Abstract
Simultaneous determination of phosphorus and boron in fertilizers was performed by Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-AES). Three different samples were analyzed, of which two were inorganic and one was of organic composition. Analysis of the samples was performed after heated acidic digestion to completely dissolve them, using two different acid mixtures. A solution of HCl + HNO3 was used to digest the inorganic fertilizers, and a solution of H2SO4 + HNO3 for the organic fertilizer. The spectral emission lines used were 213.617 nm and 214.917 nm for P and 249.772 nm, 249.677 nm and 208.957 nm for B. The detection and quantification limits for P were between 10–20 mg/kg and 40–80 mg/kg respectively, while for B they ranged between 10–30 mg/kg and 40–100 mg/kg respectively. The repeatability of the technique was found to be within the range 0.9–17.0% for P and 1.7–23.4% for B, expressed as relative standard deviation (RSD). The concentrations found by the proposed method are in good agreement with those reported on their package labels.
1. Introduction
Fertilizers contain many elements which act as nutrients for plants, but also elements which may be toxic, and which are therefore responsible for contamination of soils. This results in the accumulation of chemicals in food [1,2]. As the development of agricultural productivity is directly related to the use of fertilizers, it is necessary to analyze them with sensitive, multi-elemental technical analyzers to monitor their quality [3]. Common fertilizers are either of inorganic or organic composition, natural or synthetic. Chemical analysis and quality control of fertilizers result in improved agricultural production [4], and methods have been developed. In this context, the determination of minerals in fertilizers becomes necessary, and for this purpose, several techniques have been reported in the literature [1,2,5]. Some techniques for the determination of heavy metals are based on Graphite Furnace atomic absorption spectroscopy (GF-AAS), Continuous Source Flame Absorption Spectroscopy (HR-CS-FAAS) [1,6,7,8,9], or Cold Vapor Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (CV-AAS) for Hg [5]. In addition, methods have been developed to determine nutrients in fertilizers by LIBS [10,11], or by total X-ray fluorescence (TXRF) techniques [12]. Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES) allows rapid analysis and simultaneous determination of primary and secondary nutrients as trace elements in fertilizers [2,13,14]. ICP-AES is a well-known analytical technique suitable for simultaneous determination of almost 70 chemical elements, as it provides high sensitivity and satisfactory detectability, has a wide range of applications, and does not suffer from important spectral interferences [15,16,17], except in case of solutions with high TDS. The great advantage of simultaneous determination of various elements in fertilizers, like P and K, has already been highlighted by other researchers [18]; this becomes more attractive considering the capability of measuring also semi-metals, like boron [19], or non-metals, like phosphorus and sulfur. However, in many cases for total element fraction, it requires complete digestion of solid samples before quantitative analysis, which means a sample treatment step, which can potentially affect accuracy and overall analytical performance of the method. In the present study, a method for the simultaneous determination of total phosphorus and boron by ICP-AES in fertilizers was developed, after digestion of the samples with two different acidic solutions. The examined acid mixtures were selected according to the nature of the fertilizer samples. For determination of the total fraction of an element, inorganic fertilizers usually do not require strong oxidative media, while organic fertilizers may need strong oxidative acids and heating or incineration followed by acidic dissolution for complete decomposition or other pretreatment techniques [19,20].
2. Experimental
2.1. Instrumentation
An inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrophotometer, model OPTIMA 3100 XL (Perkin Elmer, San Francisco, CA, USA), was employed; the operating conditions are listed in Table 1. The instrument was equipped with a liquid sample introduction system, including a peristaltic pump to aspirate solutions into the nebulizer at variable flow rates. Tygon-type pump tubes were used for sample delivery, and the nebulization system consisted of a cross-flow nebulizer and a Scott double-pass spraying chamber. A quartz torch is mounted horizontally on the same axis to the spectrophotometer window (axial viewing of emission). The torch inner injector tube was composed of alumina, which is sufficiently resistant to highly acidic solutions. The radio frequency generator (RF) that maintains the plasma is 40.68 MHz; this was adjusted to an incident power of 1350 watts for this method. The spectrophotometer was equipped with a polychromator in which an echelle-type diffraction grating was installed, and the detector was a segmented charged-coupled device. The ICP-AES instrument was supplied by analytical grade argon as a plasma gas. Three phosphorous and three boron atomic spectral lines were examined, as given in Table 2. The phosphorous line at 178.221 nm was finally rejected for reasons described below.

Table 1.
Operating conditions and settings of the ICP-AES.

Table 2.
Spectral lines employed for ICP-AES measurements.
2.2. Reagents and Solutions
For the preparation of the working standard solutions, KH2PO4 (99.5%) and H3BO3 (99.5%) were obtained from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). For acid digestion of fertilizer samples, concentrated HNO3 (65%), HCl (37%), and H2SO4 (95–97%) of analytical grade were obtained from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). All dilutions and solutions were carried out using ultrapure water of Milli-Q quality (18.2 ΜΩ, Millipore, Bedford, MA, USA).
2.3. Fertilizer Samples
Inorganic and organic commercially available fertilizers from local companies in Greece were analyzed in the present study to develop a fast analytical method. The inorganic samples were crystalline, water-soluble, general-purpose fertilizers, while the organic one was a composite fertilizer for vegetables. Their indicative nutritional content, as given on their packaging, is provided in Table 3. Phosphorus and boron contents of the samples were calculated, and are presented in Table 4.

Table 3.
Nutritional content of the three fertilizer samples.

Table 4.
Concentration of P and B in the samples.
2.4. Preparation of Working Standard Solutions
A mixed standard aqueous solution containing 50 mg/L each of phosphorus and boron was prepared from standard solutions of 100 mg/L P (KH2PO4, 439.4 mg/L) and 100 mg/L B (H3BO3, 571.97 mg/L). Finally, five working standard solutions containing 0.00, 1.00, 2.50, 10.0, 25.0 mg/L of phosphorus and boron, respectively, were prepared by proper dilutions of the above stock standard solution (50 mg/L).
2.5. Acid Digestion of Samples
For the selection of the appropriate acid mixtures, dissolution tests were performed by acid digestion of all samples. The most efficient mixtures were selected for the liquid digestion process based on the solubilization effect. Thus, for the 1st and the 2nd sample (inorganic), the acid digestion procedure was performed with the addition of 5 mL of 37% HCl + 1.5 mL of 65% HNO3, and then heating for 2 min on a hot plate in high fume hood (ca 80 fpm face velocity) for nitrogen oxides fumes. For the 3rd sample (organic), the acid digestion procedure was performed by adding 5 mL H2SO4 95–97% + 1 mL HNO3 65%, followed by heating for 3 min on a hot plate in a fume hood (ca 80 fpm). For the acid digestion procedure, accurately weighed amounts of the samples were placed in 100 mL open conical flasks and heated to 130 °C. When digestion was complete, the mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature. The mixtures were then transferred to 100 mL volumetric flasks and diluted with Milli-Q water. The obtained diluted solution was further diluted at a ratio of 1:10 and 1:100 successively. The acid digestion process was repeated three times for each sample. Preparation of acidic blank mixtures was performed three times.
Standard addition samples were also prepared by the addition of standard solutions of P and B to 0.500 g of the first sample. This process was carried out to study the recovery of the analytical method. To this sample, 228 g/kg P (435 mg/L) of KH2PO4 and 174 g/kg B (0.75 mg/L) of H3BO3 were added. The sample was then subjected to acidic digestion with 5 mL HCl + 1.5 mL HNO3 and warmed up. The sample after acid digestion was diluted to 100 mL, followed by successive dilutions of 1:10 and 1:100. The whole procedure was performed three times.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Regression Analysis
The settings for the spectral lines and the operating conditions of ICP-AES were defined in the computer software. For quantitative analyses of the samples, the required calibration curves were constructed using the series of mixed working standard solutions.
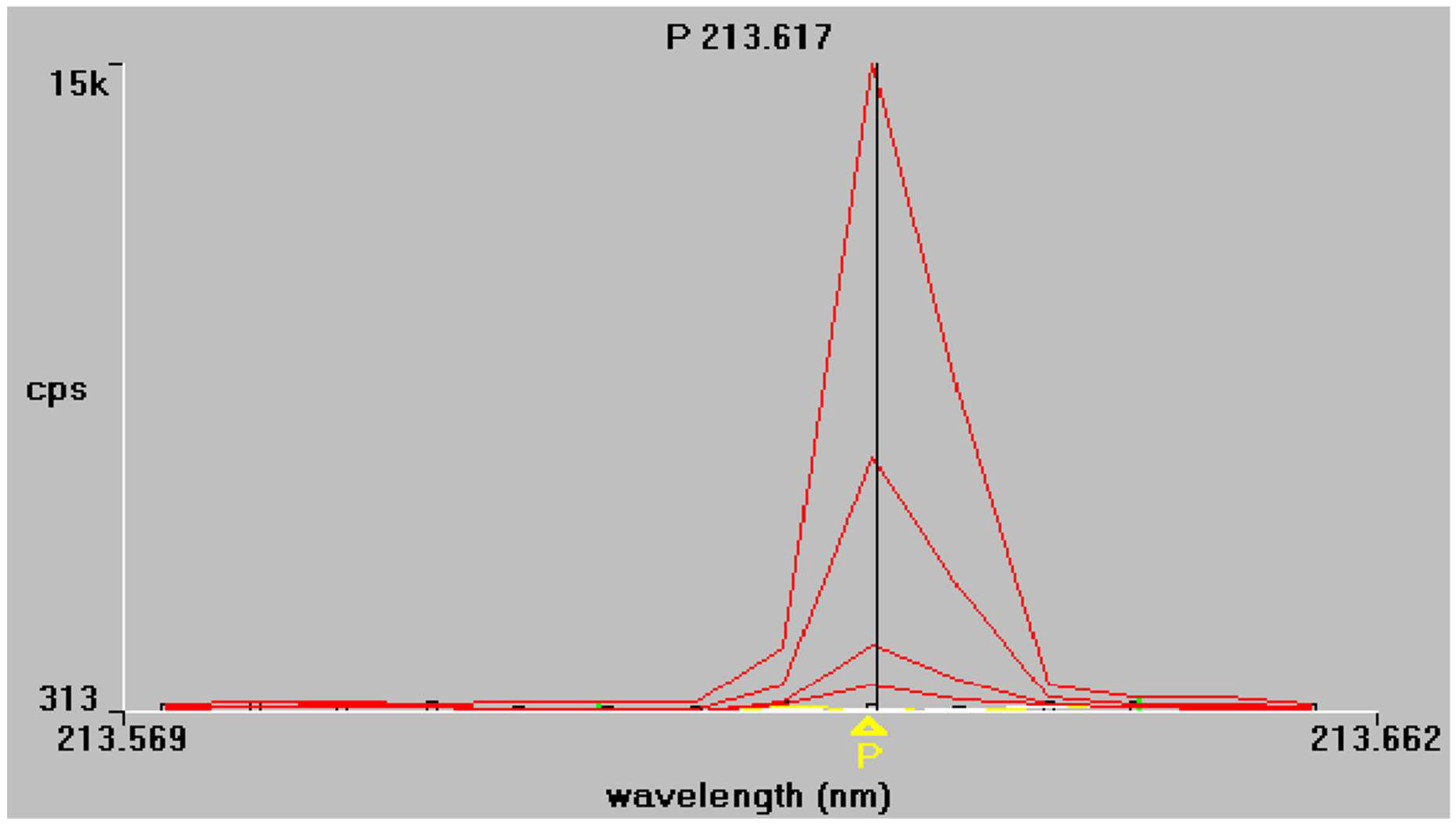
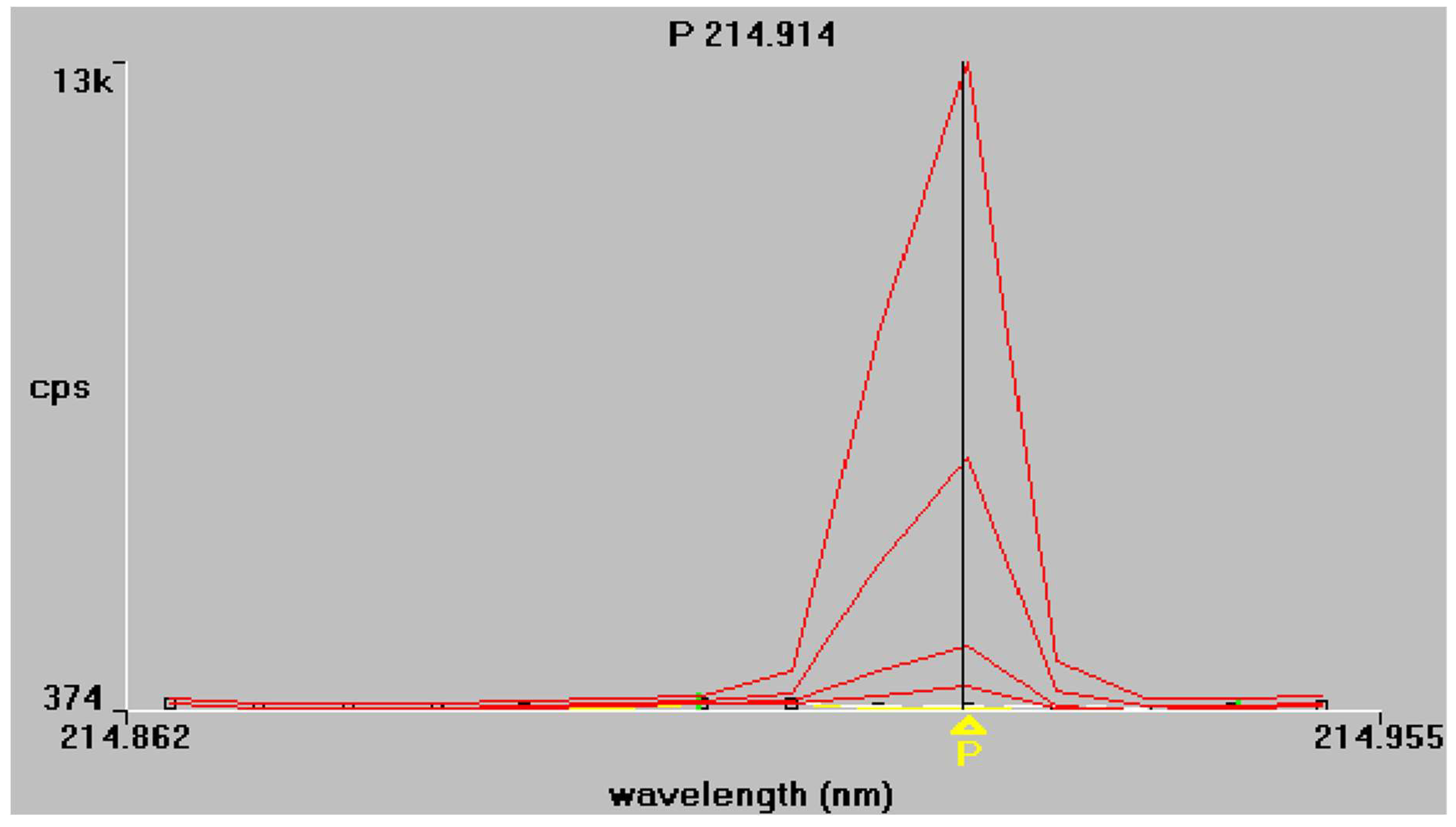
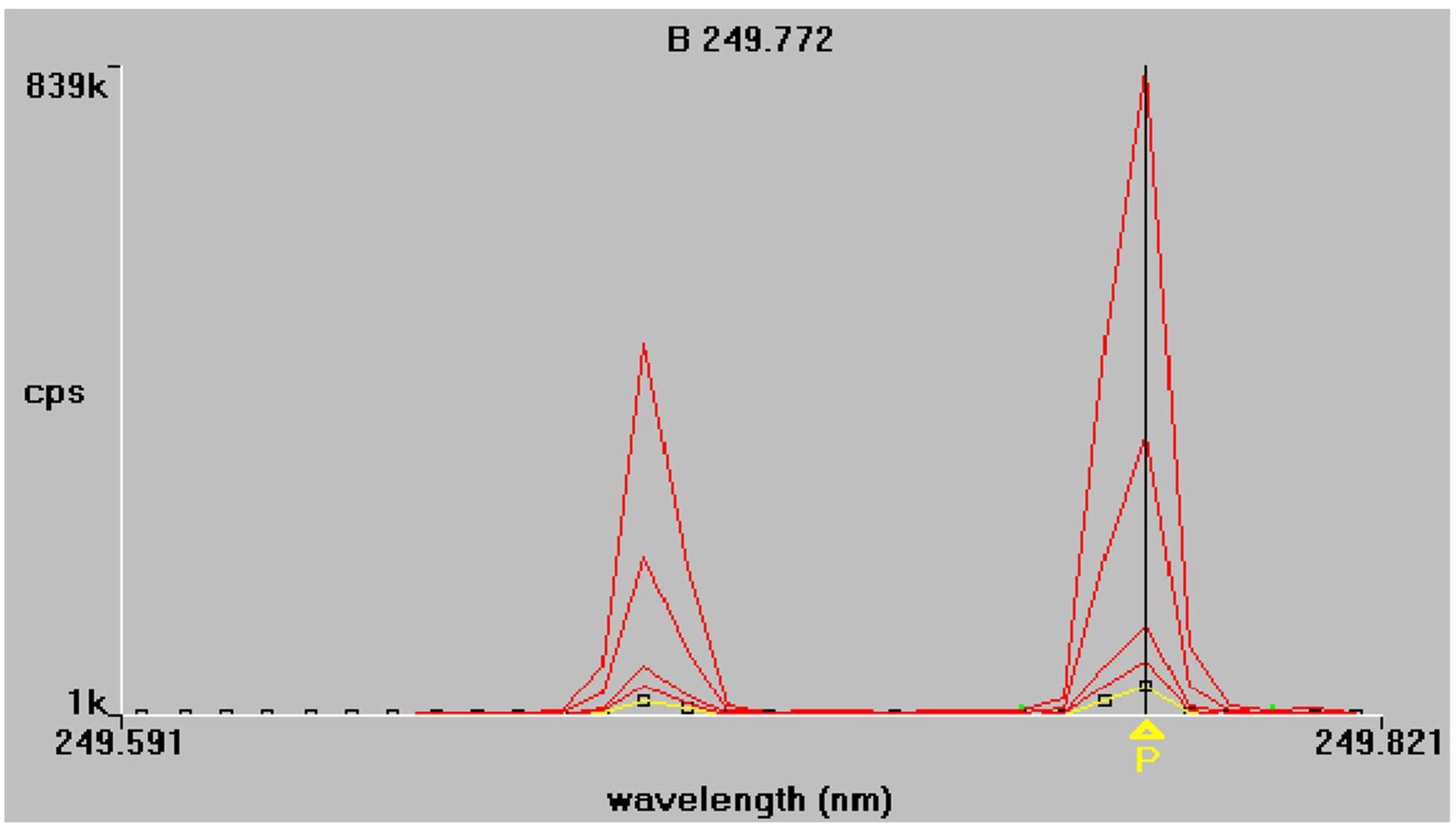
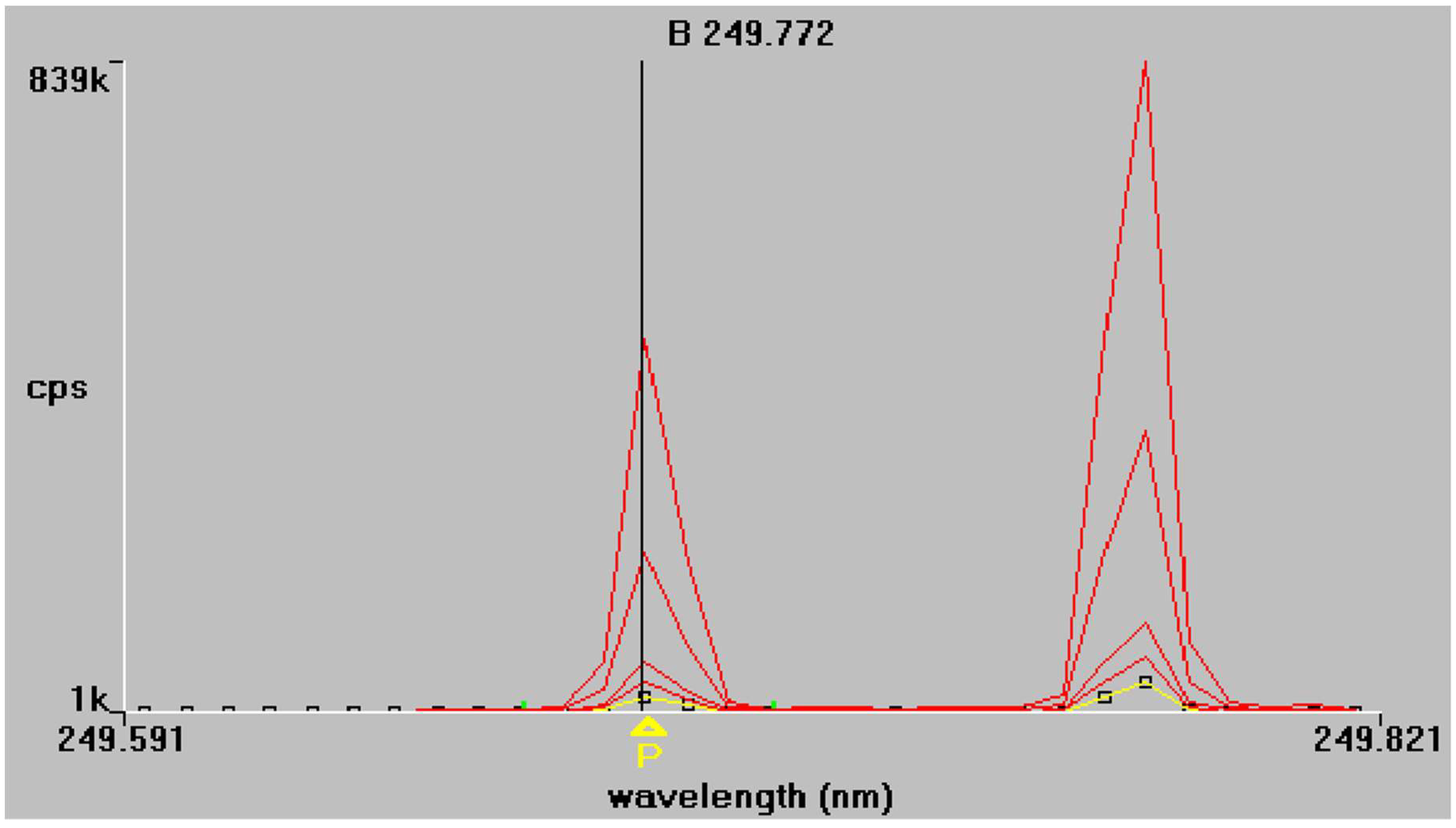
The results of the regression analysis for each element at each tested wavelength are given in Table 5. The emission spectra of P and B obtained from the mixed working standard solutions are given in Figure 1 and Figure 2 respectively. As shown in Table 5, at the examined spectral lines, both P and B showed good correlation coefficients. The correlation coefficient R is greater than 0.999 for all elements, except at the third spectral line of P (178.221 nm), where the correlation was much lower because of baseline instability. Apparently, no sensitivity is observed also, and for this reason, this spectral line P (178.221 nm) was excluded from further measurements.

Table 5.
Results of regression analysis using the mixed standard aqueous solutions of boron and phosphorus.
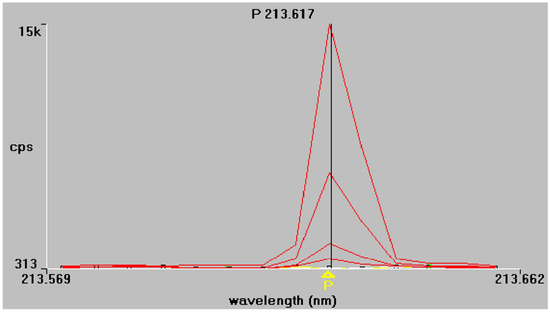
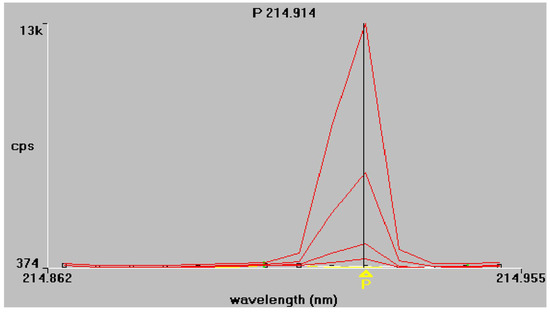
Figure 1.
Phosphorus emission spectra at 213.617 nm and 214.914 nm, respectively. Superimposed traces refer to working standard solutions of increasing concentration, as described in Section 2.4.
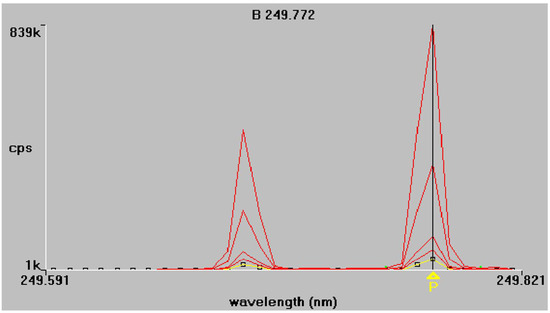
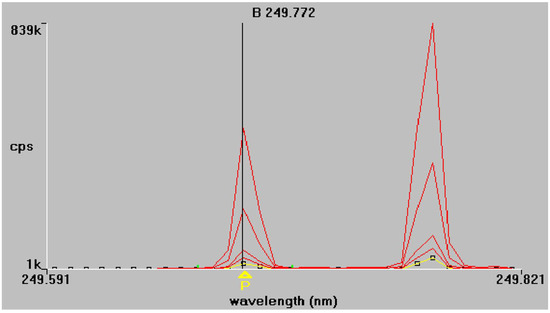
Figure 2.
Boron emission spectra at 249.772 nm and 249.677 nm respectively. Superimposed traces refer to standard solutions of increasing concentration, as described in Section 2.4.
3.2. Repeatability, Detectability and Recovery of Method
Acceptable repeatability of a method is expressed by low values of the relative standard deviation, RSD%. Repeatability testing was done by measuring the working standard three times on the same day. The solutions used were aqueous mixed solutions of P and B on all spectral lines. The concentrations used to control the repeatability were 1.00 mg/L, 2.50 mg/L, 10.0 mg/L, and 25.0 mg/L. The results are listed in Table 6. Based on these results, good repeatability is observed at concentrations of 10.0 mg/L and 25.0 mg/L, but less good at 1.00 mg/L concentration. The repeatability for P in the examined atomic lines ranged between 0.9–17%, and for B between 1.7–23.4%, respectively.

Table 6.
Method repeatability.
Limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) are defined as the minimum concentration or quantity of the analyte that can be detected or quantified respectively with reasonable certainty, according to IUPAC recommendations [21]. The detection and quantification limits of the developed method were calculated using the 3s criterion (i.e., at a 99.6% confidence level). The calculated detection limits for the examined spectral lines of phosphorus were found to be between 10–20 mg/kg, and those for B between 10–30 mg/kg. This variation is due to variability of the baseline signal values in different spectral lines and with the different acid mixtures. The corresponding limits of quantification were found to be between 40–80 mg/kg for P, and between 40–100 mg/ kg for B. The results are presented in Table 7 and Table 8. In these tables, the results are given as typical instrumental LODs and LOQs (expressed in mg/L), and also as method equivalent LODs and LOQs (expressed in mg/kg), considering a typical sample mass of 0.500 g for the analysis and initial dilution to 100 mL, as described in paragraph 2.5.

Table 7.
Detection and quantification limits using a constitutive blank of 3 mL HCl + 1 mL HNO3. LODs and LOQs were calculated as described in Section 3.2.

Table 8.
Detection and quantification limits using a constitutive blank of 5 mL H2SO4 + 1 mL HNO3. LODs and LOQs were calculated as described in Section 3.2.
Because no reference material was available, the recovery for P and B was calculated after adding an amount of the standard solution to the first sample of fertilizer. Table 9 gives the calculated recoveries for P and B in each spectral line, which are satisfactory regarding the spectral lines 213.616 nm for P and 249.772 nm for B, correspondingly. The added amount of the standard was 228 g/kg (or 435 mg/L) for P (as KH2PO4), and 176 g/kg (or 0.75 mg/L) for B (as H3BO3).

Table 9.
Recovery results.
4. Application of the Method to Fertilizers Samples
The results of the analysis of elements P and B in three samples of inorganic and organic fertilizer samples are presented in Table 10, while the corresponding label compositions are given in Table 3 and Table 4. Acid digestion was performed three times for each sample under the same conditions and with the same amounts of samples and solvents. Then, each of the three sets of samples was diluted three times, i.e., initial dilution to 100 mL, which was used for boron determination, and subsequent dilutions 1:10 and 1:100, which were used for phosphorus determination.

Table 10.
Concentration of P and B in fertilizer samples found by ICP-AES analysis after digestion.
Regarding the 1st inorganic fertilizer, the indicated content for P in the form P2O5 is 20% w/w. Thus, the concentration expressed in elemental P is 87 g/kg. The concentration using either of the two spectral lines after the analysis is in good accordance with that on the label. On the other hand, the concentration of B as given on the label is 0.015% w/w, which means 0.15 g/kg. The concentration as found after analysis i of the second and third spectral lines agrees with the indicated value.
Regarding the 2nd inorganic fertilizer, the indicated content for P given in the form of P2O5 is 10% w/w, so the concentration of elemental P is 43 g/kg. This concentration is also in agreement with the concentration resulting from sample analysis using the first spectral line of P. The B content given on the label is 100 ppm, which means 0.10 g/kg. The concentrations found from the first spectral line of boron are consistent with the reported content.
Finally, the reported content of the 3rd organic fertilizer sample is 30% w/w P2O5; therefore, the elemental P concentration is expected to be 131 g/kg, which is in accordance with the concentrations resulting from ICP-AES analysis. For B, its content is not indicated on the package. The concentration from the ICP-AES analysis was found to be at 0.12 ± 0.03 g/kg using the first emission line.
5. Conclusions
In this study, the ICP-AES technique was applied to the development of a multi-elemental fertilizer analytical method. The sample solution after heated acid wet digestion was introduced into the inductively coupled plasma atomizer. From the conducted research, the following conclusions regarding the performance of the developed method were drawn. The spectral line of P (178.221 nm) showed low correlation coefficient and poor sensitivity. The spectral lines P (213.16 nm) and P (214.914 nm) showed very good correlation, R > 0.999, with spectral line 214.914 nm being preferable in terms of sensitivity. The three spectral lines of B showed similar correlation coefficients, with a spectral line at 249.677 nm being preferable to the others in terms of sensitivity. The repeatability at high concentration levels of the working curve is better compared to the lower concentrations, and the calculated recoveries were satisfactory. Wet acid digestion of samples was completed in short pretreatment time using mixtures of HCl, HNO3, and H2SO4 acids. The developed method was applied to three different fertilizers of inorganic and organic natures. The P and B results are in accordance with those reported on the product packages. According to the results, it has been concluded that the developed method is a reliable, simple, and fast method for the simultaneous determination of P and B in fertilizers. The method can be applied to rapid examination during fertilizers production, as well as in the analysis of commercial products.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and Investigation G.Z.; Methodology E.V.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, E.V.; Writing-Review & Editing, G.Z.; Supervision, G.Z.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Borges, A.R.; Becker, E.M.; Lequeux, C.; Vale, M.G.R.; Ferreira, S.L.C.; Welz, B. Method development for the determination of cadmium in fertilizers samples using high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry and slurry sampling. Spectrochim. Acta B 2011, 66, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, P.F.; Hall, W.L., Jr. Determination of arsenic, cadmium, cobalt, chromium, lead, molybdenum, nickel, and selenium in fertilizers by microwave digestion and inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry detection: Collaborative study. J. AOAC Int. 2006, 89, 1447–1466. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soil Science Society of America. Glossary of Soil Science Terms. 2008. Available online: https://www.soils.org/publications/soils-glossary (accessed on 20 April 2018).
- Das, S.; Adhya, T.K. Effect of combine of inorganic manure and inorganic fertilizer on methane and nitrous oxide emissions from a tropical flooded soil planted to rice. Geoderma 2014, 213, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, D. Mercury in some chemical fertilizers and the effect of calcium superphosphate on mercury uptake by corn seedlings (Zea mays L.). J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1184–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Morais, C.P.; Barros, A.I.; Santos, J.D.; Ribeiro, C.A.; Crespi, M.S.; Sanesi, G.S.; Neto, J.A.G.; Ferreira, E.C. Calcium determination in biochar-based fertilizers by laser-induced. Microchem. J. 2007, 134, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Souza, S.; Froncois, L.L.; Borges, A.R.; Vale, M.G.R.; Araujo, R.G.O. Determination of copper and mercury in phosphate fertilizers employing direct solid sampling analysis and high resolution continuum source graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2015, 114, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.R.; Francois, L.L.; Becker, E.M.; Vale, M.G.R.; Welz, B. Method development for the determination of chromium and thallium in fertilizers samples using graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry and direct solid samples analysis. Microchem. J. 2015, 119, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechlin, M.A.; Fortunato, F.M.; de Silva, R.M.; Ferreira, E.C.; Neto, J.A.G. A simple and fast method for assessment of the nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium rating of fertilizers using high-resolution continuum source atomic and molecular absorption spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2014, 101, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.C.; Gustinelli, C.; de Carvallo, A.; Santos, J.D.; Krug, F.J. Determination of Cd, Cr and Pb in phosphate fertilizers by laser- induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2014, 97, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolodelli, G.; Senesi, G.S.; Perazzoli, I.L.O.; Marangoni, B.S.; Benites, U.D.M.; Milari, D.M.B.P. Double pulse laser induced breakdown spectroscopy: A potential tool for the analysis of contaminants and macro/micronutrients in organic mineral fertilizers. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resendes, L.V.; Nascentes, C.C. A simple method for the multi-elemental analysis of organic fertilizer by slurry sampling and total reflection X-ray fluorescence. Talanta 2016, 147, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nziguheba, G.; Smolders, E. Inputs of trace elements in agricultural soils via phosphate fertilizers in European countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 390, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, Y.; Hao, J.; Rui, F. Determination of seven plant nutritional element in potassium dihydrogen phosphate fertilizers from northeastern China. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2012, 16, 89–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.S.; Teixeira, L.S.G.; Araujo, R.G.O.; Fernandes, A.P.; Korn, M.G.A.; Ferreira, S.L.C. Optimization of the operating conditions using factorials design for determination of uranium by inductively plasma optical emission spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2011, 97, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Souza, S.; de Costa, S.L.; Santos, D.M.; Pinto, J.D.S.; Garcia, C.A.B.; Alves, J.D.P.H.; Araujo, R.G.O. Simultaneous determination of macronutrients, micronutrients and trace elements in mineral fertilizers by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2014, 96, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariadis, G. Inductively Coupled plasma atomic emission spectometry, A Model. In Multi-Elemental Technique for Modern Analytical Laboratory; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 18–65. [Google Scholar]
- Bartos, J.M. Determination of Phosphorus and Potassium in Commercial Inorganic Fertilizers by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry: Single-Laboratory Validation. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. Testing Methods for Fertilizers; Food and Agricultural Materials Inspection Center (FAMIC): Saitama, Japan, 2016; pp. 92–111, 259–269.
- Faithfull, N.T. The analysis of fertilizers, Cp. 6. In Methods in Agricultural Chemical Analysis: A Practical Handbook; CABI Publishing: Oxon, UK, 2002; pp. 110–118. [Google Scholar]
- International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). Compendium in Chemical Terminology, Version 2014; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1997; Available online: https://goldbook.iupac.org/html/L/L03540.html (accessed on 23 June 2018).
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).