Abstract
Industrial hemp leaves have raised much interest in nutraceuticals and functional foods areas. To expand its application ranges, the antibacterial activities of industrial hemp leaf extract on Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Bacillus cereus were evaluated and the active components were screened. As a result, the industrial hemp leaf extract was found to have strong bacteriostatic effects on E. coli and S. aureus. Bioassay-guided fractionation and isolation from fractions active against E. coli were conducted. Two compounds, cannabidivarinic acid and cannabidiolic acid, were firstly recognized by analytical HPLC by comparing the retention times and UV spectra with standards and later isolated using preparative HPLC. Moreover, the antibacterial mechanisms of cannabidivarinic acid and cannabidiolic acid were investigated by testing the alkaline phosphatase activity, β-galactosidase activity, conductivity, proteins leakage, nucleic acid leakage, and scanning electron microscope observation. The results demonstrated that cannabidivarinic acid and cannabidiolic acid could destroy the cell wall and membrane of E. coli, resulting in the inhibition of enzyme activity and leakage of contents. They could damage the bacteria cell envelope as well. Presented results pointed out cannabidivarinic acid and cannabidiolic acid as promising natural bacteriostatic agents for the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industry.
1. Introduction
Industrial hemp (IH) is an annual herbal plant of the cannabis species (Cannabaceae) which is cultivated for fiber, oil, and dietary supplements [1]. IH is widely cultivated worldwide and has a long planting history in China for its applications in textile and consumption. In recent years, various kinds of nutraceuticals and functional foods made from IH leaves (IHL) and seeds are presented [2]. The most active compounds in IHL are flavonoids, alkaloids, terpenes, and cannabinoids, which are responsible for diverse pharmacological functions [3]. As a group of unique and typical natural active compounds, cannabinoids have anti-pain activity closely related to various physiological activities such as obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, pain, and diabetes [4,5]. Specifically, cannabinol has inhibition on cancer cells [6]. Cannabidivarin could be applied in medicine, nutrition, and cosmetics, limiting the production of psychoactive and illegal cannabinoids [7]. In general, cannabinoids have great potential in scientific research and application development [8].
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is one of the bacteria that seriously endanger the healthy development of humans and animals [9]. Under certain conditions, it would cause diarrhea in humans and animals [10]. It also could cause the spoilage of food, which is the main topic in food preservation [11]. For a long time, its prevention and treatment mainly relied on antibiotics. With the concern of food safety and drug resistance, screening of natural sources, pathogenic bacteria sensitivity, and low toxicity active components to prevent and control human and animal diseases has become the current research hot spot and trend [12,13].
Research of the antibacterial activity of IHL extract (IHLE) and cannabinoids on E. coli is relatively rare. Ali et al. investigated seed oil, petroleum ether extract, and methanol extract of the whole IH for their antimicrobial activity against four bacterial strains including E. coli. The results show that the petroleum ether extract exhibited high activity against E. coli [14]. Novak investigated the activity of essential oils against potential pathogen microorganisms including E. coli. However, only one variety shows inhibition on E. coli [15]. Naveed reported the ethanol extract of the leaf of Cannabis Sativa exerted antibacterial activity against E. coli [16]. Another report shows that CBD could significantly enhance the antibacterial effect of erythromycin and rifampicin against E. coli [17].
Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive and aerobic bacterium and opportunistic pathogen [18]. The main sites of colonization for S. aureus are the skin and mucous membranes. It could cause a wide range of diseases including common problems such as skin infections, and some severe problems such as endocarditis, bloodstream infections, and osteomyelitis [19]. Bacillus cereus is a common foodborne gram-positive pathogenic bacteria existing in food, soil, and human skin [20]. It could produce cytotoxins and enzymes that cause diarrhea and vomiting, such as hemolysin BL, nonhemolytic enterotoxin, cytotoxin K, and vomitoxin. B. cereus has become a threat to the health of populations since about 1.4–12% of the world’s food poisoning is caused by it [21]. Consequently, the finding of antibacterial ingredients for these bacteria is meaningful and helpful for human health.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
IHL was provided by the Institute of Bast Fiber Crops, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, which was collected in Yunnan province in 2019. Institute of Bast Fiber Crops, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences provided E. coli, S. aureus, and B. cereus. The strains were cultured in a nutrient broth at 37 °C for 48 h with shaking. Ethanol, petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, n-butanol, and glutaraldehyde were bought from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Acetic acid and acetonitrile in HPLC grade were obtained from Macklin Inc. (Shanghai, China). Deionized water used in the experiments was supplied by an ELGA water purification system (ELGA Berkefeld, Veolia, Germany). All other chemicals were of analytical grade.
2.2. Preparation of IHLE
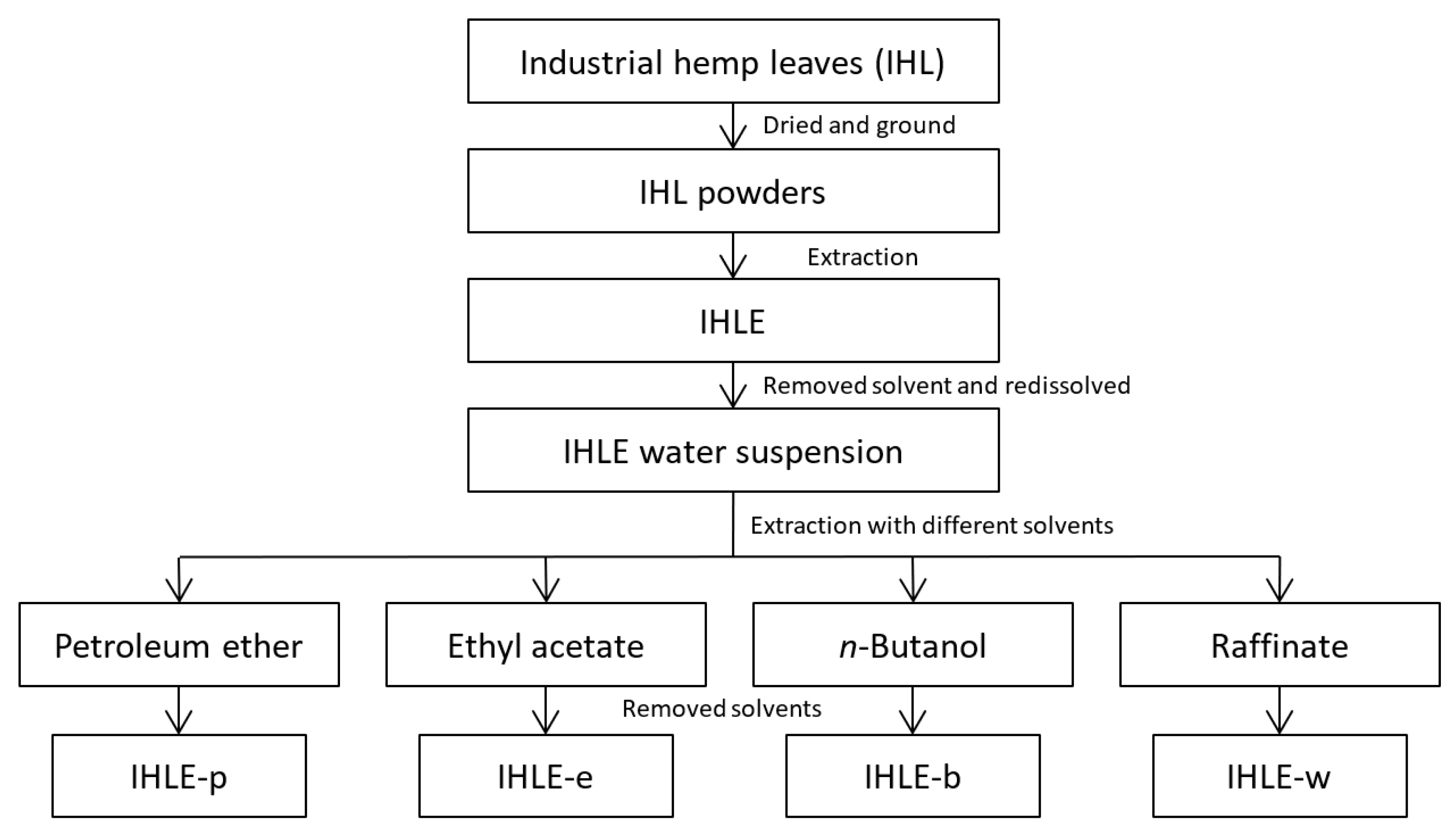
The workflow was shown in Figure 1. The collected IHL were dried in the shade and then ground into powder. A total of 25.0 g of IHL powders were weighed and poured into 250 mL of 70% ethanol solution. The solution was refluxed at 80 °C for 2 h two times and obtained extracts were combined and evaporated using a vacuum rotary evaporator to afford IHLE.

Figure 1.
The workflow of extraction and fractionation of IHLE.
For preparing the antibacterial activity test, the IHLE was re-dissolved in 70% ethanol to adjust the concentration to certain values. The IHLE was re-dissolved in water to screen active antibacterial ingredients. In sequence, the suspension was extracted with petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, and n-butanol. Organic solvents and water were evaporated to obtain appropriate extracts. Four parts of IHLE were, respectively, redissolved in 70% ethanol to certain concentrations and marked as IHLE-p, IHLE-e, IHLE-b, and IHLE-w, which were diluted with water in further experiments.
2.3. Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity
2.3.1. Determination of Bacterial Inhibition Zone
The diameter of the inhibition zone (DIZ) of extracts was determined by the paper disc diffusion method, as previous reports described [22]. Three bacteria suspensions (E. coli, S. aureus, and B. cereus) were cultured in a nutrient broth at 37 °C for 48 h and diluted to about 1 × 10−6 CFU. A total of 100 μL of bacterial suspensions was evenly spread on an agar plate. Then, sterilized filter paper discs (Φ = 6 mm) were soaked in samples with different concentrations and carefully placed on the plates. The plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h, and the DIZ was measured by a vernier caliper. A solvent without samples was used as a negative control.
2.3.2. Determination of Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
The MIC was determined by the micro-dilution broth method with some modifications [23]. Extracts with concentrations of 100.0, 50.0, 25.0, 12.5, and 6.25 mg/mL were obtained by the double dilution method. A total of 500 μL of nutrient broth and 50 μL of samples were mixed in a tube. Then, the bacterial solution (1 × 10−6 CFU) was added to the tube and incubated at 37 °C for 12 h. The absorbance at 600 nm of the bacterial suspensions was monitored by a spectrophotometer at predetermined time intervals. The nutrient broth was used as a negative control. The lowest concentration of the sample inhibiting the growth of bacteria was defined as the MIC value.
2.3.3. Effect of Extracts on the Growth Curve
To study the effect of IHL extracts on the growth curve of bacteria [24]. The sample was added to the bacteria suspensions (1 × 10−6 CFU) and incubated at 37 °C and 100 rpm. The absorbance at 600 nm of the cultures was monitored by a spectrophotometer at predetermined time intervals. The sample using nutrient broth instead of the extract was set as a control.
2.4. Analytical and Preparative HPLC Conditions
The analysis of IHL extracts was carried out on the Agilent 1260 HPLC system including a quaternary pump, an autosampler, a thermostatic column compartment, and a diode array detector (Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA). The chromatographic separation was performed on the Waters Sunfire C18 column was employed (250 mm × 4.6 mm i.d.; 5 µm, Milford, MA, USA). The mobile phase consisted of solvent A (0.1% v/v acetic acid solution) and solvent B (acetonitrile containing 0.1% v/v acetic acid) with gradient elution: 0–5 min, 5% B; 5–20 min, 5–15% B; and 20–50 min, 15–95% B; and 50–60 min, 95% B. The flow rate, temperature, injection volume, and detection wavelength were respectively controlled at 0.8 mL/min, 25 °C, 20 μL, and 220 nm. In the analysis of IHLE-pe, the elution mode was re-optimized as isocratic elution as 60% B for 40 min. The separation and isolation of target active compounds were performed by preparative HPLC (Sykam S500, Eresing, Germany) with an Innoval ODS-2 column (150 mm × 10 mm i.d.; 5 μm, Agela company, Tianjin, China). The elution mode was isocratic elution at 65% B for 25 min. The flow rate was 1.2 mL/min, and the injection volume was 200 μL. The temperature and detector were set as in previous methods.
2.5. Antibacterial Mechanism
2.5.1. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Observation
An appropriate amount of bacterial suspension was added to the liquid culture containing IHL in MIC, and the bacteria were cultured under shaking at 37 °C and 160 r/min for 12 h. Then, 10 mL of suspension was centrifuged (4000 r/min, 15 min), and fixed for 12 h with 2.5% glutaraldehyde solution. The fixed cells were pelleted and washed with PBS for 15 min 3 times. The samples were then dehydrated by gradient ethanol of 30%, 50%, 70%, and 90% respectively, and dried in freeze drying. After the spraying with gold, the morphology and structure of the bacteria were observed by SEM [25].
2.5.2. Effect on the Cell Membrane
The effect of IHL extracts and active compounds on E. coli cell membrane was studied by measuring conductivity, protein concentration, nucleic acid leakage, and β-galactosidase (β-GAL) enzyme activity [26,27]. The bacteria were treated with MIC concentration of samples for 3 h. Then, the suspension was centrifuged at 4000 r/min for 15 min, and the conductivity of the supernatant was measured with a conductivity meter after 20-fold dilution (DDSJ-308A, Shanghai Precision Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). The content of proteins in suspension was determined by bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein quantification kit (Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). The concentration of nucleic acid in the supernatant was expressed as the absorbance at 260 nm by UV–Vis spectrophotometer (UV-2700, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The activity of β-GAL was measured by the Micro β-GAL Assay Kit provided by Solarbio (Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China).
2.5.3. Effect on the Cell Wall
The cell wall integrity of bacteria was measured through an alkaline phosphatase (AKP) activity assay [28]. The bacteria were treated with MIC concentration of samples for 3 h. Then, the suspension was centrifuged at 4000 r/min for 15 min, and the supernatant was submitted for determination. The extracellular AKP level was determined by spectrophotometry method using the commercial AKP assay kit following the manufacturer’s instructions (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China).
2.6. Statistical Analysis
All values were expressed as means ± SD of triplicate experimental studies. Statistical analysis was performed by SPSS V20 software (IBM SPSS Statistics 20, New York, NY, USA). The data were then compared using Duncan’s multiple range tests at 5% significance levels, and one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test [29,30].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of IHLE
3.1.1. Screening of the Target Bacterial Strain
IHLE was acquired by traditional reflux extraction and then we screened its antibacterial activity in E. coli, S. aureus, and B. cereus. The DIZ of IHLE in various concentrations was determined by the disc diffusion method, which could reflect the sensitivity of bacterial strains [31]. The highest bacteriostatic effects were observed on E. coli and S. aureus (Table 1), with DIZ values of 15.57 ± 1.65 mm and 14.86 ± 1.37 mm when the extract was 100 mg/mL, respectively. However, the IHLE was insensitive to B. cereus and had no inhibitory effect. With the decrease in the concentration of IHLE, the antibacterial ring significantly decreased. The minimum inhibitory concentrations of E. coli and S. aureus were 12.5 mg/mL. In previous investigation of antibacterial activity of Cannabis sativa extracts against E. coli, ethyl acetate leaf extract exhibited the highest activity, ranging from 7.50 ± 0.71 to 21.50 ± 0.71 mm, which is in agreement with our results for 70% ethanol extract [32].

Table 1.
The DIZ of three strains of IHLE in different concentrations (mm).
3.1.2. Screening of the Antibacterial Fraction
To find the active ingredients in the extract, the antibacterial activities of four fractions of IHLE including IHLE-p, IHLE-e, IHLE-b, and IHLE-w on E. coli were detected. Table 2 showed the DIZ of IHLE-p, IHLE-e, IHLE-b, and IHLE-w on E. coli, and the concentration of samples was adjusted to be 20 mg/mL. As a result, IHLE-p and IHLE-e had apparent bacteriostatic effects on E. coli, whose DIZ values were 15.43 ± 1.01 mm and 16.18 ± 1.28 mm, respectively. Meanwhile, IHLE-b and IHLE-w had no inhibitory effect on E. coli. Therefore, IHLE-p and IHLE-e were used as the objects in subsequent screening research to explore the specific antibacterial active components in IHLE.

Table 2.
The DIZ of E. coli under different fractions of IHLE (mm).
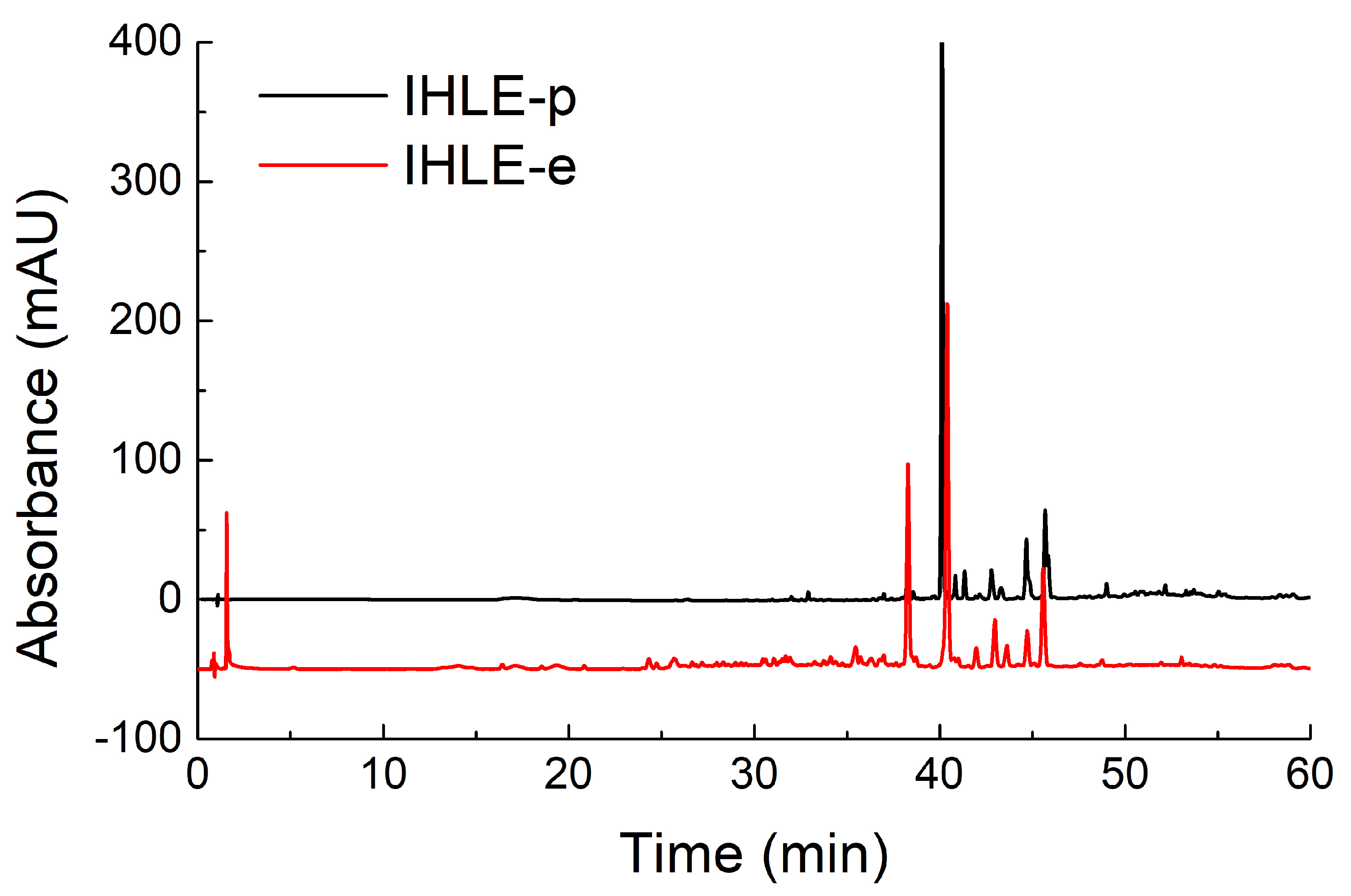
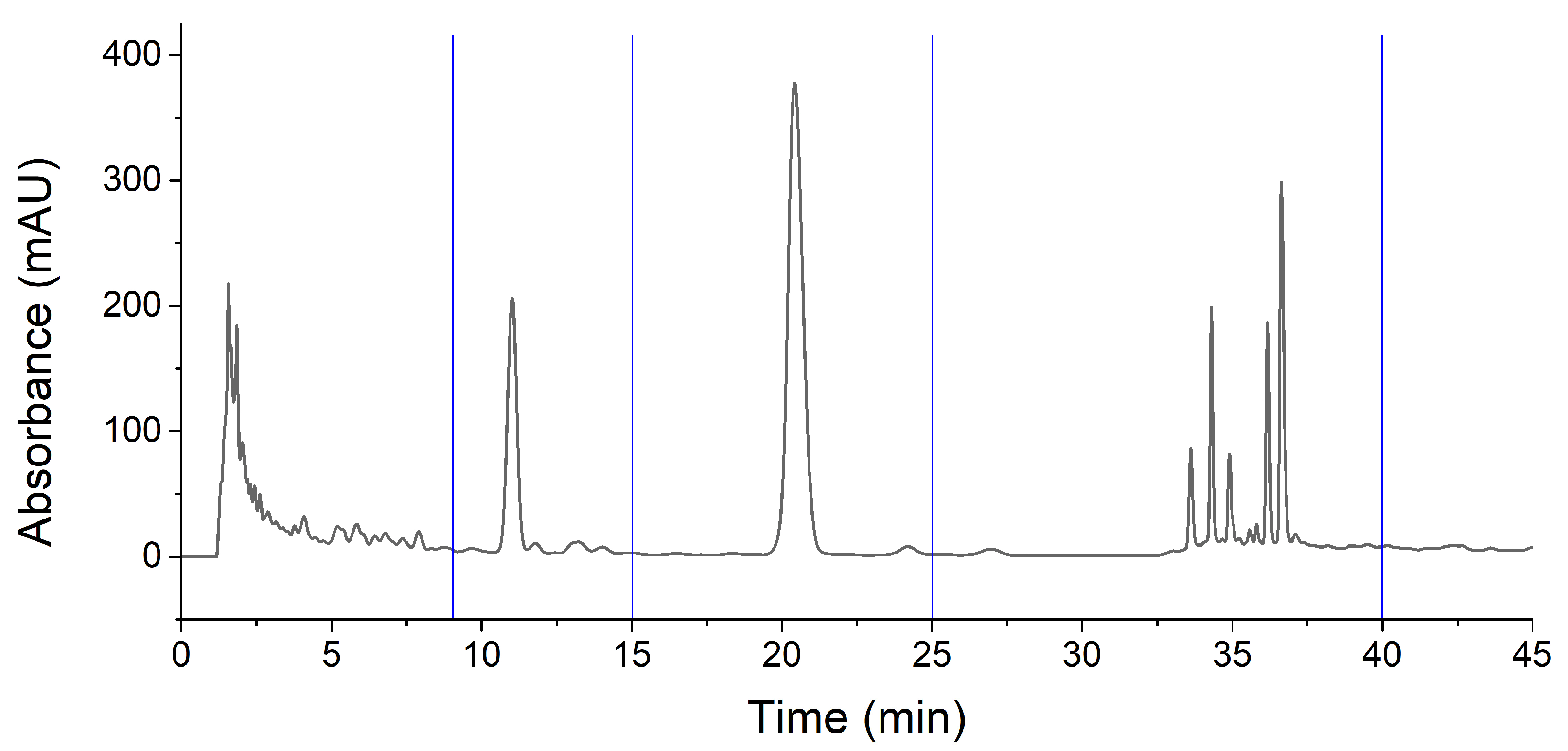
To screen the active components, HPLC analyses of fractions were conducted. According to the chromatograms of IHLE-p and IHLE-e in Figure 2, the main peaks of IHLE-p and IHLE-e were similar. Therefore, these two parts were combined as IHLE-pe, and the new fraction’s HPLC parameters were re-optimized. Under the new optimized HPLC condition, the IHLE-pe was well separated in Figure 3. According to the retention time in the chromatogram, the IHLE-pe was divided into four parts marked as IHLE-pe1 (1–9 min), IHLE-pe2 (9–15 min), IHLE-pe3 (15–25 min) and IHLE-pe4 (25–40 min).
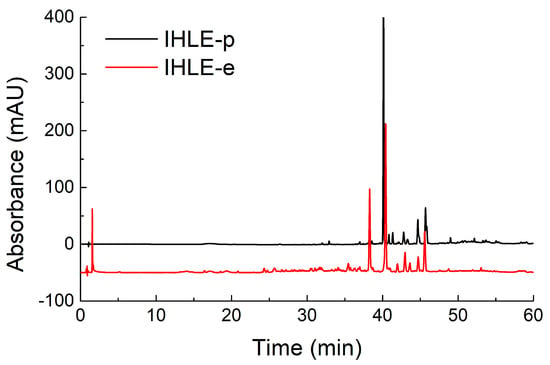
Figure 2.
The chromatograms of IHLE-p and IHLE-e in HPLC analysis.
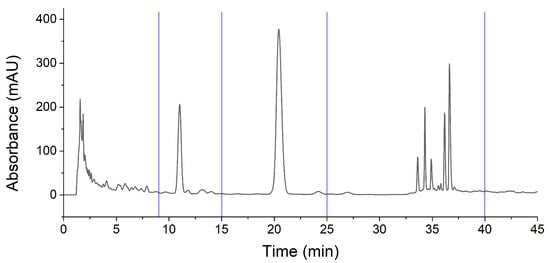
Figure 3.
The chromatograms of IHLE-pe and the division of four fractions.
For screening active ingredients in IHLE-pe, the antibacterial activities of IHLE-pe1 to IHLE-pe4 on E. coli were subsequently detected. As shown in Table 2, the DIZ of IHLE-pe2 and IHLE-pe3 were respectively 11.40 ± 1.41 mm and 12.76 ± 1.55 mm, indicating these two parts contained active compounds on E. coli. However, there was no inhibition of IHLE-pe1 and IHLE-pe4, which showed there was no active compound in these samples. Hence, IHLE-pe2 and IHLE-pe3 contained antibacterial components. According to the chromatogram in Figure 3, two peaks could be observed in IHLE-pe2 and IHLE-pe3. These two peaks would be further isolated using preparative HPLC and identified.
3.2. Identification of Antibacterial Active Components
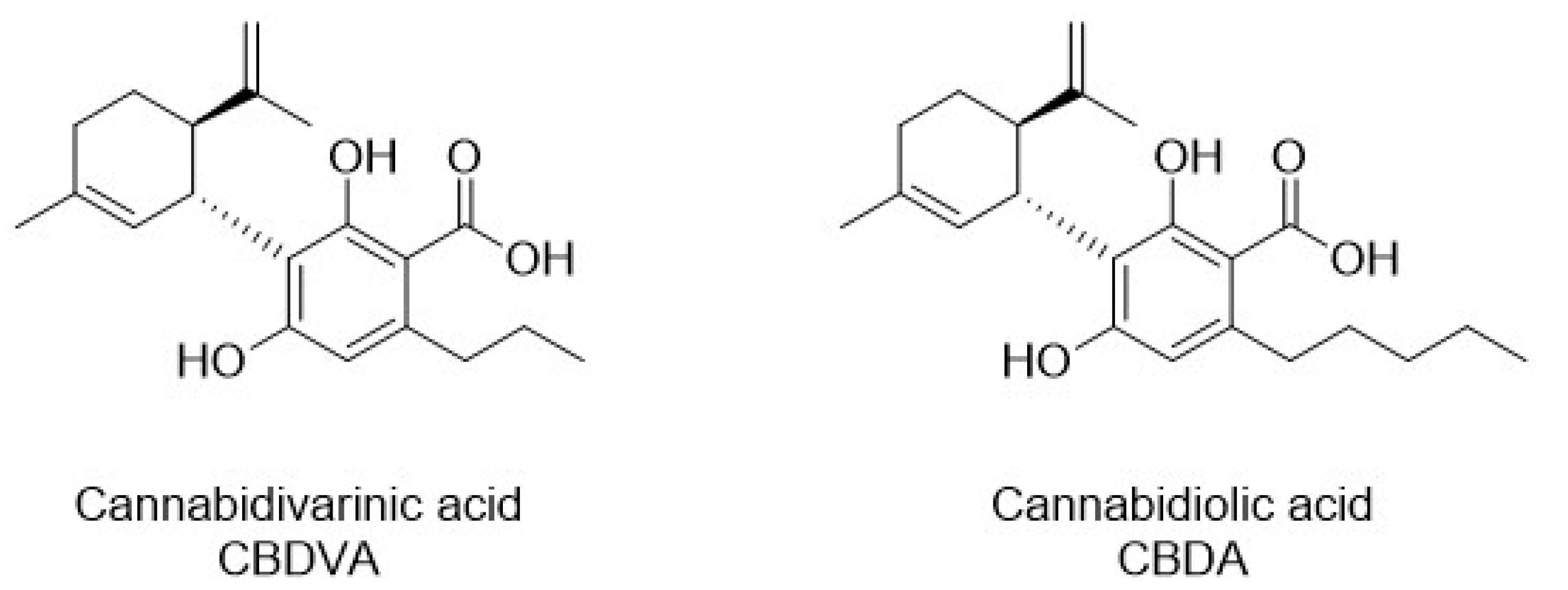
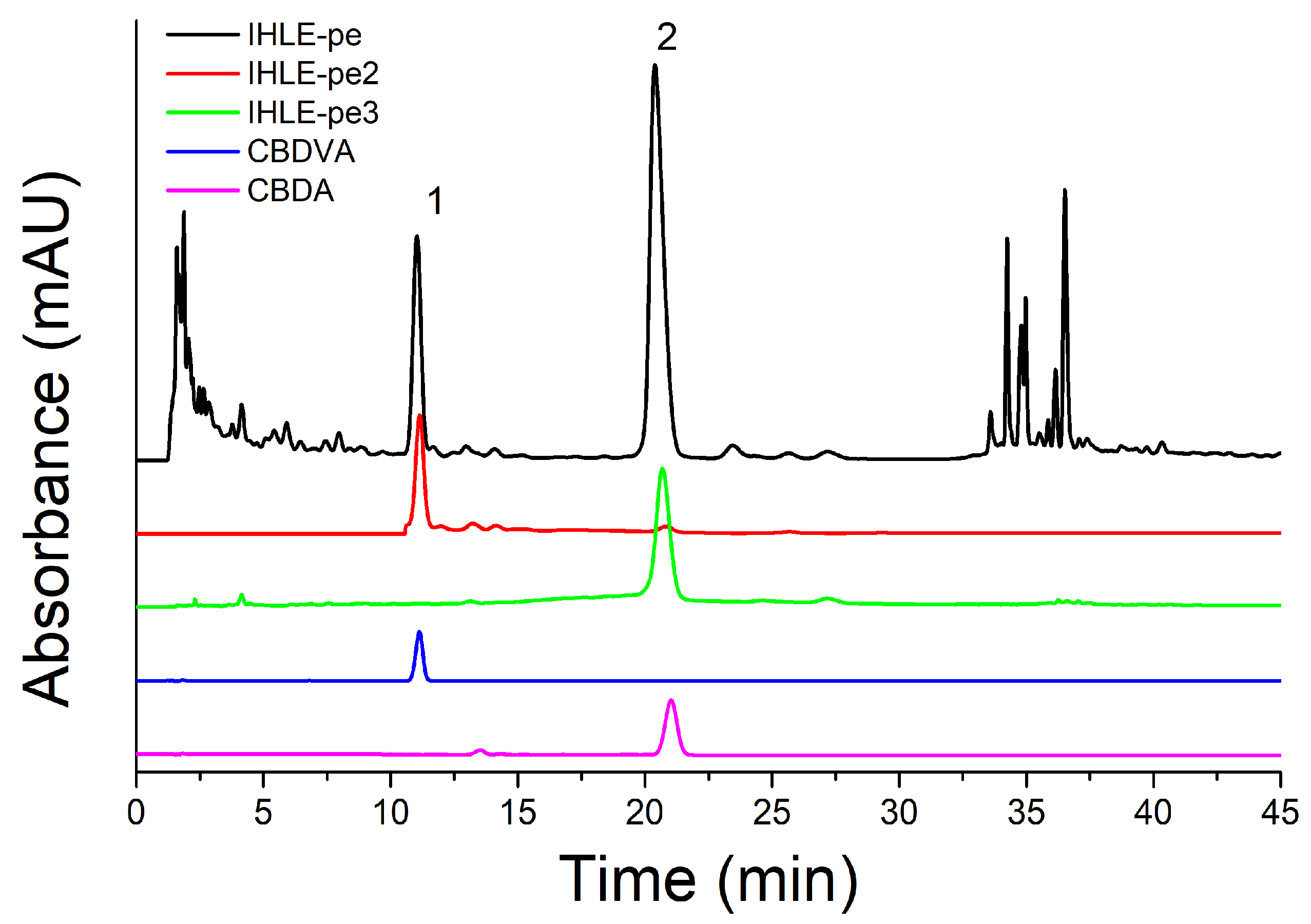
Since fractions IHLE-pe2 and IHLE-pe3 exhibited significant antibacterial activity, and both possessed one peak each, according to HPLC analyses, antibacterial activity was ascribed to these two peaks (compounds). Peaks from IHLE-pe2 and IHLE-pe3 were identified as CBDVA and CBDA using standards and the same HPLC conditions, according to the same retention times and UV spectra [33,34,35]. Both compounds were later isolated using preparative HPLC. The structures of CBDA and CBDVA were shown in Figure 4. The chromatograms of CBDA and CBDVA were illustrated in Figure 5 together with the chromatograms of IHLE-pe, IHLE-pe2, and IHLE-pe3.
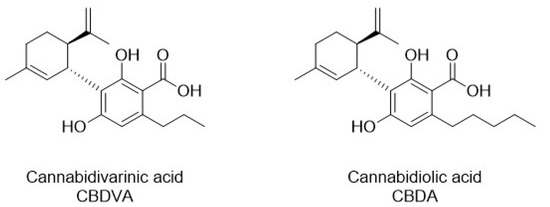
Figure 4.
The chemical structure of CBDVA and CBDA.

Figure 5.
The chromatograms of IHLE-pe, IHLE-pe2, IHLE-pe3, CBDVA, and CBDA.
3.3. Antibacterial Activity of CBDA and CBDVA
3.3.1. MIC
The DIZ and MIC values of CBDA and CBDVA were also conducted. As indicated in Table 3, CBDVA has an inhibitory effect on E. coli. Up to 4.0 mg/mL CBDVA has an apparent inhibition with the DIZ of 11.19 ± 1.54 mm. Meanwhile, CBDA exhibited more obvious inhibition with the DIZ of 14.80 ± 1.35 mm at 1.0 mg/mL. As the concentration is diluted, the inhibitions of both CBDVA and CBDA decreased gradually, and the MIC of CBDVA and CBDA were at 1.0 mg/mL and 0.1 mg/mL. The results confirmed that CBDVA and CBDA had bacteriostatic effects on E. coli. Compared with that of IHLE, their activities were higher, and their bacteriostatic zones were more uniform and transparent.

Table 3.
The DIZ of E. coli under different concentrations of CBDVA and CBDA (mm).
3.3.2. Growth Curves
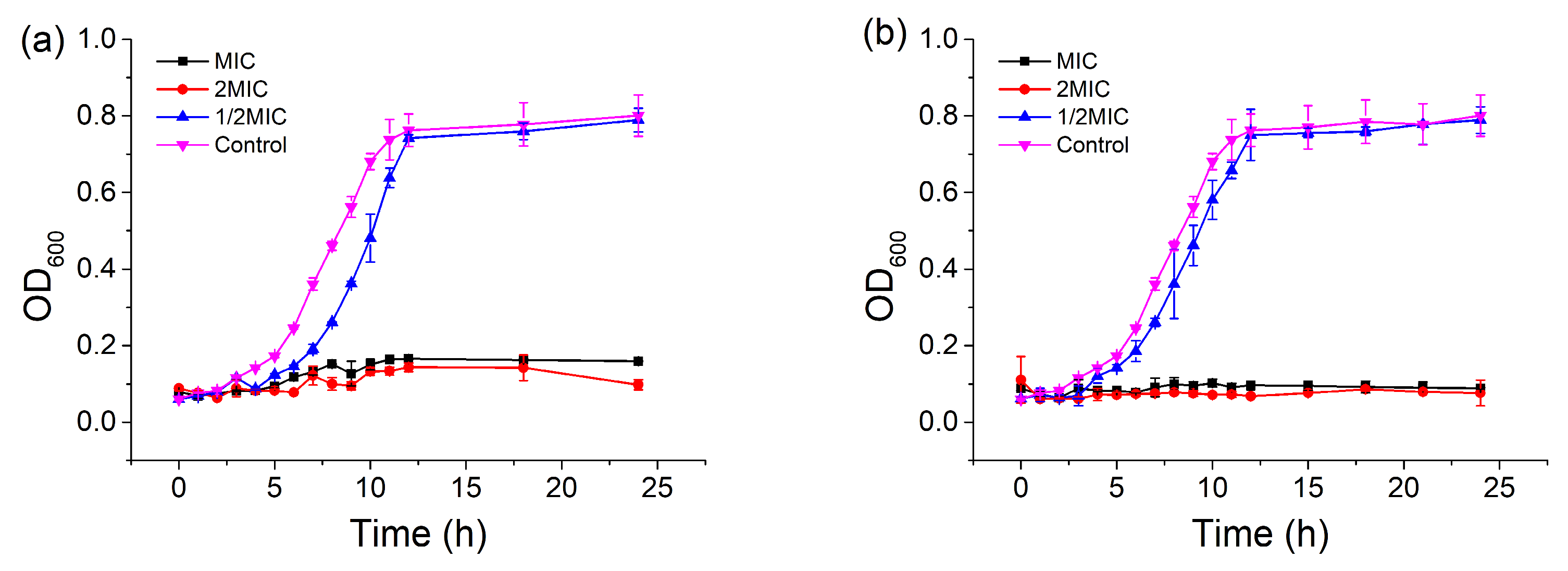
To further investigate the antibacterial activity of CBDVA and CBDA, the growth curves of the E. coli in the presence of samples at different concentrations were monitored at 600 nm for 24 h. As shown in Figure 6, the growth of E. coli in the control group was in line with the typical S-type growth and reached stable 12 h of incubation [36]. When the concentrations of CBDVA and CBDA were at 1/2 MIC, the growth of E. coli was relatively slower than that of the control, and also reached the same stable level at 15 h. However, the growth of E. coli was completely inhibited in the treatments of CBDVA and CBDA at MIC and 2MIC within 24 h of culture, indicating the bactericidal effect of these two active compounds. These results indicated that IHLE, CBDVA, and CBDA treatment could reduce and inhibit the growth rate of E. coli in a dose-dependent manner, which is consistent with the growth inhibition effect of other bacteriostatic substances on pathogenic bacteria [37,38]. Based on these results, CBDVA and CBDA could be regarded as natural antibacterial agents.
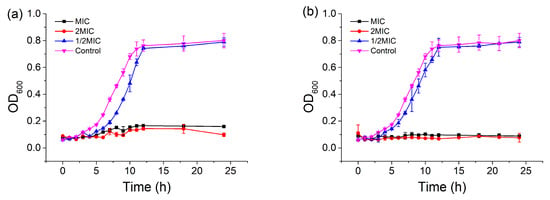
Figure 6.
Growth curves of E. coli in the presence of (a) CBDVA and (b) CBDA at different concentrations.
3.4. Effect of CBDVA and CBDA on Cell Wall Integrity
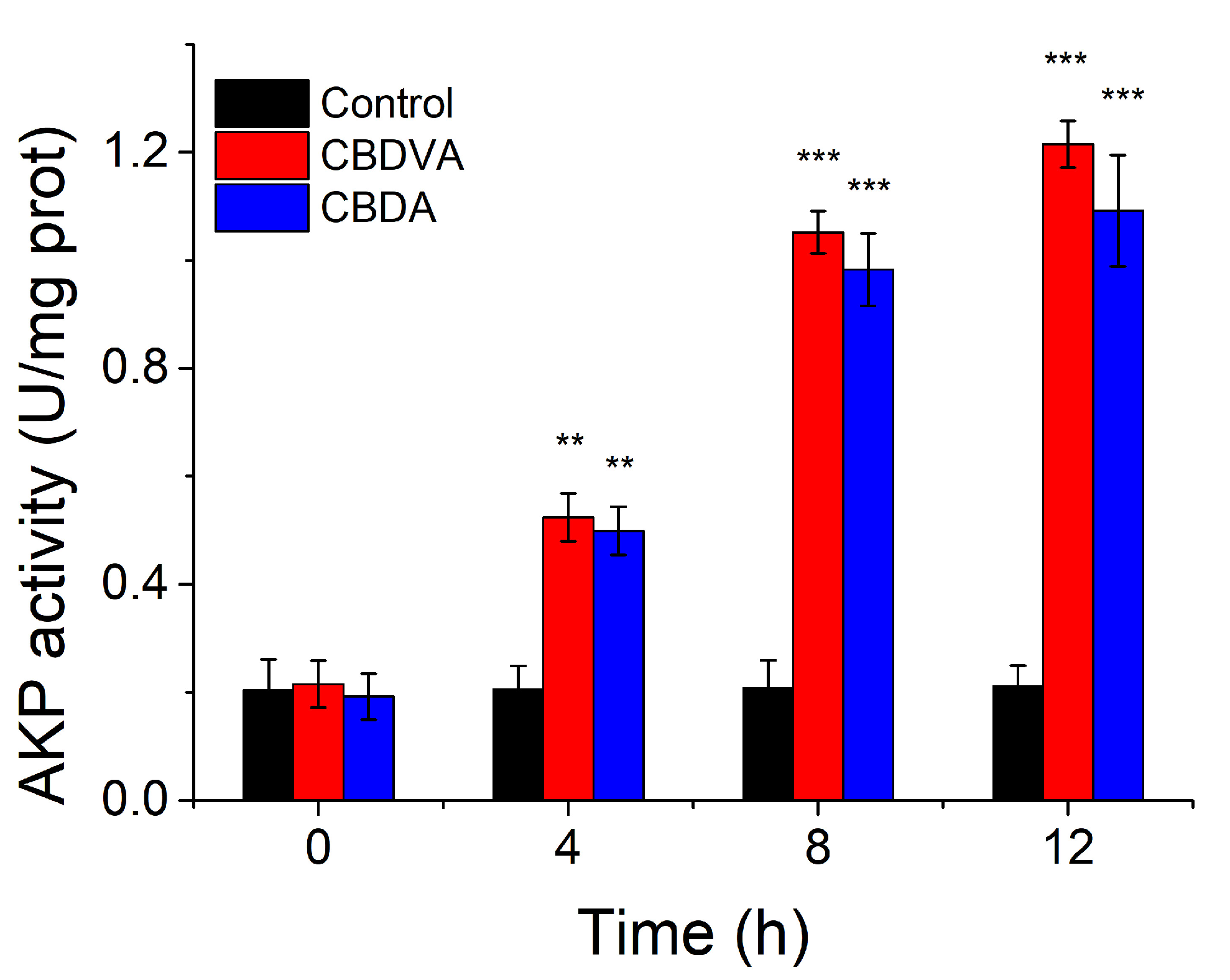
The activity of AKP could not be detected in bacterial culture when the cell wall was unbroken [39]. However, AKP would leak into the extracellular environment when the cell wall is damaged, and AKP activity assay would reflect the damage to the cell wall [28]. When the E. coli was treated with CBDVA and CBDA at MIC for 12 h, the AKP activity increased with incubation time and finally reached six times that of control at 12 h (Figure 7). In comparison, the level of AKP activity remained in the control group. Therefore, it indicated that CBDVA and CBDA could damage the cell wall of E. coli.
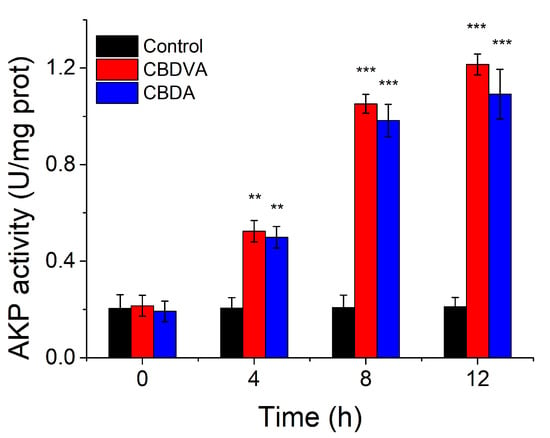
Figure 7.
The AKP activities of E. coli in the presence of CBDVA and CBDA at different times. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 in comparison to control group.
3.5. Effect of CBDVA and CBDA on the Cell Membrane
3.5.1. Cell Membrane Permeability
The effect of CBDVA and CBDA on the cell membrane of E. coli was shown in Table 4. After the treatment of cannabinoids, the conductivity respectively increased from 0.567 mS/cm to 1.562 mS/cm and 1.414 mS/cm. This phenomenon shows the cell membrane was destroyed and small molecules such as sodium and potassium ions leaked out of the cells [40].

Table 4.
The analysis of cell membrane permeability of E. coli treated by CBDVA and CBDA at MIC.
3.5.2. Cell Membrane Integrity
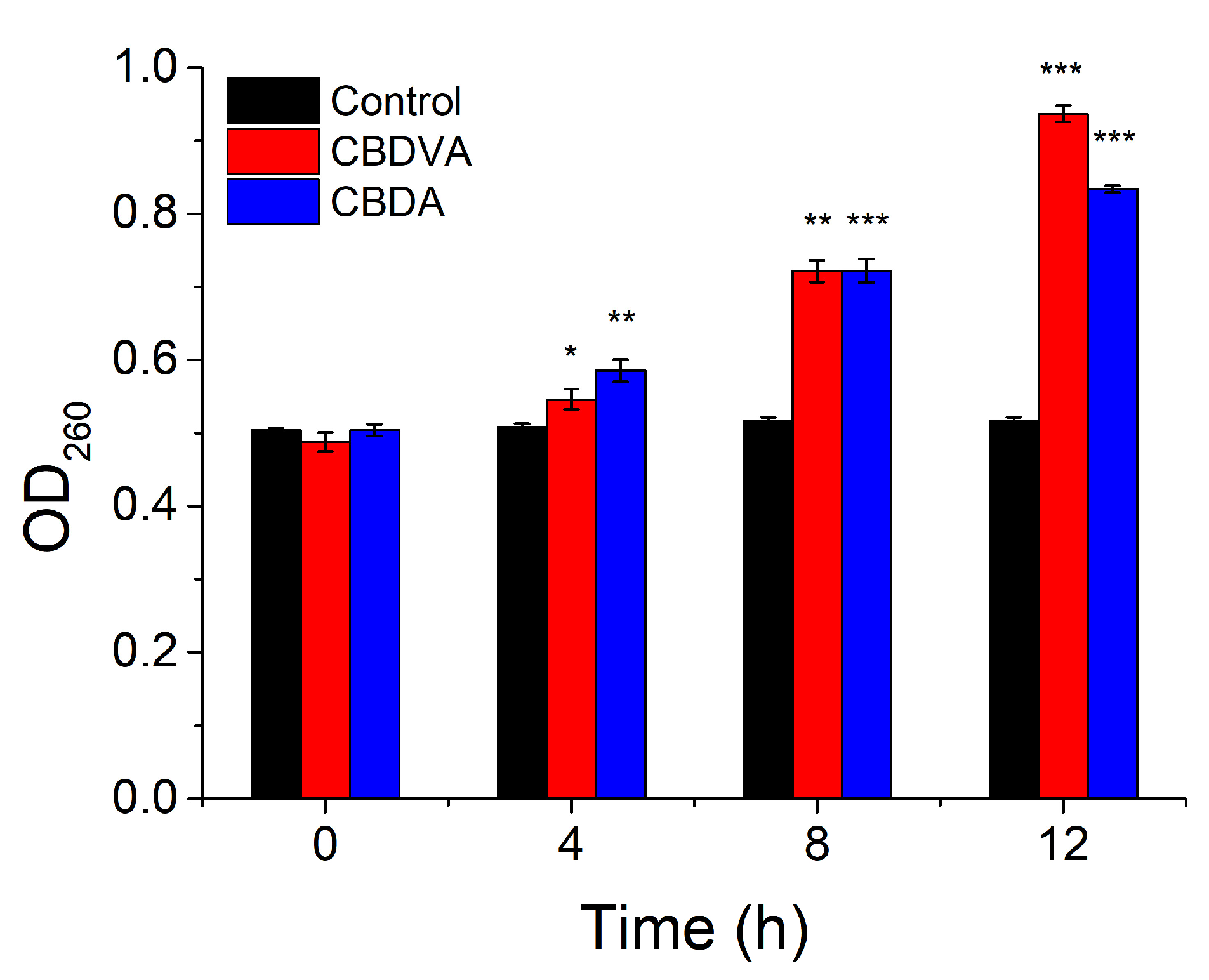
The intracellular contents, such as proteins, small ions, and nucleic acid, would leak out when the cell membrane had a problem. The nucleic acid leakage was studied by monitoring the absorbance at 260 nm [41]. As shown in Figure 8, the absorbance slowly increased through the incubation. This trend might be due to the rupture of the cell membrane and then nucleic acid release into the medium in the presence of CBDVA and CBDA. Loss of intracellular nucleic acids would affect the replication, transcription, and translation of bacterial DNA resulting in cell death. The release of proteins was also an indicator of membrane damage [42]. The protein concentrations of the supernatant were shown in Table 4. After 12 h incubation, the leakage of protein was, respectively, 270 and 268 ug/mL, compared to 200 μg/mL in the control group. β-GAL could catalyze lactose into galactose and glucose, which then affects cell metabolism [43]. The activity of β-GAL could be determined by monitoring the absorption at 405 nm. The absorption value of the treatment groups was reduced by 84.6% and 80.9%, compared to the control group. It could be found that the presence of CBDVA and CBDA would destroy the membrane structure and inhibit intracellular enzyme activity [44]. The above results demonstrated that CBDVA and CBDA could destroy the membrane structure of E. coli, leading to the inhibition of enzyme activity and leakage of contents.
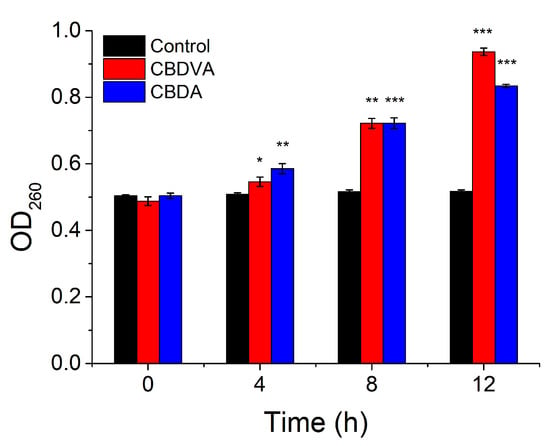
Figure 8.
The OD260 of E. coli in the presence of CBDVA and CBDA at different times. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 in comparison to control group.
3.6. Morphological Transformation
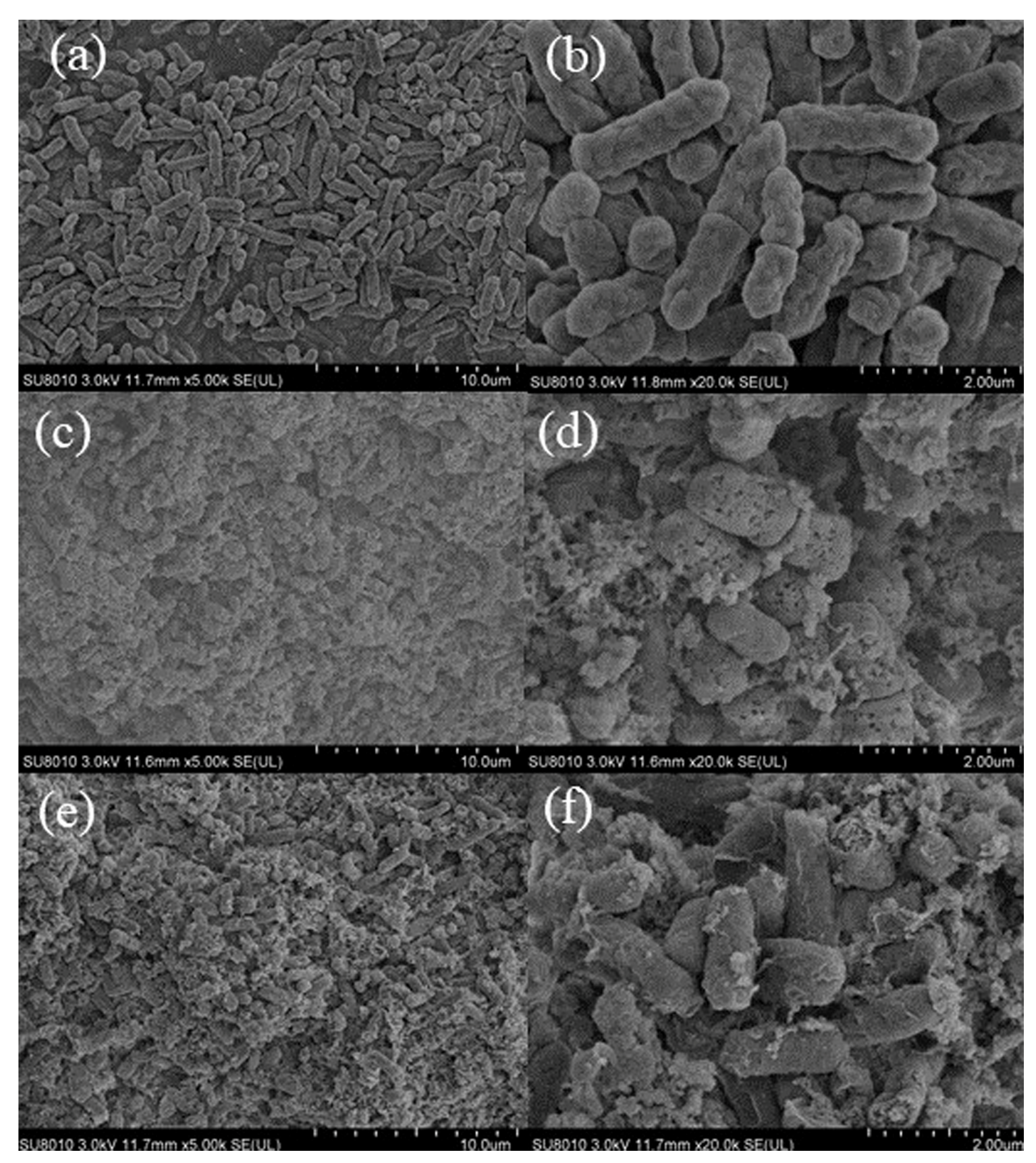
The surface morphology of E. coli in the treatment of CBDVA and CBDA at MIC was visualized by SEM. The SEM images of the three groups were shown in Figure 9. The cells in the control group (6a and 6b) were rod-shaped, regular, and intact. Whereas the surface of cells showed evident morphological changes after treatment of CBDVA and CBDA. Many breakages and collapses of the cell could be observed, and the surface became coarse and multi-holed [45]. The observed results demonstrated CBDVA and CBDA exhibiting their bactericidal activities by affecting cell envelope integrity, consisting of the cell wall and membrane affections [46].
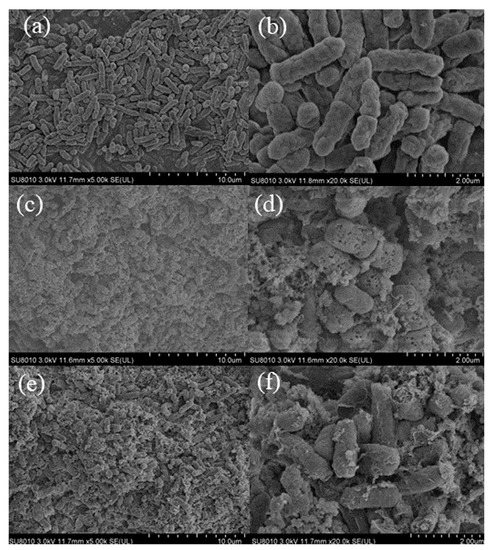
Figure 9.
SEM images of E. coli treated with CBDA and CBDVA ((a,b): control group; (c,d): CBDA treatment; (e,f): CBDVA treatment).
4. Conclusions
In this work, antibacterial activity of IHLE against E. coli and S. aureus has been presented. Bioactivity-guided isolation revealed CBDVA and CBDA as active bacteriostatic compounds. Investigations of AKP activity, conductivity, proteins leakage, nucleic acid leakage, and β-GAL activity, CBDVA and CBDA exhibited the ability to destroy the cell wall and cell membrane of E. coli, leading to the inhibition of enzyme activity and leakage of contents. The morphological evaluation also showed these active components could damage the bacteria cell envelope. The discovery of bacteriostatic activity of CBDVA and CBDA against E. coli and S. aureus makes these compounds good candidates for use in the food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industry as natural preservatives.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.Z.; data curation, Y.F.; formal analysis, Y.F.; funding acquisition, S.D.; investigation, L.L.; project administration, S.D.; writing—original draft, Y.F. and L.L.; writing—review and editing, S.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to security requirements in the institute of the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Changsha, China (Grant No. kq2202323), and the Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project (No. ASTIP-IBFC05).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Brighenti, V.; Pellati, F.; Steinbach, M.; Maran, D.; Benvenuti, S. Development of a new extraction technique and HPLC method for the analysis of non-psychoactive cannabinoids in fibre-type Cannabis sativa L. (hemp). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 143, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salentijn, E.M.J.; Zhang, Q.; Amaducci, S.; Yang, M.; Trindade, L.M. New developments in fiber hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) breeding. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 68, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, A.-P.; Cheng, H.; Liu, L.-L.; Kong, K.W.; Liu, H.-Y.; Wu, D.-T.; Li, H.-B.; Gan, R.-Y. Phytochemical differences of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) leaves from different germplasms and their regulatory effects on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in Matin-Darby canine kidney cell lines. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 902625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, M.M.; Chandra, S.; Gul, S.; ElSohly, M.A. Cannabinoids, Phenolics, Terpenes and Alkaloids of Cannabis. Molecules 2021, 26, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaseit, E.; Pérez-Mañá, C.; Pérez-Acevedo, A.P.; Hladun, O.; Torres-Moreno, M.C.; Muga, R.; Torrens, M.; Farré, M. Cannabinoids: From pot to lab. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, C.F.; Teixeira, N.; Correia-da-Silva, G.; Amaral, C. Cannabinoids in Breast Cancer: Differential Susceptibility according to Subtype. Molecules 2022, 27, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattnaik, F.; Nanda, S.; Mohanty, S.; Dalai, A.K.; Kumar, V.; Ponnusamy, S.K.; Naik, S. Cannabis: Chemistry, extraction and therapeutic applications. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chye, Y.; Kirkham, R.; Lorenzetti, V.; McTavish, E.; Solowij, N.; Yücel, M. Cannabis, Cannabinoids, and Brain Morphology: A Review of the Evidence. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2021, 6, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagha, R.; Ben Abdallah, F.; Al-Sarhan, B.O.; Al-Sodany, Y. Antibacterial and Biofilm Inhibitory Activity of Medicinal Plant Essential Oils against Escherichia coli Isolated from UTI Patients. Molecules 2019, 24, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; He, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, B.; Chen, W. Lactobacillus plantarum relieves diarrhea caused by enterotoxin-producing Escherichia coli through inflammation modulation and gut microbiota regulation. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 10362–10374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-del-Río, I.; Fernández, J.; Lombó, F. Plant nutraceuticals as antimicrobial agents in food preservation: Terpenoids, polyphenols and thiols. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 52, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, N.; Käsbohrer, A.; Mayrhofer, S.; Zitz, U.; Hofacre, C.; Domig, K.J. The application of antibiotics in broiler production and the resulting antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli: A global overview. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 1791–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrêa, R.C.G.; Heleno, S.A.; Alves, M.J.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Bacterial Resistance: Antibiotics of Last Generation used in Clinical Practice and the Arise of Natural Products as New Therapeutic Alternatives. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 815–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E.M.M.; Almagboul, A.Z.I.; Khogali, S.M.E.; Gergeir, U.M.A. Antimicrobial activity of Cannabis sativa L. Chin. Med. 2012, 3, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, J.; Zitterl-Eglseer, K.; Deans, S.G.; Franz, C.M. Essential oils of different cultivars of Cannabis sativa L. and their antimicrobial activity. Flavour Fragr. J. 2001, 16, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Tahir, A.; Khan, I.; Ali, A.; Rehman, A.-U. In Vitro antibacterial activity of Cannabis sativa leaf extracts to some selective pathogenic bacterial strains. Int. J. Biosci. 2014, 4, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Kosgodage, U.S.; Matewele, P.; Awamaria, B.; Kraev, I.; Warde, P.; Mastroianni, G.; Nunn, A.V.; Guy, G.W.; Bell, J.D.; Inal, J.M.; et al. Cannabidiol Is a Novel Modulator of Bacterial Membrane Vesicles. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Mendoza, L.; Guamba, E.; Miño, K.; Romero, M.P.; Levoyer, A.; Alvarez-Barreto, J.F.; Machado, A.; Alexis, F. Antimicrobial Properties of Plant Fibers. Molecules 2022, 27, 7999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenul, C.; Horswill Alexander, R. Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus Virulence. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 7.2.29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessberger, N.; Dietrich, R.; Granum, P.E.; Märtlbauer, E. The Bacillus cereus Food Infection as Multifactorial Process. Toxins 2020, 12, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.; An, P. Diallyl disulfide, the antibacterial component of garlic essential oil, inhibits the toxicity of Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579 at sub-inhibitory concentrations. Food Control 2021, 126, 108090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, J.; Xiao, A.; Liu, L. Antibacterial Activity of Polyphenols: Structure-Activity Relationship and Influence of Hyperglycemic Condition. Molecules 2017, 22, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, C.; Liu, Z.; Pan, F.; Meng, R.; Bu, X.; Xing, H.; Deng, Y.; Guo, N.; Yu, L. Antibacterial activity and mode of action of ε-polylysine against Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Kong, F.; Shi, X.; Han, H.; Li, M.; Guan, B.; Yang, M.; Cao, X.; Tao, D.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of lactobionic acid against Pseudomonas fluorescens and Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and its application on whole milk. Food Control 2020, 108, 106876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, C.; Shi, C.; Aliakbarlu, J.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. Antibacterial mechanisms of clove essential oil against Staphylococcus aureus and its application in pork. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 380, 109864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Lin, L. Antibacterial mechanism of oregano essential oil. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 139, 111498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.-T.; Zheng, W.; Han, X.-X.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Hu, P.-L.; Tang, Z.-X.; Shi, L.-E. The antibacterial activity and antibacterial mechanism of a polysaccharide from Cordyceps cicadae. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Chen, W.; Chen, H.; Yun, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, W. Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Linalool against Shewanella putrefaciens. Molecules 2021, 26, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, A.K.; Alqasmi, M.H.; Alrouji, M.; Kuriri, F.A.; Almuhanna, Y.; Joseph, B.; Asad, M. Antibacterial Activity of Syzygium aromaticum (Clove) Bud Oil and Its Interaction with Imipenem in Controlling Wound Infections in Rats Caused by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2022, 27, 8551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naim, N.; Bouymajane, A.; Oulad El Majdoub, Y.; Ezrari, S.; Lahlali, R.; Tahiri, A.; Ennahli, S.; Laganà Vinci, R.; Cacciola, F.; Mondello, L.; et al. Flavonoid Composition and Antibacterial Properties of Crocus sativus L. Petal Extracts. Molecules 2023, 28, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.; Cai, Y.-Z.; Brooks, J.D.; Corke, H. The in vitro antibacterial activity of dietary spice and medicinal herb extracts. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 117, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abubakar, Y.U.; Taura, D.W.; Muhammad, A.B.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Livinus, M.U. In vitro antimicrobial activity of Cannabis sativa (Hemp) extracts against avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) isolated from Broilers Chicken. Adv. Pharm. J. 2020, 5, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinenghi, L.D.; Jønsson, R.; Lund, T.; Jenssen, H. Isolation, Purification, and Antimicrobial Characterization of Cannabidiolic Acid and Cannabidiol from Cannabis sativa L. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeškalová, A.; Hájková, K.; Mikulů, L.; Sýkora, D.; Kuchař, M. Combination of UV and MS/MS detection for the LC analysis of cannabidiol-rich products. Talanta 2020, 219, 121250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, J.; Elkins, A.C.; Spangenberg, G.C.; Rochfort, S.J. High-Throughput Quantitation of Cannabinoids by Liquid Chromatography Triple-Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2022, 27, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Tang, X.; Xu, L.; Wang, S. Antibacterial properties and possible action mechanism of chelating peptides-zinc nanocomposite against Escherichia coli. Food Control 2019, 106, 106675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funatogawa, K.; Hayashi, S.; Shimomura, H.; Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T.; Ito, H.; Hirai, Y. Antibacterial Activity of Hydrolyzable Tannins Derived from Medicinal Plants against Helicobacter pylori. Microbiol. Immunol. 2004, 48, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cai, J.; Chen, H.; Zhong, Q.; Hou, Y.; Chen, W.; Chen, W. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of linalool against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 141, 103980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.W.; Liu, D.M.; Jing, L.; Xia, G.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Jiang, J.R.; Tang, J.B. Striatisporolide A, a butenolide metabolite from Athyrium multidentatum (Doll.) Ching, as a potential antibacterial agent. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Wang, P.; Wang, P.; Ma, C.; Kang, W. Antibacterial mechanism of chelerythrine isolated from root of Toddalia asiatica (Linn) Lam. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-J.; Lin, M.-Y.; Feng, S.-Y.; Gu, Q.; Chen, Y.-C.; Wang, Y.-D.; Song, D.-F.; Gao, M. Chemical composition, antibacterial activity, and mechanism of action of essential oil from Litsea cubeba against foodborne bacteria. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Li, R.; Zhang, Q.; He, S.; Wang, Y. Antibacterial Effect and Possible Mechanism of Salicylic Acid Microcapsules against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, J.; Su, X. Cascade reaction biosensor based on Cu/N co-doped two-dimensional carbon-based nanozyme for the detection of lactose and β-galactosidase. Talanta 2022, 245, 123451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, E.; An, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, M.; Iqbal, M.W.; Zabed, H.M.; Qi, X. Enhancing the antibacterial activity of Lactobacillus reuteri against Escherichia coli by random mutagenesis and delineating its mechanism. Food Biosci. 2023, 51, 102209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.-H.; Zhou, T.-T.; Wei, C.-H.; Lan, W.-Q.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, Y.-J.; Wu, V.C.H. Antibacterial effect and mechanism of anthocyanin rich Chinese wild blueberry extract on various foodborne pathogens. Food Control 2018, 94, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yang, L.; Zou, Y.; Luo, S.; Wang, X.; Liang, Y.; Du, Y.; Feng, R.; Wei, Q. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of three isomeric terpineols of Cinnamomum longepaniculatum leaf oil. Folia Microbiol. 2021, 66, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).