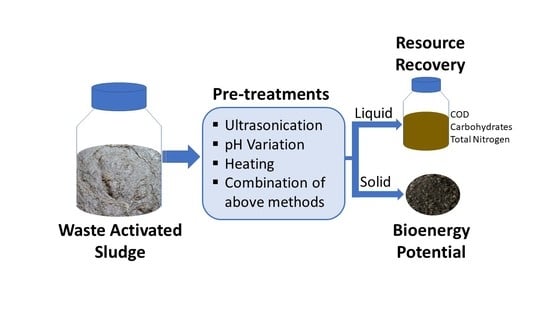
Effect of Different Pretreatments on Sludge Solubilization and Estimation of Bioenergy Potential
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Pretreatments
2.3. Sample Analyses
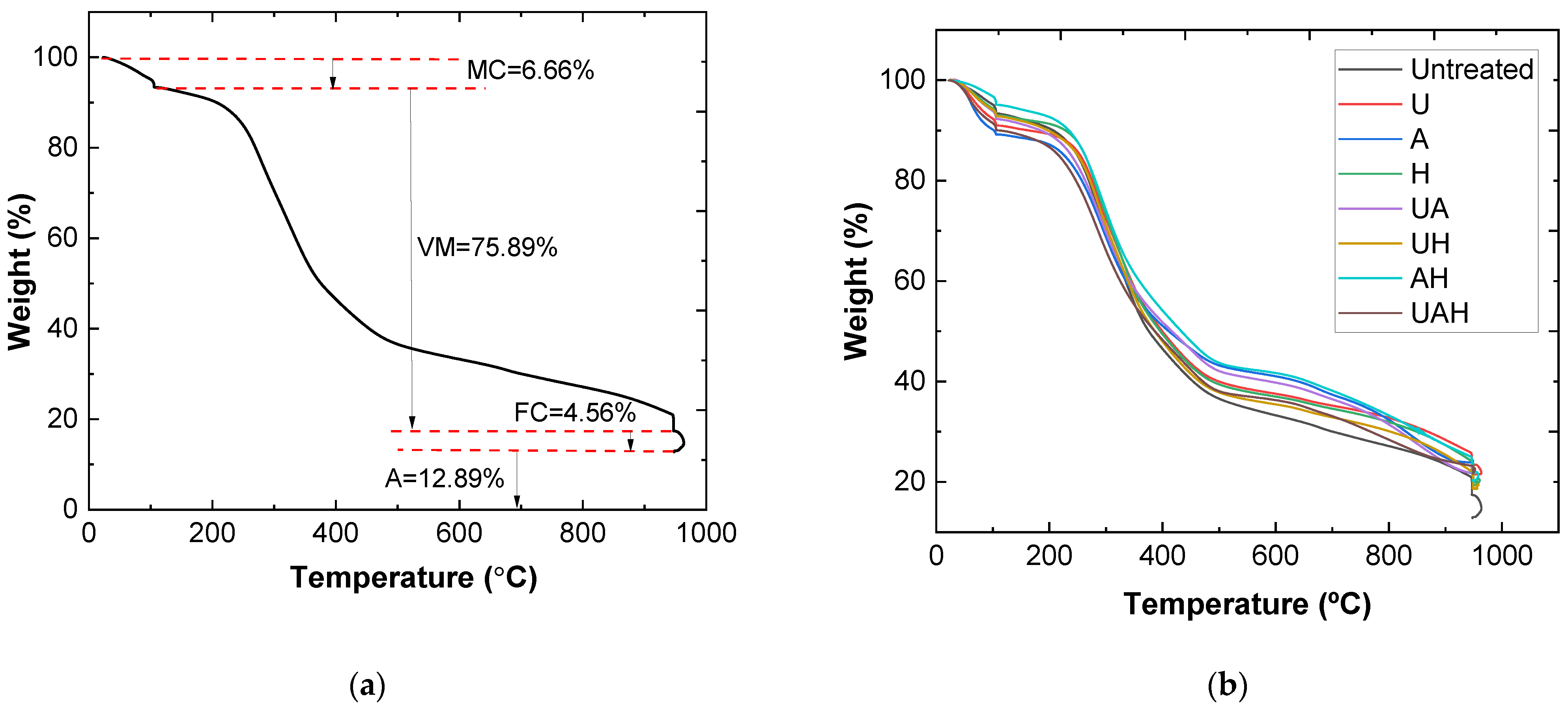
2.4. Estimation of HHV by Thermogravimetric Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
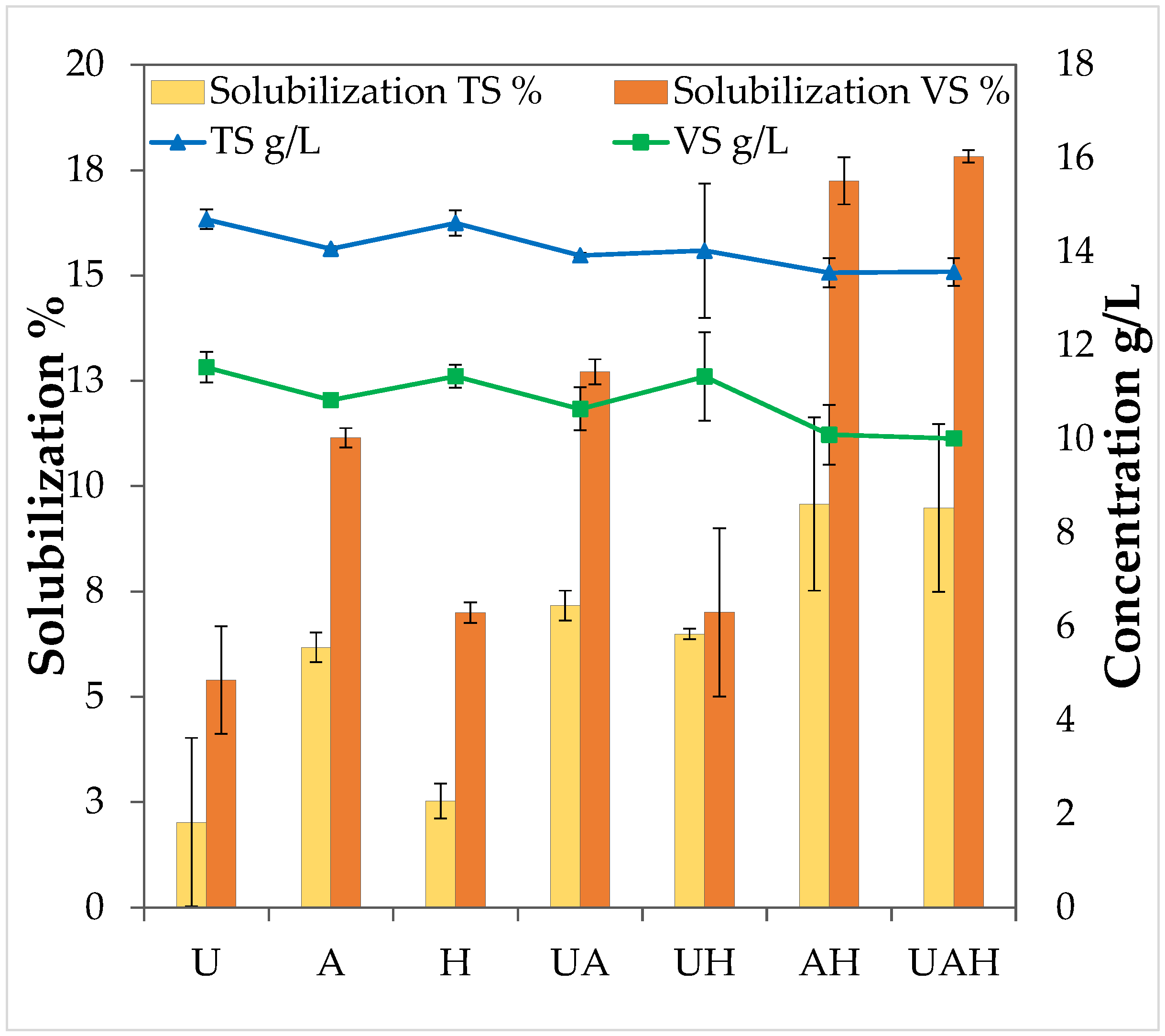
3.1. Solubilization of TS, VS
3.2. Solubilization of SCOD and Carbohydrates
3.3. Total Nitrogen and Soluble Proteins
3.4. Effect of Alkali Addition on WAS Solubilization
3.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Abbà, A.; Miino, M.C.; Torretta, V. What advanced treatments can be used to minimize the production of sewage sludge in WWTPs? Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durdevic, D.; Blecich, P.; Juric, Z. Energy recovery from sewage sludge: The case study of Croatia. Energies 2019, 12, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Yu, N.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Ren, N.; Xing, D. Enhancement of the sludge disintegration and nutrients release by a treatment with potassium ferrate combined with an ultrasonic process. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oladejo, J.; Shi, K.; Luo, X.; Yang, G.; Wu, T. A Review of sludge-to-energy recovery methods. Energies 2019, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suárez-Iglesias, O.; Urrea, J.L.; Oulego, P.; Collado, S.; Díaz, M. Valuable compounds from sewage sludge by thermal hydrolysis and wet oxidation. A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wei, W.; Gong, Y.; Yu, Q.; Li, Q.; Sun, J.; Yuan, Z. Technologies for reducing sludge production in wastewater treatment plants: State of the art. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 587–588, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samorì, C.; Kiwan, A.; Torri, C.; Conti, R.; Galletti, P.; Tagliavini, E. Polyhydroxyalkanoates and crotonic acid from anaerobically digested sewage sludge. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 10266–10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, A.; Bonfiglioli, L.; Pellegrini, M.; Saccani, C. Sewage sludge drying process integration with a waste-to-energy power plant. Waste Manag. 2015, 42, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raheem, A.; Sikarwar, V.S.; He, J.; Dastyar, W.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Wang, W.; Zhao, M. Opportunities and challenges in sustainable treatment and resource reuse of sewage sludge: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 616–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Du, G.; Chen, J. Enhancement of solubilization and acidification of waste activated sludge by pretreatment. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2614–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Jeong, E.; Oh, S.E.; Shin, H.S. Combined (Alkaline + ultrasonic) pretreatment effect on sewage sludge disintegration. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3093–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Jiang, J.; Li, D. Ultrasound coupled with fenton oxidation pre-treatment of sludge to release organic carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 532, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weemaes, M.P.J.; Verstraete, W.H. Evaluation of current wet sludge disintegration techniques. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1998, 73, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampas, P.; Parsons, S.A.; Pearce, P.; Ledoux, S.; Vale, P.; Churchley, J.; Cartmell, E. Mechanical sludge disintegration for the production of carbon source for biological nutrient removal. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1734–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khanal, S.K.; Grewell, D.; Sung, S.; Van Leeuwen, J. Ultrasound applications in wastewater sludge pretreatment: A review. Crit. Rev. Env. Sci. Technol. 2007, 37, 277–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nah, I.W.; Kang, Y.W.; Hwang, K.Y.; Song, W.K. Mechanical pretreatment of waste activated sludge for anaerobic digestion process. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2362–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jih-Gaw, L.; Chang, C.N.; Chang, S.C. Enhancement of anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge by alkaline solubilization. Bioresour. Technol. 1997, 62, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, D.; Wu, S.; Wang, C. Alkali pretreatment enhances biogas production in the anaerobic digestion of pulp and paper sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barjenbruch, M.; Kopplow, O. Enzymatic, mechanical and thermal pre-treatment of surplus sludge. Adv. Environ. Res. 2003, 7, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougrier, C.; Delgenès, J.P.; Carrère, H. Effects of thermal treatments on five different waste activated sludge samples solubilisation, physical properties and anaerobic digestion. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 139, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponsá, S.; Ferrer, I.; Vázquez, F.; Font, X. Optimization of the hydrolytic-acidogenic anaerobic digestion stage (55 °C) of sewage sludge: Influence of PH and solid content. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3972–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tytła, M. The effects of ultrasonic disintegration as a function of waste activated sludge characteristics and technical conditions of conducting the process—Comprehensive analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Cui, M.; Wong, J.W.C. Effects of different thermal pretreatments on the biodegradability and bioaccessibility of sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 2019, 94, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Hernando, M.; Martín-Díaz, J.; Labanda, J.; Mata-Alvarez, J.; Llorens, J.; Lucena, F.; Astals, S. Effect of ultrasound, low-temperature thermal and alkali pre-treatments on waste activated sludge rheology, hygienization and methane potential. Water Res. 2014, 61, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Climent, M.; Ferrer, I.; Baeza, M.d.M.; Artola, A.; Vázquez, F.; Font, X. Effects of thermal and mechanical pretreatments of secondary sludge on biogas production under thermophilic conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 133, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, S.; Kamiyama, K. Thermochemical pretreatment in the anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, S.; Kannah, Y.R.; Yeom, I.T.; Do, K.U.; Banu, J.R. Combined thermo-chemo-sonic disintegration of waste activated sludge for biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, Y.C.; Chang, C.N.; Lin, J.G.; Huang, S.J. Alkaline and ultrasonic pretreatment of sludge before anaerobic digestion. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Youn, Y. Characteristics of sludge hydrolysis by ultrasound and thermal pretreatment at low temperature. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 28, 1876–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.P.; Chang, B.-V.; Liao, G.S.; Jean, D.S.; Lee, D.J. Observations on changes in ultrasonically treated waste-activated sludge. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiehm, A.; Nickel, K.; Zellhorn, M.; Neis, U.; Tiehm, A. Ultrasonic waste activated sludge disintegration for improving anaerobic stabilization. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2003–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, P.; Gao, J.; Chen, Y. Using acoustic cavitation to improve the bio-activity of activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1497–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhang, T. Microbial effects of part-stream low-frequency ultrasonic pretreatment on sludge anaerobic digestion as revealed by high-throughput sequencing-based metagenomics and metatranscriptomics. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pilli, S.; Bhunia, P.; Yan, S.; LeBlanc, R.J.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Ultrasonic pretreatment of sludge: A review. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2011, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, N.T.; Julcour-Lebigue, C.; Delmas, H. An executive review of sludge pretreatment by sonication. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 37, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Penaud, V.; Delgenes, J.P.; Moletta, R. Influence of thermochemical pretreatment conditions on solubilization and anaerobic biodegradability of a microbial biomass. Environ. Technol. 2000, 21, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, C.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, M.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J. Effects of various pretreatments for enhanced anaerobic digestion with waste activated sludge. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2003, 95, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prorot, A.; Julien, L.; Christophe, D.; Patrick, L. Sludge disintegration during heat treatment at low temperature: A better understanding of involved mechanisms with a multiparametric approach. Biochem. Eng. J. 2011, 54, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocher, M.; Goma, G.; Pilas Begue, A.; Louvel, L.; Rols, J.L. Towards a reduction in excess sludge production in activated sludge processes: Biomass physicochemical treatment and biodegradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 51, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Noguchi, C.; Hara, Y.; Sharon, C.; Kakimoto, K.; Kato, Y. Studies on anaerobic digestion mechanism: Influence of pretreatment temperature on biodegradation of waste activated sludge. Environ. Technol. 1997, 18, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, M.K.C.; Pillai, S.C. Proteins in wastewater and wastewater sludges. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1973, 45, 1595–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. A colorimetric method for the determination of sugars. Nature 1951, 168, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, D.A.; Franson, H.M.A. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water & Wastewater, 21st ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; p. 1200. [Google Scholar]
- Malucelli, L.C.; Silvestre, G.F.; Carneiro, J.; Vasconcelos, E.C.; Guiotoku, M.; Maia, C.M.B.F.; Filho, M.A.S.C. Biochar higher heating value estimative using thermogravimetric analysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 139, 2215–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffe, A.; Fernandez, A.; Mazza, G.; Rodriguez, R. Prediction of regional agro-industrial wastes characteristics by thermogravimetric analysis to obtain bioenergy using thermal process. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2019, 37, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ASTM E1131-20. Standard Test Method for Compositional Analysis by Thermogravimetry; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, W.; Wang, W.; Xun, R.; Lu, W.; Yin, K. Sewage sludge hydrothermal treatment by microwave irradiation combined with alkali addition. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 2431–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Kamiyama, K.I.; Signey Bildan, M.L.N. Effects of thermochemical pretreatment on the anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 35, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaounakis, M.; Halvadakis, C.P. Olive Processing Waste Management. Literature Review and Patent Survey, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; p. 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlyssides, A.G.; Karlis, P.K. Thermal-Alkaline solubilization of waste activated sludge as a pre-treatment stage for anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 91, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suschka, J.; Grübel, K. Nitrogen in the process of waste activated sludge anaerobic digestion. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2014, 40, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westgate, P.J.; Park, C. Evaluation of proteins and organic nitrogen in wastewater treatment effluents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5352–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, Q.; Gu, G. Hydrolysis and acidification of waste activated sludge at different pHs. Water Res. 2007, 41, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Fang, H.H.P. Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of sludges. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 95, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, U.R.; Kumar, A.S.; Kaliappan, S.; Yeom, I.T.; Banu, R.J. Low temperature thermo-chemical pretreatment of dairy waste activated sludge for anaerobic digestion process. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 103, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Zhou, Y. Protein recovery from sludge: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 249, 119373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, V.K.; Lo, S.L.; Rajpal, A. Chemically coupled microwave and ultrasonic pre-hydrolysis of pulp and paper mill waste-activated sludge: Effect on sludge solubilisation and anaerobic digestion. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 6205–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, J.; Channiwala, S.A.; Ghosal, G.K. A correlation for calculating HHV from proximate analysis of solid fuels. Fuel 2005, 84, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thipkhunthod, P.; Meeyoo, V.; Rangsunvigit, P.; Kitiyanan, B.; Siemanond, K.; Rirksomboon, T. Predicting the heating value of sewage sludges in thailand from proximate and ultimate analyses. Fuel 2005, 84, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Pretreatments | Conditions | Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal–chemical | 130 °C, pH 12, 5 min | Enhanced biodegradability and solid solubilization | [26] |
| Thermal–chemical | 50–90 °C, pH 9–12, 5–180 min | 80 °C, pH 11 optimum | [27] |
| Thermal–chemical–ultrasonic | 80 °C, pH 11, 20 kHz, 5–180 min | Improved COD solubilization and suspended solid reduction | |
| Alkali–ultrasonic | Ambient temperature, 40 meq/L NaOH, 20 kHz, 120 W, 24 h | Enhanced production of volatile acids | [28] |
| Ultrasonic | 20 kHz, 1 h | Efficient hydrolysis on WAS | [29] |
| Thermal–ultrasonic | Thermal: 30–90 °C, 0–3 h Ultrasonication: 20 kHz, 20 min | Improved hydrolysis for thermal–ultrasonication compared to ultrasonic method | |
| Thermal–alkali | 80 °C, 80 min, 0.1 M NaOH | Improved solubilization of organic matter in thermal–alkali method | [23] |
| Thermal | 80–170 °C, 30 min–12 h |
| Parameter | Mean Value ± Standard Deviation |
|---|---|
| pH | ~7.0 |
| Total solids (TS) | 4.8 ± 0.1 g/L |
| Volatile solids (VS) | 3.7 ± 0.2 g/L |
| Soluble chemical oxygen demand (SCOD) 1 | 500 ± 10 mg/L |
| Soluble carbohydrates 1 | 143 ± 5 mg/L |
| Total nitrogen 1 | 230 ± 35 mg/L |
| Sample | HHV MJ/kg |
|---|---|
| Untreated | 13.34 ± 0.65 |
| U | 10.90 ± 0.65 |
| A | 10.00 ± 0.65 |
| H | 11.44 ± 0.65 |
| UA | 10.88 ± 0.65 |
| UH | 11.47 ± 0.65 |
| AH | 11.82 ± 0.65 |
| UAH | 10.58 ± 0.65 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Babu, R.; Capannelli, G.; Comite, A. Effect of Different Pretreatments on Sludge Solubilization and Estimation of Bioenergy Potential. Processes 2021, 9, 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9081382
Babu R, Capannelli G, Comite A. Effect of Different Pretreatments on Sludge Solubilization and Estimation of Bioenergy Potential. Processes. 2021; 9(8):1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9081382
Chicago/Turabian StyleBabu, Reshma, Gustavo Capannelli, and Antonio Comite. 2021. "Effect of Different Pretreatments on Sludge Solubilization and Estimation of Bioenergy Potential" Processes 9, no. 8: 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9081382
APA StyleBabu, R., Capannelli, G., & Comite, A. (2021). Effect of Different Pretreatments on Sludge Solubilization and Estimation of Bioenergy Potential. Processes, 9(8), 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9081382