Abstract
In the over 1,800 articles published since their inception in 2001, most deep eutectic solvents (DES) synthesized have been hydrophilic. The low cost, low toxicity, and bioavailability of DES make the solvent ‘green’ and sustainable for diverse applications. Conversely, the hydrophilicity of DES limits their practical application to only polar compounds, which is a major drawback of the solvent. For the past three years, hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents (HDES) have emerged as an alternative extractive media capable of extracting non-polar organic and inorganic molecules from aqueous environments. Due to the infancy of HDES, for the first time, this mini-review summarizes the recent developmental advances in HDES synthesis, applications, challenges, and future perspectives of the solvent. In the future, it is believed HDES will replace the majority of toxic organic solvents used for analytical purposes.
1. Introduction
Chemists and process engineers continue to search for greener solvents capable of replacing conventional toxic organic solvents in their daily activities [1,2,3,4]. Due to the environmental, health, and safety implications of some organic solvents, the impetus in solvent replacement is growing globally. The challenge stems from the difficulty to acquire more sustainable and greener alternatives to toxic volatile organic chemicals with the desired chemical and physical properties [2]. The increasing demand for solvents has been forecasted to reach 9.6 billion pounds by 2020 in the United States (US Solvent Market Projection; last accessed on 14 January 2019). This growth is driven by a strict US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations toward more eco-friendly and biodegradable solvent alternatives with reduced emissions and toxicity. A little over a decade ago, deep eutectic solvents (DES) emerged as a new generation of ionic liquids (ILs) synthesized by combining a hydrogen bond acceptor (HBA) and a hydrogen bond donor (HBD) [5,6,7] with remarkably low volatility. Since most DES are synthesized by combining naturally occurring proton donors like fatty acids, urea, glucose, and glycerol with acceptor molecules like choline chloride, the combined eutectic mixture is environmentally benign, safe, and sustainable [5,6,8,9,10,11,12]. The advantages of using DES for extraction goes beyond their simple preparation procedures, greener nature, and easy tunability [11,13,14], as they are bioavailable and have low toxicity. DES chemical and physical properties are flexible, as they can be adjusted by either changing the constituents or by adding other compounds to form a ternary or a complex mixture. It is worth understanding the phase behavior of the DES in order to tune their physicochemical properties. Despite the numerous publications about DES since their first inception in 2001 [12,15], most of the research work has concentrated mainly on hydrophilic DES, which limits the solvents utilization to polar environments [12,16].
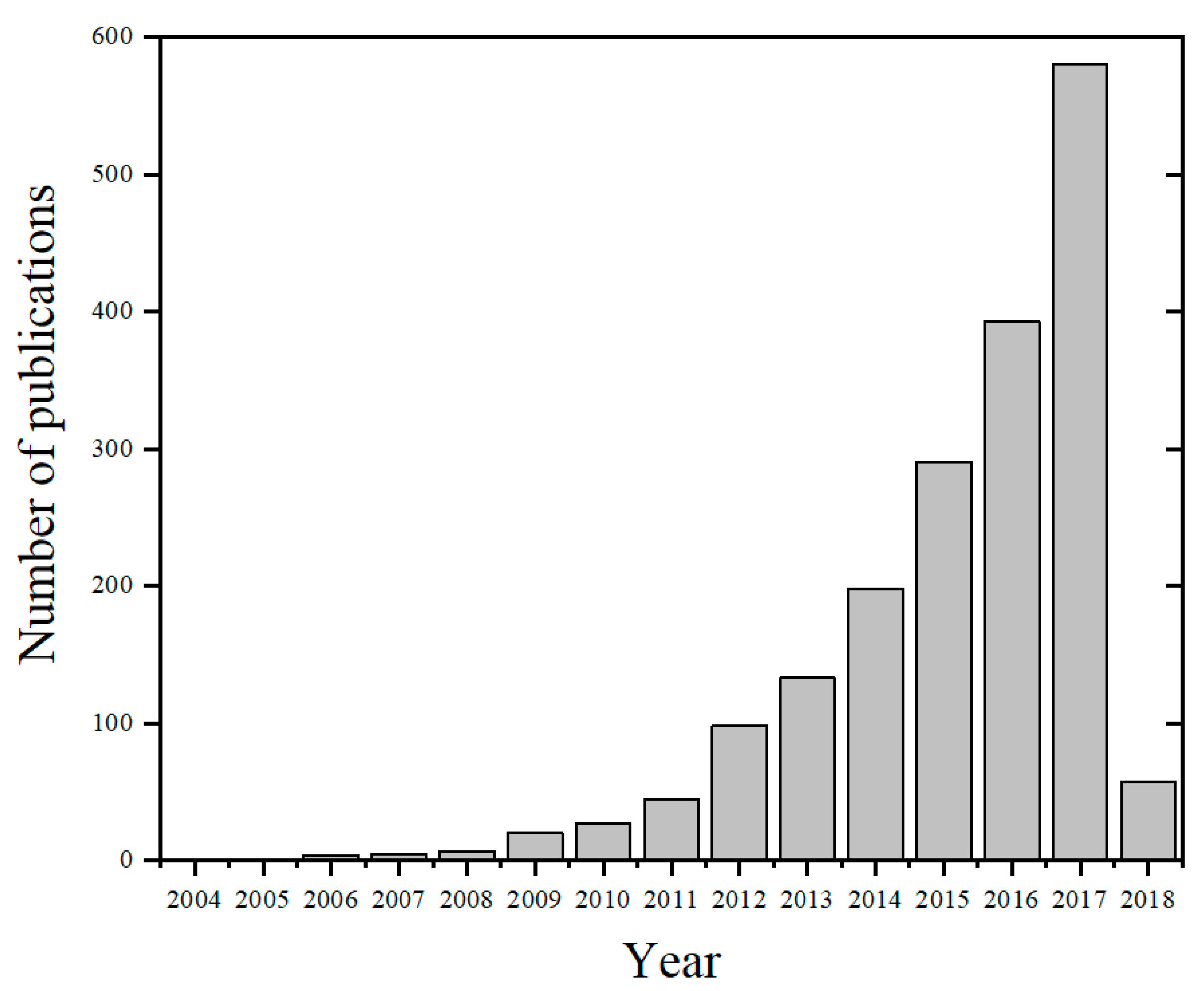
In an application that requires hydrophobic media, the common truth is that most chemists and process engineers still resort to toxic organic chemicals due to the scarcity of greener hydrophobic alternatives. This is a major drawback to the call for environmental sustainability. The availability of greener solvents in all of the four solvent categories, high basicity-low polarity, low basicity-low polarity, high basicity-high polarity, and low basicity-high polarity, is pivotal to ensuring sustainability [17]. A hydrophobic ILs involving [NTf2] anion, ([Bmim][NTf2]), was reported to be more efficient in the enzymatic synthesis of biodiesel compared to the hydrophilic [PF6] and [BF4] anionic counterparts [18]. A review of the application of hydrophobic ILs in biodiesel synthesis is available [19]. To date, nearly all deep eutectic solvents are hydrophilic and are limited in applications that require high basicity and low water content such as liquid–liquid extraction (LLE). The concept of DES in extraction is still in its infancy [20] compared to ionic liquids, nonetheless, the increasing number of yearly publications make the field very promising. In Figure 1, a web of science search of the phrase "deep eutectic solvents" shows an increasing number of publications since 2004. Out of the 1860 hits, over 88% of DES articles are from 2013 to 2018. In addition, over 175 articles are considered as DES reviews for the past 5 years. The skyrocketing numbers have been biased towards hydrophilic DES rather than their hydrophobic counterparts. The concept of hydrophobic DES (HDES) was introduced by van Osch and co-workers [21] in 2015 when they combined diverse quaternary ammonium salts (QAS) with decanoic acid (DecA). The water-immiscible solvent was applied to extract water-insoluble volatile organic compounds, which reported a high extraction yield and efficiency [21]. Since then, active research is ongoing to investigate how HDES are synthesized and its application in diverse fields.
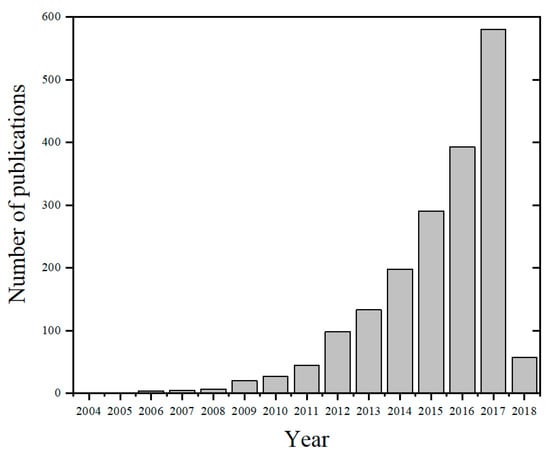
Figure 1.
Number of publications based on a web of science search for the phrase “deep eutectic solvent”. Date accessed: 10 February 2018.
This mini-review gives an overview of HDES synthesis and provides up-to-date insight into their various applications in the extraction and separation of biomolecules and inorganic metals. It should, however, be emphasized that detailed discussion on HDES synthesis, extraction techniques, and instrumental analysis of the analytes are beyond the scope of this article. Since the majority of reviews on DES captures only hydrophilic DES (DES with high water miscibility), this mini-review gives a brief and concise account on hydrophilic DES. This article differs from available DES reviews on extraction by offering a new overview of what HDES are, and further goes beyond to summarize the sporadic HDES applications in literature.
2. Formation, Classification, and Types of DES
Deep eutectic solvents are formed by mixing a hydrogen bond acceptor with hydrogen bond donor at a specific molar ratio resulting in melting point (mp) depression of the solvent. Deep eutectic solvents are classified into 4 categories (Table 1) with type III as a focus of attention in most research. The Cat+ in DES is usually quaternary ammonium, phosphonium, or sometimes sulfonium salt [12]. The X− is the anionic moiety often involved in hydrogen bonding with protons from the donor RZ group (R = alkyl group and Z = CONH2, COOH, or OH). Choline chloride is the most used QAS for DES synthesis due to its low cost, availability, biocompatibility, and low toxicity.

Table 1.
General Formula for deep eutectic solvents (DES) classification. Adapted from [12].
The chloride anion is readily available to interact with diverse proton donors through hydrogen bonding. Abbott and co-workers [12] found that choline chloride (mp = 302 °C) and urea (mp = 133 °C) interact to form a liquid at room temperature with a freezing point of 12 °C at 1:2 molar ratio. DES physicochemical properties like conductivity, viscosity, polarity, and thermal properties can easily be tuned by varying the constituent raw materials. Most of the synthesized DES reviewed [10,12,22] are hydrophilic. The type III DES are categorized into low-transition-temperature mixtures (LTTMs), natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES), carboxylic acid-based deep eutectic solvents [5,13,23], and therapeutic deep eutectic solvents (THEDES) [24,25].
3. Hydrophilic DES and Applications
The LTTMs are synthesized mostly by mixing natural high-melting-point starting materials, which form a liquid by hydrogen-bond interactions with notable applications in organic synthesis [26,27,28], biofuel processing [29,30], and catalysis [10,31]. Some of the underexplored fields of DES include biomass processing and liquid–liquid extractions or extractive distillation [22]. Nonetheless, a few reviews on DES for LLE have surfaced recently [7,20,32,33,34,35,36]. Hizaddin et al. [37] screened 94 DES by applying a conductor-like screening model for realistic solvents (COSMO-RS) and evaluated their potential usage for extractive denitrification of diesel. A comprehensive review of deep eutectic solvents and their application in modifying electrode surfaces for electrochemical sensing and biosensors has been published [38,39]. The use of DES as media for Candida antartica B lipase transesterification reactions is explained in detail [40]. Apart from LTTMs, other forms of DES from natural raw materials have evolved over the past decade in the form of natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES).
NADES were introduced when cellular constituents like fructose, glucose, citric acid, proline, and other metabolites formed a viscous liquid at defined molar ratios [41]. NADES synthesis, types, characterization and applications including their use in extraction and lignocellulosic biomass pretreatment have been previously reviewed elsewhere [36,42,43,44,45,46,47]. A recent review by Vanda et al. [48] looked into the evolution of NADES from ionic liquids and DES, and further expanded on the applications of NADES in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food, and agricultural settings. NADES can be used as solubilization agents for macromolecules and as media for enzymatic reactions [48].
Unlike LTTMs and NADES, THEDES are another subgroup of DES with one of their components as a pharmaceutically active ingredient (API). Commonly used API include acetylsalicylic acid, benzoic acid, ibuprofen, and phenylacetic acid [24,25]. In some instances, THEDES might be classified under NADES when both the active ingredients and the other raw materials are from natural sources. Developmental research is currently ongoing to develop THEDES which will be effective for drug delivery. Compared to water, choline chloride-urea and choline chloride-malonic acid DES improved their solubility with benzoic acid, danazol, griseofulvin, AMG517, and itraconazole by 5 to 22,000 folds [49]. This notable feature of DES makes them promising for pharmaceutical applications and in drug delivery. In view of this, developing HDES is eminent not only for liquid–liquid extraction but also as vehicles for drug solubilization.
4. HDES Synthesis (Common HBA and HBD)
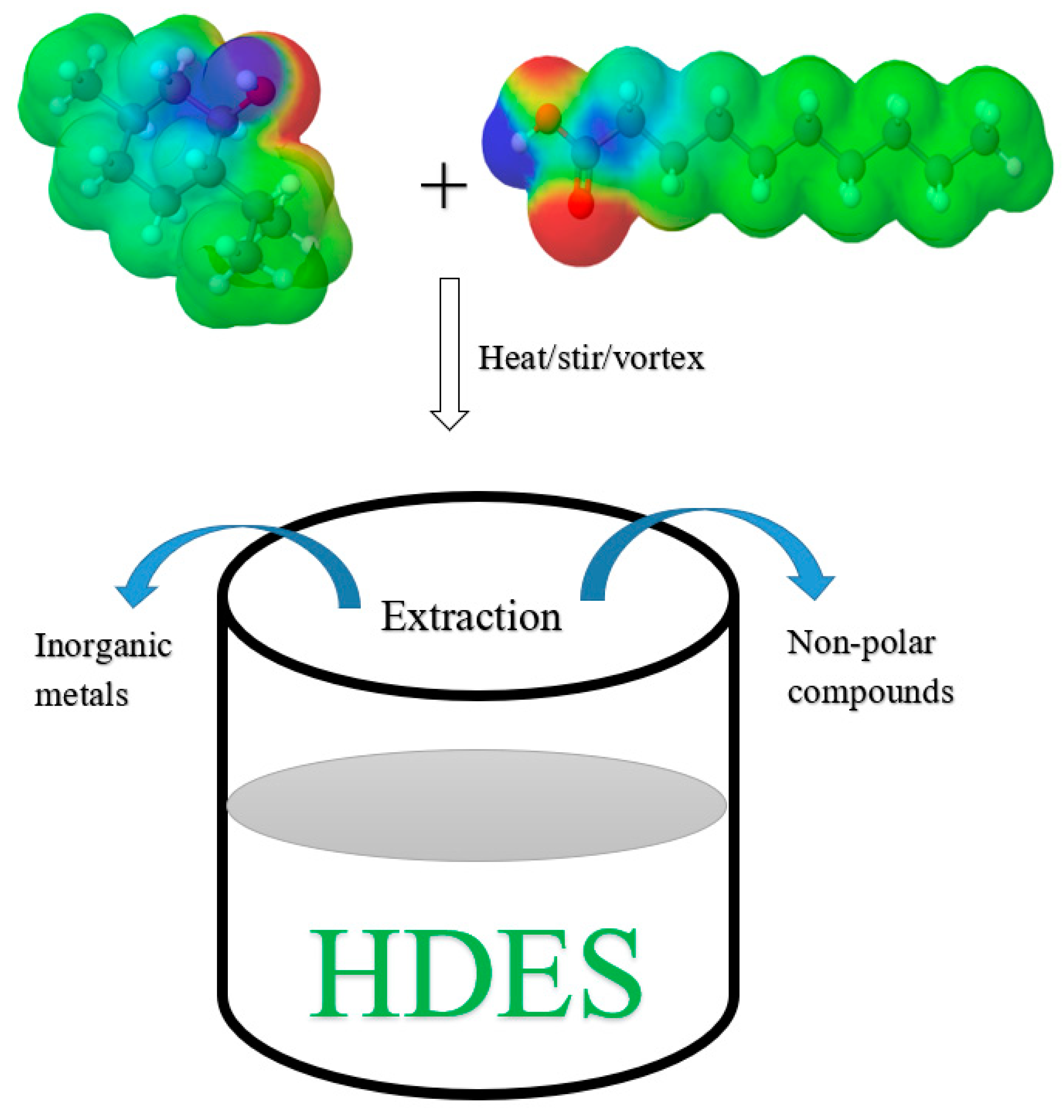
The synthesis of HDES is similar to hydrophilic DES. As shown in Figure 2, HDES can be synthesized by mixing DL-menthol (HBA) and DecA (HBD) at 1:1 molar ratio followed by heating, stirring, and/or vortexing. The cosmo polarity surface of both the donor and the acceptor molecules show three regions; blue = proton donating region with negative charge density, red = proton acceptor region with positive charge density, and green = hydrophobic region.
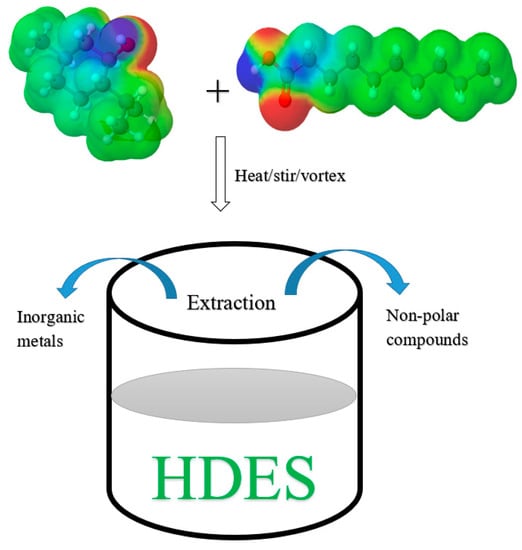
Figure 2.
Synthesis of hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents (HDES) from DL-Menthol (HBA) and Decanoic acid (HBD) at 1:1 molar ratio. The synthesized HDES can be used to extract non-polar compounds and transition metals. Graphics by MolView version 2.4.
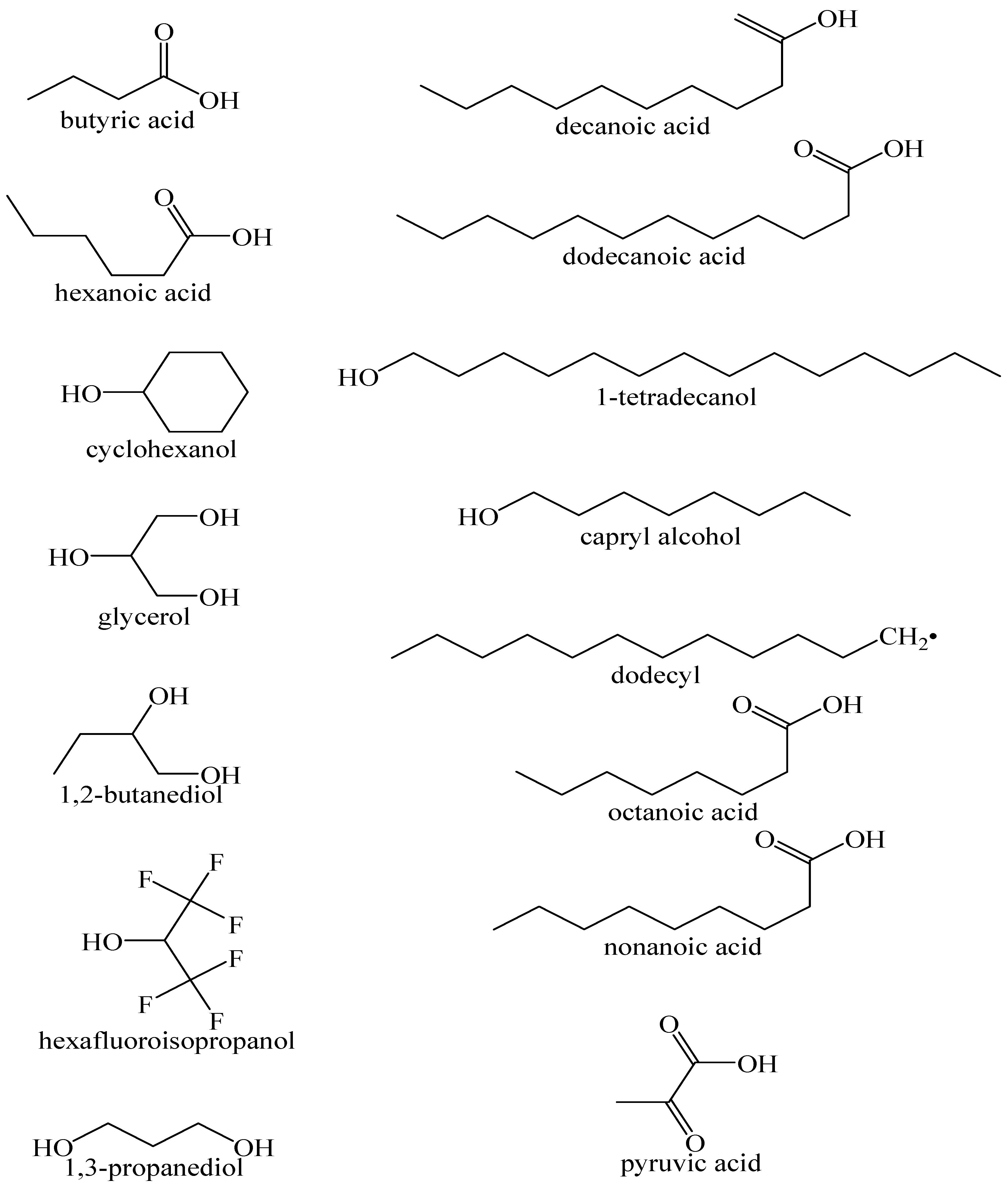
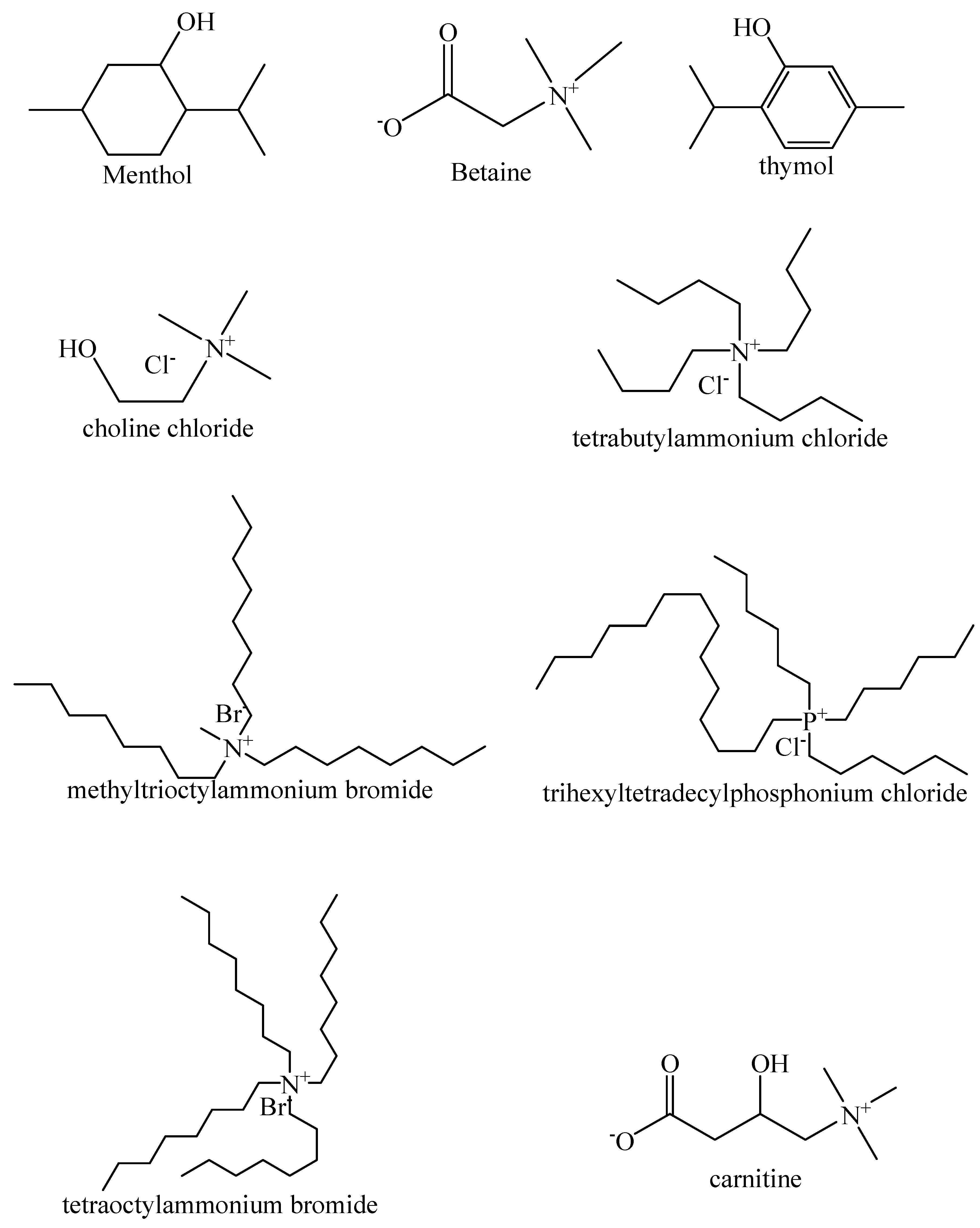
Among the HBAs, DL-menthol is gaining much popularity for its use in solvents for extraction whereas decanoic acid (DecA) is the most used HBD in HDES synthesis (Table 2). There is no single way for synthesizing HDES since this process depends on the starting raw materials. HDES can be synthesized by simply mixing the constituents at ambient temperature [50] or by heating as high as 80 °C with or without stirring [51,52]. Figure 3 and Figure 4 lists a number of hydrogen bond donors and hydrogen bond acceptors commonly used for HDES, respectively. The physicochemical properties of most HDES depend on the nature of the constituents combined. However, most HDES form clear and transparent liquids, and are viscous. Due to the hygroscopic nature of most quaternary ammonium salt, HDES synthesized are stored in a desiccator to prevent moisture absorption. The addition of water to HDES can lead to the formation of a ternary complex which could alter the physicochemical properties of the solvent.

Table 2.
Synthesis of HDES by combining HBA and HBD.
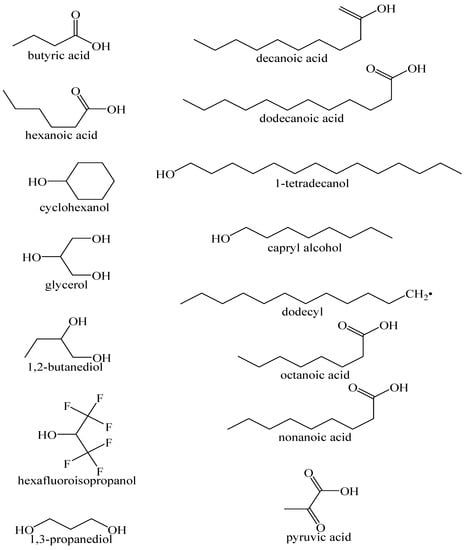
Figure 3.
Common HBD used for HDES synthesis.
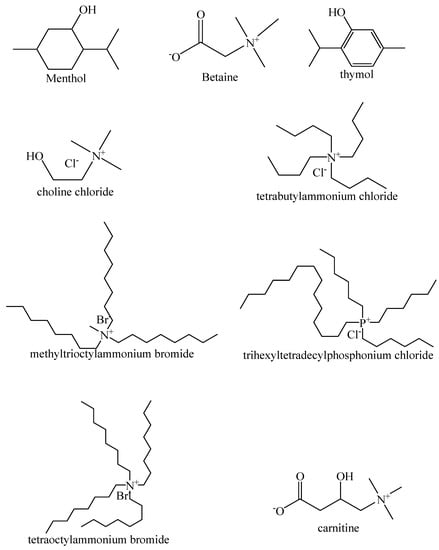
Figure 4.
Common HBA used for HDES synthesis.
In designing HDES for extraction, a critical consideration of the amount of the raw materials and their alkyl chain length should be noted. The physical and chemical properties of HDES were tailored for pyrethroids [53] and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) [54] extraction by modifying the molar ratio of the constituents. The high extraction efficiency of pyrethroids by dispersive liquid–liquid extraction (DLLE) is due to the high-density hydrogen bond donor, hexafluoroisopropanol, which is able to form water immiscible HDES with betaine or L-carnitine. During dispersive LLE, the high-density HDES containing the analyte lie at the bottom of the flask making it easier for collecting and analysis [53]. High-density HDES make dispersive LLE of nonpolar analytes from aqueous environment easier compared to most DES. In the extraction of bisphenol A, Florindo et al. [55] showed that octanoic acid (C8), nonanoic acid (C9), decanoic acid (C10), and dodecanoic acid (C12) can act as either a hydrogen bond acceptor (due to the carbonyl group) or a hydrogen bond donor (due to the hydroxyl group) to form HDES. Fatty acid-based DES can be synthesized to form a binary or a ternary mixture depending on the nature of applications required. Moderately high extraction efficiencies of 76.04%, 88.32%, and 81.81% were obtained by using C8–C12 (3:1), C9–C12 (3:1), and C10–C12 (2:1) HDES, respectively. Additionally, these phase change materials or long chain fatty acid eutectics can be modified to develop a new class of HDES to be used in water purification systems [55].
Low alkyl chain carboxylic acids like acetic acid, butyric acid, levulinic acid, hexanoic acid, and pyruvic acid have been used together with the DL-menthol or N4444-Cl for HDES synthesis [56]. Varying the alkyl chain of either the HBA or the HBD is necessary to tune the polarity of the HDES for a defined application. Martins et al. [57] recently designed and synthesized HDES from terpenes (thymol and L (-) menthol) and monocarboxylic acids and characterized the solvent through density measurements, viscosity, solid-liquid equilibria, and Kamlet-Taft solvatochromic parameters. Thymol-based HDES were found to be less viscous (1.3–50.6 mPas) and denser than L (-) menthol-based eutectic mixtures [57]. As expected, despite the similarities between thymol and L (-) menthol, the physical and chemical properties of their resulting solvent differ with thymol having higher hydrogen bonding acidity character and menthol having higher basicity behavior [57].
5. Applications of HDES in Extraction
DES hydrophobicity was introduced in 2015 by van Osch and co-workers, although the authors acknowledged earlier work involving hydrophobic menthol-based eutectic mixtures [21]. The first application of HDES involved liquid–liquid extraction of volatile fatty acids (VFAs) comprising of acetic, propionic, and butyric acid from the aqueous environment. The extraction efficiency of the VFAs was found to increase with increasing alkyl chain length. For example, N8881-Cl:DecA (1:2) efficiently extracted 38% acetic acid, 70.5% propionic acid, and 89.8% butyric acid [21]. The symmetric salt N8888-Cl and N7777-Cl, due to the steric hindrance of the alkyl chain makes the HDES much more hydrophobic and reduces its extraction capability to VFAs and accessibility to water. The high extraction efficiency of HDES compared to amine-based extractant (TOA) for VFAs could be attributed to the hydrophobicity of HDES which increases the dispersive interaction between the acid and the solvent [21,63]. Furthermore, due to the hydrogen bonding potential of HDES, the solvent could interact and/or extract both the dissociated and the undissociated forms of acetic, propionic, and butyric acid [21].
Since this first report, active research is ongoing to investigate how HDES could be synthesized from different raw materials and their possible applications in diverse fields. Table 2 provides a comprehensive overview of some up-to-date HDES synthesized and their physical appearances. Four different HDES synthesized from trioctylmethylammonium chloride and DecA (1:2), trioctylmethylammonium chloride and octanoic acid, tetrabutylammonium chloride and DecA, and tetrabutylammonium chloride and octanoic acid found the latter as an effective solvent to efficiently extract eight synthetic pigments in beverages with recoveries between 74.5–102.5% and RSD less than 5.4% [64]. The high extraction efficiency exhibited by tetrabutylammonium chloride and octanoic acid HDES is due to the low viscosity of the solvent which enhances its diffusivity [64]. Since synthetic pigments are usually soluble in water, increasing the alkyl chain length of either the HBA or the HBD decreases the extraction efficiency. Additionally, selecting the appropriate pH, HDES type, and extraction time and type is important to enhance yield. Another liquid–liquid extraction of metal uranyl nitrate ([UO2]2+) from aqueous acid using low viscous hydrophobic eutectic solvent from trioctylphosphine and phenol has been reported [65]. The presence of phenol in the mixture was crucial for generating the eutectic mixture composition rather than having a role in the uranyl complexation and extraction [65]. The thermal stability of the trioctylphosphine, phenol HDES mixture, which is defined by the loss of phenol from the liquid, is between 90–100 °C.
Recently, a low cost, highly porous, ultralight and hydrophobic HDES was synthesized (combined techniques of nanofibrillation, silylation, and freeze-drying) and the aerosol was capable of squeezing oil (superabsorbing agents) with an absorption capacity of 65–205 (g/g) [66]. The absorbed oil was recovered by mechanical squeezing and the aerosol could be used for about 30 cycles [66]. Since HDES uses low cost renewable raw materials, applying this economical solvent to mitigate environmental pollutants is a promising area for future research. A menthol-based HDES with acetic acid (1:1) showed efficient extraction of phytocannabinoids with yields ranging from 118.6% to 132.6%, which is higher than using terpenol, borneol, geraniol, and linalool as HBA [67]. This HDES has a higher extraction efficiency for phytocannabinoids than traditional liquids like methanol and ethanol [67]. Apart from acetic acid, other transparent liquid-based HDES formed by using volatile organic acids such as formic, propionic, butyric, hexanoic, octanoic, dodecanoic, lactic, phenylacetic, and mandelic acid as HBD with menthol as HBA (at 1:1 molar ratio) have been reported [67]. Menthol with oxalic, malonic, tartaric, phthalic, glycolic, malic, hippuric, pyruvic, and aspartic acid (1:1) form a solid–liquid mixture even after heat treatment at 80–95 °C [67]. A tailor-made HDES with methyl trioctyl ammonium chloride (N81-Cl) and 18 different alcohols or aliphatic acids was able to extract between 13 mg/g to 23 mg/g of polyprenyl acetates from Ginkgo biloba leaves powder [68]. The initial screening method for polyprenyl acetates extraction involved vortexing, air-bath shaking, and centrifugation with an approximate extraction time of 20 min. Apart from air-bath shaking, the authors compared polyprenyl acetates extraction efficiency with methods including ultrasonic-assisted extraction, water-bath shaking, heating, and stirring. Irrespective of the extraction temperature used (25 °C or 60 °C), polyprenyl acetates extraction by stirring gave higher yield [68]. The extraction yield of this pharmaceutically bioactive compound regardless of the method used was also higher at 60 °C compared to the same process conditions at room temperature.
Lastly, few reports on using HDES for In3+ [69] and Co3+ [70] extraction from aqueous solutions have been established. A possible explanation for metal–HDES interaction involves an ion exchange mechanism. For instance, the positive charged Co2+ ion is able to exchange with the partially positive charged lidocaine ion during a LLE with a hydrophobic solvent comprising of DecA and lidocaine [70]. During metal ions extraction, it is important to note that pH, reaction time, and temperature optimization are significant factors affecting extraction yield. As reported, HDES synthesized from lauric acid and the DL-menthol can only extract indium from aqueous environments when the pH is approximately 3 [69]. The ease of solvent regeneration, simple preparation of HDES, and low toxicity of HDES are among the numerous reasons why HDES are selected over hydrophobic ionic liquids or conventional organic solvents for transition metals extraction. For quantification purposes, HPLC coupled with UV/Vis is the most used separation and quantification technique. A low limit of detection (LOD) for amphetamine and methamphetamine is between 2 ng/mL to 5 ng/mL [50]. Other detecting techniques like HPLC-DAD, 1H-NMR, GC-MS, and NaI(Tl) well counter detector are listed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Applications of HDES in extraction.
6. Challenges, Opportunities, and Perspectives
Despite the numerous advantages of HDES in extraction, some of the notable limitations of these solvents are high viscosity, cloudiness, and difficulty in phase separation during liquid–liquid extraction [21]. Since the viscosity of DES depends on the hydrogen bond strength of the solvent, understanding the charge transfer and the molecular interaction between HBD and HBA occurring in HDES is an invaluable opportunity for future research. An investigation into HDES polarity by using solvatochromic molecular probes to measure hydrogen bonding acidity, hydrogen bonding basicity, and dipolarity/polarizability should also be encouraged to curtail phase separation problems. Due to the ever-increasing applications of HDES, in silico models for predicting extraction efficiencies would be vital for future applications. For example, a PC-SAFT ‘pseudo-pure’ method was used for the modeling of CO2 solubilities in HDES [71], a potential application in CO2 capture. Developing such models to predict extraction efficiency and physicochemical and thermodynamic properties like viscosity, density, activity coefficient, and vapor pressure would cut-down cost and save time and labor. Additionally, for the first time, Dietz et al. [72] impregnated hydrophobic DES (DecA: N8888-Br, DecA: Thymol, DecA: Menthol, and Thymol: Lidocaine) in a polyethylene support enhanced the separation of furfural and hydroxymethylfurfural from aqueous solutions. A significant transport of furfural and hydroxymethylfurfural through the polymeric membrane support was obtained by using HDES supported liquid membranes made from M3202B and thymol-lidocaine (2:1) [72]. Opportunities in tunneling HDES viscosity for enhanced transport and yield is requested [72].
Applications of HDES in biomass processing, drug solubilization and delivery, biofuels, and electrochemistry are underexplored, hence an opportunity for researchers to tailor HDES polarity for such applications. Ternary HDES systems involving water or polar solvent addition may be worthy of exploring to meet specific challenges. For example, in exploring the electrochemical behavior of ferrocenes, for the first time, Ruggeri et al. [73] demonstrated that addition of small water to tetrabutylammonium chloride and decanoic acid HDES (1:2) improved the electrical conductivity and viscosity of the solvent. Water content above 2% w/w in HDES enables effective mass transfer to and from the electrode surface [73]. Water disrupts the hydrogen bond between the donor and the acceptor to enhance the free flow of ions in the medium. In addition, the researchers showed that an aqueous solution containing a salt of metallic cation, Cr(VI), could be extracted by using a hydrophobic DES [73]. Furthermore, the electrochemical behavior of Cr(VI) species in HDES was studied for future applications in electroremediation.
Although HDES are considered as ‘green’ solvents, little has been done to monitor their toxicity, vapor pressure, or bioavailability. Moreover, since the hydrophobicity of HDES is relative, the distinction between hydrophilic and hydrophobic DES is sometimes confusing and hence a comprehensive guideline for calling DES hydrophobic should be established. Measuring the octanol-water partition coefficient (Kow) of the synthesized HDES would be vital to predict the environmental fate as well as the degree of hydrophobicity of the solvent. Determining the Kow values would also make it easier to select the best HDES for LLE of biomolecules or inorganic metals from an aqueous environment.
7. Concluding Remarks
This review summarizes the recent developments in HDES, a new subgroup of DES, mostly synthesized by using QAS or terpenes as HBA and fatty acids as HBD. Since most HDES are synthesized from natural raw materials, the solvent is considered as non-toxic, less volatile, environmentally benign and sustainable. The water immiscible or low water accessibility nature of HDES makes it promising in liquid–liquid extraction of non-polar analytes and transition metals from an aqueous environment. The development of HDES is a major breakthrough in analytical chemistry since DES and NADES are theoretically and practically limited to the extraction of only hydrophilic or polar compounds [48]. Despite only three years since its outset, the burgeoning interest in using HDES for extraction is growing rapidly. For now, almost all the applications of HDES are limited to extraction of biomolecules and transition metals, and, thus, there is an opportunity for scientists to explore their application in pharmaceutical, food, cosmetic, enzymatic, fuel, and biomass industries. Compared to DES and NADES, HDES offer a suitable medium for solubilization and delivery of non-polar drugs. A major drawback of HDES, like ILs, DES, and NADES, is that the high viscosity of the solvent affects analysis and separation of some extracts. Apart from using terpenes (thymol and menthol) and some fatty acids used as HBA, the most used long alkyl chain QAS, such as N4444-Cl, N8881-Cl, N8881-Br, N8888-Cl, and N8888-Br, are expensive, making it difficult for industrial usage.
To fully understand the behavior of HDES, due to the infancy of this new generation of DES, extensive work is required to investigate the physicochemical and thermodynamic properties by both experimental and theoretical approaches. In the future, it is believed that more sustainable and tailored HDES would be developed to replace environmentally hostile organic solvents.
Funding
This research received no external funding; however, the author is grateful to the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, SDSU, for supporting him through teaching assistantship.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank Nesta Bortey-Sam (Ph.D.), Emmanuel Blay (Ph.D.), and Sampson Asare (Ph.D.) for the constructive comments and feedbacks.
Conflicts of Interest
The author has no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- Rogers, R.D.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids--solvents of the future? Science 2003, 302, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSimone, J.M. Practical approaches to green solvents. Science 2002, 297, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichardt, C.; Welton, T. Solvents and Solvent Effects in Organic Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon, R.A. Green solvents for sustainable organic synthesis: State of the art. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Deep eutectic solvents formed between choline chloride and carboxylic acids: Versatile alternatives to ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Namieśnik, J. Ionic liquids and deep eutectic mixtures: Sustainable solvents for extraction processes. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 1784–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imperato, G.; Höger, S.; Lenoir, D.; Koenig, B. Low melting sugar–urea–salt mixtures as solvents for organic reactions—estimation of polarity and use in catalysis. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperato, G.; Eibler, E.; Niedermaier, J.; König, B. Low-melting sugar–urea–salt mixtures as solvents for Diels–Alder reactions. Chem. Commun. 2005, 1170–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruß, C.; König, B. Low melting mixtures in organic synthesis–an alternative to ionic liquids? Green Chem. 2012, 14, 2969–2982. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Gray, S. Design of improved deep eutectic solvents using hole theory. Chemphyschem 2006, 7, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and their applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florindo, C.; Oliveira, F.; Rebelo, L.; Fernandes, A.M.; Marrucho, I. Insights into the synthesis and properties of deep eutectic solvents based on cholinium chloride and carboxylic acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2416–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.-Y.; Xu, P.; Yang, F.-X.; Wu, H.; Zong, M.-H.; Lou, W.-Y. Biocompatible deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride: Characterization and application to the extraction of rutin from Sophora japonica. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2746–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Munro, H.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Preparation of novel, moisture-stable, Lewis-acidic ionic liquids containing quaternary ammonium salts with functional side chains. Chem. Commun. 2001, 0, 2010–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Vigier, K.D.O.; Royer, S.; Jérôme, F. Deep eutectic solvents: Syntheses, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessop, P.G. Searching for green solvents. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, P.; Bernal, J.M.; Vaultier, M. Towards continuous sustainable processes for enzymatic synthesis of biodiesel in hydrophobic ionic liquids/supercritical carbon dioxide biphasic systems. Fuel 2011, 90, 3461–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Baker, G.A. Ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents for biodiesel synthesis: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishov, A.; Bulatov, A.; Locatelli, M.; Carradori, S.; Andruch, V. Application of deep eutectic solvents in analytical chemistry. A review. Microchem. J. 2017, 135, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Osch, D.J.; Zubeir, L.F.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Rocha, M.A.; Kroon, M.C. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents as water-immiscible extractants. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4518–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, M.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Kroon, M.C. Low-transition-temperature mixtures (LTTMs): A new generation of designer solvents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3074–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-J.; Xiao, H.; Tang, X.-D.; Zhou, M. Green carboxylic acid-based deep eutectic solvents as solvents for extractive desulfurization. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 5411–5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroso, I.M.; Craveiro, R.; Rocha, Â.; Dionísio, M.; Barreiros, S.; Reis, R.L.; Paiva, A.; Duarte, A.R.C. Design of controlled release systems for THEDES—therapeutic deep eutectic solvents, using supercritical fluid technology. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 492, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroso, I.M.; Silva, J.C.; Mano, F.; Ferreira, A.S.; Dionísio, M.; Sá-Nogueira, I.; Barreiros, S.; Reis, R.L.; Paiva, A.; Duarte, A.R.C. Dissolution enhancement of active pharmaceutical ingredients by therapeutic deep eutectic systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 98, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, U.B.; Shendage, S.S.; Nagarkar, J.M. One-pot synthesis of nitriles from aldehydes catalyzed by deep eutectic solvent. Synthesis 2013, 45, 3295–3299. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Dai, D.Y.; Chen, Q.; He, M.Y. Rapid, Sustainable, and Gram-Scale Synthesis of Phenols Catalyzed by a Biodegradable Deep Eutectic Mixture in Water. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2013, 2, 1040–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avalos, M.; Babiano, R.; Cintas, P.; Jimenez, J.L.; Palacios, J.C. Greener media in chemical synthesis and processing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 3904–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayyan, M.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; AlNashef, I.M. A novel technique for separating glycerine from palm oil-based biodiesel using ionic liquids. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, K.; Mjalli, F.; Hashim, M.; AlNashef, I. Using deep eutectic solvents based on methyl triphenyl phosphunium bromide for the removal of glycerol from palm-oil-based biodiesel. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 2671–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, M.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Kroon, M.C. New natural and renewable low transition temperature mixtures (LTTMs): Screening as solvents for lignocellulosic biomass processing. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 2153–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural deep eutectic solvents as a new extraction media for phenolic metabolites in Carthamus tinctorius L. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6272–6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, M.W.; Zhao, J.; Lee, M.S.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, J. Enhanced extraction of bioactive natural products using tailor-made deep eutectic solvents: Application to flavonoid extraction from Flos sophorae. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Zhang, H.; Row, K.H. Application of deep eutectic solvents in the extraction and separation of target compounds from various samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Dadfarnia, S.; Shabani, A.M.H.; Tamaddon, F.; Azadi, D. Deep eutectic liquid organic salt as a new solvent for liquid-phase microextraction and its application in ligandless extraction and preconcentraion of lead and cadmium in edible oils. Talanta 2015, 144, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radošević, K.; Ćurko, N.; Srček, V.G.; Bubalo, M.C.; Tomašević, M.; Ganić, K.K.; Redovniković, I.R. Natural deep eutectic solvents as beneficial extractants for enhancement of plant extracts bioactivity. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Hizaddin, H.F.; Ramalingam, A.; Hashim, M.A.; Hadj-Kali, M.K. Evaluating the performance of deep eutectic solvents for use in extractive denitrification of liquid fuels by the conductor-like screening model for real solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2014, 59, 3470–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, C.M. Deep eutectic solvents and applications in electrochemical sensing. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2018, 10, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkuku, C.A.; LeSuer, R.J. Electrochemistry in deep eutectic solvents. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 13271–13277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, E.; Lecomte, J.; Baréa, B.; Piombo, G.; Dubreucq, E.; Villeneuve, P. Evaluation of deep eutectic solvents as new media for Candida antarctica B lipase catalyzed reactions. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 2081–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; van Spronsen, J.; Dai, Y.; Verberne, M.; Hollmann, F.; Arends, I.W.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R. Are natural deep eutectic solvents the missing link in understanding cellular metabolism and physiology? Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; van Spronsen, J.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural deep eutectic solvents as new potential media for green technology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 766, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, A.; Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Martins, M.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural deep eutectic solvents–solvents for the 21st century. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Friesen, J.B.; McAlpine, J.B.; Lankin, D.C.; Chen, S.-N.; Pauli, G.F. Natural deep eutectic solvents: Properties, applications, and perspectives. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satlewal, A.; Agrawal, R.; Bhagia, S.; Sangoro, J.; Ragauskas, A.J. Natural deep eutectic solvents for lignocellulosic biomass pretreatment: Recent developments, challenges and novel opportunities. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de los Ángeles Fernández, M.; Boiteux, J.; Espino, M.; Gomez, F.V.; Silva, M.F. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents-Mediated Extractions: The way forward for sustainable analytical developments. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lynam, J.G.; Kumar, N.; Wong, M.J. Deep eutectic solvents’ ability to solubilize lignin, cellulose, and hemicellulose; thermal stability; and density. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanda, H.; Dai, Y.; Wilson, E.G.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Green solvents from ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents to natural deep eutectic solvents. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2018, 21, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, H.G.; Sun, C.C.; Neervannan, S. Characterization of thermal behavior of deep eutectic solvents and their potential as drug solubilization vehicles. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 378, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajabi, M.; Ghassab, N.; Hemmati, M.; Asghari, A. Emulsification microextraction of amphetamine and methamphetamine in complex matrices using an up-to-date generation of eco-friendly and relatively hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent. J. Chromatogr. A 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Yang, M.; Cao, F.; Wang, J.; Su, E. Well-designed hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents as green and efficient media for the extraction of artemisinin from Artemisia annua leaves. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3270–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelps, T.E.; Bhawawet, N.; Jurisson, S.S.; Baker, G.A. Efficient and Selective Extraction of 99mTcO4–from Aqueous Media using Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Yu, L.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Deng, Z.; Xiao, Y. Hexafluoroisopropanol-based hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction of pyrethroids in tea beverages and fruit juices. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makoś, P.; Przyjazny, A.; Boczkaj, G. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents as “green” extraction media for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aqueous samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Florindo, C.; Romero, L.; Rintoul, I.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. From phase change materials to green solvents: Hydrophobic low viscous fatty acid–based deep eutectic solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3888–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Branco, L.; Marrucho, I. Development of hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for extraction of pesticides from aqueous environments. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2017, 448, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.A.R.; Crespo, E.A.; Pontes, P.V.; Silva, L.P.; Bülow, M.; Maximo, G.J.; Batista, E.A.C.; Held, C.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A. Tunable hydrophobic eutectic solvents based on terpenes and monocarboxylic acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, B.D.; Florindo, C.; Iff, L.C.; Coelho, M.A.; Marrucho, I.M. Menthol-based eutectic mixtures: Hydrophobic low viscosity solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2469–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi, A.; Ahmadi, R.; Ramezani, A.M. Vortex-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction based on hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for determination of malondialdehyde and formaldehyde by HPLC-UV approach. Microchem. J. 2018, 143, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubeir, L.F.; Van Osch, D.J.; Rocha, M.A.; Banat, F.; Kroon, M.C. Carbon dioxide solubilities in decanoic acid-based hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2018, 63, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubeir, L.F.; Romanos, G.E.; Weggemans, W.M.; Iliev, B.; Schubert, T.J.; Kroon, M.C. Solubility and diffusivity of CO2 in the ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tricyanomethanide within a large pressure range (0.01 MPa to 10 MPa). J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 1544–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Banerjee, T. Liquid–Liquid Extraction of Lower Alcohols Using Menthol-Based Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent: Experiments and COSMO-SAC Predictions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 3371–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kislik, V.S. Solvent Extraction: Classical and Novel Approaches; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Zhou, J.; Jia, H.; Zhang, H. Liquid–liquid microextraction of synthetic pigments in beverages using a hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent. Food Chem. 2018, 243, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmore, M.; McCourt, E.; Connolly, F.; Nockemann, P.; Swadzba-Kwasny, M.; Holbrey, J.D. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents incorporating trioctylphosphine oxide: Advanced liquid extractants. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, O.; Suopajärvi, T.; Österberg, M.; Liimatainen, H. Hydrophobic, superabsorbing aerogels from choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvent pretreated and silylated cellulose nanofibrils for selective oil removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 25029–25037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Křížek, T.; Bursová, M.; Horsley, R.; Kuchař, M.; Tůma, P.; Čabala, R.; Hložek, T. Menthol-based hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents: Towards greener and efficient extraction of phytocannabinoids. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 193, 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Yang, M.; Cao, F.; Wang, J.; Su, E. Tailor-made hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for cleaner extraction of polyprenyl acetates from Ginkgo biloba leaves. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 152, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tereshatov, E.; Boltoeva, M.Y.; Folden, C. First evidence of metal transfer into hydrophobic deep eutectic and low-transition-temperature mixtures: Indium extraction from hydrochloric and oxalic acids. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 4616–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Osch, D.J.; Parmentier, D.; Dietz, C.H.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Tuinier, R.; Kroon, M.C. Removal of alkali and transition metal ions from water with hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11987–11990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, C.H.; van Osch, D.J.; Kroon, M.C.; Sadowski, G.; van Sint Annaland, M.; Gallucci, F.; Zubeir, L.F.; Held, C. PC-SAFT modeling of CO2 solubilities in hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2017, 448, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, C.H.; Kroon, M.C.; Di Stefano, M.; van Sint Annaland, M.; Gallucci, F. Selective separation of furfural and hydroxymethylfurfural from an aqueous solution using a supported hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent liquid membrane. Faraday Discuss. 2017, 206, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, S.; Poletti, F.; Zanardi, C.; Pigani, L.; Zanfrognini, B.; Corsi, E.; Dossi, N.; Salomäki, M.; Kivelä, H.; Lukkari, J. Chemical and electrochemical properties of a hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent. Electrochim. Acta 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).