Simultaneous Determination and Quantification of NineNitrosamine Impurities in Semi-Solid Forms Using a GC–MS/MS Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Standard Stock Solutions and Internal Standard Stock Solutions
2.3. Preparation of Sample Solutions
2.4. Operating Conditions of GC–MS/MS
2.5. Method Validation
3. Results
3.1. System Suitability and Selectivity
3.2. Linearity
3.3. Accuracy
3.4. Precision (Repeatability)
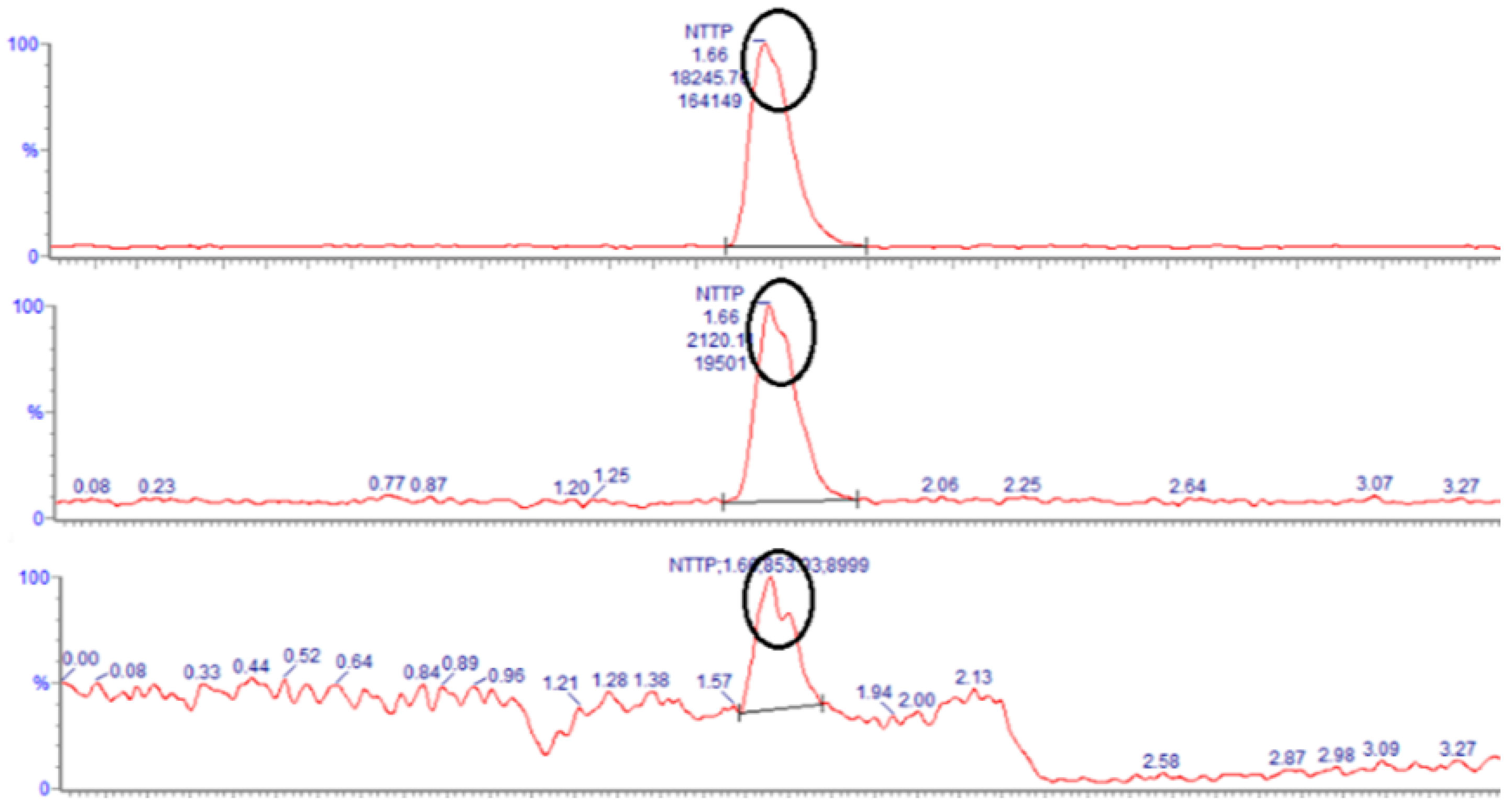
3.5. Limit of Quantification (LOQ) and Limit of Detection (LOD)
3.6. Robustness (Solution Stability)
4. Exploratory Evaluation of Method Applicability
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NDMA | N-nitrosodimethylamine |
| NDEA | N-nitrosodiethylamine |
| NMEA | N-nitrosomethylethylamine |
| NDPA | N-nitrosodipropylamine |
| NDBA | N-nitrosodi-n-butylamine |
| NPIP | N-nitrosopiperidine |
| NMOR | N-nitrosomorpholine |
| DIPNA | N-nitrosodiisopropylamine |
| EIPNA | N-nitrosoethylisopropylamine |
| PEG | Polyethyleneglycol |
| ESI | Electronic Supporting Information (Supplementary Materials) |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| MFDS | Ministry of Food and Drug Safety |
| RSD | Relative Standard Deviation |
References
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, Volume 17: Some N-Nitroso Compounds; IARC: Lyon, France, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- International Council for Harmonisation (ICH). Assessment and Control of DNA Reactive (Mutagenic) Impurities in Pharmaceuticals to Limit Potential Carcinogenic Risk M7(R1); ICH: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). FDA Updates and Press Announcements on Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker (ARB) Recalls: Valsartan, Losartan. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-updates-and-press-announcements-angiotensin-ii-receptor-blocker-arb-recalls-valsartan-losartan (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines; HealthCare (EDQM). Nitrosamine Testing Activities of the OMCL Network. Available online: https://www.edqm.eu/en/nitrosamine-testing-activities-of-the-omcl-network (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Health Canada. Information Update—Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs). Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/drugs-health-products/compliance-enforcement/information-health-product/drugs/angiotensin-receptor-blocker.html (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Taiwan Food and Drug Administration (TFDA). Nitrosamines. Available online: https://www.fda.gov.tw/ENG/siteList.aspx?sid=10360 (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Sehajpal, J.; Swann, T. Sample Preparation of Semi-Solid Pharmaceutical Formulations: Solid-Phase Extractions (SPE) of Hydrocortisone Valerate Ointment; Waters: Milford, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, K.; Migliorese, K.G.; Curtis, H. Analysis of nitrosamines in cosmetic. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1990, 41, 283–333. [Google Scholar]
- Kosure, E.R.; Bhanti, M.; Jaywant, M.A.; Han, M.; Wang, X.; Obeng, M. A GC-MS/MS Method for Trace Level Quantification of Six Nitrosamine Impurities (NDMA, NDEA, NEIPA, NDIPA, NDPA, and NDBA) in Commercially Used Organic Solvents: Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, Toluene, and O-xylene. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, E.; Bail, S.; Buchbauer, G.; Stoilova, I.; Atanasova, T.; Krastanov, A.; Jirovetz, L. Chemical Composition, Olfactory Evaluation and Antioxidant Effects of the Essential Oil from Mentha x piperita. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH). Q2 (R2) Validation of Analytical Procedures; Adopted on 1 November 2023. Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/ICH_Q2-R2_Document_Step2_Guideline_2022_0324.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- United States Pharmacopeia (USP). General Chapter <1469>: Nitrosamine Impurities; United States Pharmacopeial Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, J.; Ashworth, I.W.; Harris, L.; Hillier, M.C.; Nanda, K.K.; Scrivens, G. N-Nitrosamine Formation in Pharmaceutical Solid Drug Products: Experimental Observations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 1255–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, J.; Schlingemann, J.; Saal, C. N-Nitrosamines Impurities in Pharmaceuticals: The Abrupt Challenges that Resulted, the Evolving Science, and the Regulatory Framework. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 1161–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, U. European Pharmacopoeia Activities on Control of Nitrosamines and Other DNA-Reactive Impurities. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 1163–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Hu, S.; Wu, X.; He, Z.; Ke, C.; Hu, M. A Highly Sensitive LC-MS/MS Method for the Determination and Quantification of a Recently Identified N-Nitrosamine Impurity in the Sitagliptin Phosphate Monohydrate Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient. Anal. Methods 2023, 15, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA); Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). Control of Nitrosamine Impurities in Human Drugs Guidance for Industry; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/141720/download (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Lessons Learnt from Presence of N-Nitrosamine Impurities in Sartan Medicines; EMA: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 23 June 2020; Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/lessons-learnt-presence-n-nitrosamine-impurities-sartan-medicines_en.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS). Guideline on the Safe Management of Mutagenic and Carcinogenic Impurities in Pharmaceuticals [User Guide for Applicants]—Focusing on Nitrosamines among Impurities; MFDS: Osong, Republic of Korea, 26 September 2024. Available online: https://www.mfds.go.kr/brd/m_1060/down.do?brd_id=data0011&data_tp=A&file_seq=1&seq=15344 (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Nitrosamine Impurities. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory-overview/post-authorisation/pharmacovigilance-post-authorisation/referral-procedures-human-medicines/nitrosamine-impurities (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS). Guideline on Nitrosamine Impurities in Pharmaceuticals; Ministry of Food and Drug Safety: Cheongju, Republic of Korea, 2025. Available online: https://www.mfds.go.kr/brd/m_218/view.do?seq=33599 (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Information About Nitrosamine Impurities in Medications. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/information-about-nitrosamine-impurities-medications (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- European Commission Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety. SANTE/12682/2019: Analytical Quality Control and Method Validation Procedures for Pesticide Residues Analysis in Food and Feed; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; Available online: https://food.ec.europa.eu/system/files/2020-01/pesticides_mrl_guidelines_wrkdoc_2019-12682.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2025).
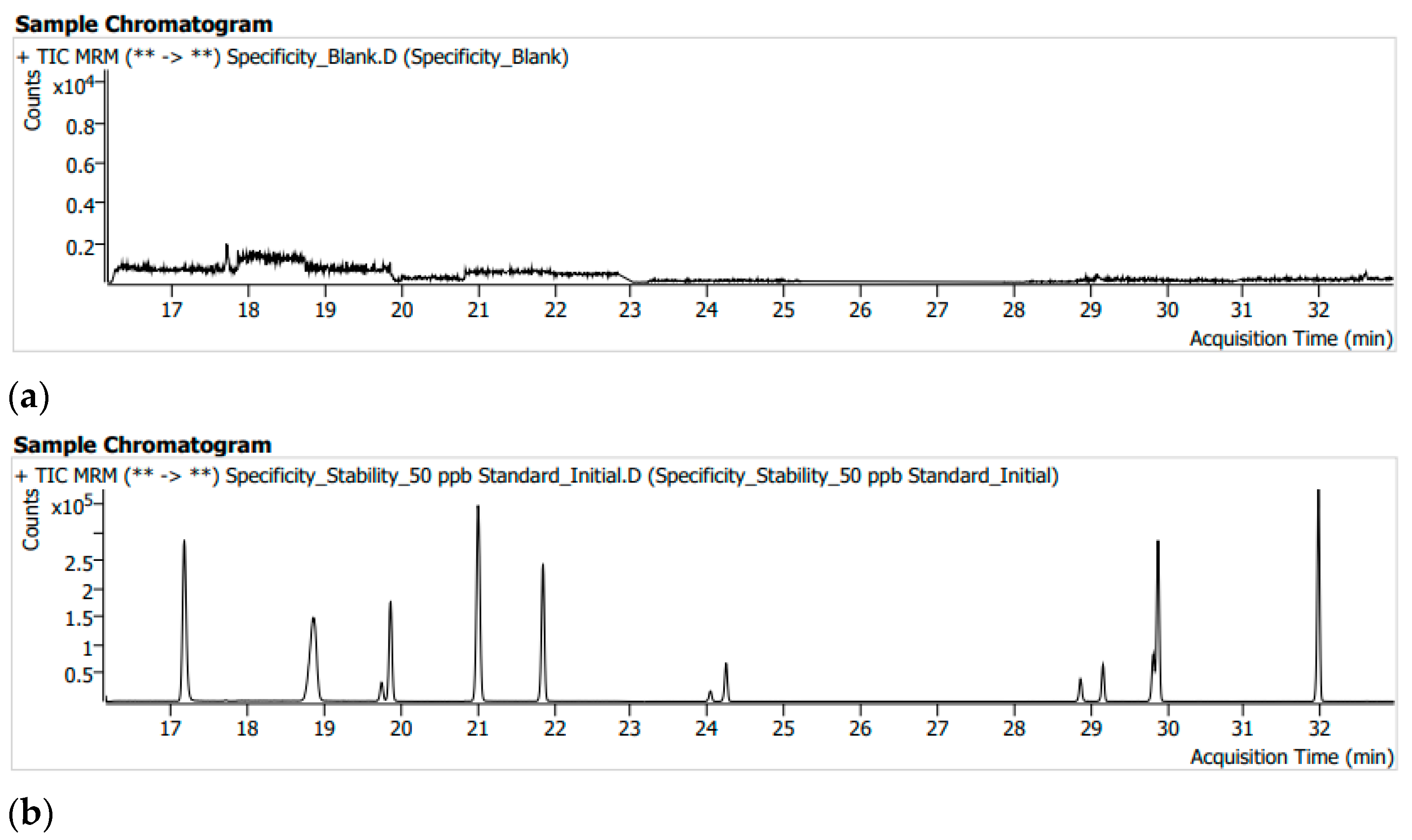
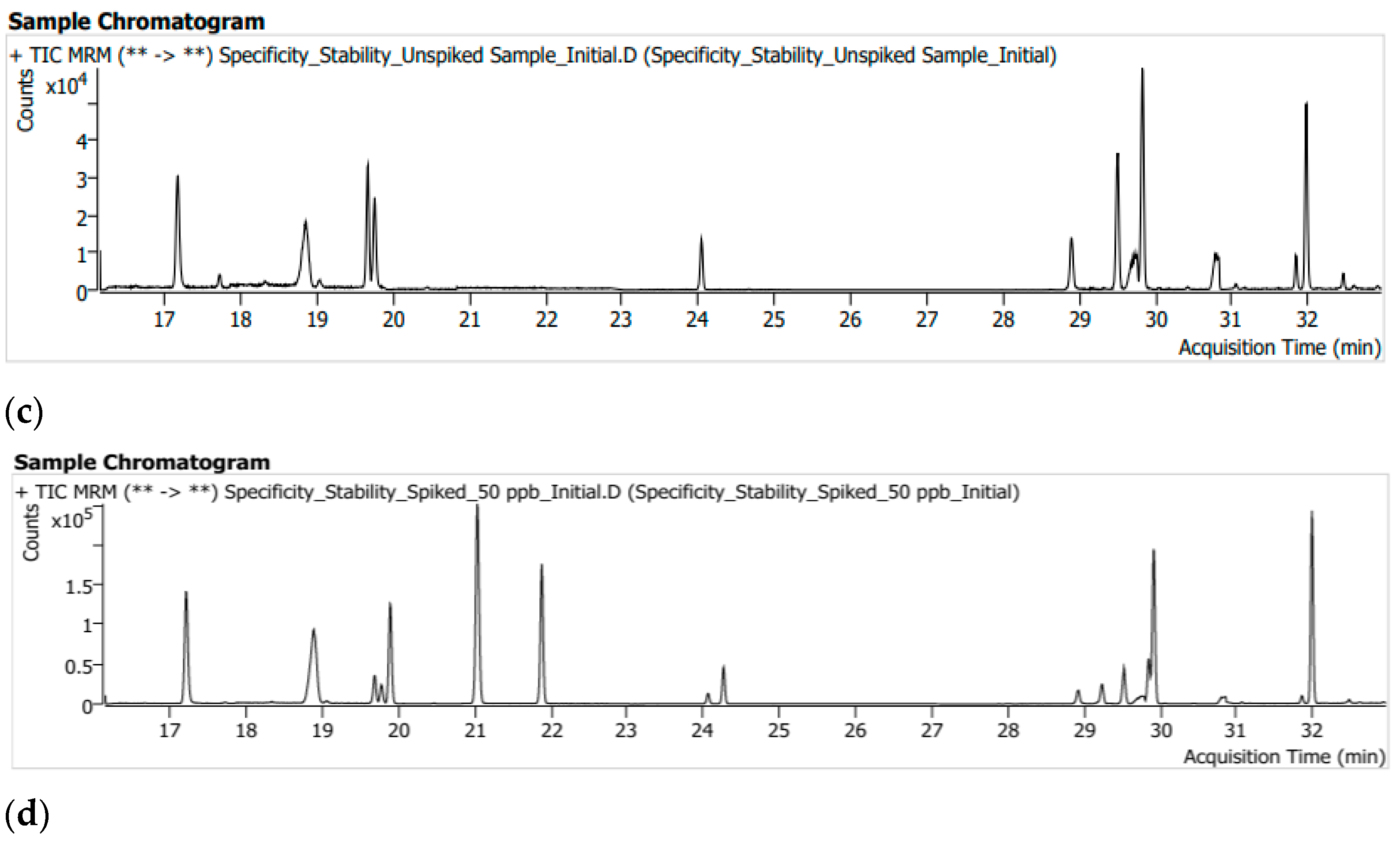
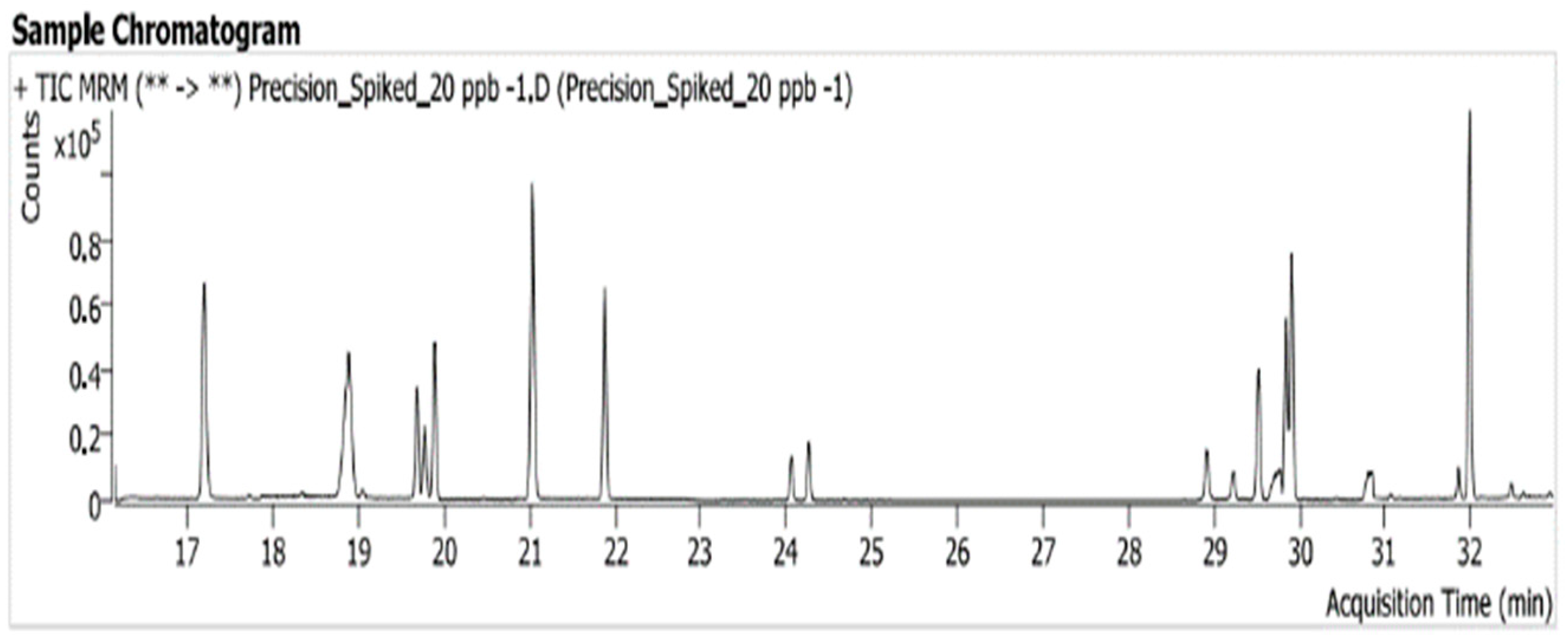
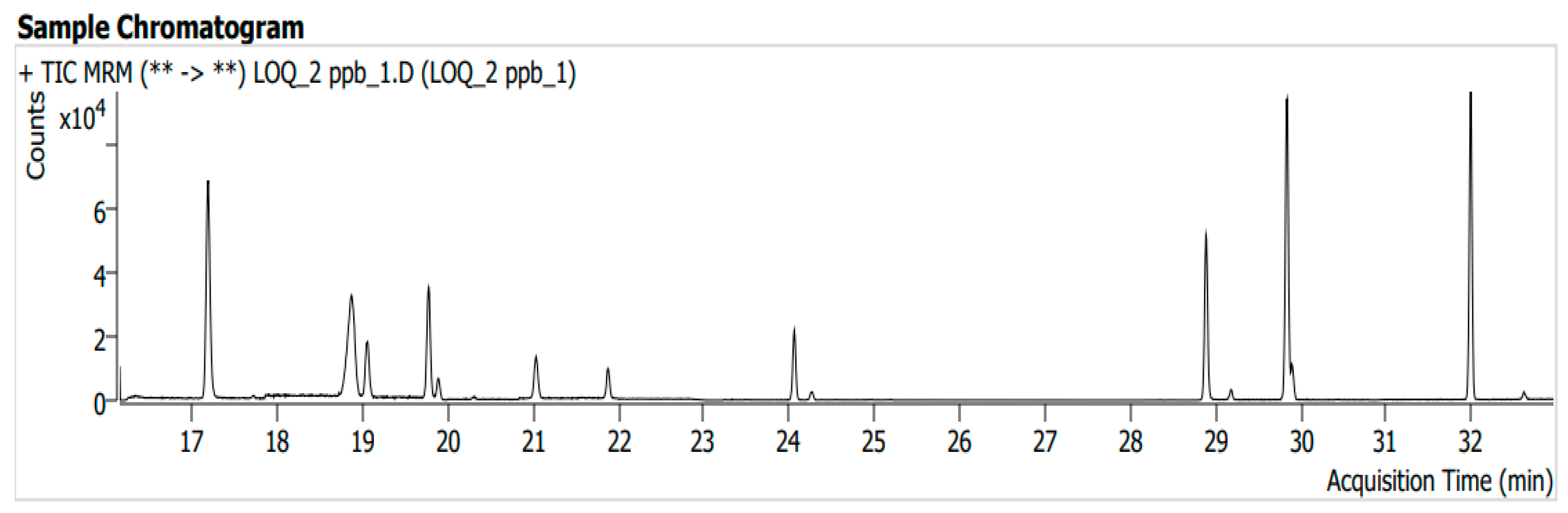
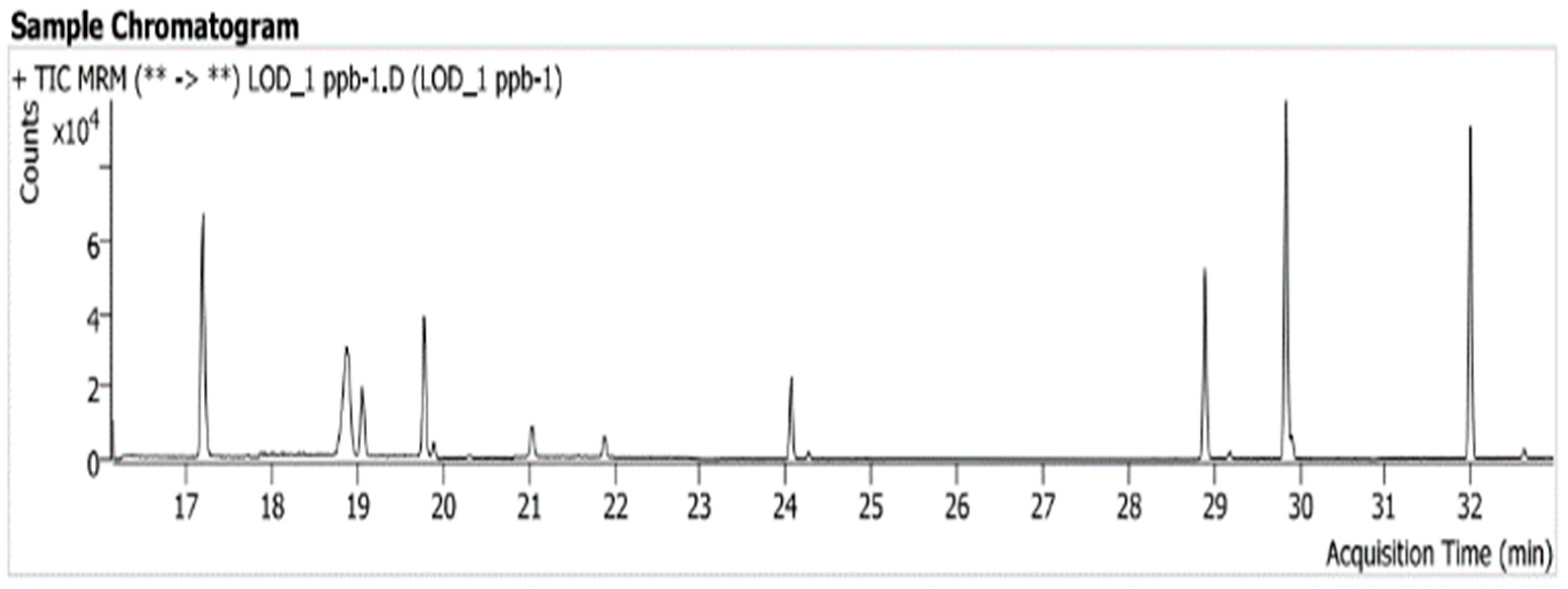

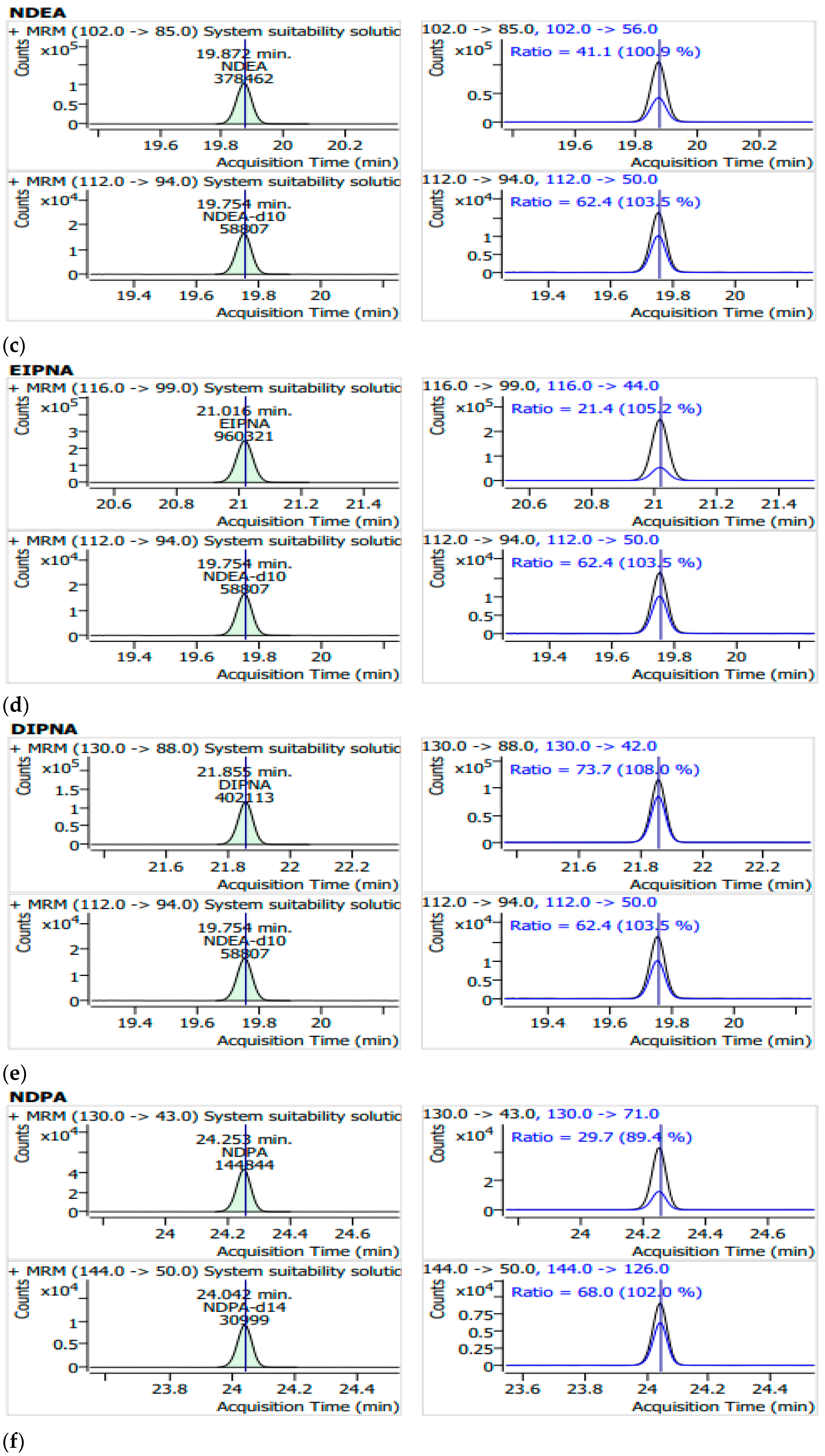

| Name of Nitrosamines and Internal Standards | Retention Time (min) | Quantifier (MRM/Collision Energies (V)) | Qualifier (MRM/Collision Energies (V)) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NDMA | 17.2 | 74 → 44/4 | 74 → 42/22 |
| NDMA-d6 | 17.2 | 80 → 50/6 | 80 → 46/20 |
| NMEA | 18.9 | 88 → 71/5 | 88 → 42/20 |
| NMEA-d3 | 18.9 | 91 → 74/3 | 91 → 46/5 |
| NDEA | 19.9 | 102 → 85/5 | 102 → 56/20 |
| NDEA-d10 | 19.8 | 112 → 94/5 | 112 → 50/10 |
| EIPNA | 21.0 | 116 → 99/5 | 116 → 44/15 |
| NDEA-d10 * | 19.8 | 112 → 94/5 | 112 → 50/10 |
| DIPNA | 21.9 | 130 → 88/5 | 130 → 42/10 |
| NDEA-d10 * | 19.8 | 112 → 94/5 | 112 → 50/10 |
| NDPA | 24.3 | 130 → 43/10 | 130 → 71/10 |
| NDPA-d14 | 24.0 | 144 → 50/20 | 144 → 126/10 |
| NDBA | 29.2 | 158 → 99/5 | 158 → 84/20 |
| NDBA-d18 | 28.9 | 94 → 62/20 | 94 → 46/20 |
| NPIP | 29.9 | 114 → 84/10 | 114 → 97/5 |
| NDPA-d14 * | 24.0 | 144 → 50/20 | 144 → 126/10 |
| NMOR | 32.0 | 116 → 86/5 | 116 → 56/25 |
| NMOR-d8 | 32.0 | 124 → 94/5 | 124 → 62/15 |
| Test Solution | Specification | Name | Min. | Max. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.0~50.0 ng/mL for nine impurity solutions | Coefficient of determination R2 ≥ 0.99 | NDMA | 0.99899 | 0.99936 |
| NDEA | 0.99831 | 0.99959 | ||
| NMEA | 0.99949 | 0.99981 | ||
| NDPA | 0.99880 | 0.99939 | ||
| NDBA | 0.99745 | 0.99812 | ||
| NPIP | 0.99870 | 0.99894 | ||
| NMOR | 0.99838 | 0.99874 | ||
| DIPNA | 0.99845 | 0.99976 | ||
| EIPNA | 0.99820 | 0.99955 |
| Test Solution | Specification | Name | Average/RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5, 10 and 50 ng/mL spiked sample | Recovery rate: 70.0~130.0% | NDMA | 114.23/5.27 |
| NDEA | 110.75/4.98 | ||
| NMEA | 110.47/4.09 | ||
| NDPA | 108.35/5.73 | ||
| NDBA | 111.62/9.34 | ||
| NPIP | 113.34/5.10 | ||
| NMOR | 99.15/6.28 | ||
| DIPNA | 112.16/4.95 | ||
| EIPNA | 114.68/4.76 |
| Test Solution | Specification | Name | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Six replicates (20 ng/mL) | RSD ≤ 20.0% | NDMA | 4.7 |
| NDEA | 3.8 | ||
| NMEA | 5.1 | ||
| NDPA | 3.8 | ||
| NDBA | 5.0 | ||
| NPIP | 5.6 | ||
| NMOR | 4.9 | ||
| DIPNA | 4.3 | ||
| EIPNA | 3.6 |
| Test Solution | Specification | Name | RSD (%) | S/N Min, Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 ng/mL solution | RSD ≤ 20.0% Signal-to-noise (S/N) ≥ 10 | NDMA | 2.222 | 26.1, 36.3 |
| NDEA | 2.505 | 19.3, 25.2 | ||
| NMEA | 4.366 | 23.6, 38.6 | ||
| NDPA | 2.968 | 28.8, 54.2 | ||
| NDBA | 7.889 | 28.2, 56.7 | ||
| NPIP | 0.712 | 11.6, 17.1 | ||
| NMOR | 1.493 | 17.0, 30.9 | ||
| DIPNA | 1.444 | 29.3, 40.0 | ||
| EIPNA | 1.605 | 20.0, 27.4 |
| Test Solution | Specification | Name | RSD (%) | S/N Min, Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 ng/mL solution | Signal-to-noise (S/N) ≥ 3 | NDMA | 2.040 | 16.3, 27.0 |
| NDEA | 5.542 | 10.1, 13.5 | ||
| NMEA | 2.156 | 17.5, 25.6 | ||
| NDPA | 0.778 | 17.0, 43.8 | ||
| NDBA | 6.230 | 15.8, 19.4 | ||
| NPIP | 4.277 | 7.5, 11.1 | ||
| NMOR | 1.695 | 10.9, 16.1 | ||
| DIPNA | 0.741 | 16.5, 20.4 | ||
| EIPNA | 1.465 | 13.1, 18.1 |
| Test Solution | Specification | Name | Change Rate (24 h, 48 h (%)) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 ng/mL spiked sample | Change rate after 24 and 48 h (%) ≤ 20.0% | NDMA | 0.75, 0.26 |
| NDEA | 0.61, 3.07 | ||
| NMEA | 0.55, 2.18 | ||
| NDPA | 1.72, 3.19 | ||
| NDBA | 0.93, 1.32 | ||
| NPIP | 4.01, 6.38 | ||
| NMOR | 2.39, 0.82 | ||
| DIPNA | 4.14, 5.95 | ||
| EIPNA | 2.21, 4.13 |
| No. | NDMA | NDEA | NMEA | NDPA | NDBA | NPIP | NMOR | DIPNA | EIPNA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 81.7 | 90.7 | 89.6 | 86.3 | 93.4 | 89.0 | 88.7 | 84.9 | 80.0 |
| 2 | 87.1 | 83.9 | 83.3 | 77.2 | 85.3 | 80.5 | 82.9 | 83.6 | 82.4 |
| 3 | 94.8 | 85.8 | 82.3 | 89.0 | 88.3 | 82.6 | 85.5 | 79.6 | 78.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, N.; Go, H.; Park, Y.-j. Simultaneous Determination and Quantification of NineNitrosamine Impurities in Semi-Solid Forms Using a GC–MS/MS Method. Separations 2025, 12, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12050120
Lee N, Go H, Park Y-j. Simultaneous Determination and Quantification of NineNitrosamine Impurities in Semi-Solid Forms Using a GC–MS/MS Method. Separations. 2025; 12(5):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12050120
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Namjin, Hyejin Go, and Young-joon Park. 2025. "Simultaneous Determination and Quantification of NineNitrosamine Impurities in Semi-Solid Forms Using a GC–MS/MS Method" Separations 12, no. 5: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12050120
APA StyleLee, N., Go, H., & Park, Y.-j. (2025). Simultaneous Determination and Quantification of NineNitrosamine Impurities in Semi-Solid Forms Using a GC–MS/MS Method. Separations, 12(5), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12050120








