Nationwide Surveillance and Cumulative Risk Assessment of Pesticide Residues in Egyptian Vegetables: Results from 2018 to 2021
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Commodity Sampling Program
2.3. Health Risk Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Pesticide Residue Detection
3.2. Regional Variation and Implications for Agricultural Practices
3.3. Risk Assessment through Dietary Exposure
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zuo, W.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, P.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, X.; Wu, S.; An, X.; Liu, X.; Cheng, X.; Yu, Y.; et al. Current-Use Pesticides Monitoring and Ecological Risk Assessment in Vegetable Soils at the Provincial Scale. Environ. Res. 2024, 246, 118023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Xiong, J.; You, J. Distribution and Ecological Risk of Neonicotinoid Insecticides in Sediment in South China: Impact of Regional Characteristics and Chemical Properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Liu, L.-Y.; Zhu, F.-J.; Ma, W.-L. National-Scale Monitoring of Historic Used Organochlorine Pesticides (OCPs) and Current Used Pesticides (CUPs) in Chinese Surface Soil: Old Topic and New Story. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storck, V.; Karpouzas, D.G.; Martin-Laurent, F. Towards a Better Pesticide Policy for the European Union. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, X.-F.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.-Y.; Zeng, E.Y. The Human and Ecological Risks of Neonicotinoid Insecticides in Soils of an Agricultural Zone within the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.K.; Tripathy, V.; Sharma, K.; Gupta, R.; Yadav, R.; Devi, S.; Walia, S. Long–Term Monitoring of 155 Multi–Class Pesticide Residues in Indian Vegetables and Their Risk Assessment for Consumer Safety. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.H.M.; Lenzen, M.; McBratney, A.; Maggi, F. Risk of Pesticide Pollution at the Global Scale. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Ghani, S.B.; Abdallah, O.I. Method Validation and Dissipation Dynamics of Chlorfenapyr in Squash and Okra. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, A.N.; Malhat, F.M.; Badawy, H.M.A.; Barakat, D.A. Dissipation Dynamic, Residue Distribution and Processing Factor of Hexythiazox in Strawberry Fruits under Open Field Condition. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APC. Agricultural Pesticides Committee, Egypt. 2019. Available online: http://www.apc.gov.eg/ar/ (accessed on 8 January 2022).
- Mansour, S.A. Environmental Impact of Pesticides in Egypt. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 196, 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, E.A.; Shalaby, S.E.M. Monitoring and Accumulative Risk Assessment of Pesticide Residues Detected in the Common Vegetables Grown in the Eastern Nile Delta, Egypt. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 3, 100518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Feng, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, M.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Mei, B.; Chen, R.; Gao, M.; et al. Pesticide Residue and Dietary Intake Risk of Vegetables Grown in Shanghai under Modern Urban Agriculture in 2018–2021. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.-L.; Deng, H.; Deng, X.-F.; Yang, J.-Y.; Jiang, Y.-M.; Zeng, D.-P.; Huang, F.; Shen, Y.-D.; Lei, H.-T.; Wang, H.; et al. Monitoring of Organophosphorus Pesticides in Vegetables Using Monoclonal Antibody-Based Direct Competitive ELISA Followed by HPLC–MS/MS. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhat, F.; Mahmoud, M.; Barakat, D.A.; Ibrahim, E.-D.; Elgammal, H.; Hussien, M.; Saber, A.N. Dissipation Behavior, Residue Distribution, and Exposure Risk Assessment of Tebufenpyrad and Milbemectin Acaricides in Strawberries under Open Field Conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 35194–35205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhat, F.; Hegazy, A.; Barakat, D.A.; Desoky, E.; Mohamed, I.; Saber, E.S. Sulfoxaflor Residues and Exposure Risk Assessment in Grape under Egyptian Field Conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 52038–52048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, E.S.; Malhat, F.; Saber, A.N.; Heikal, S.; Hussien, M. Dissipation Pattern and Dietary Risk Assessment of Chlorfenapyr and Methomyl in Corn under Egyptian Field Conditions. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2024, 38, e5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jallow, M.; Awadh, D.; Albaho, M.; Devi, V.; Ahmad, N. Monitoring of Pesticide Residues in Commonly Used Fruits and Vegetables in Kuwait. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, V.; Eslami, Z.; Molaee-Aghaee, E.; Peivasteh-Roudsari, L.; Sadighara, P.; Thai, V.N.; Fakhri, Y.; Ravanlou, A.A. Evaluation of Pesticide Residues and Risk Assessment in Apple and Grape from Western Azerbaijan Province of Iran. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CAC. Codex Alimentarius Commission Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Program; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993; p. 391.
- ISO/IEC 17025:2017; General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Llaboratories. ISO: Genevan, Switzerland, 2017. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/66912.html (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- EN-1605 (2019); EFSA, (European Food Safety Authority). Pesticide Residue Intake Model- EFSA PRIMo Revision 3.1 (Update of EFSA PRIMo Revision 3). EFSA Supporting Publication: Parma, Italy, 2019; p. 15. [CrossRef]
- WHO (World Health Organization). Human Health Risk Assessment Toolkit: Chemical Hazards, Second Edition, Harmonization Project Document No. 8. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240035720 (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- Wang, X.; Sato, T.; Xing, B.; Tao, S. Health Risks of Heavy Metals to the General Public in Tianjin, China via Consumption of Vegetables and Fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 350, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Yaqub, G.; Hafeez, T.; Tariq, M. Assessment of Health Risk Due to Pesticide Residues in Fruits, Vegetables, Soil, and Water. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 5497952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoto, O.; Azuure, A.A.; Adotey, K.D. Pesticide Residues in Water, Sediment and Fish from Tono Reservoir and Their Health Risk Implications. Springerplus 2016, 5, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Ma, Q.; Lu, C.; Guo, R. Discussion on the Current Situation of Chlorpyrifos Pesticide Residues in Vegetables and Supervision after Prohibition. J. Zhejiang Univ. 2016, 57, 2101–2102. [Google Scholar]
- Wołejko, E.; Łozowicka, B.; Jabłońska-Trypuć, A.; Pietruszyńska, M.; Wydro, U. Chlorpyrifos Occurrence and Toxicological Risk Assessment: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S.; Rahman, M.R.; Prodhan, M.D.H.; Sarker, D.; Rahman, M.M.; Uddin, M.K. Human Health Risk Assessment of Pesticide Residues in Pointed Gourd Collected from Retail Markets of Dhaka City, Bangladesh. Accredit. Qual. Assur. 2021, 26, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, M.; Kaium, A.; Khan, M.S.I.; Prodhan, M.D.H.; Begum, N.; Chowdhury, M.T.I.; Islam, M.A. Residue Level and Health Risk Assessment of Organophosphorus Pesticides in Eggplant and Cauliflower Collected from Dhaka City, Bangladesh. Food Res. 2021, 5, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalaby, S.E.M.; Abdou, G.Y.; El-Metwally, I.M.; Abou-elella, G.M.A. Health Risk Assessment of Pesticide Residues in Vegetables Collected from Dakahlia, Egypt. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2021, 61, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagi, F.F.; Budakov, D.B.; Bursić, V.P.; Stojšin, V.B.; Lazić, S.D.; Vuković, S.M. Efficacy of Azoxystrobin for the Control of Cucumber Downy Mildew (Pseudoperonospora Cubensis) and Fungicide Residue Analysis. Crop Prot. 2014, 61, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, D.; John, S. Health Risk Assessment of Pesticide Residues in Fruits and Vegetables from Farms and Markets of Western Indian Himalayan Region. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, L.S. State of the Science of Endocrine Disruptors. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, a107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. EFSA 2021 Report on Pesticide Residue Monitoring in the EU. EFSA J. 2021, 19, 6518. [Google Scholar]
- Koul, O. Development and Commercialization of Biopesticides; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Li, M.; Achal, V. A Comprehensive Review on Environmental and Human Health Impacts of Chemical Pesticide Usage. Emerg. Contam. 2025, 11, 100410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)—Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. WHO Recommended Classification of Pesticides by Hazard and Guidelines to Classification, 2019th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Bempah, C.K.; Buah-Kwofie, A.; Denutsui, D.; Asomaning, J.; Tutu, A.O. Monitoring of Pesticide Residues in Fruits and Vegetables and Related Health Risk Assessment in Kumasi Metropolis, Ghana. Res. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 3, 761–771. [Google Scholar]
- Fenske, R.A.; Kissel, J.C.; Lu, C.; Kalman, D.A.; Simcox, N.J.; Allen, E.H.; Keifer, M.C. Biologically Based Pesticide Dose Estimates for Children in an Agricultural Community. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogheim, S.M.; El-Marsafy, A.M.; Salama, E.Y.; Gadalla, S.A.; Nabil, Y.M. Monitoring of Pesticide Residues in Egyptian Fruits and Vegetables during 1997. Food Addit. Contam. 2002, 19, 1015–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, F.; Van Bruggen, A.H.C.; Jiggins, J.L.S.; Ambatipudi, A.C.; Murphy, H. Acute Pesticide Poisoning among Female and Male Cotton Growers in India. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2005, 11, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Sidhu, V.; Rong, Y.; Zheng, Y. Pesticide Pollution in Agricultural Soils and Sustainable Remediation Methods: A Review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2018, 4, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehler, L.E. Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Definition, Historical Development and Implementation, and the Other IPM. Pest Manag. Sci. 2006, 62, 787–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, D.; Acquay, H.; Biltonen, M.; Rice, P.; Silva, M.; Nelson, J.; Lipner, V.; Giordano, S.; Horowitz, A.; D’Amore, M. Environmental and Economic Costs of Pesticide Use. Bioscience 1992, 42, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaratnam, J. Acute Pesticide Poisoning: A Major Global Health Problem. World Health Stat. Q. 1990, 43, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Altieri, M.A.; Nicholls, C.I. Soil Fertility Management and Insect Pests: Harmonizing Soil and Plant Health in Agroecosystems. Soil Tillage Res. 2003, 72, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEDI. IEDI Calculations for FAO/WHO Acute Dietary Intake Assessment; IEDI: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2014.
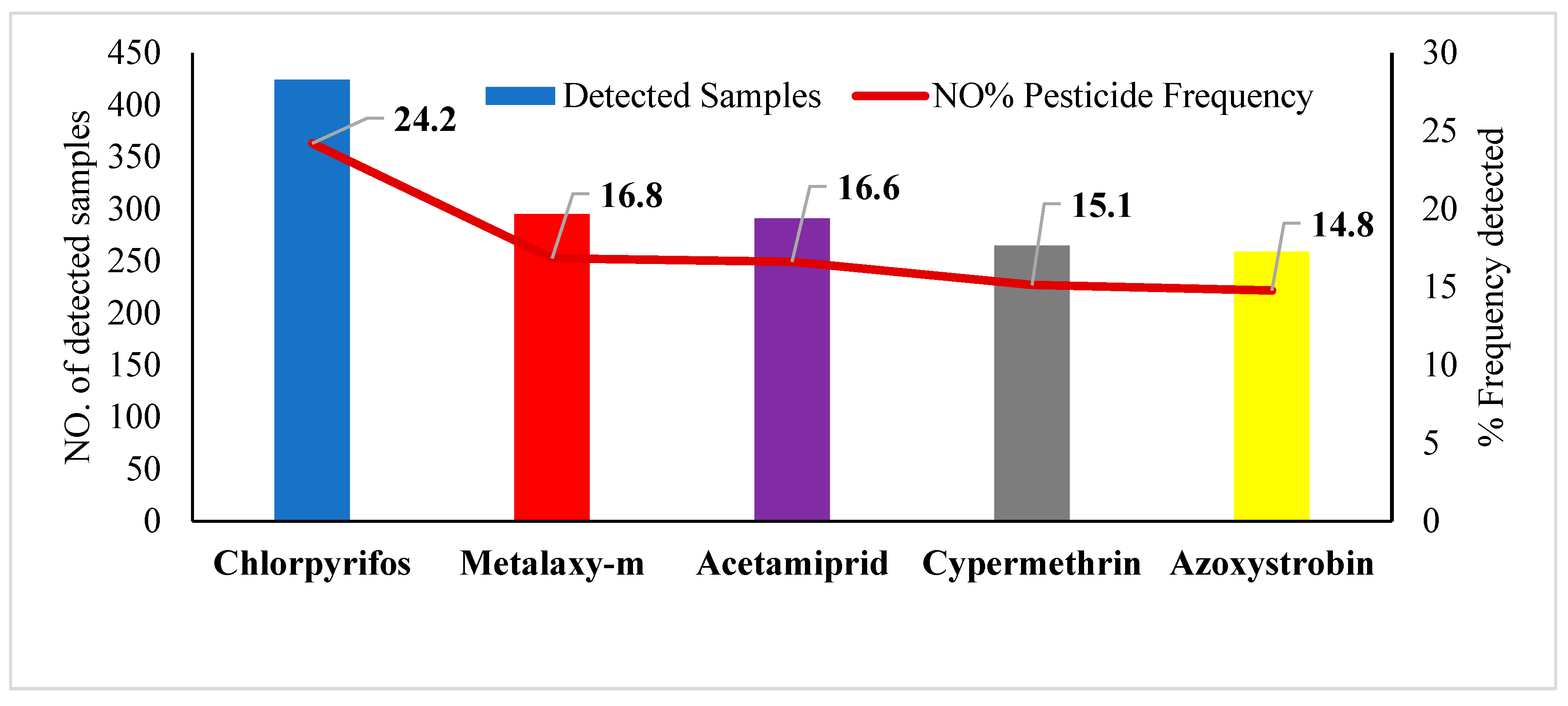
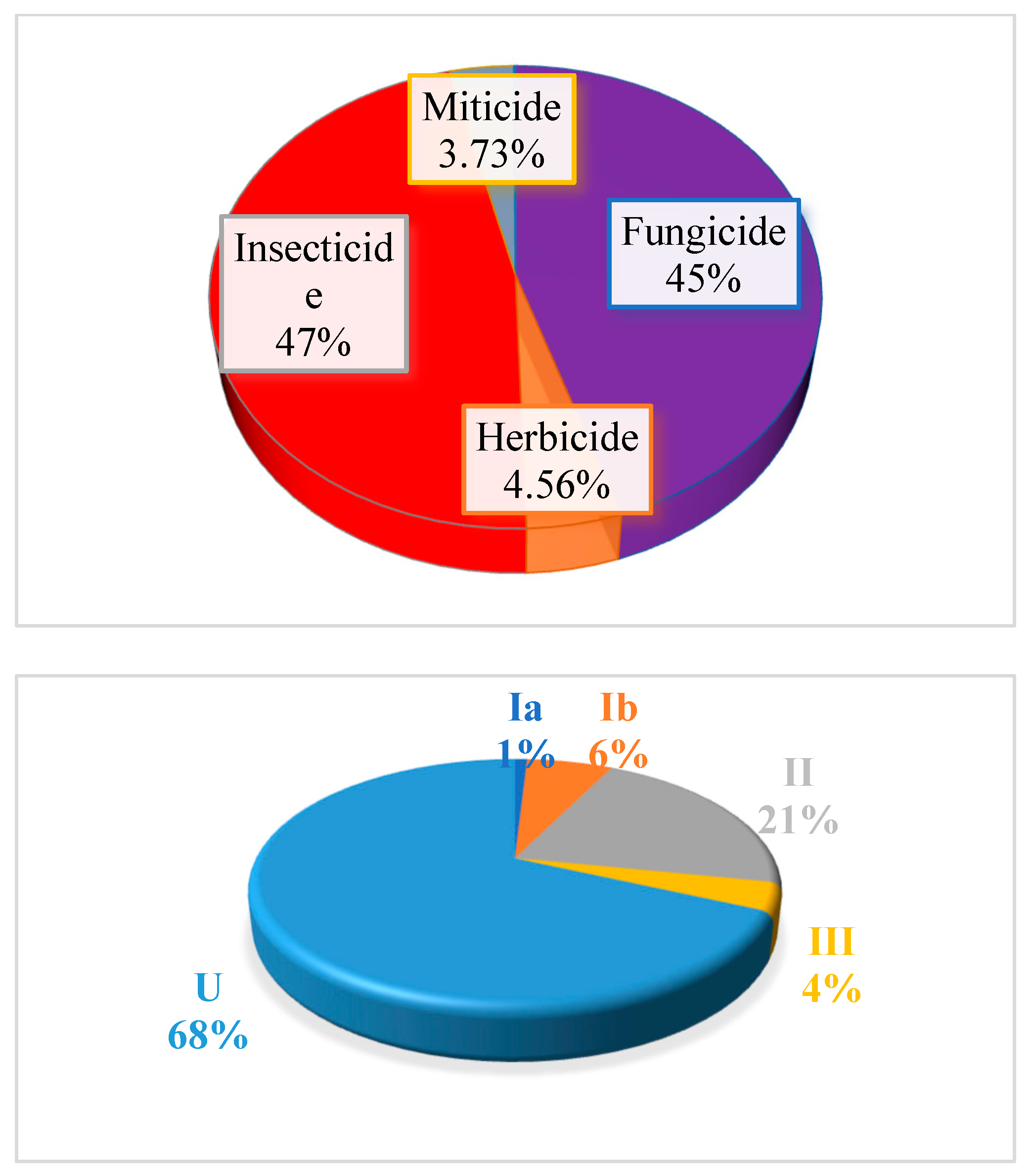
| Commodity | Number of Samples | No. Free Sample | Pesticide-Contaminated Sample | No. Sample > MRL | Sample% Have Residues > MRL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | |||||
| Cumber | 420 | 211 | 209 | 50% | 56 | 13.3% |
| Okra | 420 | 244 | 176 | 42% | 37 | 8.8% |
| Eggplant | 420 | 289 | 131 | 31% | 39 | 9.3% |
| Squash | 420 | 260 | 160 | 38% | 25 | 6.0% |
| Peas | 420 | 246 | 174 | 41% | 65 | 15.5% |
| Onion | 420 | 244 | 176 | 42% | 49 | 11.7% |
| Green onion | 420 | 259 | 161 | 38% | 75 | 17.9% |
| Lettuce | 420 | 294 | 126 | 30% | 38 | 9.0% |
| Cantaloupe | 420 | 231 | 189 | 45% | 39 | 9.3% |
| Parsley | 420 | 171 | 249 | 59% | 141 | 33.6% |
| Total No. | 4200 | 2449 | 1751 | - | 564 | - |
| Total % | - | - | - | 42% | 13% | |
| Governorate | Number of Markets | Number of Samples Collected | Samples Contaminated with Pesticides | Percentage (%) of Contaminated Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alexandria | 1 | 210 | 82 | 39% |
| Asyut | 1 | 210 | 92 | 44% |
| Beheira | 2 | 420 | 124 | 30% |
| Beni Suef | 1 | 210 | 36 | 17% |
| Cairo | 2 | 420 | 97 | 23% |
| Dakahlia | 1 | 210 | 41 | 20% |
| Damietta | 1 | 210 | 41 | 20% |
| Fayoum | 1 | 210 | 48 | 23% |
| Gharbia | 1 | 210 | 55 | 26% |
| Giza | 2 | 420 | 142 | 34% |
| Ismailia | 1 | 210 | 63 | 30% |
| Kafr El Sheikh | 1 | 210 | 46 | 22% |
| Menoufia | 1 | 210 | 55 | 26% |
| Minya | 1 | 210 | 66 | 31% |
| Qalyubia | 1 | 210 | 50 | 24% |
| Sharkia | 1 | 210 | 63 | 30% |
| Sohag | 1 | 210 | 54 | 26% |
| Commodity | EDIs (mg kg−1 bw day−1) | HI % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Min | Max | |
| Cantaloupe | 4.1 × 10−7 | 9.2 × 10−4 | 0.0002 | 4.6103 |
| Lettuce | 1.2 × 10−8 | 5.9 × 10−5 | 0.000003 | 0.591025 |
| Parsley | 1.1 × 10−8 | 1.8 × 10−4 | 0.00001 | 7.3 |
| Onion and Green Onion | 2.9 × 10−8 | 2.8 × 10−4 | 0.00001 | 3.2 |
| Peas | 5.4 × 10−7 | 2.3 × 10−3 | 0.0003 | 46.4 |
| Okra | 2.2 × 10−8 | 5.7 × 10−6 | 0.00001 | 0.09 |
| Eggplant | 2.8 × 10−7 | 1.9 × 10−4 | 0.001 | 3.2 |
| Squash | 6.7 × 10−8 | 2.1 × 10−5 | 0.00005 | 0.42 |
| Cucumber | 4.9 × 10−7 | 6.4 × 10−4 | 0.00017 | 39.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malhat, F.; Saber, A.; Saber, E.-S.; Shokr, S.A.S.; Abdel-Megeed, M. Nationwide Surveillance and Cumulative Risk Assessment of Pesticide Residues in Egyptian Vegetables: Results from 2018 to 2021. Separations 2024, 11, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11110318
Malhat F, Saber A, Saber E-S, Shokr SAS, Abdel-Megeed M. Nationwide Surveillance and Cumulative Risk Assessment of Pesticide Residues in Egyptian Vegetables: Results from 2018 to 2021. Separations. 2024; 11(11):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11110318
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalhat, Farag, Ayman Saber, El-Sayed Saber, Shokr Abel Salam Shokr, and Mohammed Abdel-Megeed. 2024. "Nationwide Surveillance and Cumulative Risk Assessment of Pesticide Residues in Egyptian Vegetables: Results from 2018 to 2021" Separations 11, no. 11: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11110318
APA StyleMalhat, F., Saber, A., Saber, E.-S., Shokr, S. A. S., & Abdel-Megeed, M. (2024). Nationwide Surveillance and Cumulative Risk Assessment of Pesticide Residues in Egyptian Vegetables: Results from 2018 to 2021. Separations, 11(11), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11110318







