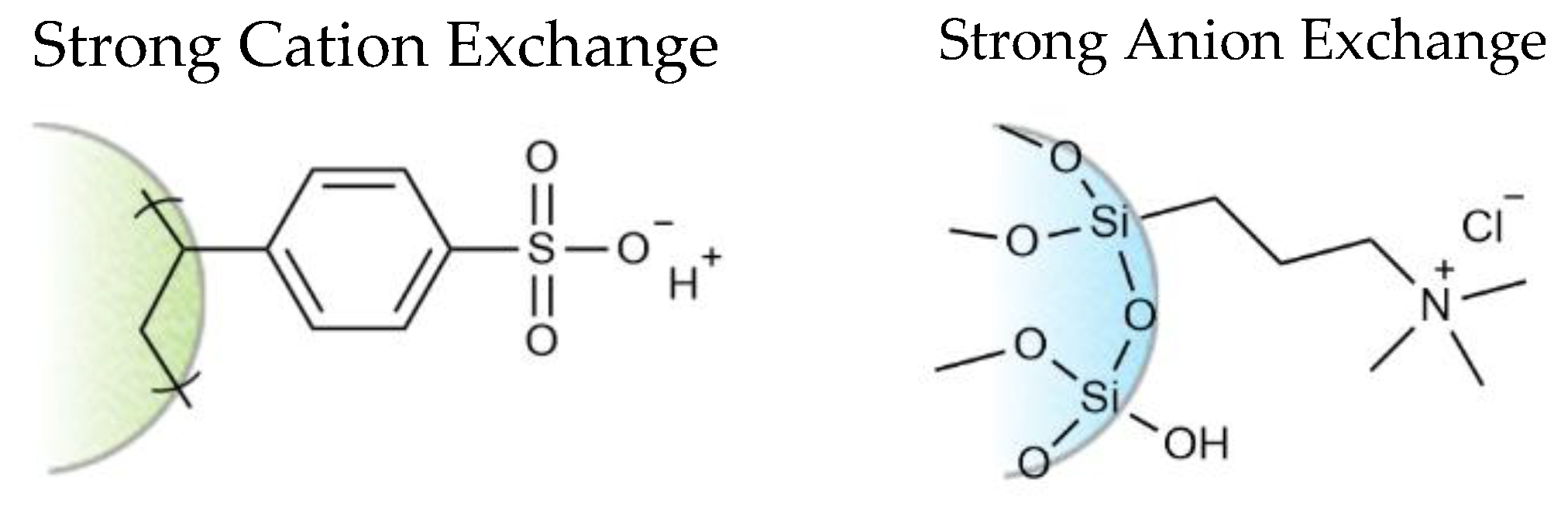Abstract
There are many advantages to using ionic liquids as solvents or catalysts in chemical processes. Their non-volatile characteristic and high cost, however, can pose economic, environmental, and long-term health concerns. As such, the recovery and recycling of ionic liquids have become essential to mitigate their environmental impact and to reduce costs. Numerous recovery and recycling methods have been reported, including distillation, extraction, membrane separation (a.k.a. filtration), adsorption, crystallization, gravity, and electrochemical separation. Whereas most of these methods recover both cations and anions of the ionic liquid as ion pairs, recycling methods such as single-phase ion exchange or mixed-ion exchange/non-ionic adsorption methods recover only one of the ionic liquid ions, typically the cation. These methods are frequently used for the recycling of ionic liquids having simple anions such as chloride or acetate, but are seldom employed for ionic liquids consisting of larger and more complex anions due to the added time and reagent costs necessary for the regeneration of the original ionic liquid. Herein, a combined cation and anion exchange adsorption-desorption method is presented that can effectively separate 1,2-dimethyl-3-propylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonimide) [DMPIm][NTf2] ionic liquid from neutral impurities. More importantly, the method is capable of recovery and recycling of the original ionic liquid. Concomitant desorption of both ionic liquid ions was achieved using 0.1 M NaCl: methanol (90:10 v/v) eluent followed by isolation using liquid–liquid extraction to afford high purity products and yields of approximately 60%.
1. Introduction
Ionic liquids are high molecular weight salts that are liquid at room temperature and typically liquid over a very broad temperature range. The first room temperature ionic liquid, [EtNH3][NO3], was introduced in 1914 [1] but notable interest did not arise until the discovery of binary ionic liquids made from aluminum (III) chloride. Chloroaluminate:imidazolium ionic liquid mixtures were first introduced by Wilkes et al. in 1982 [2] for utilization in electrochemistry, spectroscopy, and synthesis. These binary ionic liquids, however, were unstable in water and thus had limited use. Shortly before the turn of the century, the emergence of air- and water-stable ionic liquids (e.g., imidazole, pyrrole, pyridine, and alkyl phosphine salt derivatives) encouraged the development of modern-day ionic liquids consisting of a wide range of cations and anions of varying complexities and properties. These ionic liquids have many desirable characteristics, including high chemical and thermal stability, negligible vapor pressure, non-flammability, low melting point, wide electrochemical window, and ease of handling and storage. The solvent properties and behavior of ionic liquids can be tuned with relative ease by simple adjustment of cation–anion pairs and by design of cation molecular structures. This unique attribute endows ionic liquids with characteristics that are highly beneficial to various applications in organic chemistry, catalysis, electrochemistry, and separations [3,4,5]. The 1990s marked a period that saw significant growth in the interest of ionic liquids as inert solvents in chemical processes [6]. It was during this period when the benefits of imidazolium-based ionic liquids were realized as inert alternative solvents in chemical reactions such as Diels–Alder [7,8] and regioselective alkylation [9].
Ionic liquids are often referred to as “green” alternative solvents to conventional solvents because of their very low vapor pressures. Commonly used volatile organic solvents (VOCs) can be damaging to the environment and pose health concerns, especially in industrial applications where they are used in large quantities [10,11]. For this reason, the attraction to ionic liquids as alternative environmentally friendly solvents is understandable [12,13,14]. Ionic liquids touted for their “green” label have been heavily scrutinized in recent years, especially when the ionic liquid life cycle from cradle-to-grave is taken into consideration. Ironically, the non-volatile characteristic of ionic liquids responsible for their eco-friendly appeal is also the reason for their persistence in the environment. Non-volatile ionic liquids will inevitably pollute soils, sediments, and ground water through leakage during transport and storage or accidental and intentional release through wastewaters, dumpsites, etc. An increasing number of studies have been reported on the toxicological aspect and long-term environmental consequences of many commonly used ionic liquids [15,16,17,18,19]. In spite of the numerous efforts and commitment to research in this area, the understanding of ionic liquid degradation mechanisms and the toxicity of the degradation products is still very limited. Nonetheless, sufficient evidence has been presented suggesting some ionic liquids are not as green as once believed. Ionic liquids with perfluorinated anions such as BF4− and PF6−, for instance, have been observed to produce hazardous degradation products through hydrolysis reactions. The increase in cation alkyl chain length has also been reported to have a strong correlation to increased toxicity and rate of degradation of ionic liquids [20].
Despite the questionable toxicity of ionic liquids, their applications in the laboratory continue to increase at a steady pace. This is not the case, however, in industry. The potential environmental impact of ionic liquids may deter its use in large-scale operations, but it is generally not of primary concern. The lack of interest in commercial applications is largely due to the significantly higher cost of ionic liquids as compared to molecular solvents. One of the more promising biomass pretreatment methods, for example, utilizes ionic liquids for the conversion of lignocellulose into value-added chemicals and fuel products. Sadly, the prohibitive costs of ionic liquids and catalysts required for pretreatment prevent the commercialization of this technology [21,22,23]. While the costs of some ionic liquids have decreased over the years with the increase in demand, they are still considerably more expensive than molecular solvents by as much as 5 to 20 times [24,25,26]. Their inflated costs are governed, to a large extent, by their high production costs. Unlike organic solvents, ionic liquids are not readily accessible through simple isolation or conversion steps from inexpensive industrial process streams. They are produced via synthetic processes such as acid–base neutralization and metathesis reactions [4,27]. Impurities such as halides, water, amines, and organic solvents have also been observed to dramatically affect the physical properties of ionic liquids [28,29], thus necessitating stringent and often challenging isolation and purification steps to achieve desired ionic liquid purities.
The adoption of ionic liquid recycling strategies has, therefore, become essential to the economic and ecological viability of ionic liquids as practical solvent substitutes, particularly in large-scale syntheses and processes. In the last two decades, much effort has been dedicated to the development of reliable recycling methods to help mitigate the high cost of ionic liquids and reduce their potential environmental impact. Research in this area has led to the introduction of a wide breadth of recycling methods including distillation, extraction, membrane separation (a.k.a. filtration), adsorption, crystallization, gravity, and electrochemical separation that take advantage of the differences in the chemical–physical properties of ionic liquids and dissolved impurities in solution [20,29,30]. Distillation and extraction are two of the most commonly used recycling methods that are simple and easily scalable. These methods are currently employed in many chemical processes in the laboratory and in industry. However, isolation of the ionic liquids by these methods are typically accomplished by decantation which invariably leaves unwanted solutes or impurities in the ionic liquid product.
The adsorption–desorption recycling method has attracted much attention in the last two decades, owing to its excellent selectivity, robust and simple operation, relatively low cost, non-destructive separation mechanism, and scalability. Akin to retentive solid phase extraction (SPE) sample preparation techniques [31], the method utilizes an adsorption-desorption strategy based on differences in affinities of ionic liquids and impurities to a solid surface (sorbent). The adsorption method has shown much potential in the recovery of ionic liquids from wastewater [32,33,34], lignin [35], cellulosic material [36], and oil sands [37]. Anthony et al. [38] were the first to show effective recovery and recycling of ionic liquids from wastewater using activated carbon. Thereafter, scientists experimented with natural inorganic materials such as soils [39,40], clay, zeolites, and sediments [41,42]. These aforementioned sorbents are abundant and inexpensive, but their adsorption efficiencies are easily influenced by factors such as ionic liquid electrolyte architectures, particle size distribution, solution pH, and hydrophobicity of organic impurities [29,37]. The use of cation exchange sorbents, either as single-phase or combined with non-ionic sorbents (e.g., activated carbon or macroporous resin), has made headway in recent years due to the very high adsorption specificity for cationic species [36,43,44]. One of the main attractions to ion exchange recycling methods is their ability to produce ionic liquids of high purity and yields. Wide utilization of this method, however, is hampered by the method’s inability to recover the anions of the original ionic liquid. This is especially problematic when working with ionic liquids comprised of large or complex anions that are oftentimes prepared from expensive precursors.
As early as 2001, Anthony et al. postulated that a combined anionic and cationic exchange method would provide better ionic liquid recoveries as compared to activated carbon alone or mixed activated carbon/ion exchange sorbents [38]. To our knowledge, no reports have been published that demonstrate complete ionic liquid recycling by this method. In a previous report [45], we demonstrated the effective removal of 1,2-dimethyl-3-propylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonimide) [DMPIm][NTf2] and 1-methyl-3-butylpyrolidinium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonimide) [BMPy][NTf2] from solutions containing neutral explosive compounds utilizing combined cation and anion exchange SPE for sample pretreatment prior to instrumental analyses. The combination of strong anion and strong cation exchange sorbents allowed for the concomitant adsorption of ionic liquid cations and anions while neutral compounds of interest were eluted and collected. In present work, the SPE method was developed further and scaled-up to allow for the recovery and recycling of adsorbed [DMPIm][NTf2] (Figure 1). Alkylated imidazolium-based ionic liquids are promising electrolytes that have been shown to facilitate oxidation and reduction reactions in Li-ion batteries [46,47]. [DMPIm] cation is particularly important due to the presence of an electron donating substituent in the second position and a long alkyl chain in the third position which promotes charge delocalization and improved reduction stability [48]. [NTf2] is generally the preferred counteranion in battery applications due to its relatively low viscosities and extremely wide electrochemical stability windows. These characteristics are attributed to the anion’s partially delocalized charge that weaken anion–cation interactions, resulting in increased ion mobility and high lithium ion cycling efficiencies [49,50].
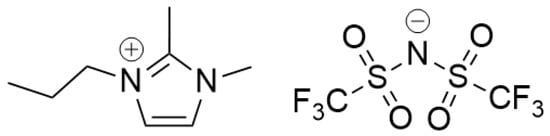
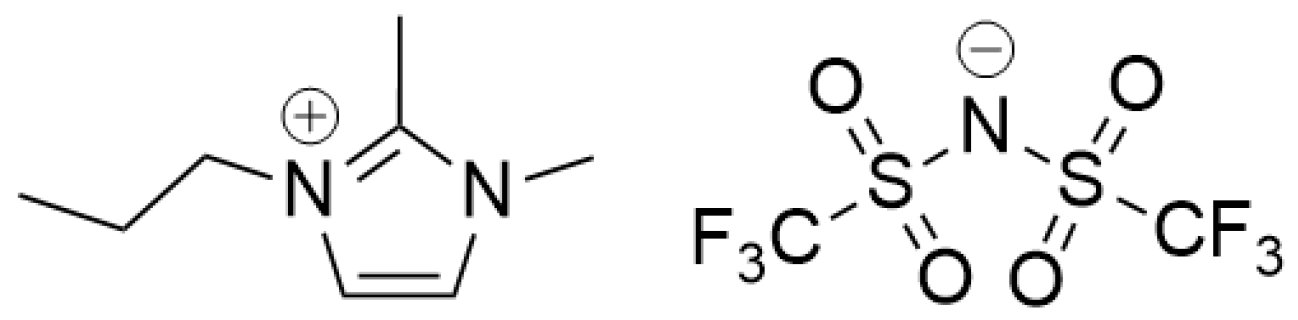
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of 1,2-dimethyl-3-propylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonimide) [DMPIm][NTf2].
In this study, several experiments were undertaken to determine optimal conditions for maximum desorption of the ionic liquid ions and the recovery and recycling of the original [DMPIm][NTf2] ionic liquid. A facile four-step extraction protocol was developed that can be scaled with ease to accommodate larger volumes of ionic liquid.
2. Experimental
Materials: [DMPIm][NTf2] ionic liquid was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) grade water and solvents, ammonium formate, and internal standard (acetaminophen) were purchased from Acros Organics (New Jersey, VA, USA). Prepacked STRATA®-SAX anion exchange cartridges (100 mg and 10 g bed size) and STRATA®-X-C cation exchange cartridges (30 mg and 10 g bed size) were purchased from Phenomenex (Torrance, CA, USA). LC-MS analyses were performed using Higgins Analytical Phalanx C18 reversed-phase columns (5 µm, 2.5 × 150 mm).
Instrumentation & equipment: A Buchi R215 rotary evaporator (New Castle, DE, USA) was used for the removal of volatile solvents. An Agilent 6210 MSD LC/UV-Vis/MS-TOF system was employed for the reversed-phase LC analyses. The recycled ionic liquids were characterized by 1H-NMR and FTIR on an Oxford Mercury 400 MHz NMR spectrometer and a Nicolet Nexus FTIR equipped with a multi-bounce ATR accessory. The apparatus used for the extractions consisted of an SPE 10-position vacuum manifold (Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA) and a Welch 2545B diaphragm vacuum pump. The manifold was fitted with an external valve and gauge to allow for regulation of the effluent flow.
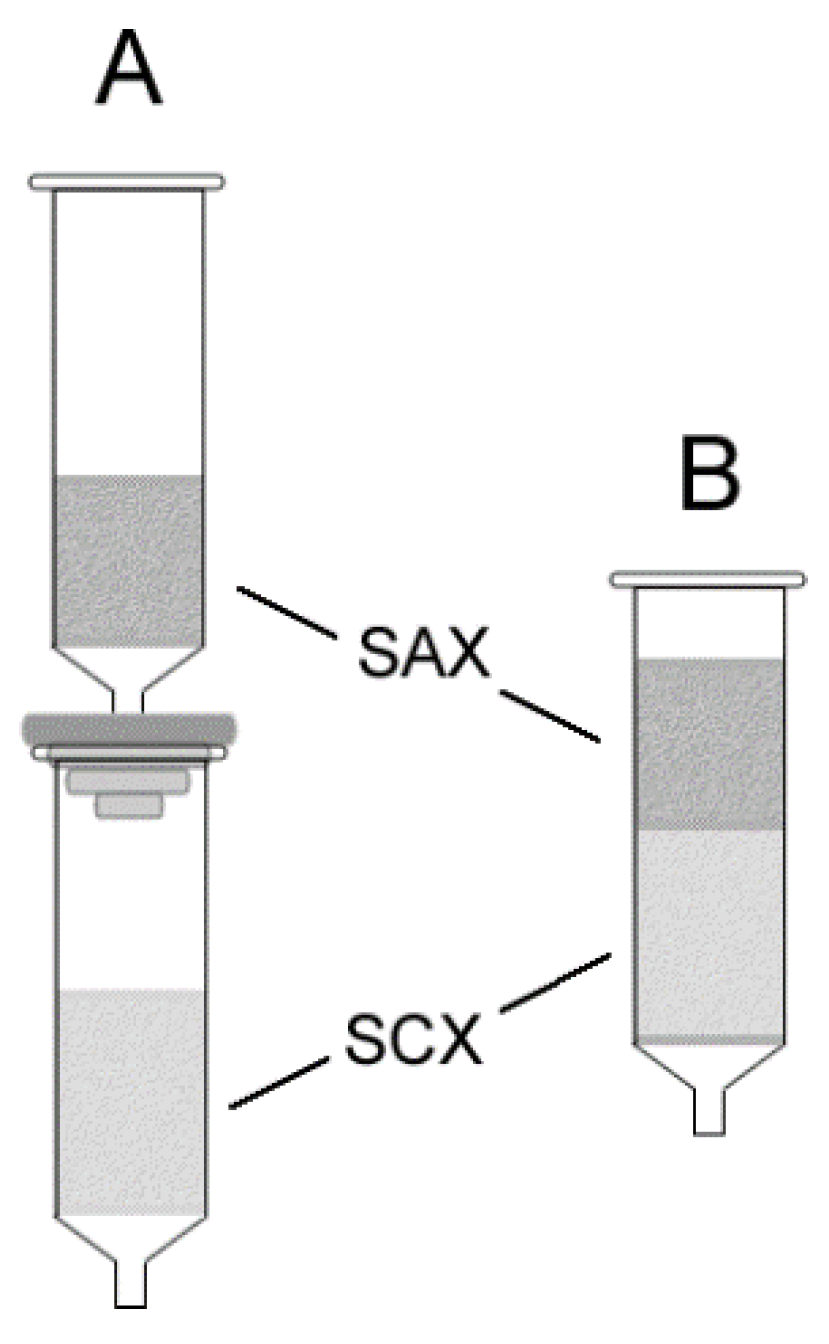
Extraction column preparation: The proposed recycling method is a dual-phase ion exchange liquid–solid extraction technique that employs combined anion exchange and cation exchange sorbents in either a single or dual cartridge format. Dual cartridge extraction columns were prepared by coupling prepacked STRATA®-SAX and STRATA®X-C cartridges (end-to-head) using a fitted coupling adapter (Figure 2A). Single cartridge extraction columns were slurry-packed in the laboratory (Figure 2B). The resin from a STRATA®-SAX cartridge was first removed and added to a beaker containing methanol to form a slurry. The slurry was then poured slowly into a prepacked STRATA®X-C cartridge while excess methanol was eluted through the cartridge by gravity flow. While still wet, the newly poured cartridge was briefly sonicated to promote even settling and tight packing of the resin particles. The sorbents were allowed to dry completely in air before use.
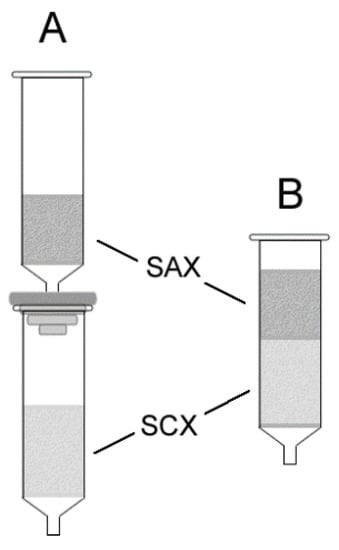
Figure 2.
Extraction column configurations in (A) dual cartridge format and (B) single cartridge format (SAX = strong anion exchange sorbent, SCX = strong cation exchange sorbent).
Extraction procedure: The extraction columns were connected to an SPE vacuum manifold to allow regulation of the effluent flowrates. The approximate eluent volumes used in the extraction steps are highlighted in Table 1. The extraction column was first washed with methanol to wet and activate the sorbent for good mass transfer. Next, the ionic liquid sample solution was loaded at the head of the column and allowed to fully enter the sorbent by gravity flow. The column was then washed with methanol to remove neutral impurities. Lastly, the bound ionic liquid ions were desorbed and recovered using an appropriate eluent. Depending on the objective of the experiment being performed, wash or desorption eluent was added until approximately 1 mL (analytical) or 100 mL (semi-preparative) of effluent was collected.

Table 1.
General extraction steps for the adsorption and desorption of [DMPIm][NTf2] ionic liquid.
Eluent and sample preparation: Unless otherwise noted, the ionic liquid working solutions used in the analytical extractions were prepared by dissolving 2 mg of [DMPIm][NTf2] in 1 mL of methanol. The working ionic liquid solutions for the semi-preparative extractions were prepared by dissolving 3–4 g of [DMPIm][NTf2] in a minimum amount of methanol. The wash and desorption eluent utilized in the analytical extractions were spiked with a neutral reference standard, acetaminophen, to a final concentration of 1 mg per mL of eluent.
Instrumental analysis: The starting eluent solution and collected effluent samples were diluted 1:20 (v/v) with methanol prior to analysis by LC/UV-Vis/MS using gradient elution from 30% to 80% methanol in 8 min at a flowrate of 0.25 mL/min and mobile phase consisting of 5 mM ammonium formate (pH 7) and methanol. A post-run wash of 95% methanol was also added for a minimum of 5 min to ensure run-to-run accuracy and reproducibility. Acetaminophen and the ionic liquid signals were monitored by UV absorbance at 254 nm and fast polarity-switching MS, respectively. The concentration of acetaminophen in the effluent was expected to remain constant which allowed for correction of variances in the volume of effluent collected through normalization of the UV chromatogram peak area for acetaminophen in the effluent relative to the peak area of acetaminophen in the starting eluent solution. Quantitation of [DMPIm][NTf2] ions was achieved through linear regression analysis of the normalized ionic liquid sample peak areas against peak areas of standard ionic liquid solutions of known concentrations.
Post-treatment of desorbed ionic liquid (semi-preparative only): Methanol was removed from the collected effluent by rotary evaporation. The residue was then reconstituted in 50 mL of chloroform and washed three times with water by liquid–liquid extraction. Chloroform was removed by rotary evaporation, leaving a colorless [DMPIm][NTf2] ionic liquid product. The final ionic liquid products were characterized by 1H-NMR (in chloroform-D) and ATR-FTIR (neat) spectroscopy.
3. Results and Discussion
A thorough study was performed consisting of a series of experiments aimed at finding optimal conditions for the desorption of [DMPIm][NTf2]. Critical extraction parameters were investigated including column configuration, sorbent order, eluent composition, and sorbent ionic capacity. The results from the experiments are summarized in Table 2. Analytical scale extraction columns (130 mg total bed size) were employed for all the experiments except for the recycling experiments, which utilized semi-preparative scale columns (20 g total bed size).

Table 2.
Experimental extraction recoveries of [DMPIm][NTf2].
3.1. Column Configuration
As mentioned earlier, the two possible column configurations utilizing prepacked ion-exchange cartridges are illustrated in Figure 2. Decidedly, column configuration A required the least amount of effort to assemble. For practical use, however, the sorbents are best stacked adjacent to each other in a single cartridge (Figure 2B) to minimize material costs and dead volume. By and large, ion exchange extraction follows classic displacement chromatography mechanism where exchange rates are rapid, leading to the elution of the displaced ions within a narrow band [51,52]. Band broadening, as a result of added dead volume in column configuration A in Figure 2, is therefore negligible, provided the eluent volume employed is adequate to fully elute the sample ions. The nearly identical percent ion recoveries for the single cartridge and dual cartridge configurations in Table 1, entries 1 and 2, respectively, demonstrates that either configuration can be used for the study. Consequently, the simpler dual cartridge column configuration was employed for the remainder of the experiments.
3.2. Sorbent Order
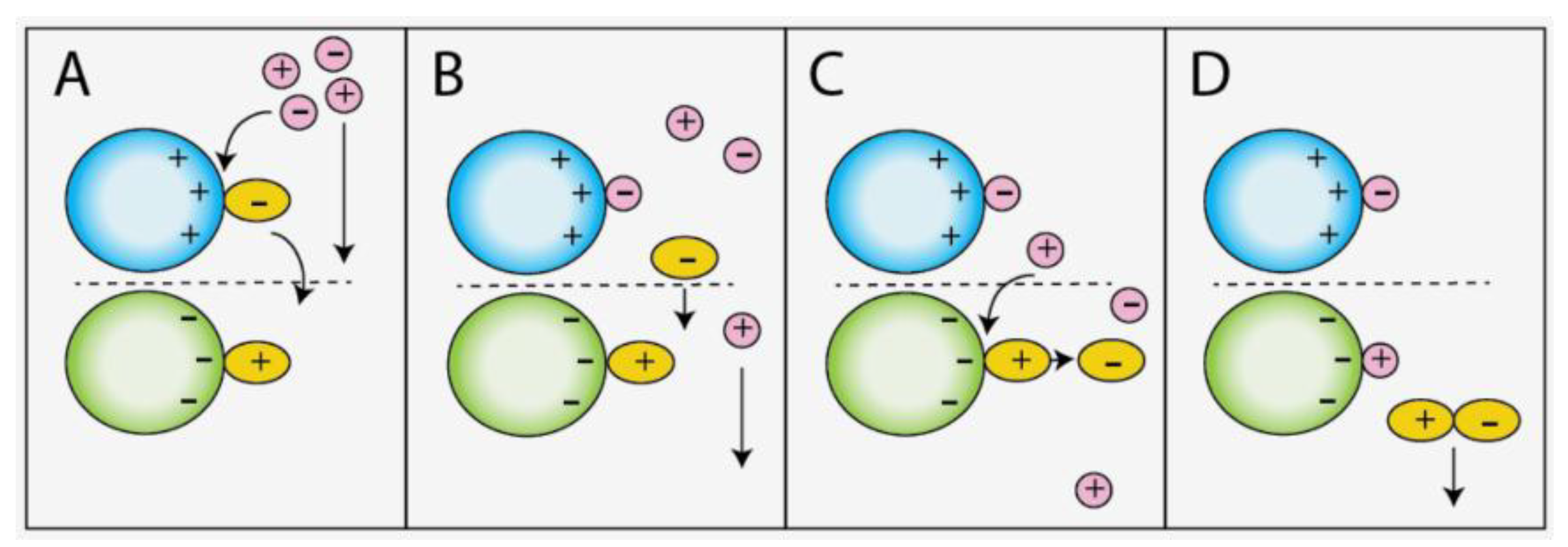
The strong cation and strong anion exchange sorbents employed in the experiments have surface chemistries of permanently fixed charged moieties bound to an aliphatic polymer backbone or spherical silica resin (Figure 3). These charged sites are capable of exchanging either a cation or anion (e.g., H+ or Cl− resin counter ions) with free cation or anions in solution. Ionic liquid ions are adsorbed on the ion exchange resins in this manner. Similarly, desorption of the bound ionic liquid ions are achieved through displacement with like-charged species in the eluent having greater electronic affinity to the resin [53]. In a typical single-phase ion exchange separation, the displaced sample ions are immediately removed through the effluent. In a stacked two-phase ion exchange system, however, the displaced ions from the upper resin can conceivably interact with bound oppositely charged species in the lower resin as they are carried down the extraction column in the effluent. To test this theory, identical extractions were performed on two separate extraction columns, one with the anion exchange sorbent on top (entry 2) and the other with sorbents in the reversed order (entry 3). The largely disparate recoveries for DMPIm+ in the two experiments indicate that the sorbent order may play some role in the displacement of the sample cation. In the case of entry 3, no exchange reaction took place with the ammonium ion in the eluent. Nothing was changed in entry 2 other than the fact that the cation exchange sorbent was on the bottom, yet DMPIm+ was detected in the effluent. This may be explained by an electrostatic attraction between the liberated NTf2− ion from the top resin and bound DMPIm+ in the lower resin that facilitated the exchange reaction with an eluent cation and the instantaneous displacement of the ionic liquid as an ion pair. Figure 4 provides a pictorial representation of the possible ionic interactions between the charged sites of the resin and free ions in the eluent during the desorption step of the recycling method.
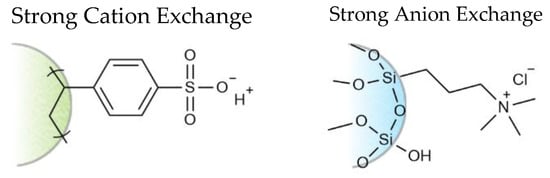
Figure 3.
Sorbent chemistries of the Phenomenex STRATA®X-C (left) and STRATA®-SAX (right).
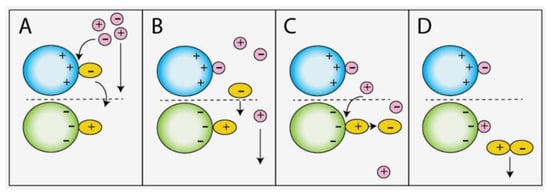
Figure 4.
Proposed desorption mechanism of bound DMPIm+ and NTf2− ions; (A) NTf2− is displaced by eluent anion, (B) Free NTf2− is carried down the column, (C) Interaction between bound DMPIm+ and NTf2− facilitates displacement of DMPIm+, (D) [DMPIm][NTf2] is eluted as an ion pair.
3.3. Eluent Composition
Ion retention in ion exchange is affected by factors including charge and size of the ion and the presence of competing ions. Thus, large ions such as DMPIm+ and NTf2− are expected to be highly adsorbed. Several salt solutions were tested for maximum desorption of the bound ionic liquid ions. (Table 2: entries 2, 4, 5, and 6). Among those tested, sodium chloride provided the highest recoveries for both ionic liquid ions (71% for DMPIm+ and 68% for NTf2−). While these values are respectable, higher recoveries are needed in order to obtain practical amounts of recycled ionic liquid.
Up to this point, we have regarded STRATA®-SAX and STRATA®X-C sorbent interactions to involve only ion exchange reactions when, in fact, the STRATA®X-C contains an aromatic functional group that can also participate in secondary non-covalent interactions such as π–π bonding and hydrophobic interaction. The alkyl substituents and aromatic imidazole ring of DMPIm+ are capable of interacting with the resin by these mechanisms, further increasing its binding energy. In reversed-phase liquid chromatography (RP-LC), elution of analytes adsorbed on the resin by hydrophobic interactions are encouraged by the addition of an organic modifier in the mobile phase. Hydrophobic interactions between the analyte and resin are disrupted when the polarity of the mobile phase becomes more favorable [54]. Analyte elution in RP-LC is therefore dependent on the relative solubility of the analyte in the mobile phase. Since [DMPIm][NTf2] ionic liquid is only marginally soluble in water and highly soluble in methanol, the addition of methanol to the 0.1 M NaCl eluent should promote desorption of the ions. In Table 1, entries 7, 8, and 9, we observed a dramatic improvement in ion recoveries as the percent of methanol organic modifier is increased. When the methanol composition was increased to 90%, greater than 95% recoveries for both ions were attained.
3.4. SAX/SCX Ion Exchange Capacity
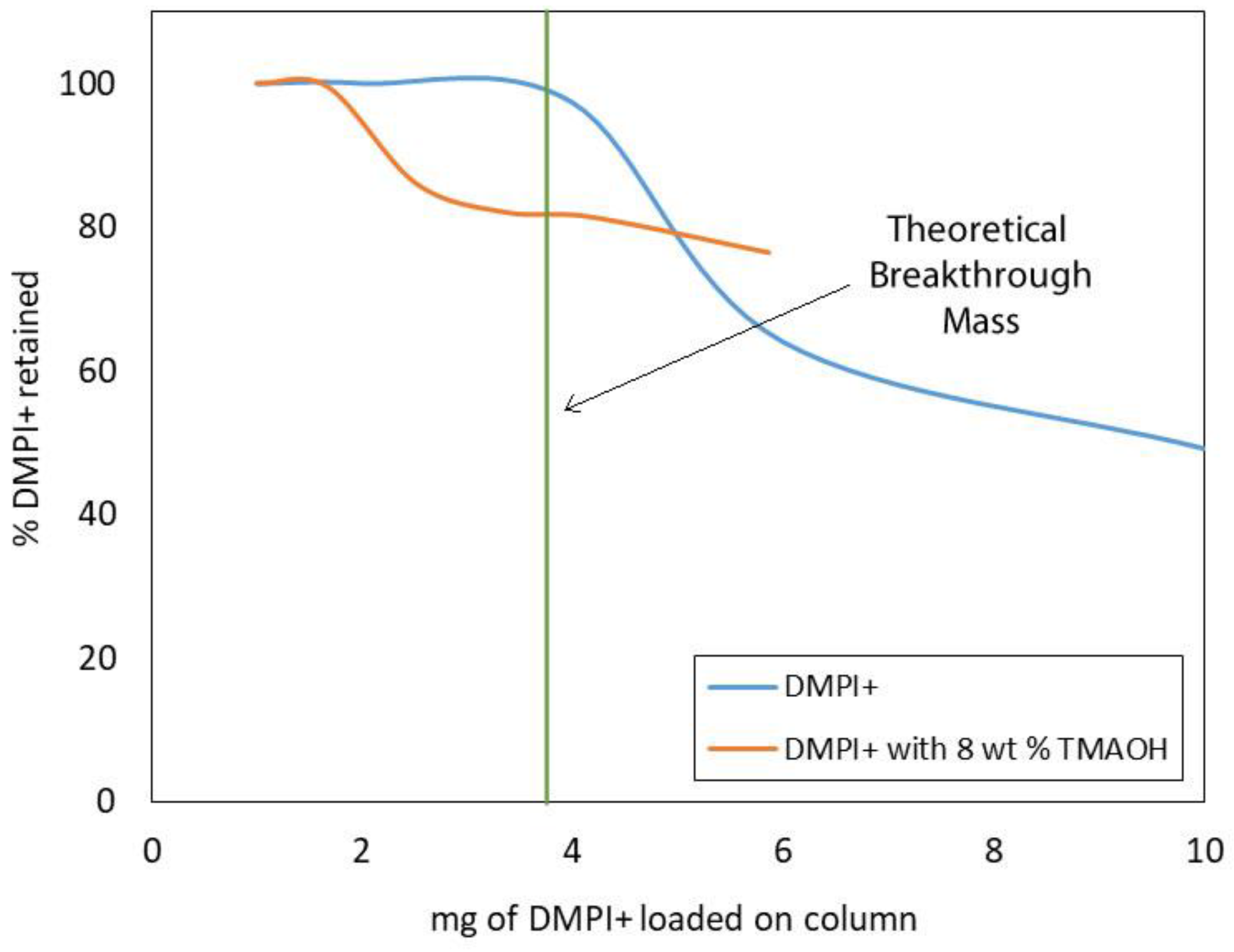
Ion exchange reactions are stoichiometric. That is, for every ion removed from the resin, it is replaced by an equivalent amount of charge from the sample or eluent. The total number of equivalents capable of ion exchange per gram of sorbent is called the “ion exchange capacity” or “ionic capacity”. For the STRATA®-SAX and STRATA®X-C sorbents, those values are 0.9 and 1.0 milli-equivalents per gram of sorbent, respectively. When the ionic equivalent of the sample loaded on the sorbent exceeds the ionic capacity of the sorbent, excess unbound sample ions are eluted in the effluent. The point at which this happens is referred to as the “breakthrough point”, and the maximum amount of sample that can be loaded onto the resin before the breakthrough point is reached is called the “breakthrough mass”. Breakthrough curves are valuable tools for determining the breakthrough mass (or volume) for a particular combination of adsorbate and resin type and volume [46]. Since the ionic capacity of the SAX/SCX analytical extraction column is limited by the volume of the STRATA®X-C sorbent, only the breakthrough curve for DMPI+ was evaluated (Figure 5). The observed breakthrough mass was in close agreement with the theoretical value of 3.75 mg, suggesting that interactions between DMPI+ and the benzylsulfonate functionality of the sorbent are predominantly ionic. Also shown in Figure 5 is the breakthrough curve for [DMPIm][NTf2] sample solution containing 8 wt% tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAOH). The influence of competing ions in the eluent is apparent, shown by the lowering of the breakthrough mass to approximately 1.5 mg.
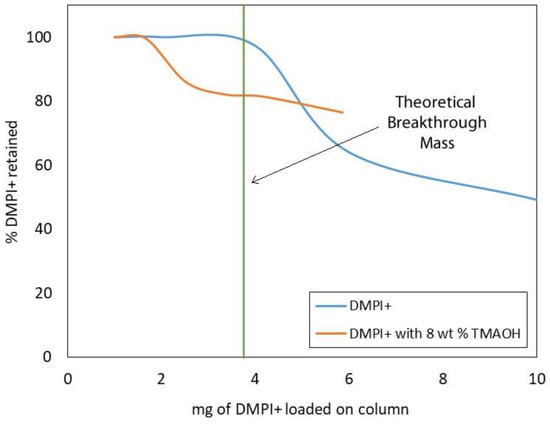
Figure 5.
Breakthrough curves for sample solutions containing [DMPIm][NTf2] and [DMPIm][NTf2] with 8 wt% TMAOH showing the effect of competing ions.
3.5. Recovery and Recycling of the Ionic Liquid
A total of four recycling experiments were performed on two semi-preparative extraction columns to examine overall method reproducibility and column recyclability (Table 3). Three to four grams of ionic liquid were loaded on the columns, which is safely below the calculated breakthrough mass of 12.5 g. The bound ionic liquid ions were desorbed using 0.1 M NaCl: 90% methanol eluent. The relatively consistent values for the observed ionic liquid product yields substantiated the robustness of the method. Moreover, the experiments showed that the extractions columns can be recycled without discernable loss of sorbent performance.

Table 3.
Recycled [DMPIm][NTf2] product yields.
4. Conclusions
The prospect of ionic liquids as solvent substitutes, particularly in large-scale operations, rely on the utilization of robust recycling methods to help mitigate costs and reduce their environmental impact. A highly selective stacked cation and anion exchange recycling method has been demonstrated for the effective purification and complete recovery and recycling of the original [DMPIm][NTf2] ionic liquid. Moreover, the ability to reuse the sorbents without the need for sorbent clean-up between applications provided additional time and resource cost savings.
The proposed method can likely be used for the recycling of ionic liquids consisting of cations and anions of similar charge, size, and hydrophobicity to DMPIm+ and NTf2−. Investigations into recoveries of other common ionic liquid ions revealed that larger and more hydrophobic cations such as [P(C8)4]+ and [PPh4]+ were not effectively desorbed using 0.1 M NaCl: 90% MeOH eluent and the more polar and smaller BF4− anion and the divalent anion Ni(dtmn)2− were not desorbed at all. On the other hand, 1-buyl-3-methylimidazolium (BMIm+) and 1-ethyl-3-imidazolium (EMIm+) cations, which differ to DMPIm+ by the number and length of the substituents, exhibited comparable ion recoveries.
The use of combined anion and cation exchange resins for the separation of ionic species in solution is not a novel idea. This is the first time, however, that the strategy is applied to the complete recovery and recycling of ionic liquids. The process of ion exchange using homogenous mixed resins has been in commercial use since 1942 and is one of the most utilized techniques for water purification (demineralization) and wastewater treatment. The efficient separation of ions in these mixed resin systems is largely credited to strong driving forces created by oppositely charged resin particles in close proximity to each other. These forces created in homogenous mixed resins can be advantageous for desorption of ionic liquid ions and merits further investigation.
Author Contributions
C.A.C. performed the conceptualization, methodology, investigation, instrumental analyses, and writing of the research article with funding acquisition, supervision, input, and editing from S.T.I.
Funding
This work was funded by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR) and the Defense Threat Reduction Agency (DTRA) − Joint Science and Technology Office for Chemical and Biological Defense.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Walden, P. Ueber die Molekulargrösse und electrische Leitfähigkeit einiger geschmolzenen Salze. Bulletin de l’Academie Imperiale des Sciences de St. Petersbourg 1914, 8, 405–422. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkes, J.S.; Levisky, J.A.; Wilson, R.A.; Hussey, C.L. Dialkylimidazolium chloroaluminate melts: A new class of room-temperature ionic liquids for electrochemistry, spectroscopy and synthesis. Inorg. Chem. 1982, 21, 1263–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koel, M. Ionic Liquids in Chemical Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Del Sesto, R.E.; Corley, C.; Robertson, A.; Wilkes, J. Tetraalkylphosphonium-based ionic liquids. J. Organomet. Chem. 2005, 690, 2536–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Chen, B.; Koo, Y.; MacFarlane, D.R. Introduction: Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6633–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welton, T. Ionic liquids: A brief history. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.; Sethi, A.; Welton, T.; Woolf, J. Diels-Alder reactions in room-temperature ionic liquids. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, M.J.; McCormac, P.B.; Seddon, K.R. Diels-Alder reactions in ionic liquids. A safe recyclable alternative to lithium perchlorate-diethyl ether mixture. Green Chem. 1999, 1, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, M.J.; McCormac, P.B.; Seddon, K.R. Regioselective alkylation in ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 1998, 2245–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakoteswararao, P.; Tulasi, S.L.; Pavani, Y. Impacts of solvents on Environmental Pollution. JCHPS 2014, 3, 132–135. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, M. Public health problems of organic solvents. Toxicol. Lett. 1992, 64–65, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, S.; Dinari, M. Green Solvents II: Properties and Applications of Ionic Liquids. In Ionic Liquids as Green Solvents: Progress and Prospects; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Chapter 1. [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh, M.A.; Huang, X. Green Solvents II: Properties and Applications of Ionic Liquids. In Organic Ionic Liquids: Ultimate Green Solvents in Organic Synthesis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Chapter 17. [Google Scholar]
- Halett, J.P.; Welton, T. Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids: Solvents for Synthesis and Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3508–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przemyslaw, P. Application of Ionic Liquids as Solvents for Polymerization Processes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 29, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, M.M.; Jernigan, M.B.; Jennigan, P.L.; Sturdivant, J.; Hought-Toutman, W.L.; Rasco, J.F.; Swatloski, R.P.; Rogers, R.D.; Hood, R.D. Developmental toxicity assessment of the ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride in CD-1 mice. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedlecka, E.M.; Czerwicka, M.; Neumann, J.; Stepnowski, P.; Fernandez, J.F.; Thoming, J. Ionic Liquids: Theory, Properties, New Approaches. In Ionic Liquids: Methods of Degradation and Recovery; InTech: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Maton, C.; Vos, N.D.; Stevens, C. Ionic liquid thermal stabilities: Decomposition mechanisms and analysis tools. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5963–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooster, T.J.; Johanson, K.M.; Fraser, K.J.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Scott, J.L. Thermal degradation of cyano containing ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Sui, H.; Jia, Z.; Yang, Z.; He, L.; Li, X. Recovery and purification of ionic liquids from solutions: A review. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 32832–32864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Hendrickson, R.; Mosier, N.S.; Ladish, M.R. Liquid hot pretreatment of cel- lulosic biomass. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 581, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balan, V. Current challenges in commercially producing biofuels from lignocellulosic biomass. ISRN Biotechnol. 2014, 463074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein-Marcuschamer, D.; Simmons, B.A.; Blanch, H.W. Techno-economic analysis of a lignocellulosic ethanol biorefi nery with ionic liquid pre-treatment. Biofuel. Bioprod. Bioref. 2011, 5, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sharifzadeh, M.; MacDowell, N.; Welton, T.; Shah, N.; Halett, J.P. Inexpensive ionic liquids: [HSO4]−-based solvent production at bulk scale. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirwardana, A.I. Industrial Applications of Ionic Liquids. In Electrochemistry in Ionic Liquids; Torriero, A., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R. Applications of ionic liquids in the chemical industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claire, B.; Sirwardana, A.; MacFarlane, D.R. Synthesis, purification and characterization of ionic liquids. Top. Curr. Chem. 2010, 290, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Seddon, K.R.; Stark, A.; Torres, M. Influence of chloride, water, and organic solvents on the physical properties of ionic liquids. Pure Appl. Chem. 2000, 72, 2275–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekalavounos, E.; Helminen, J.; Kyllonen, L.; Kilpelainen, I.; King, A. Ionic Liquids: Recycling. In Encyclopedia of Inorganic and Bioinorganic Chemistry; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Eishah, S.I. Ionic Liquids Recycling for Reuse. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/books/ionic-liquids-classes-and-properties/ionic-liquids-recycling-for-reuse (accessed on 10 October 2011).
- Thermal, E.; Mills, M.S. Solid-Phase Extraction: Principles and Practice; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Palomar, J.; Lemus, J.; Gilarranz, M.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Adsorption of ionic liquids from aqueous effluents by activated carbon. Carbon 2009, 47, 1846–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.A.; Wu, C. Efficient and recyclable removal of imidazolium ionic liquids from water using resorcinol–formaldehyde polymer resin. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 68111–68119. [Google Scholar]
- Lemus, J.; Palomar, J.; Heras, F.; Gilarranz, M.A.; Rodriguez, J.M. Characterization of Supported Ionic Liquid Phase (SILP) materials prepared from different supports. Adsorption 2011, 17, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zu, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, J. Two solid-phase recycling method for basic ionic liquid [C4mim]Ac by macroporous resin and ion exchange resin from Schisandra chinensis fruits extract. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 976–977, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faizee, N.; Rao, K.; Dadi, A.P.; Varanasi, S.; Schall, C.A. Ion Exchange Process For the Recovery of Ionic Liquids. In Proceedings of the 2007 Annual Meeting, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 7 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, H.; Zhou, J.; Ma, G.; Niu, Y.; Cheng, J.; He, L.; Li, X. Removal of Ionic Liquids from Oil Sands Processing solution by Ion-Exchange Resin. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, J.; Magnin, E.J.; Brennecke, J.F. Solution Thermodynamics of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids and Water. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 10942–10949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, S.P.M.; Silva, F.A.; Quental, M.V.; Mondal, D.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Ionic-Liquid-Mediated Extraction and Separation Processes for Bioactive Compounds: Past, Present, and Future Trends. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6984–7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman-Lewis, P.J.; Fen, J.B. Experimental Study of the Adsorption of an Ionic Liquid onto Bacterial and Mineral Surfaces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2491–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepnowski, P. Preliminary Assessment of the Sorption of some Alkyl Imidazolium Cations as used in Ionic Liquids to Soils and Sediments. Aust. J. Chem. 2005, 58, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, J.J.; Tank, J.L.; Kopacz, M. Sorption of imidazolium-based ionic liquids to aquatic sediments. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, J.B.; Raines, R.T. Fermentable sugars by chemicalhydrolysis of biomass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4516–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Dong, B.; Feng, X.; Yao, S. Recovery of benzothiazolium ionic liquids from the coexisting glucose by ion-exchange resins. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 227, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corley, C.A.; Iacono, S.T. A rapid approach to isolating nitro-explosives from imidazolium and pyrrolidinium ionic liquid solutions using solid phase extraction (SPE). Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 6911–6915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Thomas, M.; Zhang, S.; Uedo, K.; Tomohiro, Y.; Dokko, K. Application of Ionic Liquids to Energy Storage and Conversion Materials and Devices. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7190–7239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, S.I.; Sillars, F.B.; Hudson, N.E.; Hall, P.J. Physical Properties of Selected Ionic Liquids for Use as Electrolytes and Other Industrial Applications. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Miyashiro, H.; Ohno, Y.; Usami, A.; Mita, Y.; Kihira, N.; Watanabe, M.; Terada, N. Lithium secondary batteries using modified-imidazolium room-temperature ionic liquid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 10228–10230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilasari, B.; Jung, Y.; Kim, G.; Kwon, K. Effect of Cation Structure on Electrochemical Behavior of Lithium in [NTf2]-based Ionic Liquids. Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 4, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennie, A.J.R.; Martins, V.L.; Torres, R.M.; Hall, P.J. Ionic Liquids Containing Sulfonium Cations as Electrolytes for Electrochemical Double Layer Capacitors. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 23865–23874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, S.M.; Brimley, R.C. Displacement Chromatography on Synthetic Ion-exchange Resins. Biochem. J. 1952, 51, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurman, E.M.; Mills, M.S. Solid Phase Extraction Principles and Practice; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; Chapter 6. [Google Scholar]
- Thurman, E.M.; Mills, M.S. Solid Phase Extraction Principles and Practice; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; Chapter 2. [Google Scholar]
- McMaster, M.C. LC/MS.; A Practical User’s Guide; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).