Abstract
In this article, a comparison of ionization techniques is provided and discussed. Conventional liquid chromatography with an electrospray ionization source shows higher robustness and repeatability in comparison with liquid chromatography coupled with a coordination ion spray (CIS-MS) source using silver nitrate as the dopant. However, the higher sensitivity and possibility to collect more data in untargeted applications mean CIS-MS is emerging as an instrument used in specific applications. During this research, the limit of detection (LOD) for GHRP-2 and GHRP-6 was established at 0.2 ng/mL, and the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) was 0.5 ng/mL for CIS-MS. For conventional ESI-MS combined with solid-phase extraction on weak cation exchange columns, the limit of detection was found to be 1 ng/mL, and the lower limit of quantification was 2 ng/mL.
1. Introduction
Growth-hormone-releasing peptides (GHRPs) are well-known doping agents in professional sports. The abuse of GHRPs is banned by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA). Nonetheless, cases of their use, while they are not rife, do occur annually [1]. In the last testing report, WADA revealed that approximately 0.01% of samples were positive in growth-hormone-releasing factor testing [2].
In such testing, even when conducted a few days after GHRPs’ administration, there can be issues with their determination, which makes the development of methods for their determination at trace concentration levels extremely important [3,4,5,6,7,8]. There are various solutions available—for instance, using concentration methods, such as solid-phase extraction, and using high-end equipment. Often, to meet the needs of doping control laboratories, a combination of such approaches is required [9,10,11,12]. In this case, the analytes for GHRPs exist in samples in an equilibrium state—where both monocharged and polycharged ions can be observed simultaneously—but this balance can be changed by adding sufficiently strong acids, for example, trifluoroacetic acid.
According to WADA recommendations [13], the minimum required performance limit for NGPRs is 1 ng/mL. Some recently published articles showed the possibility of their determination at up to 50 pg/mL (for dried blood spots); however, most articles showed the possibility of qualitative and quantitative analysis of such compounds at 0.1–1 ng/mL. Usually, the LOD and LOQ described depend on the laboratory equipment used. In the case of well-equipped high-end instruments (especially HRMS instruments), there are no issues in finding concentrations below 1 ng/mL. The main issue with such compounds is their stability and the excretion time in urine [14,15,16]. The main sample preparation technique for such compounds, like GHRP-2 and GHRP-6, is solid-phase extraction on SCX or WCX sorbents of different volumes. Such sample preparation can be used for significant pre-concentration of the sample and its cleanup [14].
An alternative to this approach is the use of coordination ion spray mass spectrometry. In this case, lithium, sodium, potassium or silver ions are added to the mobile phase [17,18,19]. An excessive presence of sodium and potassium ions is in most cases unwelcome since the formation of such adducts is not always reproducible and is often associated with a poor quality of the solvents used. However, the occurrence of significant amounts of lithium and silver ions in the mobile phase is unlikely and can easily be used under conditions of sufficient solvent purity.
Technically, the use of a coordination ion spray combined with mass spectrometry (CIS-MS) can solve a number of problems. To give an example, the introduction of singly charged ions can significantly increase the intensity of the single charged ion produced and increase the information content of the mass spectrum during a specific isotopic pattern of adducts with silver. For instance, silver has two isotopes—107Ag and 109Ag with an abundance of 52% and 48%, respectively. Accordingly, a distinct distribution pattern emerges, with the charge being localized on the silver ion that binds to the analytes through coordination involving amino groups. Consequently, the formation of positively charged ions occurs, which facilitates convenient detection using LC-MS.
Previously, the literature described the use of a similar approach for the analysis of sulfur-containing compounds and their mixtures, as well as for the determination of lipids, steroids and phytosterols [20,21,22].
Another alternative to conventional acidification of the mobile phase is the use of the so-called “wrong-way-round ionization” technique. In this case, the mobile phase will be modified with NH4OH solution, and protonation of the analytes will be caused by transfer of the ammonia ion in the gaseous phase, with a concentration of ammonia hydroxide of up to 5 mM. However, such a methodology requires chromatographic columns, which are allowed to work with alkaline mobile phases [23,24].
This work presents a comparison study of the efficiency of conventional ESI-MS and CIS-MS and discusses the advantages and disadvantages of this approach in the analysis of releasing peptides.
2. Materials and Methods
Standard samples of GHRP-6, GHRP-2 and Delta sleep-inducing peptide (DSIP, internal standard, IS) were purchased from Canada Peptides (Montreal, QC, Canada). Gradient-grade acetonitrile (Biosolve, Jerusalem, Israel) and deionized water (18.2 MΩ × cm, Milli-Q, Millipore, France) were used for mobile phase preparation. Silver nitrate (>99%) and lithium chloride (>99%) were purchased from Vecton (Vecton, Saint Petersburg, Russia). Strata WCX cartridges (1 mL, 100 mg) for solid-phase extraction were purchased from Phenomenex.
2.1. Preparation of Solutions
We prepared 1 mg/mL stock solutions of analytes in water:methanol solution (50:50, v:v) and stored them at –20 °C. For the preparation of calibration solutions, the stock solutions were diluted with acidified water solutions (in 0.1% formic acid) to obtain calibration concentrations of 100, 50, 25, 20, 10, 5, 2.5, 2, 1, 0.5, 0.25, 0.2, 0.1, 0.05, 0.025 and 0.02 ng/mL on the day of analysis, which were stored at 4 °C in the tray of the autosampler. The IS concentration for CIS-MS was 2 ng/mL, it was 10 ng/mL for ESI-MS with SPE and it was 50 ng/mL for “dilute-and-shoot” sample preparation. Quality control solutions were prepared at three levels of concentrations—low (QC low), medium (QC med) and high (QC high) for each sample preparation and analysis technique separately, according to their linear range. For CIS-MS: the QC low solution contained 2 ng/mL of analytes, QC med—20 ng/mL, QC high—50 ng/mL. For ESI-MS combined with SPE: QC low—5 ng/mL, QC med—25 ng/mL, QC high—50 ng/mL. For ESI-MS with “dilute-and-shoot” sample preparation: QC low—25 ng/mL, QC med—50 ng/mL, QC high—100 ng/mL.
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.1. “Dilute-and-Shoot” Procedure
We diluted 200 µL of the urine sample with 800 µL of 0.1% formic acid in water:acetonitrile (50:50, v:v), which was followed by vortex mixing for 3 min and centrifugation at 10,000 rpm for 10 min. The resulting supernatant, at a volume of 800 μL, was transferred into a glass vial for the following LC-MS/MS analysis.
2.2.2. Solid-Phase Extraction
A 3 mL aliquot of urine samples containing native analytes was loaded onto SPE cartridges. The following protocol was used for WCX cartridges: preconditioning was carried out with a 2.5% aqueous solution of ammonia in water, followed by passing a mixture of acetonitrile:water (10:90, v:v). Elution was carried out with a 5% solution of ammonium acetate in methanol.
2.3. Instrumentation
A Thermo TSQ Quantum Access MAX (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), tuned at the full-width at half-maximum (FWHM) resolution of 0.7 Da, equipped with an electrospray ionization source (ESI) and coupled with a Dionex Ultimate-3000 (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) UHPLC system controlled by ThermoXCalibur 2.2 software was used. Separation was carried out on a Phenomenex Kinetex C18 (100 × 2.1 mm, 2.6 µm) analytical column with the respective guard column. The mobile phase consisted of acetonitrile (mobile phase A), 0.1 formic acid (FA) in water (mobile phase B) and 100 µg/mL dopant (potassium, lithium, silver) in water. Elution was performed in the gradient mode with a total run time of 10 min, which included column equilibration before the next analysis. The flow rates were 0.4 mL/min at the main pump and 0.05 mL/min at the additional pump. The column temperature was set at 35 °C, and samples were stored in the autosampler tray at 5 °C to prevent their degradation.
The following detection conditions were used: the heated capillary temperature was maintained at 400 °C, the sheath gas and auxiliary gas (nitrogen) pressure levels were set at 60 and 10 arbitrary units, respectively, the transfer capillary temperature was set at 320 °C, the ionization source voltage was 4 kV and the positive ion detection mode was used.
3. Results
It is known that lithium, silver, potassium and sodium salts form complexes with organic molecules containing hard or soft Lewis basic sites. As a result of such coordination with analytes, positively charged and stable complexes can be detected by mass spectrometry. In the case of coupling mass spectrometry with high-performance liquid chromatography, such a technique can be used to elucidate the structures of mixtures because of the high speed of complex production. The presence of these cations provides the formation of single-charged ions for peptides in the higher masses, free from low-molecular interferences, which also provides a greater signal-to-noise ratio. However, it should be noted that for peptides with masses above 1000 Da, such a methodology can have significant limitations related to the limitations of mass spectrometry and m/z values if triple quadrupole or orbitrap mass analyzers are used.
Previous studies published by the authors of [20] showed promising results that could be utilized to significantly improve the sensitivity of trace and ultra-trace levels of analysis and fully exploit the potential of instruments available in laboratories. Nonetheless, given the difficulties with peptide determination, we decided to test this approach on two of GHRPs that are well-known and in WADA-accredited laboratories: GHRP-2 and GHRP-6.
The principal scheme for our CIS-MS experiments is shown in Figure 1, which presents post-column coordination of the peptides with silver.
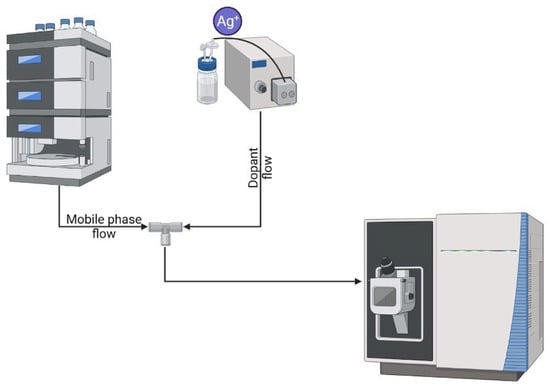
Figure 1.
Principal instrumental scheme for CIS-MS experiments.
The introduction of silver nitrate into the mobile phase can lead to chelation of the sorbent, a change in its properties and a loss of reproducibility of results [25,26,27]. Thus, several factors were taken into account during the post-column process: the flow from the additional pump had to be small and reproducible, and the capillary length had to be relatively short to avoid off-column peak smearing. Since the pressure in the system significantly drops after the column, there was no need to use two pumps with an operating pressure of more than 1000 bar. At the same time, the presence of a T-connector in the system required a sufficiently high-pressure comparable pump to avoid the flow of eluate from the column into the dopant supply line.
Accordingly, a Dionex Ultimate pump with a maximum operating pressure of 600 bar was used. The flow rate was 50 µL/min, and the dopant concentration was optimized experimentally (Figure 2).
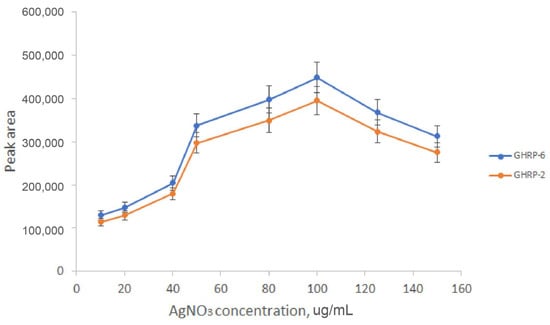
Figure 2.
The influence of the dopant concentration on the analytical signal.
An intense [M+Ag]+ ion was obtained, which was the goal of this experiment (Figure 3), and, subsequently, the stability of the ion beam when silver was introduced into the system was assessed. As can be seen from Figure 3, a typical isotopic pattern for silver adducts was observed (107Ag and 109Ag with an abundance of 52% and 48%, respectively), which could be used as an additional confirmation parameter of adduct formation. However, further fragmentation in the collision cell leads to the elimination of silver from the precursor ions, similar to non-derivatized peptide fragmentation.
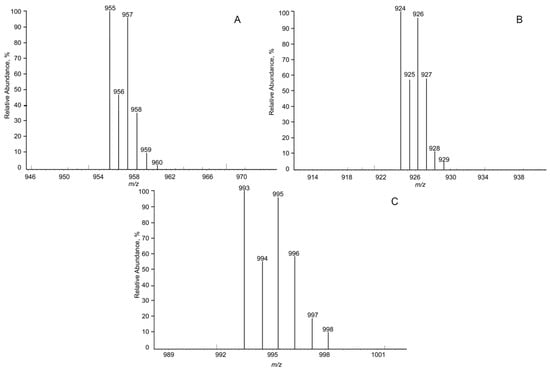
Figure 3.
CIS-MS mass spectra of analytes: DSIP (A), GHRP-2 (B), GHRP-6 (C).
To investigate the influence of the dopant concentration on the peak area of the analytes, further experiments were carried out in the absence of a matrix. As can be seen from Figure 4, for the first 20 injections, the analytical signal remained stable, and each subsequent injection led to a loss in the peak area, essentially rendering the system unusable after 35 injections.
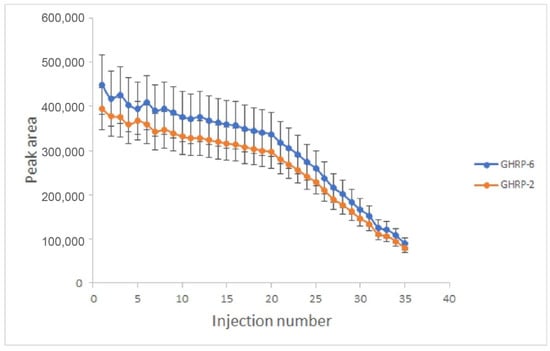
Figure 4.
Change in the value of the analytical signal depending on the number of injections (n = 3) using silver nitrate as the dopant.
To complete the experiments and prevent false results, an additional ion optics module containing a skimmer, tube lens and transfer capillary was added, because the cleanup procedure of the optics from silver requires more time than the typical cleanup. Instrument tuning was performed after each shutdown. All analysis conducted following the establishment of the metrological parameters of this methodology was completed with ISTD (DSIP). There may have been an additional load on the ion optics added by matrix components since a number of compounds that are not capable of ionization under classical electrospray ionization conditions will be effectively ionized in the presence of dopants, which also accelerate the contamination of the skimmer, transfer capillary and tube lens.
A partial solution to this problem could be the regular use of a divert valve, which sends the mobile phase to the waste line outside the transition scanning time. Alternatively, using lithium or potassium cations as dopants allows one to avoid such difficulties; however, during our research, a lack of effectiveness was noted when using these to form intense ion adducts with these metals (Table 1).

Table 1.
Comparison of the different dopants’ efficiency at a 100 µg/mL dopant concentration.
As can be seen from Table 1, the most abundant signals were obtained when using silver ions as the dopant. In the case of potassium, one of the main issues was its concentration in the mobile phase. To prepare a suitable concentration of dopant in the mobile phase, a preliminary analysis of water and the organic solvent (acetonitrile or methanol) is required to establish the dopant’s concentration in the solvent and calculate the necessary concentration and volume of its salt for the mobile-phase components. Even day-to-day concentrations could differ due to its leaching from glass, which makes it unpredictable and, as a result, leads to unstable results. Each 10–15% variability of the dopant concentration leads to significant changes in the molecular ion yield, which cannot be predicted in routine analysis. As such, the use of a naturally occurring dopant is not optimal for post-column derivatization.
Another important point when making the dopant choice is that the efficiency of the analytical signal is increasing. In this case, the most abundant and reproducible ratio between the peak area and area of the internal standard was obtained using silver. In this case, it was possible to achieve less than 15% deviation, while the use of lithium or potassium as the dopant increased that to 20%, which does not meet the FDA criteria for bioanalytical methods. On the other hand, the use of silver as the dopant leads to rapid contamination of the ion optics, while lithium and potassium require much less maintenance of the instrument. Thus, if studies are allowing for extended ranges of determination error and do not require the determination of ultra-trace amounts, then lithium or potassium is advisable as the dopant.
A comparison with the classical approach to determining these compounds using CIS-MS is given in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4, and a chromatogram, obtained from real samples, is shown in Figure 5.

Table 2.
LOD and LLOQ comparison for CIS-MS and conventional ESI-MS methods (“dilute-and-shoot” and SPE).

Table 3.
Results of the QC samples’ analysis using different techniques.

Table 4.
Observed matrix effects at QC low.
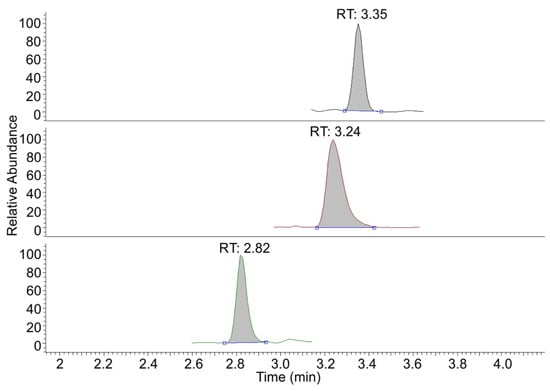
Figure 5.
CIS-MS chromatogram of DSIP (tR 2.82 min), GHRP-2 (tR 3.24 min) and GHRP-6 (tR 3.35 min) at 2 ng/mL in the extracted ion current chromatogram mode.
As can be seen from Figure 5, the total ion current collected in the MRM mode does not show any significant matrix peaks. This allows us to assert that the selected transitions have a high specificity and selectivity. It should be noted that the use of isotopic peaks is unsuitable for quantitative and qualitative analyses in this case. It caused the absence of structural information from MRMs, collected from isotopic peaks, and revealed only the elimination of the silver ions from the analyte. More important is a confirmation of the similarity of the derivative fragmentation, which confirms the basic fragments from the structure of the analyte.
According to the FDA guide for bioanalytical methods’ validation [28] and the European Medicine Academy (EMA) guidelines [29], the selectivity, linearity, accuracy, precision, limit of detection (LOD), limit of quantification (LOQ), matrix effect, recovery, carryover and stability should be established. In this research, only partial validation was conducted, which caused a significant loss of peak intensity after just 30 injections.
The result reveals that this method is inapplicable for routine analysis and that its applicability is limited to specific applications. In this case, LOD and LLOQ is still mandatory for establishing as well as matrix effects (Table 2 and Table 3).
Matrix effects were evaluated through a comparison of the results obtained for real and model solutions spiked with target analytes at the three concentration levels, which were passed through the sample preparation procedure under optimized conditions. The most pronounced matrix effects manifested when we used the dilute-and-inject procedure, which reached 24%, while for CIS-MS, they reached 20%, and the sample preparation scheme least susceptible to matrix effects was the combination with solid-phase extraction (less than 15% at QC low).
At the same time, the possibility of carryover was determined. To do this, after establishing a quality control solution with a high concentration of analytes, a blank sample was analyzed. The absence of peaks of detectable components allows us to state that there was no carryover.
Since the analytes are exogenous, their presence in blank urine samples seems unlikely, which greatly facilitates the task of establishing matrix effects (Table 4) and selectivity during research.
Another important part of the work was the study of the types of ions formed when peptides were coordinated with silver. Under normal conditions, the peptides under study are characterized by the formation of doubly charged ions, while those coordinated around silver form monocharged ions (Table 5) with a characteristic isotopic pattern (Figure 3).

Table 5.
MRM transitions for analytes’ detection.
As can be seen from Table 5, in the optimization of the MRM transition, for the ESI-MS and CIS-MS methods, the same product ions were produced; however, this required a higher collision energy, which may have been caused by the necessity of silver ions’ elimination and then analytes’ dissociation. Such a fragmentation pathway could possibly lead to early maintenance of the collision cell because of the ion optics contamination with silver. In this case, the combination of ESI and SPE looks to be preferable by a significant margin for routine applications.
4. Discussion
The utilization of silver as the dopant in CIS-MS has advantages for the analysis of GHRP-6 and GHRP-2. Firstly, CIS-MS offers enhanced sensitivity compared to conventional liquid chromatography with an electrospray ionization source. By introducing silver ions into the mobile phase, the generation of positively charged ions is facilitated, leading to improved detectability by LC-MS. This heightened sensitivity enables the determination of GHRPs at trace and ultra-trace concentration levels. Secondly, CIS-MS allows more data to be gathered in untargeted applications. The incorporation of silver ions as dopants permits the formation of intense [M+Ag]+ ions, thereby enriching the information content in the mass spectrum. This proves particularly beneficial in complex analyses, such as the determination of growth-hormone-releasing peptides. Quantitative data from this study indicate that CIS-MS provides an improved LOD and LLOQ for GHRP-6 and GHRP-2 when compared when conventional ESI-MS methods. The LOD and LLOQ values achieved with CIS-MS were 0.2 ng/mL and 0.5 ng/mL, respectively, whereas the values were higher for ESI-MS with solid-phase extraction (SPE) and “dilute-and-shoot” sample preparation. Overall, CIS-MS demonstrates high sensitivity and the capability to generate extensive data, making it a suitable analytical instrument for achieving exceptional sensitivity in the analysis of GHRP-6 and GHRP-2.
It is important, however, to acknowledge the limitations associated with CIS-MS, such as the potential instability of the ion beam when silver is introduced into the system. Beyond that, the main issue of this technique is the lack of resistance of ion optics to contamination by silver ions, which leads to a rapid loss of sensitivity. As a result, even establishing the basic metrological characteristics of the technique requires the device to be repeatedly switched off for maintenance, which is unacceptable for routine applications. Further research and optimization efforts are necessary to address these limitations and fully tap into the potential of CIS-MS in peptide analysis. At the same time, usage of lithium or even potassium salts as the dopant with the preliminary solid-phase extraction technique looks promising in order to achieve a higher sensitivity than conventional techniques for the analysis of such peptides.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.N.A. and A.T.; methodology, A.T.; software, A.A.; validation, E.G. and A.A.; formal analysis, A.A.; investigation, Y.-Q.F.; resources, A.T.; data curation, Y.-Q.F.; writing—original draft preparation, A.T.; writing—review and editing, S.N.A.; visualization, E.G.; supervision, Y.-Q.F.; project administration, A.T.; funding acquisition, Y.-Q.F. and A.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 24-43-00003), used the scientific equipment of the Center for Environmental Analysis at the Kuban State University and was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22361132526).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the local Ethics Committee of Ochapovskiy Central Clinical Hospital No. 1, protocol No. 122.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Sanka N. Atapattu was employed by the CanAm Bioresearch Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- World Anti-Doping Agency, Prohibited List. Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/sites/default/files/2023-09/2024list_en_final_22_september_2023.pdf (accessed on 19 April 2024).
- World Anti-Doping Agency, WADA Testing Figures Report. Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/sites/default/files/2023-01/2021_anti-doping_testing_figures_en.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Gil, J.; Cabrales, A.; Reyes, O.; Morera, V.; Betancourt, L.; Sánchez, A.; García, G.; Moya, G.; Padrón, G.; Besada, V.; et al. Development and validation of a bioanalytical LC-MS method for the quantification of GHRP-6 in human plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 60, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppieters, G.; Deventer, K.; van Eenoo, P.; Judák, P. Combining direct urinary injection with automated filtration and nanoflow LC-MS for the confirmatory analysis of doping-relevant small peptide hormones. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2021, 1179, 122842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, H.; Han, B.; Sung, C.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, K.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.; Son, J.; Kwon, O.-S.; Lee, J. LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous analysis of growth hormone-releasing peptides and secretagogues in human urine. Mass Spectrom. Lett. 2016, 7, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timms, M.; Hall, N.; Levina, V.; Vine, J.; Steel, R. A high-throughput LC-MS/MS screen for GHRP in equine and human urine, featuring peptide derivatization for improved chromatography. Drug Test. Anal. 2014, 6, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thevis, M.; Thomas, A.; Schänzer, W. Doping control analysis of selected peptide hormones using LC-MS(/MS). Forensic Sci. Int. 2011, 213, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, H.D.; Hughes, C.M.; Eichner, D. Detection of GHRP-2 and GHRP-6 in urine samples from athletes. Drug Test. Anal. 2015, 7, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Guerrero, N.A.; González-López, N.M.; Zapata-Velásquez, J.D.; Martínez-Ramírez, J.A.; Rivera-Monroy, Z.J.; García-Castañeda, J.E. Synthetic Peptides in Doping Control: A Powerful Tool for an Analytical Challenge. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 38193–38206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenistaya, E.; Zvereva, I.; Thomas, A.; Thevis, M.; Krotov, G.; Rodchenkov, G. Determination of growth hormone releasing peptides metabolites in human urine after nasal administration of GHRP-1, GHRP-2, GHRP-6, Hexarelin, and Ipamorelin. Drug Test. Anal. 2015, 7, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenistaya, E.; Zvereva, I.; Krotov, G.; Rodchenkov, G. Solid-phase extraction of small biologically active peptides on cartridges and microelution 96-well plates from human urine. Drug Test. Anal. 2016, 8, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Tian, T.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Shan, Y. Multi-analyte screening of small peptides by alkaline pre-activated solid phase extraction coupled with liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry in doping controls. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1676, 463272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WADA Technical Document-TD2022MRPL Document Number: TD2022MRPL Version Number: 1.0 Minimum Required Performance Levels and Applicable Minimum Reporting Levels for Non-Threshold Substances Analyzed by Chromatographic-mass Spectrometric Analytical Methods. Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/sites/default/files/resources/files/td2022mrpl_v1.0_final_eng.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Esposito, C.L.; Ac, A.G.; Laszlo, E.; Duy, S.V.; Michaud, C.; Sauvé, S.; Ong, H.; Marleau, S.; Banquy, X.; Brambilla, D. A Quantitative UHPLC-MS/MS Method for the Growth Hormone-Releasing Peptide-6 Determination in Complex Biological Matrices and Transdermal Formulations. Talanta 2021, 233, 122555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverter-Branchat, G.; Segura, J.; Pozo, O.J. On the Road of Dried Blood Spot Sampling for Antidoping Tests: Detection of GHRP-2 Abuse. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, T.; Thomas, A.; Walpurgis, K.; Thevis, M. Fully Automated Dried Blood Spot Sample Preparation Enables the Detection of Lower Molecular Mass Peptide and Non-Peptide Doping Agents by Means of LC-HRMS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 3765–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judák, P.; Esposito, S.; Coppieters, G.; van Eenoo, P.; Deventer, K. Doping control analysis of small peptides: A decade of progress. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2021, 1173, 122551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, C.; Kong, F.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, L. Selective molecular characterization of olefins in hydrocarbon mixtures by Ag+ complexation ESI high-resolution mass spectrometry. Fuel 2022, 319, 123760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedovici, A.; Lazou, K.; D’Oosterlinck, A.; Zhao, Y.; Sandra, P. Analysis of jojoba oil by LC-coordination ion spray-MS (LC-CIS-MS). J. Sep. Sci. 2002, 25, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Guerrero, N.A.; González-López, N.M.; Zapata-Velásquez, J.D.; Martínez-Ramírez, J.A.; Rivera-Monroy, Z.J.; García-Castañeda, J.E. Synthesis of polysulfanes with 20 or more sulfur atoms with characterization by UPLC-(Ag+)-coordination ion spray-MS. J. Sulfur. Chem. 2013, 34, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, E.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, K.H.; Kwon, O.S.; Lee, J. Sensitivity of GC-EI/MS, GC-EI/MS/MS, LC-ESI/MS/MS, LC-Ag+ CIS/MS/MS, and GC-ESI/MS/MS for analysis of anabolic steroids in doping control. Drug Test. Anal. 2015, 7, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, E.; Lee, K.M.; Park, K.D.; Park, K.S.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, J. Hydroxycholesterol levels in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neuromyelitis optica revealed by LC-Ag+CIS/MS/MS and LC-ESI/MS/MS with picolinic derivatization: Increased levels and association with disability during acute attack. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 0167819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virus, E.D.; Sobolevsky, T.G.; Rodchenkov, G.M. “Wrong-Way-Round Ionization” and Screening for Doping Substances in Human Urine by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry. J. Mass. Spectrom. 2012, 47, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, P.; van Onselen, R. Evaluating the “Wrong-Way-Round” Electrospray Ionization of Antiretroviral Drugs for Improved Detection Sensitivity. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seal, J.R.; Havrilla, C.M.; Porter, N.A.; Hachey, D.L. Analysis of unsaturated compounds by Ag+ coordination ionspray mass spectrometry: Studies of the formation of the Ag+/lipid complex. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2003, 14, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecchi, T.; Pucciarelli, F.; Passamonti, P.; Ferraro, S. Influence of metal impurities sorption onto a silica based C18 stationary phase on the HPLC of metal chelating analytes. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 1999, 22, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pra, M.; Greco, G.; Krajewski, M.P.; Martin, M.M.; George, E.; Bartsch, N.; Steiner, F. Effects of titanium contamination caused by iron-free high-performance liquid chromatography systems on peak shape and retention of drugs with chelating properties. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1611, 460619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA Guidance Document M10 Bioanalytical Method Validation and Study Sample Analysis. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/162903/download (accessed on 19 April 2024).
- European Medicine Academy Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-bioanalytical-method-validation_en.pdf (accessed on 19 April 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).