in combination with pioglitazone on OGTT in diabetes-induced treated rats, after 7 weeks of therapy. All values are represented as mean ± SEM, n = 10, a p < 0.0001, b p < 0.001, c p < 0.01 d p < 0.05 when compared with normal control. NS = not significant, STZ = streptozotocin, PIO = pioglitazone, CIE = Coccinia indica extract, NC = normal control (Group I), DC = diabetic control (Group II), STZ + PIO = Group IV, STZ + CIE = Group V, and STZ + PIO + CIE = Group VI.
3.3. Therapeutic Interventions Onserum Total Cholesterol and Trigylcerides
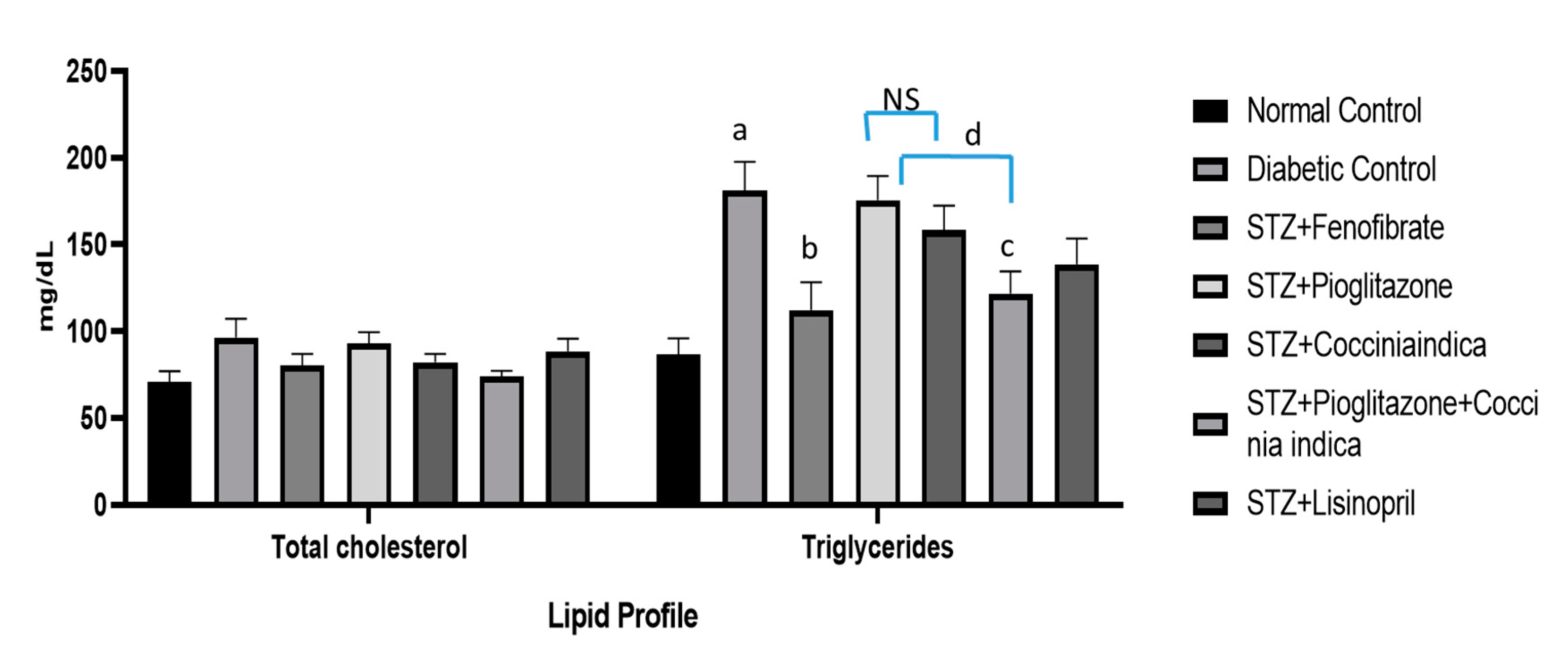
Significant increase in total triglycerides was observed in Group II (diabetic control) compared to the normal control (Group I). Fenofibrate treatment (Group III) halted diabetes-induced fluctuations in lipid profiles, but a low dose of pioglitazone (Group IV) had no significant effect on the cholesterol level (Figure 4). Diabetic rats when treated with Coccinia indica (200 mg/kg p.o.) (Group V) showed a substantial reduction in lipid concentration in comparison to untreated diabetes rats (Group II). Pioglitazone when combined with Coccinia indica leaf extract (Group VI) produced a significant reduction in lipid levels in comparison to its treatment alone (Group V). The lisinopril-treated group exhibited only a little decrease in the triglyceride levels (Figure 4).
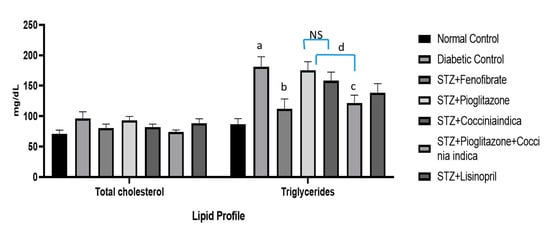
Figure 4.
Total cholesterol and triglyceride levels measured as an indicator of lipid profile. All values are represented as mean ± SEM, n = 10, a p < 0.0001 when compared with normal control group. b p < 0.001, c p < 0.01 when compared to diabetic control. d p < 0.05. NS = not significant.
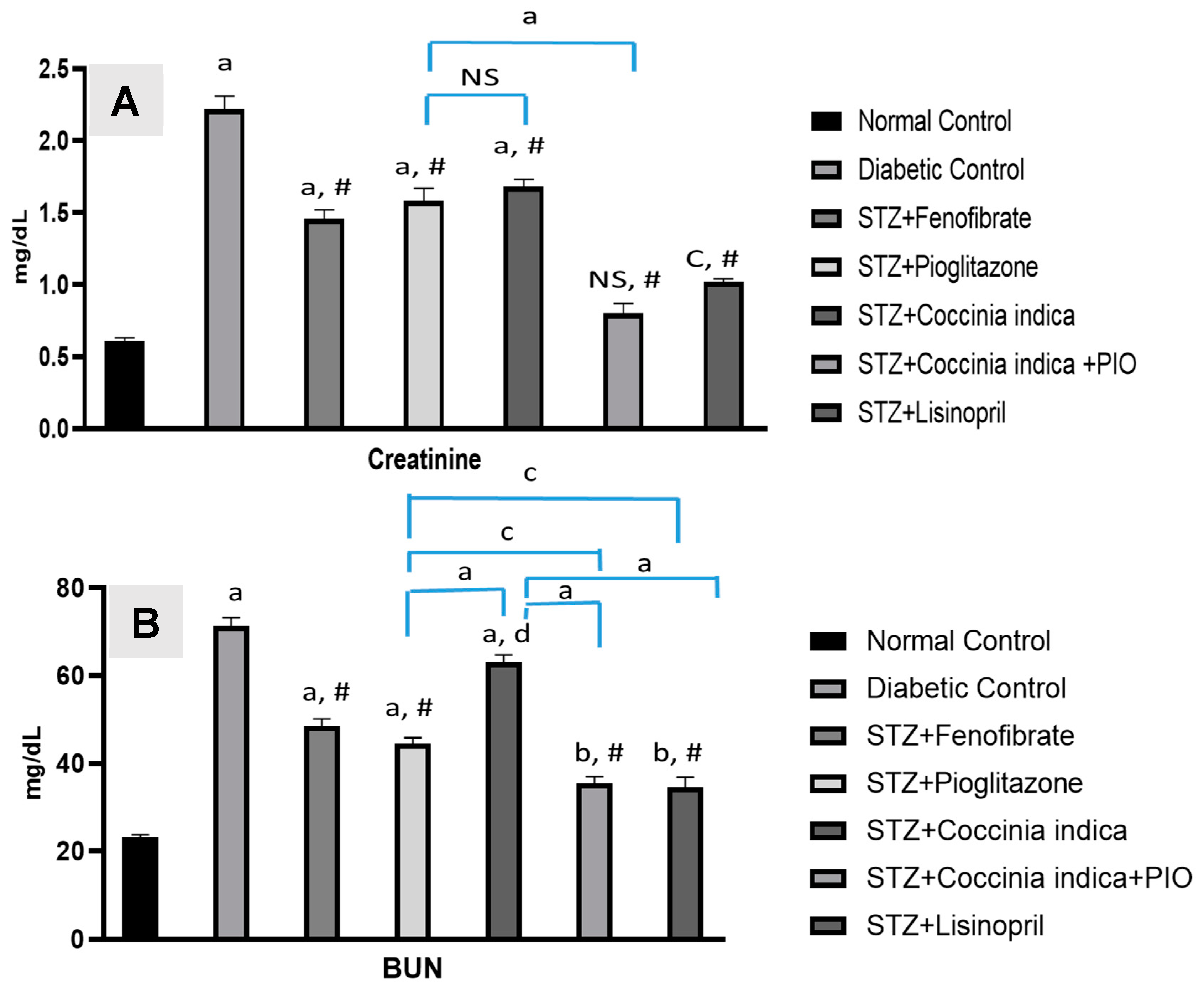
3.4. Therapeutic Interventions on Creatinine and Urea Nitrogen Level in the Blood
Serum BUN and creatinine markedly increased in Group II compared to the control. Diabetic rats treated with fenfibrate (30 mg/kg, 7 weeks) (Group III) and pioglitazone (7 mg/kg, 7 weeks) (Group IV) Coccinia indica (200 mg/kg, 7 weeks) (Group V) mildly prevented further increase in BUN as well as creatinine. The concentration of BUN and creatinine reduced significantly with a combination therapy of Coccinia indica and pioglitazone (Group VI) when compared to groups treated with either the extract or drug alone (Figure 5A,B).
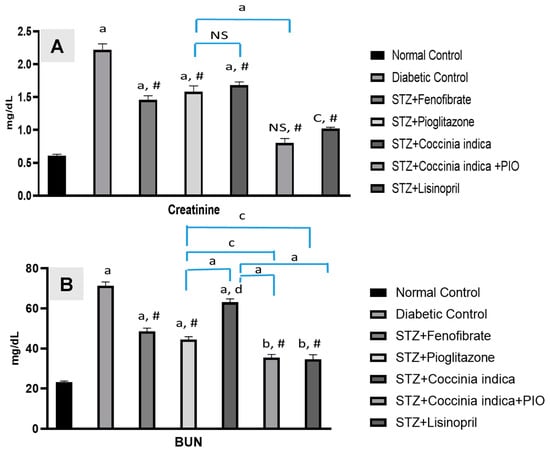
Figure 5.
(A) Serum creatinine and (B) blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels in all the treated and untreated groups. All values are represented as mean ± SEM, n = 10, a p < 0.0001, b p < 0.001, c p < 0.01 when compared with control group. # p < 0.0001, d p < 0.05 when compared with diabetic control. NS = not significant.
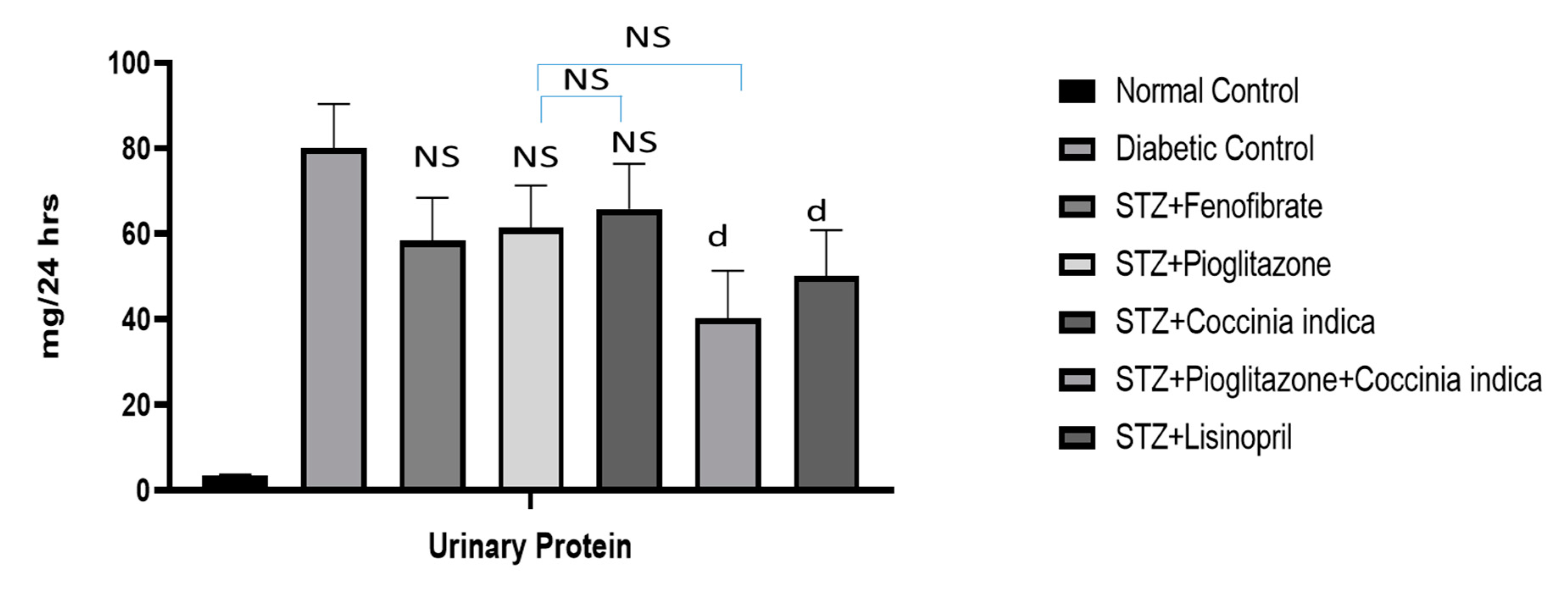
3.5. Therapeutic Interventions on Proteinuria
Diabetic rats had shown significant increase in proteinuria when compared to control group. Fenofibrate (30 mg/kg) (Group III), pioglitazone (7 mg/kg) (Group IV), and Coccinia indica (200 mg/kg p.o.) (Group V) moderately inhibited proteinuria in diabetic rats. Combined therapy of Coccinia indica (200 mg/kg) with pioglitazone (7 mg/kg) significantly slowed down the occurrence of proteinuria in comparison to rats treated with only extract vs. lisinopril (1 mg/kg, p.o.) (Figure 6).
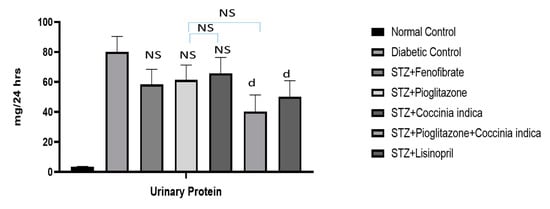
Figure 6.
Protein in urine measured in all the groups. All values are represented as mean ± SEM, n = 10. All values are represented as mean ± SEM, n = 10. d p < 0.05 when compared with diabetic control group. NS = not significant.
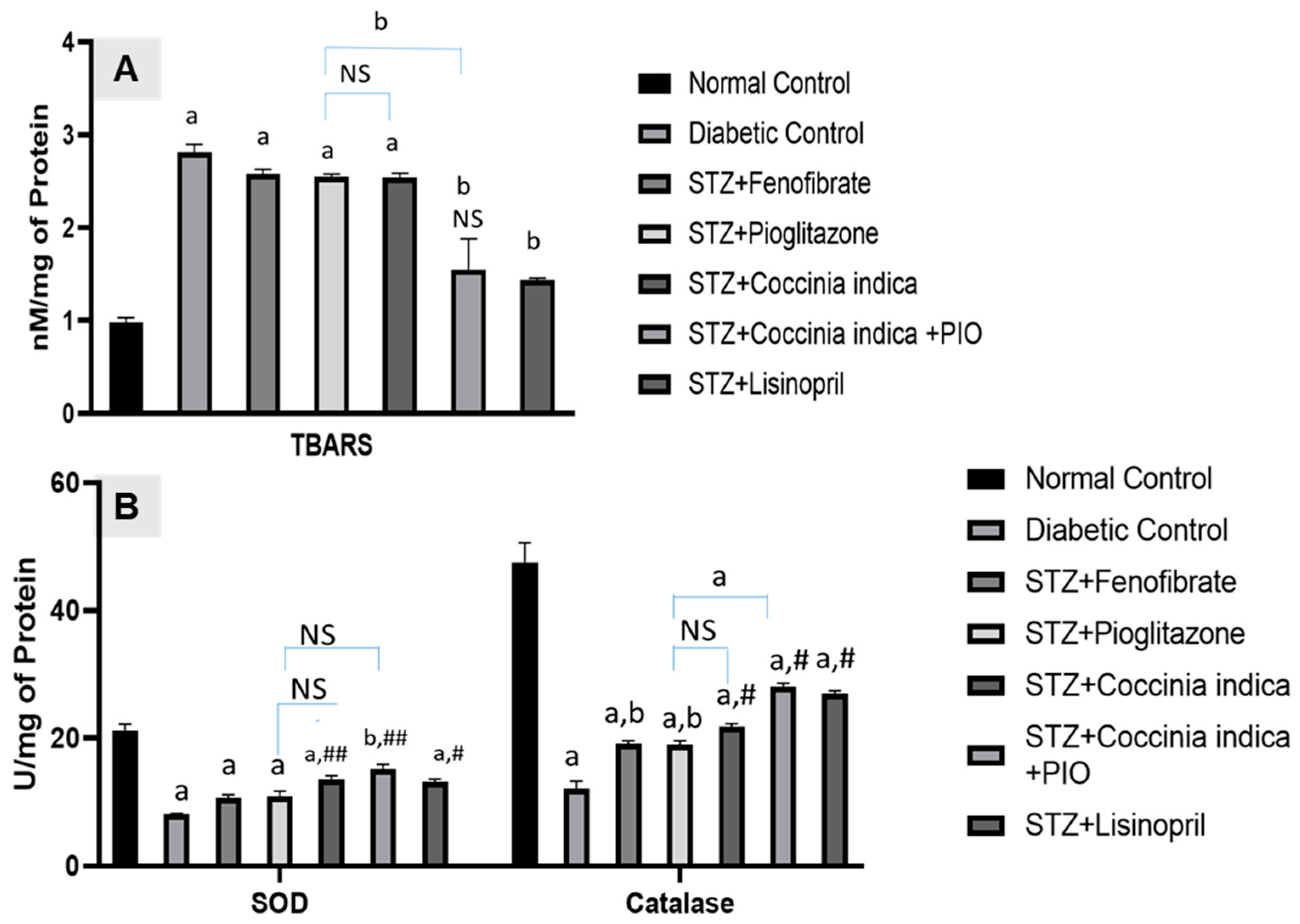
3.6. Therapeutic Interventions on Renal Oxidative Stress
Untreated diabetic rats showed increased levels of thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARS) as a byproduct of lipid peroxidation. The rats with high blood glucose concentration exhibited a reduction in levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase in serum when compared with Group I. While fenofibrate (30 mg/kg) (Group III), pioglitazone (7 mg/kg) (Group IV), and Coccinia indica leaf extract treatment alone (200 mg/kg) (Group V) mildly reduced the levels of diabetes-induced renal TBARS as well as elevated the renal SOD and catalase levels. Combination therapy of Coccinia indica leaf extract with pioglitazone (Group VI) has shown a marked therapeutic effect when compared with the treatments either involving the extract/drug alone or lisinopril (Figure 7A,B).
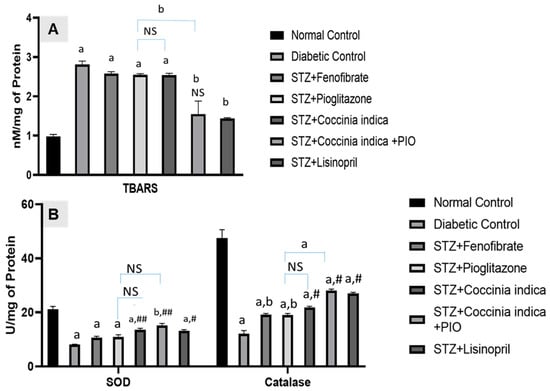
Figure 7.
(A) Thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARS) and (B) superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase activities in all the treated and untreated controls. All values are represented as mean ± SEM, n = 10, (A) a p < 0.0001, b p <0.001 when all groups were compared with control group. ## p < 0.01, # p < 0.05 when compared with diabetic control group. NS = not significant (B) a p <0.0001 when all groups were compared with control group. # p < 0.0001, b p <0.001 when compared with diabetic control group. NS = not significant.
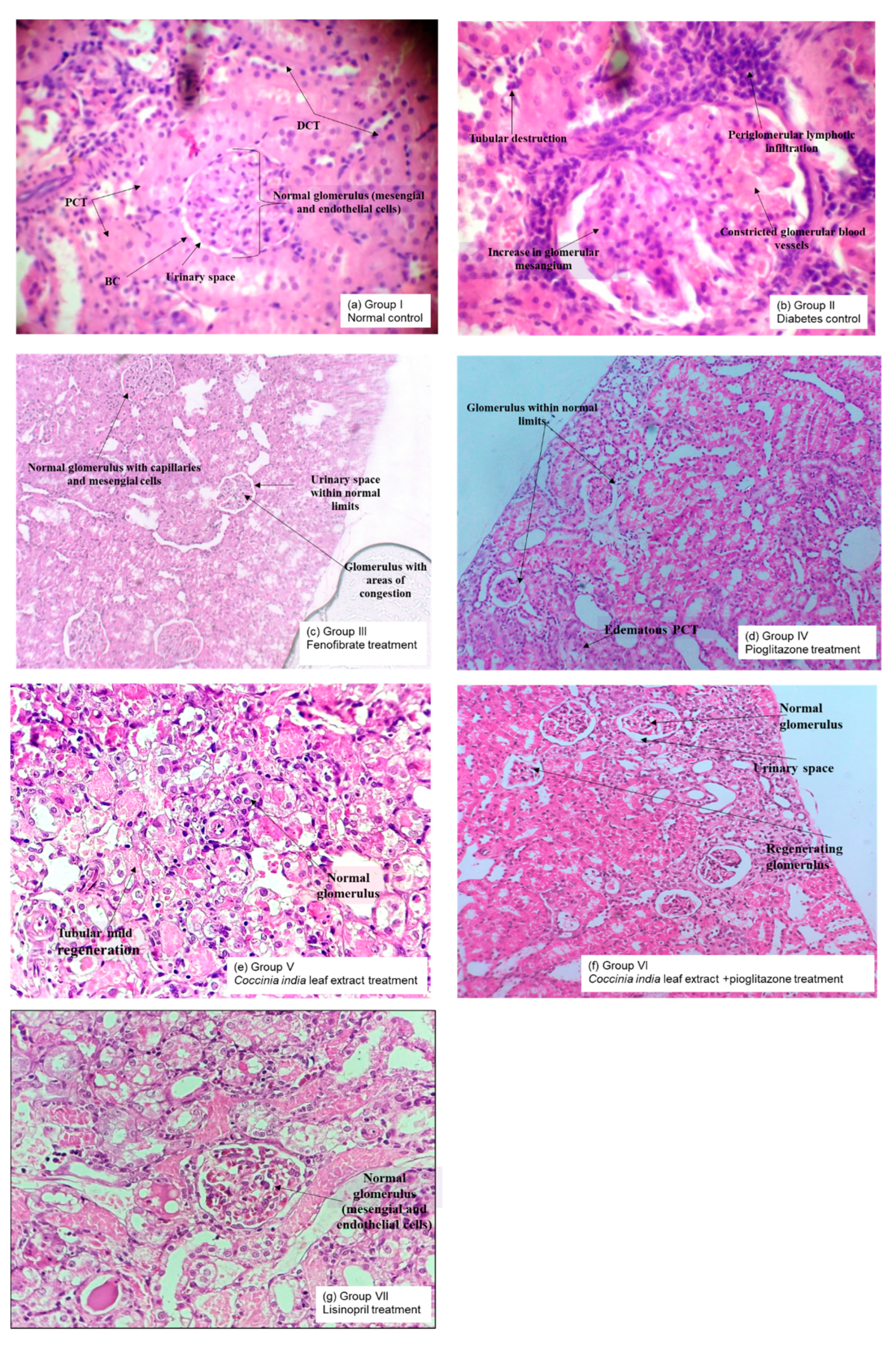
3.7. Histopathological Analysis
The pathological changes observed in the kidneys of diabetic rats (Group II) were a reduction in glomerular capillary size and an increase in glomerular mesangium compared to normal rats (Group I). Treatment with fenofibrate, pioglitazone, Coccinia indica leaf extract, combination therapy, and lisinopril for a period of 7 weeks prevented the diabetes-induced changes in glomeruli. Treatment with combination of Coccinia indica leaf extract and low-dose pioglitazone (Group VI) markedly protected the kidney from pathological structural abnormalities compared to solo treatment (Group V), it was also superior to the diabetes rats treated with lisinopril alone (Group VII). Lisinopril is frequently prescribed in diabetic nephropathy to get adequate control in proteinuria (Figure 8).
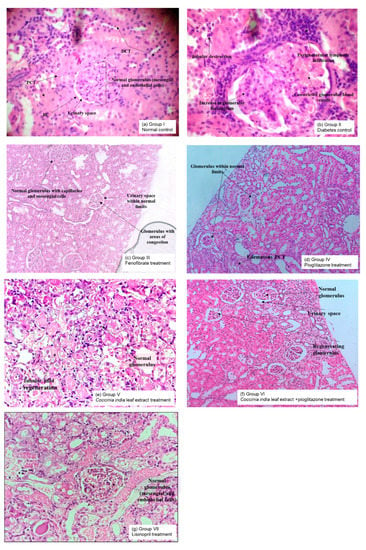
Figure 8.
Representative light microscopy (10×) photographs of hematoxylin and eosin-stained 5 μm thick renal histopathological sections of all the groups namely (a) Group I—Normal control, (b) Group II—Diabetes control, (c) Group III—Fenofibrate treated, (d) Group IV—Pioglitazone treated, (e) Group V—Coccinia indica leaf extract treated, (f) Group VI—Coccinia indica leaf extract + pioglitazone combination therapy and (g) Group VII—Lisonopril treated for observing the alterations of glomeruli. PCT = proximal convoluted tubules, DCT = distal convoluted tubules, BC = Bowman’s capsule.
4. Discussion
Diabetic nephropathy is the main complication of diabetes resulting in end-stage renal disease. Increased oxidative stress and activation of glucose-dependent pathways in kidneys cause proteinuria, glomerulosclerosis, and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. We systematically explored the renoprotective effect of Coccinia indica leaf extract through a series of experiments. We observed that the combination therapy of Coccinia indica leaf extract with pioglitazone (low dose) was not only antidiabetic (Figure 1B) but also lowered the triglycerides levels (Figure 4). The combination treatment showed normalization of elevated blood glucose level in diabetic rats without any hypoglycemic effect (Figure 3) and also reduced the oxidative stress (Figure 7). The combined therapy of Coccinia indica leaf extract with a low dose of pioglitazone showed renoprotective effect in diabetes-induced nephropathy in rats as observed from reduction in serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (Figure 5) as well as urinary protein secretion (Figure 6). The metabolism of creatine phosphate in the skeletal muscles produces creatinine, a waste product filtered by kidneys, and serum creatinine levels are dependent on glomerular filtration rate. An increase in serum creatinine is indicative of renal dysfunction and is directly correlated with the extent of damage and failure of renal function. BUN measures the waste product of protein metabolism. A substantial increase in the concentration of BUN is indicative of kidney dysfunction [32]. Worsening proteinuria (micro or macro) represent progressive glomerulosclerosis and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. When caused by diabetes, proteinuria leads to tubular cell inflammation, perpetuating the progression of interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy [33].
The presence of small quantities of albumin in urine (microalbuminuria) predicts development of clinical diabetic nephropathy [34]. The abnormalities in blood, urine, and the development of glomerular destruction coincides with prior experimental studies related to diabetic nephropathy. In our study, the untreated diabetic rats for 7 weeks presented abnormalities in serum creatinine, BUN, and proteinuria, thus suggesting the presence of diabetic nephropathy. The therapeutic intervention with either Coccinia indica leaf extract or pioglitazone mildly reduced diabetic nephropathy by lowering the abnormal serum measurements. It is important to document that the simultaneous administration of Coccinia indica leaf extract with a low dose of pioglitazone showed a synergistic effect in delaying the advancement of diabetic nephropathy when compared to treatments with either separately.
Studies indicate hyperlipidemia being an independent hazard in triggering and the advancement of diabetic nephropathy [35]. A high level of low-density lipoproteins increases production of reactive oxygen species and induces angiotensin-II-mediated mesangial cell proliferation [36]. Therefore, increased circulating lipids influence the beginning and progression of nephropathy in diabetes [6]. Our study concurs with this established paradigm and shows an increased triglyceride concentration and serum cholesterol in untreated diabetic rats. Increased lipoprotein concentration could have caused a remarkable change in the size of the glomerulus blood vessel and a consequent increase in mesangial cells that was supported by our histopathological study. PPAR α deficiency is observed during increased levels of circulating lipids and fenofibrate; a PPAR α agonist has been proven to be effective in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy [13]. Diabetic rats when treated with Coccinia indica were shown to reverse the lipid abnormalities, and this reversing capability was enhanced by combining pioglitazone with Coccinia indica leaf extract. The present study demonstrated the synergistic effect of the combination therapy of Coccinia indica with pioglitazone in reversing the lipid abnormality. This synergy in the combination treatment might be due to the anti-oxidant activity of pioglitazone enhancing the insulin sensitivity [37], which in turn, could affect the insulin-responsive genes that regulate glucose and lipid metabolism. Thiazolidinediones have been shown to increase antilipolytic action of insulin by enhancing the insulin sensitivity [38]. The additive antioxidant activity of Coccinia indica leaf extract and pioglitazone would have increased the antilipolytic action of insulin by enhancing the insulin sensitivity. Thus, due to this additive effect, the combined therapy of Coccinia indica leaf extract and pioglitazone could have resulted in the observed hypolipidemic response. A low dose of pioglitazone allows us to establish the absence of hypoglycemia when pioglitazone therapy is advised for the long term along with the concurrent benefits of anti-oxidant activity and anti-lipolytic activity, which further lead to the enhanced renoprotection.
Compared to the newer generation of anti-diabetes drugs such as Sodium-Glucose transport proteins SGLT inhibitors like empagliflozin, pioglitazone has a significant and marked reduction in myocardial infarction and stroke [39] and is more cost-effective too. Additionally, pioglitazone improves beta-cell function, causes significant reduction in glycated hemoglobin, and also reduces nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [37], thus making it an ideal candidate towards prevention of metabolic syndrome. The adverse effects are effectively reduced with lower doses and are outweighed by the other potential multiple benefits.
The proposed combination therapy is promising for preventing and delaying the progression of diabetes nephropathy as well as the other complications of diabetes, especially when treated for prolonged periods and can prevent hypoglycemia usually caused by a conventional dosage of pioglitazone.
The initiation and advancement of diabetic nephropathy is due to uncontrolled hyperglycemia. Hyperglycemia causes a reduction in mRNA levels of PPAR γ in glomerulus [5]. Renal upregulation of angiotensin II is observed in uncontrolled diabetic condition [40]. Treatment with combination of Coccinia indica leaf extract and a low dose of pioglitazone had significant effects on lowering the serum glucose concentration as measured during a glucose tolerance test. Pioglitazone exhibits its antihyperglycemic action by acting through PPARγ [7]. Similarly, Coccinia indica leaf extract is well-documented for its antihyperglycemic activity [15,16,17,18]. Long-term therapy of pioglitazone causes hypoglycemia and cardiovascular toxicity and hence in the present study a low dose of pioglitazone was chosen and combined with Coccinia indica. The adverse effects of pioglitazone can be prevented by reducing the dose of pioglitazone, and combining it with herbal extracts could synergize its antidiabetic effect. Similarly, our study results have depicted the synergistic influence of Coccinia indica leaf extract with pioglitazone in lowering blood glucose levels. In spite of partial glucose-lowering capacity, these agents protect kidneys by decreasing albuminuria and thus help to restore the endothelial function in kidneys of diabetic patients [41]. The renoprotective effect of low-dose pioglitazone in our study might be attributed by decreasing albuminuria. The synergistic glucose-lowering effect produced by the combined therapy of low-dose pioglitazone and Coccinia indica could produce more beneficial effect in protecting the kidneys from hyperglycemic state as well as preventing hypoglycemia on long term use.
Oxidative stress in the kidney is known to increase as a result of increased uptake of glucose, which then leads to increased reactive oxygen species production [42]. Increased oxidative stress leads to increased production of extra cellular matrix components [43] causing an expansion of the mesangial matrix compromising the filtration process. Histopathological analyses revealed an increase in glomerular mesangium in untreated diabetic rats when compared to normal rats. Treatment with Coccinia indica leaf extract and pioglitazone prevented these pathological changes in the glomeruli. It is hypothesized that the antioxidant properties of Coccinia indica leaf extract contribute to its renoprotectiveness [17,18]. Increased plasma concentration of TBARS indicates the induction of oxidative stress, which would increase oxidative damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Decrease in lipid peroxidation products measured as TBARS was observed following treatment with pioglitazone [44]. Coccinia indica leaf extract has the ability to control lipid peroxidation [17,18]. Treatment with Coccinia indica leaf extract or pioglitazone mildly inhibits stress caused by reactive oxygen species in diabetes-induced renal damage by decreasing renal TBARS. Simultaneously these treatments also increased SOD–catalase concentrations. Therefore, it seems that Coccinia indica leaf extract, pioglitazone, and its combination have the ability to protect the kidney through its antioxidative properties. The overarching effect of pairing Coccinia indica leaf extract and pioglitazone with the goal of inhibiting the deleterious course of diabetic nephropathy corresponds to lowering circulating lipids, proper blood glucose control, and halting Reactive oxygen species (ROS). Lisinopril has been regularly utilized as a baseline medicine for comparison due to its diabetic renoprotective effect, which is well-documented in basic and clinical studies [14]. The renoprotective impact of Coccinia indica leaf extract with a small dose of pioglitazone observed in our study was superior to lisinopril treated rats, in attenuating diabetic nephropathy.
5. Conclusions
Combined treatment with Coccinia indica leaf extract and a low dose of pioglitazone stalled the progression of diabetic nephropathy possibly by controlling blood glucose levels, normalizing lipid levels, and reducing ROS stress. This treatment may also synergistically provide protection against diabetic renal damage with simultaneous prevention of hypoglycemia caused by pioglitazones when administered for a longer period.
Regular consumption of food containing these properties might decrease the possibility of development of diabetes and can delay the advancement of diabetes complication, especially in case of a pre-diabetic state. Further long-term studies are required to evaluate the efficacy of the combined therapy of Coccinia indica leaf extract with a low dose of pioglitazone for halting the progression of diabetic renal damage in early type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.M.B., P.K.N., H.T.S., M.K.A., and S.N.; data curation, A.A. and A.H.A.; formal analysis, G.M.B., P.K.N., A.A., A.H.A., M.K.A., and S.N.; funding acquisition, G.M.B., A.A., A.H.A., and S.N.; investigation, G.M.B., P.K.N., A.A., A.H.A., H.T.S., M.K.A., and S.N.; methodology, G.M.B., P.N., A.A., A.H.A., H.T.S., M.K.A., and S.N.; project administration, G.M.B., P.K.N., A.A., A.H.A., H.T.S., and S.N.; resources, P.K.N., A.H.A., H.T.S., and S.N.; software, H.T.S. and S.N.; validation, P.K.N., A.A., A.H.A., H.T.S., and M.K.A.; visualization, A.A. and H.T.S.; writing—original draft, G.M.B., P.K.N., A.A., A.H.A., H.T.S., M.K.A., and S.N.; writing—review and editing, G.M.B., P.K.N., M.K.A., and S.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deputyship for Research & Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia for funding this research work through the project number IFT20113.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Deanship of Scientific Research, King Faisal University, Al-Ahsa, Saudi Arabia for their support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Suganya, S.; Narmadha, R.; Gopalakrishnan, V.K.; Devaki, K. Hypoglycemic effect of Costus pictus D. Don on alloxan induced type 2 diabetes mellitus in albino rats. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2012, 2, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, M.K.; Reddy, K.; Balakumar, P. The low dose combination of fenofibrate and rosiglitazone halts the progression of diabetes-induced experimental nephropathy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 636, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohilla, A.; Tiwari, S.K.; Rohilla, S.; Kushnoor, A. Diabetic Nephropathy: Pathogenesis, Prevention and Treatment. Eur. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 1, 72–80. [Google Scholar]
- Giunti, S.; Barit, D.; Cooper Mark, E. Mechanisms of Diabetic Nephropathy. Hypertension 2006, 48, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.; Fornoni, A.; Elliot, S.J.; Guan, Y.; Breyer, M.D.; Striker, L.J.; Striker, G.E. Upregulation of type I collagen by TGF-β in mesangial cells is blocked by PPARγ activation. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2002, 282, F639–F648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrass, C.K. Cellular Lipid Metabolism and the Role of Lipids in Progressive Renal Disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2004, 24, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushige, K.; Tsuji, T.; Noma, T. Pioglitazone: Cardiovascular Effects in Prediabetic Patients. Cardiovasc. Drug Rev. 2002, 20, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael Kubisch, H.; Wang, J.; Bray, T.M.; Phillips, J.P. Targeted Overexpression of Cu/Zn Superoxide Dismutase Protects Pancreatic β-Cells against Oxidative Stress. Diabetes 1997, 46, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naziroğlu, M.; Çay, M. Protective role of intraperitoneally administered vitamin E and selenium on the antioxidative defense mechanisms in rats with diabetes induced by streptozotocin. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2001, 79, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, B. Pathophysiology of oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2001, 15, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.; Lee, H.B. Reactive oxygen species as glucose signaling molecules in mesangial cells cultured under high glucose. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, S19–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-de la Cruz, M.C.; Ruiz-Torres, P.; Alcamí, J.; Díez-Marqués, L.; Ortega-Velázquez, R.; Chen, S.; Rodríguez-Puyol, M.; Ziyadeh, F.N.; Rodríguez-Puyol, D. Hydrogen peroxide increases extracellular matrix mRNA through TGF-β in human mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.W.; Kim, H.W.; Ko, S.H.; Chung, H.W.; Lim, S.W.; Yang, C.W.; Chang, Y.S.; Sugawara, A.; Guan, Y.; Breyer, M.D. Accelerated Diabetic Nephropathy in Mice Lacking the Peroxisome Proliferator–Activated Receptor α. Diabetes 2006, 55, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amann, B.; Tinzmann, R.; Angelkort, B. ACE Inhibitors Improve Diabetic Nephropathy Through Suppression of Renal MCP-1. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, R.N.; Chopra, I.C.; Hand, K.L.; Kapur, L.D. Indigenous Drugs of India, 2nd ed.; UN Dhur and Sons: Calcutta, India, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, K.; Datta, T. Coccinia indica Linn. As potential hypoglycaemic agent. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 1972, 10, 347–349. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Venkateswaran, S.; Pari, L. Effect of Coccinia indica on Blood Glucose, Insulin and Key Hepatic Enzymes in Experimental Diabetes. Pharm. Biol. 2002, 40, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswaran, S.; Pari, L. Effect of Coccinia indica leaves on antioxidant status in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 84, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, M.; Bhuvaneshwari, R.; Dhandapani, R. Hypoglycaemic activity of Coccinia indica wight & arn fruits in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Indian J. Nat. Prod. Resour. 2011, 2, 350–353. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, K.; Viswanad, B.; Asrat, L.; Kaul, C.L.; Ramarao, P. Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose streptozotocin-treated rat: A model for type 2 diabetes and pharmacological screening. Pharmacol. Res. 2005, 52, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshio, K.; Hiraga, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Kitajo, A.; Iinuma, F. Determination of Glucose in Blood using Glucose Oxidase-Peroxidase System and 8-Hydroxyquinoline-p-Anisidine. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1979, 27, 568–570. [Google Scholar]
- Allain, C.C.; Poon, L.S.; Chan, C.S.G.; Richmond, W.; Fu, P.C. Enzymatic Determination of Total Serum Cholesterol. Clin. Chem. 1974, 20, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucolo, G.; David, H. Quantitative Determination of Serum Triglycerides by the Use of Enzymes. Clin. Chem. 1973, 19, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsnes, R.W.; Taussky, H.H. On the colorimetric determination of creatinine by the jaffe reaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1945, 158, 581–591. [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett, J.K.; Scott, J.E. A rapid and precise method for the determination of urea. J. Clin. Pathol. 1960, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šperlingová, I.; Dabrowská, L.; Tichý, M.; Kučera, J. Reference material “total protein in human urine”. Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem. 1998, 361, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunatha Goud, B.K.; Mallick, A.K.; Sarsina Devi, O.; Raghuveer, C.V.; Nayal, B.; Ahsan, M.; Devaki, R.N.; Avinash, S.S. Diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria: Factors affecting collection of urine samples for microalbuminuria. Int. J. Pharma Biol. Sci. 2011, 2, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.G.; Lu, X.H.; Li, W.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, C. Protective Effects of Luteolin on Diabetic Nephropathy in STZ-Induced Diabetic Rats. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, 323171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, Y. Generation of superoxide radical during autoxidation of hydroxylamine and an assay for superoxide dismutase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1978, 186, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.J.; Obrosova, I.; Cao, X.; Van Huysen, C.; Greene, D.A. Effects of DL-alpha-lipoic acid on peripheral nerve conduction, blood flow, energy metabolism, and oxidative stress in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devasagayam, T.P.A.; Boloor, K.K.; Ramasarma, T. Methods for estimating lipid peroxidation: An analysis of merits and demerits. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 40, 300–308. [Google Scholar]
- Latini, R.; Aleksova, A.; Masson, S. Novel biomarkers and therapies in cardiorenal syndrome. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2016, 27, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, G.; Ziyadeh, F.N. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Proteinuria in Diabetic Nephropathy. Nephron Physiol. 2007, 106, p26–p31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.; Umar, R.; Shehu, N.; Wali, U.; Nasir, A. Markers of Diabetic Nephropathy in Diabetic Patients in Gusau, Zamfara State, Nigeria. Niger. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2012, 20, 130–133. [Google Scholar]
- Ravid, M.; Neumann, L.; Lishner, M. Plasma lipids and the progression of nephropathy in diabetes mellitus type II: Effect of ACE inhibitors. Kidney Int. 1995, 47, 907–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Song, C.Y.; Kim, B.C.; Hong, H.K.; Lee, H.S. Angiotensin II mediates LDL-induced superoxide generation in mesangial cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2003, 285, F909–F915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, P.J.; Chiou, H.C.; Jiang, H.J.; Lee, M.Y.; Hsieh, T.J.; Kuo, K.K. Pioglitazone Enhances Cytosolic Lipolysis, β-oxidation and Autophagy to Ameliorate Hepatic Steatosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasunari, K.; Kohno, M.; Kano, H.; Yokokawa, K.; Minami, M.; Yoshikawa, J. Mechanisms of action of troglitazone in the prevention of high glucose-induced migration and proliferation of cultured coronary smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 1997, 81, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Inzucchi, S.; Abdul-Ghani, M.; Nissen, S.E. Pioglitazone: The forgotten, cost-effective cardioprotective drug for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2019, 16, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, K.D. Angiotensin II and its receptors in the diabetic kidney. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2000, 36, 449–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, S.; Pakzad, B.; Mortazavi, M.; Akbari, M.; Seirafian, S.; Atapour, A.; Al Saeidi, S.; Shayegannejad, A. Reduction of proteinuria by pioglitazone in patients with non-diabetic renal disease. J. Res. Med. Sci. Off. J. Isfahan Univ. Med. Sci. 2011, 16, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar]
- Forbes, J.M.; Coughlan, M.T.; Cooper, M.E. Oxidative stress as a major culprit in kidney disease in diabetes. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.M.; Wahab, N.A. Extracellular matrix metabolism in diabetic nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2003, 14, 1358–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Olefsky, J.M. Thiazolidinediones in the treatment of insulin resistance and type II diabetes. Diabetes 1996, 45, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).