Abstract
This study used an experimental design approach to optimize an HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of three pharmaceutical residues (triamcinolone, nystatin, and gramicidin) in industrial wastewater samples. The goal of using an experimental design approach was to maximize the method performance through separation enhancement and shortening the time of analysis and/or minimizing the environmental effects through the reduction in wastes and sample treatment. To achieve this goal, two steps were performed: a full factorial screening design for the three chromatographic variables, and optimization design using central composite design to select the optimum conditions that accomplished the highest resolution between adjacent peaks within a minimum run time of less than 5 min. The optimal chromatographic conditions derived from Minitab software using the desirability function were applied. Separation was carried out on a Zorbax C18 column (250 mm × 4.6, 5 μm) with gradient elution of a mobile phase composed of methanol and 0.25 M potassium dihydrogen phosphate buffer (pH 3.6) at different UV detections. For the validation of the developed HPLC method, ICH guidelines were followed, and the obtained results were found to be in compliance with the acceptance criteria. Linearity was over the concentration range of 1.00–25.00 μg/mL for triamcinilone and nystatin and 10.00–50.00 µg/mL for gramicidin. The proposed method was successfully applied to quantify the three studied pharmaceutical compounds in rinsing wastewater samples.
1. Introduction
One of the new challenges in environmental chemistry is the traceability of pharmaceutical residues in wastewater, which is considered the most vital class of environmental pollution [1]. Following recent investigations, it was discovered that pharmaceutical residues are not entirely eliminated during the steps of wastewater treatment and that these residues are not biodegradable in the environment [2]. In developing countries, it was found that more than 80% of wastewater is disposed of improperly, which is considered a global problem [3]. Environmental discharges originate from different sources, such as hospital water waste and pharmaceutical industries. One of the significant sources that increases the level of organic pollutants in aquatic systems is manufacturing processes due to improper disposal and/or improper cleaning steps. Moreover, the substantial usage of pharmaceutical drugs by humans and animals is highly elevated, leading to an increasing percentage of pharmaceutical drugs present in the aquatic environment, which is recognized worldwide as an emerging case. Antimicrobials, antifungals, and corticosteroids are widely used pharmaceutical drugs detected in aquatic systems. In the literature review, we found that triamcinolone has been detected in ointment formulation [4], in human plasma [5], in biodegradable microparticles [6], in dosage form [7,8], and in bulk pharmaceutical formulation using an HPLC-UV detector and HPTLC-UV detector [9]. Nystatin has been detected in plasma and tissue with an HPLC-UV detector [10], in saliva with an HPLC-UV and fluorescence detector [11], and also with ay chemometric and HPLC-UV detector [12]. Gramicidin has been detected in bulk pharmaceutical formulations with a UPLC-PDA detector [13], and in phospholipid membranes with an HPLC-UV detector [14]. In a previous literature review, Heugten et al. developed an HPLC method for ointment formulations containing triamcinolone in the presence of its three degradation products. The developed method separated the studied drug from its degradation products with a flow rate of 1.5 mL/min within a run time of 40 min [4]. An HPLC technique with UV detection was developed by Muralidharan et al. to determine triamcinolone alone in human plasma with an analysis time of 10 min and a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min [5]. Additionally, Silva et al. established an HPLC method with UV detection for the quantification of triamcinolone microparticles in a single dosage form within a run time of 9.0 min. [6]. An HPLC-UV technique for tablet formulations containing triamcinolone was developed by Redasani et al. with a linearity range of 3.0–18.0 μg/mL, showing lower method sensitivity [7]. Sebaiy et al. established a stability indicating HPLC for the determination of benzyl alcohol and triamcinolone in tablet dosage form using a C18 column (150 mm × 4.60, 5 μm), and the studied drugs were eluted at 1.67 min. and 3.42 min, respectively [8]. Despite the fact that this established method was successful in separating the two drugs, the benzyl alcohol eluted early and close to the dead volume, according to the analytical column that was used. Furthermore, with a run time of 13 min and a wavelength of 225.0 nm, Abbass et al. established an HPLC method for the simultaneous measurement of triamcinolone and econazole in pharmaceutical preparations [9]. Groll et al. developed a chromatographic technique for nystatin that uses UV detection at 305 nm to determine nystatin alone in human plasma within an 11 min run time [10]. In addition, L1abot et al. developed two HPLC methods for determining nystatin in saliva within a 10 min run time using UV and fluorescence detectors [11]. Heneedek et al. developed HPLC-UV and chemometric methods for the simultaneous determination of nystatin and miconazole in pharmaceutical preparations with a nystatin linearity range of 10–100 μg/mL, resulting in a less sensitive method [12]. For gramicidin, Paradesh et al. established a UPLC method for the simultaneous determination of gramicidin, triamcinolone, and neomycin with a run time of 8 min [13]. These analytical methods typically employ flow rates ≥1 mL/min with an analysis run time longer than 9 min, and techniques using high flow rates have a negative impact on the pump while raising the flow rate. Therefore, these methods take a long time and use a difficult mobile phase that requires pH control. These systems require development through a low consumption of solvents and a high analysis speed. The studied drugs are administered alone or in combination in different dosage forms and occupy a significant sector of industrial pharmaceutical companies. Triamcinolone is used topically or systematically. Ocular diseases could be effectively treated with triamcinolone when used topically. Triamcinolone injections, although used to treat eye illnesses, have many complications, including endo-ophthalmic, an increase in ocular pressure, and glaucoma [15]. Due to its poor solubility and high toxicity, nystatin is primarily used to treat oral and topical infections [16]. Gramicidin has a hemolytic adverse effect; hence, it is only applied topically [17]. The use of design of experiments (DOE) provides many benefits for developing and improving approaches based on statistical analysis. An example of a DOE “multivariate optimization” is a full factorial design, which enables the simultaneous investigation of the impact of studied factors on the chromatographic method performance [18]. In the presented work, three of the most frequently used pharmaceutical drugs are selected to be analyzed simultaneously in wastewater samples. The separation and simultaneous determination of nystatin, gramicidin, and triamcinolone in pharmaceutical preparations and/or environmental samples have not yet been reported. Due to the different classes of these three drugs (Figure S1), it was a challenge to create and develop a robust method for the determination of the three drugs using the design of experiments (DoE). Thus, the proposed method aims to develop a fast, accurate, robust, and cost-effective chromatographic method for detecting and separating nystatin, triamcinolone, and gramicidin using full factorial experimental design. Additionally, the method can be successfully used for the determination of the studied drugs in industrial wastewater samples. Furthermore, the proposed method can be applied in quality control labs as a cleaning validation method for the traceability of the studied drugs. The presented developed method was validated according to ICH (Harmonization for better health) guidelines [19].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
Nystatin, triamcinolone, and gramicidin with a certified purity of 95.1%, 99.8%, and 99.50%, respectively, were kindly supplied by Hikma pharmaceutical industries, Cairo, Egypt. Methanol and acetonitrile, all of HPLC grade, were purchased from Sigma Aldrich, Taufkirchen, Germany. Phosphoric acid and potassium dihydrogen phosphate were purchased from Adwic, Giza, Egypt.
2.2. Instrumentation
Chromatographic analysis was carried out using an HPLC (1200 series) system with a gradient pump (model G1314B), manual injector (Model G1328B), and UV wavelength detector (model G1328B) fitted with a 20.0 μL loop. We also used a pH meter (Cole-Pramer Ltd., Sant Neots, UK), stirrer (VELP SCIENTIFICA., Usmate Velate MB, Italy), sonicator (Elma, Singen (Hohentwiel), Germany), and sensitive balance (RADWAG, Karkow Poland).
2.3. Chromatographic Conditions
The optimum chromatographic separation was carried out using a Zorbax C18 column (250 mm × 4.6, 5 μm) (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) with a mobile phase composed of methanol with 0.25 M potassium dihydrogen phosphate buffer (pH 3.6). The elution was carried out under gradient conditions at different detection wavelengths (224.0, 234.0, and 240.0 nm). Gradient elution started with the mobile phase ratio 77:23 (v/v) for 2.0 min., then a gradual change in the mobile phase ratio over time was made to reach 87.7:12.2 (v/v) from 2.0 to 6.0 min. The flow rate was 1.3 mL/min.
2.4. Standard Solutions
A stock of standard solution of 0.01 mg/mL of each drug was prepared separately by weighing 0.01 g of each of the studied drugs and dissolving them in 100 mL volumetric flasks with methanol to reach a concentration of 100 µg/mL for each. Further dilution was carried out using the mobile phase (87.7:12.2, v/v) to prepare working standard solutions with concentration ranges of 1.00–25.00 µg/mL for triamcinolone and nystatin separately and 10.00–50.00 µg/mL for gramicidin.
2.5. Software
Experimental design, data analysis, and desirability function calculations were carried out using Minitab® 17 [20] and Microsoft Excel 2020.
2.6. Method Development
The experimental design approach was used in the development of the analytical method by performing screening and optimization designs. By examining the impact of various variables on the separation of triamcinolone, nystatin, and gramicidin simultaneously, many trials were carried out to reach the optimal condition. Minitab® software, version 17, was used to build a two-level, three-factor design with three center points. Using a full factorial design and three variables with two levels, a screening step was conducted to determine the significant variables affecting chromatographic separation. For screening, the percentage of organic solvent in the mobile phase, pH of phosphate buffer, and flow rate were studied. For each run, the resolution between adjacent peaks and run time were recorded and chosen as responses. Polynomial equations were calculated to build the quadratic models and illustrate the interaction between variables. In the optimization step, the desirability function was used to derive the optimum condition of the proposed chromatographic method. The run time was adjusted to be at a minimum, while the resolution was at a maximum.
2.7. Method Validation
The developed chromatographic method was validated with respect to linearity, accuracy, precision, the limit of detection (LOD), the limit of quantification (LOQ), and robustness, as described by the ICH guidelines Q2 (R1) [19].
2.8. Application
The industrial wastewater samples were collected from different areas within the manufacturing equipment in the production area of the pharmaceutical plant (Hikma Pharmaceuticals, Cairo, Egypt). During the steps of washing the manufacturing machine (Fryma Chroma 400 mixer, Switzerland) with distilled water after the finishing of the production of pharmaceutical dosage form containing the studied drug, the samples were collected and stored in amber bottles at 4 °C to avoid the degradation of the studied drugs. A volume of 1.00 mL from each sample was transferred to 10.0 mL calibrated volumetric flasks after sonication for 15 min. Each solution was diluted to the mark with a mobile phase composed of methanol and 0.25 M potassium dihydrogen phosphate buffer (pH 3.6) in a ratio of 77:23 (v/v), and the diluted samples were then filtered through 0.45 µm membrane filters (Millipore, Milford, MA, USA), then injected directly into an HPLC chromatograph. The general procedures described under linearity were followed, and the concentration of each drug was calculated through substitution into the corresponding regression equation.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Method Development
The simultaneous determination of the studied drugs in a sophisticated matrix (environmental industrial wastewater samples) obstructs their quantification using a one-factor-at-a-time approach. Therefore, the chromatographic method was carried out for simultaneous determination of nystatin, triamcinolone, and gramicidin in wastewater samples by using the DOE approach. The studied analytes have different physicochemical properties, so it was challenging to find the optimal condition for their separation as there were many factors that needed to be optimized first. Therefore, controlling the variables simultaneously by trial and error is a sophisticated issue, so using DOE helps to identify, detect, understand, and control all the factors at the same time and will lead to an improvement in the quality and performance of separation. The presented method is developed using full factorial design to study the method variables determining the significance of each factor by using Pareto charts and p values.
Multiple variables might influence separation performance throughout the development of HPLC techniques, making monitoring necessary. The proposed Ishikawa diagram for the HPLC method’s performance is presented in Figure 1. For the purpose of determining the measured variables for the Ishikawa diagram, different variables were examined. Different organic solvents were examined, such as acetonitrile and methanol. Acetonitrile was chosen to achieve the goal of a short run time for the chromatographic method, since its elution strength is larger than that of methanol. Gradient elution was conducted instead of isocratic to allow good separation of the three studied drugs with acceptable resolution. Different types of buffers in different pH ranges were evaluated to study the behavior of the studied drugs over a wide pH range (2–4). The wavelengths (224.0, 234.0, and 240.0 nm) were chosen based on the absorption spectra of the studied drugs to achieve the high sensitivity of the method. In order to gain further understanding of the impacts of these pH levels (2.0–3.5), screening procedures were applied. In contrast, a flow rate scouting step was carried out to maintain an appropriate equilibrium between effective separation and fast run time. Due to their minimal impact on method performance, the other variables in the suggested Ishikawa diagram have been left at their normal levels.
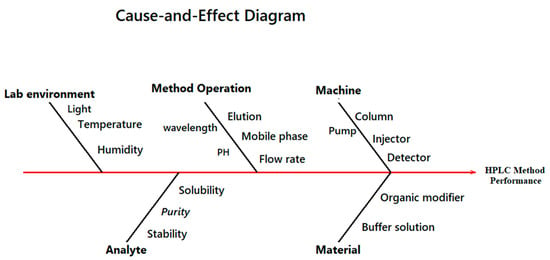
Figure 1.
Ishikawa diagram for identification of critical process variables.
3.2. Screening Design
By using DOE, screening design (full factorial design) was carried out to obtain data by performing a minimum number of experiments, as shown in Table 1, and the coded and uncoded values in the design are presented in Table S1. The analysis of the screening design showed that the variables influencing the measured responses were the amount of organic solvent, pH, and flow rate. The effect of each factor was computed using Minitab 17 [20] with respect to the resolution between peaks (RS1, RS2) and run time by using main effect plots, interaction plots, and Pareto charts. As shown in the main effect plots (Figure 2), the non-horizontal lines suggest that lower percentages of methanol and flow rates may have a positive impact on the improvement of resolutions and shortening of run times. Regarding the main effect of the pH of the phosphate buffer, the pH line and reference line are almost parallel, so the main effect is absent. The three responses are equally impacted by each pH level. From the main effect plot, we can conclude that the factor affects the time of analysis, and the resolution between peaks was the organic solvent percentage (methanol) and flow rate followed by pH. Minitab can also provide interaction plots (Figure 3), which show separate lines for each level of one factor and means for the levels of one factor along the x-axis. Figure 3 demonstrates that lowering the flow rate and percentage of methanol while using either of two pH levels results in higher resolutions and shorter run times, which is supported by the main effect plots. From factorial design, the ANOVA and model fit statistics indicate significant models with p values 0.005, 0.008, and 0.003 for the resolution between peaks (RS1, RS2) and run time, respectively. Additionally, a good model fits with adjusted R2 0.996, 0.999, and 0.902 for RS1, RS2, and run time, respectively. In Figure S2, Pareto charts report the effects of the factors on the performance of the method and categorize the factors according to their effects on critical quality attributes (responses). The graph shows the effects’ values in absolute terms in the bars, and indicates the critical t-value for an ἀ of 0.05 by drawing a vertical line on the graph. When the bar does not cross the vertical line, the effect is minimal and non-significant. Figure S2 demonstrates that the majority of the examined factors had a significant effect on the analyzed responses, with the exception of the pH of the phosphate buffer, which had no significant impact on RS2, and the percentage of methanol, which had the greatest impact on all three responses. Thus, by controlling every factor examined, an improvement in resolution (RS1, RS2) and a decrease in run time can be achieved. From the screening design, it can be concluded that the curvature and the three factors are significant in the model, since the p value ≤ 0.05. This implies that the quadratic model should be considered by using a central composite design. Therefore, using the response surface methodology (RSM) approach to optimize the factors affecting the method should be advised in order to obtain the optimum condition using desirability functions.

Table 1.
Screening design: full factorial design for HPLC method.
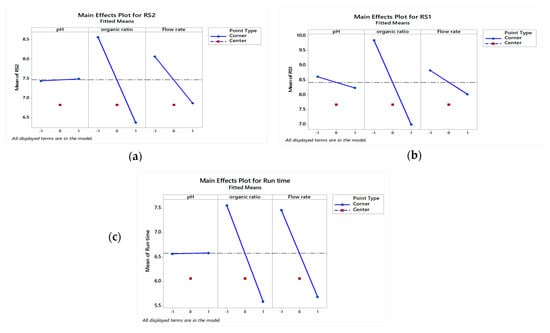
Figure 2.
Main effect of the variables and their effect on response. (a) Main effect of the variables and their effect on RS2. (b) Main effect of the variables and their effect RS1. (c) Main effect of the variables and their effect on run time.
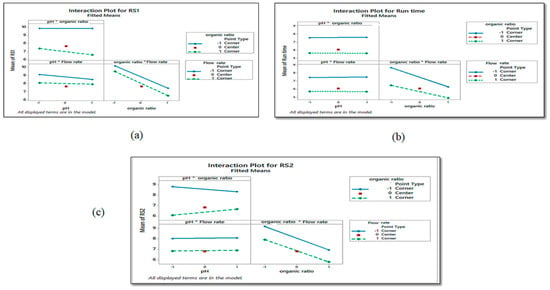
Figure 3.
Interaction plot between the variables and their effect on response. (a) Interaction plot between the variables and their effect on run time. (b) Interaction plot between the variables and their effect on RS1. (c) Interaction plot between the variables and their effect on RS2.
The equations of the models derived from Minitab software 16 for screening design were as follows:
where Y is the resolution between triamcinolone and nystatin (RS1).
where Y is the resolution between nystatin and gramicidin (RS2).
Y (RS1) = 1.22 + 0.211 pH − 0.22 methanol − 0.07 flow rate − 0.014 pH· flow rate − 0.03
pH· methanol − 0.098 flow rate· methanol − 0.26 pH · methanol· flow rate.
pH· methanol − 0.098 flow rate· methanol − 0.26 pH · methanol· flow rate.
Y (RS2) = 24.19 − 8.58 pH − 9.24· methanol − 14.2flow rate − 2.10 pH· flow rate + 2.9
pH· methanol + 5.09 pH· methanol + 6.85 pH· methanol· flow rate.
pH· methanol + 5.09 pH· methanol + 6.85 pH· methanol· flow rate.
Y (Run time) = 2.54 − 0.022 pH + 0.25 methanol + 0.015 flow rate − 0.14 pH· flow rate
+ 0.28 pH· methanol + 0.18 pH· methanol· flow rate.
+ 0.28 pH· methanol + 0.18 pH· methanol· flow rate.
3.3. Optimization Design
The experimental factors to be further studied using central composite design (CCD) were the following: the pH of the phosphate buffer (3.0), methanol percentage (87%), and flow rate (1.2 mL/min). In order to estimate the coefficients, 20 runs of CCD were performed, including 6 runs of center point to estimate the experimental error and take into account the interactions between factors. The experimental design is reported in Table 2 with the measured responses. Table S2 shows the coded and uncoded factors used in the experimental design.

Table 2.
Optimization design: central composite design for proposed HPLC method.
The polynomial quadratic equations are as follows:
where Y is the resolution between triamcinolone and nystatin (RS1).
where Y is the resolution between nystatin and gramicidin (RS2).
Y (RS1) = 14.21 − 5.99 pH − 5.84 methanol − 11.26 flow rate + 2.97 pH. pH + 0.13
methanol. methanol − 0.28 flow-rate. Flow rate + 0.3 pH. methanol + 3.3 pH. flowrate + 3.5 methanol. flow-rate.
methanol. methanol − 0.28 flow-rate. Flow rate + 0.3 pH. methanol + 3.3 pH. flowrate + 3.5 methanol. flow-rate.
Y (RS2) = 2.27 + 0.23 pH + 0.33 methanol + 0.03 flow-rate + 0.72 pH. pH − 0.27
methanol. methanol − 0.19 flow-rate. flow-rate + 0.086 pH. methanol + 0.02pH. flow-rate + 0.16 methanol. flow-rate.
methanol. methanol − 0.19 flow-rate. flow-rate + 0.086 pH. methanol + 0.02pH. flow-rate + 0.16 methanol. flow-rate.
Y (run time) = 1.15 + 0.12 pH − 0.16 methanol − 0.011 flow-rate − 0.079 pH. pH + 0.012 methanol. methanol + 0.11 flow rate. Flow rate − 0.11 pH. methanol + 0.009 pH. flow-rate − 0.036 methanol. Flow rate.
The role of RSM is to find a way to reach a complete description of the problem and, consequently, it can be effectively applied to resolve the problem and define the optimum conditions of the method. In RSM, the ANOVA and model fit statistics reveal the validity and significance of the three models, as shown in Table S3.
By applying CCD, we can estimate the optimization of the method, which is an approach to search along a response surface for an optimal range of input variables to satisfy a goal such as maximizing/minimizing/targeting a response variable.
In terms of specification for the proposed method for the resolutions between peaks, a value above 1.5 is desired, while for run time, the desired value less than 6 min. The search for a global solution was performed through optimization design in Minitab (17), as represented in the desirability plot.
The desirability plot shows how the variables influence the anticipated responses and highlights the combinations that result in desired values. The score for desirability ranges from 0 to 1, where 0 indicates that one or more responses fall outside of the acceptable range and 1.0 indicates that the case has been reached in its optimal state. The desirability plot in Figure 4 is made up of four rows and three columns, where the columns reflect the variables and the rows the predicted responses. The first row’s composite desirability score was 1.000, meaning that all predicted responses fall within a reasonable range. The optimal settings for the variables are pH = 1.27, organic solvent = 0.35, and flow rate = 45.0. The desired run time was 5.5 min., with predicted values for RS1 and RS2.This method was achieved by applying the optimum conditions derived from Minitab software using the desirability plot. The efficiency of the method was checked by determining the resolution of peaks and time of analysis during the validation step, as the resolution of all peaks should be no less than 1.5 and the time of analysis no more than 6 min. The chromatogram representing the simultaneous determination of gramicidin, nystatin, and triamcinolone in water samples obtained according to these results is shown in Figure 5.
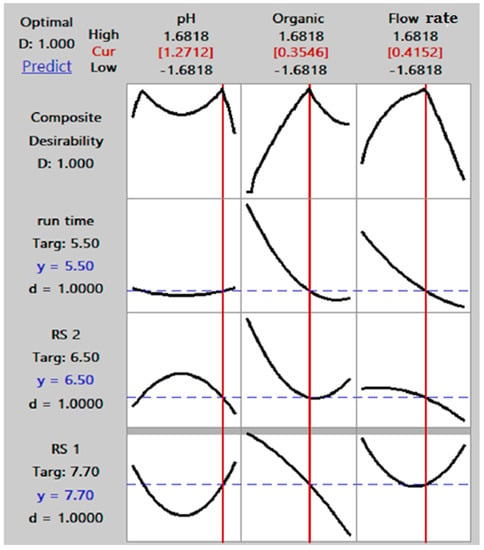
Figure 4.
Desirability plot displaying the optimum conditions of the method.
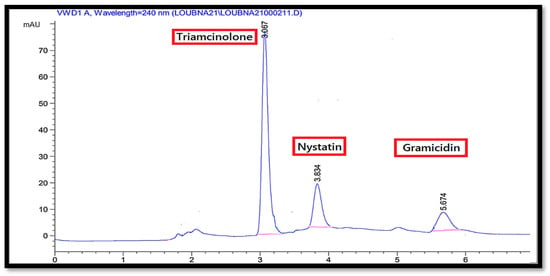
Figure 5.
HPLC chromatogram of triamcinolone (10.00 μg/mL), nystatin (10.00 μg/mL), and gramicidin (30.00 μg/mL) using gradient elution.
3.4. Method Validation
3.4.1. Linearity
The linearity of the method was evaluated by analyzing a series of six different concentrations of each studied drug. Concentrations were chosen in the range of 1.00–25.00 μg/mL for triamcinolone and nystatin and in the range of 10.00–50.00 µg/mL for gramicidin. The assay was performed according to experimental conditions previously mentioned, and each concentration was repeated three times. Linear regression analysis was carried out, and by the construction of calibration curves as presented in Figures S3–S5, the linear regression equations for each studied drug were calculated.
3.4.2. Accuracy
Accuracy was assessed by analyzing three different concentrations within the calibration curve. The resulting prepared solutions were assayed and determined, and are presented in Table S4. The mean percentage recoveries and standard deviation results were found to be 98.80 ± 0.01, 98.08 ± 0.12, and 99.70 ± 0.15 for triamcinolone, nystatin, and gramicidin, respectively. Therefore, good recovery results were obtained with a small standard deviation.
3.4.3. Precision
The precision of the method was assessed by selecting three different concentrations for each studied drug and analyzing them, as mentioned before, under linearity. The prepared solutions were repeated three times within a day (intra-day precision) and on three consecutive days (inter-day precision). The % RSD of the calculated intra-day and inter-day precisions was found to be less than 2%, revealing that the method is precise, as shown in Table S5.
3.4.4. LOD and LOQ
The LOD was 0.24, 0.57, and 1.17 µg/mL for triamcinolone, nystatin, and gramicidin, respectively, using the formula 3.3. SD/S, where SD is the standard error of the intercept and S is the slope. On the other hand, the LOQ was 0.72, 1.73, and 3.54 µg/mL for triamcinolone, nystatin, and gramicidin, respectively, using the formula 10. SD/S. This result indicates the sensitivity of the method, its applicability for studies, and its ability to detect very small quantities. All validation variables are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Validation and regression variables of proposed HPLC method for determination of triamcinolone, nystatin, and gramicidin.
Table 4 shows a statistical comparison of the results obtained by applying the HPLC method for the determination of triamcinolone, nystatin, and gramicidin. The data show no statistical difference between the reported methods and the proposed HPLC method.

Table 4.
Statistical comparison of the results obtained by applying HPLC method for determination of triamcinolone, nystatin, and gramicidin.
System suitability variables of the HPLC method, resolution, retention time, selectivity, theoretical plate number, tailing factor, and capacity factors were evaluated as presented in Table S6 [22]. The data verify that the resolution and reproducibility of the chromatographic system were adequate for analysis.
3.5. Robustness
This is a method to prove that all factors will not affect the method performance upon minor changes. Therefore, to achieve the robustness step, a new full factorial design was carried out using the pH of the buffer, methanol percentage, and flow rate around their optimum conditions (pH 3.60, organic solvent 87.70, and flow rate 1.30), as shown in Table S7. The coded and uncoded factors for the new factorial design are presented in Table S8. By analyzing the p values of all variables, this test proved their non-significant effect on the performance of the method, as their values were above 0.05. The results of the robustness design were represented by a Pareto chart revealing the non-significance of the studied factors and showing the p value for all the variables, as shown in Figure 6.
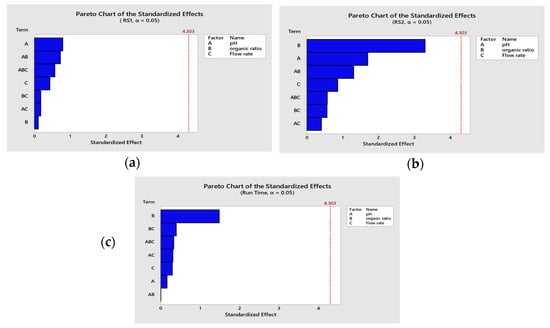
Figure 6.
Pareto charts of the variables and their effects on the response. (a) Effect of pH, organic ratio, and flow rate on resolution 1 (RS1). (b) Effect of pH, organic ratio, and flow rate on resolution 2 (RS2). (c) Effect of pH, organic ratio, and flow rate on run time.
4. Application
After validation, the developed chromatographic method was successfully applied for the simultaneous determination of triamcinolone, nystatin, and gramicidin in environmental water samples. The number of water samples was six environmental water samples, and they were analyzed under the conditions described previously. The results are presented in Table 5. Figure 7 shows the chromatogram of the simultaneous determination of the three studied drugs in real environmental samples. The proposed method is considered the first analytical method that quantifies triamcinolone, nystatin, and gramicidin simultaneously in industrial wastewater samples. The proposed method is simple, low-cost, and environmentally friendly.

Table 5.
Determination of triamcinolone, nystatin, and gramicidin in environment water samples using the proposed HPLC method.
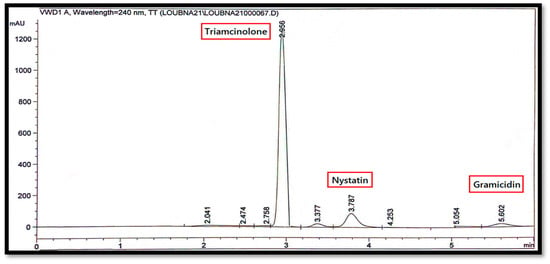
Figure 7.
Chromatogram of HPLC determination of the 49.48 µg/mL triamcinolone, 0.62 µg/mL nystatin, and 4.41 µg/mL gramicidin in real environmental samples.
5. Conclusions
The method for the determination of nystatin, triamcinolone, and gramicidin in wastewater samples developed and optimized using DOE proved to be very sensitive. The drugs were separated with no interference and efficiently from the wastewater sample. This is in addition to a complete study of the effect of the variables on resolution between peaks and run time by using a full factorial design (DOE approach). The complete separation of the drugs was reached in a short chromatographic run time (5.7 min) with no interference between peaks, so there is no need for traditional HPLC methods, which require a very long run time and a complex mobile phase, and lead to excess solvent. All the results obtained were satisfactory, proving the applicability of the method for the detection and quantification of nystatin, triamcinolone, and gramicidin in the wastewater sample. The method was successfully used to trace triamcinolone, nystatin, and gramicidin with concentrations of 1.32 µg/mL, 1.06 µg/mL, and 4.41 µg/mL, respectively, in real environmental samples.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/separations10060342/s1. Figure S1: Chemical structures of triamcinolone (a), nystatin (b), and gramicidin (c), Figure S2. Pareto charts of the parameters and their effects on the response. (a) Effect of pH, organic ratio and flow rate on RS1. (b) Effect of pH, organic ratio and flow rate on run time. (c) Effect of pH, organic ratio and flow rate on RS2. Figure S3. Calibration curve for triamcinolone (1.00-25.00 ug/mL). Figure S4. Calibration curve for nystatin (1.00-25.00 ug/mL). Figure S5. Calibration curve for gramicidin (10.00-50.00 ug/mL). Table S1. Coded and uncoded factors for the screening design for the purposed HPLC method. Table S2. Coded and uncoded factors for optimization design: Central Composite design for proposed HPLC method. Table S3. A summary list ANOVA results in optimization design. Table S4: Accuracy assessment of the proposed HPLC method for triamcinolone, nystatin and, gramicidin. Table S5. Interday and intraday results for triamcinolone, nystatin and, gramicidin by the proposed HPLC method. Table S6. System Suitability parameters of the proposed HPLC method for determination of triamcinolone, nystatin, and gramicidin. Table S7. Robustness design for the proposed HPLC method. Table S8. Coded and the uncorded factors for the robustness design for HPLC method.
Author Contributions
L.E.: Formal analysis, validation, writing—original draft; M.A.H.: supervision, writing—review and editing; A.E.E.: conceptualization, supervision, development of methodology; R.M.A.: supervision, evolution of overarching research goals, writing—review and editing, resources. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the manuscript and Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Elbalkiny, H.T.; Yehia, A.M.; Riad, S.M.; Elsaharty, Y.S. Derivative constant wavelength synchronous fluorescence spectrometry for the simultaneous detection of cefadrine and cefadroxil in water samples. Spectrochim. Acta-Part. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 229, 117903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semreen, M.H.; Shanableh, A.; Semerjian, L.; Alniss, H.; Mousa, M.; Bai, X.; Acharya, K. Simultaneous Determination of Pharmaceuticals by Solid-phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry: A case study from sharjah sewage treatment plant. Molecules 2019, 24, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempin, D.; Kot-wasik, A. The use of RP-HPLC-Q-TOF-MS as a powerful tool for wastewater composition profiling and selection of water pollution marker specific to wastewater contamination. Mon. Für Chem.-Chem. Mon. 2018, 0123456789, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Heugten, A.J.P.; de Boer, W.; de Vries, W.S.; Markesteijn, C.M.A.; Vromans, H. Development and validation of a stability-indicating HPLC-UV method for the determination of triamcinolone acetonide and its degradation products in an ointment formulation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 149, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muralidharan, S.; Venugopal, V.; Kumar, J.; Parasuraman, S. Development and Validation of a New RP-HPLC Method for the Analysis of Triamcinolone in Human Plasma. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 13, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, A.A.; Formariz, T.P.; Scarpa, M.V.; De Oliveira, A.G. Development and validation of HPLC method for quantitative analysis of triamcinolone in biodegradable microparticles. Rev. De Ciências Farm. Básica E Apl. 2006, 27, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Redasani, V.K.; Tamboli, P.S.; Surana, S.J. Development and Validation of a Stability Indicating Rp-Hplc Method for the Estimation of Triamcinolone in Bulk and in Tablet Formulation. J. Anal. Pharm. Res. 2015, 1, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebaiy, M.M.; El-Adl, S.M.; Baraka, M.M.; Mohram, M.S.; Elkady, Y.M. Stability Indicating HPLC Method for the Simultaneous Estimation of Triamcinolone Acetonide and Benzyl Alcohol in Pure Form and Epirelefan® Vial. Am. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 123, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.S.; Hegazy, M.A.; Hendawy, H.A.M.; Weshahy, S.A.; Abdelwahab, M.H. Resolution and quantitation of triamcinolone acetonide and its coformulated drug in the presence of its impurities and degradation products by HPTLC and HPLC. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groll, A.H.; Mickiene, D.; Werner, K.; Piscitelli, S.C.; Walsh, T.J. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of liposomal nystatin in plasma and tissues for pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution studies. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1999, 735, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llabot, J.M.; Allemandi, D.A.; Manzo, R.H.; Longhi, M.R. HPLC method for the determination of nystatin in saliva for application in clinical studies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 45, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneedak, H.M.; Salama, I.; Mostafa, S.; El-Sadek, M. HPLC and chemometric methods for the simultaneous determination of miconazole nitrate and nystatin. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2012, 50, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradesh, A. UPLC method design and development for gramicidin, neomycin and triamcinolone acetonide in bulk pharmaceutical formulation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 4, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Baii, M.C.; Brace, L.; Abad, C. HPLC study on the ‘history’ dependence of gramicidin A conformation in phospholipid model membranes. Sci. Pharm. 1989, 250, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Arie, Y.; Miyai, H.; Suzuki, A.; Okabe, T.; Takashima, M.; Takata, M.; Kurasawa, T.; Ito, M.; Arakawa, R.; Ogura, Y.; et al. Comparative study on pharmacokinetics and toxicity of intravitreal and sub-Tenon injection of triamcinolone acetonide in ocular tissues. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 13, 1864–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amir, A.; Levin-khalifa, M.; Dvash, T.; Methyl, N. Water Soluble Nystatin and Derivative. J. Antibiot. 2020, 20, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swierstra, J.; Kapoerchan, V.; Knijnenburg, A.; van Belkum, A.; Overhand, M. Structure, toxicity and antibiotic activity of gramicidin S and derivatives. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandpe, S.R.; Parate, V.R.; Naik, J.B. Experimental design approach, screening and optimization of system variables, analytical method development of flurbiprofen in nanoparticles and stability-indicating methods for high-pressure liquid chromatography. Futur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topic Q2 (R1) Validation of Analytical Procedure: Text and Methedology. In Proceedings of the International Conference of Harmonization, Incheon, Republic of Korea, 15–16 November 2022.
- Minitab (Version 17) Software. 2013. Available online: http://www.minitab.com/en-US/products/minitab/default.aspx (accessed on 28 August 2013).
- Orwa, J.A. A validated ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the quantification of polymyxin B in mouse serum and epithelial lining fluid: Application to pharmacokinetic studies. Liq. Chromatogr. 2001, 52, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). Reviewer Guidance’ Validation of Chromatographic Methods; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER): Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).