The Use of Natural Minerals in a Pilot-Scale MBR for Membrane Fouling Mitigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
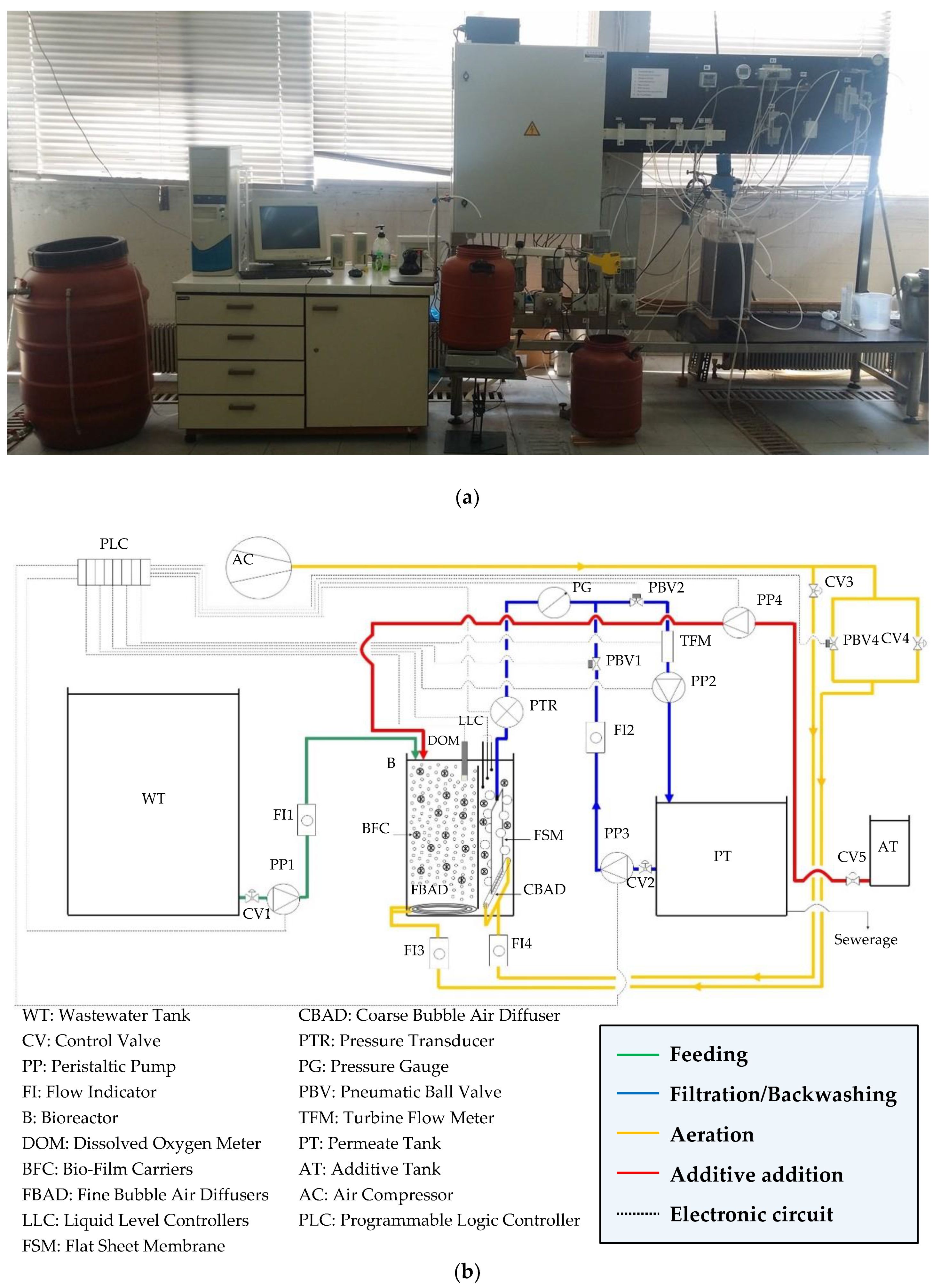
2.1. Pilot-Scale MBR Operation
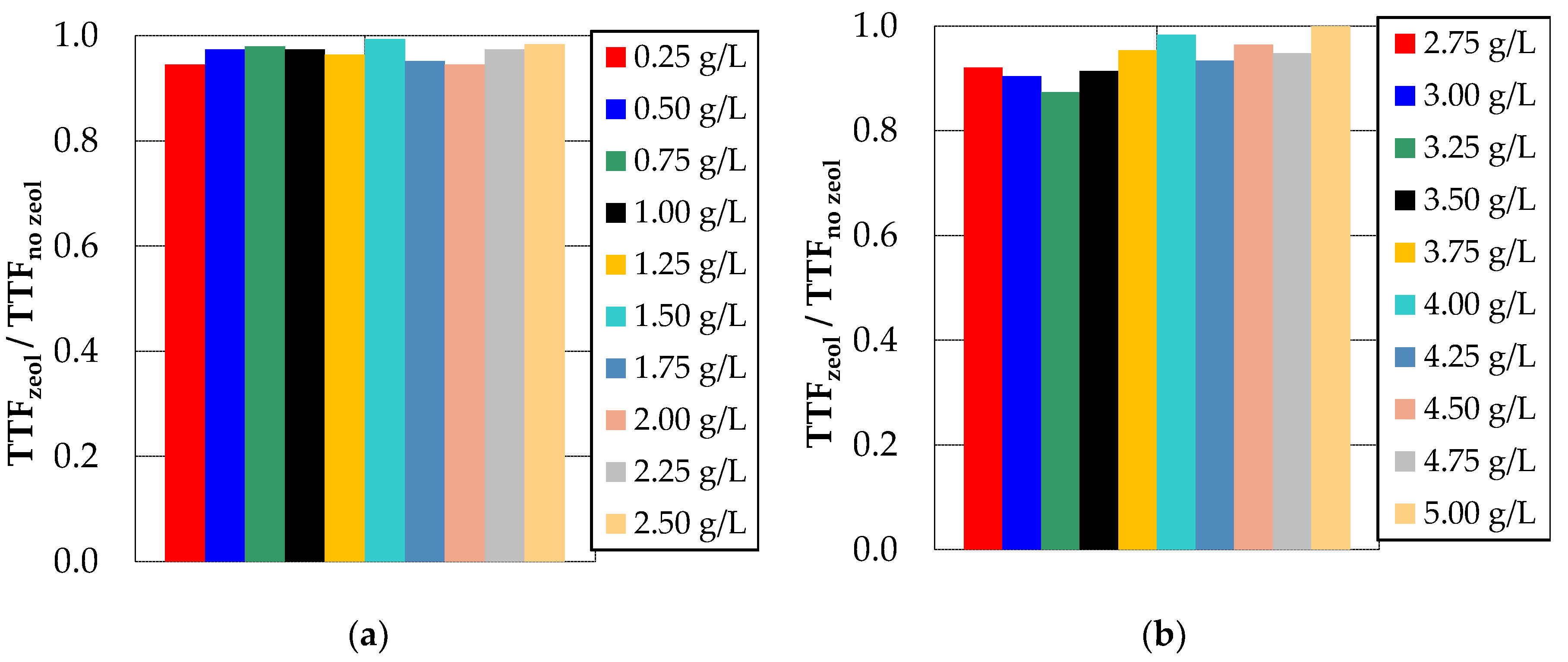
2.2. Filterability Tests by Applying the TTF (Time-To-Filter) Method
2.3. SMPc Concentration Measurements by Applying the Phenol-Sulfuric Acid Method
2.4. Determination of the Filament Index (FI) by Applying Optical Microscopy
3. Results and Discussion
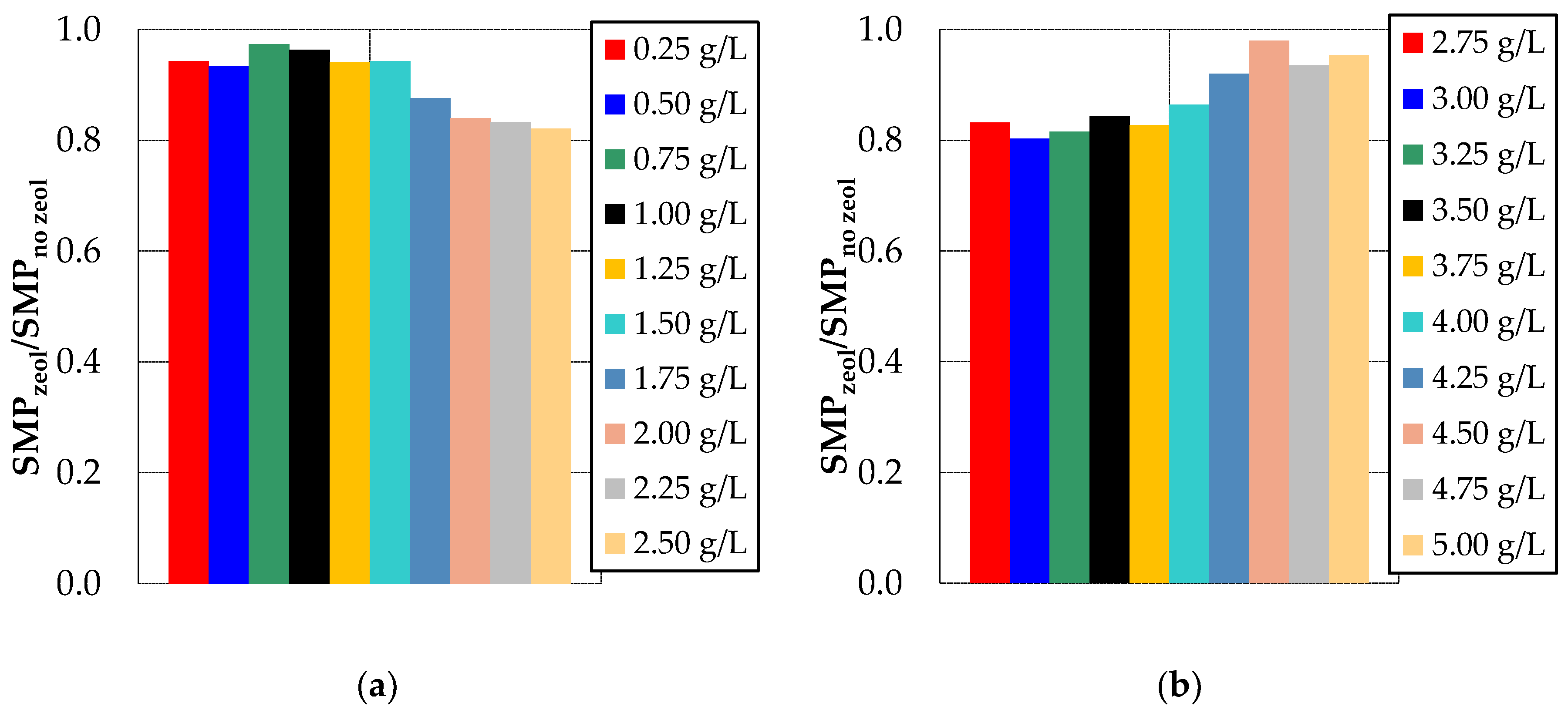
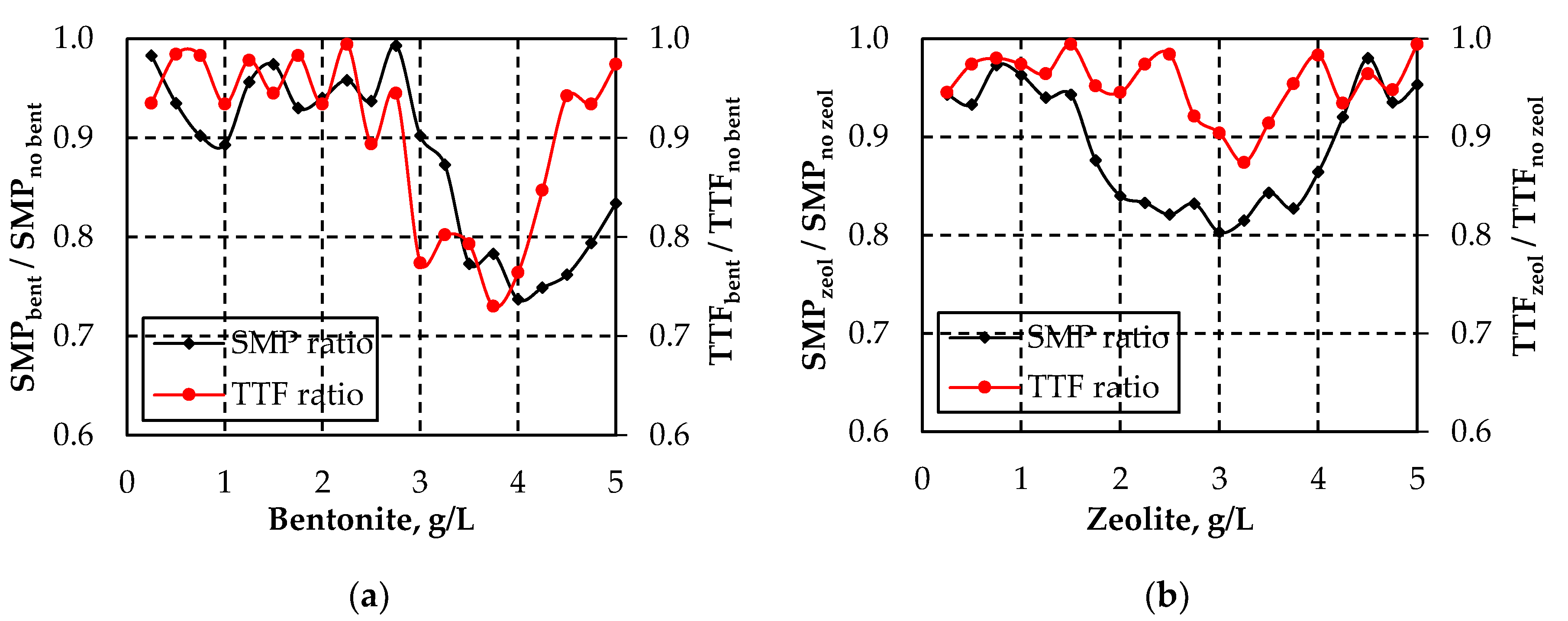
3.1. Effect of Bentonite and Zeolite on Membrane Fouling
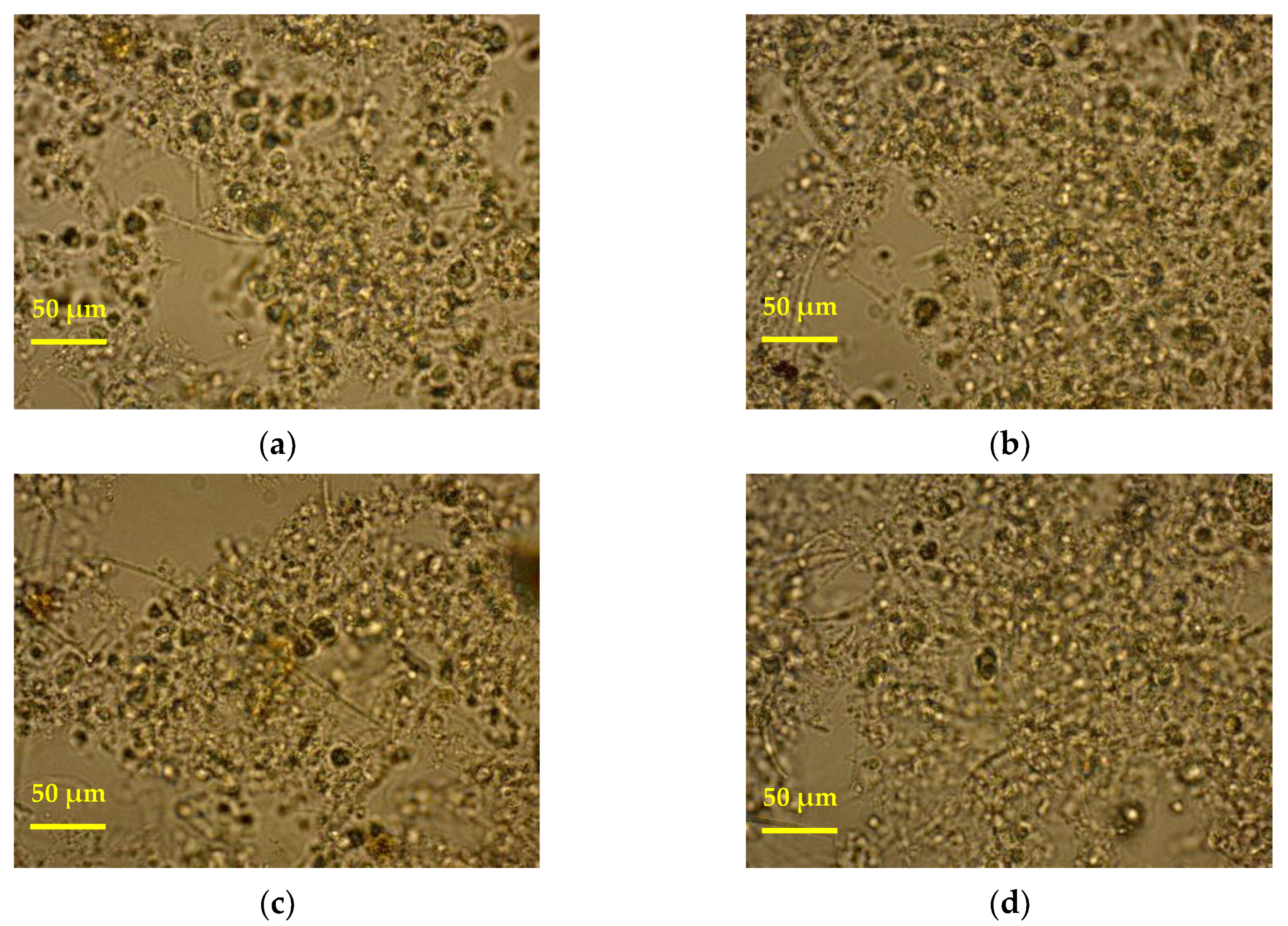
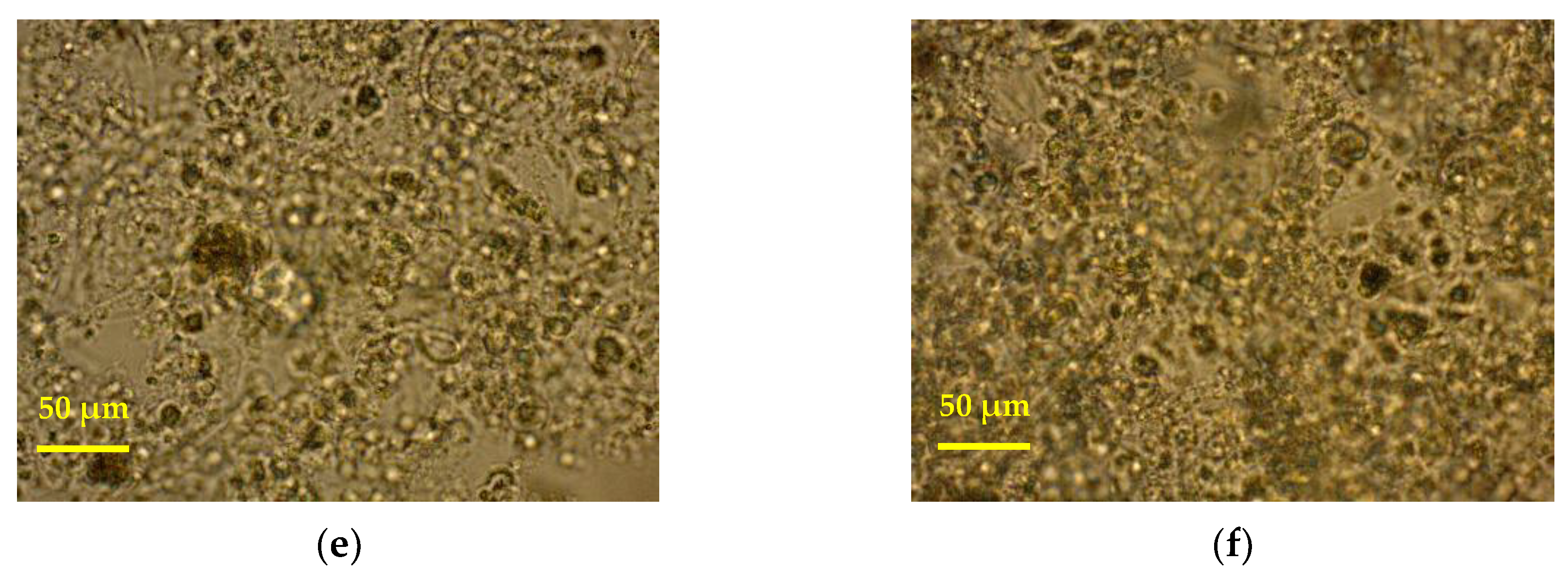
3.2. Optical Microscopy Images
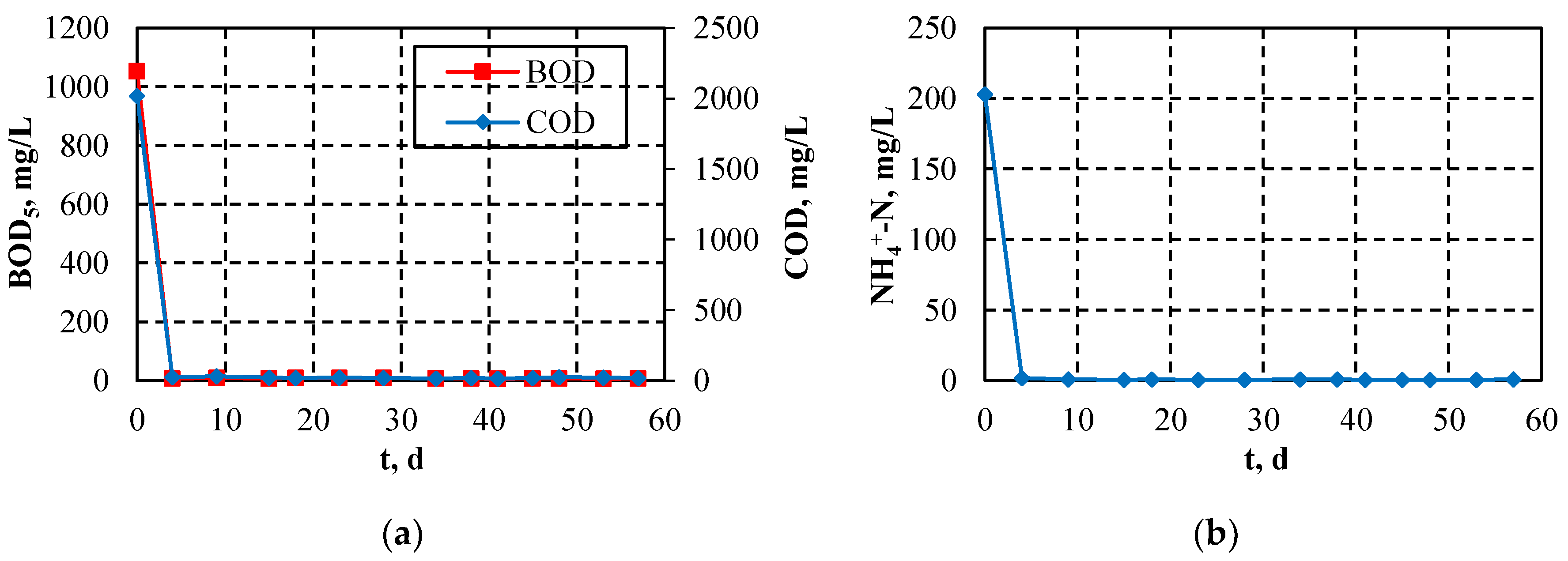
3.3. Pilot-Scale MBR Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| ASP | Activated sludge process |
| BOD5 | Biochemical oxygen demand |
| COD | Chemical oxygen demand |
| DO | Dissolved oxygen |
| EPS | Extracellular polymeric substances |
| F/M | Food to microorganisms |
| FI | Filament index |
| HRT | Hydraulic retention time |
| GAC | Granular activated carbon |
| MBR | Membrane bioreactor |
| MLSS | Mixed liquor suspended solids |
| MLVSS | Mixed liquor volatile suspended solids |
| OECD | Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development |
| PAC | Powdered activated carbon |
| POME | Palm oil mill effluent |
| SMP | Soluble microbial products |
| SMPc | Carbohydrate fraction of soluble microbial products |
| SRT | Sludge retention time |
| SS | Suspended solids |
| TMP | Trans-membrane pressure |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| TTF | Time to filter |
References
- Yoon, S.-H. Membrane Bioreactor Processes: Principles and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gkotsis, P.K.; Banti, D.C.; Peleka, E.N.; Zouboulis, A.I.; Samaras, P.E. Fouling Issues in Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs) for Wastewater Treatment: Major Mechanisms, Prevention and Control Strategies. Processes 2014, 2, 795–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, S. The MBR Book. Principles and Applications of Membrane Bioreactors for Water and Wastewater Treatment, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zouboulis, A.I.; Gkotsis, P.K.; Zamboulis, D.X.; Mitrakas, M.G. Application of powdered activated carbon (PAC) for membrane fouling control in a pilot-scale MBR system. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 2350–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.C.; Ngo, H.H.; Sun, Q.; Li, S.; Tang, J.; Yu, Z. Effects of powdered activated carbon addition on filtration performance and dynamic membrane layer properties in a hybrid DMBR process. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 327, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Cao, J.S.; Chen, L.N.; Chen, L.; Feng, Q.; Xu, H.L. Enhanced performance of dyeing wastewater reclamation by PAC addition in a membrane bioreactor. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2012, 10, 1138–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Wang, F.; Ding, L.; Hong, H.; Chen, J.; Lu, X. Enhanced performance of a submerged membrane bioreactor with powdered activated carbon addition for municipal secondary effluent treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 1509–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Zamani, F.; Lim, W.; Liao, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chew, J.W.; Fane, A.G. Effect of mechanical scouring by granular activated carbon (GAC) on membrane fouling mitigation. Desalination 2017, 403, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johir, M.A.; Shanmuganathan, S.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J. Performance of submerged membrane bioreactor (SMBR) with and without the addition of the different particle sizes of GAC as suspended medium. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 141, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skouteris, G.; Saroj, D.; Melidis, P.; Hai, F.I.; Ouki, S. The effect of activated carbon addition on membrane bioreactor processes for wastewater treatment and reclamation—A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 185, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johir, M.A.H.; Aryal, R.; Kandasamy, J.; Grasmick, A. Influence of supporting media in suspension on membrane fouling reduction in submerged membrane bioreactor (SMBR). J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 374, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damayanti, A.; Ujang, Z.; Salim, M.R. The influence of PAC, zeolite, and Moringa oleifera as biofouling reducer (BFR) on hybrid membrane bioreactor of palm oil mill effluent (POME). Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4341–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuniarto, A.; Noor, Z.Z.; Ujang, Z.; Olsson, G.; Aris, A.; Hadibarata, T. Bio-fouling reducers for improving the performance of an aerobic submerged membrane bioreactor treating palm oil mill effluent. Desalination 2013, 316, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Mernia, M.R. The influence of zeolite (clinoptilolite) on the performance of a hybrid membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 158, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamis, S.; Andreadakis, A.; Mamais, D.; Noutsopoulos, C. Comparison of alternative additives used for the mitigation of membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 5740–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Activated Sludge, Respiration Inhibition Test (Carbon and Ammonium Oxidation). In Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals (Technical Report 209); OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development): Paris, France, 2010; Guideline 16; p. 4.
- De la Torre, T.; Lesjean, B.; Drews, A.; Kraume, M. Monitoring of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) in a membrane bioreactor (MBR) and correlation with other fouling indicators. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberger, S.; Kraume, M. Filterability of activated sludge in membrane bioreactors. Desalination 2002, 151, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.; Hamilton, J.; Rebers, P.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikelboom, D.H. Process Control of Activated Sludge Plants by Microscopic Investigation, 1st ed.; IWA Publishing: Zutphen, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gkotsis, P.K.; Mitrakas, M.M.; Tolkou, A.K.; Zouboulis, A.I. Batch and continuous dosing of conventional and composite coagulation agents for fouling control in a pilot-scale MBR. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 311, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhou, H.; Cicek, N. Removal mechanisms of 17b-estradiol and 17a-ethinyl-estradiol in membrane bioreactors. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbeig, H.; Mehrnia, M.R.; Tashauoei, H.R.; Rezaei, M. Role of zeolite in reducing membrane fouling in a hybrid membrane bioreactor system applied for wastewater treatment. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 98, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banti, C.D.; Karayannakidis, P.D.; Samaras, P.; Mitrakas, M.G. An innovative bioreactor set-up that reduces membrane fouling by adjusting the filamentous bacterial population. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 542, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; APHA (American Public Health Association); AWWA (American Water Works Association); WEF (Water Environment Federation): Washington, DC, USA, 2005; p. 541.
- Kitanou, S.; Tahri, M.; Bachiri, B.; Mahi, M.; Hafsi, M.; Taky, M.; Elmidaoui, A. Comparative study of membrane bioreactor (MBR) and activated sludge processes in the treatment of Moroccan domestic wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malamis, S.; Andreadakis, A.; Mamais, D.; Noutsopoulos, C. Myths and realities concerning membrane bioreactors for municipal wastewater treatment: Can water reuse be the drive for the wider implementation of MBR technology? In Proceedings of the ‘Water Is Necessary For Life-WIN4Life’, Tinos Island, Greece, 19–21 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
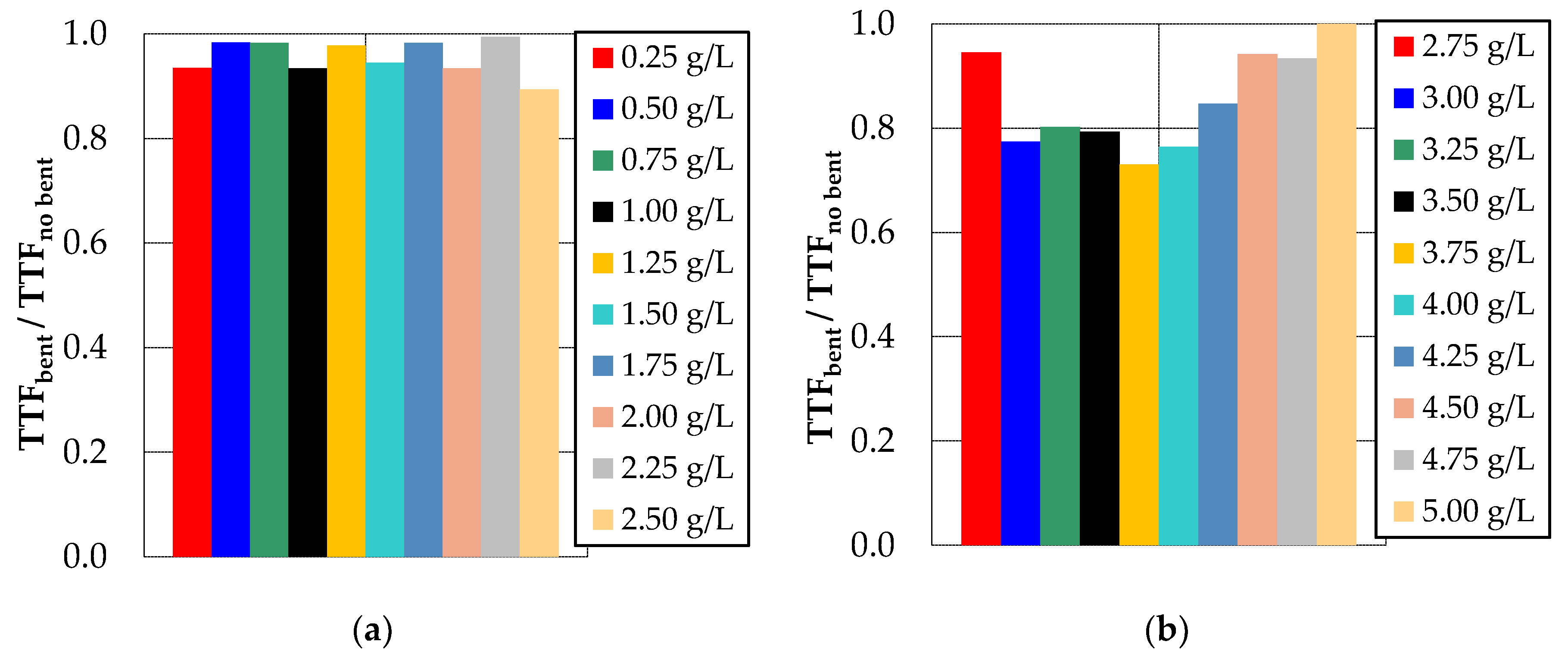
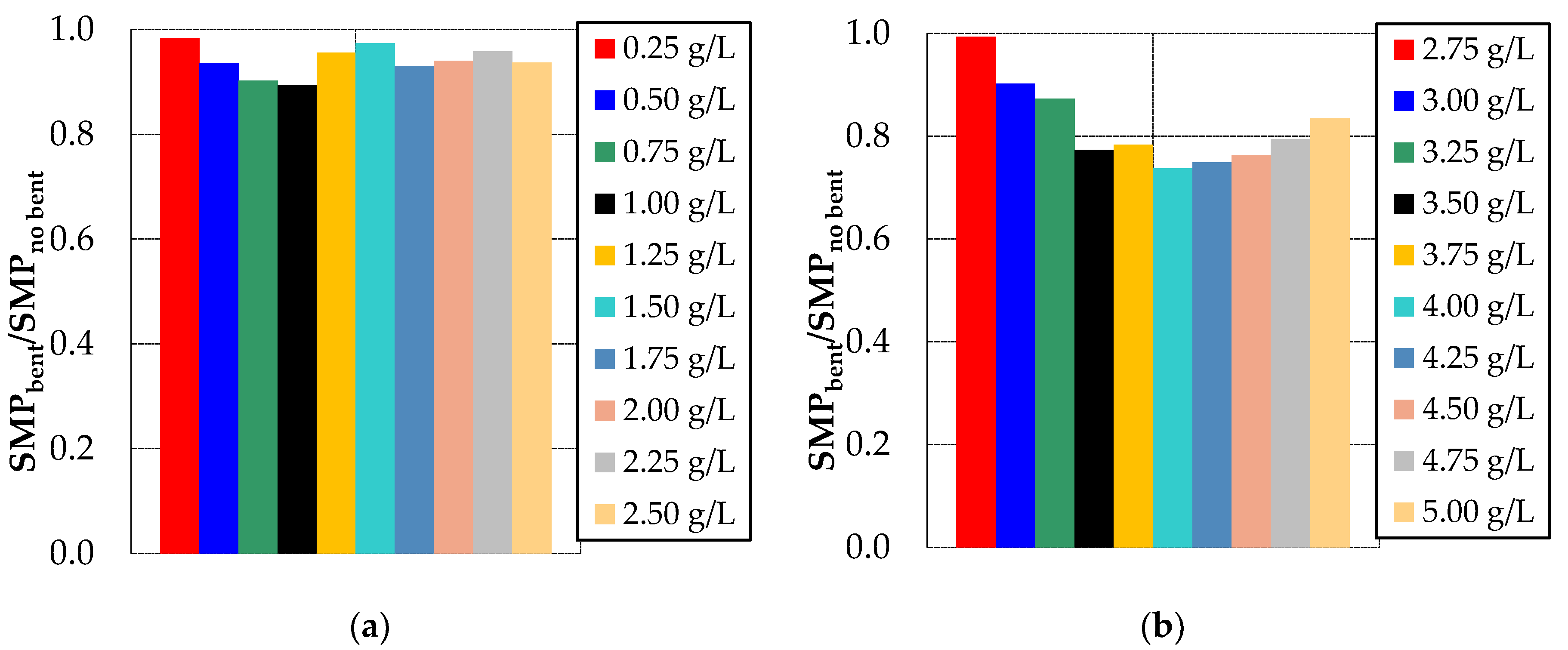
| Synthetic Wastewater According to OECD Guidelines | Synthetic Wastewater Used in the Experiments | Physical/Chemical Parameters of the Synthetic Wastewater Used in the Experiments 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Substance | Concentration, mg/L | ||
| Peptone | 160 | 1600 | |
| Meat extract | 110 | 1100 | BOD5 = 1102 ± 28 mg/L |
| Urea | 30 | 300 | CO = 1983 ± 54 mg/L |
| K2PO4 | 28 | 280 | TN = 268 ± 26 mg/L |
| NaCl | 7 | 70 | NH4+-N = 189 ± 18 mg/L |
| CaCl2∙2H2O | 4 | 40 | NO3-N = 1.6 ± 0.1 mg/L |
| MgSO4∙7H2O | 2 | 20 | PO43-P = 49 ± 5.2 mg/L |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gkotsis, P.; Peleka, E.; Zouboulis, A. The Use of Natural Minerals in a Pilot-Scale MBR for Membrane Fouling Mitigation. Separations 2020, 7, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations7020024
Gkotsis P, Peleka E, Zouboulis A. The Use of Natural Minerals in a Pilot-Scale MBR for Membrane Fouling Mitigation. Separations. 2020; 7(2):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations7020024
Chicago/Turabian StyleGkotsis, Petros, Efrosini Peleka, and Anastasios Zouboulis. 2020. "The Use of Natural Minerals in a Pilot-Scale MBR for Membrane Fouling Mitigation" Separations 7, no. 2: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations7020024
APA StyleGkotsis, P., Peleka, E., & Zouboulis, A. (2020). The Use of Natural Minerals in a Pilot-Scale MBR for Membrane Fouling Mitigation. Separations, 7(2), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations7020024






