Efficient Resource Utilization and Environmentally Safe Recovery of Platinum Group Metals from Spent Automotive Catalysts via Copper Smelting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Process
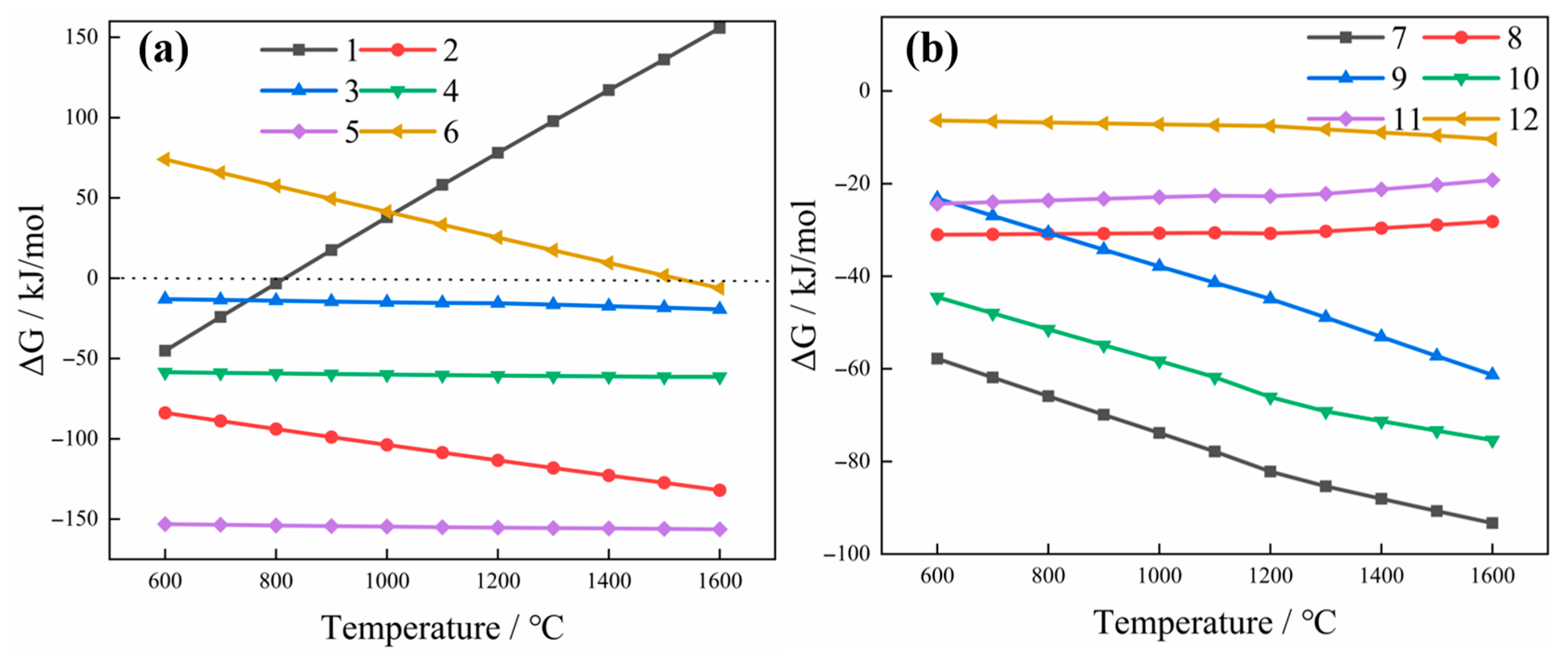
2.1. Thermodynamic Analysis
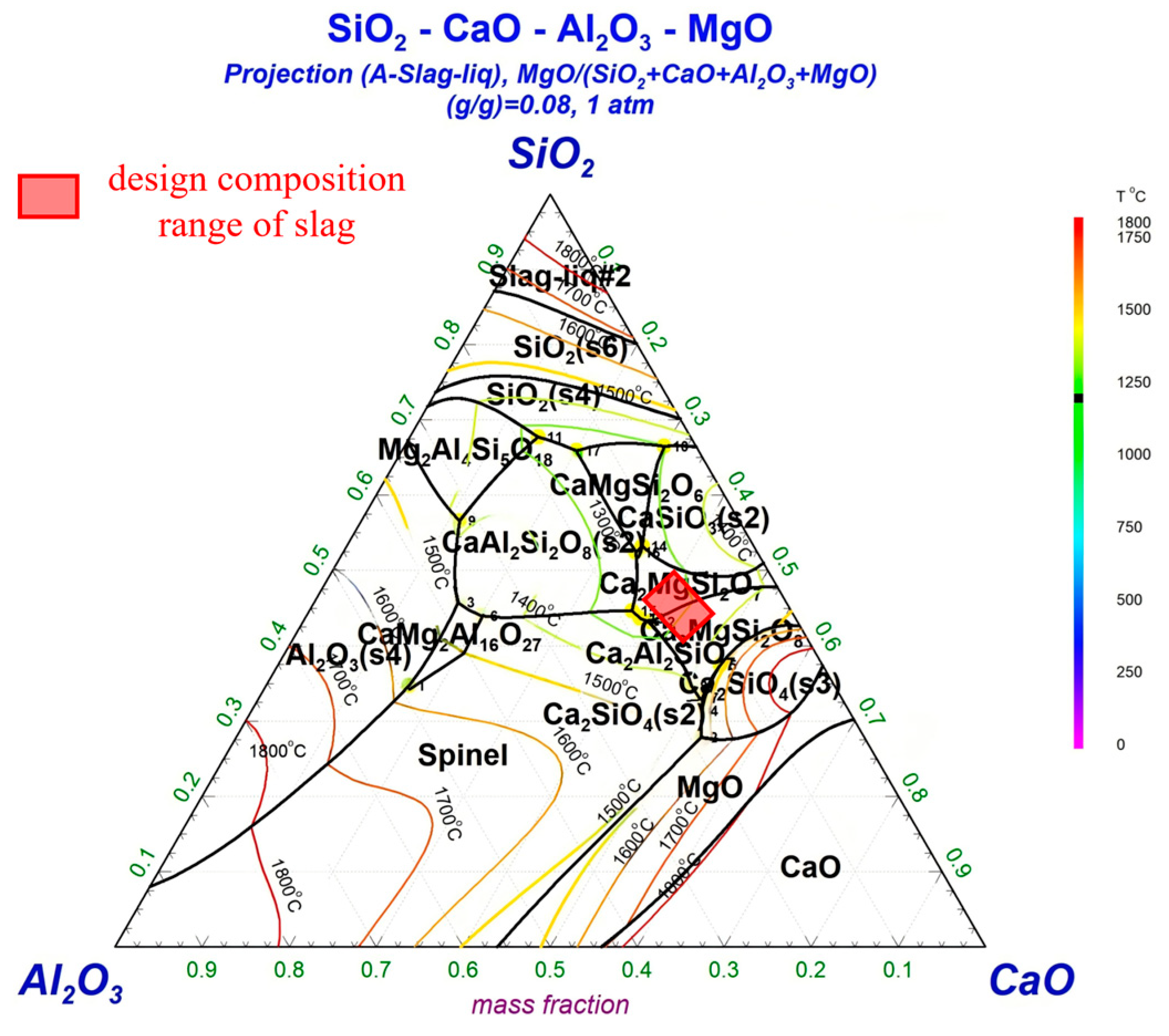
2.2. Slag Design
2.3. Recycling Process
2.4. TCLP Test
3. Results and Discussion
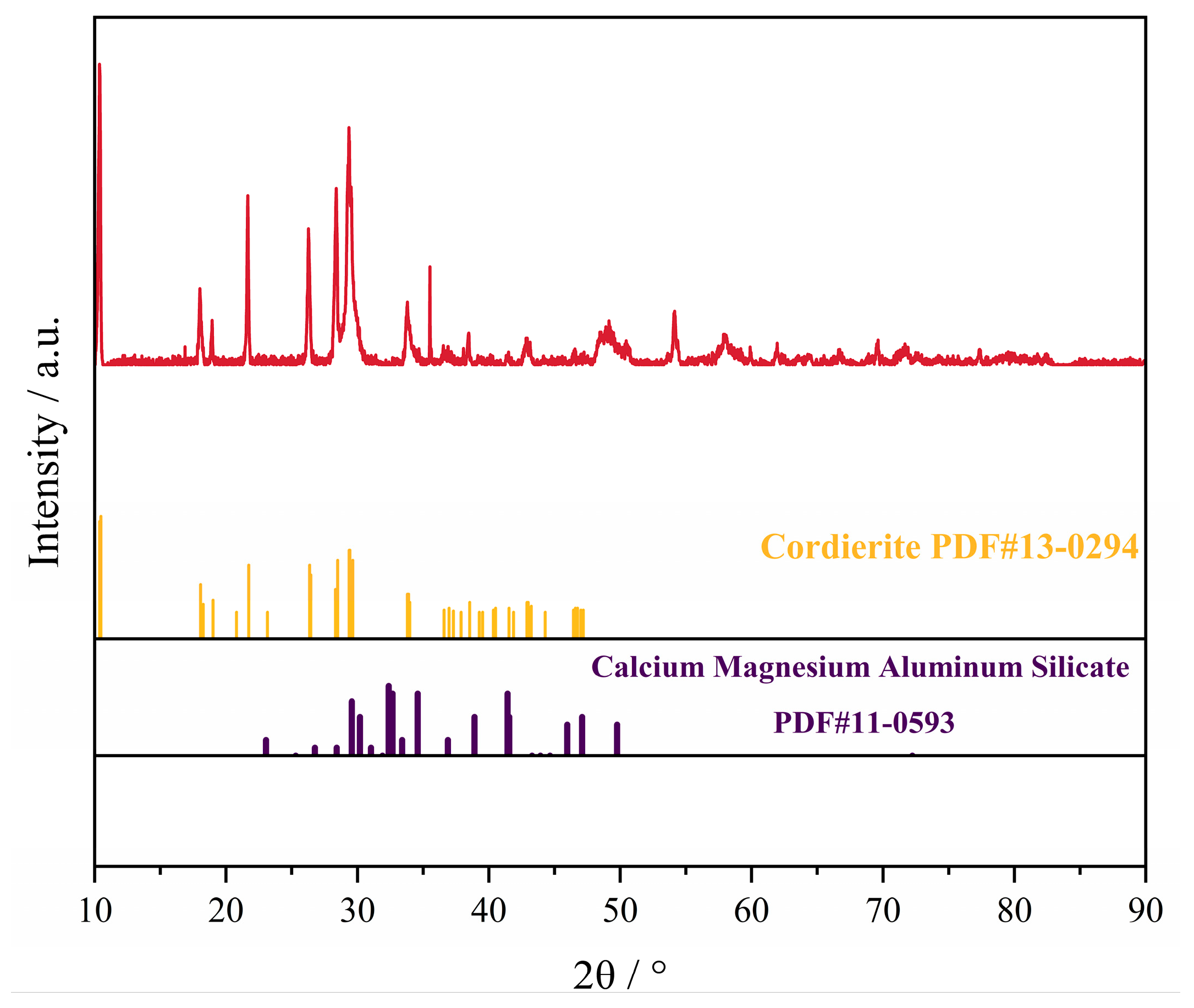
3.1. Slag Composition Selection
3.1.1. The Influence of the Mass Ratio of CaO/SiO2 on the Physical Properties of Slag
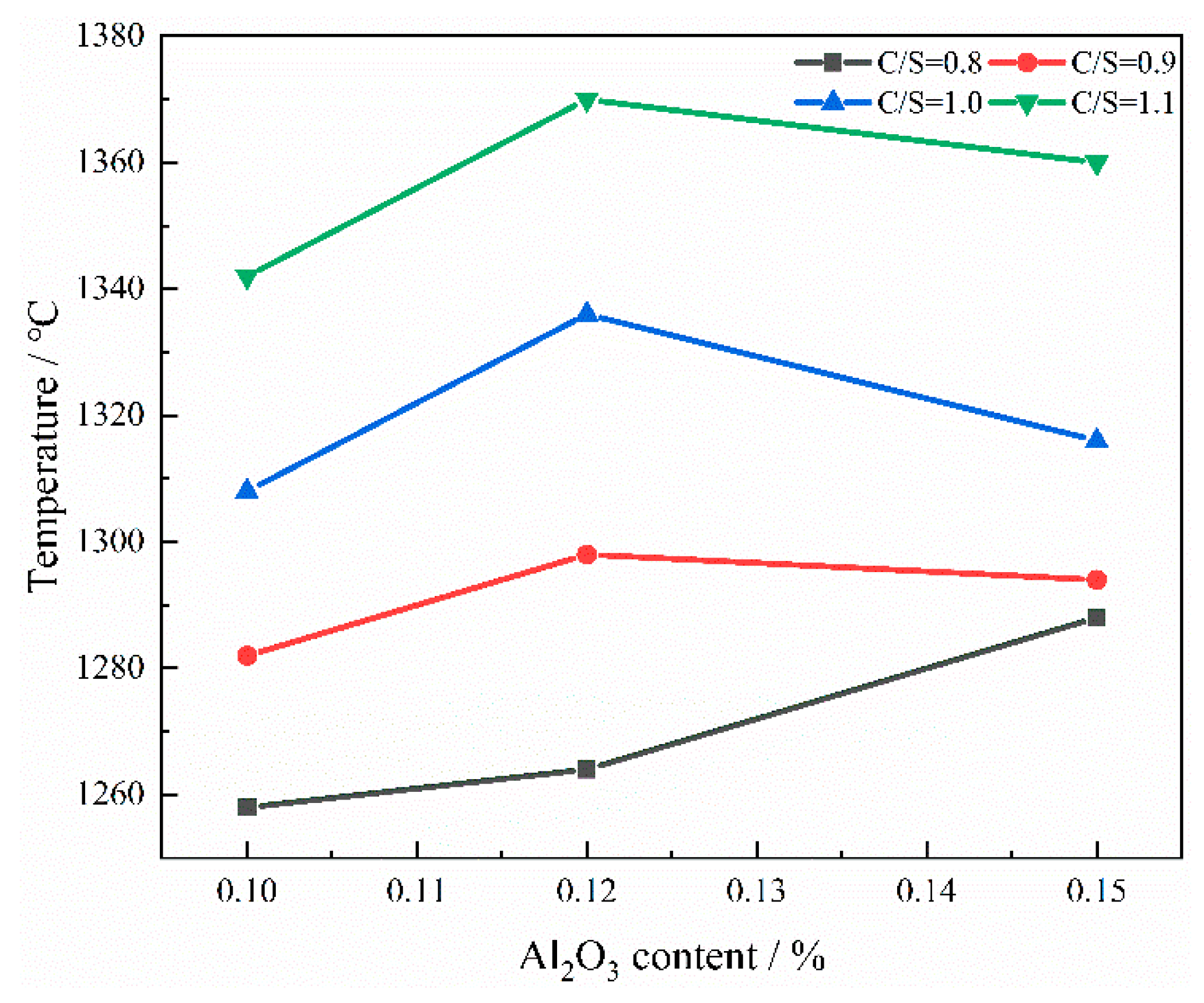
3.1.2. The Influence of Al2O3 Content on the Physical Properties of Slag
3.2. Selection of Process Conditions
3.2.1. The Effect of Copper Dosage
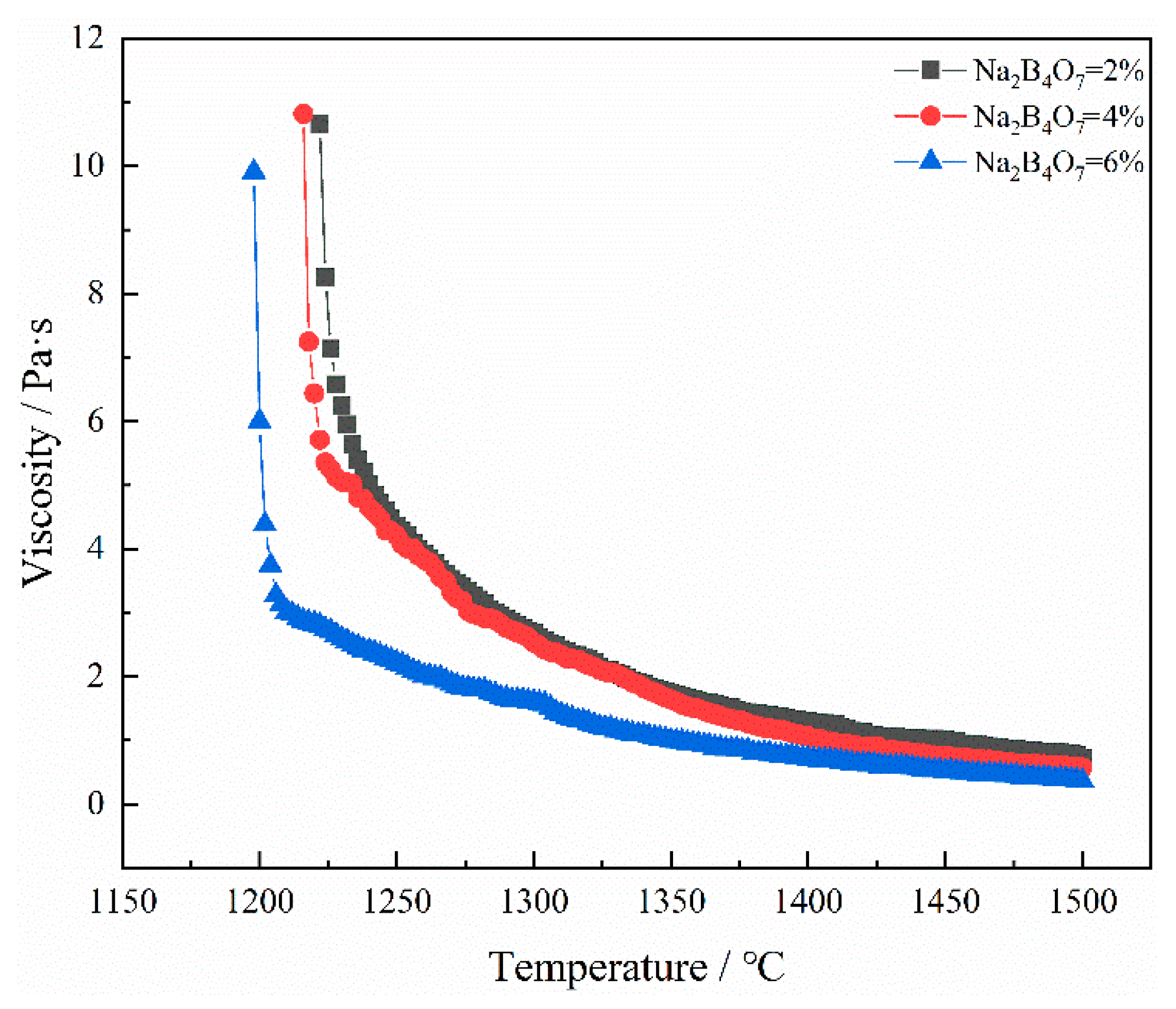
3.2.2. The Effect of Na2B4O7 Dosage
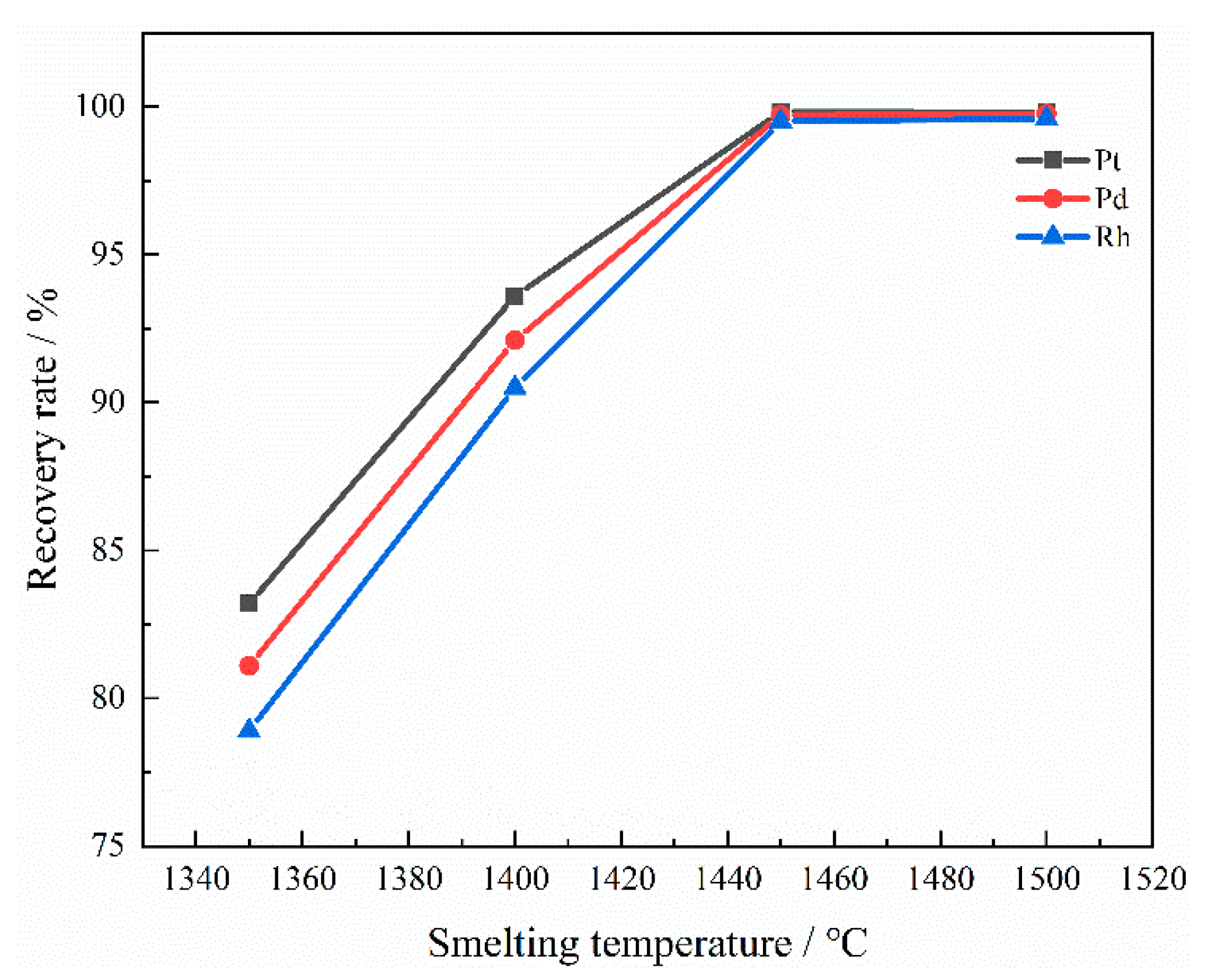
3.2.3. The Effect of Smelting Temperature
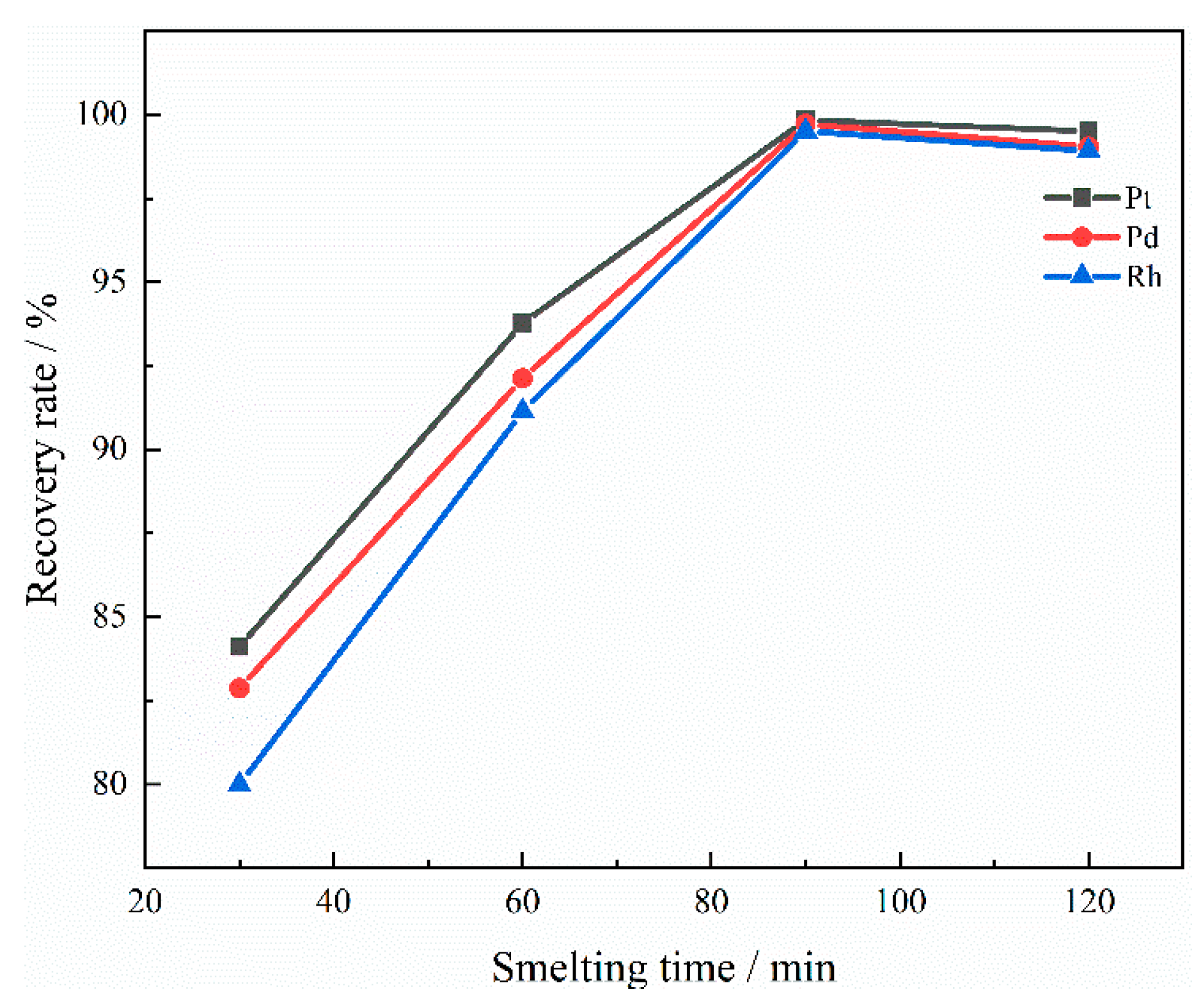
3.2.4. The Effect of Smelting Time
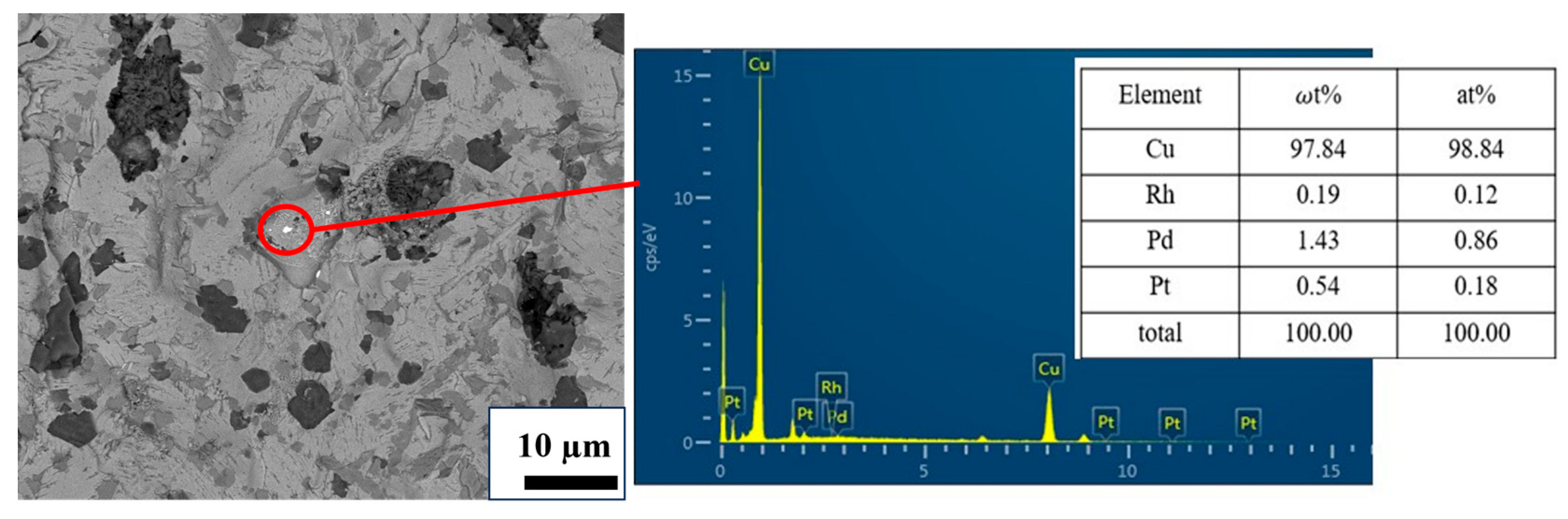
3.3. Verification Experiments
3.4. Pilot-Scale Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, A.; Chen, C.; Tian, M.; Tian, B.; Xue, T.; Qi, T.; Zhang, H. In Situ Mechanochemical Treatment of the Fe-Si-PGMs Alloy for Enhanced Platinum Group Metal Recovery: Overcoming Thermodynamic and Kinetic Barriers. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 4506–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Zheng, H.; Chang, C.-C.; Ekberg, C. Recovery of precious metals from electronic waste and spent catalysts: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Group, Focus On Catalysts. Platinum group metals market size worth $58 bn in 2032. Focus Catal. 2024, 2024, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukurugya, F.; Wouters, W.; Spooren, J. Microwave-assisted chloride leaching for efficient recovery of platinum group metals from spent automotive catalysts: An approach for chemical reagent reduction. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2025, 24, 100868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S.; Saw, H.M.; Ting, Y.-P. of green chemistry metrics for sustainable recycling of platinum group metals from spent automotive catalysts via bioleaching. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 4112–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilli, M.L.; Slobozeanu, A.E.; Larosa, C.; Paneva, D.; Yakoumis, I.; Cherkezova-Zheleva, Z. Platinum Group Metals: Green Recovery from Spent Auto-Catalysts and Reuse in New Catalysts—A Review. Crystals 2023, 13, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.P.; Piedras, F.V.; Rodrigues, P.G.; Nogueira, C.A. Hydrometallurgical recovery of platinum-group metals from spent auto-catalysts—Focus on leaching and solvent extraction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 286, 120474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Song, W.; Lyu, J.; Liu, M.; Chen, P.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, X.; Yang, Z. Novel approach for synergistic capturing of platinum group metals from spent automotive catalysts with Pb-Bi alloy. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 197, 106923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubo, A.; Sun, S.; Tu, G.; Liu, R.; Xiao, F.; Shi, R.; Sui, C.; Yu, K. Iron capture mechanism for harmless recovering platinum group metals from spent automobile catalyst. Environ. Technol. 2025, 46, 1666–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcali, M.H. A new approach to recover platinum-group metals from spent catalytic converters via iron matte. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 159, 104891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Ding, Y.; Wen, Q.; Zhao, S.; He, X.; Zhang, S.; Dong, C. Slag design and iron capture mechanism for recovering low-grade Pt, Pd, and Rh from leaching residue of spent auto-exhaust catalysts. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 802, 149830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sun, S.; Tu, G.; Xiao, F. A novel method for extraction of platinum from spent automotive catalyst: Utilization of spent fluid catalytic cracking catalyst as flux. Environ. Technol. 2021, 44, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.-F.; Yin, X.-P.; Ding, Y.-J.; Shi, Z.-S.; Zhao, B.-H.; Zheng, H.-D.; Jian, J.-X.; Zhang, S.-G.; Chang, C.-C. Slag design and optimization for iron capturing platinum group metals from alumina-based spent catalysts. Rare Met. 2023, 42, 2093–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Wu, B.; Jian, Z. Highly efficient recovery of platinum, palladium, and rhodium from spent automotive catalysts via iron melting collection. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 155, 104644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Ghahreman, A. Platinum group metals recycling from spent automotive catalysts:metallurgical extraction and recovery technologies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 311, 123357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z. An integrated capture of copper scrap and electrodeposition process to enrich and prepare pure palladium for recycling of spent catalyst from automobile. Waste Manag. 2020, 108, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xv, B.; Li, Z.; Zha, G.; Liu, D.; Yang, B.; Jiang, W. Recovery of platinum group metals from spent automotive catalysts: Review of conventional techniques and vacuum metallurgy. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2025, 215, 108103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Y.; Hua, W.; Jianhang, H. Co-treatment of electroplating sludge, copper slag, and spent cathode carbon for recovering and solidifying heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sun, S.; Tu, G.; Xiao, F. Co-treatment of spent automotive catalyst and cyanide tailing via vitrification and smelting-collection process for platinum group metals recovery. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Dang, J.; Guo, J.; Zhou, H.; Lü, X. Viscosity and structure relationship with equimolar substitution of CaO with MgO in the CaO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2 slag melts. Int. J. Miner. Met. Mater. 2024, 32, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Chu, M.; Tang, J.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Z. Effect of CaO/SiO2 and Al2O3 on Viscous Behaviors of the Titanium earing Blast Furnace Slag. Steel Res. Int. 2016, 87, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.Y.; Liu, X.H.; Li, J.; Yin, X.T.; Song, S.; Wang, Q. Influence of Al2O3 and MgO on the viscosity and stability of CaO-MgO-SiO2-Al2O3 slags with CaO/SiO2 = 1.0. Isij Int. 2017, 57, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, Z.; Chen, S.; Li, K.; Zhang, J.; Liang, W.; Sun, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. Molecular dynamics investigations on the effect of Na2O on the structure and properties of blast furnace slag under different basicity conditions. Mol. Liq. 2019, 299, 112195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusen, A.; Geveci, A.; Topkaya, Y.A.; Derin, B. Effects of some additives on copper losses to matte smelting slag. JOM 2016, 68, 2323–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; An, C.; Sun, Z.; Pulatov, B.; Wei, S.; Fan, J. Review of glass-ceramics: Solidification of toxic elements and durability. Waste Manag. 2025, 200, 114764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shubo, A.; Sun, S.; Tu, G.; Yan, Y.; Xiao, F.; Liu, R.; Sui, C.; Yu, K. Crystallization behavior of smelting slag for recovery of platinum group metals from spent automotive catalysts and preparation of foamed glass-ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 5930–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Ma, P.; Yan, J. Valorization of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash for mineral wool fiber production: Effects on vitrification process and melt viscosity. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



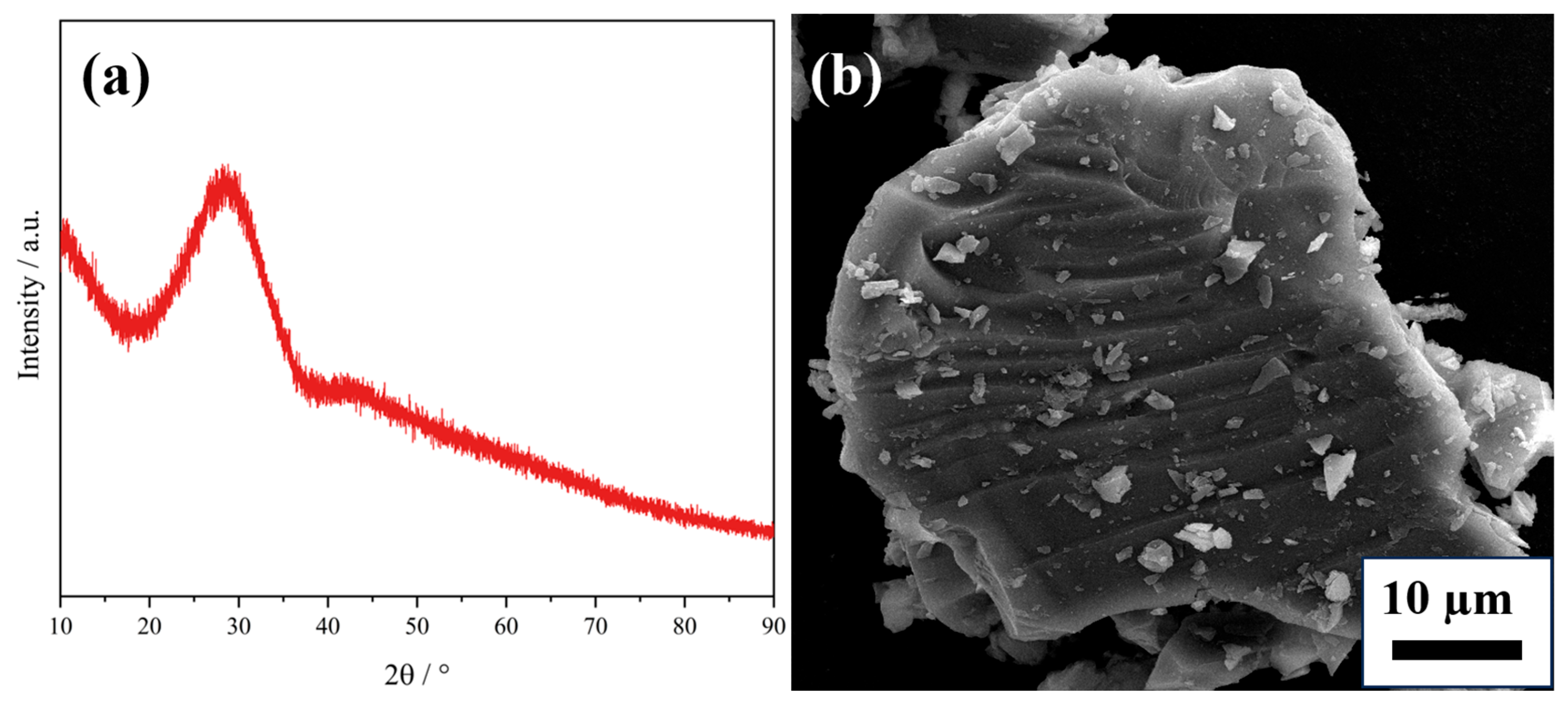
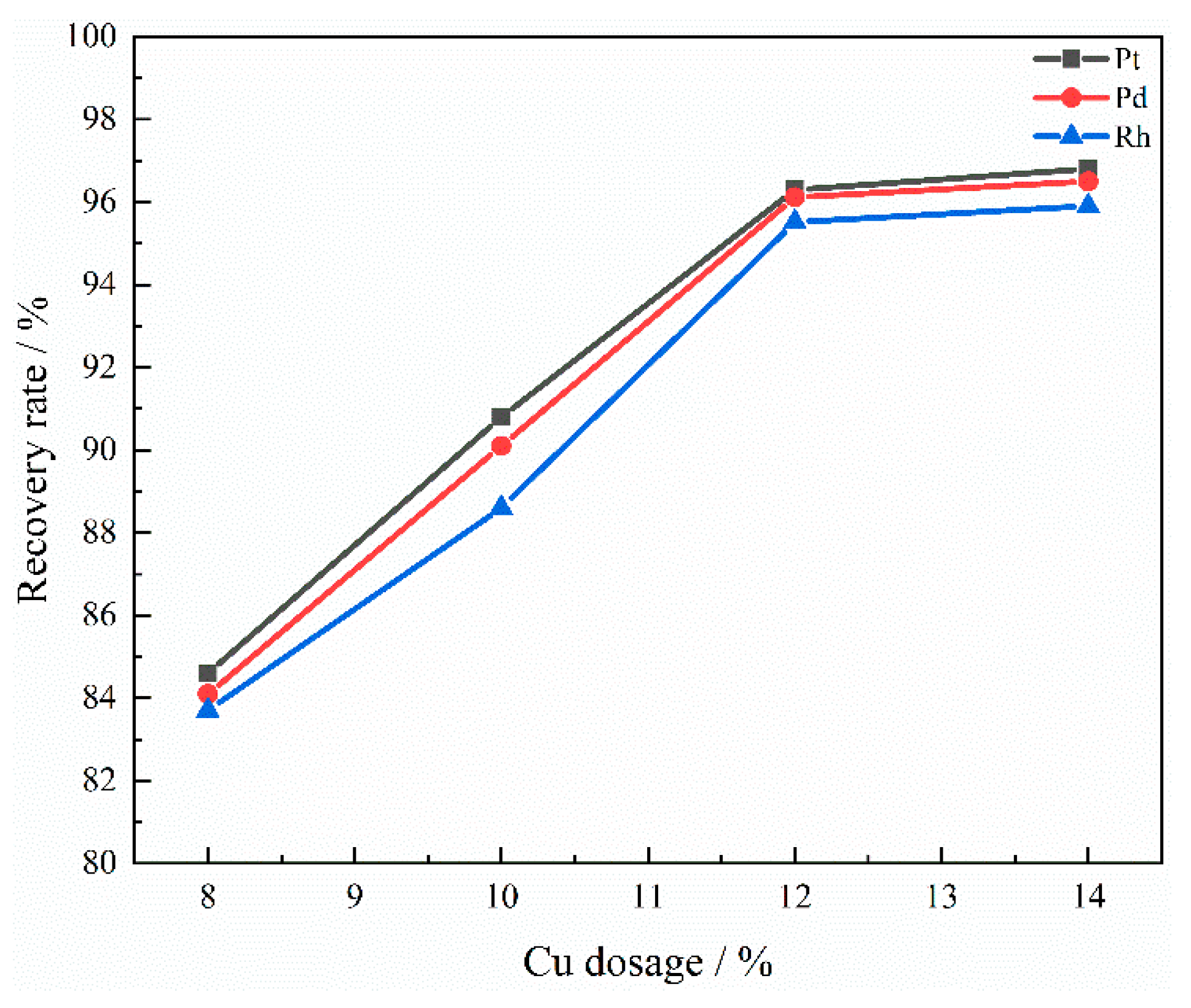
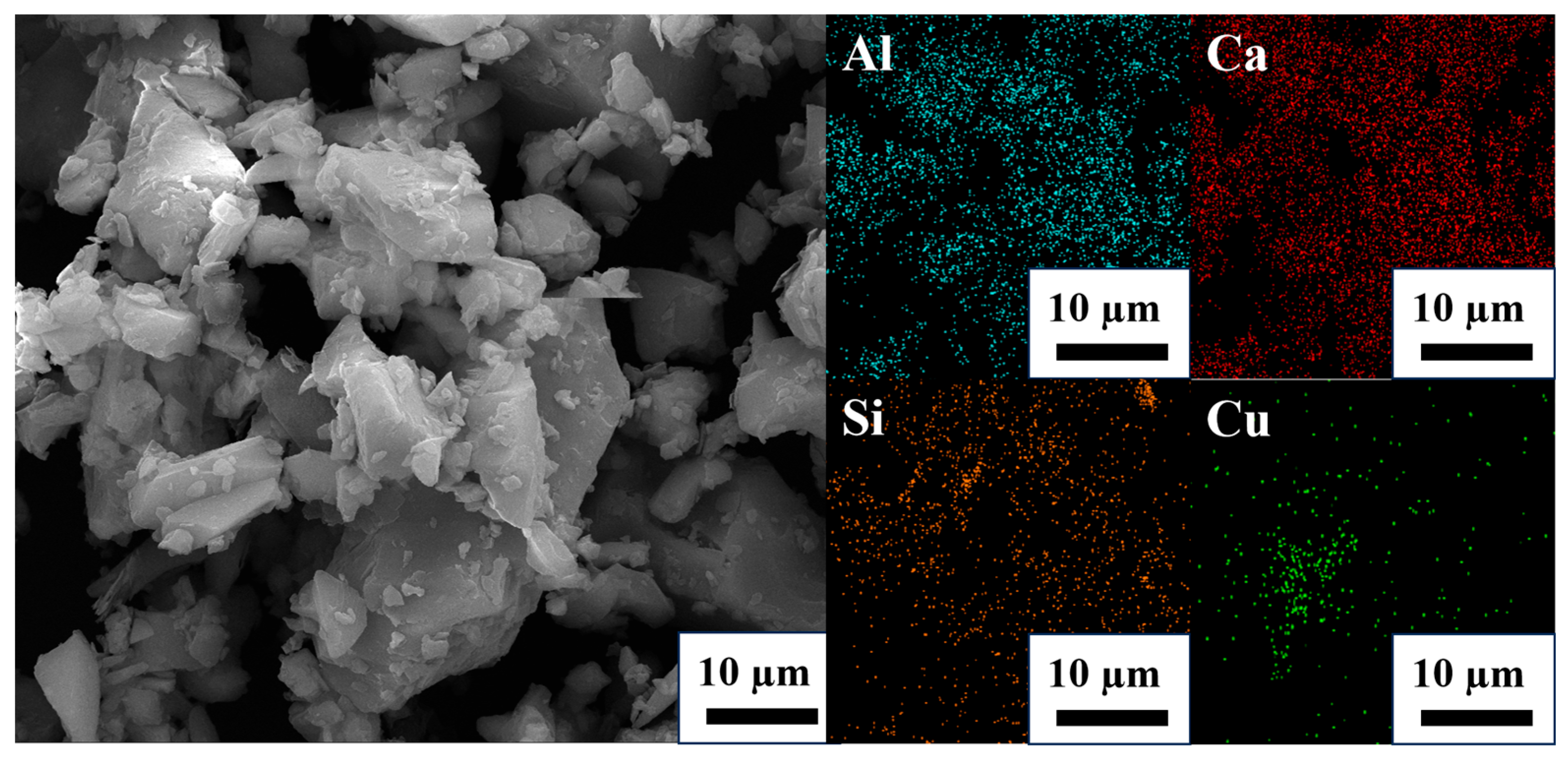
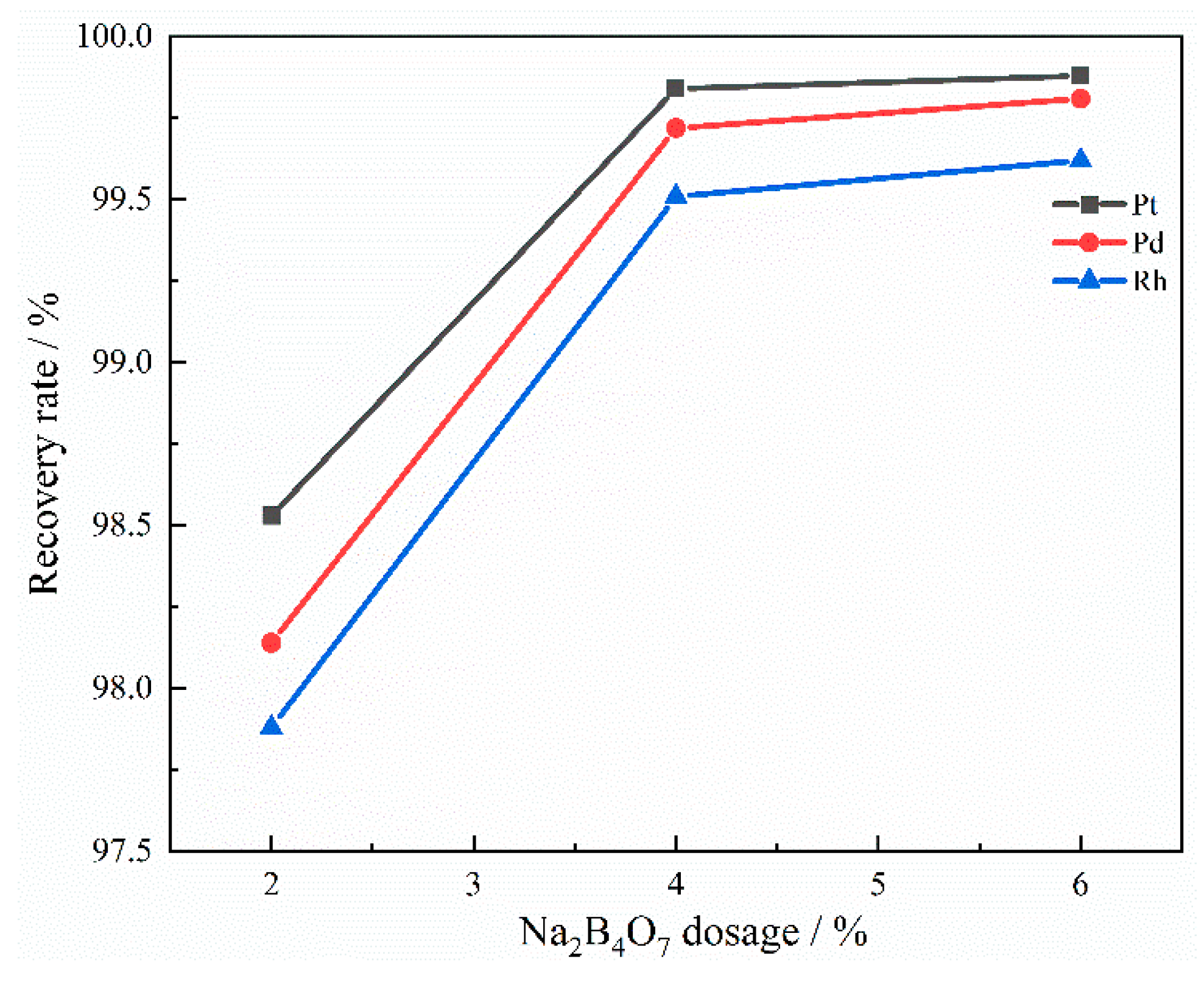



| Component | SiO2 (wt%) | CaO (wt%) | Al2O3 (wt%) | MgO (wt%) | Pt/(g/t) | Pd/(g/t) | Rh/(g/t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 35.89 | 0.26 | 34.86 | 8.79 | 310 | 2140 | 320 |
| No | CaO/SiO2 | SiO2 (wt%) | CaO (wt%) | Al2O3 (wt%) | MgO (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.8 | 46.67 | 37.33 | 10.00 | 6.00 |
| 2 | 0.8 | 45.56 | 36.44 | 12.00 | 6.00 |
| 3 | 0.8 | 43.89 | 35.11 | 15.00 | 6.00 |
| 4 | 0.9 | 44.21 | 39.79 | 10.00 | 6.00 |
| 5 | 0.9 | 43.16 | 38.84 | 12.00 | 6.00 |
| 6 | 0.9 | 41.58 | 37.42 | 15.00 | 6.00 |
| 7 | 1.0 | 42.00 | 42.00 | 10.00 | 6.00 |
| 8 | 1.0 | 41.00 | 41.00 | 12.00 | 6.00 |
| 9 | 1.0 | 39.50 | 39.50 | 15.00 | 6.00 |
| 10 | 1.1 | 40.00 | 44.00 | 10.00 | 6.00 |
| 11 | 1.1 | 39.05 | 42.95 | 12.00 | 6.00 |
| 12 | 1.1 | 37.62 | 41.38 | 15.00 | 6.00 |
| Sam | Cu/g | Na2B4O7/g | Temperature/°C | Time/min | Mass of Slag/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8 | 0 | 1450 | 90 | 289.7 |
| 2 | 10 | 0 | 1450 | 90 | 290.3 |
| 3 | 12 | 0 | 1450 | 90 | 289.1 |
| 4 | 14 | 0 | 1450 | 90 | 291.1 |
| 5 | 12 | 2 | 1450 | 90 | 292.9 |
| 6 | 12 | 4 | 1450 | 90 | 294.2 |
| 7 | 12 | 6 | 1450 | 90 | 296.5 |
| 8 | 12 | 4 | 1350 | 90 | 294.1 |
| 9 | 12 | 4 | 1400 | 90 | 294.8 |
| 10 | 12 | 4 | 1450 | 90 | 295.0 |
| 11 | 12 | 4 | 1500 | 90 | 294.3 |
| 12 | 12 | 4 | 1450 | 30 | 294.5 |
| 13 | 12 | 4 | 1450 | 60 | 294.7 |
| 14 | 12 | 4 | 1450 | 90 | 204.3 |
| 15 | 12 | 4 | 1450 | 120 | 293.9 |
| No. | Recovery Rate | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pt | Pd | Rh | |
| 1 | 99.50 | 99.23 | 99.10 |
| 2 | 99.66 | 99.59 | 99.30 |
| 3 | 99.76 | 99.60 | 99.28 |
| Metals | 1# | 2# | 3# | Standards |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | ND | ND | ND | |
| Cr | ND | ND | ND | 1 |
| As | 0.14 | ND | ND | 1 |
| Pb | ND | ND | 0.07 | 5 |
| Se | ND | ND | ND | 1 |
| Cu | 0.19 | 0.23 | 0.12 | 15 |
| Ag | ND | ND | ND | 5 |
| Cd | ND | ND | ND | 1 |
| Ba | 0.16 | ND | 0.5 | 100 |
| Hg | ND | ND | ND | 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
A, S.; Tu, G.; Sun, S.; Yan, Y.; Xiao, F.; Shi, R.; Sui, C.; Yu, K. Efficient Resource Utilization and Environmentally Safe Recovery of Platinum Group Metals from Spent Automotive Catalysts via Copper Smelting. Separations 2025, 12, 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12110315
A S, Tu G, Sun S, Yan Y, Xiao F, Shi R, Sui C, Yu K. Efficient Resource Utilization and Environmentally Safe Recovery of Platinum Group Metals from Spent Automotive Catalysts via Copper Smelting. Separations. 2025; 12(11):315. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12110315
Chicago/Turabian StyleA, Shubo, Ganfeng Tu, Shuchen Sun, Yaoyu Yan, Faxin Xiao, Ruifeng Shi, Chengfu Sui, and Kuopei Yu. 2025. "Efficient Resource Utilization and Environmentally Safe Recovery of Platinum Group Metals from Spent Automotive Catalysts via Copper Smelting" Separations 12, no. 11: 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12110315
APA StyleA, S., Tu, G., Sun, S., Yan, Y., Xiao, F., Shi, R., Sui, C., & Yu, K. (2025). Efficient Resource Utilization and Environmentally Safe Recovery of Platinum Group Metals from Spent Automotive Catalysts via Copper Smelting. Separations, 12(11), 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12110315






