Exploration of Large-Scale Application of Efficient and Clean Utilization of Low-Grade Bauxite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Calcification Process
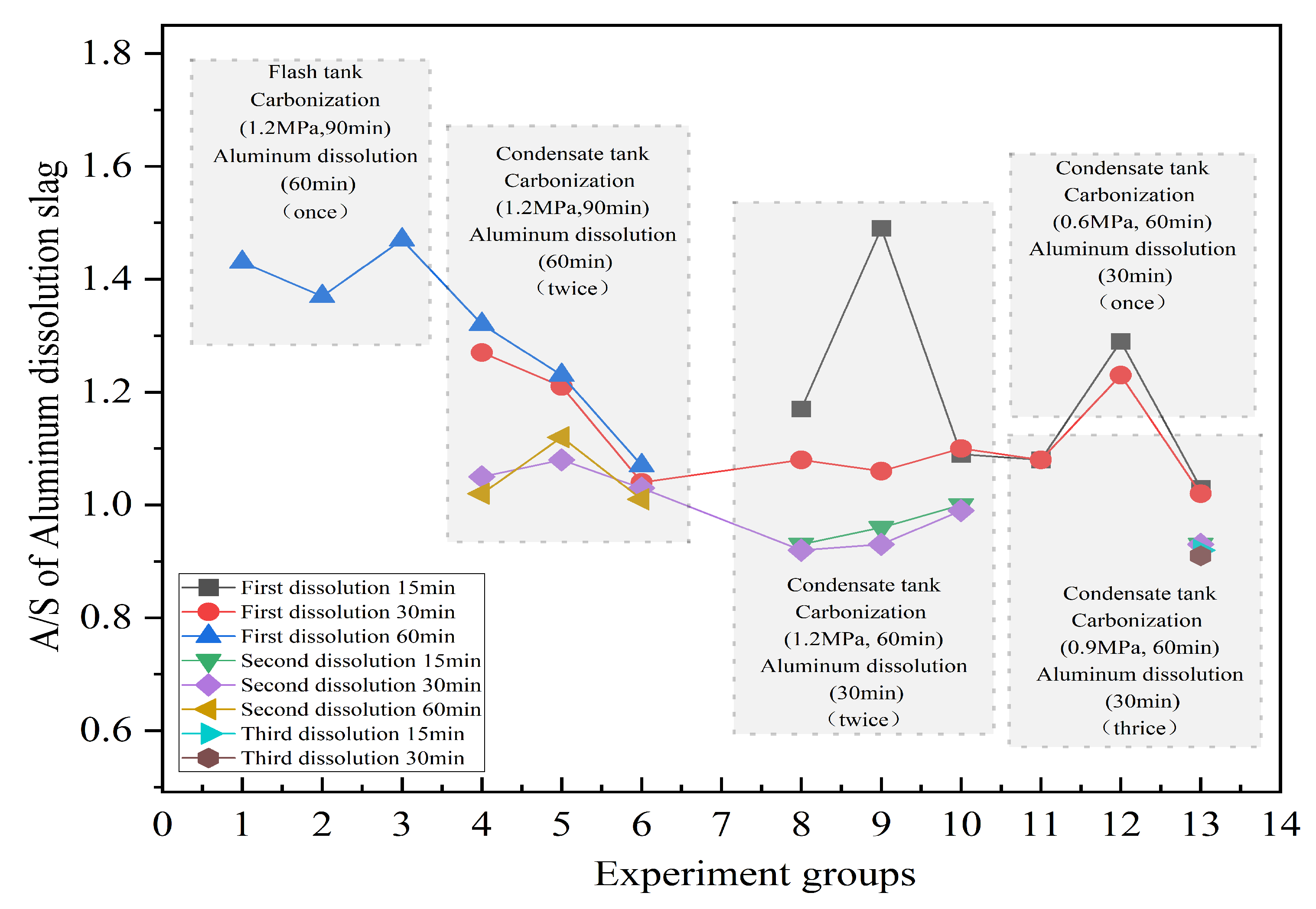
3.2. Carbonization and Aluminum Dissolution
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The added amount of calcium oxide has a large influence on the calcification dissolution process of bauxite, the mass fraction of Na2O in the calcified slag can be reduced to 0.95% when the ratio of calcium to silicon reaches 2.67:1, and the slag is a single hydrated garnet phase.
- (2)
- The optimal process conditions for the carbonization process are as follows: temperature, 120 °C; reaction time 60 min; liquid–solid ratio, 5:1; CO2 pressure, 0.9 MPa. the optimal process conditions for the aluminum dissolution process are as follows: temperature, 60 °C; reaction time, 30 min; liquid–solid ratio, 10:1; NaOH concentration, 100 g/L. Under optimal conditions, after the second carbonization–aluminum dissolution, the A/S in the final red mud can be reduced to 0.85, and the actual dissolution rate of alumina in bauxite can reach 81.32%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- USGS. Geological Survey Mineral Commodity Summaries; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Smičiklas, I.; Jović, M.; Janković, M.; Smiljanić, S.; Onjia, A. Environmental safety aspects of solid residues resulting from acid mine drainage neutralization with fresh and aged bauxite residue. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Ma, S.; Shen, S.; Xie, Z.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, Y. Research and industrialization progress of recovering alumina from fly ash: A concise review. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 357–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of sodium aluminate from the leach liquor of diasporic bauxite in concentrated NaOH solution. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 98, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikbin, I.M.; Aliaghazadeh, M.; Charkhtab, S.H.; Fathollahpour, A. Environmental impacts and mechanical properties of lightweight concrete containing bauxite residue (red mud). J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 2683–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemougna, P.N.; Wang, K.T.; Tang, Q.; Cui, X.M. Study on the development of inorganic polymers from red mud and slag system: Application in mortar and lightweight materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Min, X.B.; Ke, Y.; Chai, L.Y.; Shi, M.Q.; Tang, C.J.; Wang, Q.W.; Liang, Y.J.; Lei, J.; Liu, D.G. Utilization of red mud and Pb/Zn smelter waste for the synthesis of a red mud-based cementitious material. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Vilar, V.J.; Botelho, C.M.; Boaventura, R.A. A review of the use of bauxite residue as adsorbent for the removal of toxic pollutants from water and wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2011, 32, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.F.; Zhang, T.A.; Lü, G.Z. Kinetics of carbonated decomposition of hydro garnet with different silica saturation coefficients. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2020, 27, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunori, C.; Cremisini, C.; Massanisso, P.; Pinto, V.; Torricelli, L. Reuse of a treated bauxite residue bauxite waste: Studies on environmental compatibility. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 117, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, F. An introduction to the smelting technology and development trend of alumina and electrolytic aluminum. World Nonferr. Met. 2019, 2, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.; Zheng, C.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y. The influence of the silicon saturation coefficient on a calcification carbonization method for clean and efficient use of bauxite. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 174, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelencsér, A.; Kováts, N.; Turóczi, B.; Rostási, Á.; Hoffer, A.; Imre, K.; Nyirő-Kósa, I.; Csákberényi-Malasics, D.; Tóth, Á.; Czitrovszky, A. The Bauxite residue accident in Ajka (Hungary): Characterization and potential health effects of fugitive dust. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1608–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, T.A.; Lv, G.; Chao, X.; Yang, X. Response of soil microbial communities to bauxite residue-based stabilizer remediation of cadmium-contaminated farmland. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 109, 180–185. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Naidu, R. Hidden values in bauxite residue (bauxite residue): Recovery of metals. Waste Manag. 2014, 156, 164–173. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.; Zhang, T.A.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, F.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, C. Calcification–carbonization method for cleaner alumina production and CO2 utilization. JOM 2014, 66, 1616–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.D. Applying study on the Bayer bauxite residue as fast building dam materials. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 671–674, 1725–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Ou, S.; Wang, Q. The Comprehensive Energy saving in China Alumina Industry. Light Met. 2005, 16, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Mymrin, V.A.; Vázquez-Vaamonde, A.J. Bauxite residue of aluminum production waste is a basic component of new construction materials. Waste Manag. Res. J. Int. Solid Wastes Public Clean. Assoc. Iswa 2001, 19, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.B.; Zhang, T.A.; Liu, Y.; Lv, G.; Xie, L. Calcification-carbonization method for bauxite residue processing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 316, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Guozhi, L.V.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhihe, D.O.U. Method for Recovering Alkali and Aluminum in Course of Treatment of Bayer Bauxite Residue by Using Calcification-Carbonization Method. US9963353, 30 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, F.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Hartley, W.; Xue, S. Appropriate human intervention stimulates the development of microbial communities and soil formation at a long-term weathered bauxite residue disposal area. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Liu, Z.; Fan, J.; Xue, R.; Guo, Y.; Chen, W.; Hartley, W.; Zhu, F. Insights into variations on the dissolved organic matter of bauxite residue during soil-formation processes following 2-year column simulation. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, H. Metallurgical Process for Valuable elements recovery from bauxite residue—A review. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 155, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
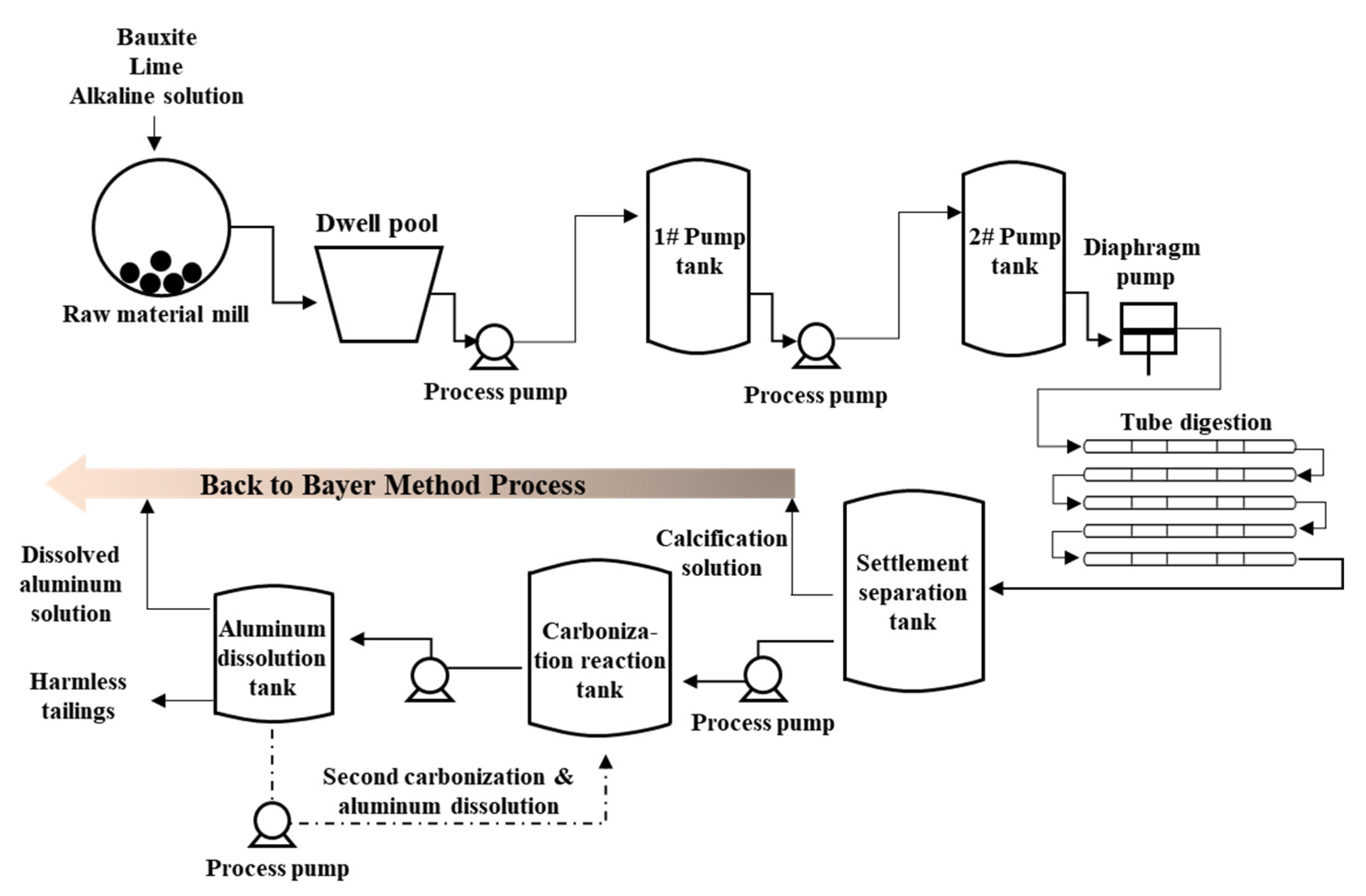
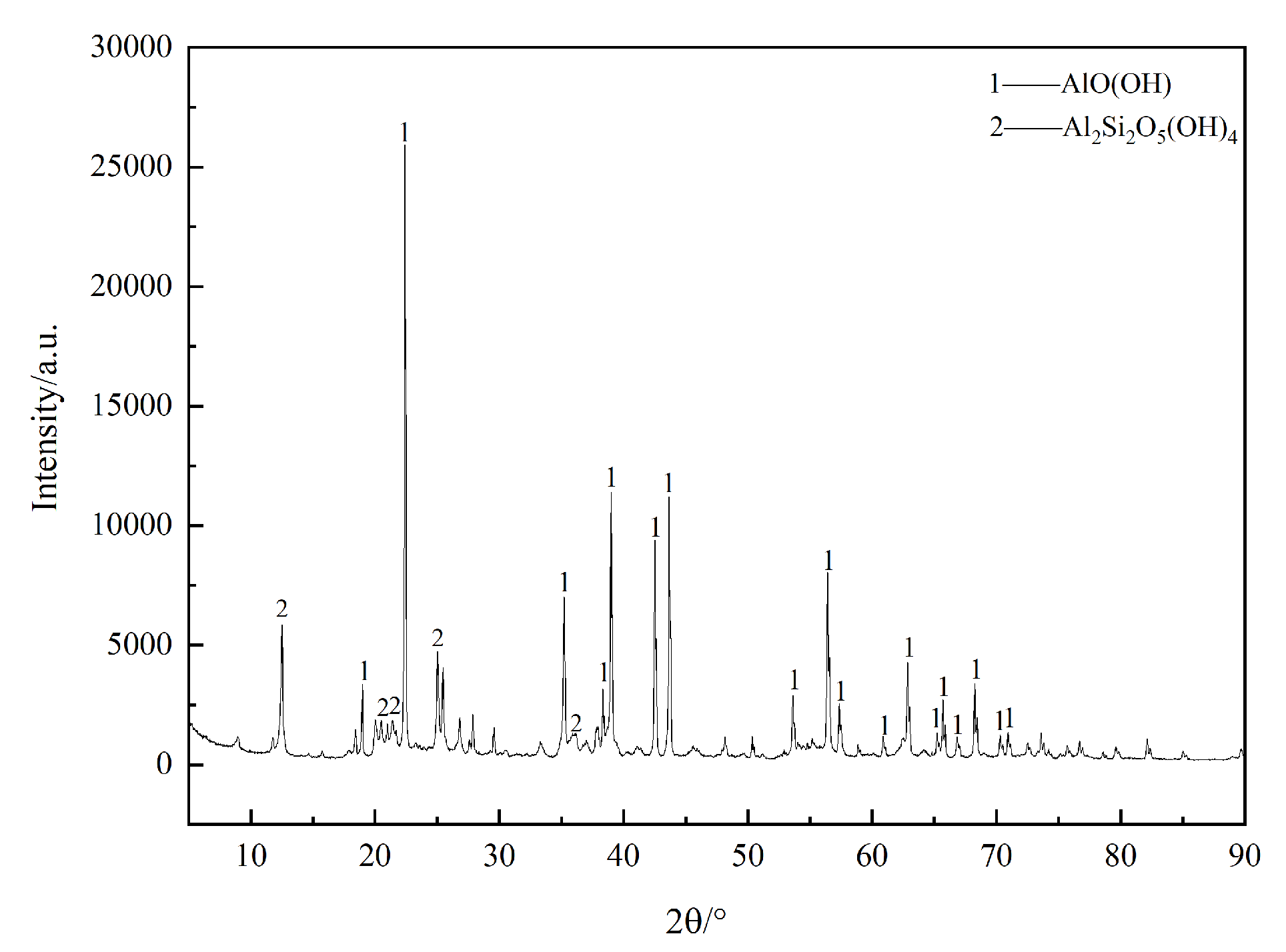

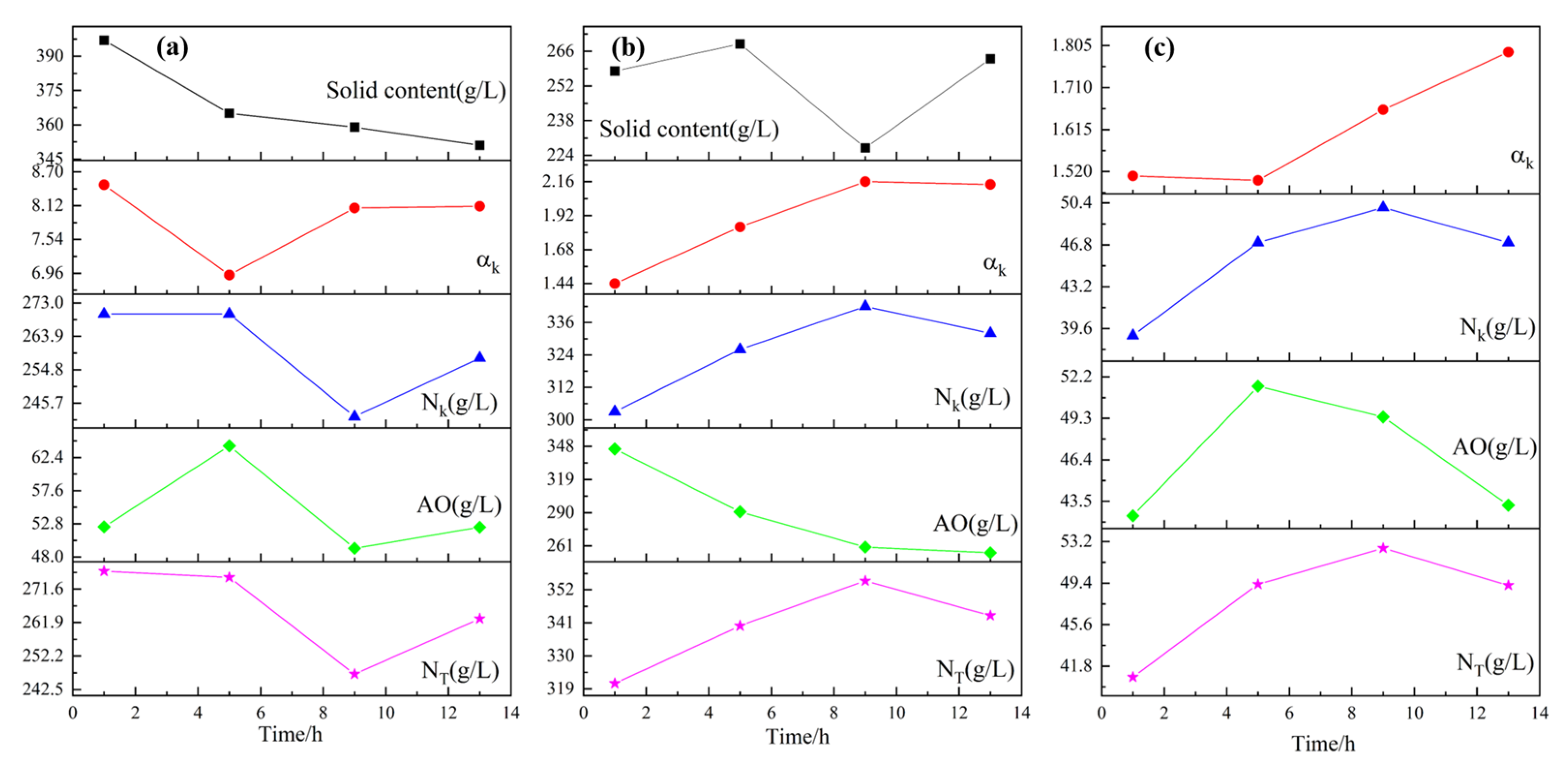

| Ingredients | Al2 O3 | SiO2 | CaO | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | Na2O | Burn Loss | A/S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 61.60 | 13.53 | 0.90 | 5.06 | 3.25 | 0.34 | 18.60 | 4.55 |
| Equipment Name | Specification | Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Raw material mill | Φ2.4*8 m | |
| Dwell pool | Φ8*10 m | |
| 1# desilicon tank | Φ6*13.5 m Effective liquid level 12.2 m | 341 m3 |
| 2# desilicon tank | Φ6*13 m Effective liquid level 11.7 m | 327 m3 |
| Settlement separation tank | Operating level 10 m | |
| Carbonization reaction tank | Effective/operating level 10.2 m/7 m Φ6*11 m | 285/196 m3 |
| Aluminum dissolution tank | Effective/operating level 3 m/2.5 m Φ3*3 m | |
| Tube digestion | 2-φ114*11 L = 80 m Run 40 | 42.5 m3 |
| Insulated dwell tanks | Φ1.8 m*20 m Run 4pcs | 45 m3 |
| Diaphragm Pumps | Maximum flow rate of 75 m3/h for a single unit, operating 3 units at 30 Hz, total flow rate 135 m3/h | |
| Sample Number | Al2O3 | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | K2O | Na2O | CaO | MgO | A/S | N/S | C/S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 22.36 | 20.48 | 7.94 | 4.25 | 1.31 | 5.76 | 21.38 | 0.97 | 1.09 | 0.28 | 1.04 |
| 2 | 21.65 | 18.42 | 6.78 | 3.7 | 0.76 | 4.42 | 27.13 | 1.13 | 1.18 | 0.24 | 1.47 |
| 3 | 21.21 | 17.02 | 6.66 | 3.43 | 0.56 | 3.44 | 30.16 | 1.18 | 1.25 | 0.20 | 1.77 |
| 4 | 20.81 | 16.36 | 6.2 | 3.19 | 0.46 | 2.51 | 32.7 | 1.34 | 1.27 | 0.15 | 2.00 |
| 5 | 20.44 | 15.78 | 5.57 | 2.86 | 0.28 | 2.03 | 35.04 | 1.06 | 1.30 | 0.13 | 2.22 |
| 6 | 20.91 | 14.75 | 4.36 | 2.58 | 0.19 | 1.3 | 37.16 | 1.17 | 1.42 | 0.09 | 2.52 |
| 7 | 20.71 | 14.42 | 4.47 | 2.56 | 0.13 | 0.95 | 38.46 | 1.14 | 1.44 | 0.07 | 2.67 |
| Carbonization–Aluminum Dissolution Times | Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3/% | SiO2/% | A/S | Dissolution Rate/% | |
| 1 | 13.92 | 14.43 | 0.96 | 78.9 |
| 2 | 11.81 | 13.89 | 0.85 | 81.32 |
| 3 | 10.58 | 12.89 | 0.82 | 81.98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Long, F.; Cao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; Lv, G. Exploration of Large-Scale Application of Efficient and Clean Utilization of Low-Grade Bauxite. Separations 2023, 10, 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060336
Chen Y, Long F, Cao X, Li Y, Zhang W, Zhang T, Lv G. Exploration of Large-Scale Application of Efficient and Clean Utilization of Low-Grade Bauxite. Separations. 2023; 10(6):336. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060336
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yang, Fei Long, Xuejiao Cao, Yibing Li, Weiguang Zhang, Tingan Zhang, and Guozhi Lv. 2023. "Exploration of Large-Scale Application of Efficient and Clean Utilization of Low-Grade Bauxite" Separations 10, no. 6: 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060336
APA StyleChen, Y., Long, F., Cao, X., Li, Y., Zhang, W., Zhang, T., & Lv, G. (2023). Exploration of Large-Scale Application of Efficient and Clean Utilization of Low-Grade Bauxite. Separations, 10(6), 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060336






