Process Design and Techno-Economic Analysis of Heat Pump-Assisted Distillation for Crude Phenol Separation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Process Design and Simulation
2.2. Economic Analysis and CO2 Emission Calculations
3. Process Design
3.1. Conventional Distillation Process
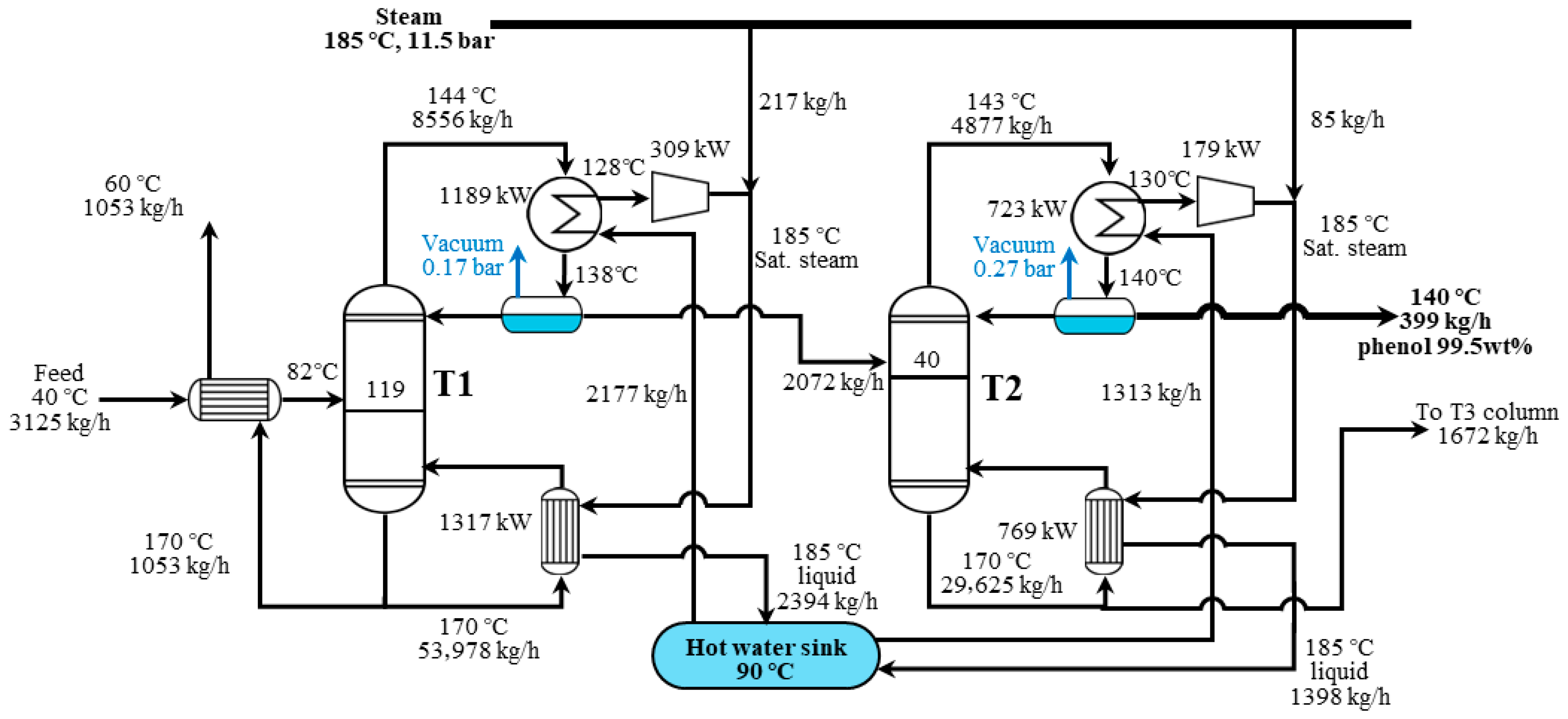
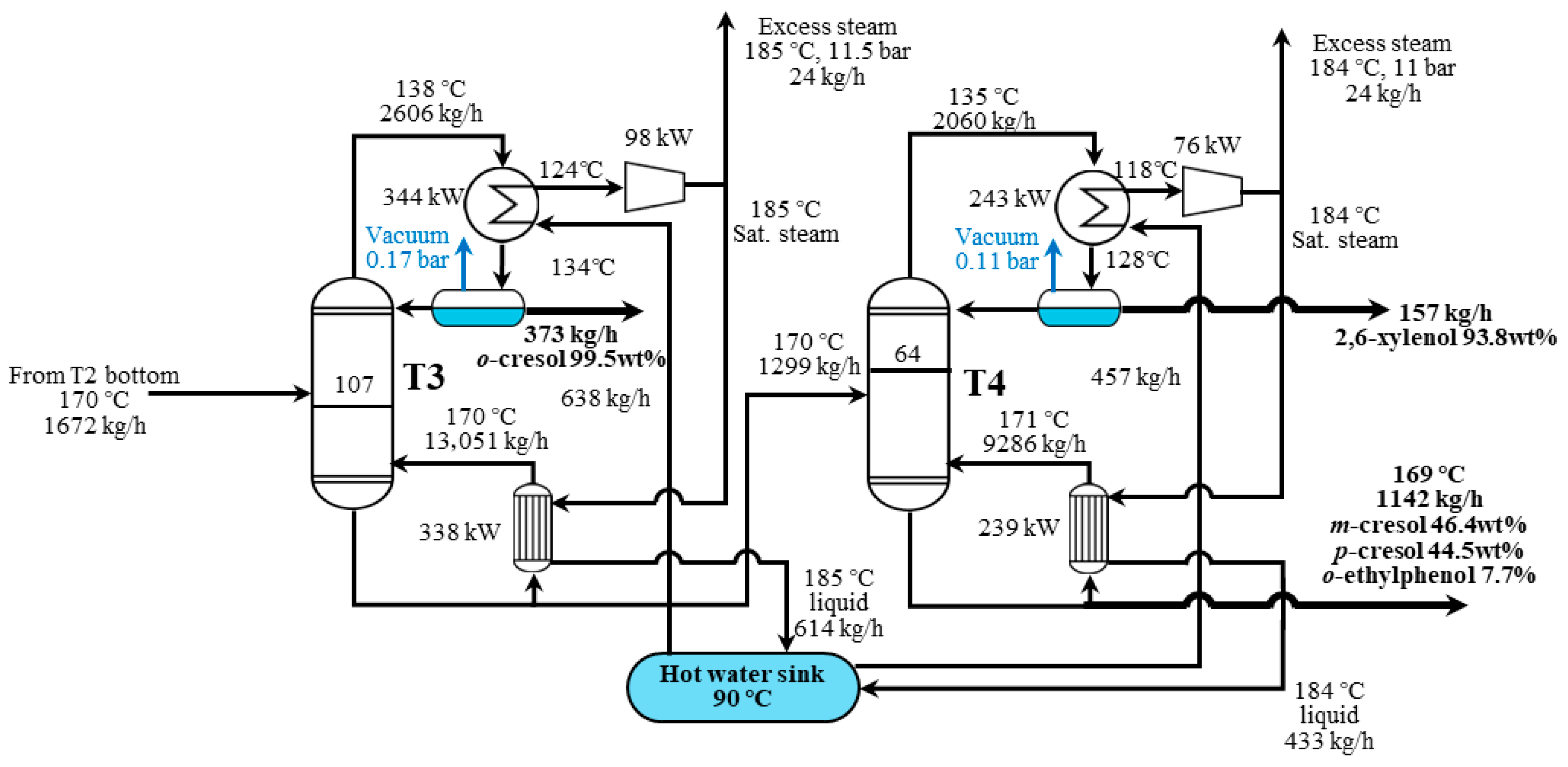
3.2. Heat Pump-Assisted Distillation Process
4. Sensitivity Analysis on Process Parameters
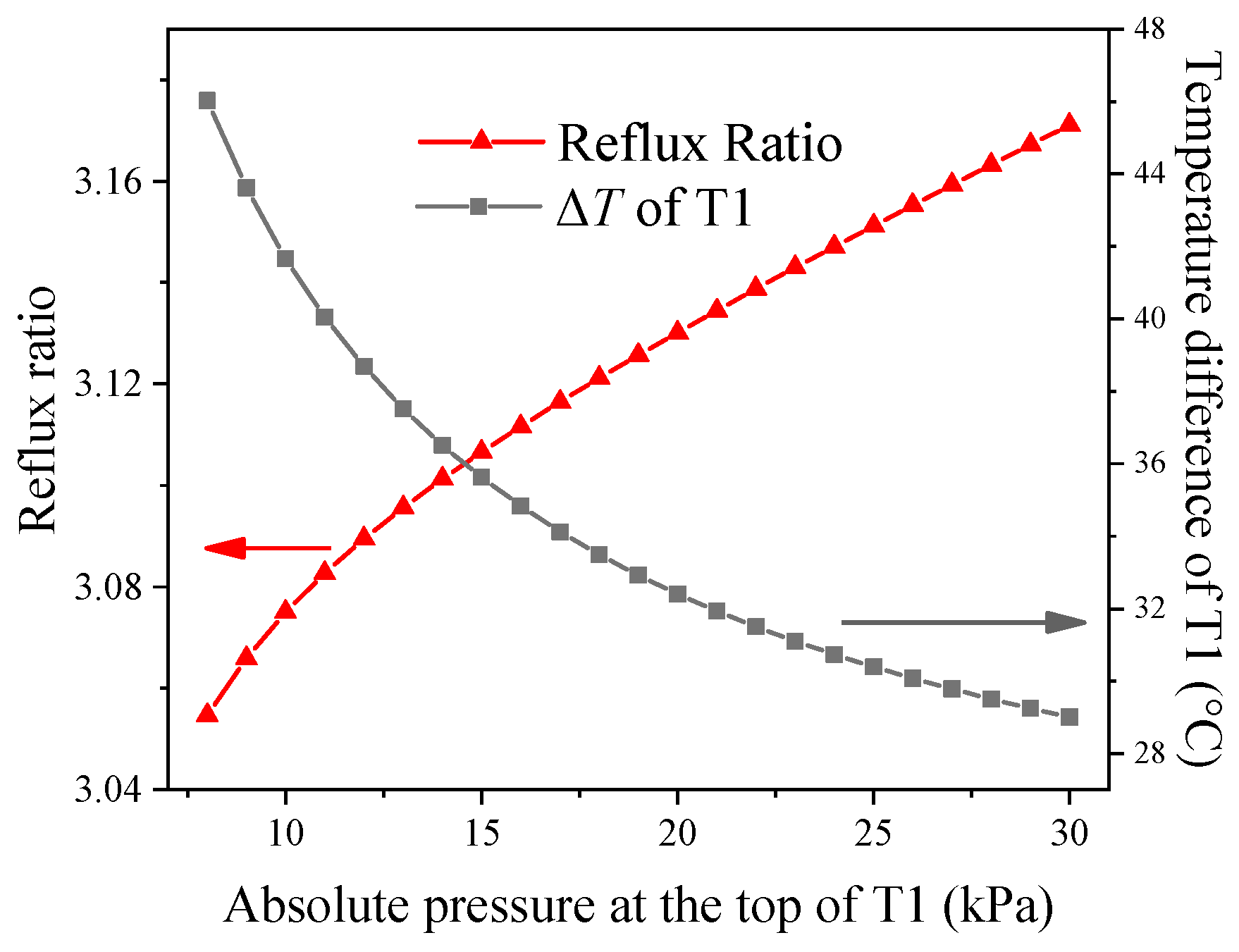
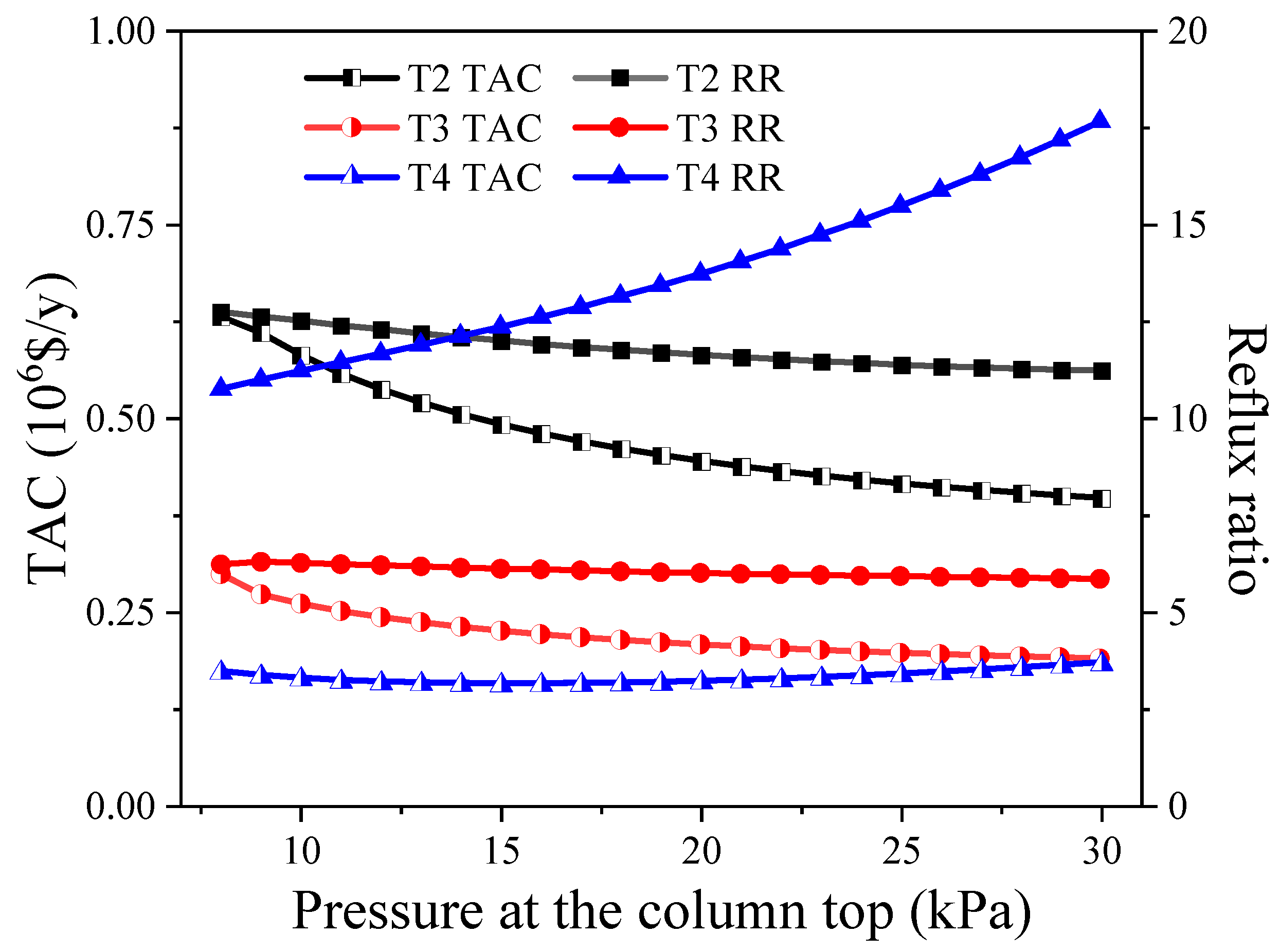
4.1. The Effect of Column Pressure
4.2. The Effect of Temperature Difference
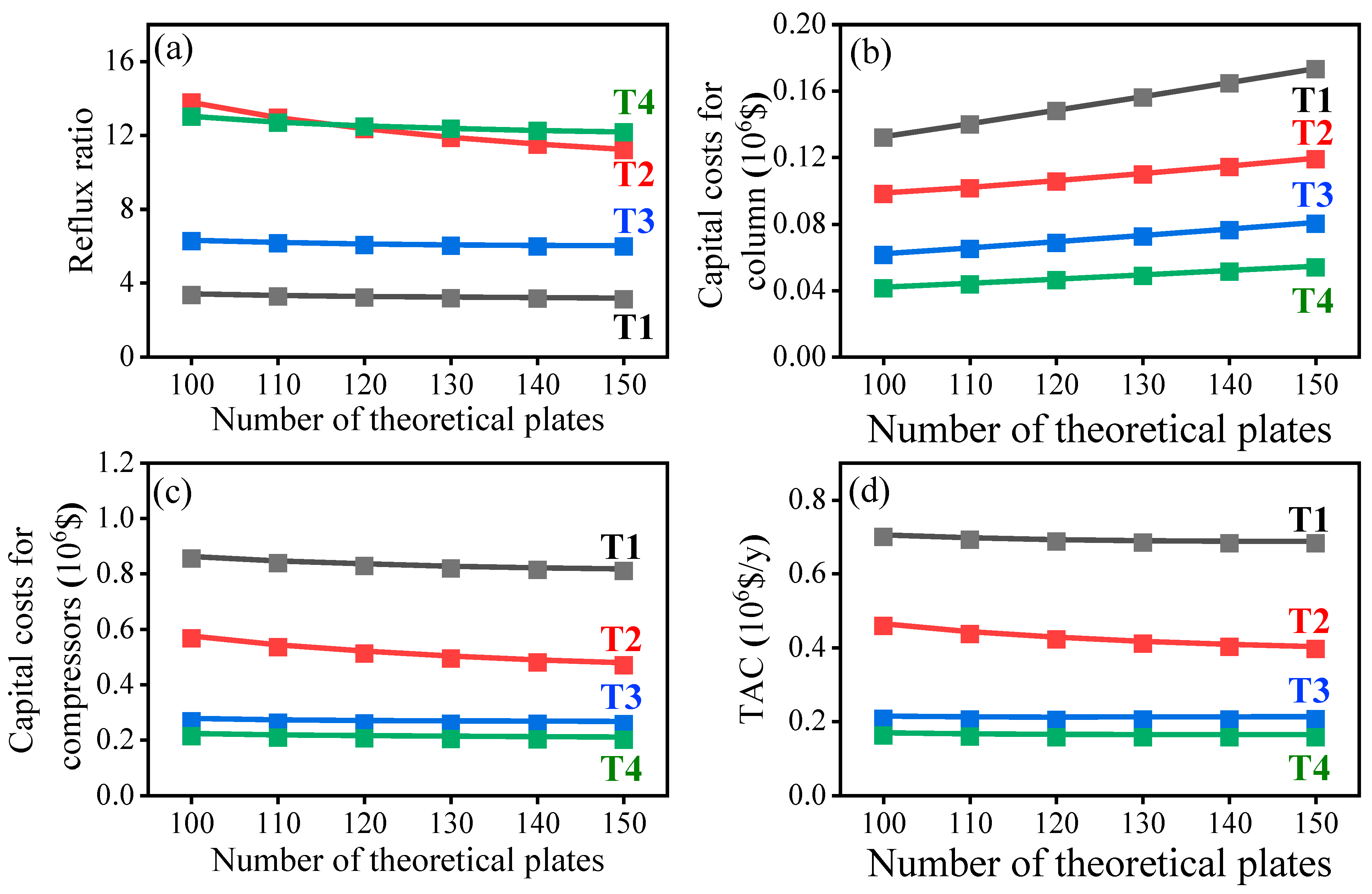
4.3. The Effect of Theoretical Stages
4.4. The Effect of Steam Cost on Process Economics
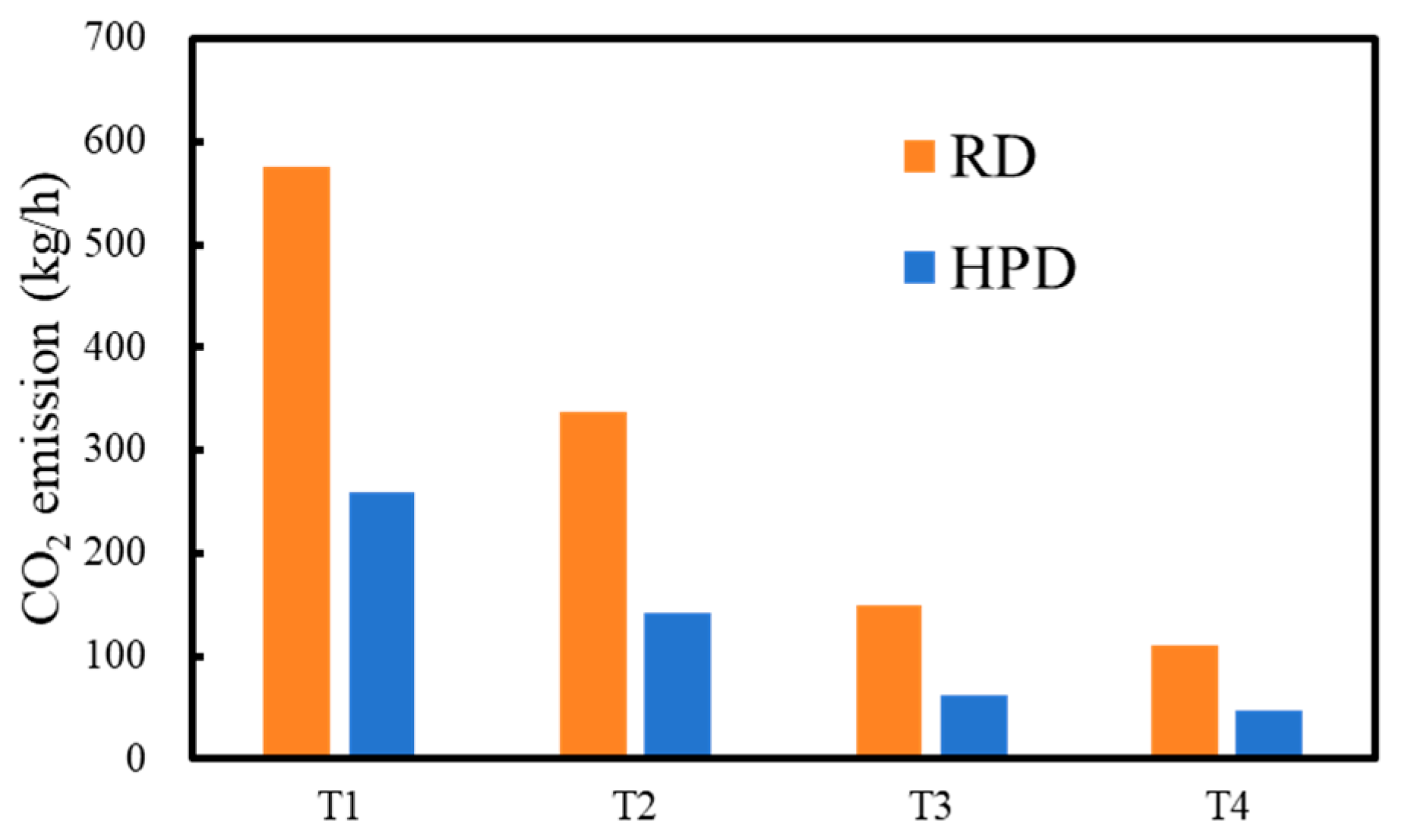
5. Environmental Impact
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richard, H.; Charles, G. Removal of Phenols from Phenol-Containing Stream. U.S. Patent 4256568A, 17 March 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, M.; Weber, M. Phenols. In Phenolic Resins: A Century of Progress; Pilato, L., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 9–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.-H.; Li, S.; Dong, X.-Q.; Ju, C.-X.; Mu, D.; Yang, Z.; Li, M.; Guo, X.-H.; Zong, Z.-M.; Cong, X.-S.; et al. Value-added utilization of hydroxy-substituted aromatics in coal-derived liquids. Fuel 2023, 340, 127492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, A.; Bibi, S.; Abu-Dieyeh, M.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. Towards sustainable physiochemical and biological techniques for the remediation of phenol from wastewater: A review on current applications and removal mechanisms. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 417, 137810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Huang, L.; Xiong, J. Process design, simulation and experimental studies of heteroazeotropic batch distillation for phenol dehydration. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 195, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, B.; Luo, H.; Yan, S.; Dai, J.; Bai, Z. Efficient recovery of phenol from coal tar processing wastewater with tributylphosphane/diethyl carbonate/cyclohexane: Extraction cycle and mechanism study. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 157, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, Z.; Ding, C.; Sun, Z.; Ma, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y. Separation of 1-methoxy-2-propanol and water by organic solvent extraction based on quantum chemistry calculation and liquid-liquid equilibrium experiment. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2024, 189, 107201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H. Energy-efficient synthesis of crude phenol separation process using advanced heat integrated technology. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 1888–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meylemans, H.A.; Groshens, T.J.; Harvey, B.G. Synthesis of Renewable Bisphenols from Creosol. Chemsuschem 2012, 5, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Hwang, S.; Won, S.; Kim, Y.; Hong, S.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Jeon, J.-K. Bisphenol F Synthesis from Formaldehyde and Phenol over Zeolite Y Extrudate Catalysts in a Catalyst Basket Reactor and a Fixed-Bed Reactor. Catalysts 2024, 14, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Brodu, N.; Mignot, M.; Youssef, B.; Taouk, B. Synthesis and characterization of phenolic resins based on pyrolysis bio-oil separated by fractional condensation and water extraction. Biomass Bioenergy 2022, 159, 106393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, A.K. Advances in heat pump assisted distillation column: A review. Energ. Convers. Manag. 2014, 77, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, A.; Mehrabani-Zeinabad, A.; Beheshti, M. Recently developed heat pump assisted distillation configurations: A comparative study. Appl. Energ. 2018, 211, 1261–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, A.A.; Smith, R. Rethinking energy use in distillation processes for a more sustainable chemical industry. Energy 2020, 203, 117788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Guo, J.; Feng, B.; Qiu, X.; Zhu, Q.; Song, H.; Gai, H.; Xiao, M.; Huang, T. Energy-saving extractive distillation process for the separation of close-boiling 2, 6-xylenol and p-cresol mixture. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2024, 159, 105505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyben, W.L. Capital cost of compressors for conceptual design. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2018, 126, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, X. Screening of Double Solvents Based on Multi-Index Evaluation Method for the Selective Separation m-Cresol from Model Oil. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 25798–25810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, W.M. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 95th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Yang, A.; Kong, Z.Y.; Huang, H.; Lv, L.; Zhou, Q.; Gu, B. The conceptual design and process intensification of the separation of ternary azeotropic mixture with heterogeneous characteristic. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2024, 204, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Hung, S.-K.; Lee, H.-Y.; Chien, I.L. Energy-Saving Designs for Separation of a Close-Boiling 1,2-Propanediol and Ethylene Glycol Mixture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 3828–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Fu, C.; Chang, H.; Li, N.; Qu, S.; Zhao, D.; Xu, C.; Qi, J.; Xu, M. Emission factors and driving forces of provincial-level CO2 from electricity production and consumption in China from 2013 to 2020. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 377, 124644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Chen, X.; Sun, X.; Xie, H. Economically and thermodynamically efficient pressure-swing distillation with heat integration and heat pump techniques. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 218, 119389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, S.; Shi, P.; Hou, W.; Zeng, A.; Ma, Y.; Yuan, X. Economically and thermodynamically efficient heat pump-assisted side-stream pressure-swing distillation arrangement for separating a maximum-boiling azeotrope. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 173, 115228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosser, F.; Jesper, M.; Vogelsang, J.; Walmsley, T.G.; Arpagaus, C.; Hesselbach, J. Large-scale heat pumps: Applications, performance, economic feasibility and industrial integration. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 133, 110219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, S.; Schmitt, B.; Vajen, K. The future of low carbon industrial process heat: A comparison between solar thermal and heat pumps. Sol. Energy 2018, 173, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpagaus, C.; Bless, F.; Uhlmann, M.; Schiffmann, J.; Bertsch, S.S. High temperature heat pumps: Market overview, state of the art, research status, refrigerants, and application potentials. Energy 2018, 152, 985–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieren, E.; Demeester, T.; Beyne, W.; Magni, C.; Abedini, H.; Arpagaus, C.; Bertsch, S.; Arteconi, A.; De Paepe, M.; Lecompte, S. The Potential of Vapor Compression Heat Pumps Supplying Process Heat between 100 and 200 °C in the Chemical Industry. Energies 2023, 16, 6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Rodriguez-Donis, I.; Gerbaud, V. Reducing process cost and CO2 emissions for extractive distillation by double-effect heat integration and mechanical heat pump. Appl. Energy 2016, 166, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 25198-2023; Pressure Vessel Heads. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2023.




| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Reducing energy consumption by recovering heat | High capital investment and longer payback periods |
| Lower operation costs | Sensitive to energy prices |
| Reduce CO2 emission and beneficial for environment | Difficulty in process integration |
| Components | Content (wt%) | Boiling Points (°C) a |
|---|---|---|
| Phenol | 12.76 | 181.8 |
| o-Cresol | 12.19 | 191.0 |
| m-Cresol | 18.02 | 202.2 |
| p-Cresol | 16.98 | 201.9 |
| 2,3-Xylenol | 1.44 | 216.9 |
| 2,4-Xylenol | 8.71 | 210.9 |
| 2,5-Xylenol | 5.17 | 211.1 |
| 2,6-Xylenol | 5.03 | 201.0 |
| 3,4-Xylenol | 0.44 | 227.3 |
| 3,5-Xylenol | 7.58 | 221.7 |
| o-Ethylphenol | 3.37 | 204.5 |
| m-Ethylphenol | 7.50 | 218.4 |
| p-Ethylphenol | 0.82 | 218.0 |
| Columns (including manufacturing cost) | 3733 USD/tonne |
| Column packing materials (BX gauze) | 615 USD/m3 |
| Capital cost for heat exchanges | 267 USD/m2 |
| Capital cost for steam compressors | 2012 USD/kW |
| Capital cost for vacuum pumps | 2051 USD/kW |
| Payback period | 3 years |
| Electricity | 0.1 USD/kWh |
| Cold water | 0.13 USD/tonne |
| Steam | 10.8 USD/GJ |
| Installation factor | 1.3 |
| Running time | 8000 h/y |
| CO2 emissions for steam | 0.0896 kg/MJ |
| CO2 emissions for electricity | 0.674 kg/kWh (0.187 kg/MJ) [21] |
| Parameters | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 |
| D/m | 1.33 | 0.98 | 0.71 | 0.64 |
| Ptop/kPa | 20 | 30 | 20 | 14 |
| RR | 3.13 | 11.22 | 5.98 | 12.16 |
| MCW/tonne·h−1 | 128.7 | 78.2 | 37.2 | 26.0 |
| Acond/m2 | 26.68 | 16.18 | 8.08 | 5.94 |
| Areb/m2 | 155.88 | 95.22 | 44.08 | 28.36 |
| Pvac/kW | 3.37 | 1.81 | 1.77 | 2.01 |
| TCC/106 USD | 0.26 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.08 |
| TOC/106 USD·y−1 | 0.65 | 0.38 | 0.17 | 0.13 |
| TAC/106 USD·y−1 | 0.74 | 0.44 | 0.21 | 0.15 |
| Parameters | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 |
| D/m | 1.33 | 0.98 | 0.71 | 0.64 |
| Ptop/kPa | 20 | 30 | 20 | 14 |
| RR | 3.13 | 11.22 | 5.98 | 12.16 |
| Acond/m2 | 204.0 | 141.3 | 63.0 | 42.2 |
| Areb/m2 | 208.0 | 130.5 | 59.1 | 40.7 |
| Pvac/kW | 3.37 | 1.81 | 1.77 | 2.01 |
| TCC/106 USD | 1.15 | 0.70 | 0.39 | 0.30 |
| TOC/106 USD·y−1 | 0.30 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.06 |
| TAC/106 USD·y−1 | 0.68 | 0.40 | 0.21 | 0.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, D.; Qin, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yan, C.; Mou, C.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, C. Process Design and Techno-Economic Analysis of Heat Pump-Assisted Distillation for Crude Phenol Separation. Separations 2025, 12, 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12110290
Meng D, Qin L, Zhao Y, Zhao J, Yan C, Mou C, Xiong J, Zhang C. Process Design and Techno-Economic Analysis of Heat Pump-Assisted Distillation for Crude Phenol Separation. Separations. 2025; 12(11):290. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12110290
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Dechang, Liying Qin, Yuan Zhao, Jiawei Zhao, Chunping Yan, Chenghong Mou, Jieming Xiong, and Chen Zhang. 2025. "Process Design and Techno-Economic Analysis of Heat Pump-Assisted Distillation for Crude Phenol Separation" Separations 12, no. 11: 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12110290
APA StyleMeng, D., Qin, L., Zhao, Y., Zhao, J., Yan, C., Mou, C., Xiong, J., & Zhang, C. (2025). Process Design and Techno-Economic Analysis of Heat Pump-Assisted Distillation for Crude Phenol Separation. Separations, 12(11), 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12110290






