The Essential Oil Composition of Eryngium galioides Lam.—An Endemic Species of the Iberian Peninsula
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Isolation of Volatile Oils
2.3. Gas Chromatography (GC)
2.4. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
2.5. Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Flora Online (‘WFO, 2024). Published on the Internet. Available online: http://www.worldfloraonline.org (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Thiviya, P.; Gunawardena, N.; Gamage, A.; Madhujith, T.; Merah, O. Apiaceae Family as a Valuable Source of Biocidal Components and their Potential Uses in Agriculture. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duretto, M.F. Apiaceae. In Flora of Victoria, Cornaceae to Asteraceae; Walsh, N.G., Entwisle, T.J., Eds.; Inkata Press: Melbourne, Australia, 1999; Volume 4, pp. 256–258. [Google Scholar]
- Vetter, J. Poison hemlock (Conium maculatum L.). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutin, T.G.; Heywood, V.H.; Burges, N.A.; Valentine, D.H.; Walters, S.M.; Webb, D.A. Flora Europaea; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1968; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Flora Ibérica. Published on the Internet. Available online: http://www.floraiberica.es/floraiberica/texto/pdfs/10_129_05%20Eryngium.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- The European Environment Agency (EEA). Published on the Internet. Available online: https://eunis.eea.europa.eu/species/152249 (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Dunkić, V.; Vuko, E.; Bezić, N.; Kremer, D.; Ruščić, M. Composition and Antiviral Activity of the Essential Oils of Eryngium alpinum and E. amethystinum. Chem. Biodivers. 2013, 10, 1894–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matejić, J.S.; Stojanović-Radić, Z.Z.; Ristić, M.S.; Veselinovic, J.B.; Zlatkovic, B.K.; Marin, P.D.; Dzamic, A.M. Chemical characterization, in vitro biological activity of essential oils and extracts of three Eryngium L. species and molecular docking of selected major compounds. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 2910–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianfaglione, K.; Blomme, E.E.; Quassinti, L.; Bramucci, M.; Lupidi, G.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Maggi, F. Cytotoxic Essential Oils from Eryngium campestre and Eryngium amethystinum (Apiaceae) Growing in Central Italy. Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14, e1700096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flamini, G.; Tebano, M.; Cioni, P.L. Composition of the essential oils from leafy parts of the shoots, flowers and fruits of Eryngium amethystinum from Amiata Mount (Tuscany, Italy). Food Chem. 2008, 107, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palá-Paúl, J.; Usano-Alemany, J.; Brophy, J.J.; Pérez-Alonso, M.J.; Soria, A.C. Essential oil composition of the different parts of Eryngium aquifolium from Spain. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landoulsi, A.; Roumy, V.; Duhal, N.; Skhiri, F.H.; Rivière, C.; Sahpaz, S.; Neut, C.; Benhamida, J.; Hennebelle, T. Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of the Essential Oil from Aerial Parts and Roots of Eryngium barrelieri Boiss. and Eryngium glomeratum Lam. from Tunisia. Chem. Biodivers. 2016, 13, 1720–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodeifian, G.; Sajadian, S.A.; Ardestani, N.S. Experimental optimization and mathematical modeling of the supercritical fluid extraction of essential oil from Eryngium billardieri: Application of simulated annealing (SA) algorithm. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 127, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefidkon, F.; Dabiri, M.; Alamshahi, A. Chemical composition of the essential oil of Eryngium billardieri F. Delaroche from Iran. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2004, 16, 42–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekhtiyari, M.S.; Moradkhani, S.; Ebadi, A.; Dastan, D. Chemical Composition of the Essential Oils from the Aerial Parts of Eryngium bornmuelleri. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2020, 56, 1154–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palá-Paúl, J.; Pérez-Alonso, M.J.; Velasco-Negueruela, A.; Varadé, J.; Villa, A.M.; Sanz, J.; Brophy, J.J. Essential oil composition of the different parts of Eryngium bourgatii Gouan from Spain. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1074, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadhosseini, M.; Mahdavi, B.; Akhlaghi, H. Characterization and Chemical Composition of the Volatile Oils from Aerial Parts of Eryngium bungei Bioss. (Apiaceae) by Using Traditional Hydrodistillation, Microwave Assisted Hydrodistillation and Head Space Solid Phase Microextraction Methods Prior to GC and GC/MS Analyses: A Comparative Approach. J. Essent. Oil-Bear. Plants 2013, 16, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanzadeh, N.; Ketabchi, S.; Alizadeh, A. Essential oil composition and antibacterial activity of Eryngium caeruleum grown wild in Iran. J. Essent. Oil-Bear. Plants 2014, 17, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, S.; Katayoun, M.S. Effect of the Essential Oil of Eryngium caeruleum on Percutaneous Absorption of Piroxicam through Rat Skin. J. Essent. Oil-Bear. Plants 2008, 11, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medbouhi, A.; Benbelaïd, F.; Djabou, N.; Beaufay, C.; Bendahou, M.; Quetin-Leclercq, J.; Tintaru, A.; Costa, J.; Muselli, A. Essential Oil of Algerian Eryngium campestre: Chemical Variability and Evaluation of Biological Activities. Molecules 2019, 24, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palá-Paúl, J.; Usano, J.; Soria, A.C.; Pérez-Alonso, M.J.; Brophy, J.J. Essential oil composition of Eryngium campestre L. growing in different soild types. A preliminary study. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2008, 3, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemabadi, D.; Kaviani, B. Chemical Constituents of Essential Oils Extracted from the Leaves and Stems of Eryngium caucasicum Trautv. from Iran. J. Essent. Oil-Bear. Plants 2011, 14, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemabadi, D.; Kaviani, B.; Erfatpour, M.; Larijani, K. Comparison of essential oils compositions of eryngo (Eryngium caucasicum Trautv.) at different growth phases by hydrodistillation method. Plant Omics 2010, 3, 135–139. Available online: https://search.informit.org/doi/10.3316/informit.282868118284755 (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Palá-Paúl, J.; Brophy, J.J.; Pérez-Alonso, M.J.; Usano, J.; Soria, A.C. Essential oil composition of the different parts of Eryngium corniculatum Lam. (Apiaceae) from Spain. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1175, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadhosseini, M. Hydrodistilled Volatile Oil from Stems of Eryngium creticum Lam. in the Marginal Brackish Regions of Semnan Province by Using Gas Chromatography Combined with Mass Spectrometry. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, N.A.; Nawwar, M.A.M.; Kubeczka, K.H. An unique n-propyl sesquiterpene from Eryngium creticum L. (Apiaceae). Pharmazie 2003, 58, 674–676. Available online: https://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/govi/pharmaz/2003/00000058/00000009/art00019# (accessed on 12 March 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palá-Paúl, J.; Pérez-Alonso, M.J.; Soria, A.C.; Brophy, J.J. Chemical Composition of the Essential Oils of the Iberian Peninsula Endemic Species Eryngium dilatatum Lam. Molecules 2024, 29, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, A.C.; Loureiro, J.; Cavaleiro, C.; Salgueiro, L.; Canhoto, J.M.; Paiva, J. Characterization and distinction of two subspecies of Eryngium duriaei J. Gay ex Boiss., an Iberian endemic Apiaceae, using flow cytometry and essential oils composition. Plant Syst. Evol. 2013, 299, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaleiro, C.; Gonçalves, M.J.; Serra, D.; Santoro, G.; Tomi, F.; Bighelli, A.; Salgueiro, L.; Casanova, J. Composition of a volatile extract of Eryngium duriaei subsp. juresianum (M. Laínz) M. Laínz, signalised by the antifungal activity. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 54, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein-Júnior, L.C.; dos Santos Passos, C.; Tasso de Souza, T.J.; Gobbi de Bitencourt, F.; Salton, J.; de Loreto Bordignon, S.A.; Henriques, A.T. The monoamine oxidase inhibitory activity of essential oils obtained from Eryngium species and their chemical composition. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brophy, J.J.; Goldsack, R.J.; Copeland, L.M.; Palá-Paúl, J. Essential oil of Eryngium L. species from New South Wales (Australia). J. Essent. Oil Res. 2003, 15, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.L.M.; Castro, G.L.S.; Viana, R.G.; Gurgel, E.S.C.; Silva, S.G.; de Oliveira, M.S.; Andrade, E.H.d.A. Physiological performance and chemical compositions of the Eryngium foetidum L. (Apiaceae) essential oil cultivated with different fertilizer sources. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 35, 5544–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrika, R.; Saraswathi, K.J.T.; Mallavarapu, G.R. Constituents of the Essential Oils of the Leaf and Root of Eryngium foetidum L. from Two Locations in India. J. Essent. Oil-Bear. Plants 2015, 18, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngang, J.J.E.; Nyegue, M.A.; Ndoye, F.C.; Kamgain, A.D.T.; Kamdem, S.L.S.; Lanciotti, R.; Gardini, F.; Etoa, F.X. Characterization of Mexican Coriander (Eryngium foetidum) Essential Oil and Its Inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes In Vitro and during Mild Thermal Pasteurization of Pineapple Juice. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banout, J.; Havlik, J.; Kulik, M.; Kloucek, P.; Lojka, B.; Valterova, I. Effect of Solar Drying on the Composition of Essential Oil of Sacha Culantro (Eryngium foetidum L.) Grown in the Peruvian Amazon. J. Food Process. Eng. 2010, 33, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, N.D.T.; Anh, T.H.; Thach, L.N. The Essential Oil Composition of Eryngium foetidum L. in South Vietnam Extracted by Hydrodistillation under Conventional Heating and Microwave Irradiation. J. Essent. Oil-Bear. Plants 2008, 11, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.P.; Salgueiro, L.R.; Proença da Cunha, A.; Vila, R.; Cañigueral, S.; Tomi, F.; Casanova, J. Essential oil composition of Eryngium foetidum from S. Tomé e Príncipe. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2003, 15, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palá-Paúl, J.; Pérez-Alonso, M.J.; Velasco-Negueruela, A.; Varadé, J.; Villa, M.A.; Sanz, J.; Brophy, J.J. Analysis of the essential oil composition of the different parts of Eryngium glaciale Boiss. from Spain. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1094, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakurte, I.; Berga, M.; Mežaka, I. Phytochemical Diversity Comparison in Leaves and Roots of Wild and Micropropagated Latvian Sea Holly (Eryngium maritimum L.). Molecules 2023, 28, 3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikowska, M.; Kalemba, D.; Dlugaszewska, J.; Thiem, B. Chemical Composition of Essential Oils from Rare and Endangered Species—Eryngium maritimum L. and E. alpinum L. Plants 2020, 9, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lajnef, H.B.; Ferioli, F.; Pasini, F.; Politowicz, J.; Khaldi, A.; D’Antuono, F.; Caboni, M.F.; Nasri, N. Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of the volatile fraction extracted from air-dried fruits of Tunisian Eryngium maritimum L. ecotypes. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 98, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriet, F.; Andreani, S.; De Cian, M.C.; Costa, J.; Muselli, A. Chemical variability and antioxidant activity of Eryngium maritimum L. essential oils from Corsica and Sardinia. Flavour Fragr. J. 2014, 29, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, A.; Bruno, M.; Formisano, C.; Rigano, D.; Senatore, F. Chemical Composition of the Essential Oils of Three Species of Apiaceae Growing Wild in Sicily: Bonannia graeca, Eryngium maritimum and Opopanax chironium. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 6–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriet, F.; Bendahou, M.; Desjobert, J.M.; Costa, J.; Muselli, A. Bicyclo [4.4.0]decane Oxygenated Sesquiterpenes from Eryngium maritimum Essential Oil. Planta Medica 2012, 78, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcetic, M.; Petrovic, S.; Milenkovic, M.; Vujisic, L.J.; Tesevic, V.; Niketic, M. Composition and antimicrobial activity of root essential oil of Balkan endemic species Eryngium palmatum. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2014, 49, 11401142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capetanos, C.; Saroglour, V.; Marinz Petar, D.; Simic, A.; Skaltsa, H.D. Essential oil analysis of two endemic Eryngium species from Serbia. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2007, 72, 961–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palá-Paúl, J.; Copeland, L.M.; Brophy, J.J.; Goldsack, R.J. Analysis by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry of the essential oil composition of Eryngium paludosum (Moore & Betche) P.W.Michael: An endemic species from eastern Australia. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2008, 20, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobos, M.I.; Rodríguez, J.L.; de Petre, A.; Spahn, E.; Casemeiro, J.; López, A.G.; Zygadlo, J.A. Composition of the essential oil of Eryngium paniculatum Cav. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2002, 14, 82–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiem, B.; Kikowska, M.; Kurowska, A.; Kalemba, D. Essential Oil Composition of the Different Parts and In Vitro Shoot Culture of Eryngium planum L. Molecules 2011, 16, 7115–7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tel-Çayan, G.; Duru, M.E. Chemical characterization and antioxidant activity of Eryngium pseudothoriifolium and E. thorifolium essential oils. J. Res. Pharm. 2019, 23, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahzadeh, A.R.; Zarei, M.; Mohammadi, S. Preliminary Phytochemical Screening, Analgesic and Anti-inflammatory effect of Eryngium pyramidale Boiss. & Husson Essential Oil in Male Rat. Entomol. Appl. Sci. Lett. 2016, 3, 140–147. [Google Scholar]
- Merghache, D.; Boucherit-Otmani, Z.; Merghache, S.; Chikhi, I.; Selles, C.; Boucherit, K. Chemical composition, antibacterial, antifungal and antioxidant activities of Algerian Eryngium tricuspidatum L. essential oil. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medbouhi, A.; Merad, N.; Khadir, A.; Bendahou, M.; Djabou, N.; Costa, J.; Muselli, A. Chemical Composition and Biological Investigations of Eryngium triquetrum Essential Oil from Algeria. Chem. Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1700343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiglia, S.; Bruno, M.; Rosselli, S.; Senatore, F. Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of the Essential Oil from Flowers of Eryngium triquetrum (Apiaceae) Collected Wild in Sicily. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palá-Paúl, J.; Brophy, J.J.; Goldsack, R.J.; Copeland, L.M.; Pérez-Alonso, M.J.; Velasco-Negueruela, A. Essential oil composition of the seasonal heterophyllous leaves of Eryngium vesiculosum from Australia. Aust. J. Bot. 2003, 51, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikowska, M.; Dworacka, M.; Kedziora, I.; Thiem, B. Eryngium creticum -ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacological activity. A review. Rev. Bras. Farm. 2016, 26, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, S.A.; Nabavi, S.F.; Orhan, I.E.; Daglia, M.; Izadi, M.; Nabavi, S.M. Blessings in disguise: A review of phytochemical composition and antimicrobial activity of plants belonging to the genus Eryngium. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 23, 1–22. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s40199-015-0136-3 (accessed on 12 March 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, J.H.A.; Seaforth, C.E.; Tikasingh, T. Eryngium foetidum L.: A review. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khalil, S. Phytochemistry of Eryngium creticum. Alexandria J. Pharm. Sci. 1994, 8, 73–75. [Google Scholar]
- Arabpoor, B.; Yousefi, S.; Weisany, W.; Ghasemlou, M. Multifunctional coating composed of Eryngium campestre L. essential oil encapsulated in nano-chitosan to prolong the shelf-life of fresh cherry fruits. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirahmadi, S.S.; Aminzare, M.; Azar, H.H.; Kamali, K. Effect of Eryngium caeruleum essential oil on microbial and sensory quality of minced fish and fate of Listeria monocytogenes during the storage at 4 degrees C. J. Food Saf. 2020, 40, e12745. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jfs.12745 (accessed on 12 March 2024). [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, A.; Rashid, U.; Ahmad, S.; Zahoor, M.; AlAjmi, M.F.; Ullah, R.; Noman, O.M.; Ullah, F.; Ayaz, M.; Khan, I.; et al. Treating hyperglycemia from Eryngium caeruleum M. Bieb: In-Vitro alpha-glucosidase, antioxidant, in-vivo antidiabetic and molecular docking-based approaches. Front. Chem. 2020, 26, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beeby, E.; Magalhaes, M.; Pocas, J.; Collins, T.; Lemos, M.F.L.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Cabral, C.; Pires, I.M. Secondary metabolites (essential oils) from sand-dune plants induce cytotoxic effects in cancer cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 258, 112803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, P.N. Influence of extraction parameters on total phenolic contents, flavonoids and antioxidant capacity of extract from Eryngium foetidum leaves. Biosci. Res. 2020, 17, 1822–1829. [Google Scholar]
- Landoulsi, A.; Hennebelle, T.; Bero, J.; Riviere, C.; Sahpaz, S.; Quetin-Leclercq, J.; Neut, C.; Benhamida, J.; Roumy, V. Antimicrobial and Light-Enhanced Antimicrobial Activities, Cytotoxicity and Chemical Variability of All Tunisian Eryngium Species. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e1900543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneshzadeh, M.S.; Abbaspour, H.; Amjad, L.; Nafchi, A.M. An investigation on phytochemical, antioxidant and antibacterial properties of extract from Eryngium billardieri F. Delaroche. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho Augusto, R.; Merad, N.; Rognon, A.; Gourbal, B.; Bertrand, C.; Djabou, N.; Duval, D. Molluscicidal and parasiticidal activities of Eryngium triquetrum essential oil on Schistosoma mansoni and its intermediate snail host Biomphalaria glabrata, a double impact. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vukic, M.D.; Vukovic, N.L.; Djelic, G.T.; Obradovic, A.; Kacaniova, M.M.; Markovic, S.; Popovic, S.; Baskic, D. Phytochemical analysis, antioxidant, antibacterial and cytotoxic activity of different plant organs of Eryngium serbicum L. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 115, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeisi, S.; Ojagh, S.M.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Quek, S.Y. Evaluation of Allium paradoxum (MB) G. Don. and Eryngium caucasicum trauve. Extracts on the shelf-life and quality of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) fillets during refrigerated storage. J. Food Saf. 2017, 37, e12321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozarowski, M.; Thiem, B.; Mikolajczak, P.L.; Piasecka, A.; Kachlicki, P.; Szulc, M.; Kaminska, E.; Bogacz, A.; Kujawski, R.; Bartkowiak-Wieczorek, J.; et al. Improvement in Long-Term Memory following Chronic Administration of Eryngium planum Root Extract in Scopolamine Model: Behavioral and Molecular Study. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rufino, A.T.; Ferreira, I.; Judas, F.; Salgueiro, L.; Celeste Lopes, M.; Cavaleiro, C.; Mendes, A.F. Differential effects of the essential oils of Lavandula luisieri and Eryngium duriaei subsp. juresianum in cell models of two chronic inflammatory diseases. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 53, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumitha, K.V.; Prajitha, V.; Sandhya, V.N.; Anjana, S.; Thoppil, J.E. Potential Larvicidal Principles in Eryngium foetidum L. (Apiaceae), An Omnipresent Weed, Effective Against Aedes albopictus Skuse. J. Essent. Oil-Bear. Plants 2014, 17, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.K.; Ramakrishna, Y.; Ngachan, S.V. Spiny coriander (Eryngium foetidum L.): A commonly used, neglected spicing-culinary herb of Mizoram, India. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2014, 61, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriet, F.; Znini, M.; Majidi, L.; Muselli, A.; Hammouti, B.; Bouyanzer, A.; Costa, J. Evaluation of Eryngium maritimum Essential Oil as Environmentally Friendly Corrosion Inhibitor for Mild Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 4328–4345. Available online: http://www.electrochemsci.org/papers/vol8/80304328.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2024). [CrossRef]
- Çelik, A.; Aydınlık, N.; Arslan, I. Phytochemical constituents and inhibitory activity towards methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains of Eryngium species (Apiaceae). Chem. Biodivers. 2011, 8, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, M.; Morteza-Semnani, K. Penetration-Enhancing Effect of the Essential Oil and Methanolic Extract of Eryngium bungei on Percutaneous Absorption of Piroxicam through Rat Skin. J. Essent. Oil-Bear. Plants 2009, 12, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khademi, S.B.; Aminzare, M.; Azar, H.H.; Mehrasbi, M.R. Eryngium caeruleum essential oil as a promising natural additive: In vitro antioxidant properties and its effect on lipid oxidation of minced rainbow trout meat during storage at refrigeration temperature. Funct. Foods Health Dis. 2021, 11, 11–23. Available online: https://ffhdj.com/index.php/ffhd/article/view/766 (accessed on 12 March 2024). [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas-Valdovinos, J.G.; García-Ruiz, I.; Angoa-Pérez, M.V.; Mena-Violante, H.G. Ethnobotany, Biological Activities and Phytochemical Compounds of Some Species of the Genus Eryngium (Apiaceae), from the Central-Western Region of Mexico. Molecules 2023, 28, 4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikowska, M.; Chanaj-Kaczmarek, J.; Derda, M.; Budzianowska, A.; Thiem, B.; Ekiert, H.; Szopa, A. The Evaluation of Phenolic Acids and Flavonoids Content and Antiprotozoal Activity of Eryngium Species Biomass Produced by Biotechnological Methods. Molecules 2022, 27, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamedi, A.; Pasdaran, A.L.; Pasdaran, A. Antimicrobial Activity and Analysis of the Essential Oils of Selected Endemic Edible Apiaceae Plants Root from Caspian Hyrcanian Region (North of Iran). Pharm Sci. 2019, 5, 138–144. Available online: https://ps.tbzmed.ac.ir/Article/PHARM_3143_20181119103515 (accessed on 12 March 2024). [CrossRef]
- Agencia Española de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios. Real Farmacopea Española, 3rd ed.; Ministerio de Sanidad y Consumo: Madrid, Spain, 2005.
- Adams, R.P. Identification of Essential Oils Components by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Allured Publishing Corporation: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, R.P. Identification of Essential Oils Components by Gas Chromatography/Quadrupole Mass Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Allured Publishing Corporation: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, R.P. Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry, 4th ed.; Allured Publishing Corporation: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Stenhagen, E.; Abrahamsson, S.; McLafferty, F.W. Registry of Mass Spectral Data; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, S.R.; Milne, G.W.A. EPA/NIH Mass Spectral Data Base; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Swigar, A.A.; Silverstein, R.M. Monoterpenes; Aldrich: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Joulain, D.; König, W.A. The Atlas of Spectral Data of Sesquiterpene Hydrocarbons; E. B.-Verlag: Hamburg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.-L.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.-J.; Fan, G.; Li, X. Production, Function, and Applications of the Sesquiterpenes Valencene and Nootkatone: A Comprehensive Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Tintino, C.D.d.M.; Santana, J.E.G.; Alencar, G.G.; Siqueira, G.M.; Gonçalves, S.A.; Tintino, S.R.; Menezes, I.R.A.d.; Rodrigues, J.P.V.; Gonçalves, V.B.P.; Nicolete, R.; et al. Valencene, Nootkatone and Their Liposomal Nanoformulations as Potential Inhibitors of NorA, Tet(K), MsrA, and MepA Efflux Pumps in Staphylococcus aureus Strains. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The National Center for Biotechnology Information Advances Science and Health by Providing Access to Biomedical and Genomic Information (NCBI). Phyllocladene. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Phyllocladene (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Food Data Base. Phyllocladene. Available online: https://foodb.ca/compounds/FDB017462 (accessed on 10 April 2024).
| Species | Main Components | Yield (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| E. aquifolium Cav. | inflorescences oil: germacrene D (30.3%) and sesquicineole (26.7%) | 0.81 | [12] |
| stems and leaves oil: germacrene D (46.0%) and myrcene (13.8%) | 0.41 | ||
| roots oil: phyllocladene isomer (63.6%) | 0.18 | ||
| E. bourgatii Gouan | inflorescences oil: phyllocladene (37.6%) and bicyclogermacrene (15.1%) | 0.33 | [17] |
| stems and leaves oil: phyllocladene (20.4%), γ-muurolene (11.8%) and (E)-caryophyllene (10.1%) | 0.11 | ||
| roots oil: γ-muurolene (15.4%) and phyllocladene (15.0%) | 0.20 | ||
| E. campestre L. | inflorescences oil: germacrene D (30.3–40.3%), β-curcumene (0.7–22.2%), myrcene (3.0–21.7%), (E)-β-farnesene (0.1–19.0%). | 0.1–0.4 | [22] |
| stems and leaves oil: germacrene D (31.1–42.4%), myrcene (0.5–23.15) | 0.1–0.2 | ||
| E. corniculatum Lam. | inflorescences oil: 2,4,6-trimethylbenzaldehyde (50.8%), α-pinene (4.0%) | 0.82 | [25] |
| stems and leaves oil: 2,4,6-trimethylbenzaldehyde (50.0%), 2,4,5-trimethylbenzaldehyde (3.8%) | 0.49 | ||
| roots oil: 2,4,6-trimethylbenzaldehyde (29.8%), phyllocladene isomer (13.0%), (E)-nerolidol (9.4%) | 0.22 | ||
| Eryngium dilatatum Lam. | inflorescences oil: α-cadinol (3.8%), bicyclogermacrene (3.5%), octanal (3.1%) and spathulenol (2.5%) | 0.29 | [28] |
| stems and leaves oil: octanal (8.1%), α-cadinol (3.7%), δ-cadinene (3.6%), (E)-caryophyllene (2.6%), bicyclogermacrene (2.5%) and spathulenol (2.4%) | 0.33 | ||
| roots oil: spathulenol (4.6%), α-cadinol (4.4%), khusinol (3.2%), α-muurolol (3.1%) and δ-cadinene (2.6%) | 0.14 | ||
| E. duriaei J. Gay ex Boiss. | populations below 1700 m: α-neocallitropsene (28–53%), β-betulenal (8.5–15.8%) and 14-hydroxy-β-caryophyllene (5.8–13.7%) | 0.2–0.3 | [29] |
| population over 1700 m: caryophyllene oxide (47%) and E-caryophyllene (6%) | |||
| Eryngium duriaei subsp. juresianum (M. Laínz) M. Laínz | aerial parts: α-neocallitropsene (26.0%), isocaryophyllen-14-al (16.2%), 14-hidroxy-β-caryophyllene (13.4%), caryophyllene oxide (7.6%) and (E)-β-caryophyllene (6.3%). | 0.15 | [30] |
| E. glaciale Boiss. | inflorescences oil: phyllocladene isomer (43.5%), (E)-caryophyllene (15.2%) and valencene (11.5%) | 0.16 | [39] |
| stems and leaves oil: phyllocladene isomer (41.3%) | 0.26 | ||
| roots oil: phyllocladene isomer (49.4%) and linalool (19.1%) | 0.30 |
| Species | Region | Main Components | Yield (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. campestre L. | Italy (Perugia) | aerial parts: germacrene D (13.8%), allo-aromadendrene (7.7%), spathulenol (7.0%) and ledol (5.7%) | 0.04 | [10] |
| Algeria (Tlemcen) | aerial parts: germacrene D (15.2%), campestrolide (10.3%), spathulenol (4.8%) and α-cadinol (5.5%) | 0.1–0.2 | [21] | |
| E. maritimum L. | Latvia | leaves (wild plants): 4βH-muurol-9-en-15-al > germacrene D > spathulenol > 4βH-cadin-9-en-15-ol | 0.15–0.54 | [40] |
| leaves (cultivated plants): germacrene D (61.13–75.05%) > eudesma-4,7-diene-1β-ol > cumene > α-muurolene | 0.15–0.54 | |||
| Poland (Poznań) | leaves: 2,3,4-trimethylbenzaldehyde (11.3%) and germacrene D (10.5%) | 0.06 | [41] | |
| fruits: germacrene D (45.2%) | 0.3 | |||
| roots: hexadecanoic acid (18.5%), menthol (16.8%) and menthone (10.9%) | 0.01 | |||
| Tunisia | fruits: germacrene D (13.62–31.71%), 15-hydroxy-α-muurolene (12.04–18.58%) and germacrene B (6.77–15.04%). | 0.31–0.93 | [42] | |
| Corsica and Sardinia | aerial parts: germacrene D (13.7–45.9%), 4βH-cadin-9-en-15-al (18.4–27.6%), 4βH-cadin-9-en-15-ol (2.2–14.3%) and 4βH-muurol-9-en-15-al (4.3–9.3%) | 0.06–0.13 fresh weight | [43] | |
| roots: 2,4,5-trimethylbenzaldehyde (39.8%), 2,3,6-trimethylbenzaldehyde (29.0%) and α-muurolene (23.5%) | 0.06–0.13 fresh weight | |||
| Sicily (Palermo) | aerial parts: germacrene D (10.4%) and 2,4,5-trimethylbenzaldehyde (8.3%) | 0.93 | [44] | |
| roots: germacrene D (15.9%) and 2,4,5-trimethylbenzaldehyde (6.7%) | 0.84 | |||
| Corsica (Quercionu) | aerial parts: isolation of 4βH-muurol-9-en-15-al, 4βH -cadin-9-en-15-al, 4βH-muurol-9-en-15-ol and 4βH-cadin-9-en-15-ol | 0.08 | [45] |
| Compound | I | I1it | %. | IM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| nonane | 869 | 900 | 1.4 | MS,1 |
| α-pinene | 932 (1012) | 939 | 0.2 | MS,2 |
| heptanol | 955 (1181) | 959 | t | MS,1 |
| sabinene | 963 (1113) | 969 | t | MS,2 |
| β-pinene | 970 (1097) | 974 | t | MS,2 |
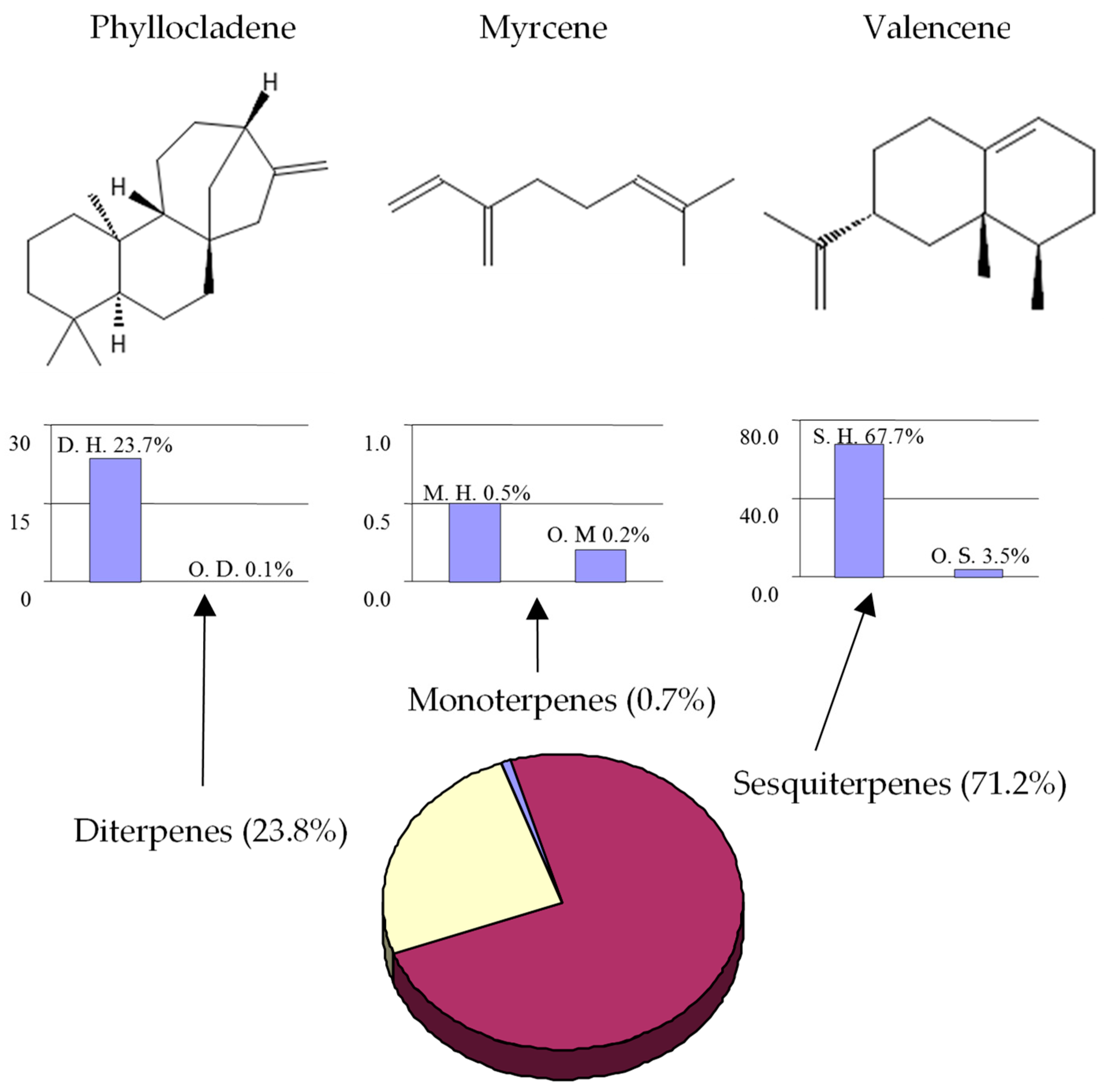
| myrcene | 985 (1160) | 988 | 0.3 | MS,2 |
| octanal | 993 (1286) | 988 | 0.2 | MS,1 |
| α-phellandrene | 1005 (1157) | 1002 | t | MS,2 |
| o-cimene | 1019 (1268) | 1022 | t | MS,2 |
| limonene | 1026 (1191) | 1024 | t | MS,2 |
| (Z)-β-ocimene | 1031 (1232) | 1032 | t | MS,1 |
| benzene acetaldehyde | 1032 | 1036 | t | MS,1 |
| (E)-β-ocimene | 1041 (1249) | 1044 | t | MS,1 |
| γ-terpinene | 1058 (1240) | 1054 | t | MS,2 |
| octanol | 1063 (1172) | 1063 | t | MS,2 |
| fenchone | 1074 (1392) | 1083 | t | MS,2 |
| linalool | 1096 (1549) | 1095 | t | MS,2 |
| undecane | 1100 | 1100 | t | MS,2 |
| cis-thujone | 1117 | 1101 | t | MS,1 |
| cryptone | 1180 (1669) | 1183 | 0.3 | MS,1 |
| α-terpineol | 1183 (1700) | 1186 | 0.2 | MS,1 |
| n-decanal | 1202 | 1201 | t | MS,2 |
| pulegone | 1231 | 1233 | t | MS,2 |
| (E,Z)-2,4-decadienal | 1301 (1229) | 1292 | t | MS,1 |
| carvacrol | 1303 | 1298 | t | MS,2 |
| 2,4,5-trimethyl benzaldehyde | 1305 (1896) | -- | t | MS,1 |
| δ-elemene | 1333 (1468) | 1335 | t | MS,2 |
| α-longipinene | 1351 | 1350 | t | MS,1 |
| α-copaene | 1366 (1480) | 1374 | 0.3 | MS,2 |
| daucene | 1370 | 1380 | t | MS,1 |
| β-elemene | 1387 (1587) | 1389 | 1.6 | MS,2 |
| α-gurjunene | 1406 (1528) | 1409 | t | MS,2 |
| (E)-caryophyllene | 1410 (1594) | 1417 | 3.0 | MS,2 |
| α-trans-bergamotene | 1432 (1583) | 1432 | t | MS,1 |
| α-guaiene | 1433 | 1437 | t | MS,2 |
| aromadendrene | 1434 (1605) | 1439 | 0.2 | MS,2 |
| α-humulene | 1447 (1667) | 1452 | 0.3 | MS,2 |
| (E)-β-farnesene | 1452 (1770) | 1454 | 0.2 | MS,2 |
| β-acoradiene | 1456 | 1469 | 0.8 | MS,1 |
| β-chamigrene | 1461 | 1476 | 6.0 | MS,1 |
| γ-muurolene | 1465 (1675) | 1478 | 3.4 | MS,2 |
| β-selinene | 1482 (1704) | 1489 | t | MS,2 |
| valencene | 1485 | 1496 | 49.7 | MS,2 |
| α-selinene | 1492 (1727) | 1498 | 0.1 | MS,2 |
| α-bulnesene | 1498 (1642) | 1509 | t | MS,2 |
| 7-epi-α-selinene | 1519 (1764) | 1520 | 0.8 | MS,1 |
| δ-cadinene | 1522 (1760) | 1522 | 1.0 | MS,2 |
| n.i. 1 | 1559 | -- | 0.5 | -- |
| selina-3,7(11)-diene | 1560 | 1545 | 0.3 | MS,1 |
| caryophyllenyl alcohol | 1569 | 1570 | 0.2 | MS,1 |
| spathulenol | 1576 (2133) | 1577 | 1.0 | MS,2 |
| caryophyllene oxide | 1580 (1987) | 1582 | 0.4 | MS,2 |
| globulol | 1583 (2064) | 1590 | 0.3 | MS,2 |
| viridiflorol | 1590 (2091) | 1592 | 0.3 | MS,1 |
| carotol | 1594 (2026) | 1594 | 0.2 | MS,1 |
| β-oplopenone | 1597 | 1607 | 0.1 | MS,1 |
| n.i. 2 | 1606 | -- | 0.4 | -- |
| epi-α-muurolol (+cubenol) | 1631 (1890) | 1640 | t | MS,1 |
| β-eudesmol | 1638 (2239) | 1649 | t | MS,2 |
| α-cadinol | 1639 (2243) | 1652 | 0.4 | MS,1 |
| selin-11-en-4-α-ol | 1645 | 1658 | t | MS,1 |
| 14-hydroxy-9-epi-(E)-caryophyllene | 1662 (1924) | 1668 | t | MS,1 |
| khusinol | 1665 | 1679 | 0.2 | MS,1 |
| acorenone | 1673 | 1692 | t | MS,1 |
| (E)-sesquilavandulyl acetate | 1775 | 1739 | t | MS,1 |
| cedr-8-(15)-en-9-α-ol acetate | 1776 | 1741 | t | MS,1 |
| 14-hydroxy-α-muurolene | 1787 (1550) | 1779 | 0.1 | MS,1 |
| notkatone | 1798 | 1806 | t | MS,1 |
| bis-(2-methylpropyl) phthalate | 1804 | -- | t | MS,1 |
| neophytadiene | 1810 | -- | t | MS,1 |
| (E,E)-farnesyl acetate | 1824 | 1845 | t | MS,1 |
| phyllocladene isomer | 1857 | -- | 23.7 | MS,1 |
| phytol | 1922 (2620) | 1942 | 0.1 | MS,1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palá-Paúl, J.; Abad-Calderón, R.; Pérez-Alonso, M.J.; Brophy, J.J.; Soria, A.C. The Essential Oil Composition of Eryngium galioides Lam.—An Endemic Species of the Iberian Peninsula. Separations 2024, 11, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11060172
Palá-Paúl J, Abad-Calderón R, Pérez-Alonso MJ, Brophy JJ, Soria AC. The Essential Oil Composition of Eryngium galioides Lam.—An Endemic Species of the Iberian Peninsula. Separations. 2024; 11(6):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11060172
Chicago/Turabian StylePalá-Paúl, Jesús, Rubén Abad-Calderón, María José Pérez-Alonso, Joseph J. Brophy, and Ana C. Soria. 2024. "The Essential Oil Composition of Eryngium galioides Lam.—An Endemic Species of the Iberian Peninsula" Separations 11, no. 6: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11060172
APA StylePalá-Paúl, J., Abad-Calderón, R., Pérez-Alonso, M. J., Brophy, J. J., & Soria, A. C. (2024). The Essential Oil Composition of Eryngium galioides Lam.—An Endemic Species of the Iberian Peninsula. Separations, 11(6), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11060172








