Abstract
Photochemical generation is an important pathway for atmospheric sulfate formation. However, the roles of atmospheric co-existing photosensitive dissolved organic matter (DOM) in sulfate formation are still unclear. The experimental results in this work provide evidence that atmospheric photosensitizers produce active intermediates to oxidize S(IV) into S(VI) under illumination. Quenching experiments of eight photosensitive model compounds (PS) demonstrate that their triplet-excited states (3PS*) dominate sulfate formation for the photosensitizing pathway with a contribution of over 90%, and 1O2 plays an important role in sulfate formation. The results using humic acid (HA) and water-soluble organic carbon in vehicle exhaust particles (WSOC) as representatives of atmospheric photosensitizers further verify that triplet-excited DOM (3DOM*) is the main reactive species for sulfate formation, which is consistent with the results of PS. Our findings provide new insights into the photochemical formation pathways of atmospheric sulfate.
1. Introduction
Globally, atmospheric aerosol nucleation contributes nearly half of all cloud condensation nuclei, thus having a significant impact on global climate change [1]. Under certain conditions, nucleated aerosol particles will grow into haze [2,3]. Sulfate is one of the main components in fine particulate aerosol samples during haze events. Oxidation of SO2 in the atmosphere produces sulfate aerosol particles, which can lead to air quality, climate, human and ecosystem health problems [4].
The formation of sulfate particles depends on several factors, including solar radiation, the background aerosol and volatile organic compound (VOC) concentrations, the availability of NH3, the temperature and the humidity [5]. As a precursor of sulfate, SO2 is extremely soluble in atmospheric water and forms SO2·H2O, HSO3− and SO32−, which increase the concentration of sulfate through the liquid phase oxidation pathway of SO2 in the atmosphere [6]. Some monitoring data have shown SO42− concentrations in cloud droplets ranging from 17.3 to 211 μM [7], but some studies have also claimed that the average SO42− concentrations in clouds, fog and rain observed in Southern California range from 9.4 to 475 mM [8]. The significant enhancement in sulfate concentrations observed in haze events since the 2013 Beijing haze incident has led to a growing interest and demand for studying sulfate formation mechanisms among scholars. Traditionally, sulfate formation mechanisms primarily include gas phase oxidation of SO2 by ·OH and the aqueous oxidation of S(IV) by H2O2, O3, organic peroxides and O2 catalyzed by transition metal ions (TMIs), such as Fe(III) and Mn(II), in cloud or fog water droplets [9]. However, the mechanisms behind sulfate formation remain poorly described, and its yield is also underestimated [10], indicating that many important pathways related to atmospheric sulfate formation have not been fully revealed.
In recent years, the triplet-excited state of dissolved organic matter (3DOM*) in atmospheric liquid water (cloud droplets, mist droplets or aerosol water) has attracted a lot of attention as a special oxidant involved in liquid-phase photochemical reactions [11,12]. Xue et al. [13] and Wang et al. [14] suggested that atmospheric microaqueous reactions may contribute significantly to sulfate production. Photochemistry has been proposed as an important chemical trigger in tropospheric particles, and it has been emphasized that several photochemical mechanisms of sulfate production mainly occur in the liquid phase. Atmospheric brown carbon, mainly derived from forest fires, biomass burning and biorelease, was shown to act as a photosensitizer and produce a variety of reactive intermediates to modify the oxidation capacity and highlighted the positive dependence of sulfate production on relative humidity (RH) [15]. Wang et al. found that the triplet-excited state could induce the conversion of SO2·H2O and HSO3− to sulfate through energy transfer, electron transfer or hydrogen atom extraction through liquid-phase reactions, suggesting that the photosensitization pathway may make a significant contribution to sulfate formation [16]. 3DOM* in natural water bodies promotes the photochemical oxidative degradation of pollutants in an aqueous environment [17,18]. Similarly, the atmospheric microaqueous phase can receive stronger sunlight, and the role played by atmospheric photosensitizers is gradually being emphasized. In fact, the discussion of the liquid-phase photosensitization pathway of sulfate in the atmosphere is still very limited. Although its important contribution has been recognized, the specific photosensitization mechanism is uncertain, and the atmospherically relevant affecting factors have not been investigated.
As the main driver of the sulfate photosensitization pathway, the types of photosensitizers in the atmosphere are closely related to local agricultural and industrial conditions. Many substances in the atmosphere can absorb light to produce 3DOM*, such as phenyl ketones [19], aromatic aldehydes [20] and benzoquinones [21]. These photosensitizers can produce certain photosensitizing effects in the atmosphere, which may impact sulfate formation. However, the effects of different photosensitizers on sulfate formation remained unclear.
This study examines the effects of photosensitizer model compounds (PS) and real environmental sample agents on sulfate formation under irradiated conditions. Active substance quenching experiments are carried out using eight types of PS, including phenyl ketones, benzaldehyde and benzoquinones, and the active intermediates in the reaction system were determined. The effect of atmospheric co-existing ions on the sulfate photosensitive formation pathway is studied by adding different concentrations of Cl− and NO3−. In addition, the mechanism of photosensitized reactions of S(IV) with real environmental substances was explored based on the photochemical reactions of humic acid (HA) and water-soluble organic carbon in vehicle exhaust particles (WSOC) as agents of real environmental samples. This work reveals a potentially important force for atmospheric photosensitizers to drive haze events, particularly for regions with high vehicle exhaust emissions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
All chemicals were used as purchased; 4-benzoylbenzoic acid (CBBP, C14H10O3, 99%), 3’-methoxyacetophenone (3-MAP, C9H10O2, 99%), 4’-methoxyacetophenone (4-MAP, C9H10O2, 98%), benzophenone (BP, C13H10O, 99%), xanthenone (Xan, C13H8O2, 98.8%), 1,4-naphthoquinone (NP, C10H6O2, 99%), p-benzoquinone (PBQ, C6H4O2, 99%) and tetrahydrofuran (THF, C4H8O, 99.5%) were purchased from Aladdin Inc. (Shanghai, China), 3,4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde (DMB, C9H10O3, 98%) and sorbic acid (SA, C6H8O2, 99%) were purchased from Rhawn (Shanghai, China), humic acid (HA, Cat no. 449752) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Shanghai, China), tert-butanol (TB, C4H10O, 99.5%) was purchased from Macklin (Shanghai, China), and other reagents were purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). In addition, all solutions were prepared using ultrapure water (18.2 MΩ·cm). We configured these hazardous chemical solutions in a fume hood and wore gas masks.
2.2. Environmental Sample Collection and Extraction
Particulate matter from vehicle exhaust was collected from the auto vent pipes of many vehicles traveling in Kunming, Yunnan Province. The collected particulate matter samples were placed in brown glass bottles, mixed well and stored away from light to dry. Then, 0.5 g of pellets were placed in a conical flask with 250 mL of ultrapure water and mixed by stirring and shaking in a constant-temperature shaking incubator at 25 °C for 24 h. The solid-liquid mixture was removed, and the suspension was filtered through a 0.45 μm polyethersulfone (PES) membrane before the filtrate (as WSOC stock solution) was collected and stored in a brown polyethylene bottle at 4 °C under refrigeration and protected from light. The dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentrations of of WSOC stock solution and HA (commercial chemical, in Section 2.3) were determined by TOC using a CD-800S total organic carbon analyzer from Hangzhou Qikun Technology Co (Hangzhou, China).
2.3. Photochemical Experiments
An OCRS-PX32T merry-go-round photochemical reactor (Kaifeng Hongxing Technology Co., Ltd., of Henan province of China) was employed, with quartz tubes to contain the investigated solutions. A water-refrigerated, 500 W high-pressure mercury lamp surrounded by 290 nm cutoff filters was used as the light source. The irradiation spectral of the light source were reported in our previous study [22], and the main irradiation wavelengths consist of 297, 302, 313, 334, 365 and 366 nm. The average light intensity at the center of the solution was 0.23 mW/m2 [22].
The initial concentration of NaHSO3 in the photochemical experiment was 1 mM. CBBP, Xan, BP, 4-MAP, 3-MAP, DMB, NP and PBQ (80 μM) as PS were employed to investigate the reactivity between S(IV) and the model photosensitizers’ triplet-excited state (3PS*). HA and WSOC were used as DOM representatives, and the initial concentration of DOM was set at 10 mg C/L, falling within the typical range in the natural atmosphere [6]. H2SO4 and NaOH were used to keep the pH of the investigated solutions to a meteorological water value of six [7,23,24]. Pure water control experiments were performed under the same conditions to see if S(IV) underwent oxidation other than the photosensitive transformation. Aliquots were removed at the same selected intervals for further analysis. Each set of experiments was repeated three times.
To clarify the role of the reactive substances (RSs), quenching experiments were performed by adding 5 mM sorbic acid (SA) to quench the 3DOM* [25], 5 mM tert-butanol (TB) to quench the ·OH [26] or 5 mM tetrahydrofuran (THF) to quench the 1O2 [27]. Aliquots were removed at selected intervals for further analysis.
2.4. Analytic Methods
The SO42− and SO32− concentrations in quartz cuvettes in a photochemical reactor were analyzed using an ion chromatograph (Shunyu Hengping IC1800, Shanghai Shunyu Hengping Instrument Co., LTD., Shanghai, China). The system was equipped with an AS256 anion analysis column and an AES-100 anion suppressor. The reacted samples were sent to the ion chromatograph (IC) for SO42− and SO32− detection after the addition of 0.1% formaldehyde (HCHO) to protect the S(IV). The anions were determined at a flow rate of 1 mL/min using an eluent of 2.0 mM Na2CO3 and 8.0 mM NaHCO3. In addition, both the Na2CO3 and NaHCO3 used in the IC eluents have chromatographic-grade purity.
2.5. Kinetic Analysis
The observed transformation rate constants for the conversion of S(IV) could be expressed as in Equation (1):
where kobs (s−1) is the pseudo-first-order rate constant of the S(IV), t (s) is the reaction time, Ct (M) is the concentration of S(IV) at t and C0 (M) is the initial concentration of S(IV).
ln(Ct/C0) = −kobst,
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Transformation Kinetics of S(IV) with Triplet Photosensitizers
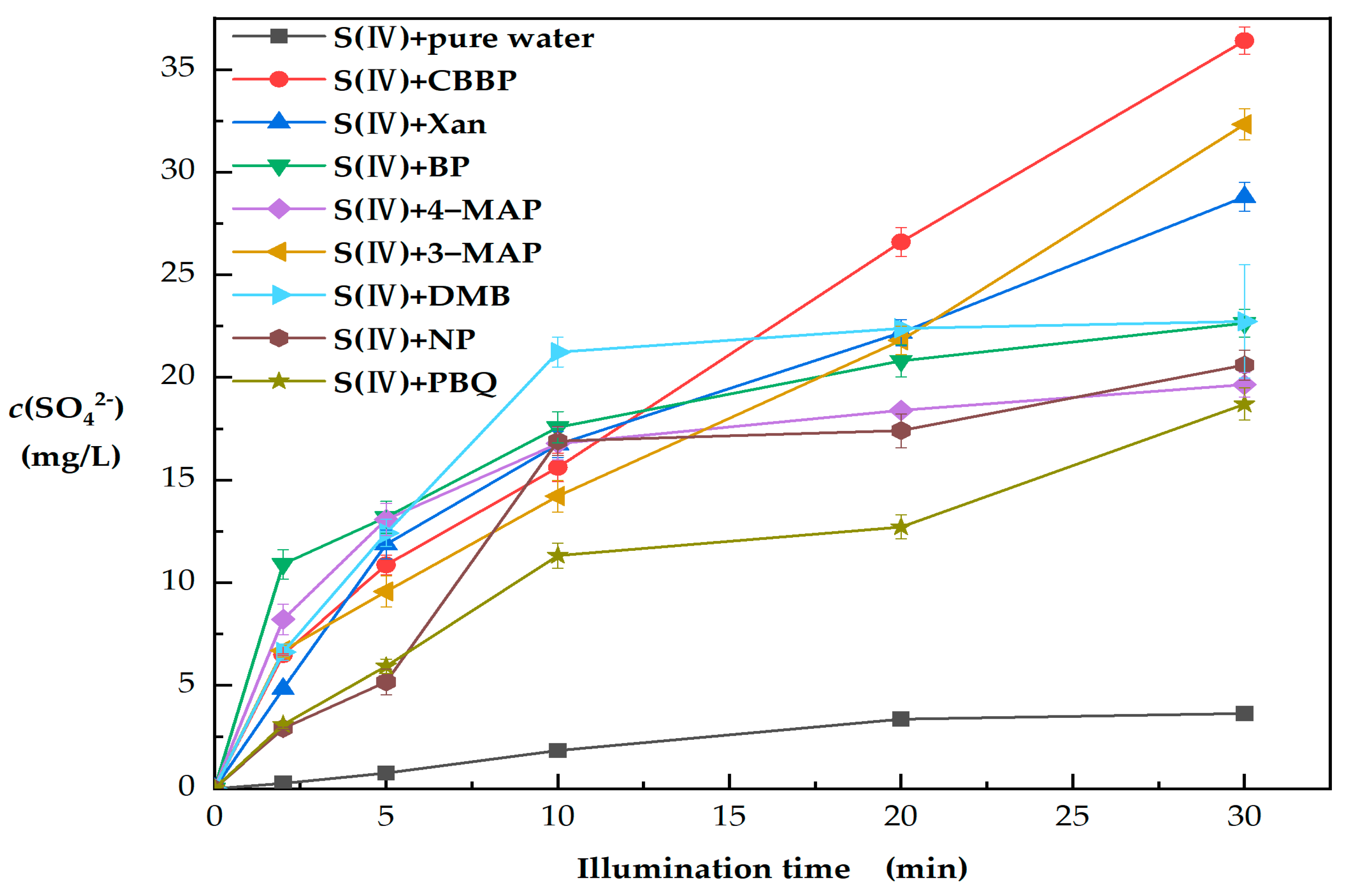
As shown in Figure 1, a significant increase in S(VI) was observed in the presence of photosensitive substances. The difference between the pure water and PS irradiated conditions suggests that the photosensitized substances promoted S(VI) production under illumination. The selected PS were triplet-excited precursors [19,20,21], which indicates that the increase in S(VI) could be attributed to the reactions between 3PS* and S(IV). It has been reported that 3PS* can also generate a variety of reactive oxidizing species (ROS) in the system through energy transfer or electron transfer, including 1O2, ·OH, ·HO2, ·O2− and H2O2 [28,29], which may affect the transformation of S(IV). For this reason, the roles of 3PS* and ROS in the transformation of S(IV) to S(VI) need to be further explored.
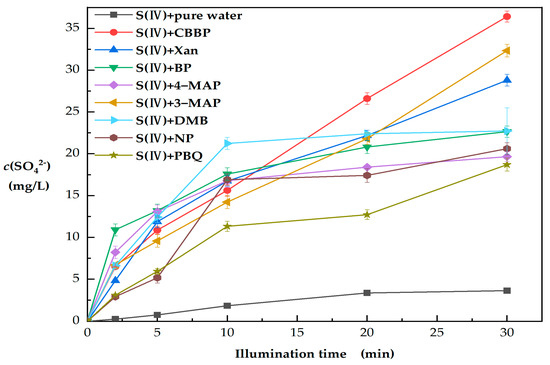
Figure 1.
Comparison of observed sulfate concentration (c(SO42−)) in different PS solutions (PS = 80 μM, S(IV) = 1 mM and pH = 6).
3.2. Roles of Reactive Intermediates in Sulfate Production by Photosensitizers
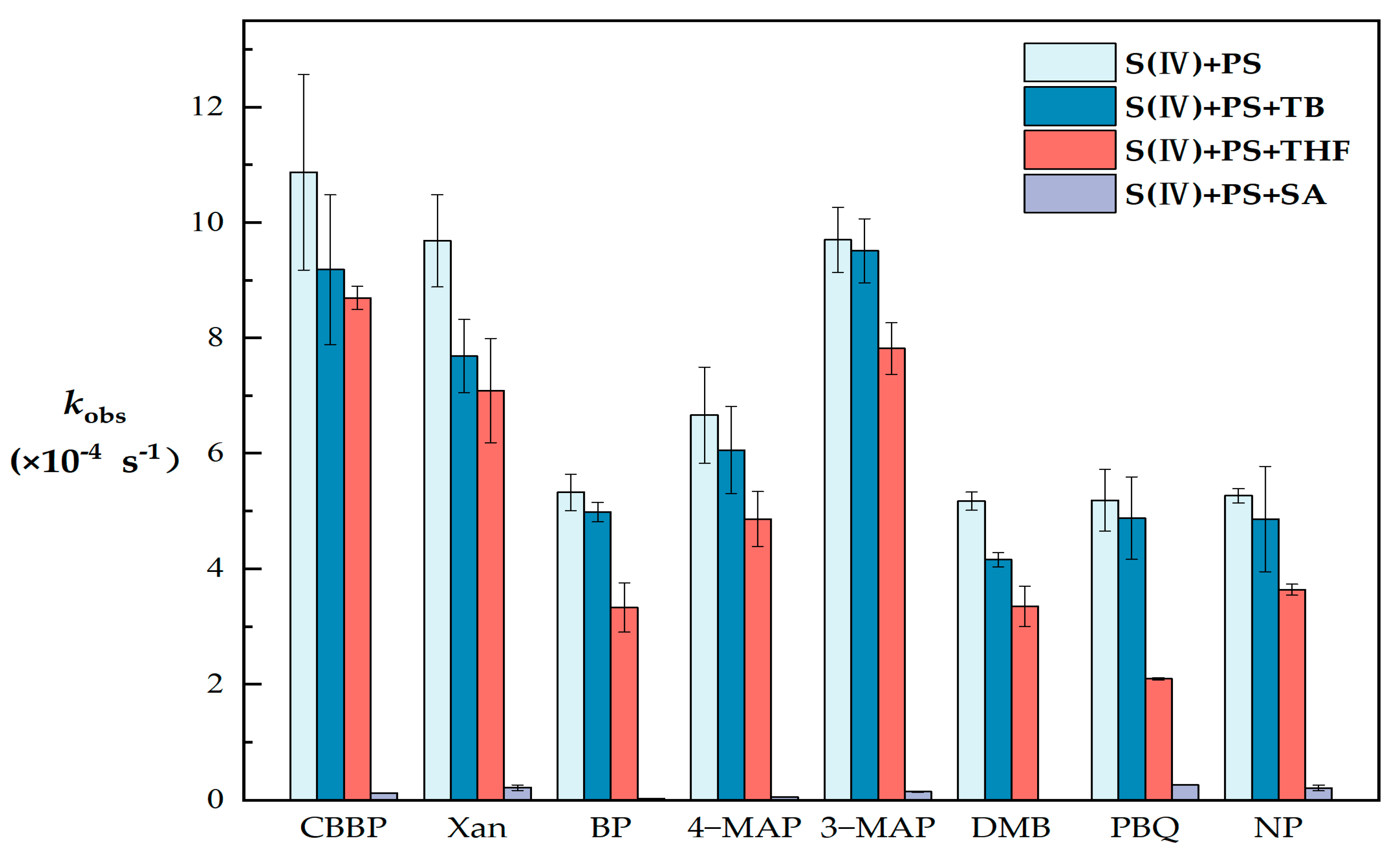
Quenching experiments were conducted to study the photosensitive active intermediates among eight types of PS (Figure 2) and to explore the mechanism of the liquid-phase photosensitive pathway of S(IV).
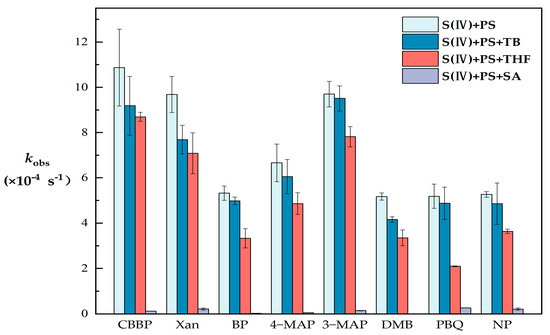
Figure 2.
Observed first-order photodegradation rate constants (kobs) of S(IV) in different PS systems (S(IV) = 1 mM, PS = 80 μM, TB = 5 mM, THF = 5 mM, SA = 5 mM, pH = 6, and radiation time = 30 min). The error bars represent each sample’s standard deviation.
In the presence of CBBP, Xan, BP, 4-MAP, 3-MAP, DMB, PBQ or NP, the kobs values decreased by 15.5%, 20.6%, 6.5%, 9.1%, 1.96%, 19.6%, 5.9% or 7.7% with the addition of TB as a quencher of ·OH. This observation indicates that PS can convert S(IV) through the photosensitized production of ·OH. Although ·OH controls the natural atmospheric oxidation capacity under most atmospheric conditions [30,31], and the gas-phase pathway of sulfate aerosol production is mainly through the reaction of SO2 with ·OH [32], our work suggests that ·OH plays a minor role in the indirect photochemical conversion of S(IV).
When THF was added as an 1O2 quencher, the kobs value decreased by 20~60%. It was observed in PBQ that 1O2 quenching resulted in a decrease of about 60% in kobs, which was the largest decrease among the eight types of PS. The kobs of CBBP and 3-MAP decreased the least (about 20%), but overall, the effect of 1O2 was significantly greater than the contribution of ·OH. This observation indicates that 1O2 plays a nonnegligible role, and the contribution of several PS to 1O2 is various, which is attributed to the difference in the energy transfer ability of 3PS* [33].
With the addition of SA as a 3PS* quencher, kobs decreased by more than 95% in all systems. As SA is a well-known triplet-excited state quencher, 3PS* is inferred to be predominant in inducing indirect photoconversion of S(IV). Wang et al. [16] also indicated that atmospheric 3DOM* played a main role in the photoconversion of S(IV). The addition of SA almost completely inhibits kobs, and therefore we inferred that the ·OH and 1O2 in the system were derived from the electron transfer and energy transfer of 3PS*, which confirms the role of 3PS*.
It has been reported that 3PS* has a strong oxidation potential (reduction potential of 1.4–1.9 eV [34]) and high energy (250 kJ/mol on average [35]), and thus it can directly degrade pollutants through oxidation or energy transfer. The difference of kobs corresponding to various PS is mainly attributed to different kinds of 3PS* redox potential [7,36,37,38] and the sensitivity of S(IV) to oxidants (E0 = −0.93 V), which may also be affected by the functional groups in PS.
3.3. Atmospheric Co-Existing Ions Influence Sulfate Photosensitization
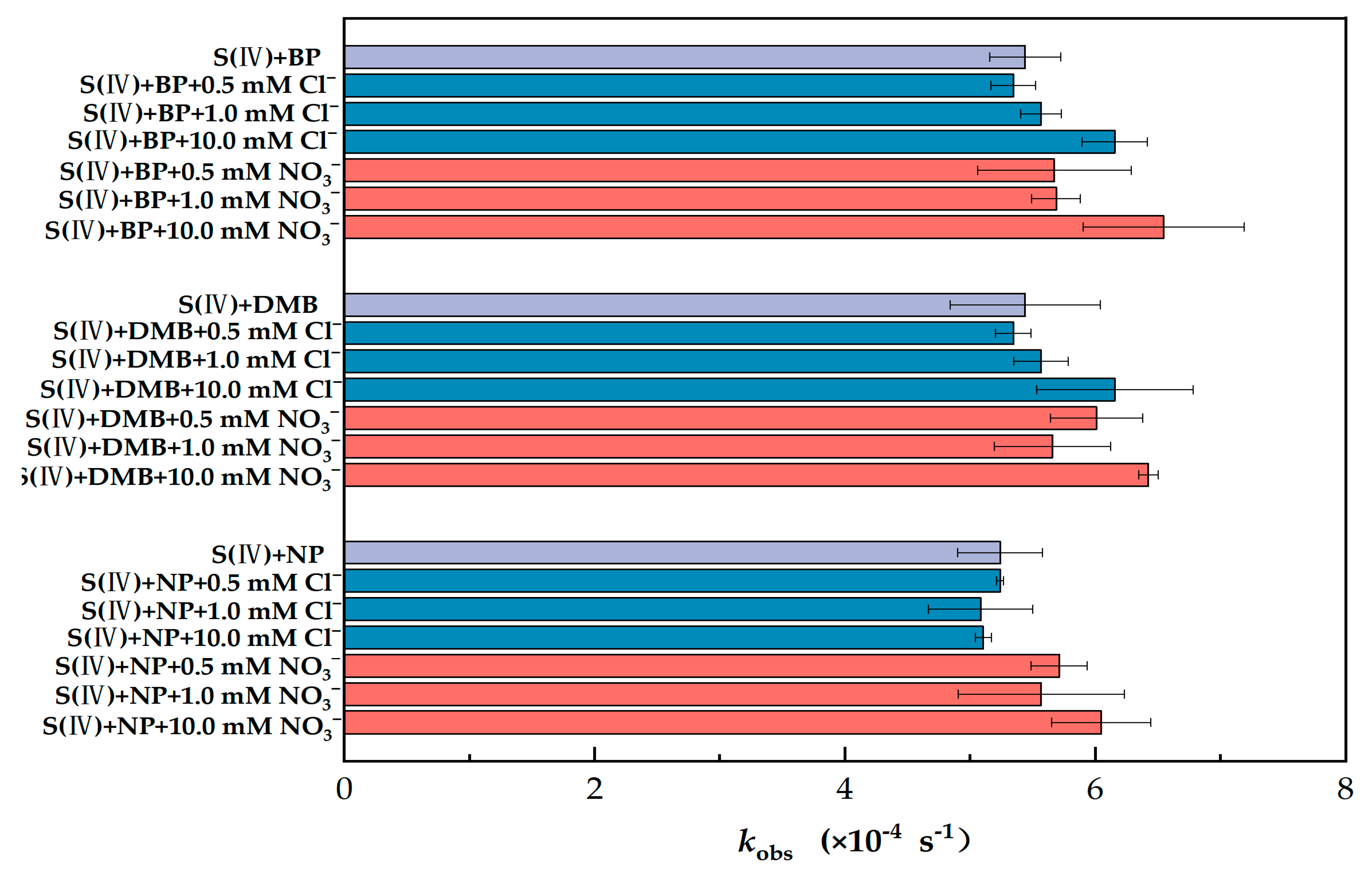
The co-existing constituents (e.g., Cl− and NO3−) in atmospheric waters may affect the transformation of S(IV) because of their importance in photochemical reactions [39,40,41]. Therefore, the effects of Cl− and NO3− on S(IV) transformation were investigated (Figure 3).
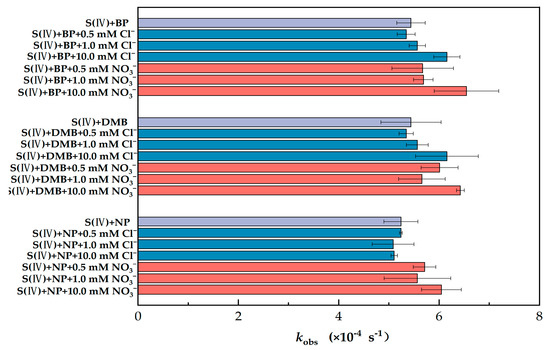
Figure 3.
Comparison of observed first-order photoconversion rate constants (kobs) of S(IV) in different PS solutions and in different ions (PS = 80 μM, S(IV) = 1 mM, pH = 6 and radiation time = 30 min). The error bars represent each sample’s standard deviation.
As shown in Figure 3, the changes in kobs for BP, DMB and NP were less than 6.8% when the concentration of Cl− was less than 1 mM, indicating that the low concentration of Cl− had little effect on S(VI) generation. In contrast, when the concentration of Cl− was increased to 10 mM, the kobs of BP, DMB and NP increased by 13.1%, rose by 30.8% and decreased by 2.6%, respectively, indicating that there were differences in the effects of high concentrations of Cl− on the different types of PS. Parker and Mitch reported that 3DOM* contributes to the formation of RHS, which in turn affects the oxidation of certain added organic compounds, and using a range of free radical quenchers, they found a strong linear relationship between 3DOM* and RHS [26]. Therefore, we inferred that Cl− may accelerate the oxidation of S(IV) by generating chlorine radicals.
Nitrate is a prevalent component of atmospheric aerosol particles [42], Nitrate’s contribution was larger in a coarse fraction compared with PM2.5 instead of sulfate. Actually, there is a balance between nitrate and sulfate that depends on their concentrations of ammonium and on the meteorological conditions, as ammonium nitrate is relatively thermally unstable [43]. Multiphase photochemical oxidation of SO2 via photolysis of nitrate particles can make an important contribution to the formation of aerosol sulfate [44]. Therefore, it is of great importance to elaborate upon the effect of different concentrations of NO3− on sulfate in the presence of photosensitizers for us to investigate the specific mechanism. With the difference in kobs between NO3− and Cl− at the same ion concentration (Figure 3), we speculated that S(IV) oxidation was more affected by NO3− than Cl−. Compared with a <0.5 mM ion concentration, the same concentration of NO3− resulted in increases in kobs all greater than 10%. Obviously, the addition of NO3− clearly had a stronger impact. In fact, there was an overall upward trend in kobs after the addition of NO3−. When 10 mM of NO3− was added, kobs increased by 29.8%, 20.9% and 17.2% for BP, DMB and NP, respectively. As a result, we suggest that the addition of NO3− had a dramatic effect on kobs. NO3− is inherently photochemically active in the photochemical range (i.e., λ > 290 nm) and can photolyze to produce highly reactive substances such as NO2, ·OH and N(III) (NO2− or HNO2) [45], all of which have an oxidizing effect on S(IV). It can be inferred that in our work, it is the effect of the photolysis of NO3− superimposed on the excited triplet state, rather than the conversion of other reactive substances caused by the excited triplet state as a precursor.
3.4. Sulfate Formation Promoted by DOM under Irradiation
Several pathways have been proposed to explain the sources of humic substances, including direct emissions from terrestrial or aquatic sources and biomass or fossil fuel combustion, as well as secondary production from the oxidative oligomerization of small organic molecules through atmospheric chemistry [46,47,48]. WSOC and HA were used as representatives of atmospheric DOM to explore the photosensitive conversion of S(IV).
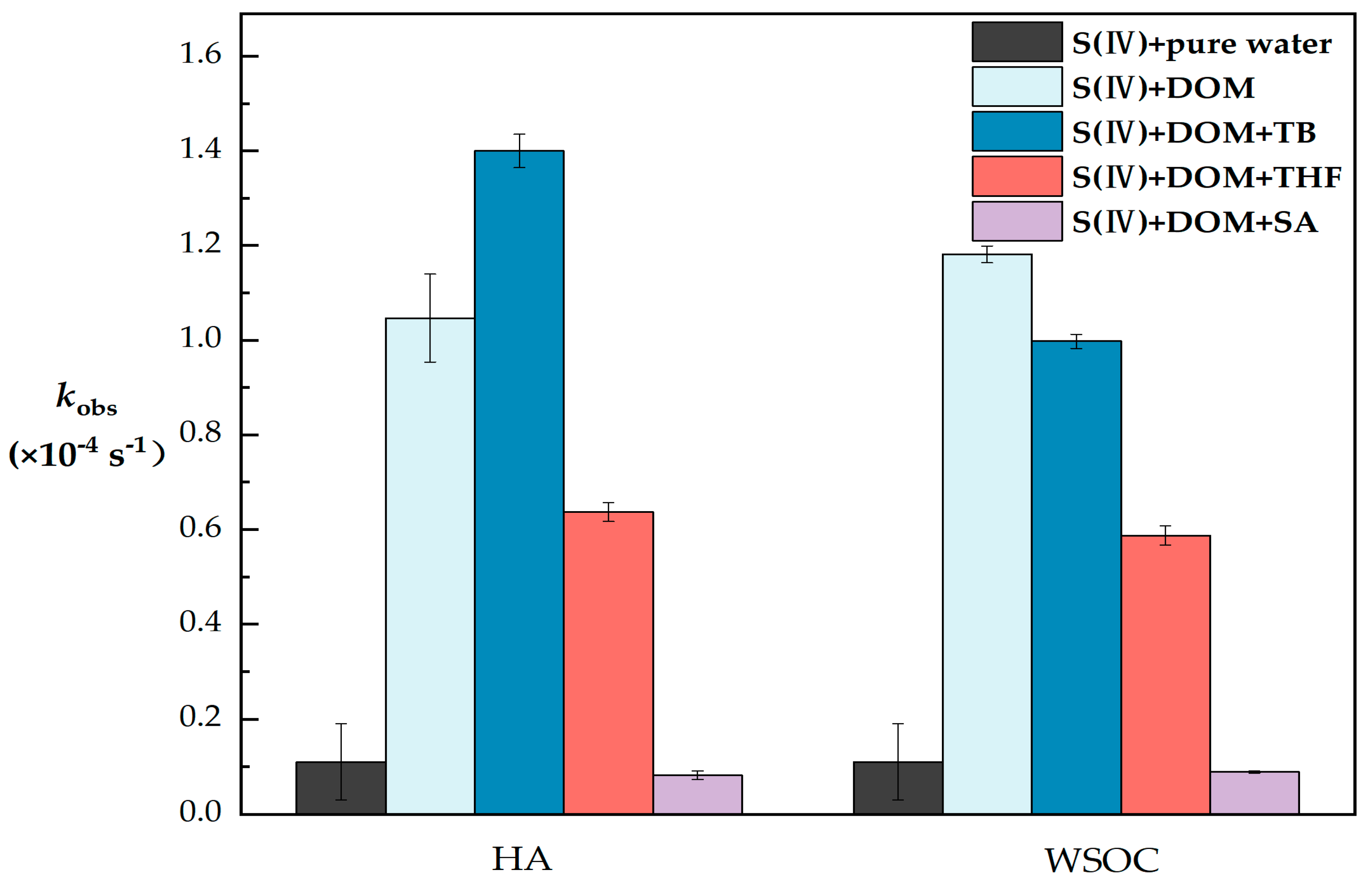
In the pure water control, no significant S(VI) production was observed, while the ln(Ct/C0) linear regression against time (t) indicated that photoconversion of S(IV) followed pseudo-first-order kinetics (R2 > 0.95). The kobs values observed in pure water were (0.11 ± 0.08) × 10−4 s−1, and for HA and WSOC, the kobs values were (1.05 ± 0.09) × 10−4 s−1 and (1.18 ± 0.02) × 10−4 s−1, respectively, as shown in Figure 4. Thus, the photogeneration rate of S(VI) in solutions containing DOM was much higher than in pure water, indicating that DOM is an effective photosensitizer for the photoconversion of S(IV).
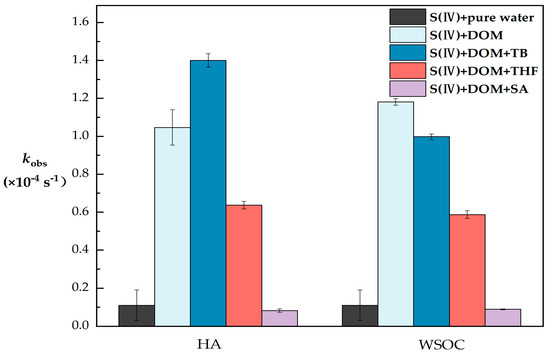
Figure 4.
Comparison of observed first-order photoconversion rate constants (kobs) of S(IV) in different DOM solutions (S(IV) = 1 mM, DOM = 10 mg C/L, TB = 5 mM, THF = 5 mM, SA = 5 mM and pH = 6). The error bars represent each sample’s standard deviation.
In the WSOC quenching experiments, the addition of TB, THF and SA resulted in a reduction in kobs of 15.5%, 50.3% and 92.1%, respectively. In the HA quenching experiments, the addition of THF and SA resulted in a kobs reduction of 39.1% and 92.1%, respectively. This achieved a high degree of agreement with the results of our quenching experiments for the photosensitizer model compounds. Significantly, in the quenching experiments of HA with ·OH, we found that the kobs was (1.40 ± 0.04) × 10−4 s−1 after the addition of TB, which was 33.7% expanded compared with the kobs without quenching, which seems to be different from the results of our previous work. It has been suggested that alcohols as scavengers may have produced substances such as H2O2 during the scavenging process, leading to a wrong estimation of the ·OH concentration [49], which together with the complex composition of HA increased the possibility of H2O2 generation, resulting in higher kobs values after quenching than without the quencher instead.
4. Conclusions
In this work, we derived a rational pathway for the liquid-phase photosensitive oxidation of S(IV) and demonstrated that 3DOM* dominates the generation of S(VI). In this process, 3DOM* can directly convert S(IV) to S(VI), which is its main mechanism. Moreover, 3DOM* can also generate 1O2 through energy transfer, which indirectly leads to S(IV) conversion, and this can even account for 50% of the conversion. Furthermore, 3DOM* is also capable of indirectly oxidizing S(IV) via electron transfer by generating very little ·OH. Previous studies [21] have documented that the concentration of triplets in typical fog water is much higher than the ·OH concentration, making the triplet state the main photooxidant.
To our knowledge, the liquid-phase photo-oxidation pathway for SO2 has been explored to a very limited extent. In this work, we propose that an alternative pathway for sulfate aerosol generation is the photosensitive conversion of DOM in the atmospheric microaqueous phase, which as a new finding for rapid sulfate formation in the atmosphere can be considered an effective driver of haze events. More importantly, we demonstrate that the atmospheric DOM acts as a potential generator of ·OH, 1O2 and 3DOM* in the troposphere under solar illumination. Therefore, more detailed studies are needed to understand the homogeneous and non-homogeneous photochemistry associated with atmospheric DOM.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.L., Y.M. and Y.L.; methodology, H.L., Y.T. and Y.L.; validation, N.W. and D.Z.; formal analysis, N.W., D.Z. and H.L.; investigation, N.W. and D.Z.; resources, H.L. and Y.M.; data curation, H.L. and Y.M.; writing—original draft preparation, N.W.; writing—review and editing, H.L.; visualization, N.W. and D.Z.; supervision, Y.L., Y.T. and Y.M.; project administration, Y.M. and Y.T.; funding acquisition, Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects (202201AT070097).
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article. The data presented in this study are as shown in the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank all who assisted in conducting this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kirkby, J.; Duplissy, J.; Sengupta, K.; Frege, C.; Gordon, H.; Williamson, C.; Heinritzi, M.; Simon, M.; Yan, C.; Almeida, J.; et al. Ion-induced nucleation of pure biogenic particles. Nature 2016, 533, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Hu, M.; Zamora, M.-L.; Peng, J.-F.; Shang, D.-J.; Zheng, J.; Du, Z.-F.; Wu, Z.; Shao, M.; Zeng, L.-M.; et al. Elucidating severe urban haze formation in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 17373–17378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerminen, V.; Wexler, A.-S. Post-fog nucleation of H2SO4-H2O particles in smog. Atmos. Environ. 1994, 28, 2399–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.-N. Acid deposition: Perspectives in time and space. Water Air Soil Poll. 1995, 85, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, C.; Daniela, C.; Marianna, C.; Antonio, D. Application of PMF and CMB receptor models for the evaluation of the contribution of a large coal-fired power plant to PM10 concentrations. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 560–561, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Chan, A.-W.-H.; Abbatt, J.-P.-D. Multiphase oxidation of sulfur dioxide in aerosol particles: Implications for Sulfate Formation in Polluted Environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 4227–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Anastasio, C. First measurements of organic triplet excited states in atmospheric waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5218–5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Pang, H.; Wang, Y.; Deng, H.; Liu, J.; Loisel, G.; Jin, B.; Li, X.; Vione, D.; Gligorovski, S. Inorganic ions enhance the number of product compounds through heterogeneous processing of gaseous NO2 on an aqueous layer of acetosyringone. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 5398–5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinfeld, J.-I. Atmospheric chemistry and physics: From air pollution to climate change. Environ. Sci. Policy Sustain. Dev. 1998, 40, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-H.; Bei, N.-F.; Cao, J.-J.; Huang, R.-J.; Wu, J.-R.; Feng, T.; Wang, Y.-C.; Liu, S.-X.; Zhang, Q.; Tie, X.-X.; et al. A possible pathway for rapid growth of sulfate during haze days in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 3301–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Mu, Z.; Xu, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Shan, M.; Fan, X.; Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Lin, P.; et al. Triplet-state organic matter in atmospheric aerosols: Formation characteristics and potential effects on aerosol aging. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 252, 118343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.-D.; Sio, V.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Anastasio, C. Secondary organic aerosol production from aqueous reactions of atmospheric phenols with an organic triplet excited state. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Yu, X.; Yuan, Z.-B.; Griffith, S.-M.; Lau, A.; Seinfeld, J.-H.; Yu, J.-Z. Efficient control of atmospheric sulfate production based on three formation regimes. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-F.; Li, J.-Y.; Ye, J.-H.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Y.-Z.; Hu, J.-L.; Liu, D.-T.; Nie, D.-Y.; Shen, F.-Z.; Huang, X.-P.; et al. Fast sulfate formation from oxidation of SO2 by NO2 and HONO observed in Beijing haze. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Fang, X.; Deng, Y.; Cheng, H.; Bacha, A.; Nabi, I.; Zhang, L. Brown carbon: An underlying driving force for rapid atmospheric sulfate formation and haze event. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gemayel, R.; Hayeck, N.; Perrier, S.; Charbonnel, N.; Xu, C.; Chen, H.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; et al. Atmospheric photosensitization: A new pathway for sulfate formation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3114–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenk, J.; von Gunten, U.; Canonica, S. Effect of Dissolved Organic Matter on the Transformation of Contaminants Induced by Excited Triplet States and the Hydroxyl Radical. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1334–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-Q.; Chen, J.-W.; Qiao, X.-L.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Uddin, M.; Guo, Z.-Y. Disparate effects of DOM extracted from coastal seawaters and freshwaters on photodegradation of 2,4-Dihydroxybenzophenone. Water Res. 2019, 151, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Hudson, B.-M.; Draper, J.; Tantillo, D.-J.; Anastasio, C. Aqueous reactions of organic triplet excited states with atmospheric alkenes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 5021–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.-D.; Kinney, H.; Anastasio, C. Aqueous benzene-diols react with an organic triplet excited state and hydroxyl radical to form secondary organic aerosol. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 10227–10237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vione, D.; Maurino, V.; Minero, C.; Pelizzetti, E.; Harrison, M.-A.-J.; Olariu, R.; Arsene, C. Photochemical reactions in the tropospheric aqueous phase and on particulate matter. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-J.; Liu, X.-L.; Zhang, B.-J.; Zhao, Q.; Ning, P.; Tian, S.-L. Aquatic photochemistry of sulfamethazine: Multivariate effects of main water constituents and mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Processes Impacts. 2018, 20, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Su, H.; Zheng, G.-J.; Wang, J.-D.; Wei, C.; Liu, L.-X.; Ma, N.; Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Poschl, U.; et al. Aerosol pH and chemical regimes of sulfate formation in aerosol water during winter haze in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 11729–11746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Kong, S.-F.; Tong, C.; Qin, J.; Chen, L.; Sui, Y.; Li, B.-Q. Characterization of reactive photoinduced species in rainwater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 36368–36380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebel, J.-E.; Pignatello, J.-J.; Mitch, W.-A. Sorbic acid as a quantitative probe for the formation, scavenging and steady-state concentrations of the triplet-excited state of organic compounds. Water Res. 2011, 45, 6535–6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, K.-M.; Mitch, W.-A. Halogen radicals contribute to photooxidation in coastal and estuarine waters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5868–5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Q.-W.; Duan, J.-Q.; Tang, X.-Y.; Yao, Q.-Z.; Su, R.-G. Indirect photodegradation of sulfachlorpyridazine in seawater. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 190–196. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.-N.; Yan, S.-W.; Song, W.-H. Photochemically induced formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) from effluent organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12645–12653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilo, R.-V.; Daniela, M.-L.; Mario, A.; Carla, T.-N.; Ricardo, S. Study of degradation of norfloxacin antibiotic and their intermediates by natural solar photolysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 41014–41027. [Google Scholar]
- Lelieveld, J.; Dentener, F.-J.; Peters, W.; Krol, M.-C. On the role of hydroxyl radicals in the self-cleansing capacity of the troposphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2004, 4, 2337–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monks, P.-S. Gas-phase radical chemistry in the troposphere. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2005, 34, 376–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, W.-R.; Calvert, J.-G. The mechanism of the HO-SO2 reaction. Atmos. Environ. 1983, 17, 2231–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-J.; Xiang, X.-Y.; Zuo, Y.-G.; Peng, J.-B.; Lu, K.; Dempsey, C.; Liu, P.; Gao, S.-X. Singlet oxygen production abilities of oxidated aromatic compounds in natural water. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, K.; Canonica, S. Triplet state dissolved organic matter in aquatic photochemistry: Reaction mechanisms, substrate scope, and photophysical properties. Environ. Sci.-Proc. Imp. 2016, 18, 1381–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepp, R.-G.; Schlotzhauer, P.-F.; Sink, R.-M. Photosensitized transformations involving electronic energy transfer in natural waters: Role of humic substances. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1985, 19, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeff, I.; Rabani, J.; Treinin, A.; Linschitz, H. Charge transfer and reactivity of n[pi]* and [pi][pi]* organic triplets, including anthraquinonesulfonates, in interactions with inorganic anions: A comparative study based on classical Marcus theory. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 8933–8942. [Google Scholar]
- Tamara, F.; Thomas, S.; Lin, H.; Hartmut, H. Aromatic carbonyl and nitro compounds as photosensitizers and their photophysical properties in the tropospheric aqueous phase. J. Phys. Chem. A 2021, 125, 5078–5095. [Google Scholar]
- Couch, K.; Leresche, F.; Farmer, C.; McKay, G.; Rosario-Ortiz, F.-L. Assessing the source of the photochemical formation of hydroxylating species from dissolved organic matter using model sensitizers. Environ. Sci.-Proc. Imp. 2022, 24, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.-Y.; Badia, A.; Wang, T.; Sarwar, G.; Fu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Fung, J.; Cuevas, C.-A.; Wang, S.-S.; et al. Potential effect of halogens on atmospheric oxidation and air quality in China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD032058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Ding, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Yan, C.; Shen, Y.; Yao, X.; Zheng, M. A clear north-to-south spatial gradience of chloride in marine aerosol in Chinese seas under the influence of East Asian Winter Monsoon. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 154929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, N.; Wang, P.; Choi, M.; Ying, Q.; Guo, S.; Lu, K.; Qiu, X.; Wang, S.; Hu, M.; et al. Impacts of chlorine chemistry and anthropogenic emissions on secondary pollutants in the Yangtze river delta region. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.-K.; Yao, X. Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesari, D.; De Benedetto, G.-E.; Bonasoni, P.; Busetto, M.; Dinoi, A.; Merico, E.; Chirizzi, D.; Cristofanelli, P.; Donateo, A.; Grasso, F.-M.; et al. Seasonal variability of PM2.5 and PM10 composition and sources in an urban background site in Southern Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gen, M.; Zhang, R.; Huang, D.-D.; Li, Y.; Chan, C.-K. Heterogeneous SO2 oxidation in sulfate formation by photolysis of particulate nitrate. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, K.-B.; McFall, A.-S.; Anastasio, C. Quantum yield of nitrite from the photolysis of aqueous nitrate above 300 nm. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4387–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, K.; Han, J.; Ying, Q.; Hopke, P.-K. Sources of humic-like substances (HULIS) in PM2.5 in Beijing: Receptor modeling approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Huang, R.; Yang, L.; Ni, H.; Wang, T.; Cao, W.; Duan, J.; Guo, J.; Huang, H.; Hoffmann, T. Concentrations, optical properties and sources of humic-like substances (HULIS) in fine particulate matter in Xi'an, Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, F.; Lin, Y.; Hong, Y.; Fan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Xie, F. Light absorption and source apportionment of water soluble humic-like substances (HULIS) in PM2.5 at Nanjing, China. Environ. Res. 2022, 206, 112554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, B.; Dionysiou, D.-D.; Chen, B.; Yang, J.; Li, J. Overlooked formation of H2O2 during the hydroxyl radical-scavenging process when using alcohols as scavengers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 3386–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).