Abstract
The water-rich liquid layer immobilized on the surface of the polar stationary phases is critical to the retention of polar compounds in hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC). Although the presence of the adsorbed water layer has been investigated and confirmed by multiple techniques, there is a lack of quantitative measures that can be easily determined and linked to chromatographic parameters. This study proposes a simple measure termed volume ratio (the ratio of the adsorbed water layer volume and the mobile phase volume) that can be easily determined using toluene elution volume. The volume ratio values measured using the proposed method indicate that the volume of the adsorbed water layer varies in a wide range in the stationary phases commonly used in HILIC separation. It was observed that the volume ratio increases with the acetonitrile content and ammonium acetate concentration in the mobile phase. In addition, increasing the column temperature had the effect of reducing the volume ratio and diminishing the adsorbed water layer.
1. Introduction
Hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC) offers practical advantages to the separation of polar compounds over reversed-phase liquid chromatography (RPLC), and has been widely applied to challenging analysis in biomedical and pharmaceutical fields [1,2,3,4,5,6]. The retention mechanism in HILIC, on the other hand, has been shown to be very complicated possibly involving multiple interactions [7,8]. As postulated by Alpert in his seminal HILIC paper, a major retention mechanism is based on partitioning of polar solutes between a hydrophobic mobile phase and a water-rich liquid layer immobilized on the surface of the polar stationary phase [9]. In addition, other polar interactions (e.g., adsorption and hydrogen bonding) may also be involved depending on the stationary phase chemistry and solute structures [9,10,11]. If both the stationary phase and the solutes are charged in the mobile phase, electrostatic interactions—either attractive or repulsive—can have significant effects on retention [7,11,12,13]. The attractive interactions between oppositely charged stationary phases and solute molecules enhance the retention; whereas the repulsive interactions reduce the retention, but may provide a unique separation mechanism as in electrostatic repulsion - hydrophilic interaction chromatography (ERLIC) [14].
Based on the hydrophilic partitioning model, the water-rich liquid layer immobilized on the surface of the polar stationary phase is critical to the retention of polar solutes in HILIC. The existence of the water-rich liquid layer has been investigated and confirmed in recent studies using various techniques, including frontal analysis, 1H-NMR, coulometric titration, and molecular dynamic simulation [15,16,17,18]. Uwe and McCalley used the toluene elution time to estimate the percentage of the pore volume occupied by the water-rich liquid layer in the polar stationary phases [19]. Dinh and coworkers determined water uptake on the polar stationary phases by coulometric titration and estimated both pore occupancies and water layer thickness [17]. The NMR data and molecular dynamic simulation demonstrate the complex structure of the water-rich liquid layer [15,18]. The immobilized water-rich liquid layer on the polar surface is not homogenous and has a complex structure with a tightly bound water layer close to the polar surface and a diffuse layer with a gradually increasing acetonitrile component.
The data of pore occupancy and water layer thickness is related to solute retention based on hydrophilic partitioning, but is very difficult to quantitatively correlate to any chromatographic parameters. Dinh and coworkers converted the water uptake data to the phase ratio for a limited number of polar stationary phases; however, no significant correlation was found between the retention factors and the phase ratio [17]. In addition, the water uptake data was obtained by coulometric titration, which required the availability of the packing materials and was not practical to perform on a routine basis. A more practical approach is needed to generate a quantitative measure for the adsorbed water on the polar stationary phases, which can also be linked to chromatographic parameters. The quantitative measure can facilitate the evaluation of various polar stationary phases and may provide a better understanding of the retention mechanism in HILIC.
Instead of measuring the absolute amount or volume of the adsorbed water layer, a quantitative ratio of the volumes of the adsorbed water layer and the mobile phase is proposed for the evaluation of the polar stationary phases. A simple method based on toluene elution volume was developed to measure the volume ratio without the need to acquire the packing materials. This method was used to generate the volume ratio data for 25 polar stationary phases with different surface chemistry and packing properties selected for this study. Experimental factors that can influence the volume ratio have also been investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
All the polar stationary phases selected for this study were either purchased from or kindly donated by the column manufacturers. Table 1 presents the details of all the stationary phases including stationary phase chemistry, particle size, pore size, and column dimension. HPLC grade acetonitrile (ACN) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Water was obtained from an in-house Milli-Q water purification system (Millipore, Bedford, USA). Ammonium acetate (ultrapure grade) was provided by Amresco (Solon, OH, USA). Stock solutions of ammonium acetate (100 and 200 mM) were prepared by dissolving the appropriate amount of ammonium acetate in purified water. The pH of the stock ammonium acetate solutions was in the range of 6.8 to 7.0 and no additional pH adjustment was made. The mobile phase was mixed online by quaternary gradient pumps from acetonitrile, water, and the ammonium acetate stock solutions at various proportions to achieve the desired acetonitrile content and ammonium acetate concentration. Toluene was spiked into a mixture of ACN and water with the composition matching that of the mobile phase as much as possible. Toluene concentration was adjusted to obtain an appropriate peak size.

Table 1.
Detailed Information of the polar stationary phases.
An Agilent 1260 HPLC system (Palo alto, CA, USA) equipped with an online vacuum degasser, a quaternary gradient pump, an autosampler, a thermostatted column compartment, and a variable UV detector was used for all the experiments. Toluene was detected at 254 nm and the elution time was recorded by ChemStation for LC and LC/MS (Rev. C. 01. 06., Agilent Technologies). The flow rates (1.0, 0.5, and 0.2 mL/min) were adjusted based on the column inner diameters (4.6, 3.0, and 2.1 mm ID columns). The injection volume was 2 µL.
3. Results
3.1. The Volume Ratio
Toluene is considered unable to penetrate into the water layer adsorbed on the surface of polar stationary phases, and has been used to estimate the pore volume occupied by the water-rich liquid layer [19]. Both coulometric titration and frontal analysis results demonstrate that the amount of the adsorbed water on the polar surface is minimal when the acetonitrile content is above 99% (v/v) [16,17]. Hence, it is reasonable to assume that the residual amount of water remaining on the polar surface is negligible in pure acetonitrile. In the mobile phase of an acetonitrile and water mixture, the toluene elution time (tM) has been found to decrease as the water content increases in the mobile phase, indicating a thicker water-rich liquid layer on the stationary phase [10,20]. Therefore, the difference of the toluene elution volumes in the pure acetonitrile (VACN) and a mobile phase containing a specific level of acetonitrile (VM) provides a good estimate of the volume of the water-rich liquid layer (VW):
whereas tACN and tM are the toluene elution time in the pure acetonitrile and the mobile phase, respectively, and F is the flow rate. The molecular simulation study by Tallarek and coworkers reveals that a diffuse liquid layer exists on the top of the tightly bound water layer adsorbed on the polar surface of the stationary phase, and there is an increasing amount of acetonitrile in the diffuse layer extending to the bulk mobile phase [18]. However, there is not a clear boundary between the diffuse layer and the bulk mobile phase due to miscibility of acetonitrile and water. It should be pointed out that the volume of the water-rich liquid layer estimated by the toluene elution time is not the same as the volume of the adsorbed water as determined by the direct titration method (e.g., Karl Fischer). Furthermore, the volume (VW) measured by the above equation only provides an estimate of the water-rich liquid layer since the actual values might slightly vary if another hydrophobic probe compound is used.
Since toluene is not retained on the polar stationary phases, the toluene elution volume also represents the mobile phase volume (VM). Knowing the volume of the water-rich liquid layer (VW) and the mobile phase volume (VM), a volume ratio (β) can be calculated for the mobile phase containing specific acetonitrile levels:
The volume ratio (β) indicates the relative volume of the water-rich liquid layer normalized by the mobile phase volume. In the hydrophilic partitioning model, the water-rich liquid layer can be considered as de facto stationary phase, and hence the volume ratio can be used as an estimate of the phase ratio. In the mobile phase conditions where other retention mechanisms (e.g., adsorption) have significant contributions to the overall retention, the water-rich liquid layer does not represent the entire stationary phase and the volume ratio (β) should not be used to estimate the actual phase ratio. The phase ratio involved in the adsorption mechanism is more related to the surface area of the packing material [17].
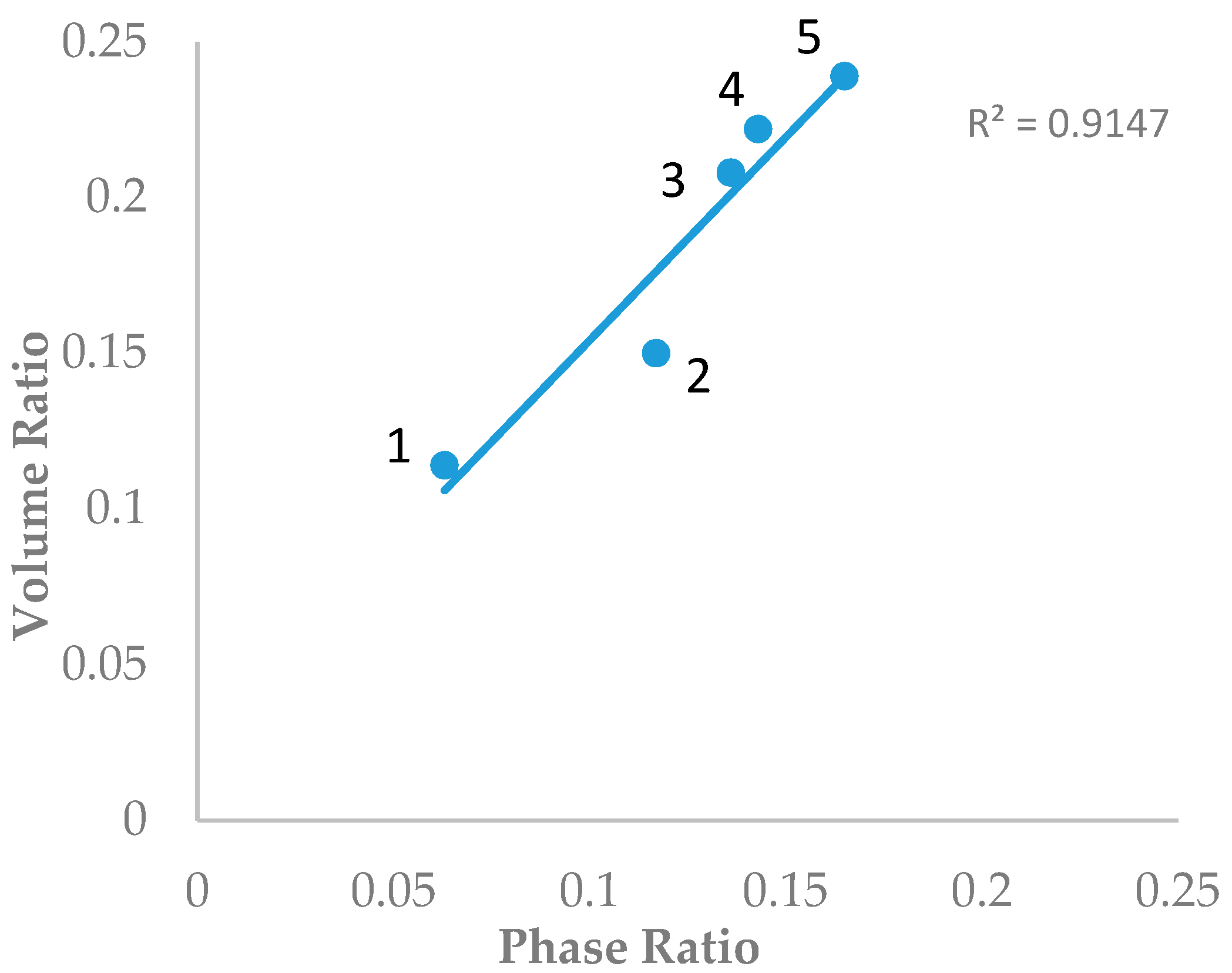
Dinh and coworkers calculated the phase ratio values of 12 columns using the water uptake data [17]. Five columns (ZIC-HILIC (200 Å), ZIC-cHILIC (100 Å), Atlantis HILIC (110 Å), TSKgel-Amide 80 (100 Å), and Polyhydroxyethyl A (200 Å)) were also included in this study. The volume ratio values (β) of the five stationary phases were determined using the toluene elution volume in the same mobile phase condition (80% ACN and 5 mM ammonium acetate) as in Dinh’s study. Figure 1 shows the plot of the volume ratio values (β) determined by the toluene elution volume and the phase ratio calculated from the water uptake data. A significant correlation (r2 ~ 0.915) was obtained by linear regression, indicating that the new method based on toluene elution volume is able to provide a reasonable estimate of the volume of the water-rich liquid layer. It is also noted that the volume ratio values based on the toluene elution volume are slightly higher than the phase ratio calculated from the water uptake data (Figure 1). A recent molecular dynamics study demonstrated that the immobilized liquid layer on the polar surface is not homogenous and has a complex structure, with a tightly bound water layer close to the polar surface and a diffuse layer with a gradually increasing acetonitrile component [18]. The water uptake data determined by the coulometric titration method in Dinh’s study is only the amount of water in both the bound and diffuse layers. The solubility of toluene is reported to be only 0.11% in the water–acetonitrile mixture containing 8.35% acetonitrile [21]. The toluene elution volume depends on the depth of penetration into the diffusion layer and definitely includes some acetonitrile in the diffuse layer. Hence, the volume of the water-rich liquid layer probed by toluene should be slightly higher than the volume of the adsorbed water determined by Karl Fischer titration.
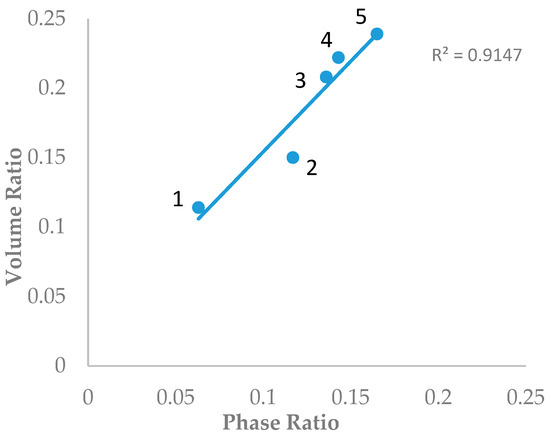
Figure 1.
Correlation of the volume ratio based on the toluene elution time and the phase ratio based on the water uptake data. Columns labels: 1: Atlantis hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC) column (5 µm, 96 Å, 250 mm); 2: ZIC-HILIC (3.5 µm, 200 Å, 150 mm); 3: Hydroxyethyl A column (5 µm, 100 Å, 200 mm); 4: TSKgel Amide-80 column (3.5 µm, 100 Å, 100 mm); and 5: ZIC-cHILIC column (3 µm, 100 Å, 150 mm).
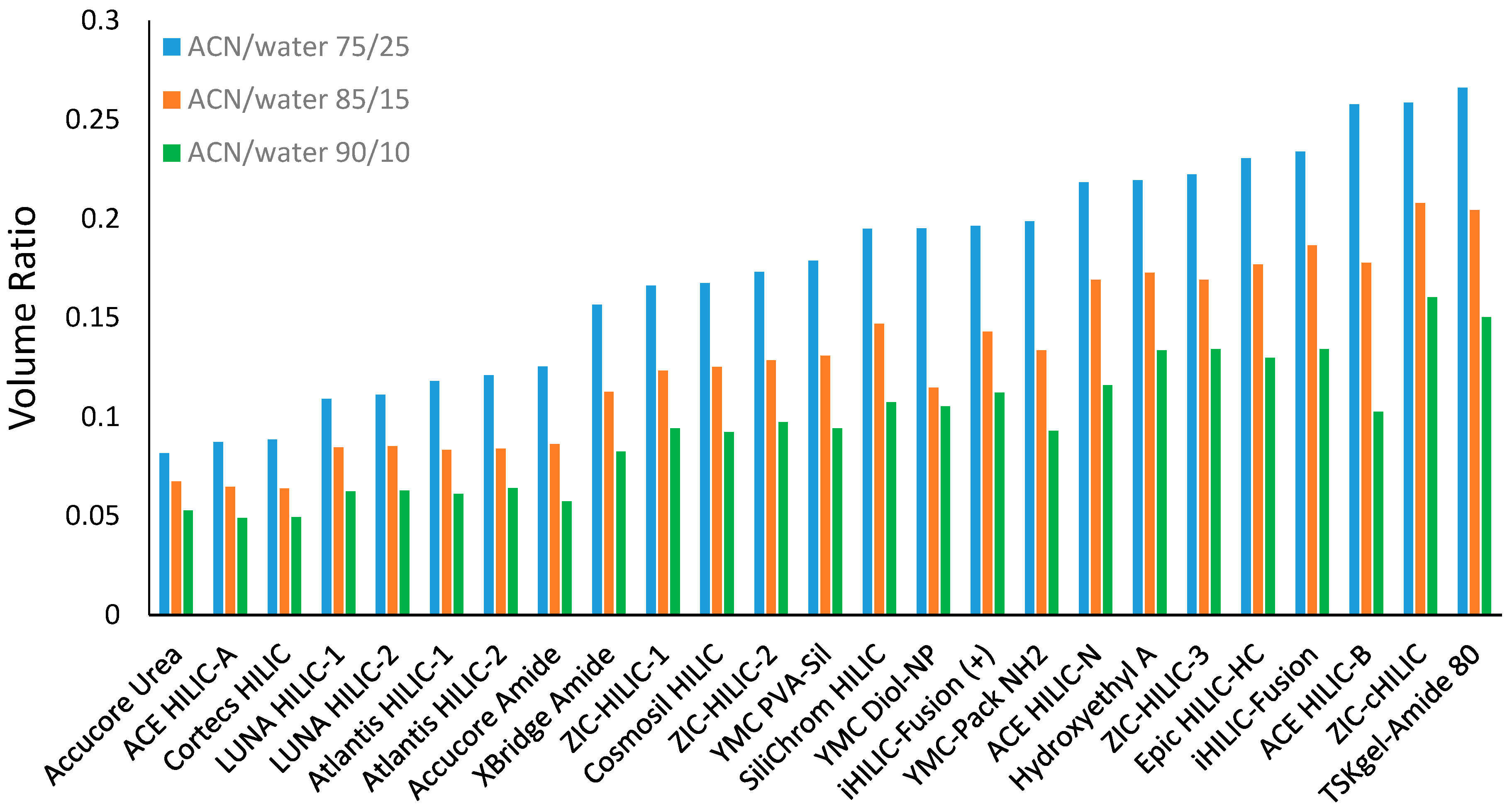
The volume ratio values were determined for all the selected stationary phases using the toluene elution volume in the mobile phase containing 75%, 85%, or 90% ACN and 5 mM ammonium acetate. As shown in Figure 2, the volume ratio varies significantly among the stationary phases investigated in this study. The TSKgel-Amide 80 column was found to have the highest volume ratio among all the selected stationary phases. The zwitterionic phases have been reported to have relatively thicker water-rich liquid layers [16,17]. Some zwitterionic phases (e.g., ZIC-cHILIC, iHILIC-fusion, and ZIC-HILIC phases) exhibited relatively higher volume ratio values. However, it is noticed that the volume ratio was lower for two ZIC-HILIC phases (ZIC-HILIC-1 and ZIC-HILIC-2 in Figure 2), both with a large pore size (200 Å). The ZIC-HILIC phase with the pore size of 200 Å had a significantly lower volume ratio than the one with the pore size of 100 Å but the same particle size (3 µm). In contrast, the bare silica phases (e.g., Cortecs HILIC and Atlantis HILIC) showed very small volume ratios in line with low water adsorption and water uptake data as previously reported [16,17]. It is also interesting to note that relatively low volume ratio values were observed in the superficially porous silica-based phases (Cortecs HILIC, Accurcore Urea, and Accurcore Amide), probably because the superficially porous materials had smaller total surface area. In addition, only a small difference in the volume ratio was found in the stationary phases (Atlantis HILIC, LUNA HILIC, and ZIC-HILIC) with different particle size but similar pore size.
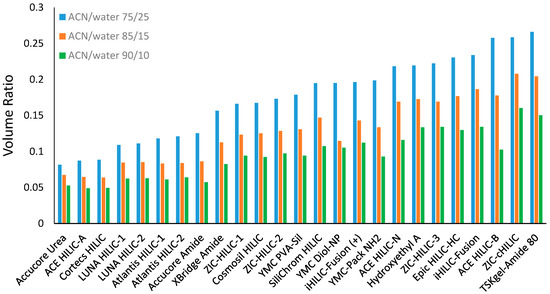
Figure 2.
The volume ratio values (β) for the selected stationary phases in the mobile phase containing 75%, 85%, and 90% ACN. All the mobile phase contains 5 mM ammonium acetate. Column temperature is 25 °C.
3.2. Factors Afffecting the Volume Ratio
It is well known that the acetonitrile content in the mobile phase has a direct effect on the water-rich liquid layer [10,20]. The effect of the mobile phase composition is expected to impact the volume ratio values. Figure 2 shows the volume ratio values of all the stationary phases measured in the mobile phase containing 75%, 85%, and 90% acetonitrile. In general, the volume ratio decreases as the acetonitrile content increases from 75% to 85% and 90% in the mobile phase, indicating a diminished water-rich liquid layer. Comparing to the volume ratio in the mobile phase containing 75% acetonitrile, the volume ratio decreases by 26 ± 5% (range 17–41%) and 45 ± 5% (range 35–60%) in the mobile phase containing 85% and 90% acetonitrile, respectively. It is worth noting that there is still a significant volume of the water-rich liquid layer in the mobile phase containing 90% acetonitrile. This implies that hydrophilic partitioning may play an important role in determining the retention in the mobile phase with high acetonitrile content.
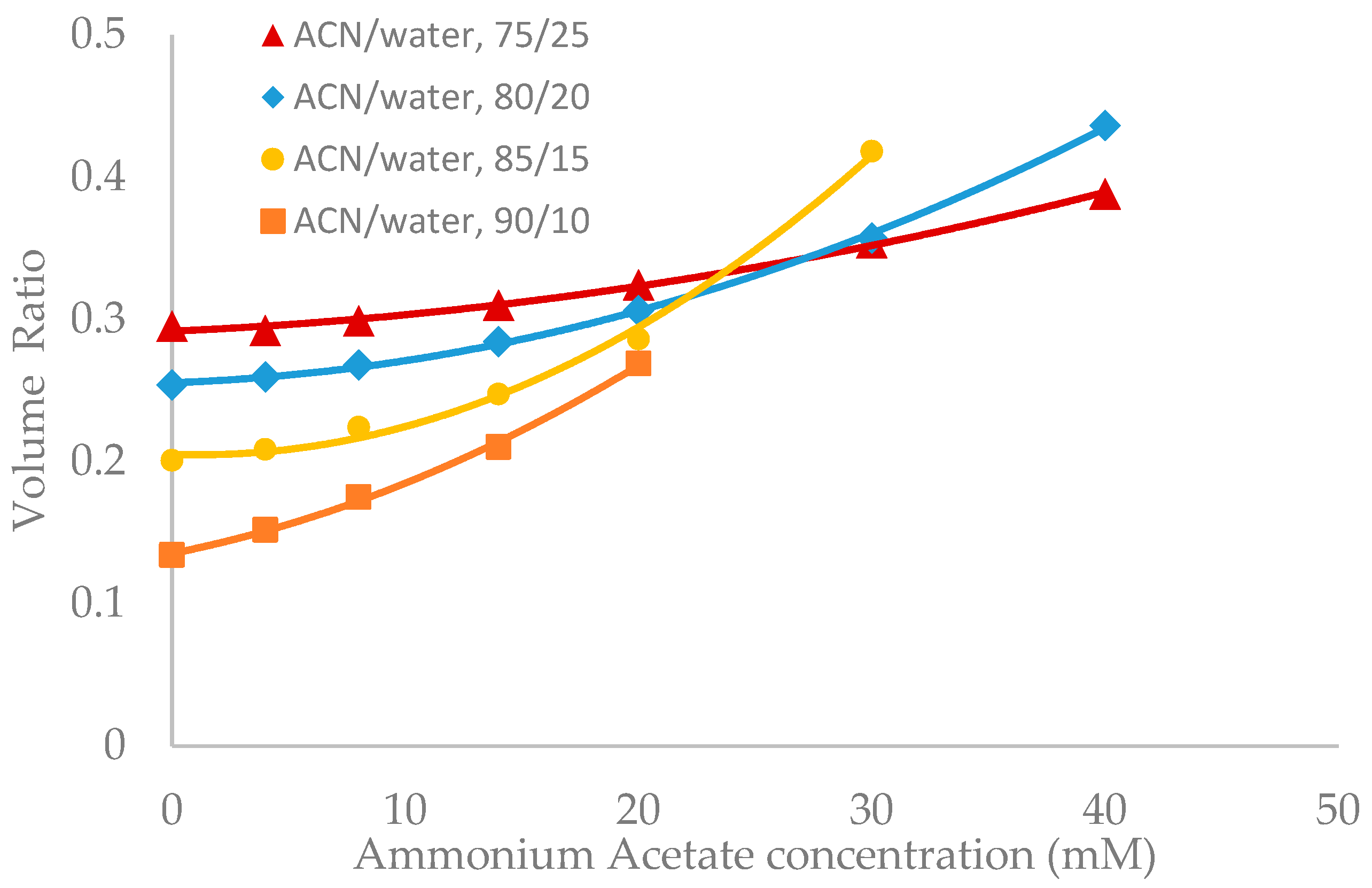
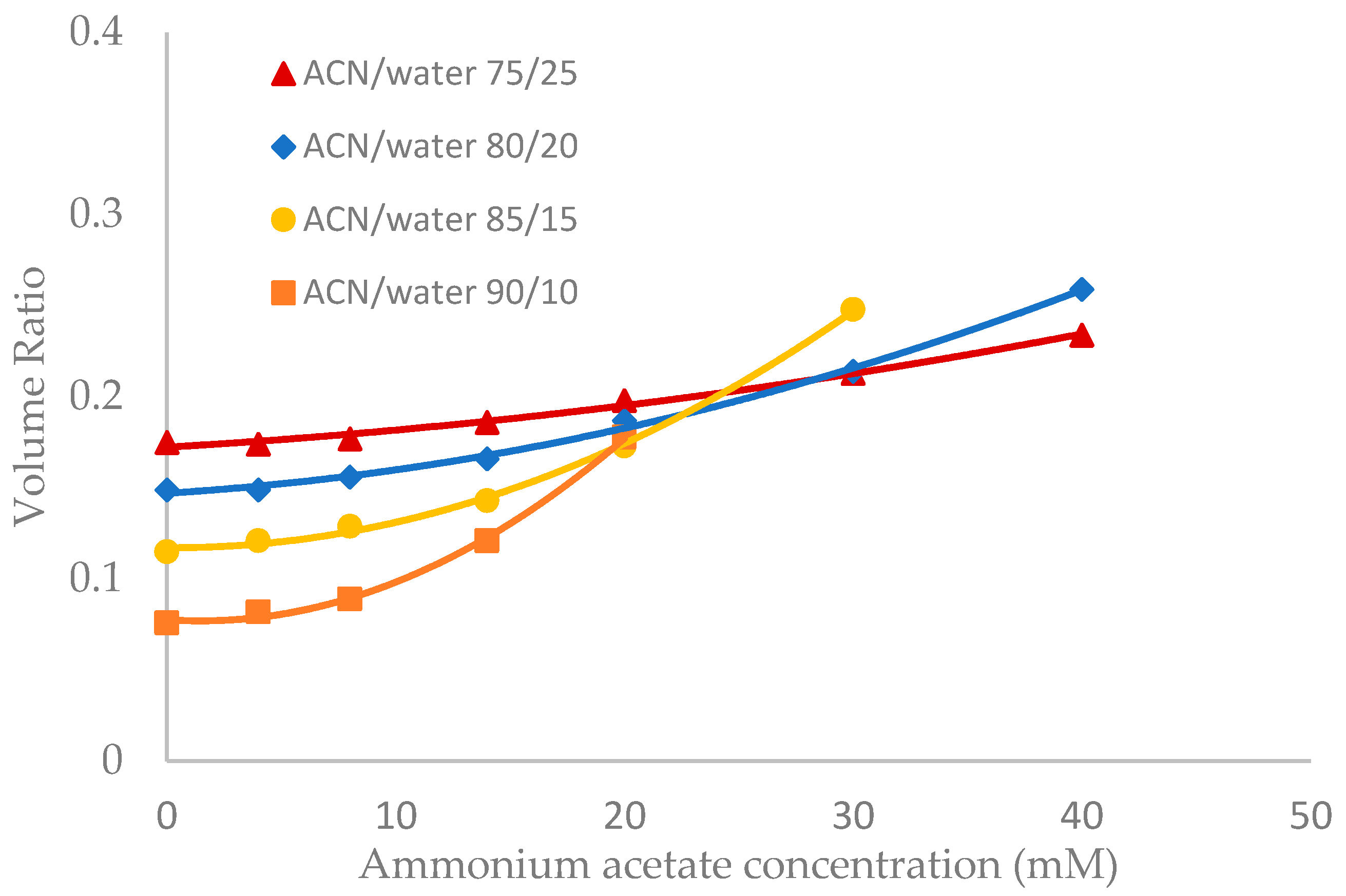
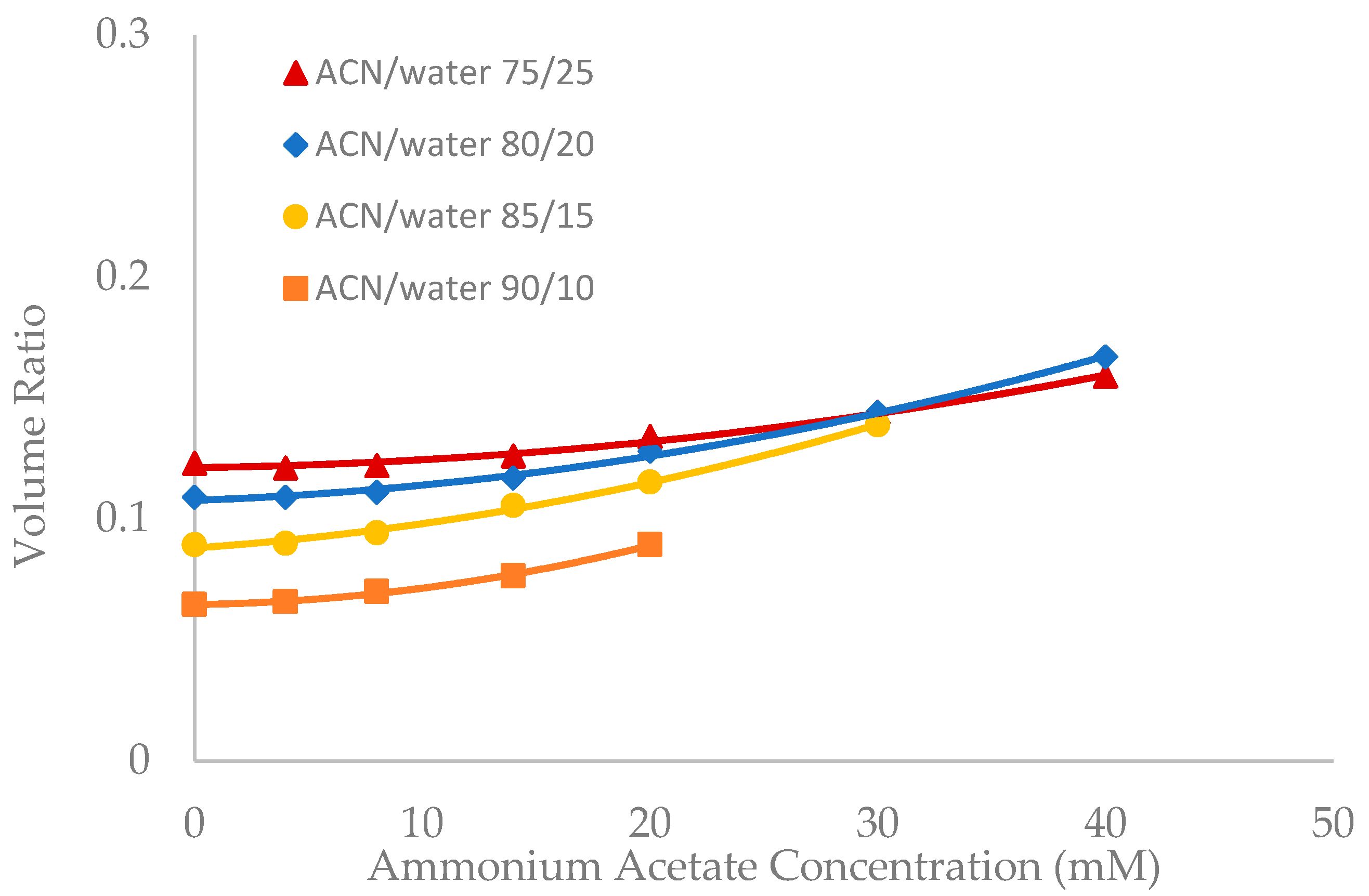
Salt concentration in the mobile phase has been observed to have a significant effect on the retention of polar compounds in HILIC even in the mobile phase condition where there are no electrostatic interactions between the solutes and the stationary phase [10,13,21]. The toluene elution time was found to decrease with increasing salt concentration in previous studies [10,20]. This would be translated into an increase in the volume ratio values. The volume ratio values of three stationary phases (ZIC-HILIC, XBridge Amide and LUNA HILIC) were determined in the mobile phase containing various acetonitrile levels and ammonium acetate concentration. Ammonium acetate concentration ranged from 4 to 40 mM in the mobile phase containing 75% and 80% acetonitrile, but was decreased to 30 mM and 20 mM in the mobile phase containing 85% and 90% acetonitrile out of solubility concerns. As shown in Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5, the volume ratio values of the three stationary phases increase in a nonlinear fashion with ammonium acetate concentration in all the mobile phase conditions. The increase in the volume ratio provides a more direct evidence that there is an expansion of the water-rich liquid layer, most likely the diffuse layer at higher ammonium acetate concentrations as originally speculated by the author [13]. The volume ratio data in the mobile phase containing various levels of acetonitrile reveals that ammonium acetate concentration seems to have a more significant effect on the water-rich liquid layer when the acetonitrile level is high in the mobile phase (85% and 90%). The volume ratio values for the ZIC-HILIC and XBridge Amide phases in the mobile phase containing 85% acetonitrile are even higher than that in the mobile phase containing 75% and 80% acetonitrile at 30 mM ammonium acetate (Figure 3 and Figure 4). In comparison, the volume ratio of the LUNA HILIC phase increases less dramatically in the mobile phase containing higher levels of acetonitrile (85% and 90%) possibly due to its weaker ability to retain the water-rich liquid layer (Figure 5). These results demonstrate that increasing the salt concentration can be an important means to manipulate the adsorbed water layer and in turn the retention in HILIC. It should be pointed out that these results are on valid for ammonium acetate. Caution should be taken when extending the conclusion to other types of salts, as point out by Alpert [21].
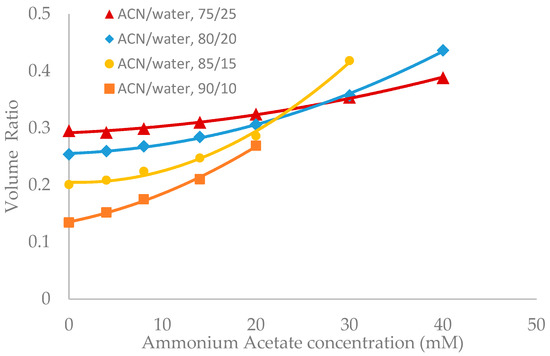
Figure 3.
The effect of ammonium acetate concentration on the volume ratio values (β) for ZIC-HILIC (3.5 µm, 100 Å, 4.6 × 150 mm). Column temperature is 25 °C.
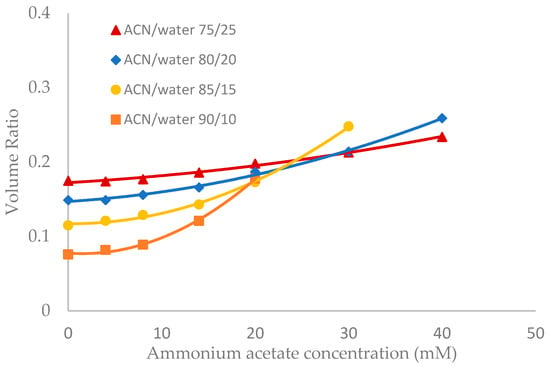
Figure 4.
The effect of ammonium acetate concentration on the volume ratio values (β) for XBridge Amide (3.5 µm, 142 Å, 4.6 × 150 mm). Column temperature is 25 °C.
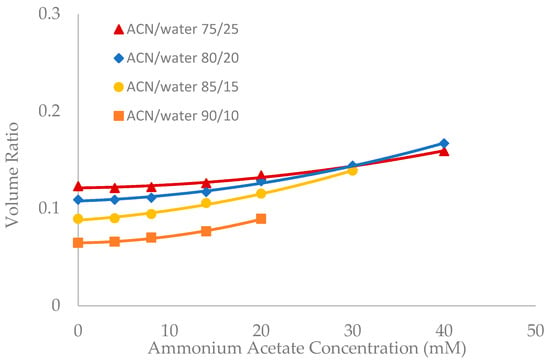
Figure 5.
The effect of ammonium acetate concentration on the volume ratio values (β) for LUNA HILIC (3.0 µm, 187 Å, 4.6 × 150 mm). Column temperature is 25 °C.
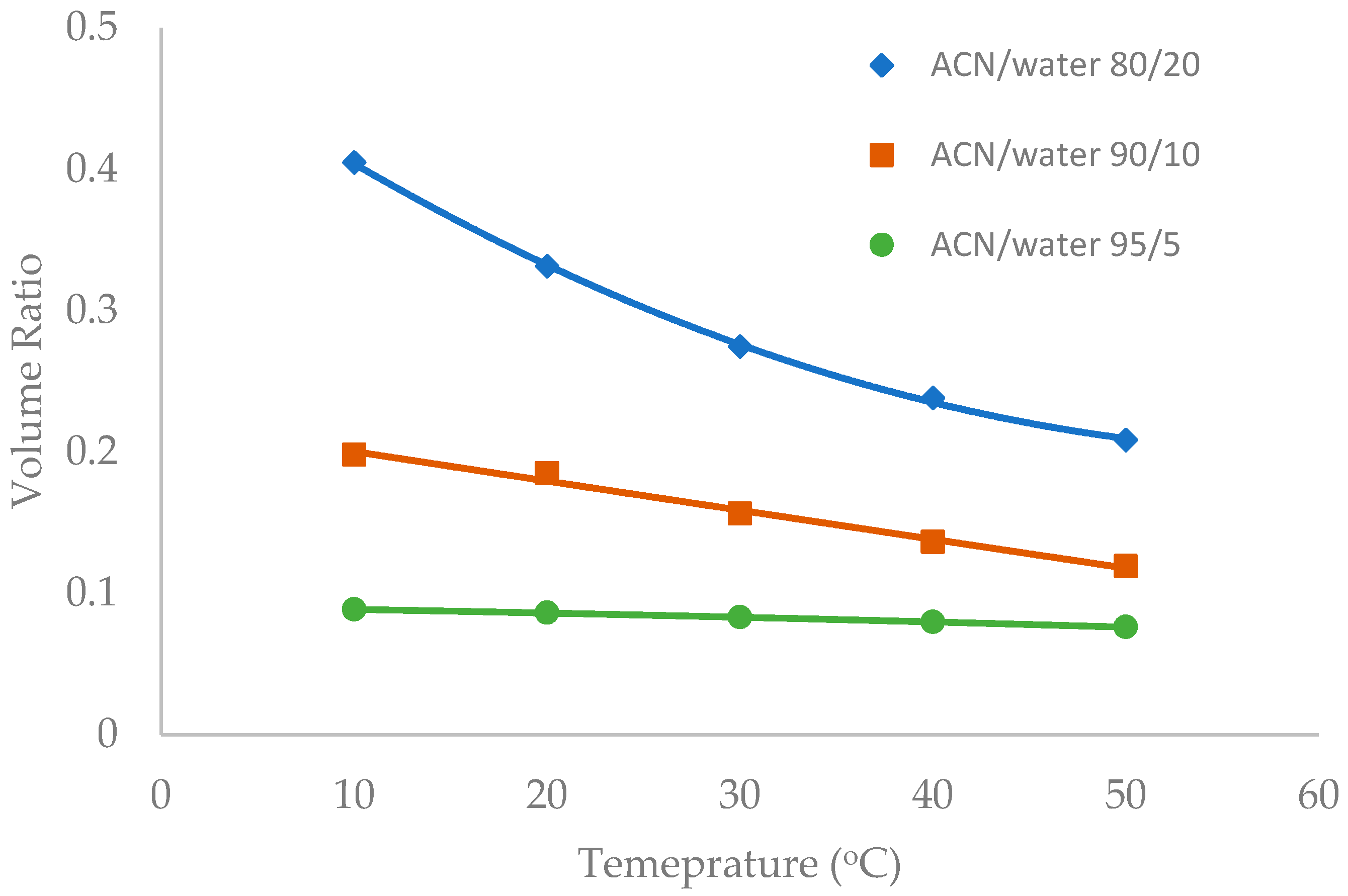
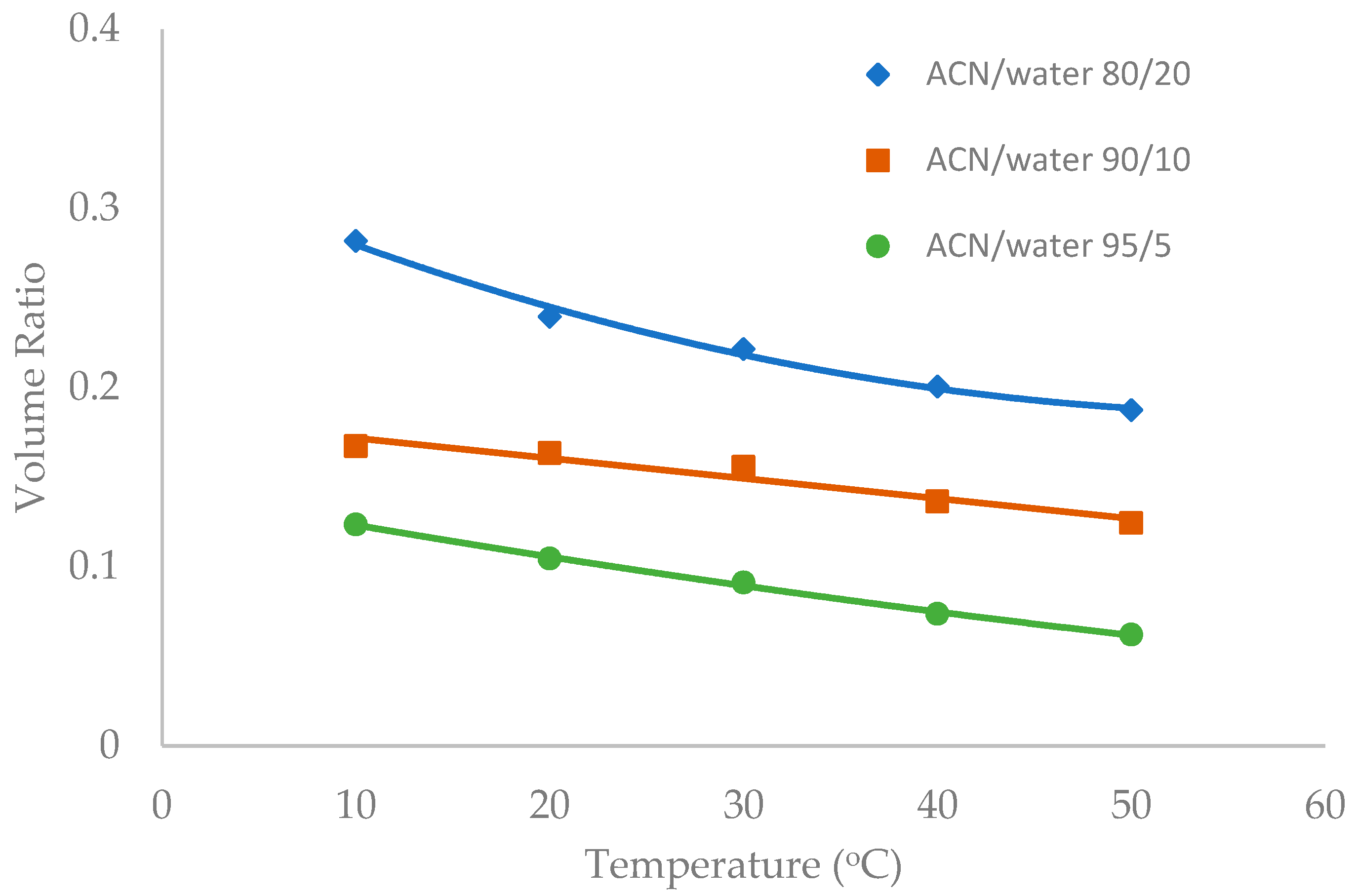
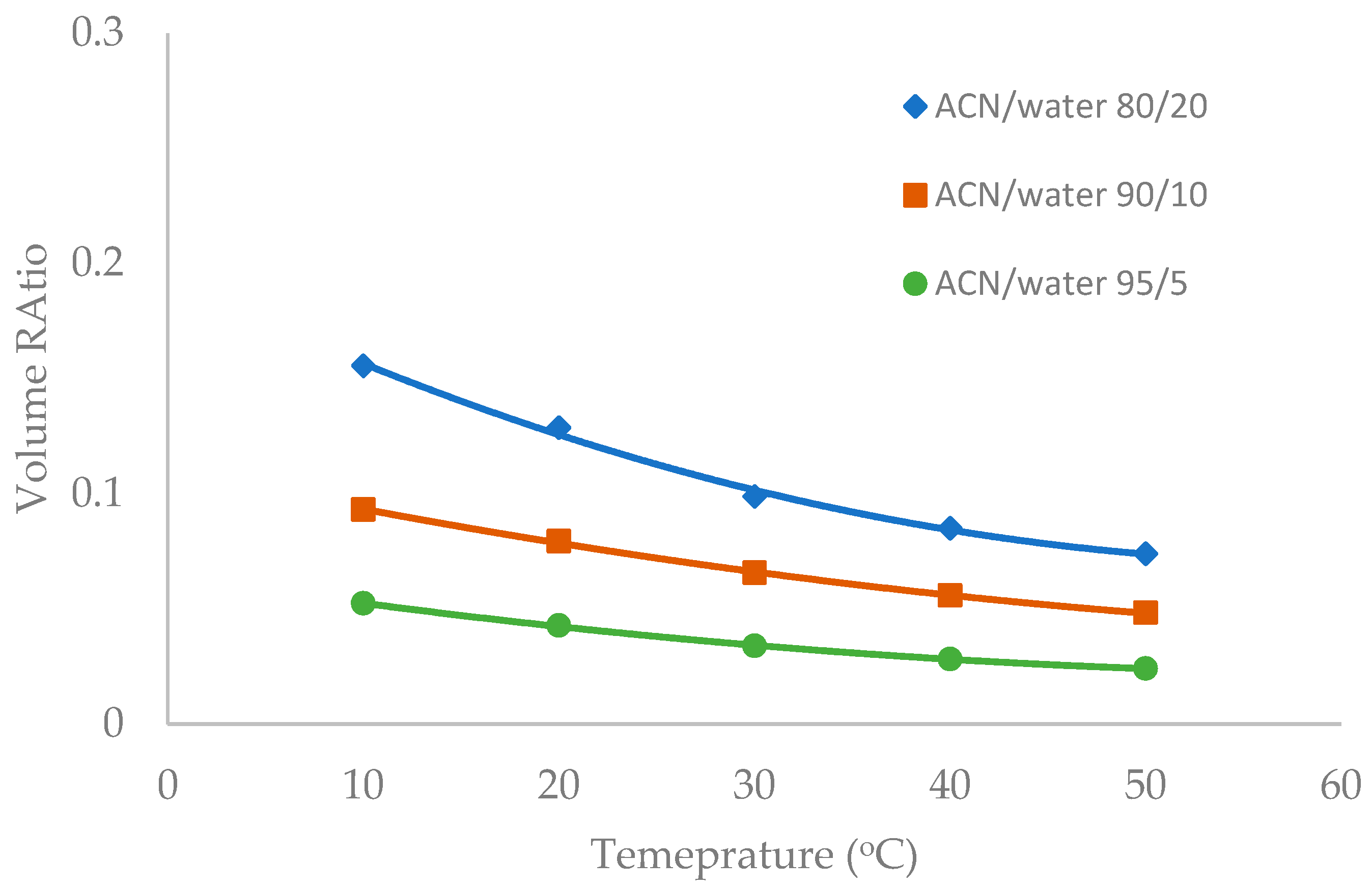
Temperature was observed to have an influence on the toluene elution time in our previous study [10]. The temperature effect was further investigated in this study in the mobile phase containing multiple levels of acetonitrile (80%, 90%, and 95%). Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8 show the volume ratio values for three stationary phases (TSKgel-Amide 80, ZIC-HILIC-3, and LUNA HILIC) in the temperature range of 10 to 50 °C. In general, increasing temperature leads to a decrease in the volume ratio in all the mobile phase conditions, indicating that the water-rich liquid layer is reduced at higher temperature. The temperature effect seems to be more prominent in the mobile phase containing 80% acetonitrile. Hydrogen bonding is believed to be involved in the formation of the adsorbed water layer on the polar surfaces [18], and the strength of hydrogen bonding is temperature dependent [22]. Increasing temperature may weaken hydrogen bonds holding water molecules together, thus reducing the water-rich liquid layer.
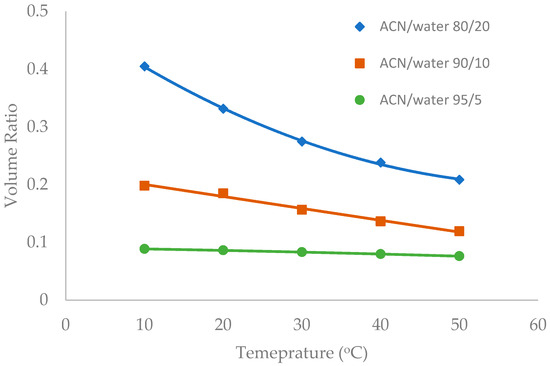
Figure 6.
The effect of column temperature on the volume ratio (β) values for TSKgel Amide-80 column (3.5 µm, 100 Å, 4.6 × 150 mm). The mobile phase contains 5 mM ammonium acetate.
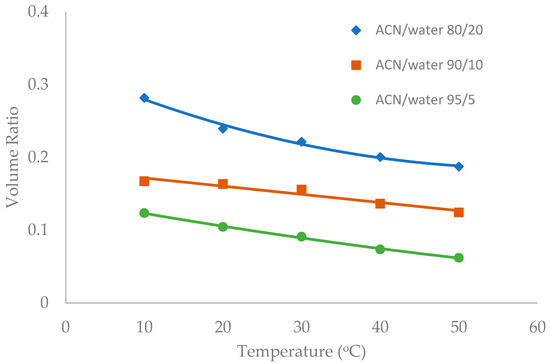
Figure 7.
The effect of column temperature on the volume ratio (β) values for XBridge Amide column (3.5 µm, 142 Å, 4.6 × 150 mm). The mobile phase contains 5 mM ammonium acetate.
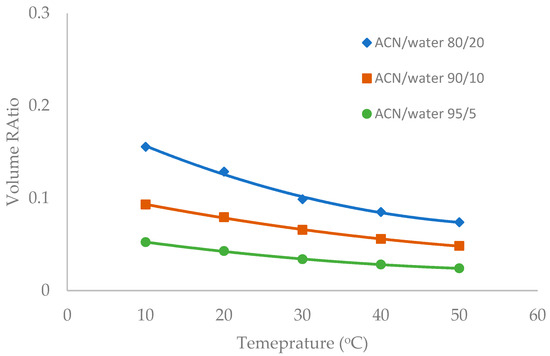
Figure 8.
The effect of column temperature on the volume ratio (β) values for LUNA HILIC column (3.0 µm, 187 Å, 4.6 × 150 mm). The mobile phase contains 5 mM ammonium acetate.
4. Conclusions
The volume ratio is proposed to be a quantitative measure of the water-rich liquid layer on the surface of the polar stationary phases in HILIC and can be easily determined using the toluene elution volume. Significant correlation between the volume ratio values and the water uptake data from coulometric titration suggests that the volume ratio is a valid alternative measure of the water-rich liquid layer. In the hydrophilic partitioning model, the volume ratio would be indicative of the phase ratio, which may be directly related to the retention in HILIC. The volume ratio values were generated for 25 stationary phases including those commonly used in HILIC separation. The results indicate that the water-rich liquid layer varies significantly in the stationary phases with different surface chemistry. The pore size seems to be a more important factor than the particle size in influencing the water-rich liquid layer. In addition, the acetonitrile content and salt concentrations in the mobile phase have significant effects on the volume ratio. Higher acetonitrile content decreases the volume ratio and reduces the water-rich liquid layer, but high ammonium acetate concentration has the opposite effect. Higher column temperature is also found to diminish the water-rich liquid layer especially in the mobile phases containing lower levels of acetonitrile. These findings have a great potential to be used as the effective means in adjusting the retention in method development.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.G.; data curation, N.B., B.F., I.S.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.G.; writing—review and editing, Y.G.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Wen Jiang and David Lentz for providing some of the stationary phases used in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ikegami, T. Hydrophilic interaction chromatography for the analysis of biopharmaceutical drugs and therapeutic peptides: A review based on the separation characteristics of the hydrophilic interaction chromatography phases. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 130–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, F.Q.; Ge, L.; Hu, Y.J.; Xia, Z.N. Recent applications of hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography in pharmaceutical analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 49–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, I.; Giera, M. Recent advances in liquid-phase separations for clinical metabolomics. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periat, A.; Krull, I.S.; Guillarme, D. Applications of hydrophilic interaction chromatography to amino acids, peptides, and proteins. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isokawa, M.; Kanamori, T.; Funatus, T.; Tsunoda, T. Recent advances in hydrophilic interaction chromatography for quantitative analysis of endogenous and pharmamceutical compounds in plasma samples. Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 2421–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novakova, L.; Havlikova, L.; Vlckova, H. Hydrophilic interaction chromatography for polar and ionizable compounds by UHPLC. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 63, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panderi, I.; Taxiarchi, E.; Pistos, C.; Kalogria, E.; Vonaparti, A. Insights into the mechanism of separation of biophsphonates by zwitterionic hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography: Application to the quantitation of risedronate in pharmaceuticals. Separations 2019, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y. Recent progress in the fundamental understanding of hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Analyst 2015, 140, 6452–6466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, A.J. Hydrophilic-interaction chromatography for the separation of peptides, nucleic acids and other polar compounds. J. Chromatogr. A 1990, 499, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Shah, R. Detailed insights into the retention mechanism of caffeine metabolites on the amide stationary phase in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1463, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCalley, D.V. Understanding and manipulating the separation in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1523, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCalley, D.V. Study of the selectivity, retention mechanisms and performance of alternative silica-based stationary phases for separation of ionized solutes in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1273, 3408–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Gaiki, S. Retention behavior of small polar compounds on polar stationary phases in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1074, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpert, A.J. Electrostatic repulsion hydrophilic interaction chromatography for isocratic separation of charged solutes and selective isolation of phosphopeptides. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikberg, E.; Sparrman, T.; Viklund, C.; Jonsson, T.; Irgum, K. A 2H nuclear magnetic resonance study of the state of water in neat silica and zwitterionic stationary phases and its influence on the chromatographic retention characteristics in hydrophilic interaction high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 6630–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soukup, J.; Jandera, P. Adsorption of water from aqueous acetonitrile on silica-based stationary phases in aqueous normal-phase liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1374, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, N.P.; Jonsson, T.; Irgum, K. Water uptake on polar stationary phases under conditions for hydrophilic interaction chromatography and its relation to solute retention. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1320, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melnikov, S.M.; Holtzel, A.; Seidel-Morgenstern, A.; Tallarek, U. Adsorption of water-acetontrile mixtures to model silica surface. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 6620–6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCalley, D.V.; Neue, U.D. Estimation of the extent of the water-rich layer associated with the silica surface in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A. 2008, 1192, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, G.; Grosse, S.; Letzel, T. Study of the retention behavior in zwitterionic hydrophilic interaction chromatography of isomeric hydroxyl- and aminobenzoic acids. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1235, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, A. Effect of salts on retention in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1538, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougherty, R.C. Temperature and pressure dependence of hydrogen bond strength: A perturbation molecular orbital approach. AIP J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 109, 7372–7378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).