Optimization and Application of a GC-MS Method for the Determination of Endocrine Disruptor Compounds in Natural Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Standard Preparation
2.3. Extraction and Elution
2.4. Derivatization
2.5. Gas Chromatography in Tandem with Mass Spectrometry
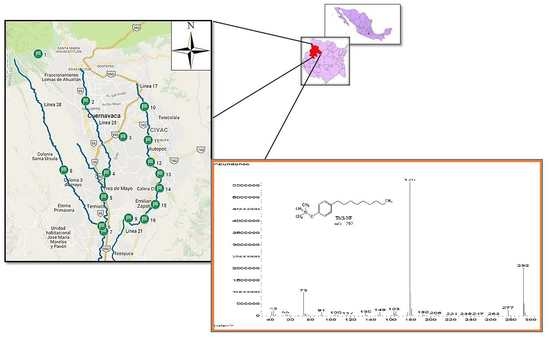
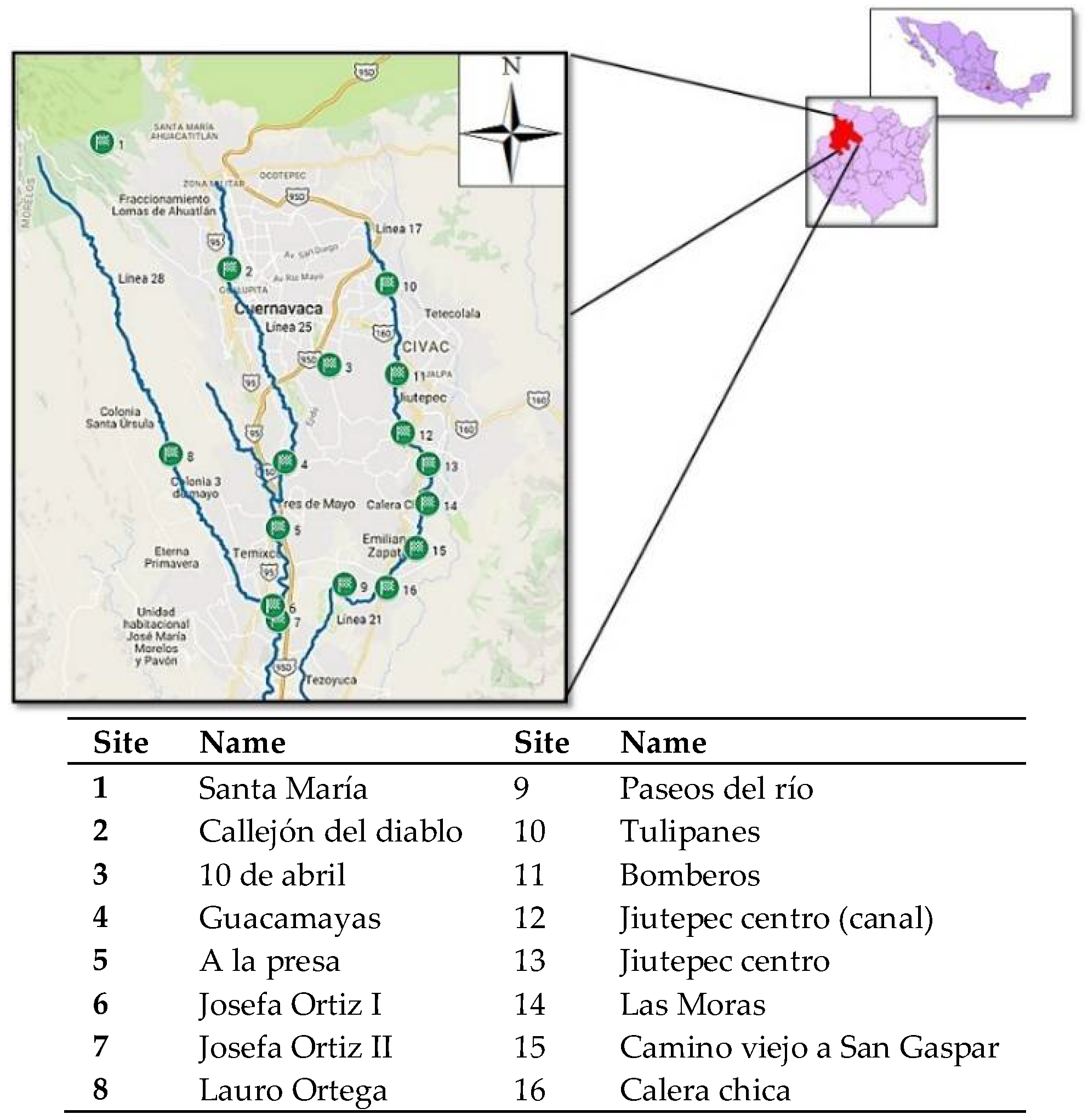
2.6. Application on Natural Water Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of the Analytical Conditions
3.2. Application on Natural Water Samples
3.3. Evaluation of Health Risk by EDC Exposure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campbell, C.G.; Borglin, S.E.; Green, F.B.; Grayson, A.; Wozei, E.; Stringfellow, W.T. Biologically directed environmental monitoring, fate, and transport of estrogenic endocrine disrupting compounds in water: A review. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 1265–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azpilcueta, M.E.; Pedroza, A.; Sanchez, I.; Salced, M.; Del, R.; Trejo, R. Calidad química de agua en un área agrícola de maíz forrajero (Zea mays L.) en la Comarca Lagunera, México. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2017, 33, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón, K.O.; Pinedo, C.; Rentería, M. Evaluación de elementos traza en agua de río y manantial del área minera de Ocampo, Chihuahua, México. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2016, 32, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Colis, G.; Thalasso, F.; Ramírez-López, E.M.; Rodríguez-Narciso, S.; Guerrero-Barrera, A.L.; Avelar-González, F.J. Evaluación espacio-temporal de la calidad del agua del río San Pedro en el Estado de Aguascalientes, México. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2011, 27, 115–127. [Google Scholar]
- Mancilla-Villa, Ó.R.; Ortega-Escobar, H.M.; Ramírez-Ayala, C.; Ramos-Bello, R.; Reyes-Ortigoza, A.L. Metale pesados totales y arsénico en el agua para riego de Puebla y Veracruz, México. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2012, 28, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- CEAGUA. Programa Estatal Hídrico de Morelos 2014–2018. Available online: http://marcojuridico.morelos.gob.mx/archivos/reglamentos_estatales/pdf/VPHIDRICOMO.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2018).
- CONAGUA. La Cuenca del río Apatlaco. Recuperemos el Patrimonio Ambiental de los Morelenses 2008. Available online: http://centro.paot.org.mx/documentos/semarnat/cuenca_rio_apatlaco.pdf (accessed on 11 January 2017).
- EPA. Method 1698: Steroids and Hormones in Water, soIl, Sediment, and Biosolids by HRGC/HRMS; EPA Method; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; pp. 1–69.
- Miller, J.N.; Miller, J.C. Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry, 6th ed.; Pearson Education: Harlow, UK, 2010; pp. 124–126. ISBN 978-0-273-73042-2. [Google Scholar]
- INEGI. Anuario Estadístico y Geográfico de Morelos 2016. Available online: http://internet.contenidos.inegi.org.mx/contenidos/Productos/prod_serv/contenidos/espanol/bvinegi/productos/nueva_estruc/anuarios_2016/702825084349.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2018).
- Gibson, R. Determination of acidic pharmaceuticals and potential endocrine disrupting compounds in wastewaters and spring waters by selective elution and analysis by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1169, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz Torres, E.; Gibson, R.; González Farías, F.; Zarco Arista, A.E.; Mazari Hiriart, M. Endocrine disruptors in the Xochimilco Wetland, Mexico City. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. EPA-HQ-OPPT-2010-0812-0001 (Testing of Bisphenol A). Revised 20 April 2017. Available online: https://www.regulations.gov/document?D=EPA-HQ-OPPT-2010-0812-0001 (accessed on 2 February 2018).
- EPA. EPA-822-R-05-005: Aquatic Life Ambient Water Quality Criteria Nonylphenol. Available online: www.epa.gov/waterscience/criteria/aqlife.html (accessed on 2 February 2018).
- Scientific Committee on Health and Environmental Risks (SCHER). Opinion on Draft Environmental Quality Standards under the Water Framework Directive—17β-estradiol; European Commission, DG Health & Consumers, Directorate C: Public Health and Risk Assessment, Unit C7—Risk Assessment: Bruselas, Belgium, 2011; Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/environmental_risks/docs/scher_o_131.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2018). [CrossRef]
- Scientific Committee on Health and Environmental Risks (SCHER). Opinion on Draft Environmental Quality Standards under the Water Framework Directive—Ethinylestradiol; European Commission, DG Health & Consumers, Directorate C: Public Health and Risk Assessment, Unit C7—Risk Assessment: Bruselas, Belgium, 2011; Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/environmental_risks/docs/scher_o_146.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2018). [CrossRef]
- EPA. Ecological Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund: Process for Designing and Conducting Ecological Risk Assessments, 239. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/ecological-risk-assessment-guidance-superfund-process-designing-and-conducting-ecological-risk (accessed on 2 February 2018).

| Compound | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Trimethylsilyl Derivated Compound | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Ion Quantitation | Ion Confirmation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4NP | 220.35 | TMS-4NP | 292.54 | 292 | 207, 277 |
| BPA | 228.29 | TMS-BPA | 372.65 | 357 | 372, 207, 73 |
| E2 | 272.38 | TMS-E2 | 416.75 | 416 | 285, 232, 129 |
| EE2 | 296.40 | TMS-EE2 | 440.77 | 425 | 440, 300, 285 |
| Compound | TR | r | Repeatability (3) (% RSD) | Reproducibility (4) (% RSD) | % Recovery (2) | IDL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4NP | 9.7 | 0.9927 | 8.2 | 5.2 | 107.6 ± 22.5 | 26.6 |
| BPA | 11.6 | 0.9904 | 0.9 | 7.2 | 111.0 ± 6.2 | 37.0 |
| E2 | 15.8 | 0.9917 | 3.1 | 10.5 | 71.8 ± 17.3 | 29.0 |
| EE2 | 16.9 | 0.9800 | 6.3 | 5.1 | 78.3 ± 20.5 | 24.7 |
| Site | 4NP | BPA | E2 | EE2 | Activity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morelos State | ||||||
| 1 | Santa María | ND | ND | ND | ND | Urban area |
| 2 | Callejón del Diablo | ND | ND | ND | ND | Urban area |
| 3 | 10 de abril | ND | ND | ND | 624.3 ± 19.9 | Urban area |
| 4 | Guacamayas | ND | ND | 70.1 ± 10.7 | 31.2 ± 9.4 | Urban area |
| 5 | A la presa | 85.5 ± 11.6 | 88.8 ± 6.2 | 103.6 ± 11.1 | 91.5 ± 9.2 | Urban area |
| 6 | Josefa Ortiz I | ND | 39.1 ± 6.2 | 39.1 ± 6.2 | 181.9 ± 9.7 | Urban area |
| 7 | Josefa Ortiz II | ND | ND | ND | 231.7 ± 10.4 | Urban area |
| 8 | Lauro Ortega | ND | ND | ND | ND | Natural water |
| 9 | Paseos del río | ND | 43.3 ± 6.2 | 37.3 ± 10.6 | 126.3 ± 9.3 | Commercial area |
| 10 | Tulipanes | ND | ND | ND | ND | Commercial area |
| 11 | Bomberos | ND | ND | ND | 159.0 ± 9.5 | Urban area |
| 12 | Jiutepec centro (canal) | ND | ND | ND | 138.5 ± 9.2 | Urban area |
| 13 | Jiutepec | ND | ND | ND | 147.9 ± 9.4 | Urban area |
| 14 | Las Moras | ND | ND | ND | 91.4 ± 9.2 | Urban area |
| 15 | Camino viejo a San Gaspar | ND | ND | ND | ND | Urban area |
| 16 | Calera chica | ND | 174.6 ± 6.2 | ND | ND | Urban area |
| Hidalgo State [11] | ||||||
| Residual water | 16.7 ± 2.2 | 2.50 ± 0.4 | 0.022 ± 0.0 | ND | Farming | |
| Spring water | ND | ND | ND | ND | Farming | |
| Xochimilco channel [12] | ND | ND | ND | ND | ||
| 4 | Tlicuilli | ND | 140,000 | ND | ND | Livestock |
| 10 | Candelaria | ND | 8420–29,350 | ND | ND | Urban area |
| 11 | Santa Cruz | ND | ND | ND | ND | Urban area |
| 12 | Nuevo León | ND | ND | ND | ND | Urban area |
| 13 | Caltongo | ND | ND | ND | ND | Urban area |
| 18 | La Draga | ND | ND | ND | ND | Effluent |
| 19 | San Diego | ND | ND | ND | ND | Effluent |
| 7 and 9 | Puente Urrutia y Tlapechicalli | ND | 4370–18,032 | ND | ND | Farming |
| 1, 3 and 8 | Tlilac, el Bordo | ND | 15,200–22,370 | 980–1680 | ND | Farming and livestock |
| el Humedal | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Site | Compound | Concentration (ng/mL) | Exposition Rate in Adults (mg/kg*day) | Exposition Rate in Children (mg/kg*day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 de abril | EE2 | 624 | 6.5 | 22.8 |
| Guacamayas | E2 | 70.1 | 0.7 | 2.6 |
| EE2 | 31.2 | 0.3 | 1.1 | |
| A la presa | NP | 85.5 | 0.9 | 3.1 |
| BPA | 88.8 | 0.9 | 3.2 | |
| E2 | 104 | 1.1 | 3.8 | |
| EE2 | 91.5 | 1.0 | 3.3 | |
| Josefa Ortiz I | BPA | 39.1 | 0.4 | 1.4 |
| EE2 | 182 | 1.9 | 6.6 | |
| Josefa Ortiz II | EE2 | 232 | 2.4 | 8.5 |
| Paseos del río | BPA | 43.3 | 0.5 | 1.6 |
| E2 | 37.7 | 0.4 | 1.4 | |
| EE2 | 126 | 1.3 | 4.6 | |
| Bomberos | EE2 | 159 | 1.7 | 5.8 |
| Jiutepec centro (canal) | EE2 | 138 | 1.4 | 5.1 |
| Jiutepec centro | BPA | 8.72 | 0.9 | 3.2 |
| EE2 | 148 | 1.5 | 5.4 | |
| Las Moras | BPA | 40.3 | 0.4 | 1.5 |
| EE2 | 91.4 | 1.0 | 3.3 | |
| Calera Chica | BPA | 175 | 1.8 | 6.4 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ronderos-Lara, J.G.; Saldarriaga-Noreña, H.; Murillo-Tovar, M.A.; Vergara-Sánchez, J. Optimization and Application of a GC-MS Method for the Determination of Endocrine Disruptor Compounds in Natural Water. Separations 2018, 5, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations5020033
Ronderos-Lara JG, Saldarriaga-Noreña H, Murillo-Tovar MA, Vergara-Sánchez J. Optimization and Application of a GC-MS Method for the Determination of Endocrine Disruptor Compounds in Natural Water. Separations. 2018; 5(2):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations5020033
Chicago/Turabian StyleRonderos-Lara, José Gustavo, Hugo Saldarriaga-Noreña, Mario Alfonso Murillo-Tovar, and Josefina Vergara-Sánchez. 2018. "Optimization and Application of a GC-MS Method for the Determination of Endocrine Disruptor Compounds in Natural Water" Separations 5, no. 2: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations5020033
APA StyleRonderos-Lara, J. G., Saldarriaga-Noreña, H., Murillo-Tovar, M. A., & Vergara-Sánchez, J. (2018). Optimization and Application of a GC-MS Method for the Determination of Endocrine Disruptor Compounds in Natural Water. Separations, 5(2), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations5020033